
Single and cooperative bioleaching of sphalerite by two kinds of bacteria——Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans
XIA Le-xian(夏乐先), LIU Jian-she(柳建设), XIAO Li(肖 利), ZENG Jia(曾 嘉),
LI Ban-mei(李邦梅), GENG Mei-mei(耿梅梅), QIU Guan-zhou(邱冠周)
School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 24 October 2006; accepted 25 December 2006
Abstract: A cooperative bioleaching (Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans) and single bioleaching (Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans or Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans) of sphalerite were investigated by X-ray diffractometry, energy dispersive spectrography and scanning electron microscopy. The experimental results show that the leaching rate of zinc in the mixed culture is higher than that in pure culture and the sterile control. In these processes, two kinds of bacteria perform different functions and play a cooperative role during leaching of sphalerite. The bioleaching action carried out by Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans (A. ferriooxidans) is not directly performed through Fe2+ but Fe3+, and its role is to oxidize Fe2+ to Fe 3+ and maintain a high redox potential. Moreover, the addition of an appropriate concentration of ferric iron to the leaching systems is beneficial to zinc dissolution. In the leaching systems without Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans (A. thiooxidans), elemental sulfur layers are formed on mineral surface during the dissolution of zinc and block continuous leaching. Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, however, eliminate the passivation and cause the bioleaching process to continue in the leaching systems. At the same time, protons from the bacterial oxidization of the elemental sulfur layers also accelerate the leaching of zinc.
Key words: Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans; Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans; bioleaching; Fe3+; Fe2+; sphalerite
1 Introduction
At present, most zinc metal around the world is extracted by hydrometallurgical process. The traditional zinc hydrometallurgical technology has many disadvantages with long flow sheet, high cost and serious pollution contrary to biohydrometallurgical process. Therefore, more attention has been paid to the biohydrometallurgical technology and a more extensive investigation has been done[1].
In recent decades, great progresses have been made in our understanding of the bioleaching mechanism and industrialization of sphalerite. BOON and HEIJNEN[2] conducted a synthetic ZnS bioleaching experiment with ferric iron while maintaining a constant redox potential in solution, and found that in the presence of bacteria, the rate of zinc dissolution in the systems was almost similar to that of the abiotic systems (containing ferric iron). A great difference in the rate of zinc dissolution, however, was observed between the systems with ferric ion and without bacteria and the systems with bacteria and without ferric iron. The zinc dissolution rate of the former was higher than that of the latter. Based on these studies, an indirect mechanism of zinc sulfide mineral bioleaching proposed by BOON and HEIJNEN[2] is extensively accepted by most researchers.
SAND et al[3] further realized two kinds of pathways (polysulfide and thiosulfate), where sulfide was oxidized to polysulfide and then elemental sulfur, as indicated in other papers on pyrite and chalcopyrite bioleaching published in the hydrometallurgy issue[4-5]. TRIBUTSCH[6] proposed three different bioleaching strategies, that is, indirect, contact and cooperative bioleaching.
RODRIGUEZ et al[7] reported that bioleaching of the sphalerite concentrate took place via a cooperative bioleaching strategy involving contact bioleaching of the pyritic phase of the concentrate and the indirect bioleaching of the sphalerite.
Many conclusions were drawn from the bioleaching of zinc sulfide mineral by iron-oxidizing bacteria, especially A. ferriooxidans. However, some experiments in recent years have shown that sulphur-oxidizing microorganisms play a significant role in the ZnS bioleaching process[8].
In this work, we evaluated the effect of single and cooperative bioleaching of sphalerite on rate of zinc dissolution by two kinds of typical mesophilic iron and sulphur-oxidizing bacteria, A. ferriooxidans and A. thiooxidans. A reasonable mechanism was used to explain the difference of zinc dissolution rate between single and mixed culture.
