DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.01.001
细菌作用下斑铜矿表面物理化学性质变化
赵红波1, 2,王军1, 2,邱建强1, 2,杨勰1,覃文庆1, 2,邱冠周1, 2
(1. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 中南大学 生物冶金教育部重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:采用相同培养基培养的嗜热硫氧化硫杆菌(Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans,S. t菌)和氧化亚铁钩端螺旋菌(Leptospirillum ferrooxidans,L. f菌)浸出斑铜矿,通过接触角和Zeta电位测定,分析其吸附之后斑铜矿表面物理化学性质的变化,主要包括表面润湿性和表面电性的变化,并对比分析2种细菌对斑铜矿表面物理化学性质改变的异同。研究结果表明:单独9K培养基对于斑铜矿表面润湿性无明显影响,在2种细菌作用下,由于在浸出过程中斑铜矿表面亲水铜硫化合物和硫酸盐的产生导致斑铜矿表面接触角持续减小;斑铜矿和细菌的Zeta电位随溶液pH的升高而逐渐下降,斑铜矿Zeta电位和等电点分别朝细菌的Zeta电位和等电点方向偏移,表面细菌在斑铜矿表面发生了特性吸附;混合菌作用下斑铜矿Zeta电位和等电点正好介于2种细菌的动电位和等电点之间,说明2种细菌均能同时有效吸附于斑铜矿表面。
关键词:细菌;斑铜矿;表面物理化学性质;Zeta电位;接触角
中图分类号:TD982 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)01-0001-05
Surface physicochemical properties of bornite in presence of bacteria
ZHAO Hongbo1, 2, WANG Jun1, 2, QIU Jianqiang1, 2, YANG Xie1, QIN Wenqing1, 2, QIU Guanzhou1, 2
(1. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Biometallurgy, Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans cultured in the same 9K medium were used for the bioleaching of bornite. The variation of surface physicochemical properties mainly of surface wettability and surface electrical property were investigated by contact angle measurement and Zeta potential measurement. The results show that single 9K medium has no significant effect on the surface wettability of bornite, while the contact angles of bornite continue to decrease in the presence of bacteria, which can be attributed to the formation of intermediates of hydrophilic Cu-Fe-S compounds and sulphates. The Zeta potential of bornite and bacteria decreases with the increase of solution pH, the Zeta potential and isoelectric point of bornite shift toward the Zeta potential and isoelectric point of bacteria, indicating that bacteria can effectively adsorb on bornite surface. The Zeta potential and isoelectric point of bornite in the presence of mixed bacteria are between those of S. thermosulfidooxidans and L. ferriphilum, revealing that the two bacteria can effectively adsorb on bornite at the same time.
