硬质合金疲劳裂纹的萌生与扩展行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2014年第12期
论文作者:张忠健 赵声志 彭 文 张倩霞 陈 鼎
文章页码:3031 - 3042
关键词:硬质合金;疲劳裂纹;萌生;扩展
Key words:cemented carbide; fatigue crack; initiation; propagation
摘 要:硬质合金的服役环境通常十分恶劣,需要承受循环应力、温度(如高温或循环温度)和腐蚀环境的共同影响,机械疲劳、热疲劳和腐蚀疲劳等多种疲劳断裂机制是导致硬质合金材料失效的重要原因。从疲劳裂纹的萌生和扩展两方面系统地阐述硬质合金疲劳性能的影响因素。疲劳裂纹易沿着粗大的WC颗粒、孔洞、夹杂物和粘结相池等缺陷处萌生,而疲劳裂纹的扩展行为受到各种因素的影响,如应力比、频率、温度和环境等外部因素以及显微结构和化学成分等内部因素。
Abstract: Cemented carbides are often served in extreme environments, under which they need to suffer mutual influence of cyclic stress, temperature (such as high temperature and cyclic temperature) and corrosive environment. Various fatigue fracture mechanisms, such as mechanical fatigue, thermal fatigue and corrosion fatigue, are the main reasons for the failure of the alloys. In terms of the fatigue crack initiation and propagation, the fatigue performance in cemented carbide was systematically discussed. The analysis shows that the fatigue crack is prone to initiate at coarse WC grains, pores, inclusions or binder phase pools, while the propagation performance of fatigue crack is influenced by various factors, including external factors of stress ratio, frequency, temperature and environment, and internal factors of microstructure and chemical composition.
文章编号:1004-0609(2014)12-3031-11
张忠健1,赵声志1,彭 文1,张倩霞2,陈 鼎2
(1. 硬质合金国家重点实验室,株洲 412000;
2. 湖南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410082)
摘 要:硬质合金的服役环境通常十分恶劣,需要承受循环应力、温度(如高温或循环温度)和腐蚀环境的共同影响,机械疲劳、热疲劳和腐蚀疲劳等多种疲劳断裂机制是导致硬质合金材料失效的重要原因。从疲劳裂纹的萌生和扩展两方面系统地阐述硬质合金疲劳性能的影响因素。疲劳裂纹易沿着粗大的WC颗粒、孔洞、夹杂物和粘结相池等缺陷处萌生,而疲劳裂纹的扩展行为受到各种因素的影响,如应力比、频率、温度和环境等外部因素以及显微结构和化学成分等内部因素。
关键词:硬质合金;疲劳裂纹;萌生;扩展
中图分类号:TB303 文献标志码:A
ZHANG Zhong-jian1, ZHAO Sheng-zhi1, PENG Wen1, ZHANG Qian-xia2, CHEN Ding2
(1. State Key Laboratory of Cemented Carbide, Zhuzhou 412000, China;
2. College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China)
Abstract: Cemented carbides are often served in extreme environments, under which they need to suffer mutual influence of cyclic stress, temperature (such as high temperature and cyclic temperature) and corrosive environment. Various fatigue fracture mechanisms, such as mechanical fatigue, thermal fatigue and corrosion fatigue, are the main reasons for the failure of the alloys. In terms of the fatigue crack initiation and propagation, the fatigue performance in cemented carbide was systematically discussed. The analysis shows that the fatigue crack is prone to initiate at coarse WC grains, pores, inclusions or binder phase pools, while the propagation performance of fatigue crack is influenced by various factors, including external factors of stress ratio, frequency, temperature and environment, and internal factors of microstructure and chemical composition.
