DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.05.018
深部岩体在掏槽爆破过程中的损伤演化机制
谢理想1, 2, 3,卢文波1, 2,姜清辉1, 2,张乾兵3,王高辉1, 2,陈明1, 2,严鹏1, 2
(1. 武汉大学 水资源与水电工程科学国家重点实验室,湖北 武汉,430072;
2. 武汉大学 水工岩石力学教育部重点实验室,湖北 武汉,430072;
3. 莫纳什大学 土木工程系,澳大利亚 墨尔本,VIC 3800)
摘要:为研究深部岩体掏槽爆破过程中岩体的损伤演化机制,将Cowper-Symonds硬化模型与拉压损伤模型耦合以后的模型嵌入到LS-DYNA软件中对其进行数值模拟研究。数值模拟结果表明:地应力及临空面的存在对岩体的损伤演化机制有影响,地应力存在对应力波所诱发的压力载荷产生抵制作用,使得岩体受压力荷载作用产生的损伤范围受到影响,随着地应力增大,掏槽爆破岩体的损伤范围变小;掏槽爆破中的中心孔有充当临空面的作用,使得应力波在遇到临空面时形成拉伸波,并造成中心孔附近岩体的拉损伤往岩体内部扩展,最终有加大掏槽孔周围岩体的损伤范围作用。
关键词:深部岩体;掏槽爆破;拉压损伤模型;地应力;抵制作用;损伤范围
中图分类号:TU443 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2017)05-1252-09
Damage evolution mechanism of deep rock mass in process of cut blasting
XIE Lixiang1, 2, LU Wenbo1, 2, JIANG Qinghui1, 2, ZHANG Qianbing3, WANG Gaohui1, 2, CHEN Ming1, 2, YAN PENG1, 2
(1. State Key Laboratory of Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China;
2 Key Laboratory of Rock Mechanics in Hydraulic Structure Engineering of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China;
3. Department of Civil Engineering, Monash University, Melbourne VIC 3800, Australia)
Abstract: For the purpose of research on the damage evolution mechanism of deep rock mass in the process of cut blasting, a coupled model between the Cowper-Symonds hardening model and tension-compression damage model was implemented into commercial software LS-DYNA to simulate the damage evolution mechanism of deep rock mass in the process of cut blasting. The numerical results show that the in-situ stress and existence of free surface have an influence on the damage evolution mechanism of deep rock mass in the process of cut blasting. Since the in-situ stress exerts the resistance on the pressure load induced by blasting load in the rock mass, the damage scope of the rock mass surrounding the cut holes is influenced accordingly, and the damage scope decreases with the increase of the in-situ stress. However,