Key words: bacteria; bornite; surface physicochemical properties; Zeta potential; contact angle
微生物冶金因其具有流程短、设备简单和环境友好等技术优势,在湿法冶金领域已获得广泛关注[1-3]。吸附是微生物与矿物作用的第1步。由于细菌对硫化物的吸附及氧化是在矿物表面发生的,因此,矿物的表面性质(包括表面元素分布、表面电性、缺陷、表面能和表面的不均匀性等)对细菌在矿物表面的吸附及氧化过程具有重要影响。Devasia等[4]认为细菌在矿物表面的吸附不仅改变了细菌的生化性质,同时也改变了浸矿体系中各种界面性质。van Loosdrecht等[5]认为细菌表面性质中决定吸附的主要是表面疏水性和动电位,暴露于矿物的细菌表面有NH3,NH2,NH,CONH,CO,CH3,CH2,CH和COOH等官能团存在。Gehrke等[6]通过对浸矿细菌A.ferrooxidans的胞外多聚物(EPS)分析后认为,EPS在细菌解离金属硫化矿物的第1步中起到重要作用,是细菌粘附在黄铁矿和单质硫等固态底物过程的先决条件。顾帼华等[7]通过对原子力显微镜表面进行表征及摇瓶浸出实验,考察了不同能源(Fe2+、单质硫和黄铜矿)培养的氧化亚铁硫杆菌(Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans,A. f菌)对黄铜矿表面性质的影响及其与黄铜矿浸出的关系,发现驯化的A. f菌在矿表面的附着能力更强,并显著改变黄铜矿表面性质,导致黄铜矿表面疏水性先增强再降低,黄铜矿Zeta电位朝细菌Zeta电位偏移。Liu等[8]考察了不同离子强度和pH条件下培养的氧化亚铁硫杆菌(Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans,A. f菌)对黄铁矿表面性质的影响,发现细菌导致黄铁矿等电点(IEP)朝细菌等电点(IEP)偏移,并提出了双电层作用模型。硫化矿物的细菌浸出体系是一个矿物-细菌-溶液三相界面相互作用体系,该体系十分复杂,受许多因素如表面电荷、表面疏水性、表面聚合物的存在及构型的影响,因而,对硫化矿物体细菌浸出体系中表面性质的研究可以为解释细菌复杂界面作用机理提供有效参 数[9-10]。细菌在矿物表面的吸附可以极大地改变矿物表面性质,而选矿过程(如浮选和絮凝)主要取决于矿物表面性质,故通过生物处理实现对矿物之间的有效分离具有重要意义。许多研究者利用细菌选择性地在黄铁矿表面或煤表面富集,通过改变黄铁矿的亲水性或煤的疏水性,增大欲分离矿物间可浮性的差异,从而强化后续分选作业[11-12]。综上所述,研究微生物对矿物表面物理化学性质影响具有重要意义。目前,人们对此类问题的研究主要集中于黄铁矿、黄铜矿等矿物,而关于斑铜矿的研究鲜有报道。目前,在生物冶金领域,主要研究和应用对象是硫氧化菌和铁氧化菌,这2类细菌对硫化矿物具有不同的吸附和腐蚀机理,为此,本文作者选用2种重要的浸矿即细菌-嗜热硫氧化硫杆菌(Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans,S. t菌)和氧化亚铁钩端螺旋菌(Leptospirillum ferrooxidans,L. f菌),分别考察其对斑铜矿表面性质的影响,着重研究对比这2种细菌浸出前后斑铜矿表面接触角和动电位变化。
1 实验
1.1 实验材料和仪器
实验材料为:纯斑铜矿,取自广东梅州,经过磨矿、干式筛分之后,取粒度小于0.074 mm的矿粒,再经玛瑙研磨至粒度小于5 μm,用于测定Zeta电位;结晶良好的块状斑铜矿,经切割、打磨、抛光,用于接触角测定;S. t菌和L. f菌,均取自中南大学生物冶金教育部重点实验室。
实验仪器为:HZQ-C培养箱(哈尔滨东联电子技术有限公司制造),用于细菌的培养;Usk-Ⅱ型不锈钢电热蒸馏水器(上海三申医疗器械有限公司制造),用于自制蒸馏水;YX280A型手提式不锈钢蒸汽消毒器(上海三申医疗器械有限公司制造),用于仪器灭菌;PHSJ-4A型pH计(上海精密仪器有限公司制造),用于测试矿浆酸度;JJC-1型接触角测定仪(长春市第五光学仪器有限公司制造),用于测量接触角;TDL5-A-5型台式离心机(上海安亭科学仪器厂制造),用于离心细菌集合体;Coulter Dels44osx型 Zeta电位测定仪(美国贝克曼库尔特公司制造),用于测试动电位。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 菌种培养
