Effects of wall thickness and material on flame stability in a planar micro-combustor
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2019年第8期
论文作者:范爱武 LIU Lei(刘磊) ZHAO Liang(赵亮)
文章页码:2224 - 2233
Key words:micro-combustor; flame stability; flame inclination; blowout limit; heat recirculation; heat loss
Abstract: Flame is prone to lose its stability in micro-combustors due to the large amount of heat loss from the external walls. On the other hand, heat recirculation through the upstream combustor walls can enhance flame stability. These two aspects depend on the structural heat transfer, which is associated with the thickness and thermal conductivity of the combustor walls. In the present study, the effects of wall thickness and material on flame stability were numerically investigated by selecting two thicknesses (d=0.2 and 0.4 mm) and two materials (quartz and SiC). The results show that when d=0.2 mm, flame inclination occurs at a certain inlet velocity in both combustors, but it happens later in SiC combustor. For d=0.4 mm, flame inclination still occurs in quartz combustor from a larger inlet velocity compared to the case of d=0.2 mm. However, flame inclination in SiC combustor with d=0.4 mm does not happen and it has a much larger blowout limit. Analysis reveals that a thicker wall can enhance heat recirculation and reduce heat loss simultaneously. Moreover, SiC combustor has larger heat recirculation ratio and smaller heat loss ratio. In summary, the micro-combustor with thicker and more conductive walls can harvest large flame stability limit.
Cite this article as: LIU Lei, ZHAO Liang, FAN Ai-wu. Effects of wall thickness and material on flame stability in a planar micro-combustor [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(8): 2224-2233. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4168-6.

ARTICLE
J. Cent. South Univ. (2019) 26: 2224-2233
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4168-6
LIU Lei(刘磊)1, ZHAO Liang(赵亮)2, FAN Ai-wu(范爱武)2
1. China Tabacco Hubei Industrial Limited Liability Company, Wuhan 430014, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Coal Combustion, Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430074, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2019
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2019
Abstract: Flame is prone to lose its stability in micro-combustors due to the large amount of heat loss from the external walls. On the other hand, heat recirculation through the upstream combustor walls can enhance flame stability. These two aspects depend on the structural heat transfer, which is associated with the thickness and thermal conductivity of the combustor walls. In the present study, the effects of wall thickness and material on flame stability were numerically investigated by selecting two thicknesses (d=0.2 and 0.4 mm) and two materials (quartz and SiC). The results show that when d=0.2 mm, flame inclination occurs at a certain inlet velocity in both combustors, but it happens later in SiC combustor. For d=0.4 mm, flame inclination still occurs in quartz combustor from a larger inlet velocity compared to the case of d=0.2 mm. However, flame inclination in SiC combustor with d=0.4 mm does not happen and it has a much larger blowout limit. Analysis reveals that a thicker wall can enhance heat recirculation and reduce heat loss simultaneously. Moreover, SiC combustor has larger heat recirculation ratio and smaller heat loss ratio. In summary, the micro-combustor with thicker and more conductive walls can harvest large flame stability limit.
Key words: micro-combustor; flame stability; flame inclination; blowout limit; heat recirculation; heat loss
Cite this article as: LIU Lei, ZHAO Liang, FAN Ai-wu. Effects of wall thickness and material on flame stability in a planar micro-combustor [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(8): 2224-2233. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4168-6.
1 Introduction
It is well known that the energy densities of hydrogen and hydrocarbon fuels are much higher than chemical batteries. Therefore, combustion- based micro- and meso-scale energy conversion and power generation systems have attracted extensive attentions in the past decades [1]. Unfortunately, flame stability in micro-combustors faces rigorous challenge from increased heat loss ratio [2]. Various flame dynamics, such as flame inclination [3, 4], periodic extinction and ignition [5, 6], have been observed in both premixed and diffusion combustion in micro-combustors. To anchor the flame in micro-combustors, flame holders like backward facing step [7, 8], bluff body [9], cavity [10-13], have been proposed by researchers.
Heat conduction in the solid wall can play a significant role in flame stability limits and flame propagation speed in micro-combustors [14, 15]. NORTON et al [16] and VEERARAGAVAN [17] numerically demonstrated that the wall thermal conductivity has an essential influence on the flame stability in micro-channels. ZHOU et al [18] investigated catalytic combustion of H2–air mixture in micro-combustors made of different materials. They found that the hotspot temperature can be reduced by a larger wall thermal conductivity. RAN et al [19] scrutinized the impacts of heat transfer processes on the catalytic CH4/air combustion in a micro-tube. The results show that the wall thermal conductivity should exceed 0.49 W/(m·K) to maintain stable combustion and conductive walls are more appropriate to manufacture micro- combustors. CHEN et al [20] examined the influence of heat and mass transfer on combustion stability in catalytic micro-combustors and they found that transport properties are usually key factors determining combustion stability. KANG et al [21] experimentally explored the flame stability limits of a planar combustor made of pyrolytic graphite, whose axial thermal conductivity is 100 times that in the normal direction. It was shown that, compared to isotropic stainless steel, pyrolytic graphite had a larger velocity limit owing to more heat recirculation and less heat loss. FAN et al [22] proposed a micro- combustor with double-layered walls, namely, the inner and outer layers are made of materials with high (SiC) and low (quartz) thermal conductivities, respectively. It is demonstrated that this structure can increase the combustion efficiency of lean H2/air mixture by enhancing heat recirculation and reducing heat loss simultaneously.