in the process of cut blasting, the center hole as a free surface can enlarge the damage scope surrounding the cut holes. That is because the stress waves change into tensile stress waves upon the reflection at the free surface, here, and the tensile damage caused by tensile stress waves at the free surface propagates toward the inner rock mass, and eventually the damage scope of the rock mass surrounding the cut holes is enlarged.
Key words: deep rock mass; cut blasting; tension-compression damage model; in-situ stress; resistance; damage scope
我国水电建设、交通运输工程建设、地下矿产资源的开发以及我国锦屏暗物质实验室的建设等均涉及深部岩体的掏槽爆破开挖过程。深部岩体由于受到高地应力的作用使其具有不同于浅部岩体的特征[1-2],浅部岩体由于承受地应力较小,其破坏特性为脆性能或断裂韧度控制破坏,而深部岩体受高地应力的影响,其破坏转化为由侧向应力控制的断裂生长破坏,更进一步,由浅部的脆性力学响应转化为深部岩体潜在的延性行为力学响应[3-8],加上岩体动载强度有明显的应变率效应[9-10],会使得深部岩体的强度较高,最终使得深部岩体的掏槽爆破开挖在高地应力的夹制作用下出现困难。而掏槽爆破在爆破开挖过程中又起到至关重要的作用,因为掏槽爆破能否形成临空面以及临空面形成的好坏关系到后续其他爆破工序能否顺利进行,由此可见深入研究深部岩体在爆破开挖下岩体损伤演化力学机制具有重要意义。可以从理论上认识岩体在爆破荷载作用下造成损伤的原因以及高地应力在岩体受到爆炸荷载作用损伤时所起到的作用,从而可以为深部岩体的爆破开挖设计提供理论上的指导作用。在研究深部岩体掏槽爆破的损伤演化机制时,需要选择一种合适的损伤本构模型。现有对爆破损伤本构模型的研究中,以GK模型、TCK模型以及KUS模型为代表的损伤模型,认为岩体仅在体积拉伸条件下存在损伤效应,而没有很好地考虑岩体受到冲击波作用时而引起的压剪损伤[11-15],为此,许多研究者建立了能够反映岩石压剪损伤及拉损伤的本构模型[16-20],从而可以较好地模拟岩体在爆破荷载作用下的损伤过程。由此可见拉压损伤模型是模拟掏槽爆破损伤演化机制比较理想的模型。已有的深部岩体工程爆破实践表明:在深部岩体采用掏槽爆破时,由于岩体受到高地应力的夹制作用,通常要采取增大装药量及在掏槽爆破时布置中心孔充当自由面等措施,以达到形成临空面的目的[21],由此可见地应力和自由面影响掏槽爆破岩体的损伤演化机制,在分析掏槽爆破岩体损伤演化机制时,既要考虑地应力因素对掏槽爆破损伤演化机制造成的影响,也要考虑中心孔在掏槽爆破过程中对岩体破坏损伤所起的作用。现有模拟岩体的掏槽爆破过程时,采用施加等效荷载在等效弹性边界上的方法,忽略了深部岩体掏槽爆破开挖岩体所应具有的自由边界条件的影响。本文作者为了能够反映深部岩体掏槽爆破的损伤演化机制,除了采用在LS-DYNA软件中二次开发的拉压损伤本构模型外,还在掏槽孔中心布置中心孔来考虑掏槽爆破开挖所具有的自由边界条件,同时分析地应力对岩体损伤演化所造成的影响。
1 数值计算
1.1 数值模型
为了简化数值模拟的计算量,本文采用有限元平面模型来模拟,数值模型长×宽为200 m×200 m。为了提高计算速度及计算精度,在所关注的炮孔周围近区细化单元,在离炮孔远区采用较大的单元尺寸,数值模型中单元总数为266 172个,最小单元尺寸为炸药模型单元尺寸,其值为4 mm,最大单元尺寸为1.3 m。在数值模型中布置1圈掏槽孔,其炮孔直径为42 mm,其他参数设置如表1所示。本文中为了比较地应力对深部岩体在爆破开挖中的应力波在岩体中所诱发的压力荷载以及所诱发的岩体损伤所造成的影响,只考虑静水压力条件下均匀应力场的情况。上边界及左右边界施加静水压力及无反射边界条件,并在底边施加法向约束。其模型局部网格放大图如图1所示。
由于深部岩体受到高地应力的作用,在分析深部岩体掏槽爆破岩体损伤演化时,需要给模型施加初始应力,因此,深部岩体掏槽爆破岩体损伤演化计算涉及到动静耦合计算。LS-DYNA显式方法对短时间的瞬态动力学计算是比较理想的,但采用LS-DYNA显式方法对静态问题进行分析,没有ANASYS的隐式算法在处理计算静态问题时那么有效,为此采用ANASYS LS-DYNA隐-显式连续求解的方法分析深埋硐室爆破岩体损伤演化过程。采用隐式分析生成初始地应力,然后通过单元转换,由隐式分析转换成显式分析[22]。在显式计算中,炸药采用ALE算法,岩体采用Lagrange算法,并将炸药与岩体通过流固耦合方式来模拟深部岩体爆破岩体损伤演化过程。
表1 炮孔参数
Table 1 Parameter of blast holes
