文章编号:1004-0609(2007)11-1803-05
Ti3Al合金激光焊接接头高温拉伸性能及显微组织
王国庆,赵 玥,吴爱萍,邹贵生,任家烈
(清华大学 机械工程系 教育部先进成形制造重点实验室,北京 100084)
摘 要:研究Ti-24Al-17Nb合金激光焊接接头的室温及高温拉伸性能,并分析接头显微组织和拉伸断口。研究结果表明,室温下焊缝为单一β/B2相柱状晶组织,室温横向拉伸时接头强度与母材强度相当、塑性有所下降、但仍有25%左右的伸长率,断裂大部分发生在母材部位、少部分断裂在焊缝;高温拉伸时断裂均发生在焊缝部位。高温拉伸时,接头组织发生变化,α2相和B2相向O相转变;焊缝β/B2相向O相转变的切变相变,使原来柱状晶晶界应变集中、容易产生微裂纹,使接头高温强度和塑性明显降低,高温拉伸断口呈现沿晶断裂和解理断裂的脆性断裂形式。
关键词:Ti3Al合金;激光焊接;高温拉伸性能;显微组织
中图分类号:TG406 文献标识码:A
Microstructure and high-temperature tensile properties of Ti3Al alloys laser welding joint
WANG Guo-qing, ZHAO Yue, WU Ai-ping, ZOU Gui-sheng, REN Jia-lie
(Key Laboratory for Advanced Materials Processing Technology; Ministry of Education;
Department of Mechanical Engineering; Tsinghua University; Beijing 100084, China)
Abstract: The high-temperature and room-temperature tensile properties of Ti-24Al-17Nb (mole fraction, %) alloys laser welding joints were investigated, and the microstructure and fracture of the joints were studied. The results indicate that the microstructures of the welds are consisted of β/B2 with columnar crystals, the strength of the joints tensioned transversely at room-temperature is almost same as that of the base metal, and the ductility reaches 25%. Cracks occur in the base metal. During the high-temperature tension the cracks occur in the welds. After high-temperature tension, some of the phase α2 and phase B2 of the base metal and HAZ in joints turn to phase O, and phase B2 of the welds turn to phase O. The phase changes bring about strain concentration, and induce fracture. The strength and ductility of the joints at high temperature descend significantly. The fracture types of high-temperature tension joints are intergranular fracture and cleavage fracture.
Key words: Ti3Al alloy; laser welding; high-temperature tensile property; joint microstructure