As mentioned above, heat recirculation in straight micro-channels can be enhanced by using materials with high thermal conductivity. In addition, heat recirculation can also be realized by heat exchange between burnt hot gas and incoming fresh mixture through separating walls. LI et al [23] designed a heat recirculation cup, which significantly expands the stable combustion range of n-heptane in a micro-combustor. TAYWADE et al [24] also notably enhanced the flame stability with a heat recirculation cup for a micro-combustor with multiple steps. TANG et al [25] designed a micro-combustor with heat recirculation channels. Their experimental investigation shows that the blowout limit of this combustor is three times that of the straight-channel combustor. WAN et al [26] studied the effects of solid materials (stainless steel, SiC and copper) on the flame stability of a micro-combustor with a flame holder and preheating channels. The results showed that the copper combustor can achieve the largest blowout limit due to its best heat recirculation effect. SITZKI et al [27] applied the classic heat- recirculating structure, i.e., Swiss-roll, to improve flame stabilization in micro-combustors. KIM et al [28] experimentally investigated the flame stability and emission characteristics of miniature Swiss-roll combustors. VIJAYAN et al [29] revealed that flame stability in micro Swiss-roll combustors is closely associated with the heat transfer process. ZHONG et al [30] designed micro Swiss-roll combustors with double spiral-shaped channels, which can greatly enhance flame stability in the combustor center. FAN et al [31] extended the flame blowout limit by 10 m/s in a micro Swiss-roll combustor by addition of a bluff body. Very recently, WANG et al [32] designed a meso-scale Swiss-roll combustor for non-premixed combustion. Their experimental study demonstrated that flame can be sustained at very small fuel flow rate and very low equivalence ratio (<0.3). Addition of various porous media in micro-combustors has also been widely adopted [33, 34] as a heat recirculation method to improve flame stability for both premixed [35, 36] and non-premixed combustion [37, 38].
From the above literature survey, it can be known that for straight micro-channels, most of the previous studies were focused on the impact of wall thermal conductivity on flame stability [14-22]. In contrast, the influence of wall thickness was only investigated in limited works [15, 17]. Moreover, in most two-dimensional numerical studies, only half of the micro-channel was adopted as the computational domain and axi-symmetric boundary condition was applied along the central axis [14-17]. This treatment cannot reveal some flame instability such as flame inclination [3]. Motivated by these facts, in the present study, we numerically investigate the combined effects of wall thickness (d=0.2 and 0.4 mm) and material (quartz and SiC) on flame inclination and blowout limit applying a full two-dimensional model.
2 Numerical methods
2.1 Physic model
The schematic of the planar micro-combustor is shown in Figure 1. The channel width is assumed to be infinitely large and the present configuration can thus be treated as a two-dimensional problem. Stoichiometric H2/air mixture (i.e., equivalence ratio φ=1.0) is fed into the micro-combustor from the left inlet. The height (H) and length (L) of the micro-combustors are 1 mm and 10 mm, respectively. Two values of the wall thickness (i.e., δ=0.2 mm, 0.4 mm) are chosen to explore its effect on flame stability.
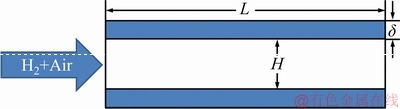
Figure 1 Schematic of planar micro-combustor
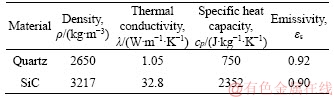
To scrutinize the effect of wall materials on the flame stability, quartz and SiC are selected for the combustor walls, as shown in Table 1. The first reason is because these two materials can endure a very high temperature (>1700 K). The other reason is that the thermal conductivity of SiC (32.8 W/(m·K)) is around 30 times that of quartz glass (1.05 W/(m·K)), while they have almost identical surface emissivity (0.9) [30]. This facilitates the investigation on the impact of structural heat conduction on flame stability.