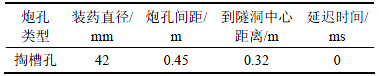

图1 数值模型
Fig. 1 Numerical model
1.2 炸药状态方程
在模拟炸药对岩体破坏作用时,由于JWL状态方程能够在较大的压力范围内具有适用性,因此,炸药材料选用JWL状态方程材料模型[23-25]。其JWL状态方程如式(1),JWL 7个状态方程参数A,B,R1,R2,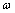 ,
,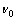 和E0如表2所示。
和E0如表2所示。
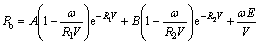 (1)
(1)
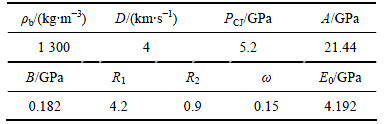
表2 炸药材料参数及JWL状态方程参数
Table 2 Explosive material parameters and JWL state equation parameters
1.3 岩体材料模型
本文采用与应变率响应有关Cowper-Symonds硬化模型[26],岩体的屈服应力与应变率之间的关系如下:
 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
式中: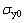 为岩体处于受压状态下的初始屈服应力;E0为弹性模量;
为岩体处于受压状态下的初始屈服应力;E0为弹性模量; 为加载应变率;C和P为Cowper- Symonds应变率参数,是由材料应变率特性决定的常量;EP为岩体塑性硬化模量,为切线模量;
为加载应变率;C和P为Cowper- Symonds应变率参数,是由材料应变率特性决定的常量;EP为岩体塑性硬化模量,为切线模量;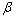 为各向同性硬化与随动硬化的贡献的硬化参数,0≤
为各向同性硬化与随动硬化的贡献的硬化参数,0≤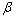 ≤1;
≤1;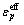 为有效塑性应变,按下式定义:
为有效塑性应变,按下式定义:
 (4)
(4)
 (5)
(5)
根据深部岩体所表现的力学变形破坏特性,损伤演化采用拉损伤和压剪损伤组合破坏准则,采用1个通式表示为
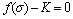 (6)
(6)
式中:K为岩石破坏强度,随着应力状态的变化而变化。如果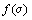 ≥K,说明岩石达到破坏,本文采用拉损伤和压剪组合损伤。岩体的拉损伤可以采用最大拉应力准则
≥K,说明岩石达到破坏,本文采用拉损伤和压剪组合损伤。岩体的拉损伤可以采用最大拉应力准则 ≥
≥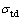 (
(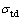 为材料的动态抗拉强度)判别,压剪损伤采用经验公式
为材料的动态抗拉强度)判别,压剪损伤采用经验公式 ≥
≥ (
( 为材料的动态抗压强度,Ac为岩石材料常数)[27],因此,
为材料的动态抗压强度,Ac为岩石材料常数)[27],因此,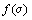 表示如下:
表示如下:
 (7)
(7)
式中: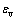 为体应变,用其判别岩体所处的力学状态,
为体应变,用其判别岩体所处的力学状态,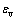 ≤0表示岩石材料处于抗拉状态,
≤0表示岩石材料处于抗拉状态,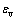 >0表示岩石材料处于抗压状态, 是与岩石材料损伤程度有关的常数,大多数岩石的Ac取值范围为0.4~0.6,本文取值为0.5。
>0表示岩石材料处于抗压状态, 是与岩石材料损伤程度有关的常数,大多数岩石的Ac取值范围为0.4~0.6,本文取值为0.5。
岩石类材料在动载作用下有明显的应变率效应,可以将动态抗压强度与抗拉强度与应变率之间的关系表示为[28]:
 (8)
(8)
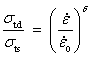 (9)
(9)
式中: =3.0×10-6,为岩石在受压条件下的参考应变率;
=3.0×10-6,为岩石在受压条件下的参考应变率; =3.0×10-6,为岩石在受拉条件下的参考应变率;