Ti3Al合金具有质量轻和抗氧化性能强、抗蠕变性能好等优点,特别是其突出的高温性能使其在高技术领域的高温结构材料中有着广阔的应用前景[1?5]。相比钛基合金600 ℃以下的工作温度,Ti3Al合金600~ 750 ℃的工作温度有相当大的优势;与镍及高温合金相比,Ti3Al合金能减轻质量40%左右,从而大大提高发动机单位质量的推动力,而且能改善发动机的其它性能。Ti3Al合金的焊接性能影响着其应用与性能的发挥,虽然国内外已经进行了不少对于Ti3Al合金焊接的研究[6?11]。对于激光焊接Ti3Al合金[12?15],研究主要集中在焊接工艺对焊缝成型与接头室温性能的影响上,而缺少对于含铌量相对较高的α2+O+β三相合金激光焊接接头的高温性能及高温时的组织变化的研究。
本文作者研究了Ti-24Al-17Nb合金激光焊接接头的高温性能,初步分析了接头室温状态组织以及该组织经过高温拉伸试验后的变化情况,并探讨了激光焊接接头高温性能变化的原因,研究结果对改善Ti
3Al合金的激光焊接接头的性能,促进其实际应用有参考价值。
1 实验
Ti3Al合金为400 mm×160 mm×3 mm的板材,长度方向(400 mm)为轧制方向,其成分及基本性能列于表1和表2。Ti3Al合金的制备过程为:真空自耗+真空凝壳熔炼、β/B2相区开坯、α2+B2相区自由锻造、α2+B2+O相区轧制,最后进行980 ℃空冷热处理。母材组织为α2+B2/β+O三相组织。
表1 Ti3Al合金化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of Ti3Al alloy (mass fraction, %)

表2 Ti3Al合金主要力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of Ti3Al

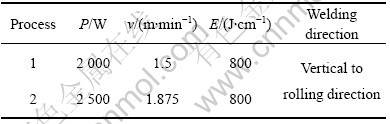
激光焊接是在额定功率为3 000 W的快速轴流CO2激光器系统PRC?3000上进行的,焊接时采用轴向、环向、托尾、背面4个方向的氦气保护。母材经过机械抛光去除表面氧化皮,焊接前先用丙酮后用酒精擦拭表面。焊接采用连续功率输出模式,焦点位于被焊板材表面,焊接具体工艺参数列于表3。
表3 焊接工艺参数
Table 3 Processing parameter of welding
接头室温拉伸和高温拉伸实验分别按照GB/T228—2002和GB/T4338—1995进行。室温实验温度为26 ℃;高温拉伸温度为650 ℃。拉伸试样在焊接试板中的取样方式及试样的尺寸如图1所示。每种条件的拉伸试样为4个。
在光学显微镜下观察接头横截面的组织形貌,试样经过1%~3% HF+4%~6% HNO3+H2O(体积分数)腐蚀液腐蚀。用于进行焊缝XRD分析的试样是沿焊缝中心截取的纵截面试样(分析面完全位于焊缝中),XRD分析设备为D/Max-RB改进型转靶X射线衍射仪,扫描范围为10?~90?。断口分析在扫描电子显微镜(JSM?6301F)上进行。
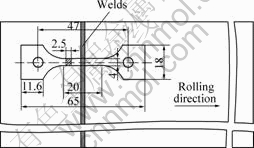
图1 拉伸试样的取样方式及试样尺寸
Fig.1 Taking and size of tensile sample (unit: mm)
2 结果与分析
激光焊接接头的焊缝成型良好,除出现轻微咬边外,焊缝熔透良好,无气孔、夹杂、裂纹等缺陷。
2.1 接头室温与高温拉伸试验结果
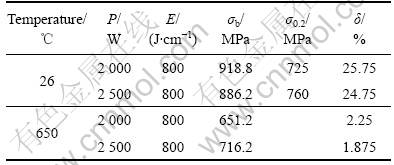
两种焊接规范下,接头的室温和高温拉伸试验结果列于表4。接头室温横向拉伸时,平均拉伸强度与母材的拉伸强度相当,拉伸塑性(伸长率)有所降低,但仍达到25%左右的伸长率,焊缝区域和母材均有一定的塑性变形。接头高温拉伸时,拉伸强度为615~715 MPa,伸长率只有1.88%~2.25%,拉伸时均断在焊缝中,母材和焊缝中均未见明显的塑性变形。
表4 接头室温和高温拉伸实验结果
Table 4 Experimental results of high-temperature tension and room-temperature tension
2.2 接头显微组织分析
光学显微镜下观察的接头横截面形貌及组织如图2和图3所示。焊缝纵截面XRD谱如图4所示。由图2、图3和图4(a)可以看出,激光焊接形成的焊缝基本上是由单一β/B2相组成,焊缝的柱状晶方向性十分明显。
经过650 ℃高温拉伸空冷到室温后接头中母材区域和焊缝及热影响区的显微组织如图5所示。焊缝区域XRD谱如图4(b)所示,母材区域高温拉伸后XRD谱如图6所示。通过比较高温拉伸前后XRD谱可以发现,经过高温拉伸后,焊缝区域为O相;母材中B2相和α2相减少,O相增多,组织以O相为主,只含有少量的B2和α2相。根据组织的变化结果可以推断,室温下由B2相组成的焊缝组织,650 ℃高温拉伸时,发生B2→B2+O的转变,使焊缝组织转变为O相组织。虽然相组成发生了改变,但焊缝的柱状晶形貌并没有发生明显的改变。

