Relationship between hydrogen concentration and mechanical properties of 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2021年第3期
论文作者:孙永伟 陈继志 王灵水
文章页码:699 - 711
Key words:5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel; slow strain rate test; thermal desorption spectroscopy; finite element analysis; hydrogen embrittlement
Abstract: The qualitative relationship between hydrogen concentration and notch tensile strength has been investigated for 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel with different strength. The notch tensile strength was determined by means of slow strain rate test (SSRT) on circumferentially notched round bar specimens with the notch root radius of 0.15 mm after hydrogen charging. Meanwhile, the hydrogen diffusion behaviors of various strength steel were studied by thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS) analysis. The SSRT results show that the T460 steel has higher susceptibility of hydrogen embrittlement in contrast with T520 steel. The activation energies and microstructure indicate that the dislocations and interfaces of martensitic laths are hydrogen traps in 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel. By SSRT, the elastic limit of charged specimen loaded in air is higher than the flow stress without hydrogen charging before unloading, while the difference is defined as hydrogen-induced stress. The value of hydrogen-induced stress s* increases linearly with hydrogen concentration: s*=-0.622+2.015C0. The finite element analysis results of stress distributions near the notch tip have shown that the maximum principal stress increases with the notch root radius decreasing.
Cite this article as: SUN Yong-wei, CHEN Ji-zhi, WANG Ling-shui. Relationship between hydrogen concentration and mechanical properties of 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(3): 699-711. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4639-4.

J. Cent. South Univ. (2021) 28: 699-711
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4639-4

SUN Yong-wei(孙永伟)1, 2, CHEN Ji-zhi(陈继志)1, 2, WANG Ling-shui(王灵水)1, 2
1. Luoyang Sunrui Special Equipment Co., Ltd., Luoyang 471000, China;
2. Luoyang Ship Material Research Institute, Luoyang 471000, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021
Abstract: The qualitative relationship between hydrogen concentration and notch tensile strength has been investigated for 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel with different strength. The notch tensile strength was determined by means of slow strain rate test (SSRT) on circumferentially notched round bar specimens with the notch root radius of 0.15 mm after hydrogen charging. Meanwhile, the hydrogen diffusion behaviors of various strength steel were studied by thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS) analysis. The SSRT results show that the T460 steel has higher susceptibility of hydrogen embrittlement in contrast with T520 steel. The activation energies and microstructure indicate that the dislocations and interfaces of martensitic laths are hydrogen traps in 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel. By SSRT, the elastic limit of charged specimen loaded in air is higher than the flow stress without hydrogen charging before unloading, while the difference is defined as hydrogen-induced stress. The value of hydrogen-induced stress s* increases linearly with hydrogen concentration: s*=-0.622+2.015C0. The finite element analysis results of stress distributions near the notch tip have shown that the maximum principal stress increases with the notch root radius decreasing.
Key words: 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel; slow strain rate test; thermal desorption spectroscopy; finite element analysis; hydrogen embrittlement
Cite this article as: SUN Yong-wei, CHEN Ji-zhi, WANG Ling-shui. Relationship between hydrogen concentration and mechanical properties of 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(3): 699-711. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-021-4639-4.
1 Introduction
In order to avoid economic losses, it is necessary to consider safe and reliable hydrogen-loaded components, to develop hydrogen-based energy and clean society. The use of high strength alloy steels for such components is facing with hydrogen environment embrittlement [1-4]. Hydrogen embrittlement of high strength alloy steel has been commonly investigated for decades [5].
Meanwhile, there are many mechanisms for interpreting the nature of hydrogen induced cracking [6-8]. Among all the mechanisms proposed for hydrogen embrittlement of steels, hydrogen enhanced local plasticity [9] and hydrogen enhanced decohesion [10] are considered as the powerful persuasiveness and accepted by many researchers all over the world.
The hydrogen enhanced local plasticity mechanism believes that hydrogen atoms can form a Cottrell atmosphere around dislocation cores, and therefore reduce barriers for dislocation moving and effectively stimulate dislocations at lower stress levels. With the effect of hydrogen atoms, the highly localized slips near the crack or notch root induce localized plastic failure eventually.
Therefore, hydrogen enhanced local plasticity is consistent with toughness degradation mechanism rather than hydrogen embrittlement [11]. The hydrogen enhanced decohesion has a relationship with the cohesive strength of the steel. Due to the segregation of hydrogen into defects, such as microcracks, grain boundaries, second phase particles, and so on, the localized reduction in cohesive strength will aggravate embrittlement of steels [12]. However, single mechanism of hydrogen embrittlement cannot completely account for various phenomenon of hydrogen induced cracking. And no matter what mechanism we choose for hydrogen embrittlement, it is still necessary to obtain the hydrogen concentration in materials so as to estimate the susceptibility of hydrogen embrittlement [13, 14]. And hydrogen diffusion in the steel has been also difficult to be experimentally determined recently, especially for notched parts [15]. The hydrogen concentration under stress-driven diffusion condition is different with the size of notch root radius. Accordingly, it is important to understand the stress-driven hydrogen diffusion and accumulation in the case of specimens with stress gradient, and the numerical analysis of hydrogen transport near a blunting crack tip is described in Ref. [16].
Martensitic stainless steel is widely used as bolt in the equipment or parts [17]. Though it has some excellent mechanical and corrosion-resistance performances, the steel is susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement when served in a hydrogen gas environment, particularly for high strength level. Recently, high strength 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel is usually used as bolts. And it is often sensitive to hydrogen due to the stress concentration which is induced by the notch part. To date, researches on hydrogen embrittlement of medium carbon alloy steels and carbon steels for bolts and fasteners are found all over the world, but the hydrogen induced cracking (HIC) of 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel for bolt under the environment of hydrogen producing has been rarely reported. Ignoring the HIC, the catastrophic nature of some failures usually poses a serious safety and reliability threat to industries, such as marine equipment, aviation, and so on [18]. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the HIC of notched parts, especially as to the bolts and fasteners exposed in hydrogen gas environment.
In this paper, the stress distribution in the notch root of the specimen is calculated by the finite element analysis (FEA) so as to illustrate the effect of the stress concentration on the notch tensile strength. The aim of this work is to study the qualitative relationship between the hydrogen concentration and the notch tensile strength of quenched and tempered 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel at different strength levels. Meanwhile, the thermal desorption spectroscopy analysis is performed in order to investigate the hydrogen desorption activation energy and trapping in this steel. The effect of hydrogen on the flow stress of the steel with plastic pre-deformation is investigated, too. That is to say, the paper is focused on measure the relationship between hydrogen-induced stress and hydrogen concentration. In a word, the work aims to lay a foundation for further research in the safe use of notched parts.
2 Experimental
A commercial alloy steel 5Ni-16Cr-Mo was prepared by vacuum induction melting and electroslag remelting, and then quenched and tempered to obtain various strength levels. The as-received steel bar was first austenitizing at 960 °C for 3.5 h, and was water cooled after that. Then it was tempered at 460 °C, and 520 °C for 4 h with various strength, respectively, and was air cooled later. According to the tempering temperature, the experimental steel was divided into T460 and T520 steel, corresponding to the tempering temperatures of 460 and 520 °C, respectively. And the T460 steel was treated by cryogenic treatment before tempering to improve the tensile strength, which was due to the transformation of retained austenite and variation of microstructure [19]. The details of heat treatment process wouldn’t be illustrated here. The chemical compositions of the steel were listed in Table 1.
In order to investigate the effect of stress concentration on the notch tensile strength, the circumferentially notched round bar specimens were prepared accompanied with the notch root radius (R) of 0.15 mm corresponding to the theoretical stress concentration factor of 3.9 estimated following Nishida’s method [20], and used for mechanical tensile tests. The schematic of specimen is shown in Figure 1.
Table 1 Chemical compositions of experimental steel (wt%)