=3.0×10-6,为岩石在受拉条件下的参考应变率;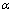 和
和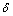 分别为岩石在动载作用下抗压与抗拉强度的应变率响应常数。为了利于将本构模型嵌入到LS-DYAN软件,本文在考虑应变响应的条件下,将岩石动态抗拉与抗压强度取为常数。岩体在炮孔周围的应变率范围为100~105 s-1,压损伤区作用范围较小,其内部应变率响应较大,一般应变率
分别为岩石在动载作用下抗压与抗拉强度的应变率响应常数。为了利于将本构模型嵌入到LS-DYAN软件,本文在考虑应变响应的条件下,将岩石动态抗拉与抗压强度取为常数。岩体在炮孔周围的应变率范围为100~105 s-1,压损伤区作用范围较小,其内部应变率响应较大,一般应变率 的范围为102~104 s-1,拉损伤区作用范围较大,其内部应变率响应较小,一般应变率
的范围为102~104 s-1,拉损伤区作用范围较大,其内部应变率响应较小,一般应变率 的范围为100~103 s-1。根据炮空周围岩石的拉压损伤区内岩石的应变率响应范围,以及岩石的动态抗压与抗拉强度与静态抗压与抗拉强度经过量纲一化后与应变率之间的拟合曲线关系[8],可以将岩石在动态抗压时
的范围为100~103 s-1。根据炮空周围岩石的拉压损伤区内岩石的应变率响应范围,以及岩石的动态抗压与抗拉强度与静态抗压与抗拉强度经过量纲一化后与应变率之间的拟合曲线关系[8],可以将岩石在动态抗压时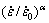 的值取为4,岩石在动态抗压时
的值取为4,岩石在动态抗压时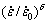 的值取为1.5,根据文献[29]中的岩石力学参数,岩石的动态抗压强度取值为600 MPa,岩石的动态抗拉强度取值为15 MPa,岩石的其他动态力学参数如表3所示。
的值取为1.5,根据文献[29]中的岩石力学参数,岩石的动态抗压强度取值为600 MPa,岩石的动态抗拉强度取值为15 MPa,岩石的其他动态力学参数如表3所示。
表3 岩体力学参数
Table 3 Rock mechanical parameters

由于岩石类材料内部结构的微元单元所具有的强度不同,并考虑岩体的变形破坏是一个连续的过程,进行如下假设:1) 岩石材料性质宏观上表现出各向同性;2) 岩石微元破坏前服从胡克定律,即微元具有线弹性性质;3) 各微元的强度服从Weibull分布,其概率密度函数为
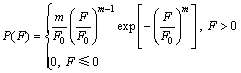 (10)
(10)
式中:F为分布参数(例如强度、弹性模量等);F0为微元体内参数的平均值;m为岩石材料内部微元强度的分布集中程度。F0和m为材料的Weibull分布参数。
岩石的损伤是由其中的微元体不断渐进破坏所引起的。假定岩石内部单元受到荷载作用时,其内部已破坏的微元数为Nf,定义统计损伤为已破坏的微元体数目与总微元体数N之比为
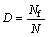 (11)
(11)
在任意区间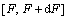 内已破坏的微元数为
内已破坏的微元数为 。当载荷加载到某一水平F时,已破坏微元数目为
。当载荷加载到某一水平F时,已破坏微元数目为
 (12)
(12)
将式(12)代入式(11)得到损伤变量
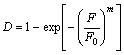 (13)
(13)
式中:D为损伤因子,0≤D≤1表示岩体的损伤程度,D=0表示完好岩体,D=1表示岩体完全失去承载能力,发生破坏。
由于 可以反映岩石材料内部结构变形破坏的强度,因此,可以作为岩石微元强度随机分布的1个分布变量,可以令
可以反映岩石材料内部结构变形破坏的强度,因此,可以作为岩石微元强度随机分布的1个分布变量,可以令
 (14)
(14)
由此可以得到岩石类材料的损伤演化变量定义为:
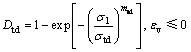 (15)
(15)
 (16)
(16)
 (17)
(17)
式中:Dtd为岩石在拉损伤破坏时的Weibull分布参数;Dcd为岩石在压损伤破坏时的Weibull分布参数,本文根据文献[30]中对mtd和mcd取值方法,mtd取值为2.5,mcd本文取值为4.5。
采用应力等效的方法[31]将拉压损伤和Cowper- Symonds硬化模型进行耦合,并将耦合后的损伤模型在LS-DYNA软件提供的二次开发接口对模型进行二次开发,并将模型嵌入到LS-DYNA软件中对岩体的损伤演化计划机制进行数值模拟研究,其二次开发本构模型的流程如图2所示。

图2 Cowper-Symonds硬化模型与拉压损伤模型的耦合流程