2 Experimental
2.1 Ore sample
A sphalerite supplied from Shuikousan in Hunan province, China, was used in this work. Mineral content was as follows: 54.79% Zn, 29.74% S, 9.52% Fe, 0.32% SiO2 and 5.63% Sn. The mineral samples in leaching experiment were infused for some minutes to refresh the surface of the ore particles and their particle sizes were about 0.074 mm. The mineral samples were preleached in iron-free 9K media at pH of 2 for 2 d before inoculation in order to level off pH value and discard the oxidized surface components.
2.2 Leaching media
Bioleaching of sphalerite was carried out in shake flasks containing 1% mineral sample (m/V) and iron-free 9K nutrient media; the pH value was adjusted to 2 with 5 mol/L sulfuric acid.
2.3 Cultivation of bacteria
A. ferriooxidans and A. thiooxidans, which utilize ferrous ion and elemental sulfur as their energy source, were used in the bioleaching of sphalerite. Before the bioleaching phase of the experiment, these bacteria had been sub-cultured in 9K medium containing 1% sphalerite samples at 30 ℃ for 20 d so that they could adapt to the mineral circumstance faster. The bacteria were filtrated through a 0.45 ?m-whatman filter paper, and the bacterial concentration was adjusted to 107/mL with iron-free 9K nutrient medium. The initial pH value was adjusted to pH 2. Inocula was 5% (volume fraction) in single culture, and 2.5% A.ferrooxidans and 2.5% A. thiooxidans in mixed culture, respectively. The same volume of sterile iron-free 9K was instead of inocula in the sterile control. All studies were carried out in 500 mL flasks with 150 mL of medium in an orbital shaker (180 r/min) incubated at 30 ℃, and water lost by evaporation was compensated by the addition of deionized water. All experiments were carried out in duplicate.
2.4 Analytical methods
During the experiments, the redox potential, pH value and zinc concentration of the supernatant were measured as a function of time. The concentration of dissolved zinc ion in leaching solution was analyzed by an atomic absorption spectrophotometry(AAS). The redox potential(Eh) which indicates the changes of the concentration of Fe3+ and the mole ratio of Fe3+ to Fe2+ was measured with a Pt electrode to estimate the ratio changes of ferric ion to ferrous ion, and a saturated calomel electrode was used as the reference electrode. The pH value was measured with a Leici pH meter.
The leached solid residues were dried at 30 ℃ for 48 h and the minerals were analyzed using X-ray diffractometry(XRD), energy dispersive spectrography (EDS) and scanning electron microscopy(SEM) in order to detect compounds produced on the substrate surfaces. The samples were not carbon-coated due to the good conductivity of the sphalerite that results from the presence of Fe in the crystal lattice instead of partial Zn.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Bioleaching of sphalerite with different micro- organisms
There is an obvious difference in the leaching rate and the maximum dissolved zinc ratio (Fig.1) when sphalerite is processed by mixed culture or pure culture. The sphalerite bioleaching ability of A.ferrooxidans is stronger than that of A.thiooxidans that possesses little capability to dissolve zinc. 61% dissolved zinc is extracted when using A.ferrooxidans, but only 20% zinc is extracted by A. thiooxidans after 18 d of leaching.
