文章编号: 1004-0609(2006)02-0351-06
基于GA-BP的NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷阳极优化设计
李 劼, 刘代飞, 秦庆伟
(中南大学 冶金科学与工程学院, 长沙 410083)
摘 要: 采用BP神经网络对铝电解NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷惰性阳极的电解腐蚀过程进行了系统辨识。 建立了以Al2O3质量浓度、 电解温度、 分子比、 面积比和电流密度为输入, 腐蚀率为输出的网络模型。 在材料的设计中, 采用了GA-BP优化方法, BP网络参与GA迭代计算时对个体的评价。 应用结果表明, NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷惰性阳极的电解腐蚀率预测结果与实测值吻合; 优化设计的结果与实验值很接近。
关键词: 铝电解; 惰性阳极; 腐蚀; 人工神经网络; 遗传算法
中图分类号: TF821 文献标识码: A
Optimization designs of NiFe2O4 cermet inert
anodes based on GA-BP hybrid neural net work
LI Jie, LIU Dai-fei, QIN Qing-wei
(School of Metallurgical Science and Engineering,
Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The corrosion processes of 5%Ni-NiFe2O4 inert anodes were recognized by back propagation neural net works and the prediction model was presented. The structures of neural net work include four input nodes, alumina concentration, bath temperature, cryolitic ratio, and area ratio of cathode to anode, current density, and one output node, corrosion rate. The hybrid neural network, genetic algorithms and back propagation neural networks, were applied when optimizing the design of the trial parameters. Some trial strategies were deduced by the hybrid model. The application and experimental results shows that, the neural prediction values of the corrosion rate of NiFe2O4 inert anodes fit in with the trial values, and the hybrid neural network model has guidance signification for material design.
Key words: aluminum electrolysis; inert anode; corrosion; artificial neural network; genetic algorithms
在现代铝电解工业(Hall-Héroult法)中, 电极的行为直接关系到生产的高产、 优质、 节能和原材料的利用, 因而历来受到高度重视, 并进行了大量的研究工作[1-3]。 其中惰性阳极的研究是国际铝业界和材料界的一项关注重点和研究热点[4, 5]。 惰性阳极是不消耗性阳极, 生产中不需要周期性地更换阳极因而保证了生产的稳定, 不会发生阳极效应, 阳极排出的是氧气, 不排放CO2和碳氟化合物, 环境大为改善, 其投资也大为减少。 由于在若干年内铝生产仍将以冰晶石—氧化铝熔盐电解法这种生产方法为主, 因此惰性阳极的研究与应用意义重大。