Fig. 2 Coupling process of Cowper-Symonds hardening model and tension-compression damage model
2 数值计算结果与分析
由于深部岩体岩体受到高地应力的作用,当爆炸应力波在岩体中传播时,地应力不可避免的对爆炸应力波产生作用,由此可见深部岩体岩体的损伤是地应力与应力波耦合作用的结果。为了能够很好地分析掏槽爆破损伤演化机制,本文将从2个方面进行分析:一是分析掏槽孔爆破的损伤演化过程;二是分析地应力对爆炸应力波的影响及对爆炸应力波作用下岩体的损伤范围影响。
2.1 爆炸应力波对掏槽孔损伤作用过程
为了分析掏槽孔爆破岩体的损伤演化过程,并且验证临空面边界条件的存在对损伤演化过程的影响,将对存在较小临空面(中心孔)的掏槽爆破的损伤演化过程进行分析。图3所示为掏槽孔在16 MPa地应力条件下爆破开挖时岩体的损伤演化过程。
由图3可以看出:掏槽孔首先受到爆炸载荷与孔壁岩体作用产生的冲击波作用,产生压剪损伤(图3(a)和(b))。随着应力波沿孔径方向往外传播,冲击波衰减为应力波,此时的应力波波阵面径向分量已不能满足岩体压剪损伤破坏强度要求,但在切向方向分量产生拉应力大于有较小抗拉强度的岩体的拉应力[32],使得孔壁周围产岩体生的拉损伤在压剪损伤区的基础上继续扩展(图3(c))。随着应力波的继续传播,当两应力波波阵面相遇后,会形成应力波叠加区,在切向上的叠加拉应力超过岩体的抗拉强度后,岩体会在应力波叠加区继续产生拉损伤往炮孔方向传播(图3(d)),并且随着应力波叠加作用,损伤范围加大(图3(e)),应力波叠加作用产生的损伤区随着应力波叠加作用区往炮孔方向传播而往炮孔方向延伸,使得掏槽孔之间的损伤区连通(图3(f))。随着应力波的继续传播,当遇到临空面时,会在临空面上产生反射拉伸波,拉伸波相遇也会产生叠加,此时由单独拉伸波产生的拉损伤以及拉伸波叠加作用产生的拉损伤会使得临空面上的损伤区往岩体内部扩展,并加大掏槽孔周围既有损伤区的范围(图3(g)~(i))。
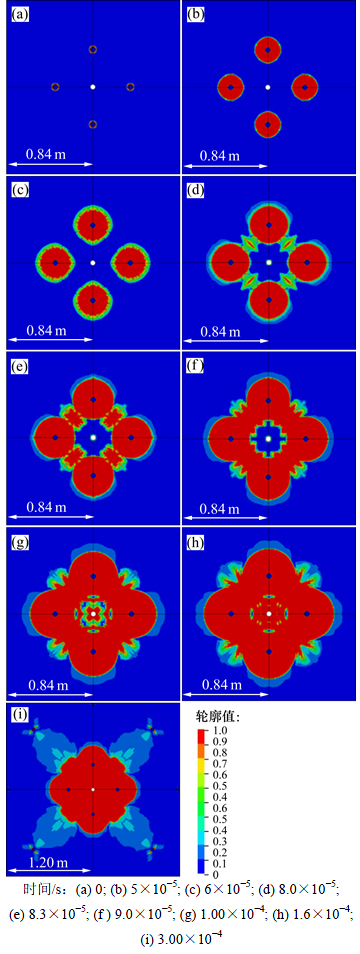
图3 掏槽孔爆破开挖损伤演化过程
Fig. 3 Damage evolution processes in of cut blasting excavation
从上面的分析可知:掏槽爆破岩体损伤演化过程受应力波强度、应力波的叠加作用以及临空面对应力波反射作用影响,使得掏槽爆破岩体的损伤演化分为4个过程:1) 冲击波作用在炮孔周围产生压剪损伤区;2) 随着冲击波衰减为应力波,应力波在其切向方向的应力分量使得产生拉损伤区,使得原有的压剪损伤发展为拉损伤,使得损伤区的范围继续扩展;3) 由应力波相遇叠加后产生拉应力损伤集中区,使得损伤掏槽孔的拉应力损伤区连通;4) 由应力波在中心孔的临空面上产生的反射拉伸波所产生的拉损伤以及反射拉伸波叠加作用产生的拉损伤使得损伤由临空面往岩体内部扩展,并最终使得掏槽孔周围岩体的损伤在既有的损伤基础进一步加大。
2.2 地应力对掏槽孔爆炸应力波和岩体损伤范围的影响
为了分析地应力对应力波在掏槽孔爆破应力波的抵抗作用以及地应力对掏槽爆破岩体损伤范围的影响,选择掏槽孔在不同地应力条件下的岩体损伤演化过程进行分析。图4(a)所示为0~48 MPa不同地应力作用下爆炸应力波在炮孔径向所产生的压力时程曲线,图4(b)所示为图4中(a)中绿色线内的不同压力地应力条件下压力载荷曲线压力谷值局部放大图,图 4(c)所示为图4(a)中蓝色线内不同压力载荷曲线的压力峰值局部放大图,图5(a)~(d)所示分别为0 MPa与8~48 MPa不同地应力条件下损伤对比演化曲线,图6所示为0~48 MPa不同地应力条件下损伤范围曲线。
由图4(b)可以看出:在相同时刻,在无地应力条件下,卸载时的压力要比有地应力条件下卸载时的压力曲线要低。从图4(b)和(c)可以看出:随着地应力的增加,处于受压状态的岩体中的压力荷载峰值增大,处于受拉状态的岩体中的压力荷载谷值逐渐减小,说明初始地应力的存在径向方向有减小拉应力、增大压应力的作用,从而说明地应力的存在对爆炸应力波作用下岩体中产生的压力载荷有抵制作用。这主要是由于岩体处在正压作用的卸载阶段时,压力荷载P在受到地应力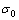 的耦合作用时会产生叠加,由于初始地应力的方向与炮孔周围径向方向的压力荷载方向相同,叠加后的压力荷载要比无地应力条件下的压力荷载大,使得压力荷载受到不同地应力作用时,处在正压卸载阶段的压力荷载有随着地应力的增大而增大的趋势;当岩体处在负压作用时,压力荷载P在受到地应力