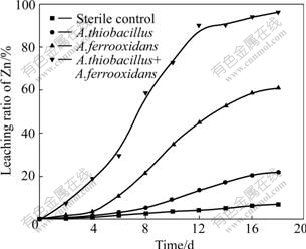
Fig.1 Effect of pure culture (A.ferrooxidans or A. thiooxidans) and mixed culture (A. ferrooxidans and A. thiooxidans) on zinc dissolution (pulp density 1%)
When A.thiooxidans and A.ferrooxidans were mixed and inoculated into leaching systems, 97% zinc was extracted from ore and the rate of dissolved zinc added up to 0.3 g/(L?d) compared with 0.17 g/(L?d) using A.ferrooxidans and 0.06 g/(L?d) using A.thiooxidans. Furthermore, with mixed culture, it only took 12 d (2-3 d faster than pure culture) to attain the maximum dissolved zinc ratio when compared with pure cultures. The dissolved zinc ratio of the sterile control also reached 8.9%, and the result indicated that zinc could be partly leached from sphalerite by proton illustrated in Eqn.(1):
ZnS+2H+→Zn2++H2S (1)
In Fig.2, the pH value is shown as a function of time using mixed culture (A.ferrooxidans and A. thiooxidans), pure culture (A.ferrooxidans or A. thiooxidans) and an abiotic control, respectively. The evolution of the pH values was divided into two phases except that of sterile control. pH values in the first phase dropped and ascended in the second phase with the leaching time. The mixed culture systems exhibited the greatest change of pH range (2.08 to 1.6). The first phase was due to the chemical dissolution of the sulfide, producing Zn2+ that consumed protons, and then, H2S produced in the first phase was followed by the bacterial oxidation of these species to cause a decrease of pH value[9]:
2H2S+O2 2S+H2O (2)
2S+H2O (2)
2S+3O+2H2O 2H2SO4 (3)
2H2SO4 (3)

Fig.2 Evolution of pH during leaching of sphalerite with pure culture, mixed culture and sterile culture
3.2 Influence of ferric, ferrous iron on bacterial leaching of sphalerite
To determine the roles of A.thiooxidans and A.ferrooxidans in cooperative bioleaching, Fe2+ and Fe3+ were separately added to the leaching systems, moreover, the redox potential and dissolved Zn2+ were measured at 2 d intervals. The addition of Fe2+ to leaching systems did not enhance the rate of dissolved zinc in the absence of bacteria. However, the dissolving rate of zinc increased from 8.9% to 87.2% in the presence of bacteria. This strongly suggested bacteria played a key role in enhancing the dissolving rate. Considering that A.ferrooxidans could oxidize Fe2+ to Fe3+ for its growth and gained higher leaching rate, these evidences indicate that Fe3+ should be the rate determining factor in leaching of sphalerite, and the role of the bacteria is to oxidize Fe2+ to Fe3+ and regenerate a higher redox potential in leaching solution. Moreover, this also explained why A.thiooxidans exhibited little capability to leach sphalerite (little iron was present in leaching system) due to its no oxidization of Fe2+ to Fe3+. This evidence also supported the indirect mechanism assented by some authors[10-11]. In addition, the rates and ratio of zinc extraction in the presence of bacteria with Fe2+ and bacteria with Fe3+ were compared. It is seen that the dissolved zinc of the former lagged behind that of the latter (Fig.3). Moreover, zinc dissolution of the former only starts to be accelerated after bioleaching for 4 d but 87.2% zinc is extracted and surpassed that of the latter at the end of leaching experiments. This is possibly attributed to the transformation time taken from Fe2+ to Fe3+, that is, Fe3+ is required for startup of bioleaching zinc, and therefore bioleaching process only begins after some Fe2+ has been oxidized to Fe3+. The accumulation of Fe3+ in the system leads to an increase in the zinc dissolution rate.