Figure 1 Dimensions of notched round bar specimens for slow strain rate test (mm)
Qualitative characterizations of the microstructures were carried out by means of optical microscopy with Leica DMI 500M and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with JEM-2100 operating at 200 kV. The morphologies of the fracture surfaces of broken specimens were analyzed by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with Quanta650 FEG making use of secondary electron signal.
Thermal desorption spectroscopy (TDS) analysis specimens had a diameter of 5 mm and a length of 50 mm, which were machined from experimental steel and polished using the machine tool. The hydrogen charging solution in the TDS experiment was 0.1 mol/L NaOH aqueous solution while the charging time and current density were 96 h, 2 mA/cm2, respectively. And after hydrogen charging, the pre-charged specimens were quickly put into TDS analysis equipment using a quadrupole mass spectrometer for hydrogen measurements. The TDS equipment has an exact accuracy of 0.01×10-6 for hydrogen measurement. In order to calculate the activation energy of hydrogen desorption using the method that was reported by CHOO et al [21], the heating rate was designed at 100, 200, 300, 400 °C/h, respectively, and the final heating temperature was 800 °C. The test was performed at room temperature (25 °C). The aim of this part was to establish a comparison and correlation among various strength steels so as to determine hydrogen concentration and trapping energies.
The circumferentially notched round bar specimens were carried out by WLDM-100 testing machine for slow strain rate test (SSRT). The specimens for SSRT were charged in 0.1 mol/L NaOH aqueous solution by means of electrochemical cathodic hydrogen charging at room temperature (25 °C). The different hydrogen concentration of specimens was obtained by hydrogen charging at different charging densities and time, such as from 2 to 10 mA/cm2 for 72 or 96 h. After hydrogen charging, the SSRT specimens were performed on the tensile testing machine at a constant crosshead speed of 0.005 mm/min, corresponding to a nominal strain rate of 2.1×10-6 s-1. The fracture time of the SSRT specimens ranged from 1 to 5 h, associating with the fracture stress. The notch tensile strength, σbH, was evaluated as follows [22]:
 (1)
(1)
where FbH is the maximum tensile load and S0H is the initial cross-section net area of the notch. After SSRT, one of the fracture parts of the specimen was used for fracture surface observation, and the other one was used to determine the hydrogen content.
The elastic-plastic stress analysis was performed by ABAQUS standard with the use of standard Mises material model. And the applying stress-strain data was from laboratory conventional tensile test at the room temperature (25 °C), as shown in Figure 2. The elastic modulus of the steel is 209 GPa while Poisson ratio is 0.295. In order to investigate the effect of different root radii on notch strength theoretically, other two root radii of 0.3 and 0.5 mm were established in the finite element model (FEM).
The smooth specimens were carried out by WLDM-100 testing machine so that the effect of hydrogen on flow stress of the 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel could be investigated. The hydrogen uncharged specimens were loaded in air so as to obtain more than 1% plastic strain at a strain rate of 2.1×10-6 s-1 and then were unloaded. The unloaded specimens were charged for 72 h with various current densities, and reloaded at the same strain rate to yield in succession. Therefore, the relationship of flow stress sf with hydrogen uncharged and the elastic limit se with hydrogen charging for the 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel could be described as: s*=se-sf. The value of s* is defined as hydrogen-induced stress, which acts together with external stress to get the characteristic of stress-strain of the experimental steel. With this work, the interaction between hydrogen and plasticity deformation was helpful for improving the safety of bolts served under the overload condition.