Key words: cemented carbide; fatigue crack; initiation; propagation
硬质合金是由脆性的过渡族金属碳化物硬质相和韧性的铁族金属粘结相以及一些其他微量元素组成的复合材料。硬质相和粘结相的结合使其具有高硬度、高强度和较好的韧性,广泛应用于刀具材料、钻探工具和耐磨零件等[1-4]。在这些应用领域,硬质合金往往要承受交变应力、腐蚀介质和温度变化等的共同作用,疲劳是导致硬质合金材料失效和断裂的主要因素[5-6]。因此,研究硬质合金的疲劳性能,特别是在复杂使用条件下的疲劳性能,对提高硬质合金的使用性能具有重要的指导意义。
与其他材料相似,硬质合金疲劳性能的研究方法也存在总寿命法和损伤容限法[7]。总寿命法是对光滑试样施加不同的应力幅S(或应变幅),并记录试样产生疲劳破坏所需的应力循环次数N(或应变循环次数)的方法。结果表明:硬质合金的S和N呈现较好的线性关系,在这种研究方法中,S-N直线的斜率(疲劳敏感性能)和标准差(数据分散度)是两个重要的疲劳性能参数。疲劳敏感性能可以在一定程度上反映材料抵抗疲劳裂纹扩展的能力,S-N直线的斜率越小,表明材料抵抗疲劳裂纹扩展的能力越好,对循环应力的变化越不敏感,疲劳敏感性越低。而数据分散度则反映了疲劳性能对微观缺陷的敏感程度,数据分散度越大,则疲劳性能对微观缺陷越敏感。另一种研究方法损伤容限法通常是研究疲劳裂纹扩展速率da/dN和裂纹尖端应力场强度因子幅△K或最大应力场强度因子Kmax之间的关系,以及裂纹扩展门槛值Kth来表征材料的疲劳性能。
本文作者总结了目前关于硬质合金的疲劳研究的现状,从疲劳裂纹萌生和扩展两个方面系统阐述了硬质合金的微观结构、成分和外界环境因素对疲劳性能的影响。
1 疲劳裂纹萌生行为
硬质合金作为一种粉末冶金制品,往往会存在一系列的缺陷,如孔隙、微裂纹、粗大的WC硬质相和第二相颗粒以及粘结相池等[8],这些缺陷在循环应力的作用下容易发生微观不可逆的形变,从而成为疲劳裂纹的形核点,使疲劳裂纹容易在此萌生。研究并尽可能消除这些缺陷对开发高性能长寿命硬质合金制品具有重要意义。
前苏联学者SHARROCK[9]认为,当石墨存在时孔隙参与断裂的部分显著减少,这种情况下断裂源往往是石墨。研究表明:硬质合金表面有凹穴,在凹穴中心有石墨质点。在疲劳实验的变形过程中,在石墨夹杂附近形成孔隙,这些孔隙促使裂纹生成。粗大颗粒(直径大于10 μm)的WC具有较低硬度,并容易在较低的应力下被破坏,从而促使疲劳裂纹产生和扩展。另外这些粗晶的聚积危害特别大,因为一个晶粒的破坏会通过接触区破坏引起其他晶粒的连接破坏。当在合金中没有石墨、η1相和粗大WC晶粒时,硬质合金试样的所有疲劳断口表明:产生疲劳断裂的主要原因是孔隙,这些孔隙存在于试样的表面和内部。
20世纪70年代初期,日本学者铃木寿和林宏尔[10]对硬质合金的断裂机理进行了系统研究,提出硬质合金的破坏起源于白点,所谓白点是一个直径很小(0.3~0.5 mm)的较平滑区域,在偏光下平滑区为微白色,并且有放射状形态,这种硬质断裂源有3种情形:直径为10~120 μm的孔隙,直径为3~20 μm的粗粒WC,直径为10~100 μm的Co泡。
还有很多研究者对硬质合金疲劳裂纹萌生行为进行了研究,如 等[11]研究了WC-12%Co(质量分数)的室温疲劳性能,试样形状是沙漏形状的,对疲劳断裂的试样进行统计分析,发现并不是所有的试样都从最小截面处断裂,有些试样可能从远离最小截面的10 mm处的缺陷处开始断裂,这些缺陷包括孔隙、粗的WC颗粒和Co含量稀少的区域。他们认为这些不同尺寸的缺陷是导致疲劳数据具有很大分散性的原因。TORRES等[12]对细晶WC-10%Co(质量分数)疲劳行为的研究表明:单调载荷和循环载荷下的裂纹源是一样的,裂纹起源于试样次表面的孔洞、异常粗的碳化物颗粒、无粘结剂的碳化物聚集区和不连续的WC-Co的团聚区。PADOVANI和GOUVEA[13]通过SEM观察WC-Co疲劳断裂面,发现疲劳微裂纹起源于亚表面Co池和孔隙。LI等[14]的研究表明,与单调递增载荷相比,循环载荷下的疲劳裂纹源的种类更多,疲劳裂纹通常起源于切口尖端附近的微孔或WC聚集区。李亚林等[15]比较了WC-6%Co梯度结构硬质合金和均质硬质合金的疲劳断口,结果表明:两种硬质合金的疲劳裂纹均在距表面约100 μm处形核,而Co相在应力集中效应、循环应力作用下发生的马氏体相变是裂纹在亚表面萌生的主要原因。
等[11]研究了WC-12%Co(质量分数)的室温疲劳性能,试样形状是沙漏形状的,对疲劳断裂的试样进行统计分析,发现并不是所有的试样都从最小截面处断裂,有些试样可能从远离最小截面的10 mm处的缺陷处开始断裂,这些缺陷包括孔隙、粗的WC颗粒和Co含量稀少的区域。他们认为这些不同尺寸的缺陷是导致疲劳数据具有很大分散性的原因。TORRES等[12]对细晶WC-10%Co(质量分数)疲劳行为的研究表明:单调载荷和循环载荷下的裂纹源是一样的,裂纹起源于试样次表面的孔洞、异常粗的碳化物颗粒、无粘结剂的碳化物聚集区和不连续的WC-Co的团聚区。PADOVANI和GOUVEA[13]通过SEM观察WC-Co疲劳断裂面,发现疲劳微裂纹起源于亚表面Co池和孔隙。LI等[14]的研究表明,与单调递增载荷相比,循环载荷下的疲劳裂纹源的种类更多,疲劳裂纹通常起源于切口尖端附近的微孔或WC聚集区。李亚林等[15]比较了WC-6%Co梯度结构硬质合金和均质硬质合金的疲劳断口,结果表明:两种硬质合金的疲劳裂纹均在距表面约100 μm处形核,而Co相在应力集中效应、循环应力作用下发生的马氏体相变是裂纹在亚表面萌生的主要原因。
根据疲劳裂纹形核的微观机理[16],疲劳裂纹形核位置包括:1) 金属晶体材料的滑移带在样品表面上形成的挤出和侵入造成应力集中萌生的疲劳裂纹[17-19];2) 金属多晶体中大角度晶界对滑移带所携带位错具有塞积作用,多次循环变形引起应力集中逐步加剧,最终导致疲劳裂纹沿大角度晶界萌生扩展[20];3) 合金中存在夹杂物、第二相粒子或其他外来缺陷,在往复循环中上述缺陷与基体发生塑性应变不协调导致疲劳裂纹萌生。
宋士泓和李健纯[21]通过疲劳变形试样的扫描和透射电镜的观察得出如下结论:1) WC晶体中位错之间以及位错与层错之间可以在有序点阵中形成高能的局部缺陷,在足够大的外加应力作用下,缺陷可以作为裂纹胚芽而转变成微裂纹;2) 微裂纹形核与WC晶体中运动位错在WC晶内的亚晶界和WC/WC晶界附近的塞积密切相关,微裂纹总是在这两种界面上形核扩展的;3) 减小WC亚晶粒尺寸可以减小位错在WC晶界和亚晶界的堆积现象,减小内界面附近的部分应力集中现象,从而降低WC晶内微裂纹形核几率,使合金的断裂韧性得到提高。该研究解释了大颗粒WC的穿晶微裂纹在WC-Co硬质合金起主要作用的原因。