铝电解生产过程是一个高度复杂的高温、 强腐蚀过程, 其控制对象是一个复杂的多变量控制对象, 具有不确定、 强耦合、 大滞后、 非线性、 状态不完全可测等特性。 对于惰性阳极而言, 其腐蚀率的大小直接影响到原铝质量, 因此, 有必要采用一种 有效的方法建立模型预测腐蚀率与电解参数的关系, 使操作人员能即时、 准确了解惰性阳极的工作状态, 即时调整工作制度, 使惰性阳极始终处于最佳工作状态, 从而提高原铝质量。
人工神经网络(artificial neural networks, ANN)模型具有很强的容错性、 学习性、 自适应性和非线性的映射能力, 特别适于解决因果关系复杂的非确定性推理、 判断、 识别和分类等问题。 由于网络是基于数据驱动的, 它不需要明确对象的过程机理, 并能实现对任意非线性系统的映射, 它的自学习能力还可跟踪对象系统的动态变化。 而遗传算法(genetic algorithms, GA)是一类借鉴生物界的进化规律(适者生存, 优胜劣汰遗传机制)演化而来的随机化搜索方法。 遗传算法使用群体搜索技术, 通过对当前群体施加选择、 交叉、 变异等一系列遗传操作, 从而产生新一代的群体, 并逐步使群体进化到包括或接近最优解的状态。 具有思想简单、 易于实现、 应用效果明显等优点。 本文作者结合人工神经网络、 遗传算法对陶瓷阳极优化设计开展了研究。
1 GA-BP优化方法
1.1 BP神经网络
人工神经网络是用大量简单的处理单元广泛连接组成的复杂网络, 用以模拟人类大脑神经网络结构和行为, 使它具有人脑功能的基本特征, 从而为解决了人工智能研究中的某些局限性开辟了新的途径。 目前在工程上应用比较广泛的是BP(back propagation neural networks, BP)网络。 在BP神经网络模型中, 网络不仅有输入层节点、 输出层节点, 而且有隐层节点。 隐层可以是一层, 也可以是多层。 首先信号由输入层节点传到隐层节点, 经过作用函数后, 再把隐层节点的输出信号传播到输出层节点, 经过处理后给出输出结果。 其输出与输入的关系式为
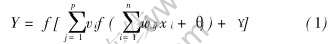
式中 Y为输出变量, xi(i=1, 2, …, n)为输入变量; wij为输入层神经元i与中间层神经元j的连接强度, 即连接权值; vj为中间层神经元j与输出层神经元的连接强度; θj和γ分别为中间层神经元和输出层神经元的阈值; 特性函数f(x)取S型函数[6, 7], 可表示为:

BP算法由正向传播和反向传播组成。 正向传播是输入信号从输入层经隐含层传向输出层, 若输出层得到了期望的输出, 则学习算法结束, 否则, 转向反向传播; 反向传播就是将误差信号(样本输出与网络输出之差)按原连接通路反向计算, 由梯度下降法调整各层神经元的权值和阈值, 使误差信号最小。 评价的目标函数通常采用:

式中 yi为网络计算输出, oi为网络实际输出。
1.2 遗传算法
遗传算法是由美国密执安大学的Holland教授于1975年首先提出来的一种解决复杂问题的有效方法。 它是以达尔文的生物进化论为启发而创建的, 是基于进化中优胜劣汰、 自然选择、 适者生存和物种遗传思想的搜索算法。
设群体由n个串组成, 第i个串的适应度为fi, 则遗传算法表示方法如下:
1) k=0, 随机产生n个串, 构成初始群体。
2) 计算各串的适应度(值)fi, i=1, 2, …, n。
3) 按下列步骤产生新的群体, 直到新群体中串的总数达到n:
① 以概率fi∑fi、 fj/∑fj从群体中选出两个串Si、 Sj;
② 以概率Pc对Si、 Sj进行交换, 得到新的串S′[KG-*4]i、 S′[KG-*4]j;
③ 以概率Pm使S′[KG-*4]i、 S′[KG-*4]j中的各位产生突变。
4) k=k+1返回②。