Figure 2 Plastic part of stress-strain curve for experimental steel performed in elastic-plastic stress analysis:
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure and mechanical properties
Figure 3 shows the optical and TEM micrographs of the experimental steel. The 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel is martensitic stainless steel with a lath martensitic microstructure. From Figure 3, the T460 steel has the similar grain size to the T520 steel, but the morphology and width of lath martensite for the two series steel show a little difference. The T520 steel presents a few martensites, and the corresponding diffraction spots were shown in Figure 3(d). There are some reversed austenites in the 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel under the condition of high tempering temperatures in the our previous work. And the twin martensites in the T520 steel may be the onset of formation of reversed austenite with the volume fraction of 7%. It can be also observed from Figures 3(a) and (c) that there are some inclusions along the grain boundaries, which may be act as hydrogen trapping sites.
Mechanical properties of the tested steel, measured by tensile tests on smooth samples, are summarized in Table 2.
And the mechanical properties of this steel after different tempering temperatures are shown in Figure 4 in the previous work marked as the blacked one [23]. The tensile strength increases with the decrease of tempering temperatures without cryogenic treatment. It can be observed that the strength reaches a steady state of around 1150 MPa, and does not increase any more. It is necessary to improve the performance by cryogenic treatment so as to reach the expected values in this paper, and the mechanism of cryogenic treatment is related to Ref. [24]. The measured mechanical properties are in agreement with the desired values for all the experimental steel.
3.2 Hydrogen desorption and trapping
Figure 5 shows the TDS results for all the materials. It can be seen from the TDS curves that only one peak exists and the area below the curves of all series steel with hydrogen uncharged have the smallest amount of hydrogen desorption corresponding to the hydrogen concentration less than 1×10-6. For hydrogen charged samples, the TDS curves exhibit two desorption peaks corresponding to the temperatures below 300 °C marked as the shadow rectangle. The two desorption peaks are called the first and the second peak, respectively. In addition, the desorption capacity of T520 steel is smaller under the same hydrogen charging conditions. The hydrogen concentration of T520 steel and T460 steel corresponds to about 12×10-6 and 15×10-6, respectively, which shows that the concentration of hydrogen increases with the steel strength. And this is consistent with the results of our previous work.
The activation energies of the different hydrogen traps correspond to the particular microstructural features of the steel. LEE et al [25] had done a lot of research on the calculation of activation energy. In addition, a reaction kinetics formula making possible the determination of the activation energy in differential thermal analysis in Ref. [26] is commonly used. And Eq. (2) is expressed by the following:
 (2)
(2)
where Φ is the heating rate which represents the degree of heating for TDS specimen, °C/h; Tp is the TDS peak temperature, °C; Ea is the activation energy for hydrogen desorption from different hydrogen traps, kJ/mol; and R is the gas constant, J/(K·mol). Through different heating rate, the values of ln(Φ/Tp2) and 1/Tp can be calculated so as to get the activation energy. TDS measurements were carried out on all pre-charged specimens at four different heating rates, i.e., 100, 200, 300, 400 °C/h, respectively. The TDS measurement results for 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel are shown in Figure 6. Then the activation energy of each temperature peak can be obtained from the relationship between  and 1/Tp as shown in Figure 7. And the calculated activation energy is shown in Table 3.
and 1/Tp as shown in Figure 7. And the calculated activation energy is shown in Table 3.