原始菌株用9K培养基培养,pH调节为2.0,9K培养基成分为:3.00 g/L (NH4)4SO4,0.10 g/L KCl,0.50 g/L K2HPO4,0.50 g/L MgSO4·7H2O,0.01 g/L Ca(NO3)2,整个实验过程均采用现制备的蒸馏水。培养S. t菌时加入10.0 g/L硫粉作为能源物质,培养L. f菌时加入44.7 g/L FeSO4·7H2O作为能源物质。培养基在灭菌锅中灭菌20 min(压力为0.1 MPa,温度为 121 ℃)。细菌接种量均为5%(体积分数),细菌培养均在摇床中进行,转速为170 r/min,温度为48 ℃。
1.2.2 接触角测定
测量矿物接触角时,用微量进样器(2.0 mL)将蒸馏水在距待测固体表面约3.0 mm处垂直滴加在待测固体表面,形成座滴,快速测量,读取9次接触角值,计算平均值作为接触角。
细菌接触角的测定时,首先将已制成菌悬液的细菌溶液用微孔过滤膜(孔径0.22 μm)过滤,形成一定的厚度,将附有细菌的生物膜在室温条件下晾干,平铺在盖玻片上,按照上述方法测定细菌的接触角。
1.2.3 Zeta电位的测定
将0.1 g斑铜矿粉分别加入到离子浓度I为0.010 mol/L和0.001 mol/L的NaCl溶液中,调节pH,搅拌5 min后,放入洗净的样品槽,将样品槽放入电位测定仪中,测定斑铜矿的Zeta电位;将0.1 g矿粉加入到细菌浓度为2×108 个/mL,pH为2.0的NaCl溶液中,搅拌60 min后,离心法分离出矿粒,控制矿浆质量浓度为1 g/L,在离子强度I=0.010 mol/L的NaCl溶液中测定细菌作用后矿物Zeta电位;同理,在离子强度为I=0.010 mol/L的NaCl溶液中加入细菌(L. f和S. t)悬液,细菌浓度为2×108 个/mL,调节pH,测定不同pH条件下细菌的Zeta电位。测试中用HCl和NaOH溶液调节pH,每个样品测量3次,取平均值。
2 实验结果与讨论
2.1 接触角的测定
斑铜矿的原始接触角如表1所示。斑铜矿的接触角达55°,说明斑铜矿润湿性较小,主要由于斑铜矿的分子以共价键为主,偏向于非极性结构,从而导致斑铜矿的水溶性不是很好,在浸出过程中常需要 细磨[14]。
S. t 菌和L. f菌的接触角分别如表2和表3所示。从表2和表3可见:S. t 菌和L. f菌这2种浸矿细菌的接触角都很小,表明它们润湿性较大,有很好的亲水性。这主要是由于细菌在生长过程中,黏膜中分布了许多膜蛋白,其中含有多种极性基团如羟基(—OH)、羧基(—COOH)、巯基(—SH)、氨基(—NH2)等,这些极性基团对极性水分子具有很强的亲和性,有利于细菌与矿物的相互作用,降低体系自由能[15]。
许多研究者认为,斑铜矿的微生物浸出过程主要包括以下化学反应[13-17]:
Cu5FeS4+12Fe3+→ 5Cu2++13Fe2++4S0 (1)
4Fe2++O2+4H+ →4Fe3++2H2O (2)
2S0+3O2+2H2O → +4H+ (3)
+4H+ (3)
4Cu5FeS4+37O2+2OH-→20Cu2++4Fe3++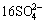 +10H2O (4)
+10H2O (4)
由于斑铜矿细菌浸出过程不仅包含了细菌的作用,还包含了培养基的影响,因此,在研究过程中必须了解培养基溶液在这个过程中的作用。斑铜矿分别浸泡于9K培养基、含S. t菌和L. f菌的9K培养基体系中,接触角的变化如图1所示。从图1可见:在单独9K培养基作用下,斑铜矿接触角变化不明显,因此,单独的9K培养基对于斑铜矿表面润湿性无明显影响。而含S.t菌和L.f菌的9K培养基中,斑铜矿表面接触角持续减小,亲水性增强。由此推断主要是由于斑铜矿在S. t菌和L. f菌作用下,发生了上述(2)~(4)的反应。由于斑铜矿表面亲水性较强的铜硫化合物和硫酸盐的产生,使矿物表面亲水性增强。
表1 斑铜矿的原始接触角
Table 1 Contact angle of bornite

表2 S. t菌的接触角
Table 2 Contact angle of S. t bacteria

表3 L. f菌的接触角
Table 3 Contact angle of L. f bacteria


图1 不同浸出体系中斑铜矿表面接触角的变化
Fig. 1 Variations of contact angle of bornite in different systems
随着浸出过程的进行,斑铜矿的接触角变化很大,并且不断接近所用细菌的接触角,由此可推断:可能是由于浸矿过程中不断有细菌吸附在其表面,通过在矿物表面产生胞外聚合物(extracellular polymeric substances,EPS),从而使斑铜矿表面润湿性不断接近相应浸矿微生物的润湿性[18-20]。
2.2 Zeta电位的测定