Table 1 Thermophysical properties of quartz and SiC at 300 K
2.2 Mathematical model
First of all, we evaluate the value of the Knudsen number, Kn=Lg/Lc, where Lc is the characteristic scale of the channel (1 mm) and Lg is the mean free path of gaseous mixture. Our calculation shows that Kn is far below the criterion (i.e., 10-3 [39]). Hence, the reacting flow can be treated as continuum and the Navier-Stokes equations are still applicable herein. Moreover, the laminar model is employed in the numerical simulation since the maximum Reynolds number is around 1700. The governing equations for the reacting flow are presented as follows.
Continuity:
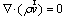 (1)
(1)
Momentum:
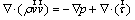 (2)
(2)
Energy:
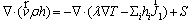 (3)
(3)
Species:
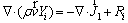 (4)
(4)
where 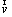 , p, ρ,
, p, ρ, 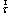 , λ, h and T denote the velocity, pressure, density, stress tensor, thermal conductivity, specific enthalpy and temperature of the gaseous mixture, respectively; S is the chemical reaction heat; Yi, hi and Ri represent the mass fraction, specific enthalpy, and generation or consumption rate of the i th species, respectively;
, λ, h and T denote the velocity, pressure, density, stress tensor, thermal conductivity, specific enthalpy and temperature of the gaseous mixture, respectively; S is the chemical reaction heat; Yi, hi and Ri represent the mass fraction, specific enthalpy, and generation or consumption rate of the i th species, respectively;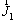 is the diffusion flux which is computed by
is the diffusion flux which is computed by
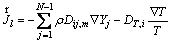 (5)
(5)
where Dij,m and DT,j are the molecular diffusion coefficient and thermal diffusion coefficient, respectively.
Heat conduction in the combustor walls is also considered, which can be computed through:
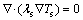 (6)
(6)
where λs and Ts are the thermal conductivity and temperature of the solid walls, respectively.
2.3 Boundary conditions
The heat loss rate from the exterior wall is calculated through Eq. (7):
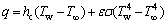 (7)
(7)
where hc is the convection heat transfer coefficient (20 W·m-2·K-1) [40]; Tw and T∞ are the outer wall temperature and the ambient temperature (300 K) respectively; ε is the surface emissivity (refer to Table 1); σ is the Stephan–Boltzmann constant (5.67×10-8 W·m-2·K-4).
At the combustor entrance, a uniform velocity distribution of atmospheric H2/air mixture at 300 K is specified. A pressure boundary condition (101.325 kPa) is imposed on the combustor exit. The inner wall surfaces are regarded as no-slipping boundaries; however, surface to surface radiation between the inner surfaces is considered by using the discrete ordinates (DO) model [31]. The gas-phase radiation was pretested with the WSGGM model and the results showed that it has a negligible effect.
2.4 Numerical schemes
The reaction mechanism reported by LI et al [41] is applied to modeling the combustion of H2/air mixtures. It consists of 13 species and 19 reversible elementary reactions. Detailed transport properties of the gaseous mixture are computed with the CHEMKIN database [42]. The laminar finite-rate model was adopted as the combustion model because the laminar flow model was used. The computation domain is meshed with regular square grids by the pre-processing package. The second- order upwind scheme is adopted to discretize the set of differential equations. Meanwhile, the “SIMPLE” algorithm is applied to coupling the pressure and velocity. The popular CFD software FLUENT 15.0 [43] is employed to solve the conservation equations. Iteration convergence is judged based on a criterion that the residuals of all variables drop below 1.0×10-6.
2.5 Model validation
First, the computational result is verified to be independent on the grid number by comparing the centerline temperature distributions in the quartz combustor with d=0.2 mm for different grid resolutions under vin=6 m/s, as illustrated in Figure 2. It is demonstrated that the numerical results obtained by 35000 and 62000 grids are almost identical. Thereby, the grid system with a total grid number of 35000 (Dx=Dy=0.02 mm) is used in the final computation.
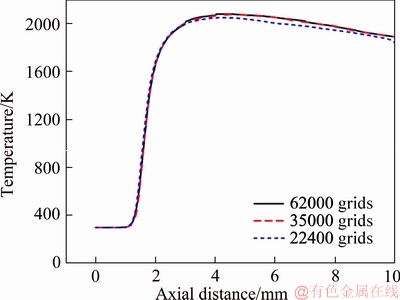
Figure 2 Centerline temperature profiles in quartz combustor with d=0.2 mm for different grid resolutions under vin=6 m/s
In addition, the accuracy of the numerical model is validated by comparing the computed centerline temperature profile of the outer wall with the experimental data by TANG et al [44], as shown in Figure 3. The height, width and length of the channel are 3 mm, 8 mm and 18 mm, respectively. The flow rate of H2/air mixture is 200 mL/min, which falls in the laminar flow regime since Re=38. The maximum relative error between the predicted and measured data is 6.38%, which confirms the reasonable accuracy of the numerical results in this paper.
