Effect of salts on earthen materials deterioration after humidity cycling
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2017年第4期
论文作者:谌文武 沈云霞 匡静 杜伟飞
文章页码:796 - 806
Key words:earthen archaeological sites; wet-dry cycles; deterioration; salt content; salt crystallization
Abstract: Salt weathering leads to destruction of many valuable cultural heritage monuments and porous building material. The present study aims at providing more laboratory evidence for evaluating the effects of salt precipitation on the deterioration process. In view of this, the remoulded soil specimens were mixed with three kinds of salts (i.e., NaCl, Na2SO4 and their mixture) with different salt concentrations, and the specimens were kept in environment cabinet for undergoing different wet-dry cycles. After each cycle, the ultrasound velocity measurements were employed to monitor the deterioration process. For the specimens that have suffered three wet-dry cycles, the mechanical properties (i.e. shear strength and compression strength) were determined to evaluate the degree of deterioration. Furthermore, considering the realistic conservation environment of earthen sites, mechanical stability of these specimens against sediment-carrying wind erosion was conducted in a wind tunnel. These experiments results indicate that the overall average velocities of the specimens after the third cycle are significantly lower than those subjected to only one cycle. Ultrasound velocity, mechanical strength and wind erosion rate decrease when salt content increases. However, the internal friction angle increases firstly, and then decreases with the increase in salt content added to the specimens. Na2SO4 contributes most of the surface deterioration, while NaCl plays little role in the deterioration. The damage potential of the salt mixture is less obvious and largely dependent on the crystallisation location.
Cite this article as: SHEN Yun-xia, CHEN Wen-wu, KUANG Jing, DU Wei-fei. Effect of salts on earthen materials deterioration after humidity cycling [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(4): 796-806. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-017-3482-0.
J. Cent. South Univ. (2017) 24: 796-806
DOI: 10.1007/s11771-017-3482-0
SHEN Yun-xia(沈云霞)1, 2, CHEN Wen-wu(谌文武)1, 2, KUANG Jing(匡静)3, DU Wei-fei(杜伟飞)4
1. Key Laboratory of Mechanics on Disaster and Environment in Western China (Lanzhou University),
Lanzhou 730000, China;
2. School of Civil Engineering and Mechanics, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 73000, China;
3. Gansu Building Research Institute, Xijin East Road 575, Lanzhou 730050, China;
4. China JK Institute of Engineering Investigation and Design, Xianning Road 52, Xi’an 710043, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2017
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2017
Abstract: Salt weathering leads to destruction of many valuable cultural heritage monuments and porous building material. The present study aims at providing more laboratory evidence for evaluating the effects of salt precipitation on the deterioration process. In view of this, the remoulded soil specimens were mixed with three kinds of salts (i.e., NaCl, Na2SO4 and their mixture) with different salt concentrations, and the specimens were kept in environment cabinet for undergoing different wet-dry cycles. After each cycle, the ultrasound velocity measurements were employed to monitor the deterioration process. For the specimens that have suffered three wet-dry cycles, the mechanical properties (i.e. shear strength and compression strength) were determined to evaluate the degree of deterioration. Furthermore, considering the realistic conservation environment of earthen sites, mechanical stability of these specimens against sediment-carrying wind erosion was conducted in a wind tunnel. These experiments results indicate that the overall average velocities of the specimens after the third cycle are significantly lower than those subjected to only one cycle. Ultrasound velocity, mechanical strength and wind erosion rate decrease when salt content increases. However, the internal friction angle increases firstly, and then decreases with the increase in salt content added to the specimens. Na2SO4 contributes most of the surface deterioration, while NaCl plays little role in the deterioration. The damage potential of the salt mixture is less obvious and largely dependent on the crystallisation location.