对于Co相对裂纹萌生的作用,也有一些学者进行研究。SHARROCK[9]认为,根据塑性变形理论,在正常条件下钴粘结剂的行为和一般面心立方晶格金属一样随着位错增殖,位错被WC晶粒拦截和制止;但是硬质合金变形时钴相中无滑移线,变形过程中面心立方β-Co相通过马氏体切变转变为密排六方的Co相。钴的面心立方晶型在室温下不稳定性导致大量的堆垛层错产生,这些层错缺陷可能存在硬质合金未变形状态中,这些缺陷可以看作密排六方晶型在β-Co中的显微夹层。姜勇等[22]研究表明:疲劳变形的Co相产生大量明锐的层错条纹,并出现板条状或针片状的组织(马氏体相变)。在马氏体相变过程中,伴随孪晶亚结构的存在,密排六方结构的Co相在外力作用下很快丧失其松弛协调的应变能力。
2 疲劳裂纹扩展行为
硬质合金由于不可避免地具有很多微观缺陷,因此疲劳裂纹的萌生是比较容易的,KENKICHI等[23]研究了WC-5%Co、WC-15%Co、WC-25%Co硬质合金的疲劳性能,发现疲劳裂纹萌生寿命仅占疲劳寿命的1/10。因此硬质合金的疲劳裂纹扩展阶段对整个疲劳过程有着更为重要的影响。
硬质合金是由韧性的粘结相和脆性的硬质相所组成的,其增韧机制主要是桥联增韧机制,图1所示为桥联增韧机制的示意图[24]。当裂纹扩展时,在裂纹尖端的尾部会形成一个多韧带区,在这个区域内,韧性相会对裂纹起到牵扯作用,从而起到阻碍裂纹扩展和增韧的作用。疲劳裂纹穿过韧性相后,会在断裂面上形成韧窝,可以根据韧窝的性质来判断桥联增韧作用的大小[23]。
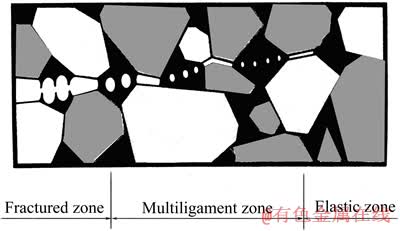
图1 桥联增韧机制的示意图[24]
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of binder damage in multi-ligament zone of WC-Co alloy[24]
2.1 裂纹断裂路径
在研究合金断裂机理的过程中,很多研究者都同时研究其断裂路径。GURLANA[25]认为无论是低Co还是高Co合金,断裂都有避开Co相的倾向,多发生在碳化物相和WC-WC边界上。当WC晶粒尺寸不超过1~2 μm时,裂纹仅分布在Co层内,且大多数沿WC-Co相界面[26]。日本三菱金属公司[27]用扫描电镜研究了抗拉试样的裂纹行径,发现裂纹都是穿过相边界和粘结相,因此提出WC-Co边界断裂取代碳化物晶粒断裂机理。日本东芝公司采用电子显微镜研究了WC-Co断裂现象,并将断裂特征分为3个类型:1) A型-WC晶粒剪断出现在WC晶粒大于5 μm、Co含量少于15%的合金中;2) BC型-WC或WC-Co界面断裂,出现在WC晶粒小于2 μm、Co含量少于7%的合金中;3) D型-Co相断裂,出现在WC尺寸小于4 μm、Co含量大于20%的合金中。此外还有混合型断裂,出现于3种合金的中间区域。德国学者SIGL和EXNER[28]提出WC-Co合金中裂纹扩展路径有4种:1) B路径,贯穿粘结相;2) B/C路径,沿着粘结相/碳化钨界面;3) C/C路径,沿着碳化物之间的晶界扩展;4) C路径,碳化钨中穿晶扩展。并且确定了这4种机制对整个裂纹扩展区域的贡献,研究表明:B/C路径不会出现黏结相/碳化钨的界面上,而是在粘结相内,离黏结相/碳化钨界面很近并平行于该界面的区域上。与B路径相比,裂纹经B/C路径扩展会形成更细小的韧窝结构。
图2所示为WC-Co裂纹尖端区域传播路径示意图[28]。裂纹分为断裂区、多韧带区和弹性区。裂纹明显扩展穿过WC基体(白区),被韧性黏结相(黑区)包围和桥联,形成韧带。当裂纹继续张开时,韧带会伸展直至破裂,裂纹在黏结相区域是沿B还是B/C路径伸展取决于微观结构局部的几何形貌(见图2)。裂纹尖端周围区域观察不到像陶瓷材料的那种分散的微裂纹[29-30]。韧带断裂过程如下:如果周围的碳化物骨架保持完整的话,黏结相的塑性变形将受到严重的制约。当碳化物与黏结相中裂纹毗连时,黏结相受到高的局部变形;当韧带延伸时,由于韧带与WC的连续性阻碍其侧面的收缩,为了维持黏结相的体积不变,裂纹尖端将会钝化,韧带中也会出现微孔和空洞[31]。钝的裂纹尖端和内部孔隙的长大和合并会导致韧带破裂,裂纹失稳。韧带区的长度大致为合金碳化物平均自由程的5倍,EVANS等[32]将其称为多韧带区。

图2 WC-Co裂纹传播路径[28]
Fig. 2 Crack propagation path of WC-Co alloy[28]
2.2 硬质合金的疲劳裂纹扩展模式
硬质合金的疲劳裂纹扩展存在两种模式:1) 真疲劳(循环断裂模式)。裂纹扩展速率da/dN仅与应力场强度因子幅△K有关,该种机制在金属材料中比较常见。2) 静态疲劳(静态断裂模式)。裂纹扩展速率da/dN仅与最大应力场强度因子Kmax及其作用时间有关,该种机制在脆性材料中比较常见。当真疲劳占据主导地位时,在硬质合金中桥联作用的效果会减弱,因此断裂面上往往呈现脆性断裂的特征,而当静态疲劳模式占据主导地位时,桥联增韧会起到作用,断裂面则与静载断裂面相同,具有明显的韧窝特征。
关于哪种断裂模式在硬质合金的疲劳损伤中占据主导地位的问题,不同的研究者得到不同的结论。LUETH等[33]的研究发现,硬质合金的疲劳断裂模式主要为静态模式,韧性粘结相呈现韧窝断裂特征,断裂形貌与静载断裂相同。而ALMOND和 ROEBUCK[34]的研究认为,其疲劳断裂模式主要是真疲劳断裂模式,虽然粘结相还会发生少量的塑性变形,但是循环载荷导致Co相加工硬化造成的疲劳脆断才是主要的断裂形式。FRY和GARRE[35]认为在硬质合金的疲劳裂纹扩展过程中这两种机制同时存在,断裂形貌以晶间断裂为主,Co相发生塑性变形并形成韧窝,还伴随着WC晶粒的解理断裂。而TORRES等[12]和LANES等[36]的研究也认为这两种断裂机制是共同存在的,他们除了从微观断裂形貌上证实了这点外,还从裂纹扩展速率与应力场强度因子之间的关系证实了上述结论,并且发现硬质合金裂纹扩展速率更加符合Paris-Erdogan公式:da/dN=C(Kmax)m(△K)n,且m远大于n,表明硬质合金中两种断裂模式都存在,其中静态失效模式起主导作用。图3所示为疲劳敏感性和Co相平均自由程的关系图,图中Kth/KIC定义为疲劳敏感性,该值愈大则疲劳敏感性愈低,材料循环载荷下的疲劳行为越接近陶瓷材料特性,断裂模式愈接近静疲劳模式,材料粘结相越容易发生韧性断裂。反之该值愈小,则材料在循环载荷条件下的疲劳断裂行为越接近金属,粘结相越易发生疲劳断裂,韧性得不到发挥,增韧机制的有效性降低。