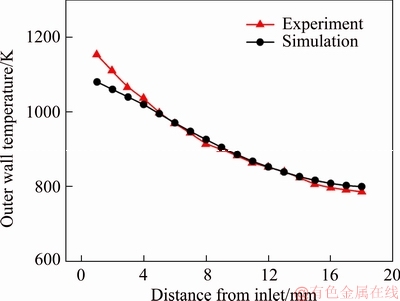
Figure 3 Validation of present numerical model with experimental data by TANG et al [44]
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Flame inclination and blowout limits
First, we present the temperature fields of the micro-combustors made of quartz and SiC with d=0.2 mm in Figure 4. It can be seen from Figure 4 that when the inlet velocity is very low (e.g., vin=1 m/s), the flames are planar ones in both combustors. With the increase of inlet velocity (e.g., vin=6 m/s), the flame front turns into a V-shaped structure due to the stretch effect. At a certain velocity, flame inclination occurs in both combustors, which has been reported by PIZZA et al [3] and WAN et al [11]. The corresponding inlet velocity is termed as “inclination limit”. Figure 4 shows that the direction of flame inclination is stochastic. Meanwhile, it is noted that flame inclination in the SiC combustor occurs later than that in the quartz combustor. As the inlet velocity is raised to a sufficient large value, the flame will be eventually blown out and this critical inlet velocity is called “blowout limit”.
The temperature fields of the micro- combustors made of quartz and SiC with d=0.4 mm are depicted in Figure 5. It is demonstrated that flame inclination still occurs in the quartz combustor at a certain velocity that is larger than that for d=0.2 mm. However, it is interesting to see that for the SiC combustor with a thicker wall,flame inclination does not appear any longer. Moreover, flame blowout happens at larger inlet velocities in the combustors with d=0.4 mm compared to the counterparts of d=0.2 mm.
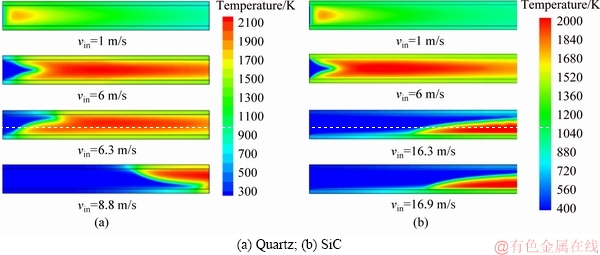
Figure 4 Temperature field of micro-combustors made of quartz and SiC at d=0.2 mm:
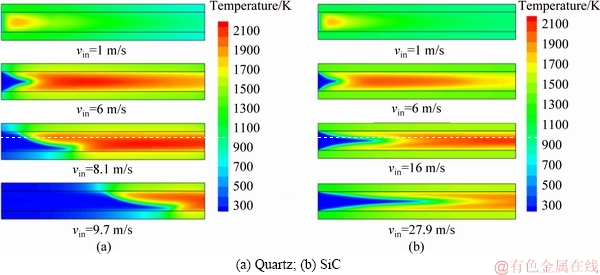
Figure 5 Temperature field of micro-combustors made of quartz and SiC at d=0.4 mm:
Figure 6 shows the specific values of flame inclination limit and blowout limit for quartz combustor and SiC combustor with a wall thickness of d=0.2 mm and 0.4 mm. It is clearly seen that for each combustor, both the inclination limit and blowout limit increase as the wall thickness is increased from 0.2 mm to 0.4 mm (Note: when d=0.4 mm, the flame inclination does not occur in the SiC combustor). Moreover, under the identical wall thickness, the inclination limit and blowout limit of SiC combustor are obviously larger than the counterparts of quartz combustor. Furthermore, the difference between the two combustors made of different materials grows even greater when the wall thickness is d=0.4 mm. To be specific, that blowout limit of SiC combustor is 27.9 m/s while that of quartz combustor is only 9.7 m/s, namely, the former is about 2.9 times that of the latter. However, the difference between the SiC combustor and quartz combustor is only about 1.9 times when d=0.2 mm. In summary, increasing the wall thickness is more effective to enhance the flame stability in the micro-combustor made of materials with a high thermal conductivity.
3.2 Discussion about heat recirculation effect and heat loss effect
It is well known that the flame stability in micro-channels depends on the competition between the heat recirculation effect and heat loss effect because the former is a positive effect while the latter is a negative one. Meanwhile, both the heat recirculation effect and heat loss effect are closely associated with two-dimensional heat conduction in the solid walls. More specifically, the heat recirculation effect has a closer relationship with the axial heat conduction, while the heat loss effect relies largely on the heat conduction in the normal direction. From the basic knowledge of heat transfer, it is known that the conductive thermal resistance in the normal direction is proportional to the wall thickness whereas the axial counterpart is inversely proportional to the wall thickness. At the same time, both of normal and axial conductive thermal resistances have an inverse proportional relationship with the thermal conductivity of solid walls. In the following discussion, the case of vin=3 m/s is chosen for comparison.