Figure 3 Optical and TEM micrographs of steel after different tempering temperatures:
Table 2 Mechanical properties of 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel after different tempering temperatures
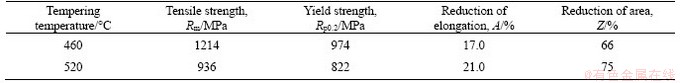
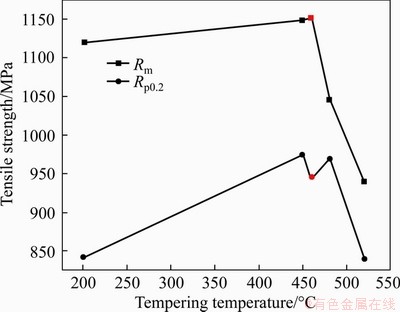
Figure 4 Mechanical properties of 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel with different tempering temperatures

Figure 5 TDS curves for hydrogen uncharged and charged specimens

Figure 6 TDS curves for different heating rates of 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel:
All steels have different activation energies due to different heat treatments. Clusters of dislocations may exist in T460 steel after cryogenic tempering. These dislocations can increase the local hydrogen concentration and make it deep trapped. As shown in Figure 5, the hydrogen desorption peak temperatures of T460, T520 steel at the heating rate of 100 °C/h are 169.2 and 248.9 °C, 172.1 and 225.0 °C, respectively. From the values of ln(Φ/Tp2) and 1/Tp, the calculated activation energies of T520 and T460 steel at the first and second hydrogen desorption peaks are 17.74 and 21.77 kJ/mol, 18.91 and 19.47 kJ/mol, respectively. It can be seen from Table 3 that the two hydrogen desorption peaks correspond to different hydrogen traps.

Figure 7 Relationship between and 1/Tp:
and 1/Tp:
Table 3 Calculated activation energies for different heat treatment steels at various desorption peaks

A number of scientific literatures have referred to some ideas about the activation energy of some possible traps. For example, the activation energies of grain boundary correspond to the values from 20 to 58 kJ/mol [27], while activation energies of dislocation correspond to the values from 19 to 30 kJ/mol [28], and the values found for martensite are around 30 kJ/mol, et al [29]. In this work, 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel is the martensitic stainless steel, which was treated by quenching, cryogenic treatment and tempering. Therefore, compared with lath martensite, the material in this experiment has higher density dislocation. Dislocations, inclusions, grain boundaries, solute atoms and interfaces of martensitic lath can be regarded as hydrogen trapping sites [30].
According to the relevant experiments [31], the peaks which below 300 °C correspond to diffusible hydrogen and difficult to escape from the trapping over 300 °C. The activation energies obtained by the method in Ref. [26] usually suit for certain traps. For the steel, there is no irreversible potential traps with activation energy over than 60 kJ/mol. The hydrogen atoms must be trapped by dislocations, and the interfaces of martensitic laths corresponding to the calculated activation energies.
It is difficult to avoid the error of activation energy of hydrogen trapping. The error may be consistent with the accuracy of the TDS equipment. These uncertainties are related to surface treatment, such as surface defects, the accuracy of temperature measurement systems, and some thermal effects on microstructure stability. Therefore, combining other technologies with hydrogen capture behavior will be significance in future research, such as electrochemical permeation technology.
Referring to microstructure, the temper temperature affects the change of microstructure in steel, and the dislocation density decreases with the increase of tempering temperature, but the quantity of dislocations hardly affect the hydrogen desorption character at all.
Hydrogen desorption activation energy for steel is just an intrinsic behavior. The purpose of this paper is to establish the relationship between trapping activation energy and microstructure, which can be helpful to decrease susceptibility of hydrogen embrittlement.
3.3 Effect of hydrogen concentration on notch tensile strength
Figure 8 shows the dependence of the notch tensile strength on hydrogen concentration for the T460 and T520 steel with the notch root radius 0.15 mm. Macroscopically, all the hydrogen charged steel shows a lower notch tensile strength than that of the uncharged experimental steel (such as C0<1×10-6), corresponding to hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of the 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel. For instance, the notch tensile strength of the T460 steel corresponding to the hydrogen concentration about 7.3×10-6 is less than 900 MPa, resulting in a loss of about 1200 MPa compared to that of the uncharged steel. The results show that the notched tensile strength of T460 and T520 steel decreases with the increase of hydrogen concentration. For the two series steel, it exists with the decrease of steady stage when the hydrogen concentration is less than 5×10-6, as well as the sharp stage when the hydrogen concentration is more than 6×10-6. It is noted that hydrogen concentration of mechanical specimens in this paper is obtained by melt extraction at high temperature (about 2000 °C), which is different with the TDS analysis.