的耦合作用时会产生叠加,由于初始地应力的方向与炮孔周围径向方向的压力荷载方向相同,叠加后的压力荷载要比无地应力条件下的压力荷载大,使得压力荷载受到不同地应力作用时,处在正压卸载阶段的压力荷载有随着地应力的增大而增大的趋势;当岩体处在负压作用时,压力荷载P在受到地应力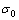 的耦合作用时两者的荷载方向不同,叠加后荷载会使得负压阶段的压力荷载的绝对值有随着地应力的增大而减小的趋势。当岩体中由爆破所诱发的压力荷载处于卸载阶段、不同地应力条件下的压力荷载曲线卸载到相同值时,在高地应力的条件下压力卸载曲线要延迟于低地应力条件下的压力卸载曲线,说明地应力的存在有延缓压力荷载下降的作用。通过以上可以看出地应力对爆破在岩体中诱发的压力荷载会产生抵抗性,并有延缓压力荷载下降的作用。
的耦合作用时两者的荷载方向不同,叠加后荷载会使得负压阶段的压力荷载的绝对值有随着地应力的增大而减小的趋势。当岩体中由爆破所诱发的压力荷载处于卸载阶段、不同地应力条件下的压力荷载曲线卸载到相同值时,在高地应力的条件下压力卸载曲线要延迟于低地应力条件下的压力卸载曲线,说明地应力的存在有延缓压力荷载下降的作用。通过以上可以看出地应力对爆破在岩体中诱发的压力荷载会产生抵抗性,并有延缓压力荷载下降的作用。

图4 崩落孔在不同地应力条件下压力时程曲线
Fig. 4 Pressure and time curve of cut holes under different in-situ stress conditions
由于地应力对爆炸应力波产生作用,最终使得在地应力与爆炸应力波共同作用下的掏槽孔爆破周围岩体的损伤范围也受到影响。从图5和图6可以看出:随着地应力增加,掏槽孔爆破开挖引起岩体损伤范围减小,说明地应力的存在将对应力波作用下岩体损伤演化起到抵制作用。同时,从图6可以看出:在小于16 MPa低地应力条件下,随着地应力增加,损伤范围明显的减小,在大于16 MPa的高地应力条件下,随着地应力增大,虽然损伤范围减小,但减小的梯度没有在低地应力条件下的梯度大。主要是由于在地应力小于16 MPa下,岩体在静水压力条件下径向方向应力处于线弹性变形状态,径向方向的应力随着静水压力的增大也会表现出明显的增加趋势,使得对岩体中所诱发的压力载荷曲线的抵制作用的梯度也较大,使得地应力在小于16 MPa状态下,随着地应力的增大,损伤的范围减小比较明显。当岩体处于地应力大于 16 MPa时,岩体处于非线弹性及塑性变形状态,此时径向方向应力上升的梯度较小,使得对岩体中诱发的压力载荷曲线的抵抗作用增加的梯度较小,并使得损伤范围的减小梯度也较小。

图5 掏槽孔在不同地应力条件下爆破开挖损伤对比
Fig. 5 Damage comparison of cut blasting excavation under different in-situ stress conditions
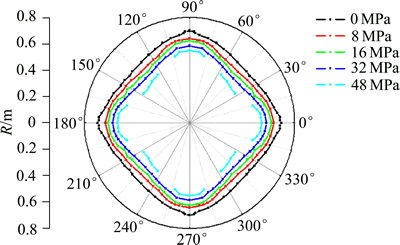
图6 损伤影响范围
Fig. 6 Influence scope of damage
从以上对地应力作用下压力载荷曲线的分析以及地应力作用下岩体的损伤范围可知,地应力条件的存在对压力载荷曲线有抵制作用,掏槽孔周围岩体的损伤范围在这种抵制作用下也受到影响。对压力载荷曲线的影响主要表现在地应力条件的存在有增大压应力减小拉应力的作用,并在这种作用下,掏槽爆破岩体损伤范围随着地应力的增大而减小,并最终出现掏槽孔难以连通的情况,如图6中静水压力大于32 MPa后,当受到的静水压力为48 MPa时,掏槽孔之间的损伤难以连通,不能达到损伤破坏岩体的作用。
3 结论
1) 在掏槽爆破过程中,炮孔中炸药爆炸在岩体中形成的冲击波、应力波使得炮孔周围岩体相继产生压剪损伤区和拉损伤区。随着应力波传播,应力波之间会发生相遇和叠加,当遇到自由面时会发生反射,产生反射拉伸波。叠加应力波会使得岩体产生拉应力损伤集中区,使得炮孔周围的拉损伤区连通,反射拉伸波使得损伤由临空面往岩体内部扩展,进一步加大岩体既有损伤区的范围。
2) 爆炸应力波受到地应力耦合作用后,会使得岩体在受压状态时径向方向的压力载荷压力峰值增大,岩体在受拉时的压力峰值减小。应力波与地应力耦合后使得在岩体中诱发的压力载荷曲线在下降过程变得缓慢,当下降到地应力水平时,此时岩体卸荷效应的存在使得压力载荷曲线达到地应力水平后继续下降。
3) 地应力条件的存在对爆炸应力波产生抵抗作用,使得深部岩体爆破岩体损伤范围受到影响,地应力越大,掏槽孔爆破时岩体的损伤变形范围越小,当地应力超过32 MPa以上时,掏槽孔爆破会出现炮孔之间的损伤难以连通。
4) 岩体在不同的地应力条件下,掏槽爆破的损伤影响范围随着地应力的增大不是线性地减小,当地应力小于16 MPa地应力时,掏槽孔损伤范围的减小呈一定的线性,当地应力大于16 MPa时,损伤范围减小的梯度变小,并呈一定的非线性。
参考文献:
[1] 王永岩, 魏佳, 齐军, 等. 深部岩体非线性蠕变变形预测的研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2005, 30(4): 409-413.