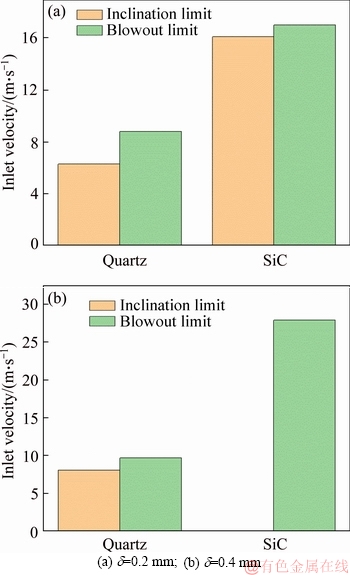
Figure 6 Flame inclination limit and blowout limit of micro-combustors made of quartz and SiC with d=0.2 mm and 0.4 mm (Note: flame inclination in SiC combustor with d=0.4 mm does not occur):
Figure 7 shows the temperature profiles of the outer and innerwalls for quartz combustors with d=0.2 mm and 0.4 mm. It is seen that the outer wall temperature level of the micro-combustor with d=0.4 mm is lower than that of d=0.2 mm, except for the very upstream segment. On the contrary, the innerwall temperature level of the micro-combustor with d=0.4 mm is a little higher than that of d=0.2 mm. Meanwhile, the peak location of d=0.4 mm shifts slightly downstream compared with d=0.2 mm. Furthermore, the temperature distribution of the thicker wall is more uniform than the thinner wall, which was also reported by PENG et al [45]. These features reflect the two-dimensional heat conduction in the combustor walls.
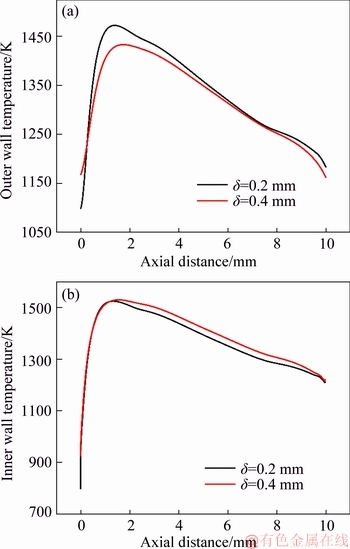
Figure 7 Outer (a) and inner (b) wall temperature profiles at vin=3 m/s for quartz combustors with d=0.2 mm and 0.4 mm
Figure 8 illustrates the outer and inner wall temperature profiles of quartz and SiC combustors with d=0.4 mm. It can be seen that there is an obvious peak in the wall temperature distribution of quartz micro-combustor. In contrast, the wall temperature distribution of SiC combustor is fairly uniform. As a result, except for the middle segment, the temperature levels of the upstream and downstream walls of SiC combustor are higher than the counterparts of quartz combustor.
Figure 9 shows the heat recirculation ratio and heat loss ratio of the quartz combustors with d=0.2 mm and 0.4 mm. In the present study, the heat loss ratio is defined as the ratio of the heat loss rate from external walls to the input energy rate. Here, the heat loss rate can be obtained by an integral of Eq. (7) on the external walls, while the input energy rate is the enthalpy of incoming fuel per unit time.
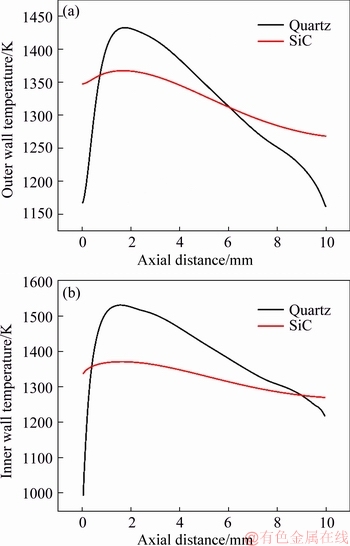
Figure 8 Outer (a) and inner (b) wall temperature profiles at vin=3 m/s for quartz and SiC combustors with d=0.4 mm
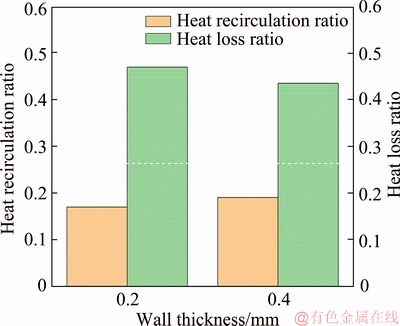
Figure 9 Heat recirculation ratio and heat loss ratio of quartz micro-combustors with d=0.2 mm and 0.4 mm at vin=3 m/s
Meanwhile, the heat recirculation ratio is defined as the ratio of the heat absorbed by the fresh mixture from upstream inner walls to the input energy rate. This figure demonstrates that as the wall thickness is increased from d=0.2 mm to 0.4 mm, the heat recirculation ratio is intensified by 13% while the heat loss ratio is weakened by 6.9%. This is because the conductive thermal resistance is reduced in the axial direction while increased in the normal direction. As a result, the flame stability can be enhanced by a relatively thicker wall. VEERARAGAVAN [17] also indicated that thicker walls can increase the ability of flame to tolerate higher heat losses without extinction.