Figure 8 Influence of hydrogen concentration on notch tensile strength for T460 and T520 steel
It also can be seen that the notch tensile strength of the T460 steel decreases more sharply than that of the T520 steel, showing a greater sensitivity to hydrogen embrittlement. The fractography of various series of steels can reflect sensitivity to hydrogen embrittlement.
In order to explain the degradation of mechanical properties, it is defined as the hydrogen atom induced by stress gradient is redistributed by the hydrogen enhanced mobility of dislocations so that the hydrogen concentration in the lath boundaries increases. And the enhanced transport of hydrogen by dislocations has been studied by various techniques [32]. In terms of hydrogen embrittlement, the plasticity plays an important role in hydrogen induced cracking. The distribution of hydrogen atoms between different traps depends on it. The higher hydrogen concentration in the lath boundary will reduce the mechanical properties, whether strength or plasticity.
Figure 9 shows that the fractographs of T520 and T460 steel are different due to the strength difference at the similar level of hydrogen concentration, corresponding to the value of 6.4×10-6 and 6.8×10-6, respectively. The width of brittle regions for T460 and T520 steel are about 400 and 100 μm, respectively, as shown in Figures 9(a) and (c). Compared with the T520 steel with lower strength, the T460 steel has more quasi- cleavage surface.
Meanwhile, it can be observed from Figures 9(a) and (c) that there are some secondary cracks near the notch tip in both steels. In the process of loading, hydrogen will accumulate at the crack tip, resulting in stress concentration, which eventually induce the initiation of cracking.
The effect of hydrogen on the mechanical properties and the fracture behavior of 5Ni-16Cr-Mo martensitic steel has been tested and observed, respectively. According to the fractographs of the two steels, the quasi-cleavage is the remarkable feature of the brittle zone and is considered to be the typical form of hydrogen embrittlement. It has been reported that for hydrogen charged martensitic steel, the fracture path is along lath boundaries for the quasi-cleavage fracture surfaces, and the fracture path of the hydrogen induced quasi-cleavage is consistent with the {110} slip plane, corresponding to a lath habit plane [33, 34]. Meanwhile, it is supported by the TDS results that the lath boundaries are the main traps steel, which is mentioned in the above. At the boundary of the strip, more and more hydrogen accumulates, which leads to the decrease of the bond strength and the initiation and propagation of cracks along the boundary.

Figure 9 SEM fractographs of experimental steel:
3.4 Stress distribution near notch tip
The ABAQUS standard was used to analyze the stress of two-dimensional notched specimen model. The geometries represent cylinder tensile specimens with V-shaped, whose notch root radius are 0.15, 0.3 and 0.5 mm, respectively. Due to the symmetry, only half of the specimen were modeled. The elements are of 4-node bilinear axisymmetric plane strain type in the stress analysis. The left boundary is loaded, while the right boundary is fixed in all the directions. The mesh size was refined near the notch tip area (about 3 μm). As shown in Figure 10, the path of the maximum principal stress analysis is along the radial direction of the model.

Figure 10 Analysis model of notched specimens:
Figure 11 shows the results of the FEA analysis of the radial distribution of the maximum principal stress as a function of the distance from the notch root with different notch root radii. In the case of notched specimens with an applied net load equal to 0.9Rm, the maximum principal stress along the path of radial direction exists with a maximum value corresponding to a distance away from the notch root. It can be seen from Figure 12 that the maximum value and its position are different due to different root radius of notch and different heat treatment methods. With the increase of notch root radius, the distance from the notch root tip increases and the maximum value of maximum principal stress decreases. This is consistent with the theoretical calculation results in Ref. [35].
It can be observed from Figure 12 that the peak of maximum principal stress differs with the different strength levels, corresponding to different tempered temperatures. With the increase of strength, the peak of maximum principal stress shifts left, which can be explained by the terms of elastic-plastic stress field mechanisms near the notch tip, that is to say, the location and area of plastic region will change with the strength level. The HILL’s slip line field solution shows the relationship between strength and plasticity width, as following [36]:
 (3)
(3)
where R0 represents the width of plasticity region; KI is the stress intensity factor; Rp0.2 is the yield strength. It can well explain the phenomenon of peak value shifting, i.e., with the increase of strength, the plasticity width R0 becomes small, and shifts toward to the notch tip.

Figure 11 FEA calculation results on distributions of maximum principal stress with different notch root radii for T520 steel

Figure 12 FEM calculation results on distributions of maximum principal stress with T460 and T520 steel at constant value of notch root radius (R=0.15 mm)
The stress distribution near the notch root will well account for the fracture surfaces of the hydrogen charged specimens. For the specimens with the condition of stress concentration, the peak of stress distribution exists in certain distance from notch root in the FEA results. Accordingly, the quasi-cleavage and tear ridges are found in the vicinity of the notch root. The initiation of cracking will be formed in the position of stress concentration. Moreover, the tear ridges seem to be related to high plastic strain in the T520 steel, owing to the higher plasticity compared to the T460 steel. In addition, the higher stress peak of the T460 steel corresponds to more quasi-cleavage regions. All the observed fractures surfaces are consistent with the stress peak in the FEA, which is helpful to realize the hydrogen embrittlement process of notched parts.
3.5 Effect of hydrogen concentration on flow stress of 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel
Figure 13 shows the effect of hydrogen charging on the flow stress of T520 steel. From Figure 13(a), it can be seen that the hydrogen atoms increase the elastic limit or the yield strength, but the variable quantity is not more than 10%. In addition, if hydrogen concentration in the steel is too low, such as C0=0.3×10-6, the effect of hydrogen concentration on the flow stress is too small to be measured. From Figure 13, the fitting line shows that the value of hydrogen-induced stress s* between the flow stress at point a and the yield strength at point b increases linearly with hydrogen concentration. The linear equation is expressed by the following:
s*=-0.622+2.015C0 (4)
These results are different from Zhang’s research [37] that the hydrogen atom can induce tension stress, and the yield strength of specimens after hydrogen charging increases with the increase of hydrogen concentration. To date, the effect of hydrogen on tensile strength, yield strength, hardness is a complex, sometimes controversial issue, which was extensively discussed elsewhere [38, 39]. Some studies showed that hydrogen atom could reduce the yield strength and tensile strength, but others exhibited different results. The formers explained that hydrogen atoms could enhance dislocation emission and motion, or decrease the resistant force for dislocation emission and motion. Thereby, the flow stress at point a was higher than the yield strength at point b. There are many reports to support the viewpoint. For example, BIRNBAUM et al [9] interpreted that in a hydrogen-free sample, it existed with a resistant force for dislocation motion, tD, which was acting between two dislocations. When hydrogen atoms were introduced into sample, the additional stress tH induced by hydrogen atmosphere around the dislocation would act on one dislocation, but the stress direction was opposite to the tD. Therefore, the resultant resistant force for dislocation moving tD+tH was lower than tD. ZHANG et al [40] indicated that a hydrogen atmosphere around a screw dislocation would become asymmetrical, if an external stress was applied. As a result, an additional stress tH would act on the dislocation and help the external force tex to enhance dislocation multiplication and motion.