图2 接头横截面宏观形貌
Fig.2 Macrostructure of joint (cross-section)
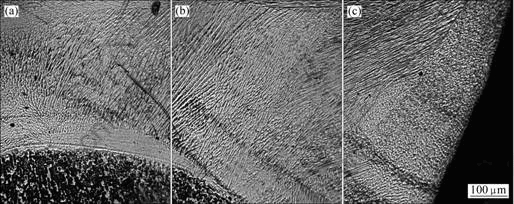
图3 接头横截面形貌及光学显微组织
Fig.3 OM microstructures of joint (cross-section)
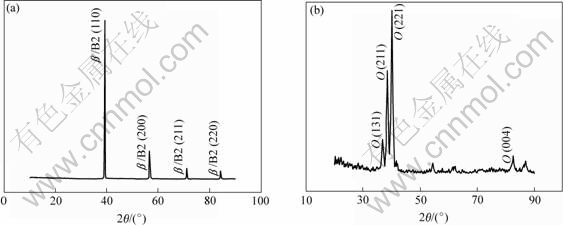
图4 焊缝纵截面XRD谱
Fig.4 XRD patterns of weld (longitudinal section): (a) Before high-temperature tension; (b) After high-temperature tension
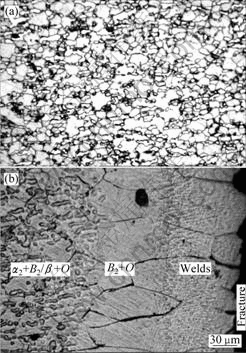
图5 高温拉伸后接头的显微组织
Fig.5 OM microstructures of joints after high-temperature tension: (a) Base metal; (b) Fracture zone of tensile sample (upper side)

图6 母材的XRD谱
Fig.6 XRD patterns of base metal: (a) Before high-temperature tension; (b) After high-temperature tension
2.3 断口观察结果
扫描电子显微镜下观察断裂在焊缝的室温拉伸试样的断口如图7(a)所示。可以看出,断裂区域基本上是由准解理单元组成。高温拉伸断口如图7(b)所示,主要由沿晶和解理单元组成。

图7 拉伸试样断口形貌(断裂在焊缝处)
Fig.7 Morphologies of fractures (cracking at weld zone): (a) Room-temperature tension; (b) High-temperature tension
2.4 结果分析与讨论
组织观察结果表明,激光焊接下的Ti-24Al-17Nb合金接头,其焊缝组织是由不稳定的β/B2单相组织组成,焊缝的柱状晶方向性明显。在激光焊接条件下,焊缝及热影响区的冷却速度高达3 000~9 500 K/s,参考Ti-24.5Al-12.5Nb-1Mo的TTT转变图[1],冷却速度超过10 K/s的高温β相将可能保留到室温。因此激光焊接的Ti-24Al-17Nb焊缝组织,基本上是由不稳定的β/B2组成的。β相是体心立方结构,其塑性比六方结构的α2相好,因此室温横向拉伸时,焊缝也可以产生一定的塑性变形,但由于柱状晶的方向性,其变形不均匀、容易集中。由于接头拉伸时包含焊缝,而焊缝变形量小,所以接头伸长率低于单纯母材拉伸的伸长率。
根据Ti3Al-Nb伪二元相图[1],Ti-24Al-17Nb合金650 ℃时的稳态组织为O相组织,因此焊缝中的室温不稳定的β相将转变成O相。母材是在980 ℃保温并进行空冷后获得的组织,空冷的冷却速度已超过稳态相变的冷却速度,因此室温下母材中也存在β/B2相。650 ℃高温拉伸时,α2相以及β/B2相也向O相转变,因此母材由α2+β/B2+O三相组织转变成以O相为主、加少量α2+β/B2的组织。
β相向O相转变是通过切变形式完成的,由于焊缝组织为柱状晶组织,切变容易在晶界产生应变集中,造成晶界微裂纹产生,高温拉伸时极易沿晶界开裂,其他部位的断裂以解理形式进行,因此断口呈现出沿晶加解理断裂的形貌。β相向O相的切变转变造成的应变集中、拉伸时容易产生沿晶断裂,使焊缝的强度和塑性降低。
3 结论
1) Ti-24Al-17Nb合金激光焊接接头焊缝组织为单相β/B2柱状晶组织。室温横向拉伸时虽然β相有较好的塑性,但由于其柱状晶组织的方向性,使其变形不均匀,接头宏观塑性与单纯母材拉伸相比有所降低,但仍有25%左右的伸长率,接头的强度与母材相当。断裂在焊缝的断口,其断口形貌均为准解理断口。
2) 激光焊接接头650 ℃高温拉伸时,不稳定β相将转变为O相,该相变通过切变完成,因此β柱状晶的晶界容易产生应变集中,使高温塑性显著降低,只有2%左右,而且对接头高温强度也有影响。高温横向拉伸时断口呈现沿晶和解理的断裂形式。
REFERENCES
[1] 张永刚, 韩雅芳, 陈国良, 等. 金属间化合物结构材料[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2001.