Figure 10 depicts the heat recirculation ratio and heat loss ratio of the micro-combustors made of quartz and SiC with the same wall thickness of d=0.4 mm. It is noted that compared to the quartz combustor, the heat recirculation ratio of SiC combustor is intensified by 23% while the heat loss ratio is weakened by 3.2%. The former is because the conductive thermal resistance is reduced in the axial direction. Meanwhile, the latter is due to the reduction of conductive thermal resistance in the normal direction, which leads to a more uniform outer wall temperature distribution (Figure 8). Consequently, the flame stability in SiC combustor can be improved.
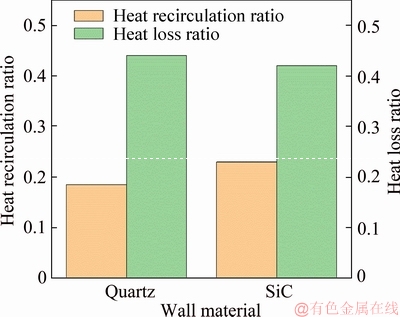
Figure 10 Heat recirculation ratio and heat loss ratio of quartz and SiC micro-combustors with d=0.4 mm at vin= 3 m/s
Figure 11 shows the reaction rate profiles of the first elementary reaction (H+O2=O+OH) along the inner wall of the four micro-combustors. The inlet velocity is 3 m/s. It can be seen that when the solid wall is identical, the reaction rate peak is higher for the micro-combustor with d=0.4 mm. Meanwhile, for the same wall thickness, the reaction rate peak is higher for the SiC micro- combustor as compared with the quartz combustor. Furthermore, the peak value of the reaction rate in the SiC micro-combustor with d=0.4 mm is far greater than the other three cases. These indicate that the elementary reaction is more intense in the micro-combustor with a thicker wall or/and with a high thermal conductivity, which is a combined effect of enhanced heat recirculation and weakened heat loss.
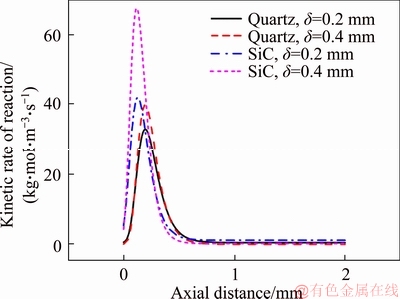
Figure 11 Reaction rate profile of R1 (H+O2=O+OH) along inner wall of four micro-combustors at vin=3 m/s
4 Conclusions
Flame stability of H2/air mixture in micro-combustors with different wall thicknesses (d=0.2 mm and 0.4 mm) and materials (quartz and SiC) was numerically compared. The results show that when d=0.2 mm, flame inclination will occur at a certain inlet velocity in combustors made of quartz and SiC, but it happens later in the SiC combustor. When the wall thickness is increased to d=0.4 mm, flame inclination still occurs in the quartz combustor at a larger inlet velocity compared to combustor with d=0.2 mm. However, the flame inclination in SiC combustor with d=0.4 mm does not happen. Quantitative analysis demonstrates that a thicker wall can enhance heat recirculation and reduce heat loss simultaneously. In addition, SiC combustor has a bigger heat recirculation ratio and a smaller heat loss ratio. In summary, the micro-combustor which has a relatively thicker wall made of material with a high thermal conductivity can achieve a larger flame stability limit.
References
[1] JU Y, MARUTA K. Microscale combustion: Technology development and fundamental research [J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2011, 37: 669-715.
[2] TILLAND A, PORTHA J, FALK L, TARDIVAT C. Impact of reducing the channel diameter on heterogeneous gas reactions in an isothermal monolith [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processes: Process Intensification, 2015, 95: 317-326.
[3] PIZZA G, FROUZAKIS C E, MANTZARAS J, TOMBOULIDES A G, BOULOUCHOS K. Dynamics of premixed hydrogen/air flames in microchannels [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2008, 152: 433-450.
[4] LI L H, YUAN Z L, XIANG Y, FAN A W. Numerical investigation on mixing performance and diffusion combustion characteristics of H2 and air in planar micro-combustor [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43: 12491-12498.
[5] MARUTA K, KATAOKA T, KIM N I, MINAEV S, FURSENKO R. Characteristics of combustion in a narrow channel with a temperature gradient [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2005, 30: 2429-2436.