Key words: earthen archaeological sites; wet-dry cycles; deterioration; salt content; salt crystallization
1 Introduction
Earthen architecture is the most ancient and most widespread existing construction in the world. According to UNESCO, approximately one fifth of the places on its World Cultural Heritage list are made of earth [1]. For example, a large number of precious ancient earthen archaeological sites, such as the Jiaohe Ruins (in China), Ajina Tepa (in Tajikistan), Merv (in Turkmenistan) [1-3], are still remaining along the Silk Road. Those sites have been the main passages for commercial and cultural exchange between Asia and Europe for thousands of years. However, the conditions of these earthen heritages are not as good as we thought. Due to continuous deterioration under adverse environmental conditions, only a small proportion of the ancient relics have been survived to the present. According to field investigations, these earthen structures have being suffered by the diverse hazards such as extensive erosion caused by winds and heavy rainfall, structural degradation by fluctuation in terms of humidity and temperature [2-5]. The vital issue is dissolution and transportation of soluble salts, leading to material’s strength loss, weathering and crumbling [6-9]. Especially, bottom covings develop due to the salt attack in combination with abrasion from wind and windblown silt [3]. Finally, the upper and middle parts of the wall have a possibility to fall when their support is undermined by covings [3, 5], as presented in Fig. 1. However, fundamental research of this phenomenon is still sorely insufficient. Therefore, the present study aims at providing more laboratory evidences for uncovering the effects of salt precipitation on the deterioration process.
It is widely recognized that soluble salts greatly limit the durability of porous material. A century and a half ago, as a pioneer in the research on salt deterioration, LAVALLE [10] provided the evidence that growing crystals can exert pressure. GOUDIE and VILES [6] proved that salt weathering is one of the most efficient agents of rock weathering in various environments. Based on this, many studies have been carried out using experimental laboratory simulations to assess stone durability produced by salt weathering, such as ultrasonic wave velocities [11], compressive and tensile strength [12]. In addition, the mechanisms of salt damage including thermodynamic aspects were also studied, such as crystallization pressure calculated [7, 13], the physicochemical interactions between particles caused by salt solution [14] and molality-based model for the prediction of phase equilibria in multicomponent salt systems [15]. Although these mechanisms are applied universally in porous materials, the applicability on earthen relics still remains unknown due to the lack of relevant research.

Fig. 1 Main deterioration of earthen heritage sites:
For the earthen heritage sites in northwest China, sodium sulphate and sodium chloride are the common salts [2, 16-18]. Despite the crystallisation mechanisms of these two salts being not yet understood completely, the crystallisation conditions are fairly well defined [19-24]. Preliminary studies of salt damage to earthen material were conducted, including the influence of salt content on particle size distribution, limit moisture content [25] and pore size distribution [26]. Moreover, the variation relationship between the shear strength of the sodium chloride contaminated soil and salt content was also analyzed [27]. Thus, the study of the salt deterioration of earthen materials is suitable based on these both kinds of salts.
In this work, sodium sulphate, sodium chloride and their mixture are employed to study the salt deterioration of contaminated earthen material under wet-dry cycles at a certain temperature. There are three major objectives of this study: 1) ultrasound velocity evolution during repeated wetting and drying is used to estimate the soil deterioration induced by the salt crystallisation pressure. The ultrasonic method is one of the most effective non-destructive testing techniques. It is frequently adopted for reflecting the constituents and physical structure of the material [28]. Herein, this method would be applied to monitor the development of soil deterioration. 2) Conventional mechanical performance tests, including direct shear test and unconfined compression test are conducted on soil specimens after three dry-wet cycles to investigate the damage potential of different salts corresponding with different salt contents. 3) Sediment-carrying wind erosion tests are carried out, to evaluate the effect of salt treatment for mechanical stability of soil specimens by material loss determination.