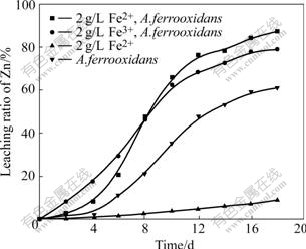
Fig.3 Effect of addition of Fe2+, Fe3+ and A.ferrooxidans on extraction of zinc from sphalerite (pulp density 1%)
The turnover of Fe3+ and Fe2+ is evident from the redox potential profiles, as shown in Fig.4. When Fe3+ is added to the systems, the redox potential first decreases and this initial change suggests that zinc is immediately extracted from the ore through the oxidation of Fe3+. The analysis can be explained as
ZnS+2Fe3+→Zn2++2Fe2++S (4)

Fig.4 Evolution of Eh in solution with addition of Fe2+, Fe3+ during leaching processes by A.ferrooxidans or abiotic control
Then, the population of bacteria also increases with the reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+ and the subsequent accumulation of Fe2+. Eh curves show that the whole process can be divided into two continuous periods when Fe3+ exists in the leaching systems. Firstly, the dissolution of zinc is due to an attack of ore by Fe3+, as a result of attack, Fe3+ is reduced to Fe2+ and causes the increase of Fe2+ concentration in leaching solution, then, bacteria use Fe2+ as an energy source consequently, which leads to a rapid increase in bacterial population and the regeneration of Fe3+ upon Fe2+ reduction. Therefore, a cycle between Fe3+ and Fe2+ is built and zinc is continuous leached. When A.ferrooxidans is incubated in the leaching systems containing the same Fe concentration, the dissolved zinc in the systems with Fe2+ is slightly higher than that of systems with Fe3+ (Fig.3). The difference of zinc dissolution is attributed to the formation of jarosite and some elemental sulfur on mineral surface that blocks further zinc leaching in the systems containing Fe3+[12]. However, in leaching systems with Fe2+ and A.ferrooxidans, bacteria oxidizes Fe2+ to Fe3+ little by little and Fe3+ is continually consumed through attacking mineral. At last, less Fe3+ is accumulated in solution. Consequently, no jarosite is produced. The redox potential data also support the above conclusions. As a result of the formation of jarosite and decrease of Fe3+ concentration in final solution, the leaching rate and redox potential of systems with Fe3+ and A.ferrooxidans are lower than those of the systems with Fe2+ and A.ferrooxidans at the end of experiments (Eqn.(5) and Fig.4).
K++H2O+ +3Fe3+→KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6+8H+ (5)
+3Fe3+→KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6+8H+ (5)
The zinc dissolution rate in the systems containing Fe3+ and A. ferrooxidans is higher than that in the system with A. ferrooxidans alone (78.9% and 61% respectively) although X-ray diffraction analysis indicates that jarosite is formed (Fig.3, Fig.5(c)). This result shows that the addition of an appropriate concentration of ferric iron to leaching systems is beneficial to zinc dissolution.
2.3 Analysis of raw samples and leached residues
Raw mineral and residues after leaching with bacteria were analyzed by X-ray diffractometry, energy dispersive spectrography and scanning electron microscopy. Significant differences were shown from the XRD profiles of the raw mineral and the leached residues. The leached residues from the system with Fe2+, A.ferrooxidans and without A.thiooxidans are mainly composed of undissolved sphalerite and elemental sulfur produced during the leaching process (Eqn.(2), Eqn.(4) and Fig.5(b)). However, in the leaching systems with A.ferrooxidans, A.thiooxidans and without Fe3+, no elemental sulfur is detected, and this could be attributed to its oxidation to sulfuric acid by the sulphur-oxidizing bacteria A.thiooxidans (Eqn.(3) and Fig.5(d)). A.ferrooxidans can also oxidize elemental sulfur, but it prefers Fe2+ to sulfur when there are sulfur and ferrous iron in leaching solution altogether[13-14]. Thus, A.ferrooxidans could not completely oxidize elemental sulfur. Consequently, elemental sulfur lays on the surface of residues from systems without A.thiooxidans contained. A compact elemental sulfur layer on mineral surface inhibited the contact between bacteria and mineral. Consequently, this decreases the leaching rate when compared to that of A.thiooxidans and A.ferrooxidans (Figs.5(b), 5(c) and Fig.1). On the contrary, A.thiooxidans oxidizes elemental sulfur and prevents the accumulation of elemental sulfur on the surface of leached residues (Fig.5(d)). The bioleaching process is not interrupted, thereby allowing the continuous liberation of zinc from the ore. Thus, the maximum zinc dissolution is obtained using mixed culture. In addition, Fig.5(c) shows that jarosite peaks are obvious, indicating that a high concentration of jarosite is produced in the leaching system with Fe3+. Whereas, spectral lines of sphalerite become very weak and jarosite does not seem to have an impact on the concentration of dissolved zinc (78.9% recovered), which is consistent with the leaching date (Fig.3). Nevertheless, this result is inconsistent with other studies in which jarosite interrupts the attack of the mineral surface by Fe3+ and causes a decrease in the concentration of dissolved zinc in solution[15-16]. This might be caused by unsynchronized zinc dissolution and jarosite formation. That is, most of the zinc has been extracted from the ore before the formation of a large amount of jarosite because sphalerite is easier to leach than other ores. The jarosite produced in the later leaching period has less effect on zinc dissolution. A kinetic study about the formation of jarosite is necessary to confirm this finding.
