Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 24(2014) 2107-2111
Microstructural evolution in Al-Zn eutectoid alloy by hot-rolling
Toshiaki MANAKA1, Goroh ITOH2, Yoshinobu MOTOHASHI2, Takaaki SAKUMA2
1. School of Science and Engineering, Ibaraki University, 4-12-1 Nakanarusawa, Hitachi, Ibaraki 316-8511, Japan;
2. College of Engineering, Ibaraki University, 4-12-1 Nakanarusawa, Hitachi, Ibaraki 316-8511, Japan
Received 17 October 2013; accepted 8 April 2014
Abstract: The Al-Zn eutectoid alloy has been widely known as a typical superplastic metallic material, where fine-grained microstructure is usually obtained by heat treatment. Recently, thermo-mechanical controlled process has also been reported to provide a fine-grained microstructure. In the present study, Al-Zn alloy ingots of 20 mm in thickness were homogenized and hot-rolled to a thickness of 2 mm under three processes: 1) the specimen was air-cooled after homogenization and hot-rolled; 2) the specimen was water-quenched after homogenization and hot-rolled; 3) the specimen was immediately hot-rolled after homogenization. Microstructural observation showed that, in processes 1 and 3, lamellar microstructure was formed after homogenization, and became fragmented to fine-grained microstructure as the hot rolling process proceeded. In process 2, fine-grained microstructure without lamellar microstructure was attained throughout the hot-rolling process. A minimum grain size of 1.6 μm was obtained in process 3. Tensile tests at room temperature showed that the elongation to failure was the largest in process 3.
Key words: aluminum-zinc alloy; eutectoid; microstructure control; hot-rolling; superplastic material
1 Introduction
The Al-Zn eutectoid alloy has been known to exhibit superplasticity at high testing temperatures, where fine-grained microstructure is usually obtained by solution treatment, water-quenching and subsequent aging at elevated temperatures [1]. This alloy had been used as cases of a printer and a ticket machine produced by superplastic forming [2]. Recently, severe plastic deformation, such as equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE) and high pressure torsion (HTP), has been reported to provide ultrafine-grained microstructure in this alloy [3-6]. Thermo-mechanical controlled process (TMCP), where hot-rolling is conducted by controlling temperature, cooling way, etc, has also been reported to provide a fine-grained microstructure. The microstructure in the Al-Zn alloy rolled by TMCP was reported to provide a grain size of about 1 μm with a nanocrystalline substructure, and the alloy was reported to exhibit superplastic behavior at room temperature [7-9]. Since the critical cooling rate in TMCP is slower than that in the above-mentioned traditional process, it can be applied to thick-gage components. In Japan, plates produced by TMCP have been used as a seismic damper in high-rise buildings and wooden detached houses for the protection against earthquakes [10-12]. However, condition to obtain fine-grained microstructure in TMCP and its mechanism have not been elucidated yet.
Therefore, in the present study, control conditions in hot rolling such as cooling way after homogenization, rolling timing have been investigated in an Al-Zn eutectoid alloy to obtain fine-grained microstructures by hot-rolling. Also, tensile tests were performed at room temperature to assess the mechanical properties.
2 Experimental
The material used in the present study was an Al-Zn eutectoid alloy. The composition of the alloy is shown in Table 1. This alloy exists as a solid solution α′ phase above eutectoid temperature (275 °C). The α′ phase decomposes into two phases, α and β, where α is Al-rich, FCC structure and β is Zn-rich, HCP structure below eutectoid temperature. Pure Al (99.99%), pure Zn (99.99%) and Al-40%Cu alloy were melted in a graphite crucible and then cast into ingots of 27 mm in thickness, 32 mm in width and 200 mm in height. Three different ingots, air-cooled or water-quenched after homogenization at 350 °C for 5 h and as-cast were cut and scalped into specimens with 20 mm in thickness, 30 mm in width and 60 mm in length.