2.3 影响疲劳裂纹扩展的外在因素
2.3.1 应力比对疲劳裂纹扩展的影响
ISHIHARA等[37-38]的研究表明:对于给定的Kmax,当裂纹扩展速率较小(约为1×10-11 m/cycle)时,da/dN随着应力比R的减小而增加;当裂纹扩展速率较大(约为1×10-7 m/cycle)时,da/dN仅由Kmax决定,与应力比R无关。作者认为当裂纹扩展速率较小(1×10-11 m/cycle)时,循环应力会削弱碳化物相与粘结相的界面结合强度,在界面处出现许多显微裂纹,减弱了韧带区的桥联增韧效果,而这种削弱效果随着R值的减小而增加,因此da/dN随着应力比R的减小而增加。但BOO等[39]认为应力比的影响主要体现在对Co相马氏体相变的影响:当Kmax一定时,应力比R越小,粘结剂Co相的循环变形程度越大,Co相中的堆垛层错数量增加,更多的Co相发生马氏体相变。与面心立方Co相比,密排六方结构的马氏体Co相的滑移系十分有限,几乎不可能发生滑移或孪晶变形,表现为脆性断裂。随着应力比R的增加,硬质合金的断裂形式会从脆性断裂转变为韧性断裂。LANES等[36]和TORRES等[12]通过观察断口形貌,发现应力比R越小时,真疲劳失效越明显,此时Co相不会发生很大的塑性变形,断口上呈现脆性断裂特征;而应力比R越大时,粘结相的韧性断裂越明显。这也进一步表明随着应力比R的增加,硬质合金的断裂模式越来越接近静态断裂模式。HIROSE等[40]的研究也得到了相似的结论。

图3 硬质合金疲劳敏感性和Co相平均自由能关系[36]
Fig. 3 Relationship between fatigue sensitivity of WC-Co cemented carbides and mean free energy of Co phase[36]
还有少数人研究了应力比R对硬质合金S-N曲线的影响,研究结果存在一定的差异。 等[11]发现不同应力比R下的硬质合金S-N曲线是不相同的,随着应力比R的减小,即平均压缩应力的增加,疲劳寿命和疲劳裂纹扩展门槛值△Kth都会相应增加。而FERREIRA等[41]的研究表明:硬质合金的S-N曲线与应力比无关,疲劳寿命主要取决于最大应力。
等[11]发现不同应力比R下的硬质合金S-N曲线是不相同的,随着应力比R的减小,即平均压缩应力的增加,疲劳寿命和疲劳裂纹扩展门槛值△Kth都会相应增加。而FERREIRA等[41]的研究表明:硬质合金的S-N曲线与应力比无关,疲劳寿命主要取决于最大应力。
2.3.2 频率对疲劳裂纹扩展的影响
一般认为硬质合金在循环载荷下存在着静态模式和真疲劳模式两种断裂机制。当疲劳为真疲劳断裂模式时,疲劳行为与频率无关,只与循环次数相关;当疲劳为静态断裂模式时,频率会影响疲劳裂纹扩展速率。但大多数研究并没有发现加载频率对硬质合金或金属陶瓷的疲劳裂纹扩展速率有显著的影响,这种现象很可能是由于实验的频率范围太窄或者粘结相含量太高所致[35, 42-43]。
2.3.3 温度对疲劳裂纹扩展的影响
硬质合金用作切削刀具材料时,除了承受复杂的机械载荷外,往往还要承受循环的温度变化和高温环境,因此有必要了解硬质合金的高温疲劳破坏机理。
ISHIHARA等[38]认为高温的影响主要体现在以下三个方面:1) 在高温下,金属粘结相会发生高温扩散,从而导致碳化物与金属粘结相的界面结合强度下降,降低了桥联增韧效果,减小裂纹扩展阻力;2) 在高温下,金属粘结相的屈服强度下降,从而导致裂纹尖端塑性区的尺寸增加,当塑性区尺寸大于碳化物尺寸,即使当裂纹撞到碳化物时,裂纹主要以穿碳化物和在其周围萌生微裂纹的方式进行扩展,这种扩展方式使得裂纹扩展速率增加。3) 温度还会显著的影响裂纹扩展路径。当室温下裂纹扩展速率很低时,裂纹沿着WC/Co界面扩展;当裂纹扩展速率很高时,裂纹既会沿着WC/Co界面扩展,又会穿过WC颗粒扩展。而在高温下裂纹都是沿着WC/Co界面扩展[38]。
而KINDERMANN和SOCKEL[44]则认为温度主要会影响到Co相的马氏体相变、氧化、塑性以及碳化物的韧脆转变。他们研究了温度对于疲劳敏感性的影响,结果如图4和5所示[44]。在室温时,循环载荷会导致WC-Co硬质合金中的Co相发生FCC-HCP相变而变得更脆,进而减弱了裂纹尖端前沿的屏蔽效应和裂纹尖端尾部的桥联增韧作用,疲劳敏感性很大;当温度升高到300 ℃时,由于Co相的马氏体相变减少,同时Co相的塑性增加并且未发生明显的氧化,屏蔽效应和桥联增韧效果增强,疲劳敏感性减小;当温度升高到500 ℃时,Co相沿着亚临界裂纹扩展方向发生显著的氧化而脆化,疲劳敏感性增大;当温度继续升高到700 ℃时,碳化物发生脆韧转变,疲劳敏感性又减小。而金属陶瓷的实验现象与硬质合金的有所不同,由于粘结相Co和Ni几乎不发生马氏体相变,当温度为25~500 ℃时,疲劳敏感性几乎不变;温度升高到700 ℃时,由于碳化物相发生脆韧转变,疲劳敏感性减小;当温度继续升高到900 ℃时,由于粘结相和碳化物相的氧化脆化,其疲劳敏感性增加[44-45]。

图4 P4M硬质合金的疲劳敏感性和温度的关系[44]
Fig. 4 Relationship between fatigue sensitivity of P4M cemented carbide and temperature variation[44]
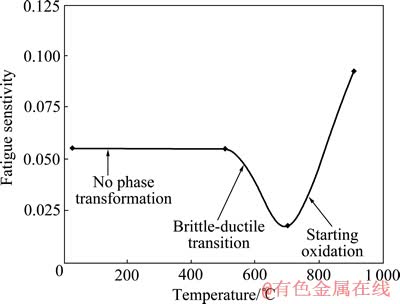
图5 HT7金属陶瓷的疲劳敏感性和温度变化的关系[44]
Fig. 5 Relationship between fatigue sensitivity of HT7 cermet and temperature variation[44]
DARY等[46]和ROEBUCK等[47]发现:温度的变化还会导致硬质相和粘结相的残余应力的变化,从而影响硬质合金的疲劳寿命。
WC-Co类硬质合金在使用过程中有温度冷热交替的变化,内部有温度梯度的产生,WC相和Co相的热膨胀系数相差3倍,合金导热性差,很多工具材料同时受到压应力和剪切应力的作用。GOPAL[48]认为,硬质合金工具材料磨损或断裂失效的最主要原因是热疲劳裂纹形成和扩展。AKERMAN和ERICSON[49]认为当温度升高时Co相承受压应力,当温度下降时,Co相承受拉应力。由热胀冷缩产生的热应力值大于硬质合金的抗弯强度时,将导致WC/Co相界面弱化,使Co粘结相界面弱化,弱化和破坏Co相对WC颗粒的支撑粘连作用,WC相由于缺少Co粘结相的粘结作用,而不断被剥落产生微孔洞。随着孔洞不断变大,相邻孔洞连成微裂纹,裂纹沿着WC/Co界面和WC相向深处扩展,发展成热疲劳典型特征—龟裂纹。