ZHANG Yong-gang, HAN Ya-fang, CHEN Guo-ling, et al. Intermetallic compound structural materials[M]. Beijing: National Deference Industry Press, 2001.
[2] 陈国良, 林均品. 有序金属间化合物结构材料物理金属学基础[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1999.
CHEN Guo-liang, LIN Jun-pin. Physical metallurgical foundation of ordered intermetallic compound structural materials[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1999.
[3] Djanarthany S, Viala J C, Bouix J. An overview of monolithic titanium aluminide based on Ti3Al and TiAl[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2001, 72: 301?319.
[4] Zhang J W, Li S Q, Zou D X, et al. Processing and microstructure control of (α2+β+O) alloy sheet in Ti-Al-Nb system[J]. Intermetallics, 2000(8): 699?702.
[5] Ding H, Song D, Zhang C B, et al. Superplastic behavior of a β-forged Ti3Al-Nb alloy[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, 281: 248?252.
[6] David S A, Horton J A, Goodwin G M, et al. Weld ability and microstructure of a titanium aluminide[J]. Welding Journal, 1990, 69(4): 133?s?140?s.
[7] Baeslack III W A, Mascorella T J, Kelly T J. Weld ability of a titanium auminide[J]. Welding Journal, 1989, 68(12): s483?s498.
[8] Cieslak M J, Headley T J, Baeslack III W A. Effect of thermal processing on the microstructure of Ti-26Al-11Nb: Applications to fusion welding[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1990, 21(5): 1273?1286.
[9] 吴会强, 冯吉才, 何 鹏, 等. 钛铝基金属间化合物熔焊工艺的研究进展[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2004(5): 10?14.
WU Hui-qiang, FENG Ji-cai, HE Peng, et al. Titanium aluminide base intermetallic compound[J]. Aerospace Materials and Technology, 2004(5): 10?14.
[10] 吴会强, 冯吉才, 何景山, 张秉刚. 焊接工艺对高铌Ti3Al合金电子束焊接接头显微组织和显微硬度的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(8): 1313?1317.
WU Hui-qiang, FENG Ji-cai, HE Jing-shan, ZHANG Bing-gang. Microstructure evolution of high Nb containing Ti3Al based alloy electron beam welding joints[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(8): 1313?1317.
[11] ZOU J Y, CUI Y Y, YANG R. Electron beam welding of Ti-24Al-17Nb-0.5Mo alloy[C]//PRICM 5: The Fifth Pacific Rim International Conference on Advanced Materials and Processing, Beijing, China, Nov 2?5 2004. Switzerland: Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2005: 821?824.
[12] Martin G S, Albright C E, Jones T A. An evaluation of CO2 laser beam welding on a Ti3Al-Nb alloy[J]. Welding Journal, 1995, 74(2): s77?s82.
[13] WU Ai-ping, ZOU Gui-sheng, REN Jia-lie, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-24Al-17Nb(at.%) laser beam welding joints[J]. Intermetallics, 2002(10): 467?452.
[14] 吴爱萍, 邹贵生, 张红军, 等. Ti-24Al-17Nb合金激光焊接[J]. 航天材料工艺, 2001(6): 58?62.
WU Ai-ping, ZOU Gui-sheng, ZHANG Hong-jun, et al. Laser welding of Ti-24Al-17Nb alloys[J]. Aerospace Materials and Technology, 2001(6): 58?62.
[15] CHEN Li, HU Lun-ji, GONG Shui-li. A study on the porosity of CO2 laser welding of titanium alloy[J]. China Welding, 2006, 15(3): 1?5.
收稿日期:2007-02-06;修订日期:2007-09-20
通讯作者:吴爱萍,教授;电话:010-62773859;E-mail: wuaip@tsinghua.edu.cn
(编辑 何学锋)