Table 1 Chemical composition of specimen (mass fraction, %)
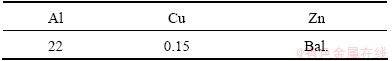
Conventional rolling mill without a heating device was used for hot-rolling. In order to obtain the final sheet of 2 mm in thickness from a 20 mm-thick ingot, i.e. a total rolling reduction of 90%, the hot rolling process was conducted under conditions shown in Fig. 1. In process 1, the specimen was air-cooled after homogenization, and heated to 250 °C in 30 min, hot-rolled to underlined thickness, re-heated to 250 °C in 10 min and then subjected to repetitive hot rolling and re-heating steps. In process 2, the specimen was water-quenched after homogenization, heated to 250 °C in 30 min, hot-rolled to underlined thickness, water- quenched, re-heated to 250 °C in 30 min and then subjected to repetitive hot rolling and re-heating steps. In process 3, the specimen was immediately hot-rolled after homogenization to underlined thickness, re-heated to 250 °C in 10 min and then subjected to repetitive hot rolling and re-heating steps. Specimen measured with a thermocouple until it broke during hot rolling process is shown in Fig. 2.
After hot rolling process, L-LT, L-ST and LT-ST sections (perpendicular to the ST (short transverse), LT (long transverse) and L (longitudinal) directions, respectively) were cut from final and intermediate sheets. Microstructural observation was conducted on mirror-finished samples by a HITACHI S-2150 scanning electron microscope (SEM) at an accelerating voltage of 20 kV. Degree of grain refinement was evaluated with average grain size l.
l=1.75d (1)
where d is the linear intercept length and averaged in two directions for the three sections [1].
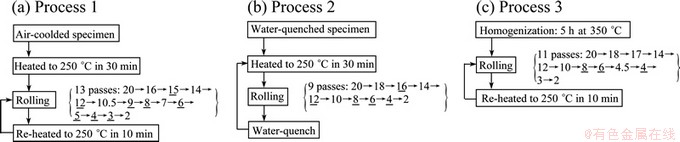
Fig. 1 Three kinds of hot-rolling process
Fig. 2 Thermal and rolling pass history of specimens during hot-rolling process
To carry out tensile tests at various strain rates, tensile test piece with 6 mm in gauge length and 3 mm in width was cut from the final sheets produced under the three conditions. The gauge was parallel to a rolling direction. Tensile tests were performed at 27 °C in air at strain rates ranging from 1.4×10-4 s-1 to 1.4×10-1 s-1.
3 Results and discussion
Figure 3 shows SEM images in L-LT section of the specimen hot-rolled under process 1. The dark and bright phases shown in each image correspond to the Al-rich α and Zn-rich β phases, respectively. At every stage, lamellar microstructure is observed. However, it is observed that a granular microstructure replaces a part of the initial lamellar microstructure and resultantly microstructure becomes fragmented into a fine-grained microstructure as the hot rolling process proceeds. The average grain size of a granular microstructure in 2 mm-thick sheet is 2.0 μm. Fine-grained microstructure without lamellar microstructure is shown in Fig. 4 for the specimens hot-rolled under the process 2. The average grain size tended to increase from 1.6 to 3.2 μm as the process proceeded. A minimum grain size of 1.6 μm is observed in 8 mm-thick sheet. Microstructural observations in processes 1 and 2 give similar results with the previous studies [13,14]. Figure 5 shows SEM images in L-LT section of the specimen hot-rolled under process 3. With process 1, lamellar microstructure is observed at every stage and microstructure becomes fragmented into a fine-grained microstructure as the hot rolling process proceeds. It is noted that lamellar spacing of the specimen hot-rolled under process 3 is finer than that under process 1. The average grain size of a granular microstructure in 2 mm-thick sheet is 1.6 μm. Figure 6 shows the true stress-strain curves examined at 27 °C in air at strain rates ranging from 1.4×10-4 s-1 to 1.4×10-1 s-1. At any strain rate and process, the stress decreases to failure without work hardening after the maximum stress. Figure 7 shows strain rate dependency of flow stress (the maximum stress in Fig. 6) and elongation to failure. At any strain rate, the elongation in process 3 is the largest among the three processes. The elongation at room temperature in process 3 is ~100% at strain rate of 1.4×10-4 s-1.