2.3.4 腐蚀环境对疲劳裂纹扩展的影响
硬质合金在使用过程中往往会接触到腐蚀性介质,如硬质合金刀具常用于切割各种金属、塑料和纤维板等,在工作时可能接触到腐蚀性化合物[50-51]。研究表明:腐蚀性介质会与机械应力发生交互作用,进而影响到硬质合金的疲劳性能,但是这种交互作用仅仅会在某一中间应力范围内出现,相关的研究结果如图6所示[51]。
当应力幅大于某一临界值时,机械载荷引发的裂纹扩展速率很大,腐蚀作用的有效时间很短,因此在空气中和在腐蚀性环境中试样的疲劳寿命相当。当应力幅在500 MPa和临界值之间时,腐蚀性环境中试样的疲劳寿命明显低于在空气中的疲劳寿命,并且随着应力幅的降低,疲劳寿命减少的程度更大。PUGSLEY和SOCKEL[51]认为应力幅的降低会导致机械载荷引发的裂纹扩展速率减小,从而使腐蚀作用的有效时间延长,腐蚀疲劳效应显著。而当应力幅低于500 MPa时(最大应力低于屈服强度),粘结相只能发生弹性变形,不会出现塑性变形和腐蚀介质的交互作用。另外频率会对金属陶瓷的腐蚀疲劳性能会产生影响,随着频率的减小,腐蚀作用的有效时间得到延长,从而显著降低其疲劳强度。

图6 在频率为4 Hz单宁酸环境中与空气中的硬质合金S-N曲线(箭头代表实验结束时仍未断裂的试样[51])
Fig. 6 S-N diagram for hardmetal tested in tannic acid environment and in air at frequency of 4 Hz (Arrows indicate specimens that remained unbroken at end of test period[51])
2.3.5 裂纹模式对疲劳裂纹扩展的影响
裂纹模式也会对疲劳裂纹扩展产生影响,但有关这方面的报道较少,TORRES等[52]研究了裂纹从Ⅰ型模式逐渐变为Ⅱ型模式时的疲劳性能的变化。研究认为Ⅱ型模式(剪切模式)的裂纹闭合效应更加显著,而且还存在着剪切摩擦效应,故当加载模式从Ⅰ型变为Ⅰ+Ⅱ型混合模式时,疲劳裂纹扩展门槛值Kth会增加。
2.4 影响裂纹扩展的内在因素和增韧处理
影响疲劳裂纹扩展的内在因素包括碳化物和粘结剂的化学成分和显微结构。显微结构参数包括碳化物和粘结剂的含量、碳化物的晶粒尺寸、碳化物的形状和分布等,其中独立的显微结构参数是粘结相的平均自由程和硬质相的邻接度。
2.4.1 化学成分对裂纹扩展的影响
WC/Co是开发最早也是应用最为广泛的硬质合金,其产量占到总产量的一半以上[53]。但是WC基的耐腐蚀性和耐氧化性较差以及金属钨的自然资源变得越来越少,这些因素限制了WC基硬质合金的广泛应用。无钨硬质合金的出现可以解决这一难题,目前代替WC的碳化物主要有TiC、TiCN和(Ta、Nb)C等。由于金属钴的价格昂贵、耐腐蚀性和耐氧化性相对较差,人们开发了新型粘结相成分的硬质合金,如采用Ni、Cr和Fe部分或全部取代Co,也有采用Ni3Al、NiAl、Fe3Al和FeAl等作为粘结相[54]。
硬质合金是由脆性硬质相和韧性粘结相组成的复合材料,因此硬质相和粘结相的化学成分都会显著影响硬质合金的疲劳性能。研究表明在循环载荷下,TiC基金属陶瓷和WC基硬质合金中的各相尤其是碳化物相的塑性会显著降低,循环载荷后TiC的塑性大于WC,故WC基硬质合金的疲劳敏感性大于TiC基金属陶瓷的疲劳敏感性[55-57]。SCHLEINKOFER等[58-60]研究了粘结相为Co的硬质合金和粘结相为CoNi的金属陶瓷的室温疲劳,发现循环载荷下的亚临界裂纹扩展主要发生在粘结相中。较高的累积变形或应力导致硬质合金中的粘结剂Co相发生马氏体相变,从而导致多韧带区的Co相韧性下降和裂纹尖端尾部的屏蔽效应减弱,疲劳敏感性很大。但金属陶瓷中的Co-Ni相没有发生明显的马氏体相变,具有更高的韧性,故疲劳敏感性更小。SAILER等[61]的研究表明,在Co粘结相中加入Fe和Ni后也会降低马氏体相变程度,导致硬质合金的疲劳敏感性减小。KURESAWE等[62]采用TEM观察疲劳断面时发现:在WC-Co硬质合金中存在堆垛层错,该层错是应力诱发Co相发生马氏体相变的形核处,但在WC-Co(Ni、Fe)中没有堆垛层错。LISOVSKY等[63]在生产WC-Co硬质合金时添加微量的Ta和Mo,研究认为Ta和Mo在WC相颗粒间形成了一层复杂的碳化物,有部分Mo元素溶入Co粘结相中,改善了粘结相成分和结构,提高了合金耐磨性和抗热冲击性。XU等[64]在WC-Co中加入适量的稀土(Ce和Y等)或化合物,提高了合金的强度和韧性,研究认为稀土的加入减少了β-Co向ε-Co(HCP)的转变,材料表现出良好的抗疲劳性。
2.4.2 粘结相的平均自由程对裂纹扩展的影响
早期研究表明:疲劳裂纹扩展抗力随着粘结相的平均自由程λCo的增加而增加[35, 65-66]。FRY和GARRE[35]认为裂纹尖端尾部Co相的韧带断裂导致了疲劳裂纹的扩展,而该机理可解释裂纹扩展速率随着Co相的平均自由程增加而减小的现象。但是LANES等[36]的研究却认为粘结相的影响并不只有这么简单,研究结果如图7所示。当粘结相的平均自由程λCo增加(与碳化物的邻接度成反比)时,金属粘结相的韧性将会明显增加,硬质合金的疲劳行为由类陶瓷行为转变为类金属行为,即更易发生真疲劳断裂。随着λCo的增加,虽然断裂韧性是单调增加的,但是疲劳裂纹扩展门槛值Kth却先增加后减小,断裂韧性和疲劳裂纹扩展抵抗力之间并不表现出单调的关系。研究认为主要原因是在循环载荷下,硬质合金中的粘结相既是增韧相,同时又是易受疲劳影响相,两者之间存在一个临界点。一方面,裂纹桥联和钴相受约束的塑性延伸是断裂时最主要的能量耗散点;另一方面,粘结相具有金属材料易受疲劳损伤影响的本质特征,特别是粘结相中发生了FCC-HCP马氏体相变的情况下,这不仅导致了裂纹尖端尾部韧带的过早失效,同时也减小了裂纹尖端屏蔽效应。

图7 给定应力比为R时硬质合金的λCo与裂纹扩展门槛值Kth和断裂韧性KIC的关系[36]
Fig. 7 Relationship between λCo and Kth and KIC at given stress ratio of R[36]