Figure 13 Nominal stress-strain curves of T520 steel with hydrogen charged (a); fitting line between flow stress at point a and yield strength at point b
The latter views are consistent with our previous work. The effect of hydrogen on the flow stress of the T520 steel is that the hydrogen can induce geometric hardening. When hydrogen atoms are introduced into the steel by cathodic hydrogen charging, the hydrogen concentration and stress gradient will appear in the surface of sample. And this can enhance local plastic deformation on the surface of the sample. With the sample being loaded, the work hardening occurs on the surface of specimen before the whole specimen is yielded. And the following plasticity is retarded by the work hardening, which corresponds to the geometric hardening of specimens induced by hydrogen [41]. The condition of hydrogen induced hardening is described as [9]:
 (5)
(5)
where tH1 is the flow stress in the presence of hydrogen and slip localization; tH is the flow stress of hydrogen charged specimen; t0 is the flow stress of hydrogen uncharged specimen; a is the constant value; r is the density of movable dislocations; m is the stress exponent; l is the length of specimen; subscripts H represents the hydrogen charged specimen.
Accordingly, in this work, the yield strength of the 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel increases by cathodic hydrogen charging, which is higher than the flow stress of the specimen loaded without hydrogen charged in air. Meanwhile, from Figure 13(a), it can be observed that the plasticity has little effect on the flow stress of the experimental steel. Under the condition of the similar hydrogen concentration, the s* value that measured with the plastic strain about 2% in air is almost the same to that of the plastic strain 1% loaded in air, as shown in the curves with hydrogen concentration C0=11.0×10-6 and 11.5×10-6.
4 Conclusions
1) FEA calculation results indicate that the peak value of maximum principal stress near the notch tip has a relationship with the stress concentration and strength level. The peak value increases with the increase of strength, and also increases with the notch root radius decreasing.
2) From the results of TDS analysis of 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel after hydrogen charging, it shows that the first and second hydrogen desorption peaks of T460, T520 steel at the heating rate of 100 °C/h are 169.2 and 248.9, 172.1 and 225.0 °C, respectively. Correspondingly, the activation energies are 18.91 and 19.47, 17.74 and 21.77 kJ/mol, respectively. The hydrogen must be trapped by reversible trapping site, such as dislocations, the interfaces of martensitic laths.
3) Compared to the T520 steel, the T460 steel has much more susceptibility of hydrogen embrittlement. For both steels, the notch tensile strength decreases with the increase of hydrogen concentration. The notch tensile strength of higher strength T460 steel decreases sharply with the hydrogen concentration over 6×10-6.
4) The value of hydrogen-induced stress s* between the flow stress at point a and the yield strength at point b increases linearly with hydrogen concentration: s*=-0.622+2.015C0, which acts together with the external stress to affect the flow stress of the 5Ni-16Cr-Mo steel, if a load is applied.
Contributors
CHEN Ji-zhi provided the concept and edited the draft of manuscript. SUN Yong-wei conducted the literature review and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. WANG Ling-shui edited the draft of manuscript.
Conflict of interest
SUN Yong-wei, CHEN Ji-zhi, and WANG Ling-shui declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
[1] TAKASAWA K, IKEDA R, ISHIKAWA N, ISHIGAKI R. Effects of grain size and dislocation density on the susceptibility to high-pressure hydrogen environment embrittlement of high-strength low-alloy steels [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(3): 2669-2675. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.10.099.
[2] VILLALOBOS J C, DEL-POZO A, MAYEN J, SERNA S, CAMPILLO B. Hydrogen embrittlement suscetibility on X-120 microalloyed steel as function of tempering temperature [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(15): 9137-9148. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020. 01.094.
[3] DEPOVER T, PEREZ ESCOBAR D, WALLAERT E, ZERMOUT Z, VERBEKEN K. Effect of hydrogen charging on the mechanical properties of advanced high strength steels [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(9): 4647-4656. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.12.190.