在不同离子强度I为0.010 mol/L和0.001 mol/L的NaCl溶液中,测量不同pH下斑铜矿的Zeta电位,结果如图2所示。从图2可见:斑铜矿的Zeta电位随溶液pH的升高而逐渐下降;当离子强度I=0.010 mol/L 时,斑铜矿的Zeta电位较离子强度 I=0.001 mol/L 时黄铜矿的Zeta电位明显负移。根据古依–切普曼–斯特恩(GCS)双电层模型[21-22],在离子强度较低时,斯特恩电位可以等同于动电位,分散层可以等效为平行板电容,则斯特恩电位ψ(即Zeta电位)的表达式可简化为: (其中,c为电解质浓度,q为表面电荷密度,F为法拉第常数,
(其中,c为电解质浓度,q为表面电荷密度,F为法拉第常数,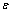 为介电常数,R为气体摩尔常数,T为热力学温度)。由此式可知:随着电解质浓度增大,溶液离子强度增大,Zeta电位因双电层被压缩而变小。
为介电常数,R为气体摩尔常数,T为热力学温度)。由此式可知:随着电解质浓度增大,溶液离子强度增大,Zeta电位因双电层被压缩而变小。

图2 不同离子强度的氯化钠条件下斑铜矿Zeta电位
Fig. 2 Zeta potential of bornite in sodium chloride solution with different ionic strengths
当离子强度为I=0.001 mol/L时,S. t菌和L. f菌的Zeta电位与pH的关系如图3所示。从图3可知:S. t菌的等电点大约为pH=3.2,而L. f菌的等电点大约是pH=6.1。2种菌的动电位都是随pH的增大呈下降趋势。其主要原因是:随着体系中pH的上升,体系中OH-浓度增大,吸附到细菌表面后使细菌的负电性增强,导致细菌的Zeta电位向负方向移动。L. f菌的动电位随pH变化更显著,其等电点值更大。
细菌与斑铜矿作用后,斑铜矿Zeta电位变化如图4所示。从图4可知:斑铜矿与细菌相互作用后的动电位都是随pH的增大呈减小趋势,L. f菌作用下斑铜矿动电位比S. t菌作用下高,且等电点也更高。细菌的吸附使斑铜矿的等电点朝细菌的等电点方向偏移,这表明在矿物表面发生了细菌的特性吸附,改变了原来斑铜矿的双电层结构。混合菌作用下动电位和等电点正好介于2个细菌的动电位和等电点之间,说明2种细菌均能同时有效吸附于斑铜矿表面。不同细菌作用后斑铜矿展现出不同的电动行为,表明不同的细菌对斑铜矿表面性质的改变能力不同,吸附能力也不同。

图3 I=0.001 mol/L时,不同pH下2种菌的Zeta电位
Fig. 3 Zeta potential of two bacteria at different pH when I=0.001 mol/L

图4 I=0.001 mol/L时,不同细菌作用后斑铜矿Zeta电位
Fig. 4 Zeta potential of bornite after treated by different bacteria when I=0.001 mol/L
3 结论
1) 斑铜矿的接触角较大,亲水性较弱,2种浸矿细菌(S. t和L. f菌)的接触角均很小,亲水性较强。
2) 在S. t菌和L. f菌作用下,斑铜矿表面接触角持续减小,推测主要由于斑铜矿表面亲水性较强的铜硫化合物和硫酸盐的产生,使矿物表面亲水性增强。
3) 细菌的吸附使斑铜矿的Zeta电位和等电点分别朝细菌的Zeta电位和等电点方向偏移,这表明在矿物表面发生了细菌的特性吸附;混合菌作用下斑铜矿动电位和等电点正好介于2个细菌的动电位和等电点之间,说明2种细菌均能同时有效吸附于斑铜矿表面。
参考文献:
[1] 白静, 温建康, 黄松涛, 等. 不同成矿条件下黄铜矿微生物浸出研究概况[J]. 稀有金属, 2012, 36(4): 644-650.
BAI Jing, WEN Jiankang, HUANG Songtao, et al. Review on bioleaching of chalcopyrite with different mineralizations[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2012, 36(4): 644-650.
[2] 尹升华, 吴爱祥, 王洪江, 等. 微生物浸出低品位矿石技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2010, 30(1): 46-49.
YIN Shenghua, WU Aixiang, WANG Hongjiang, et al. Current status and present situation and developing trend of low grade ore bioleaching technology[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2010, 30(1): 46-49.