WANG Yongyan, WEI Jia, QI Jun, et al. Study on prediction for nonlinear creep deformation of deep rocks[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2005, 30(4): 409-413.
[2] 何满潮, 谢和平, 彭苏萍, 等. 深部开采岩体力学研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(16): 2803-2813.
HE Manchao, XIE Heping, PENG Suping, et al. Study on rock mechanics in deep mining engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(16): 2803-2813.
[3] 王汉军, 杨仁树, 李清. 深部岩巷爆破机理分析和爆破参数设计[J]. 煤炭学报, 2007, 32(4): 373-376.
WANG Hanjun, YANG Renshu, LI Qing. Analysis of blasting mechanism for deep rock tunneling and blasting parameters design[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2005, 32(4): 373-376.
[4] 李春睿, 康立军, 齐庆新, 等. 深部巷道围岩分区破裂与冲击地压关系初探[J]. 煤炭学报, 2010, 35(2): 185-189.
LI Chunrui, KANG Lijun, QI Qingxin, et al. Probe in to relationship between zonal fracturing and rock burst in deep tunnel[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2010, 35(2): 185-189.
[5] 周宏伟, 谢和平, 左建平. 深部高地应力下岩石力学行为研究进展[J]. 力学进展, 2005, 35(1): 91-99.
ZHOU Hongwei, XIE Heping, ZUO Jianping. Development in researches on mechanical behaviors of rocks under the condition of high ground pressure in the depths[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2005, 35(1): 91-99.
[6] 刘泉声, 张华, 林涛. 煤矿深部岩巷围岩稳定与支护对策[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(21): 3732-3737.
LIU Quansheng, ZHANG Hua, LIN Tao. Study on stability of deep rock roadways in coal mines and their support measures[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(21): 3732-3737.
[7] 贺永年, 韩立军, 邵鹏, 等. 深部巷道稳定的若干岩石力学问题[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2006, 35(3): 288-295.
HE Yongnian, HAN Lijun, SHAO Peng, et al. Some problems of rock mechanics for road ways stability in depth[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2006, 35(3): 288-295.
[8] 张炜, 张东升, 邵鹏, 等. 深部高应力岩巷快速钻爆施工技术[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(1): 43-49.
ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Dongsheng, SHAO Peng, et al. Fast drilling and blasting construction technology for deep high stress rock roadway[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(1): 43-49.
[9] ZHANG Qianbing, ZHAO Jian. A review of dynamic experimental techniques and mechanical behavior of rock materials[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2014, 47(4): 1411-1478.
[10] 殷志强. 高应力储能岩体动力学扰动破裂特性研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学资源与安全工程学院, 2011.
YING Zhiqiang. Research on fracture characteristics of rock with high energy accumulation under dynamic disturbance[D]. Changsha: Central South University. School of Resources and Safety Engineering, 2011.
[11] GRADY D E, KIPP M E. Continuum modeling of explosive fracture in oil shale[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences and Geomechanics Abstracts, 1980, 17(3): 147-157.
[12] TAYLOR L M, CHEN E P, KUSZMAUL J S. Microcrack- induced damage accumulation in brittle rock under dynamic loading[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1986, 55(3): 301-320.
[13] KUSZMAUL J S. A new constitutive model for fragmentation of rock under dynamic loading[C]// Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Rock Fragmentation by Blasting. Columbia, USA, 1987: 412-423.
[14] 刘殿书. 岩石爆破破碎的数值分析[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学力学与土木工程学院, 1992: 15-96.
LIU Dianshu. Numerical analysis on rock fragmentation[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology. School of Mechanics and Civil Engineering, 1992: 15-96.