[4] CHENG X Y, ZHANG H X. A new perspective on hydrogen diffusion and hydrogen embrittlement in low-alloy high strength steel [J]. Corrosion Science, 2020, 174: 108800. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108800.
[5] NAGUMO M. Hydrogen related failure of steels—A new aspect [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2004, 20(8): 940-950. DOI: 10.1179/026708304225019687.
[6] TEHRANCHI A, ZHOU X, CURTIN W A. A decohesion pathway for hydrogen embrittlement in nickel: Mechanism and quantitative prediction [J]. Acta Materialia, 2020, 185: 98-109. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2019.11.062.
[7] PANAGOPOULOS C N, GEORGIOU E P, CHALIAMPALIAS D. Cathodic hydrogen charging of zinc [J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 79: 16-20. DOI: 10.1016/ j.corsci.2013.10.016.
[8] TEHRANCHI A, CURTIN W A. The role of atomistic simulations in probing hydrogen effects on plasticity and embrittlement in metals [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2019, 216: 106502. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019. 106502.
[9] BIRNBAUM H K, SOFRONIS P. Hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity—A mechanism for hydrogen-related fracture [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1994, 176(1, 2): 191-202. DOI: 10.1016/0921-5093(94)90975-X.
[10] ORIANI R A. Whitney award lecture—1987: Hydrogen— the versatile embrittler [J]. Corrosion, 1987, 43(7): 390-397. DOI: 10.5006/1.3583875.
[11] TORIBIO J. Hydrogen embrittlement of prestressing steels: The concept of effective stress in design [J]. Materials & Design, 1997, 18(2): 81-85. DOI: 10.1016/S0261- 3069(97)00067-8.
[12] SEREBRINSKY S, CARTER E A, ORTIZ M. A quantum-mechanically informed continuum model of hydrogen embrittlement [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2004, 52(10): 2403-2430. DOI: 10.1016/ j.jmps.2004.02.010.
[13] KOTAKE H, MATSUMOTO R, TAKETOMI S, MIYAZAKI N. Transient hydrogen diffusion analyses coupled with crack-tip plasticity under cyclic loading [J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2008, 85(8): 540-549. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpvp.2008.02.002.
[14] LUFRANO J, SOFRONIS P. Numerical analysis of the interaction of solute hydrogen atoms with the stress field of a crack [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1996, 33(12): 1709-1723. DOI: 10.1016/0020-7683(95)00119-0.
[15] TAKAI K, CHIBA Y, NOGUCHI K, NOZUE A. Visualization of the hydrogen desorption process from ferrite, pearlite, and graphite by secondary ion mass spectrometry [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33(8): 2659-2665. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-002-0387-8.
[16] SOFRONIS P, MCMEEKING R M. Numerical analysis of hydrogen transport near a blunting crack tip [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1989, 37(3): 317-350. DOI: 10.1016/0022-5096(89)90002-1.
[17] CHEN Ji-zhi, WANG Jia-min, YIN Jiang-ning, ZHANG Xin-cheng. Study on fatigue properties of 0Cr16Ni5Mo stainless steel [J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2002, 17(3): 6-10. DOI: 10.19515/j.cnki.1003-1545. 2002.03.002. (in Chinese)
[18] RAYKAR N R, MAITI S K, SINGH RAMAN R K, ARYAN S. Study of hydrogen concentration dependent growth of external annular crack in round tensile specimen using cohesive zone model [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2013, 106: 49-66. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2013.04.007.
[19] MOHAN LAL D, RENGANARAYANAN S, KALANIDHI A. Cryogenic treatment to augment wear resistance of tool and Die steels [J]. Cryogenics, 2001, 41(3): 149-155. DOI: 10.1016/S0011-2275(01)00065-0.
[20] NISHIDA M. Stress concentration [M]. Tokyo: Morikita Shuppan, 1973.
[21] CHOO W Y, LEE J Y. Thermal analysis of trapped hydrogen in pure iron [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1982, 13(1): 135-140. DOI: 10.1007/BF02642424.
[22] WANG Mao-qiu, AKIYAMA E, TSUZAKI K. Effect of hydrogen and stress concentration on the notch tensile strength of AISI 4135 steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 398(1, 2): 37-46. DOI: 10.1016/ j.msea.2005.03.008.
[23] SUN Yong-wei, CHEN Ji-zhi, LIU Jun, FAN Fang-xiong. Effect of cryogenic treatment on microstructure and properties of 0Cr16Ni5Mo martensitic stainless steel [J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2014, 35(10): 148-153. DOI: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2014.10.028. (in Chinese)
[24] LI Wen-xian, GONG Hao-ran, BO Zhen-hai, CHEN Ding. Deep cryogenic treatment of metal materials [J]. Materials Review, 2000, 14(3): 16-18. (in Chinese)