Fig. 3 SEM images in L-LT section of specimen processed under process 1 with specimen thickness of 8 mm (a), 4 mm (b) and 2 mm (c)
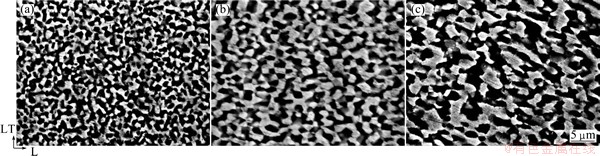
Fig. 4 SEM images in L-LT section of specimen processed under process 2 with specimen thickness of 8 mm (a), 4 mm (b) and 2 mm (c)
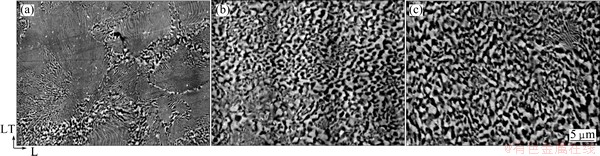
Fig. 5 SEM images in L-LT section of specimen under processed process 3 with specimen thickness of 8 mm (a), 4 mm (b) and 2 mm (c)
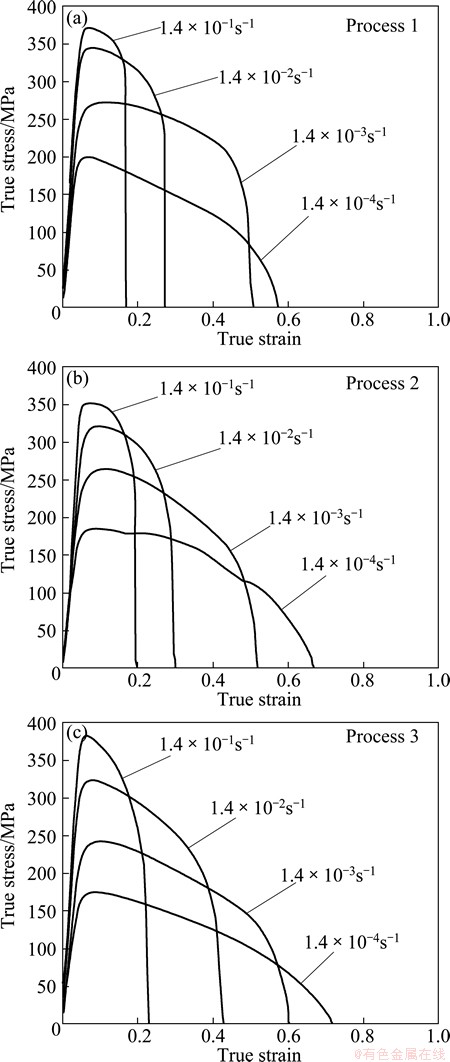
Fig. 6 True stress vs strain curves of specimens processed under process 1 (a), process 2 (b) and process 3 (c)
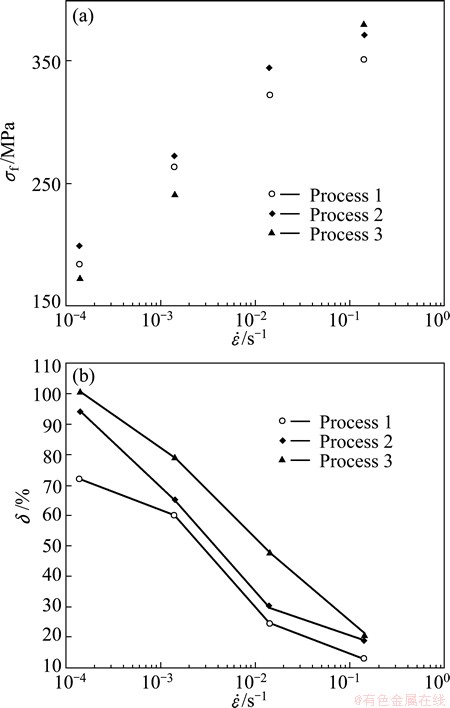
Fig. 7 Strain rate dependency of flow stress σf (a) and elongation to failure δ (b)
When eutectoid reaction occurs in this alloy, if the transformation occurs at higher temperature than 100 °C, the lamellar microstructure is formed. The higher the transformation temperature is, the coarser the lamellar spacing is. When the transformation temperature is lower than 50 °C, a fine-grained microstructure is formed [15]. Therefore, the difference whether lamellar microstructure was formed or not was resulted from cooling rate after homogenization. In process 2, the average grain size tended to increase as the hot-rolling process proceeded. It seemed that repetitive heating steps led to grain growth.