2 Study area
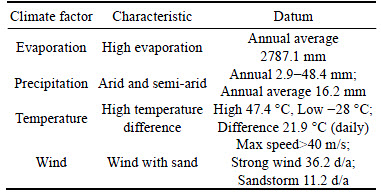
The Jiaohe Ruins, which is located in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, an arid and semi-arid area in the northwest of China, is the largest, oldest and best-preserved earthen relics over the world. The main climate characteristic of the area is low rainfall and high evaporation. Details are summarized in Table 1. In 2014, as part of the Silk Road, UNESCO added the Jiaohe Ruins to the List of World Heritage sites. The total area of the Jiaohe site is more than 35×104 m2, including a construction area of 22×104 m2, as large as a city. As one of the world’s architectural wonders, most buildings of the Jiaohe Ruins were dug from earth. These soils were used for the manufacture of mud bricks, rammed earth and cob, reusing for building construction. After thousands of years of exposure to the environment, these structures inevitably show significant decay such as erosion, cracks and even collapse.
Table 1 Climate characteristics of Jiaohe Ruins
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Characteristic of mineralogical and physical properties
Soil for the experiments was collected from blocks of a collapsed part of the cliff of the Jiaohe Ruins. The soil consists of undisturbed earthen material, raw soil. It has been chosen for two reasons: a) this is a typical kind of soil using in the earthen archaeological sites that located in the central Asian loess belt and; b) it can be obtained without damaging the earthen sites. In order to avoid the effect of the original salt content in the material, all the soil samples were desalinated using distilled water until the electrical conductivity of the filtered water was less than 300 μs/cm, followed by drying at 105 °C [29]. Physical properties of the desalinated soil were evaluated according to the Chinese National Standards GB/T50123 [29]. The particle size distribution for testing material is: clay (11.5%), silt (88.3%) and very minor sand (0.2%). It is a low plasticity soil, with a liquid limit of 29.9% and a plastic limit of 19.6%. The specific gravity of the grains is 2.76 g/cm3. Basic physical and geotechnical properties of the sample are summarized and listed in Table 2.
Mineralogical analysis was carried out by X-ray diffractometer (XRD). The results of semi-quantitative XRD analysis using the method suggested by Moore and Reynolds [30] show that quartz (39.4%) and clay (26.1%) are the major minerals of the soil (Table 3).
3.2 Sample preparation
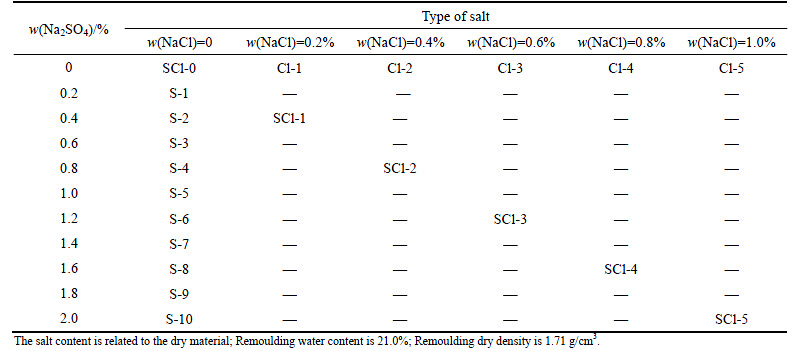
The salt content was determined on the basis of analyzing the ion concentration of aqueous extracting from more than 100 samples collected from many different earthen sites. The results indicate that the contents of Na2SO4 and NaCl in these materials are up to 2% and 1% (mass fraction), respectively. Therefore, these two particular single salts and mixtures of them were used for the laboratory deterioration experiments, as listed in Table 4.
Only artificial specimens were used in this study owing to the desalinated. All samples were statically compacted in a cube mould with an edge of 7.07 cm [31].