[6] XIANG Y, YUAN Z L, WANG S X, FAN A W. Effects of flow rate and fuel/air ratio on propagation behaviors of diffusion H2/air flames in a micro combustor [J]. Energy, 2019, 179: 315-322.
[7] YANG W M, CHOU S K, SHU C, XUE H, LI Z W, LI D T, PAN J F. Microscale combustion research for application to micro thermophotovoltaic systems [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2003, 44: 2625-2634.
[8] E J Q, HUANG H J, ZHAO X H. Numerical investigations on effects of bluff body in flat plate micro thermophotovoltaic combustor with sudden expansion [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23: 975-982.
[9] WAN J L, FAN A W, YAO H, LIU W. Experimental investigation and numerical analysis on the blow-off limits of premixed CH4/air flames in a mesoscale bluff-body combustor [J]. Energy, 2016, 113: 193-203.
[10] LI Y, CHEN G, HSU H, CHAO Y. Enhancement of methane combustion in microchannels: Effects of catalyst segmentation and cavities [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 160: 715-722.
[11] WAN J L, FAN A W, LIU Y, YAO H, LIU W, GOU X L, ZHAO D Q. Experimental investigation and numerical analysis on flame stabilizationof CH4/air mixture in a mesoscale channel with wall cavities [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2015, 162: 1035-1045.
[12] ZHANG P, RAN J, LI L, DU X, QI W, NIU J, YANG L. Effects of convex cavity structure, position and number on conversion of methane catalytic combustion and extinction limit in a micro-channel: A numerical study [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processes: Process Intensification, 2017, 117: 58-69.
[13] YANG W, LI L H, FAN A W, YAO H. Effect of oxygen enrichment on combustion efficiency of lean H2/N2/O2 flames in a micro cavity-combustor [J].Chemical Engineering and Processes: Process Intensification, 2018, 127: 50-57.
[14] LEACH T T, CADOU C P. The role of structural heat exchange and heat loss in the design of efficient silicon micro-combustors [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2005, 30: 2437-2444.
[15] NORTORN D G, VLACHOS D G. Combustion characteristics and flame stability at the microscale: A CFD study of premixed methane/air mixtures [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2003, 58: 4871-4882.
[16] NORTORN D G, VLACHOS D G. A CFD study of propane/air microflame stability [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2004, 138: 97-107.
[17] VEERARAGAVAN A. On flame propagation in narrow channels with enhanced wall thermal conduction [J]. Energy, 2015, 93: 631-640.
[18] ZHOU J H, WANG Y, YANG W J, LIU J Z, WANG Z H, CEN K F. Combustion of hydrogen–air in catalytic micro-combustors made of different material [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34: 3535-3545.
[19] RAN J Y, YANG L, ZHANG L. The wall heat transfer phenomenon of premixed CH4/air catalytic combustion in a Pt coated micro tube [J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2014, 136: 21201-21209.
[20] CHEN J J, YAN L F, SONG W Y, XU D G. Effect of heat and mass transfer on the combustion stability in catalytic micro-combustors [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 131: 750-765.
[21] KANG X, VEERARAGAVAN A. Experimental investigation of flame stability limits of a mesoscale combustor with thermally orthotropic walls [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 85: 234-242.
[22] FAN A W, LI L H, YANG W, YUAN Z L. Comparison of combustion efficiency between micro combustors with single- and double-layered walls: A numerical study [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processes: Process Intensification, 2019, 137: 39-47.
[23] LI J W, HUANG J H, CHEN X J, ZHAO D, SHI B L, WEI Z J, WANG N F. Effects of heat recirculation on combustion characteristics of n-heptane in micro combustors [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 109: 697-708.
[24] TAYWADE U W, DESHPANDE A A, KUMAR S. Thermal performance of a micro combustor with heat recirculation [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2013, 109: 179-188.
[25] TANG A K, CAI T, DENG J, XU Y M, PAN J F. Experimental investigation on combustion characteristics of premixed propane/air in a micro-planar heat recirculation combustor [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 152: 65-71.
[26] WAN J L, FAN A W. Effect of solid material on the blow-off limit of CH4/air flames in a micro combustor with a plate flame holder and preheating channels [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2015, 101: 552-560.
[27] SITZKI L, BORER K, SCHUSTER E, RONNEY P D. Combustion in microscale heat-recirculating burners [C]// The Third Asia-Pacific Conference on Combustion. Seoul, Korea: June 24-27, 2001.
[28] KIM N I, KATO S, KATAOKA T, YOKOMORI T, MARUYAMA S, FUJIMORI T, MARUTA K. Flame stabilization and emission of small Swiss-roll combustors as heaters [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2005, 141: 229-240.