GA就是对这群串进行基因操作: 再生、 交换和变异, 产生出新的一代串群, 比父代更适应“环境”, 这样不断重复, 直至满足条件。
1.3 优化过程
在GA和BP的混合应用的过程中有两种结合方式。 一是利用遗传算法对神经网络模型进行寻优。 将BP网络拓扑结构参数及学习参数、 预定输入参数作为遗传因子, 经训练后, 再对预报集进行预测, 用预测的平均误差的单调递减函数作为遗传算法的评价函数, 即遗传因子的个体适应值。 通过遗传算子复制、 杂交、 变异不断作用于遗传算法群体的遗传因子, 筛选出优良的遗传因子, 从而获得可靠的神经网络模式[8]。 二是BP网络参与GA迭代计算时对个体的评价。 本文作者采用了这种方式来对材料进行优化设计。
GA-BP求解问题的模式可表示为
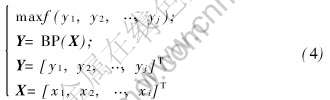
式中 xi为BP网络的输入, yj为BP网络的输出, f为非线性的优化指标综合评价函数。 优化过程是(如图1示): 对建立好的系统模型, 随机产生多组输入向量X(输入向量X的各分量必须在其值域内)。 通过BP网络求得相应的输出向量Y, 再由评价函数f计算出各个输出向量Y的目标适应度。 利用GA算法, 通过适应度值来重新调整输入向量X。 调整方法为遗传操作: 选择、 复制、 交叉、 变异等。 正如生物的进化与遗传一样, 在给定的综合评价函数的指导下(通过适应度值选择个体), 新产生的输入向量X较之旧值具有更好的适应性。 通过遗传计算后, 可得到具有最优或次优的优化目标Y, 相应的X也即为此目标时的优化结果。
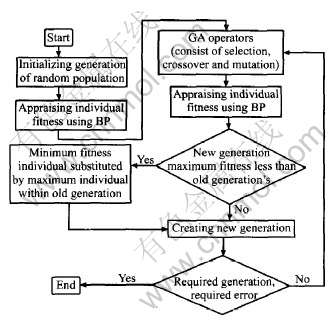
图1 GA-BP优化过程
Fig.1 Procedure of GA-BP optimization
2 惰性阳极腐蚀率预测
2.1 网络输入参数的确定
惰性阳极的耐腐蚀性不仅与本身的材料组成、 结构有关, 而且还取决于它的使用条件(电解参数)。 一旦惰性阳极材料成分确定, 耐腐蚀性仅能通过改进特性或改变操作条件来加以调整。 对NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷阳极的初步电解评估发现, 5%Ni-NiFe2O4阳极容易实现较高的致密度, 因此, 本文作者以这种电极为基础来探讨的腐蚀率与电解参数的关系。
以腐蚀率为铝电解惰性阳极系统中的评价指标, 通过灰关联分析(计算过程参见文献[9]), 得出影响惰性阳极腐蚀率程度的电解参数顺序为: Al2O3质量浓度>电解温度>分子比>阴极面积/阳极浸入面积>电流密度。 其中Al2O3质量浓度和电解温度对惰性阳极的腐蚀率影响最大, 这是由于惰性阳极组元在欠量下料时会分解[10, 11], 发生“灾变腐蚀”, 如下所示(以Fe2O3为例):
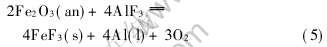
低温电解对降低腐蚀率较有意义, 这因为陶瓷相的腐蚀是一个被激活的过程, 陶瓷与电解质的界面张力增大, 电极组元传质[12-14]减缓, 从而降低腐蚀率。 惰性阳极的正常腐蚀主要由下列反应引起:
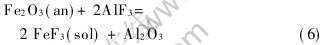
因此, 较低的摩尔比对降低惰性阳极的腐蚀率不利, 应在兼顾电解温度、 摩尔比、 Al2O3质量浓度的基础上确定一个适宜的摩尔比(在研究分子比的影响时, 电流强度按底部1A/cm2计, 电流密度按浸入面积计, 约为0.25A/cm2)。 阴极面积与阳极面积的比例也是较重要的, 它与电极组元在阴极上的还原速率直接相关, 影响着阳极的溶解过程。 一定的电流密度对惰性阳极的工作有利, 在一定程度上阻碍阳极/电解液界面上产生腐蚀反应, 但若电流密度过小, 不足以抑制铝的还原作用, 而电流密度过大, 又会加剧阳极气体冲刷的腐蚀作用。
2.2 基于神经网络的腐蚀率预测模型
上世纪80年代末, Carroll和Dickinson等[15]分别用不同的方法证明了仅含有一个隐层的三层前向神经网络具有以任意精度逼近任意非线性映射的能力。 因此, 腐蚀率预测模型的神经网络模拟模型采用三层前向神经网络。 输入参数为5个, 即氧化铝浓度、 电流密度、 摩尔比、 阴极面积与阳极面积的比例、 电解温度。 输出参数为腐蚀率。