They were remoulded with the optimum moisture content (21.0%) and the maximum dry density (1.71 g/cm3), which were determined by the compaction test. Before being remoulded, the dried soil was ground and screened through a 2-mm sieve, thoroughly mixed with the brine, then placed in plastic bags and kept in a humidity-controlled room (> 95% relative humidity) for at least 48 h to achieve uniform distribution of moisture. When all the specimens have been remoulded, they were then stored in the curing room (temperature: 25 °C; relative humidity: 95%/15%) for wet-dry cycles. Each specimen was experienced up to three cycles of wetting (95% RH; RH is the relative humidity) and drying (15% RH) before ready for the tests. Each wet-dry cycle cost two month: at least one month for wetting until the specimens reached around 20% water content, while the remaining time for the drying process, to maintain the final water content of the samples less than 2%.
Table 2 Basic physical and geotechnical properties of desalinated soil
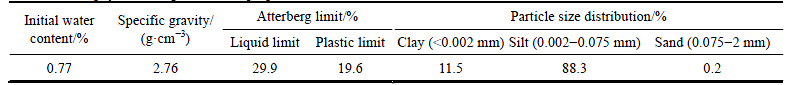
Table 3 Mineralogical composition of desalinated soil
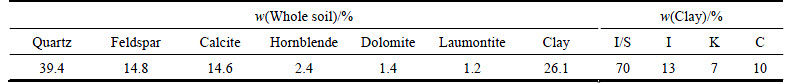
Table 4 Salts and salt contents used in laboratory deterioration experiments
3.3 Experimental methods
3.3.1 Ultrasonic test
The basic principle of the ultrasonic test is to analyze the change of the ultrasound velocity through the sample to estimate its internal structures. The primary wave (P-wave) is normally used in such test due to its fast velocity and low interference [32]. In order to monitor the effect of the salt content and the number of wet-dry cycles on the soil deterioration induced by salts, the ultrasound velocities of all the specimens were determined after each wet-dry cycle. In the measurements, the two transducers (a transmitter and a receiver) having a frequency of 50 kHz were used. Additionally, an ultrasonic couplant was used to improve the surface contact between the transducers and the test samples, resulting in a significant improvement in the signal to noise ratio. The instrument was calibrated with a standard material before every test. Each sample was measured three times in dry conditions, at room temperature.
3.3.2 Mechanical performance tests
The direct shear test and unconfined compression test were carried out after three dry-wet cycles to evaluate the mechanical properties of the samples. Strain-controlled direct shear apparatus was employed to conduct direct shear tests, which has a circular shear box with a diameter of 61.8 mm and a height of 20 mm. The shear rate was set to be 0.8 mm/min [29]. Due to the limited acceptable sample height of the apparatus, the specimens for the shear test were cut from the cubic samples. Therefore, only the shear strength close to the surface of the specimens was measured. However, the mechanical properties of the whole cubic specimens were approximately reflected by the unconfined compressive strength (UCS). In view of this, unconfined compressive tests were conducted on the electro- hydraulic servo universal testing machine (CSS- WAW300DL), whose axial pressure and axial displacement can be controlled and recorded automatically. The uniaxial loading applied to the samples was a constant rate of 3 mm/min [29].
3.3.3 Wind erosion tests
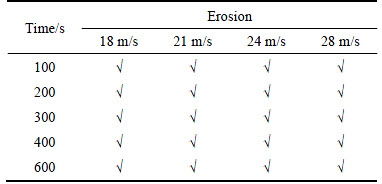
Sediment-carrying wind erosion can be a common problem for monuments in arid and semi-arid areas. The present experiments were performed with the specimens that have been subjected to three dry-wet cycles, in the multifunction environmental wind tunnel (Fig. 2) of the Key Laboratory of Mechanics on Disaster and Environment in Western China, China [33]. The wind tunnel had a total length of 55 m and a working section of 20 m length, 1.3 m width and 1.4 m height. Roughness elements were well distributed from the entrance to the front edge of the working section so as to ensure that so-called “steady” turbulence flow in the boundary layer. The axial airflow velocity can be continuously regulated from 1.0 to 40.0 m/s, which is controlled by a computer. In this case, four wind-sand flow speeds with different duration erosion were used [34-36], as listed in Table 5. The samples were placed on the top of a steel frame, which was about 20 cm high in order to make sure the air-sand flow applied on the samples uniform. Afterwards, all samples were weighed each time to calculate the mass loss under the different erosion conditions.