JUN et al [16] have reported that lamellar colonies in Zn-15%Al alloy gradually changed into equi-axed grains during cold rolling due to dynamic recrystallization. However, adequate investigations on dynamic recrystallization during cold rolling have not been carried out. Therefore, it is difficult to conclude that the microstructural change is due to dynamic recrystallization. In the present study, lamellar microstructure changed into fine-grained microstructure during hot rolling. We suppose that this microstructural change was resulted from shear deformation by rolling.
The average grain size of a granular microstructure in 2 mm-thick sheet was smaller in process 3 than in process 1, corresponding to the original lamellar spacing. In processes 1 and 3, lamellar microstructure became fragmented into a granular microstructure as hot-rolling process proceeded. Hence, the grain size of a granular microstructure produced by fragmentation of the lamellae depends on lamellar spacing. In other words, the finer the lamellar spacing is, the finer the grain size is.
4 Summery
The Al-Zn eutectoid alloy ingots of 20 mm in thickness, air-cooled, water-quenched and immediately after homogenization were hot-rolled to 2 mm in thickness. Microstructural observation showed that, in processes 1 and 3, lamellar microstructure was formed and became fragmented into fine-grained microstructure as the hot rolling process proceeded. In process 2, fine-grained microstructure without lamellar microstructure was attained. The minimum grain size of 1.6 m was obtained in process 3. The elongation was the largest in process 3 and ~100% at strain rate of 1.4×10-4 s-1 at room temperature.
References
[1] MOTOHASHI Y, SHIBATA T. Effects of grain size on mechanical properties of superplastic Al-Zn eutectoid alloy at 4.2 to 523 K [J]. Journal of the Japan Institute of Light Metals, 1980, 30(11): 634-642. (in Japanese)
[2] MOTOHASHI Y, ITOH G. Development in applied research of superplasticity [J]. Science of Machine, 2001, 53: 1115-1126. (in Japanese)
[3] FURUKAWA M, HORITA Z, NEMOTO M, VALIEV R Z, LANGDON T G. Fabrication of submicrometer-grained Zn-22%Al by torsion straining [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 1996, 11(9): 2128-2130.
[4] TANAKA T, WATANABE H, HIGASHI K. Microstructure in Zn-Al alloys after equal-channel-angular extrusion [J]. Material Transactions, 2003, 44(9): 1891-1894.
[5] KUMAR P, XU C, LANGDON T G. Mechanical characteristics of a Zn-22%Al alloy processed to very high strains by ECAP [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 429: 324-328.
[6] KAWASAKI M, LANGDON T G. Developing superplasticity and a deformation mechanism map for the Zn-Al eutectoid alloy processed by high-pressure torsion [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 6140-6145.
[7] MAKII K, MIMURA Y, UEDA H, OKADA T. Japan patent office, 11-222643 [P]. 1999.
