低温合成LiFePO4/C正极材料及其电化学性能
来源期刊:中南大学学报(自然科学版)2006年第3期
论文作者:张宝 李新海 朱炳权 王志兴 郭华军
文章页码:505 - 508
关键词:LiFePO4/C;液相沉淀;碳热还原;前驱体
Key words:LiFePO4/C; aqueous precipitation; carbothermal reduction; precursor
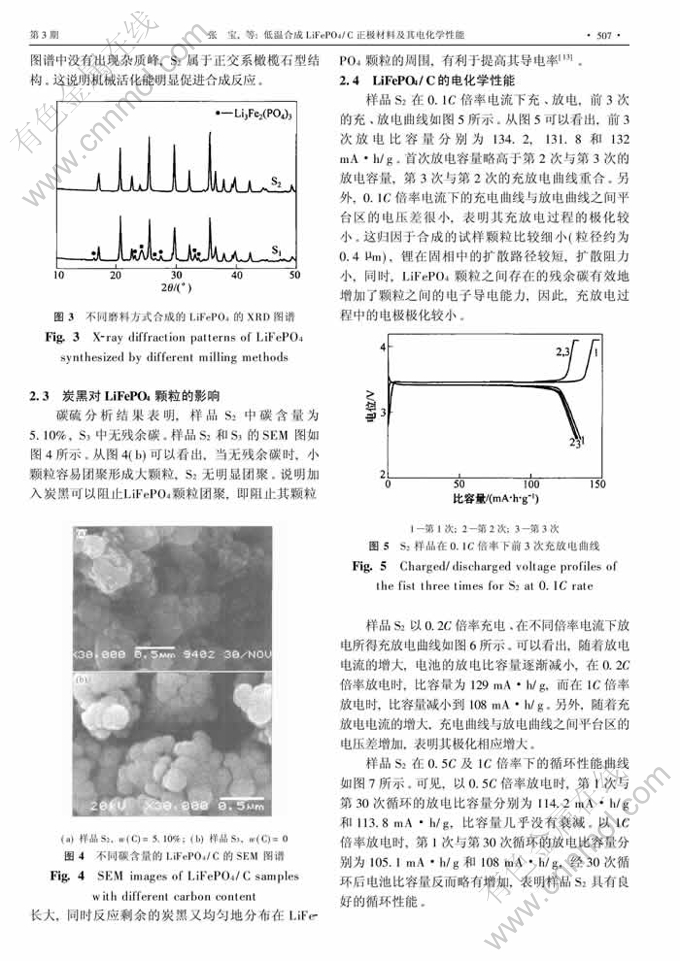
摘 要:以FeSO4·7H2O, NH4H2PO4和H2O2为初始原料,通过液相沉淀制得前驱体FePO4·2H2O,然后通过碳热还原得到LiFePO4/C。X射线衍射和扫描电镜分析结果表明:将FePO4·2H2O, Li2CO3与炭黑球磨2 h后再在Ar气气氛、500℃下煅烧10 h能得到无其他杂相的LiFePO4/C材料,反应剩余的碳黑分布在LiFePO4颗粒之间,阻碍LiFePO4颗粒团聚,并有利于提高其电子导电率;制得的LiFePO4/C的粒径为0.3~0.4μm,且具有良好的循环性能;以0.1C倍率电流放电的首次放电比容量为134.2 mA·h/g, 1C倍率下的放电比容量为104 mA·h/g。
Abstract: LiFePO4/C powders were prepared by carbothermal reduction of Li2CO3 with FePO4·H2O, which was synthesized by aqueous precipitation from solution of FeSO4·7H2O and NH4H2PO4 with H2O2 as the oxidizing agent. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope. At first, the mixtures of FePO4·H2O and Li2CO3 and carbon were ball milled for 2 h, and then calcined at 500℃. Finally, the homogenous LiFePO4/C was successfully synthesized with average particle size of 0.3-0.4μm. The discharge capacity of the material synthesized under the optimum conditions is 134.2 mA·h/g at 0.1C rate and 104mA·h/g at 1C rate. The residual carbon is coated on LiFePO4, preventing the aggregation of particles and resulting in the enhancement of the material’s electronic conductivity.
基金信息:国家自然科学基金资助项目