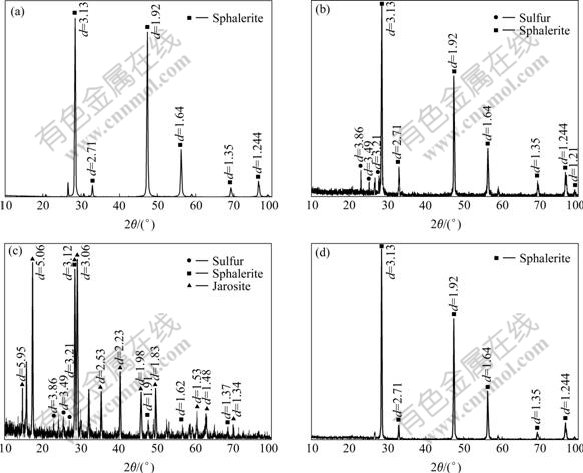
Fig.5 XRD patterns of raw mineral samples and solid residues: (a) Raw mineral samples; (b) Leached residues with ferrous iron and A.ferrooxidans; (c) Leached residues with ferric ion and A.ferrooxidans; (d) Leached residues with A.ferrooxidans and A.thiooxidans
The SEM images and EDS patterns, as shown in Figs.6 and 7, also confirm the XRD results. Elemental sulfur layers only exist on the surface of residues bioleached by A.ferrooxidans (Fig.6.(b)) and are not detected in the presence of A.ferrooxidans and A.thiooxidans (Fig.6(a)). This attributes to the oxidization of the sulfur by A.thiooxidans to sulfuric acid. However, because of formation of passive layers, the surfaces of mineral can not be continuously attacked by bacteria and are more level than those surfaces that undergo continuous attack by A.ferrooxidans and A.thiooxidans (Fig.6). Fig.6(b) also shows a clear cranny on the surface of mineral particles probably due to the dehydration of the elemental layers during drying. Furthermore, based on EDS analysis on the surface chemical composition of the leached residues by mixed culture or only A.ferrooxidans, the ratio of various atoms (Zn?Fe?S) also changes from 35?13?52 (Fig.7(a)) to 11?15?74 (Fig.7(b)). The increase of sulfur atoms strongly indicates that the elemental sulfur layers are on the surface of the leached residues. This evidence explains how A.thiooxidans enhances the leaching capability of A.ferrooxidans and why mixed culture attains the maximum dissolved zinc compared with other cultures (Fig.1).

Fig.6 SEM images on surface of sphalerite mineral particle bioleached with A.ferrooxidans and A.thiooxidans (a) and with A.ferrooxidans and without A.thiooxidans (b)
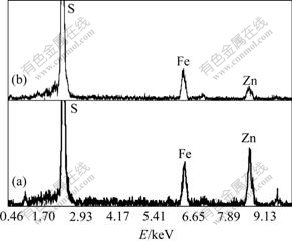
Fig.7 EDS patterns of surface of sphalerite mineral particle after bioleaching with A.ferrooxidans and A.thiooxidans (a) and with A.ferrooxidans and without A.thiooxidans (b)
4 Conclusions
1) The leaching rate of zinc with a mixed incubation of Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans is higher than that of Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans or Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans alone. Moreover, the addition of an appropriate concentration of ferric iron to the leaching systems is beneficial to zinc dissolution. Too high Fe3+ concentration reduces the rate of zinc dissolution due to the formation of jarosite (confirmed by XRD). In addition, XRD, SEM and EDS analyses of the residues also indicate that elemental sulfur layers exist on the surface of sphalerite leached without bacteria or only with Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans. These layers block the mineral surface from being attacked by the bacteria. The residues bioleached by Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, however, show no sulphur existed.