有关粘结相的平均自由程对硬质合金S-N曲线的影响的研究也存在着争论。PADOVANI和GOUVEA[13]和NAKAJIMA等[67]的研究表明:随着粘结相含量的增加,硬质合金的疲劳敏感性减小。但是,SAILER等[61]对细晶硬质合金的疲劳性能的研究表明:疲劳敏感性随着Co含量增加而增加,与WC晶粒度的相关性却相对弱一些,原因是疲劳损伤主要发生在韧性粘结相中,而高粘结相含量的硬质合金中这种效应更加显著。KURESAWE等[62]的研究表明:粘结相含量对WC-Co的疲劳行为几乎没有影响,但粘结相含量对WC-Co(Ni、Fe)合金的疲劳敏感性有显著影响,他们认为这是由于疲劳损伤主要集中在钴池的剪切带和发生马氏体相变的Co中所导致。
2.4.3 WC的晶粒度对裂纹扩展的影响
一般来说细晶的裂纹扩展速度大于粗晶的裂纹扩展速度,CHERMANT[68]研究表明,在给定WC粘度时KIC值与钴层夹杂平程厚度之间呈线性关系;当粘结相夹层平均值不变时,KIC与WC平均粒度的平方根之间呈线性关系。
美国Smith公司[69]发表了“粗晶低Co”的矿用钻头的断裂和耐磨性专利,所谓粗晶化是指WC晶粒度大于4 μm,钴含量低于14%(质量分数),当WC晶粒度增大时,WC结晶完整,亚晶粒增大,缺陷减少,粒度均匀,减少了WC/WC界面、WC/Co界面和WC颗粒的聚集区,从而有效减少了热疲劳裂纹源存在数量,改善了合金韧性,提高了合金的抗热疲劳性能和抗热冲击性能。
总的来说,增大WC的晶粒度,降低Co含量,加入适量的微量元素,增强合金能量的吸收能力,对硬质合金进行热处理,采用非均匀结构和梯度结构合金以及改进烧结工艺都能够起到增韧硬质合金和提高疲劳性能的作用。
3 结论
目前,关于硬质合金疲劳性能的研究方法主要有两种:总寿命法与损伤容限法,不同的研究方法采用不同的参数来表征硬质合金的疲劳性能。
硬质合金是由脆性硬质相和韧性粘结相组成的复合材料,疲劳裂纹容易在硬质合金的缺陷处萌生,既可能在硬质相中萌生也可能在韧性相中萌生,这些缺陷包括孔隙、微裂纹、粗大硬质相和第二相颗粒以及粘结相池等,消除这些显微缺陷对于提高硬质合金的疲劳性能具有重要意义。硬质合金的疲劳裂纹的扩展是十分复杂的,真疲劳和静态疲劳机制都可能成为其扩展机制,两者还可能共同存在。影响硬质合金的疲劳裂纹扩展的因素有很多,包括各种外部因素和内部因素,外部因素包括应力比、温度、腐蚀环境和裂纹模式等,内部因素包括硬质相的的体积分数、成分、晶粒尺寸、韧脆转变温度、粘结相的含量和成分以及马氏体相变等。这些错综复杂的因素交错在一起,使得对于硬质合金疲劳性能的研究变得十分的复杂,目前的研究也尚未形成统一的理论,还有待进一步的研究。
硬质合金是“工业的牙齿”,硬质合金的使用几乎涉及到国民经济的各个部门,是不可或缺的结构材料和工具材料。了解硬质合金的疲劳断裂机理和提高其疲劳性能将是硬质合金领域的一个重要研究方向,有助于提升我国硬质合金产品的内在质量。同时在使用过程中,硬质合金往往需要承受交变应力、腐蚀介质和温度变化等复杂的使用环境,目前的疲劳研究还未涉及多种疲劳共同耦合的作用,有待于进一步深入研究。
REFERENCES
[1] 张武装, 刘 咏, 贺跃辉, 羊建高, 龙郑易. 具有梯度结构的涂层硬质合金刀片[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(5): 757-762.
ZHANG Wu-zhuang, LIU Yong, HE Yue-hui, YANG Jian-gao, LONG Zheng-yi. Coated cemented carbide with gradient structure[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(5): 757-762.
[2] 程剑兵, 庞思勤, 王西彬, 于启勋, 林晨光. 硬质合金刀具车削GH2132高温合金磨损及破损试验[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2013, 33(9): 911-915.
CHENG Jian-bin, PANG Si-qin, WANG Xi-bin, YU Qi-xun, LIN Chen-guang. Wear and breakage lifespan study of ultrafine-grained hardmetais tool for turning GH2132 superalloy[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2013, 33(9): 911-915.
[3] 杨玉红, 麻俊方, 石国洲. 硬质合金钻头修磨与涂层技术的应用探索[J]. 工具技术, 2012, 46(5): 64-66.
YANG Yu-hong, MA Jun-fang, SHI Guo-zhou. Resharp and coating technology used on carbide drill[J]. Tool Engineering, 2012, 46(5): 64-66.
[4] 彭 文, 邓 涛. 硬质合金先进技术在大规格顶锤制造中的应用[J]. 超硬材料工程, 2013, 25(1): 25-29.
PENG Wen, DENG Tao. Application of advanced technology of cemented carbide in manufacturing large size anvil[J]. Superhard Material Engineering, 2013, 25(1): 25-29.
[5] 陈振华, 姜 勇, 陈 鼎, 张忠健, 徐 涛, 彭 文. 硬质合金的疲劳与断裂[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(10): 2394-2401.
CHEN Zhen-hua, JANG Yong, CHEN Ding, ZHANG Zhong-jian, XU Tao, PENG Wen. Fatigue and fracture of cemented carbides[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(10): 2394-2401.
[6] 郭圣达, 张正富. WC-Co 类硬质合金疲劳特性研究现状[J]. 材料导报, 2009, 23(11): 69-72.
GUO Sheng-da, ZHANG Zheng-fu. Study on fatigue property of WC-Co cemented carbide[J]. Material Review, 22009, 23(11): 69-72.