[8] MAKII K, SEKI Y, KUSHIBE A, HIGASHI K. Realizing high strain rate super plasticity at room temperature using thermo mechanical controlling process [C]//The Fourth Pacific Rim International Conference on Advanced Materials and Processing (PRICM4). Honolulu, 2001: 1977-1978.
[9] TANAKA T, MAKII K, KUSHIBE A, HIGASHI K. Room temperature deformation behavior of Zn-22mass%Al alloy with nanocrystalline structure [J]. Materials Transactions, 2002, 43(10): 2449-2454.
[10] MAKII K, UEDA H, OKADA T, KATO M, MIMURA Y, TABUCHI M. High-speed superplasticity at room temperature for seismic device applications [J]. Kobe Steel Engineering Reports, 2001, 51: 34-37. (in Japanese)
[11] TANAKA T, MAKII K, UEDA H, KUSHIBE A, KOHZU M, HIGASHI K. Study on practical application of a new seismic damper using a Zn-Al alloy with a nanocrystalline microstructure [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2003, 45: 1599-1612.
[12] TAKAGI T, MAKII K, KUSHIBE A, AOKI K, HIGASHI K, CHAING L. Room-temperature super-plastic ultra fine grained Zn-Al alloys and their application to seismic dampers in wooden detached houses [J]. Kobe Steel Engineering Reports, 2005, 55: 41-44. (in Japanese)
[13] LOC T N, ITOH G, YI Y, MOTOHASHI Y, SAKUMA T. Microstructural Control of a Zn-Al eutectoid alloy by hot-rolling [C]//International Conference on Processing and Manufacturing of Advanced Materials Processing, Fabrication, Properties, Applications (THERMEC 2011). Quebec City, 2011: 77-80.
[14] MANAKA T, ITOH G, LOC T N, MOTOHASHI Y, SAKUMA T. Microstructural control of a Zn-22Al alloy by rolling process [C]// 11th International Conference on Superplasticity in Advanced Materials (ICSAM2012). Albi City, 2012: 289-294.
[15] KATO M, KAWAI E, MUTSUZAKI K, MIYAGAWA M. Effects of microstructure changes in aging on the mechanical behavior of eutectoid Zn-22%Al alloy at room temperature [J]. Journal of the Japan Institute of Metals, 1974, 38: 539-545. (in Japanese)
[16] JUN J H, SEONG K D, KIM J M, KIM K T, JUMG W J. Strain-induced microstructural evolution and work softening behavior of Zn-15% Al alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 434-435: 311-314.
热轧Al-Zn共析合金的显微组织演变
Toshiaki MANAKA1, Goroh ITOH2, Yoshinobu MOTOHASHI2, Takaaki SAKUMA2
1. Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Ibaraki University, 4-12-1 Nakanarusawa, Hitachi-City 316-8511, Japan;
2. College of Engineering, Ibaraki University, 4-12-1 Nakanarusawa, Hitachi-City 316-8511, Japan
摘 要:Al-Zn共析合金是一种典型的超塑性金属材料,其细小晶粒组织一般通过热处理获得。近来,热力学控制过程已经运用于微观组织细化。据此,将20 mm厚的铸锭分别按以下3种方案进行均匀化,并热轧至2 mm厚以获得细化微观组织。这3种方案分别为:1)均匀化后空冷和热轧;2)均匀化后水淬和热轧;3)均匀化后立即热轧。微观组织观察表明:采用方案1和3均匀化后形成片层组织,并且在热轧进行的时候破碎成细小的晶粒组织。采用方案2处理时,细小的晶粒组织直接通过热轧过程获得,中间没有形成层片组织。结果表明,采用方案3处理后获得的材料晶粒最小,其尺寸为1.6 μm;室温下拉伸测试结果表明,采用方案3处理的材料的伸长率最大。
关键词:Al-Zn合金;共析;微观组织控制;热轧;超塑性材料
(Edited by Xiang-qun LI)
Corresponding author: Toshiaki MANAKA; Tel: +81-29-438-5042; E-mail:08t1077s@gmail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63319-7