1) 隐含层节点数的确定
神经网络在实际实现时, 关键问题是如何确定隐层节点数目, 用剪除法来确定隐含层节点。 在这种方法中隐含层节点是可变的, 开始时以比实际问题要求的大得多的网络开始训练, 在训练的过程中, 根据一定的判据不断地剪除掉那些对网络性能不起作用或作用不大的连接权和结点, 最终得到适宜的网络结构。
2) 附加动量法
附加动量法使得网络在修正其权值时, 不仅考虑误差梯度上的作用, 而且考虑在误差曲面上变化趋势的影响, 其作用如同一个低通滤波器, 它允许网络上的微小变化特性, 在没有附加动量的作用下, 网络可能陷入局部极小值。 该方法是在反向传播时, 在每一个权值变化的基础上加上一项正比于前次权值变化量的值, 并根据反向传播算法来产生新的权值变化, 其公式为
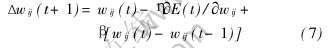
式中 0〈β〈1为动量因子。
3) 自适应调整学习速率
在训练网络过程中, 为了加快收敛, 采用自适应调整学习速率方法。 调节学习速率的准则是: 当新误差超过旧误差一定的倍数时, 学习速率将减少, 否则其学习速率保持不变。 当新的误差小于旧误差时, 学习速率将增加。 该方法可以保证网络总是以最大的可接受的学习速率进行训练。 自适应学习速率调整公式如式(8)所示, 其中SSE为网络输出误差和[16]。

4) 学习效果与预测结果
在训练时发现, 当隐含层节点数为19, 网络结构为5-19-1时, 经10万次迭代后可使系统误差小于10-5 , 部分学习的结果见表1, 预测结果见表2。
从以上结果可看出: 人工神经网络能很好的预测惰性阳极腐蚀率, 并且具有较高的预测精度。
表1 学习结果
Table 1 Learning results
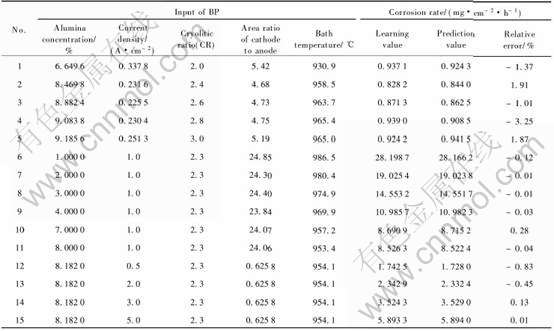
表2 腐蚀率预测结果
Table 2 Predictive results of corrosion rate
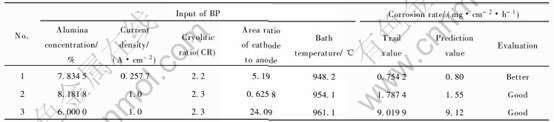
表 3 GA-BP优化设计结果
Table 3 Optimization results of GA-BP hybrid model
3 腐蚀率参数优化
通过实验样本数据对神经网络进行学习训练后, 神经网络对“NiFe2O4阳极-电解参数”体系有了一定的认识。 现在便可将之用于NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷阳极腐蚀率的优化设计了, 即寻求氧化铝浓度、 电流密度、 摩尔比、 阴极面积、 阳极面积的比例、 电解温度这5个适当的参数值, 使得惰性阳极腐蚀率尽可能的小。
优化计算初始条件: Al2O3浓度: 1.0%~8.3%; 电流密度: 0.2~6.0A/cm2; 摩尔比(CR): 2.0~3.0; 阴极面积/阳极面积的比例: 0.5~25.0; 电解温度: 920.0~990.0℃。 GA-BP优化可得到多组参选解, 表3所列为部分结果数据。
从以上结果看出: 用GA-BP优化可以找到使惰性阳极腐蚀率尽可能的小时的电解参数, 并且优化结果和实际的实验结果相接近。
4 结论
通过对5%Ni-NiFe2O4惰性阳极腐蚀体系的研究, 运用神经网络来识别和构建了模型。 以电解参数作为输入指标, 建立了惰性阳极的腐蚀率的预测体系, 为解决不同电解参数下的腐蚀率预测提供了一条新途径, 具有较高的预测精度。 在材料的开发设计时采用的GA-BP的优化方法可以得出合适的结果, 优化与实验结果很接近。 优化求解得出的多组参选解对材料设计具有前瞻性的指导。 在优化设计时还要注意以下几点: 1) 为了提高神经网络的预报精度, 训练样本应尽可能的大; 2) 为了提高GA-BP优化设计的可靠性, 前期实验参数数值点的组合应采用正交设计。
REFERENCES
[1]刘业翔. 铝电解惰性阳极与可湿润性阴极的研究与开发进展[J]. 轻金属, 2001(5): 26-29.