[7] SURESH S. 材料的疲劳[M]. 王中光, 译. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1999: 8-9.
SURESH S. The fatigue of materials[M]. WANG Zhong-guang, translating. Beijing: National Defence of Industry Press, 1999: 8-9.
[8] 陈振华, 陈 鼎. 现代粉末冶金原理[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2013: 461.
CHEN Zhen-hua, CHEN Ding. The principle of modern powder metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Publisher, 2013: 461.
[9] SHARROCK M. 硬质合金的强度和寿命[M]. 黄鹤翥, 译. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1987.
SHARROCK M. The strength and life of cemented carbides[M]. HUANG He-zhu, transl. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1987.
[10] SUZUKI H, HAYSASHI K. Relations between transverse rupture strength and fracture orign in WC-10%Co cemented carbides[J]. Journal of the Japan Institute of Metals, 1974, 38(11): 1013-1019. (in Japanese)
[11]  T, MARSONER S, EBNER R, PIPPAN R, GLATZLE J, PUSCHEL A. Effect of microstructure on fatigue properties of WC-Co hard metals[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2010, 2: 2001-2010.
T, MARSONER S, EBNER R, PIPPAN R, GLATZLE J, PUSCHEL A. Effect of microstructure on fatigue properties of WC-Co hard metals[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2010, 2: 2001-2010.
[12] TORRES Y, ANGLADA M, LLANES L. Fatigue mechanics of WC-Co cemented carbides[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2001, 19: 341-348.
[13] PADOVANI U, GOUVEA D. Fatigue life of tungsten carbide plungers operating in reciprocating compressors for ethylene [EB/OL]. [2013-08-03]. http://www.artigocientifico.com.br/ upload/artc_1152724378_43.pdf.
[14] LI An-hai, ZHAO Jun, WANG Dong, GAO Xin-liang, TANG Hong-wei. Three-point bending fatigue behavior of WC-Co cemented carbides[J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 45: 271-278.
[15] 李亚林, 刘 咏, 周永贵, 李 昆, 赵中伟. 梯度结构硬质合金的疲劳断裂[J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2011, 16(5): 747-754.
LI Ya-lin, LIU Yong, ZHOU Yong-gui, LI Kun, ZHAO Zhong-wei. Fatigue fracture of functionally-graded cemented carbides[J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy, 2011, 16(5): 747-754.
[16] 张哲峰, 张 鹏, 田艳中, 张青科, 屈 伸, 邹鹤飞, 段启强, 李守新, 王中光. 金属材料疲劳损伤的界面效应[J]. 金属学报, 2009, 45(7): 788-800.
ZHANG Zhe-feng, ZHANG Peng, TIAN Yan-zhong, ZHANG Qing-ke, QU Shen, ZOU He-fei, LI Shou-xin, WANG Zhong-guang. Interfacial effects of fatigue crack in metallic materials[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009, 45(7): 788-800.
[17] ESSMANN U, GOSELE U, MUGHRABI H. A model of extrusions and intrusions in fatigued metals Ⅰ. Point-defect production and the growth of extrusions[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1981, 44: 405-426.
[18] BASINSKI Z S, PASCUAL R, BASINSKI S J. Low amplitude fatigue of copper single crystals. Ⅰ. The role of the surface in fatigue failure[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1983, 31(4): 591-602.
[19] HUNSCHE A, NEUMANN P. Quantitative measurement of persistent slip band profiles and crack initiation[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1986, 34: 207-217.
[20] LIU W, BAYERLEIN M, MUGHRABI H, DAY A, QUESTED P N. Crystallographic features of intergranular crack initiation in fatigued copper polycrystals[J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1992, 40(7): 1763-1771.
[21] 宋士泓, 李健纯. WC-Co合金微裂纹形核过程的探讨[J]. 金属学报, 1987, 23(6): A521-A525.
SONG Shi-hong, LI Jian-chun. Initiation of microcracks in WC-Co alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 1987, 23(6): A521-A525.
[22] 姜 勇, 李中权, 钟益平, 陈振华. WC-Co硬质合金疲劳断裂机制研究[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2012, 30(5): 341-347.
JIANG Yong, LI Zhong-quan, ZHONG Yi-ping, CHEN Zhen-hua. On the fatigue and fracture features of WC-Co cemented carbides[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2012, 30(5): 341-347.
[23] KENKICHI S, MASANOHU Y, TOMOYUKI A. Compression fatigue failure in WC-Co cemented carbides[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers Series A, 1992, 58: 2293-2298.
[24] SIGL L S, SCHMAUDER S. A finite element study of crack growth in WC-Co[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1988, 36: 305-317.
[25] GURLAND J. The fracture strength of sintered tungsten carbide-cobalt alloys in relation to composition and particle spacing[J]. Trans TMS-AIME, 1963, 227: 1146-1152
[26] 黄培云. 粉末冶金原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1997.
HUANG Pei-yun. Principles of powder metallurgy[M]. Beijing: MetallurgicalIndustryPress, 1997.
[27] 《国外硬质合金》编写组. 国外硬质合金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1976.
《Foreign cemented carbides》Editorial committee. Foreign cemented carbides[M]. Beijing: MetallurgicalIndustryPress, 1976.
[28] SIGL L. S. EXNER H E. Experimental study of the mechanics of fracture in WC-Co alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1987, 18: 1299-1308.
[29] EVANS A G, CANNON R M. Overview no. 48: Toughening of brittle solids by martensitic transformations[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1986, 34 (5): 761-800.
[30] ALMOND E A. In Speciality Stells and Hard Materials[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1983.
[31] EVANS A G, MCMEEKING R M. On the toughening of ceramics by strong reinforcements[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1985, 34(12): 2435-2441.
[32] EVANS A G, HEUER A, PORTER D L. Toughening mechanisms in cemented carbides[C]// TAPLIN D M R. Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Fracture. University of Waterloo: University of Waterloo Press, 1977.
[33] LUETH R C. Fatigue of WC-Co cemented carbide[J]. JournalofEngineering Materialsand Technology, 1981, 103: 180.
[34] ALMOND E A, ROEBUCK B. Fatigue crack growth in hardmetalWC-Co[J]. Metals Technologies, 1980, 7:83-85.
[35] FRY P, GARRE G. Fatigue crack growth behaviour of tungsten carbide-cobalt hardmetals[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1988, 23: 2325-2338.
[36] LANES L, TORRES Y, ANGLADA M. On the fatigue crack growth behavior of WC-Co cemented carbides: kinetics description, microstructural effects and fatigue sensitivity[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50: 2381-2393.
[37] ISHIHARA S, GOSHIMA T, YOSHIMOTO Y, SABU T. The influence of the stress ratio on fatigue crack growth in a cermet[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2000, 35: 5661-5665.