[15] 卢文波, 董振华. 确定周边控制爆破围岩影响深度的动力损伤计算方法[J]. 工程爆破, 1996, 2(4): 55-59.
LU Wenbo, DONG Zhenhua. Calculation on dynamic damage of surrounding rock caused by contour blasting[J]. Engineering Blasting, 1996, 2(4): 55-59.
[16] WU Chenqing, LU Yong, HAO Hong. Numerical prediction of blast-induced stress wave from large-scale underground explosion[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2004, 28(1): 93-109.
[17] 胡英国, 卢文波, 陈明, 等. 不同开挖方式下岩石高边坡损伤演化过程比较[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2013, 32(6): 1176-1184.
HU Yingguo, LU Wenbo, CHEN Ming, et al .Comparison of damage evolution process of high rock slope excavationted by different methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2013, 32(6): 1176-1184.
[18] 王志亮, 黄景忠, 范书群, 等. 岩石爆破中塑性压剪损伤的数值模拟[J]. 火炸药学报, 2006, 29(5): 1-4.
WANG Zhiliang, HUANG Jingzhong, FAN Shuqun, et al. Numerical simulation on blast-induced plastic compression and shear damage in rock blasting[J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives and Propellants, 2006, 29(5): 1-4.
[19] 陈明, 胡英国, 卢文波, 等. 深埋隧洞爆破开挖扰动损伤效应的数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(5): 1531-1538.
CHEN Ming, HU Ying guo, LU Wenbo. Numerical simulation of blasting excavation induced damage to deep tunnel[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(5): 1531-1538.
[20] 朱万成, 唐春安, 左宇军. 深部岩体动态损伤与破裂过程[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 85-190.
ZHU Wancheng, TANG Chunan, ZUO Yujun. Dynamic damage and failure process for deep rock mass[M].Beijing: Science Press, 2014: 85-190.
[21] 林大能, 陈寿如. 直眼掏槽效率敏感因子的理论与试验分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2005, 30(1): 40-44.
LIN Daneng, CHEN Shouru. Theoretical and testing study on factors affecting parallel hole cut blasting[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2005, 30(1): 40-44.
[22] 郝好山, 胡仁喜, 康士廷, 等. ANSYS12.0 LS-DYNA非线性有限元分析从入门到精通[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2010: 190-259.
HAO Haoshan, HU Renxi, KANG Shiting, et al. ANSYS12.0 LS-DYNA nonlinear finite element analysis from the entry to the master[M]. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, 2010: 190-259.
[23] KURY J W, HORNING H C, LEE E L, et al. Metal acceleration by chemical explosives[C]// 4th Symp (Int) on Detonation. White O ak, M D, 1965: 3-13.
[24] SUN Chengwei, WEI Yuzhang, ZHOU Zikui. Applied detonation physics[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2000: 90-94.
[25] 赵铮, 陶钢, 杜长星. 爆轰产物JWL状态方程应用研究[J]. 高压物理学报, 2009, 23(4): 277-283.
ZHAO Zheng, TAO Gang, DU Changxing. Application research on JWL equation of state of detonation products[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2009, 23(4): 277-283.
[26] LSTC. Ls-Dyna keyword user’s manual[M]. California: Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2003: 785-786.
[27] CAI M, KAISER P K, TASAKA Y, et al. Generalized crack initiation and crack damage stress thresholds of brittle rock masses near underground excavations[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2004, 41(5): 833-847.
[28] Ayman Tawadrous. Hard rocks under high strain-rate loading[D]. Kingston: Queen’s University. Department of Mining, 2010: 109-114.
[29] LI Haibo, XIA Xiang, LI Jianchun, et al. Rock damage control in bedrock blasting excavation for a nuclear power plant[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Science, 2011, 48(2): 210-218.
[30] 曹文贵, 方祖烈, 唐学军. 岩石损伤软化统计模型之研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 1998, 17(6): 628-633.
CAO Wengui, FANG Zulie, TANG Xuejun. A study of statistical constitutive model for soft and damage rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1998, 17(6): 628-633.
[31] HALLQUIST J O. Ls-Dyna theory manual[M]. California: Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2006: 437-450.
[32] HUSTRULID W. Blasting principles for open pit mining, Volume 2-Theoretical foundations[M]. New York: A A Balkema, 1999: 456-460.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2016-06-26;修回日期:2016-08-30
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51125037);国家重点基础研究发展规划(973计划)项目(2011CB013501);中央高校基本科研业务费专项(2014210020202) (Project(51125037) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2011CB013501) supported by the National Basic Research Development Program (973 Program) of China; Project(2014210020202) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities)
通信作者:谢理想,博士,从事爆破工程与岩石动力学研究;E-mail: xielixiang7688@126.com