LIU Ye-xiang. Progress of research and development of inert anode and cathodes for aluminum electrolysis[J]. Light Metal, 2001(5): 26-29.
[2]Adolf K, Jomar T, Trygve E. An impedance study of the kinetics and mechanism of the anodic reaction on graphite anodes in saturated cryolite-alumina melts[J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1996, 143(6): 1840-1847.
[3]Thonstad J, Fellner P, Haarberg G M, et al. Aluminium Electrolysis: Fundamentals of the Hall-Héroult Process(3rd Ed)[M]. GmbH Aluminium-Verlag Marketing & Kommunikation, 2001, 145-215.
[4]Pawlek R P. New materials for cells of the primary aluminium industry[J]. Aluminium, 1997, 73(1-2): 40-44.
[5]吕子剑. 对于铝电解惰性阳极的选材与研究方向的思考[J]. 轻金属, 2003(10): 3-5.
LU Zi-jian. Material selection and research trend of inert anode for aluminum reduction[J]. Light Metal, 2003(10): 3-5.
[6]蒋宗礼. 人工神经网络导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2001. 40-54.
JIANG Zong-li. Introduction to Artificial Neural Network[M]. Beijing: High Education Press, 2001. 40-54.
[7]阎平凡, 张长水. 人工神经网络与模拟进化计算[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2000. 17-26.
YAN Ping-fan, ZHANG Chang-shui. Artificial Neural Network and Simulated Evolutionary Computation[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2000. 17-26.
[8]周祥, 何小荣, 陈丙珍. 基于最优变异因子的遗传算法在ANN训练中的应用[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 42(5): 619-621.
ZHOU Xiang, HE Xiao-rong, CHEN Bing-zhen. Best mutation coefficient genetic algorithm for ANN training[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Sci & Tech), 2002, 42(5): 619-621.
[9]赖延清, 陈湘涛, 秦庆伟, 等. NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷阳极腐蚀因素分析及腐蚀率预测[J]. 中南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 35(6): 896-901.
LAI Yan-qing, CHEN Xiang-tao, QIN Qing-wei, et al. On the corrosion behavior of NiFe2O4 cermet inert anodes in cryolite-based melts[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology (Sci &Tech), 2004, 35(6): 896-901.
[10]Thonstad J, Fellner P, Haarberg G M, et al. Aluminium Electrolysis: Fundamentals of Hall-Héroult Process[M]. Düsseldorf: Aluminium - Verlag, 2001. 77-78.
[11]Jomar T, Espen O. Cell operation and metal purity challenges for the use of inert anodes[J]. JOM, 2001, 53(5): 36-38.
[12]Olsen E, Thonstad J. Nickel ferrite as inert anodes in aluminum electrolysis: PartⅠ Materials fabrication and preliminary testing[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 29(3): 293-299.
[13]Olsen E, Thonstad J. Nickel ferrite as inert anodes in aluminum electrolysis: PartⅡ Material performance and long-term testing[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 29(3): 301-311.
[14]Keller R, Rolseth S, Thonstad J. Mass transport considerations for the development of oxygen—evolving anodes in aluminum electrolysis[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1997, 42(12): 1809-1817.
[15]Carroll S M, Dickinson B W. Construction of neural nets using the radon transform[A]. Proceedings of Neural Networks, 1989[C]. IJCNN., 1989, 1: 607- 611.
[16]张秀玲.神经网络自适应控制的研究进展及展望[J]. 工业仪表与自动化装置, 2002(1): 10-14.
ZHANG Xiu-ling. The advancement of vista of a neural network adaptive control[J]. Industrial Instrumentation & Automation, 2002(1): 10-14.
(编辑何学锋)
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(E041803); 国家重点基础研究发展规划资助项目(2005CB623703); 湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(03JJY308)
收稿日期: 2005-06-11; 修订日期: 2005-09-09
作者简介: 李 劼(1963-), 男, 教授, 博士
通讯作者: 刘代飞; 电话: 0731-8830474; E-mail: dfcanfly@tom.com