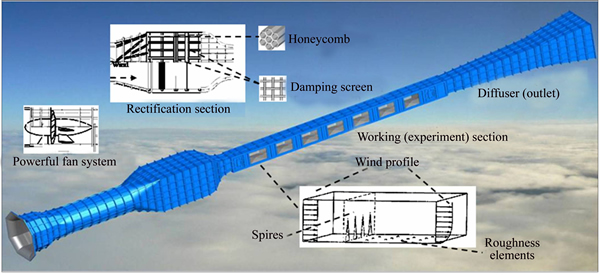
Fig. 2 Sketch map of wind tunnel of Lanzhou University, China
Table 5 Wind-sand flow speeds and duration of erosion employed in wind erosion tests
4 Results
4.1 Ultrasonic test
In Fig. 3, the average ultrasound velocities of all specimens after different wet-dry cycles are illustrated. In each subfigures, the overall average velocities of the specimens after the third cycle (720-934 m/s) are significantly lower than those subjected to only one cycle (976-1100 m/s). It also can be seen that in each case, the average velocity loss ΔVp gradually increases with amount of salt added in the sample. The specimen mixed with 3% salt mixture presents the largest reduction of 26.3%, while specimens treated by 2% Na2SO4 and 1% NaCl have relatively lighter deteriorations of 23.5% and 17.5%, respectively. In summary, there is more deterioration accompanied by an increase in the salt content within the samples after repeated wetting and drying cycles.
4.2 Evaluation of mechanical strength
4.2.1 Unconfined compression test
According to the test results, the relationship between the unconfined compressive strength and salt content of the samples after three wet-dry cycles is depicted in Fig. 4. It can be seen that compressive strength of the samples ranges from 3.57 MPa to 5.66 MPa, and that the strength varies with both total salt content and salt category added to the samples. For all samples in this study, the compressive strength decreases when salt content increases, confirming the strong influence of the salt content on the magnitude of damage. In terms of compressive strength at the same salt content for each sample treated with different salts, it was found that samples treated with the salt mixtures represented the lowest compressive strength, while Na2SO4 seemed to show more damage than NaCl respect to the compressive properties of the soil.
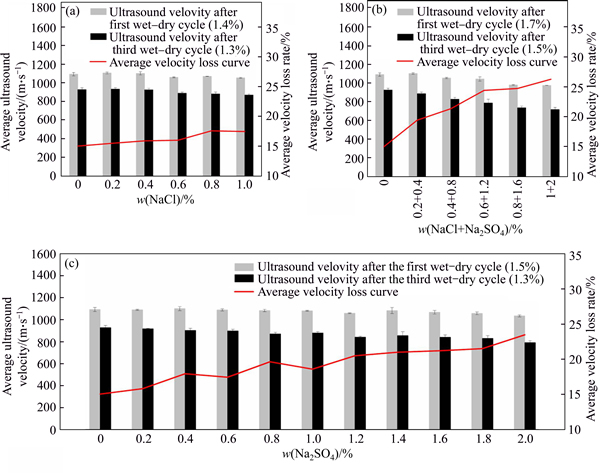
Fig. 3 Ultrasound velocity and velocity loss curve of salt contaminated soil after different wet-dry cycles
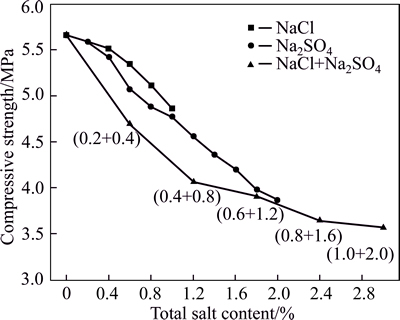
Fig. 4 Relationship between compressive strength and salt content of samples after three wet-dry cycles
4.2.2 Direct shear test
Usually, the shear strength of the soil is mainly determined by the cohesion, which reflects the shear capacity of the soil structure, whereas the internal friction angle of the soil reflects the size and shape of the soil particles. Figure 5 presents the representative results of the direct shear test of the samples. With increase in salt content, variations of the cohesions of all samples exhibit a decrease trend with those of the shear strength, which is consistent with the experimental result of compressive strength. However, the internal friction angle increases firstly, and then decreases with the increase in salt content added to the specimens. Furthermore, salt categories also affect the mechanical properties of the soil to a certain