[25] LEE J Y, LEE S M. Hydrogen trapping phenomena in metals with B.C.C. and F.C.C. crystals structures by the desorption thermal analysis technique [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 1986, 28(3, 4): 301-314. DOI: 10.1016/ 0257-8972(86)90087-3.
[26] KISSINGER H E. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1957, 29(11): 1702-1706. DOI: 10.1021/ac60131a045.
[27] GU J L, CHANG K D, FANG H S, BAI B Z. Delayed fracture properties of 1500 MPa bainite/martensite dual-phase high strength steel and its hydrogen traps [J]. ISIJ International, 2002, 42(12): 1560-1564. DOI: 10.2355/ isijinternational.42.1560.
[28] PRESSOUYRE G M. A classification of hydrogen traps in steel [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1979, 10(10): 1571-1573. DOI: 10.1007/BF02812023.
[29] PEREZ ESCOBAR D, VERBEKEN K, DUPREZ L, VERHAEGE M. Evaluation of hydrogen trapping in high strength steels by thermal desorption spectroscopy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2012, 551: 50-58. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.04.078.
[30] LIU Yan, WANG Mao-qiu, LIU Guo-quan. Effect of hydrogen on ductility of high strength 3Ni-Cr-Mo-V steels [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 594: 40-47. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.11.058.
[31] LI Song-jie, ZHANG Zuo-gui, AKIYAMA E, TSUZAKI K, ZHANG Bo-ping. Evaluation of susceptibility of high strength steels to delayed fracture by using cyclic corrosion test and slow strain rate test [J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(5): 1660-1667. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2010.02.005.
[32] HWANG C, BERNSTEIN I M. Dislocation transport of hydrogen in iron single crystals [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1986, 34(6): 1001-1010. DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(86)90209-9.
[33] DE NAGAO A, SMITH C D, DADFARNIA M, SOFRONIS P, ROBERTSON I M. The role of hydrogen in hydrogen embrittlement fracture of lath martensitic steel [J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(13, 14): 5182-5189. DOI: 10.1016/ j.actamat.2012.06.040.
[34] WAKASA K, WAYMAN C M. The morphology and crystallography of ferrous lath martensite. Studies of Fe-20%Ni-5%Mn—I. Optical microscopy [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1981, 29(6): 973-990. DOI: 10.1016/0001- 6160(81)90051-1.
[35] YOKOBORI A T Jr, NEMOTO T Jr, SATOH K Jr, YAMADA T Jr. Numerical analysis on hydrogen diffusion and concentration in solid with emission around the crack tip [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1996, 55(1): 47-60. DOI: 10.1016/0013-7944(96)00002-1.
[36] HILL R. The mathematical theory of plasticity [M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1954.
[37] ZHANG T, CHU W Y, GAO K W, QIAO L J. Study of correlation between hydrogen-induced stress and hydrogen embrittlement [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 347(1, 2): 291-299. DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(02) 00600-7.
[38] DELAFOSSE D, MAGNIN T. Hydrogen induced plasticity in stress corrosion cracking of engineering systems [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2001, 68(6): 693-729. DOI: 10.1016/S0013-7944(00)00121-1.
[39] WANG Mao-qiu, AKIYAMA E, TSUZAKI K. Effect of hydrogen on the fracture behavior of high strength steel during slow strain rate test [J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(11): 4081-4097. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2007.03.038.
[40] ZHANG Tong-yi, CHU Wu-yang, HSIAO C M. Mechanism of hydrogen induced softening [J]. Scripta Metallurgica, 1986, 20(2): 225-230. DOI: 10.1016/0036-9748(86) 90131-6.
[41] MATSUI H, KIMURA H, MORIYA S. The effect of hydrogen on the mechanical properties of high purity iron [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1979, 40: 207-227. DOI: 10.1016/0025-5416(79)90191-5.
(Edited by ZHENG Yu-tong)
中文导读
5Ni-16Cr-Mo钢的力学性能与氢含量之间的本构关系
摘要:本文定性研究了不同强度级别5Ni-16Cr-Mo钢的缺口拉伸强度与氢含量之间的关系。利用慢应变速率拉伸试验,对缺口半径为0.15 mm的圆棒状试样进行了充氢后缺口拉伸强度的测定。同时,利用升温脱氢分析试验,研究了不同强度级别试验钢的氢扩散行为。慢应变速率拉伸试验结果表明,相比T520钢,T460钢具有较高的氢脆敏感性。试验钢的氢逸出激活能和微观组织表明,位错和板条马氏体间隙为5Ni-16Cr-Mo钢的氢陷阱。此外,利用慢应变速率拉伸试验测定了试样的氢致内应力,结果表明,空气中充氢试样在加载条件下其弹性极限大于未加载时未充氢试样的流变应力。试验钢中氢致内应力与氢含量呈线性关系,可表示为s*=-0.622+2.015C0。利用有限元分析模拟了试验钢缺口根部的应力分布,其最大主应力随着缺口半径的减小而增大。
关键词:5Ni-16Cr-Mo钢;慢应变速率拉伸试验;升温脱氢分析;有限元分析;氢脆
Foundation item: Project(3220024018) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Luoyang Sunrui Special Equipment Co., Ltd., China
Received date: 2020-08-20; Accepted date: 2021-01-05
Corresponding author: SUN Yong-wei, PhD, Senior Engineer; Tel: +86-379-64829071; E-mail: weiyong09@163.com; ORCID: https:// orcid.org/0000-0002-1716-4947