[29] VIJAYAN V, GUPTA A K. Combustion and heat transfer at meso-scale with thermal recuperation [J]. Applied Energy, 2010, 87: 2628-2639.
[30] ZHONG B J, WANG J H. Experimental study on premixed CH4/air mixture combustion in micro Swiss-roll combustors [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2010, 157: 2222-2229.
[31] FAN A W, ZHANG H, WAN J L. Numerical investigation on flame blow-off limit of a novel microscale Swiss-roll combustor with a bluff-body [J]. Energy, 2017, 123: 252-259.
[32] WANG S X, YUAN Z L, FAN A W. Experimental investigation on non-premixed CH4/air combustion in a novel miniature Swiss-roll combustor [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processes: Process Intensification, 2019, 139: 44-50.
[33] CHOU S K, YANG W M, LI J, LI Z W. Porous media combustion for micro thermophotovoltaic system applications [J]. Applied Energy, 2010, 87: 2862-2867.
[34] LIU Y, NING D G, FAN A W, YAO H. Experimental and numerical investigations on flame stability of methane/air mixtures in mesoscale combustors filled with fibrous porous media [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2016, 123: 402-409.
[35] XU K, LIU M, ZHAO P. Stability of lean combustion in mini-scale porous media combustor with heat recuperation [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processes: Process Intensification, 2011, 50: 608-613.
[36] LI J, WANG Y T, CHEN J X, SHI J R, LIU X L. Experimental study on standing wave regimes of premixed H2-air combustion in planar micro-combustors partially filled with porous medium [J]. Fuel, 2016, 167: 98-105.
[37] PENG Q, E J Q, CHEN J, ZUO W, ZHAO X, ZHANG Z. Investigations on effects of wall thickness and porous media on the thermal performance of a non-premixed hydrogen fueled cylindrical micro combustor [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 155: 276-286.
[38] NING D G, LIU Y, XIANG Y, FAN A W. Experimental investigation on non-premixed methane/air combustion in Y-shaped mesoscale combustors with/without fibrous porous media [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 138: 22-29.
[39] BESKOK A, KARNIADAKIS G E. A model for flows in channels, pipes, and ducts at micro- and nano-scales [J]. Microscale Thermal Engineering,1999, 3: 43-77.
[40] HOLMAN J P. Heat transfer [M]. 9th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002.
[41] LI J, ZHAO Z W, KAZAKOV A, DRYER F L. An updated comprehensive kinetic model of hydrogen combustion [J]. International Journal of Chemical Kinetics, 2004, 36: 1-10.
[42] CHEMKIN-PRO release 15101 [M]. San Diego, CA: Reaction Design Inc, 2010.
[43] ANSYS FLUENT release 15.0 [M]. Canonsburg, PA: ANSYS Inc., 2013.
[44] TANG A K, XU Y, SHAN C, PAN J F, LIU Y. A comparative study on combustion characteristics of methane, propane and hydrogen fuels in a micro-combustor [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40: 16587-16596.
[45] PENG Q G, E J Q, YANG W M, XU H P, CHEN J W, ZHANG F, MENG T, QIU R Z. Experimental and numerical investigation of a micro-thermophotovoltaic system with different backward-facing steps and wall thicknesses [J]. Energy, 2019, 173: 540-547.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
中文导读
壁面厚度和材料对平板型微燃烧器中火焰稳定性的影响
摘要:微燃烧器中的火焰由于外壁面的散热损失较大而容易失去稳定性,通过上游壁面的热循环则能使火焰稳定性得到增强。这两方面都依赖于燃烧器的壁面传热过程,它和壁面厚度及导热系数密切相关。本文选择两个壁面厚度(d=0.2和0.4 mm)和两种壁面材料(石英和碳化硅),通过数值模拟研究了这两个参数对平板型微燃烧器中氢气/空气火焰稳定性的影响。结果显示:当壁厚d=0.2 mm时,两种材料的微燃烧器内火焰都发生了倾斜现象,但是碳化硅燃烧器出现得更晚。当壁厚为d=0.4 mm时,石英燃烧器在更大速度时(相对于d=0.2 mm)仍然发生了火焰倾斜现象,但是碳化硅燃烧器中不再出现。分析表明:壁厚增大能够强化热循环,同时减少散热损失;此外,相对于石英燃烧器来说,碳化硅燃烧器的热循环比例更大,散失损失比例更小。总之,当微燃烧器的壁厚和导热系数较大时,它能获得更大的稳燃极限。
关键词:微燃烧器;火焰稳定性;火焰倾斜;吹熄极限;热循环;热损失
Foundation item: Project(51576084) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2019-04-20; Accepted date: 2019-06-11
Corresponding author: FAN Ai-wu, PhD, Professor; Fax: +86-27-87540724; Tel: +86-27-87542618; E-mail: faw@hust.edu.cn; ORCID: 0000-0003-1798-2154