[3] Brierley J, Brierley C. Present and future commercial applications of biohydrometallurgy[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59(2): 233-239.
[4] Devasia P, Natarajan K, Sathyanarayana D, et al. Surface chemistry of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans relevant to adhesion on mineral surfaces[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1993, 59(12): 4051-4055.
[5] van Loosdrecht M, Lyklema J, Norde W, et al. Electrophoretic mobility and hydrophobicity as a measured to predict the initial steps of bacterial adhesion[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1987, 53(8): 1898-1901.
[6] Gehrke T, Telegdi J, Thierry D, et al. Importance of extracellular polymeric substances from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for bioleaching[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1998, 64(7): 2743-2747.
[7] 顾帼华, 陈明莲, 苏丽君, 等. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌对黄铜矿表面性质及其浸出的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 41(3): 807-812.
GU Guohua, CHEN Minglian, SU Lijun, et al. Effects of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on surface properties of chalcopyrite and bioleaching[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2010, 41(3): 807-812.
[8] LIU Jianshe, WANG Zhaohui, CHEN Hong, et al. Interfacial electrokinetic characteristics before and after bioleaching microorganism adhesion to pyrite[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(3): 676-680.
[9] DONG Yingbo, LIN Hai, XU Xiaofang, et al. Bioleaching of different copper sulfides by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and its adsorption on minerals[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2013, 140: 42-47.
[10] DONG Yingbo, LIN Hai, XU Xiaofang, et al. Comparative study on the bioleaching, biosorption and passivation of copper sulfide minerals[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2013, 84(S1): 29-34.
[11] YANG Huifen, LI Tian, TANG Qiongyao, et al. Development of a bio-based collector by isolating a bacterial strain using flotation and culturing techniques[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2013, 123: 145-151.
[12] Ohmura N, Kitamura K, Saiki H. Mechanism of microbial flotation using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for pyrite suppression[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 1993, 41(6): 671-676.
[13] QIN Wenqing, WANG Jun, ZHANG Yansheng, et al. Electrochemical behavior of massive bornite bioleached electrodes in the presence of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus caldus[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2009, 71: 417-420.
[14] Brierley J A. Biotechnology for the extractive metals industries[J]. JOM Journal of the Minerals,Metals and Materials Society, 1990, 42(1): 28-30.
[15] WANG Jun, QIN Wenqing, ZHANG Yansheng, et al. Bacterial leaching of chalcopyrite and bornite with native bioleaching microorganism[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(6): 1468-1472.
[16] Bevilaqua D, Garcia O, Tuovinen O. Oxidative dissolution of bornite by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2010, 45(1): 101-106.
[17] Klauber C. A critical review of the surface chemistry of acidic ferric sulphate dissolution of chalcopyrite with regards to hindered dissolution[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2008, 86(1): 1-17.
[18] Kinzler K, Gehrke T, Telegdi J, et al. Bioleaching: A result of interfacial processes caused by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS)[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2003, 71(1): 83-88.
[19] Sand W, Gehrke T. Extracellular polymeric substances mediate bioleaching/biocorrosion via interfacial processes involving iron (Ⅲ) ions and acidophilic bacteria[J]. Research in Microbiology, 2006, 157(1): 49-56.
[20] Pogliani C, Donati E. The role of exopolymers in the bioleaching of a non-ferrous metal sulphide[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 1999, 22(2): 88-92.
[21] 王淀佐, 邱冠周, 胡岳华. 资源加工学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 173-200.
WANG Dianzuo, QIU Guanzhou, HU Yuehua. Minerals processing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 173-200.
[22] Henderson D, Boda D. Insights from theory and simulation on the electrical double layer[J]. Phys Chem Phys, 2009, 11(20): 3822-3830.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2014-01-20;修回日期:2014-03-25
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51374248);教育部博士点新教师基金资助项目(20120162120010);教育部新世纪人才计划项目(NCET-13-0595);博士后特别资助基金资助项目(2014T70692) (Project(51374248) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(20120162120010) supported by the Doctoral Discipline Foundation for Young Teachers in the Higher Education Institutions of Ministry of Education; Project(NCET-13-0595) supported by Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University; Project(2014T70692) supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation)
通信作者:王军,博士,副教授,从事矿物加工研究;E-mail: wjwq2000@126.com