2) The mechanism of accelerating the zinc dissolution rate through the mixed culture is as follows. Acidithiobacillus ferriooxidans regenerate the oxidative reagent-ferric iron that is consumed in the leaching process and keep a high redox potential so that the leaching could continue. The role of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans is to oxidize elemental sulfur layers to sulfuric acid, which is beneficial to chemical leaching of the sphalerite and threw off the “passivation”. Two kinds of bacteria perform different functions and cooperative leached sphalerite.
References
[1] HUS C H, HARRISON R G. Bacterial leaching of zinc and copper from mining wasters [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1995, 37(2): 169-179.
[2] BOON M, HEIJNEN J J. Mechanism and rate limiting steps in bioleaching of sphalerite, chalcopyrite and pyrite with Thiobacillus ferrooxidans [C]// Biohydro-Metallurgical Technologies, Warrendate, Pensylvannia: TMS, 1993. 27.
[3] SAND W, GEHRKE T, JOZSA, P G, SCHIPPERS A. Direct versus indirect bioleaching [C]// Proceedings of the International Biohydrometallurgy Symposium IBS’99. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1999: 27-49.
[4] RODR?GUEZ Y, BALLESTER A, BL?ZQUEZ M L, GONZ?LEZ F, MU?OZ J A. New information on the pyrite bioleaching mechanism at low and high temperature [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71(1): 37-46.
[5] RODR?GUEZ Y, BALLESTER A, BL?ZQUEZ M L, GONZ?LEZ F, MU?OZ J A. New information on the chalcopyrite bioleaching mechanism at low and high temperature [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71(1): 47-56.
[6] TRIBUTSCH H. Direct versus indirect bioleaching [C]// Proceedings of the International Biohydrometallurgy Symposium IBS’99. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1999: 51-60.
[7] RODR?GUEZ Y, BALLESTER A, BL?ZQUEZ M L, GONZ?LEZ F, MU?OZ J A. New information on the sphalerite bioleaching mechanism at low and high temperature [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71(1): 57-66.
[8] FOWLER T A, CRUNDWELL F K. The role of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans in the bacterial leaching of some sulphides [C]// Proceedings of the International Biohydrometallurgy Symposium IBS’99. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1999: 273-281.
[9] PISTORIO M, CURUTCHET G, DONATI E,TEDESCO P. Direct zinc sulphide bioleaching by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and Thiobacillus thiooxidans [J]. Biotechnology Letters, 1994, 16(4): 419-424.
[10] HELMUT TRIBUTSCH. Direct versus indirect bioleaching [J]. Hydro Metallurgy, 2001, 59: 177-185.
[11] ROHWERDER T, GEHRKE T, KINZLER K, SAND W. Bioleaching review (part A): Progress in bioleaching: fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation [J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2003, 63: 239-248.
[12] SHI Shao-yuan, FANG Zhao-heng, NI Jin-ren. Comparative study on the bioleaching of zinc sulphides [J]. Process Biochemistry, 2006, 41: 438-446.
[13] PRONK J T, LIEM K, BOS P, KUENEN J G. Energy transduction by anaerobic ferric iron respiration in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1991, 57: 2063-2068.
[14] SUGIO T, HIROSE A, OTO A, INAGAKI T T. The regulation of sulfur use by ferrous ion in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans [J]. Agric Biol Chem, 1990, 54: 2017-2022.
[15] DA SILVA G. Relative importance of diffusion and reaction control during the bacterial and ferric sulphate leaching of zinc sulphide [J]. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 73: 313-324.
[16] POGLIANI C, DONATI E. Immobilisation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: Importance of jarosite precipitation [J]. Process Biochem, 2003, 35: 997-1004.
Foundation item: Project(2004CB619204) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Projects(50374075, 50321402) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: LIU Jian-she; Tel: +86-731-8836372; E-mail: ljscsu@263.net
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)