[38] ISHIHARA S, SHIBATA H, GOSHIMA T. Effect of environmental temperature on the fatigue crack propagation behavior of cemented carbides[J]. Journal of Thermal Stresses, 2008, 31: 1025-1038.
[39] BOO M H, OH H W, PARK Y C, HIROSE Y. The effect of Co content on fatigue crack growth characteristics of WC-Co cemented carbide[EB/OL]. [2013-08-03]. http://www.icdd.com/ resources/axa/vol41/V41_59.pdf.
[40] HIROSE Y, BOO M, MATSUOKA H, PARK Y C. Influence of stress ratio and WC grain size on fatigue crack growth characteristics of WC-Co cemented carbides[J].Journal of Society of Materials Science in Japan, 1997, 46: 1402-1409.
[41] FERREIRA J A M, AMARAL M P A, ANTUNESS F V, COSTA J D M. A study on the mechanical behaviour of WC/Co hardmetals[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2009: 27: 1-8.
[42] SCHLEINKOFER U, SOCKEL H G, GORTING K, HEINRICH W. Fatigue of hard metals and cermets[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996, 209: 313-317.
[43] SERGEJEV F, KLAASEN H, KUBARSEPP J, PREIS I. Fatigue mechanics of carbide composites[J]. International Journal of Materials and Product Technology, 2011, 40: 140-163.
[44] KINDERMANN P, SOCKEL H G. Mechanisms of fatigue in cemented carbides at elevated temperatures[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2000, 6: 1438-1656.
[45] KINDERMANN P, SCHLUND P, SOCKEL H G, HERR M, HEINRICH W, GORTING K, SCHLEINKOFER U. High-temperature fatigue of cemented carbides under cyclic loads[J]. International Journal of Refractory MetalsandHard Materials, 1999, 17: 55-68.
[46] DARY F C, ROEBUCK B, GEE M G. Effects of microstructure on the thermo-mechanical fatigue response of hardmetals using a new miniaturized testing rig[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 1999, 17: 45-53.
[47] ROEBUCK B, MADERUD C J, MORRELL R. Elevated temperature fatigue testing of hardmetals using notched testpieces[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2008, 26: 19-27.
[48] UPADHYAYA G S. Cemented tungsten carbides: Production, properties, and testing[M]. New Jersey: Noyes Publications, 1997: 241.
[49] AKERMAN J, ERICSON T. Cemented carbide body with improved high temperature and thermomechanical properties: US, 6692690B2[P]. 2004-02-17.
[50] PUGSLEY V A, KORN G, LUYCKX S, SOCKEL H G, HEINRICH W, WOLF M, FELD H, SCHULTE. The influence of a corrosive wood-cutting environment on the mechanical properties of hardmetal tools[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2011, 19: 311-318.
[51] PUGSLEY V A, SOCKEL H G. Corrosion fatigue of cemented carbide cutting tool materials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 366: 87-95.
[52] TORRES Y, SARIN V K, ANGLADA M, LLANES L. Loading mode effects on the fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth resistance of WC-Co cemented carbides[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005, 52: 1087-1091.
[53] PRAKASH L J. Application of fine grained tungsten carbide based cemented carbides[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 1995, 13: 257-264.
[54] 林春芳, 杜玉国, 孙 丹, 陈蓓瑾, 刘莹华. Ni、Cr 对碳化钨基硬质合金耐腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2010, 31: 678-682.
LIN Chun-fang, DU Yu-guo, SUN Dan, CHEN Bei-jin, LIU Ying-hua. Influence of Ni and Cr on anti-corrosion performance of tungsten carbide base hard alloy[J]. Corrosion and Protection, 2010, 31: 678-682.
[55] KUBARSEPP J, KLAASEN H, SERGEJEV F. Performance of cemented carbides in cyclic loading wear conditions[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2007, 534/536: 1221-1224.
[56] KLAASEN H, KUBARSEPP J, SERGEJE F. Strength and failure of TiC based cermets[J]. Powder Metallurgy, 2009, 52: 111-115.
[57] KLAASEN H, KUBARSEPP J, PREIS I. Wear behaviour, durability, and cyclic strength of TiC base cermets[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2004, 20: 1006-1010.
[58] SCHLEINKOFER U, SOCKEL H G, GORTIN K, HEINRICH W. Fatigue of hard metals and cermets-new results and a better understanding[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 1997, 15: 103-112.
[59] SCHLEINKOFER U, SOCKEL H G, SCHLUND P, GORTING K, HEINRICH W. Behaviour of hard metals and cermets under cyclic mechanical loads[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1995, 194: 1-8.
[60] SCHLEINKOFER U, SOCKEL H G, GORTING K, HEINRICH W. Microstructural processes during subcritical crack growth In hardmetals and cermets under cyclic loads[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1996, 209: 103-110.
[61] SAILER T, HERR M, SOCKELH G, SCHULTE R, FELD H, PRAKASH L J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine-grained hardmetals[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2001, 19: 553-559.
[62] KURESAWE S, POTT P H, SOCKER H G, HEINRICH W, WOLF M. On the influence of binder content and binder composition on the mechanical properties of hardmetals[J]. International Journal of Refractory MetalsandHard Materials, 2001, 19: 335-340.
[63] LISOVSKY A F, GRACHEVA T E, KULAKOVSKY V N. Composition and properties of (Ti,W)C-WC-Co sintered carbides alloyed by MMT-process[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 1995, 13(6): 379-383.
[64] XU Chong-hai, AI Xing, HUANG Chuan-zhen. Research and development of rare-earth cemented carbides[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2001, 19(3): 159-168.
[65] KNEE N, PLUMBRIDGE W. The influence of microstructure and stress ratio on fatigue crack growth in WC-Co hardmetals[J]. Fracture, 1984, 84: 2685-2692.
[66] FRY P R, GARRETT G G. The inter-relation of microstructure, toughness and fatigue crack growth in WC-Co hardmetals[J]. Speciality Steels and Hard Materials, 1983: 375-381.
[67] NAKAJIMA T, HOSOKAWA H, SHIMOJIMA K. Influence of cobalt content on the fatigue strength of WC-Co hardmetals[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2007, 534/536: 1201-1204.
[68] Chermant J L, Osterstock F. Fracture toughness and fracture ofWC-Cocomposites[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1976, 11: 1939-1951.
[69] REN Xiao-yong, MIAO He-zhou PENG Zhi-iian.. A review of cemented carbides for rock drilling: An old but still tough challenge in geo-engineering[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2013, 39(1): 61-77.
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:湖南省“十一五”重大科技专项(2007FJl002);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(14JJ1013)
收稿日期:2014-03-07;修订日期:2014-09-24
通信作者:陈 鼎,教授,博士;电话:0731-88821648;E-mail: Ma97chen@hotmail.com