extent. According to Fig. 5(a), specimens prepared with Na2SO4 show lower shear resistance value compared to other specimens that treated with NaCl in all of total salt contents range, again showing that the damage potential of Na2SO4 is higher than that of NaCl. The samples contaminated by salt mixture, however, show the highest shear resistance with various salinity levels. An apparent contradiction exists in the results between the compression and direct shear tests. Because the shear parameter was determined by small cylindrical specimens (6.18 cm diameter, 2 cm height) that were cut from the intact ones, it only represents the soil characteristics near the surface of the specimen.
In general, the total internal friction angle varies between 19.8° and 32.0° in a total salt content range of 0-3% (Fig. 5(b)). For the samples treated with single salt, including both the NaCl and Na2SO4, internal friction angles reach a peak value at relatively small salt content (around 0.6% and 0.4%, respectively) and then display agradual reduction. However, for those with salt mixture, internal friction angle presents a slight variation for all salt contents, in which a maximum friction angle (29.2°) appears at the total salt content of 1.2%.
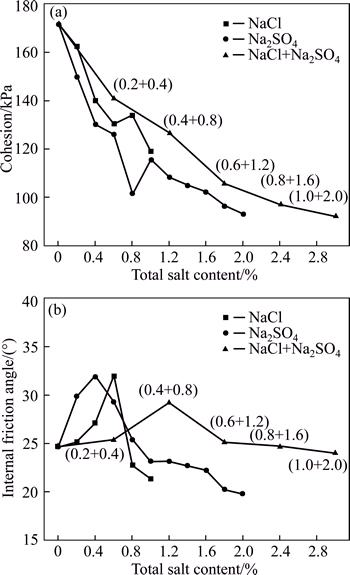
Fig. 5 Relationship between shear strength parameters and salt content of samples after three wet-dry cycles
4.3 Wind erosion test
The following observations are considered in order to evaluate the effect of salt treatments for mechanical stability of soil specimens against wind-sand flow erosion. According to the results of mechanical performance tests, the degree of deterioration in the specimen is inhomogeneous from interior to the surface. And the rate of abrasion usually varied with duration of exposure [37]. Thus, the average wind erosion rate (AER) at the same wind speed and different erosion durations is an average index to quantify the mechanical stability of soil against erosion. AER is calculated as
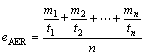
where eAER is average wind erosion rate at the same wind speed; mi is mass loss after ti; ti is wind erosion duration; n is 5 (the total number of employed durations).
Figure 6 shows the variation of average wind erosion rate with salt content for specimens, which are obtained at different wind speeds. As shown in Fig. 6, the accession of salts leads to significant reduction in resistance of soil to wind-sand flow abrasion. On the other hand, it shows that the AER value increases with salt content in each group. Furthermore, it also can be observed from the figure that the AER value largely depends on the employed wind-sand flow speed. In detail, the greater the wind speed is, the higher the average wind erosion rate, and vice versa. For low wind speeds (18 m/s and 21 m/s), the difference between the AER value of the samples with the same salt content is indistinctive, especially in the case having low salt content. However, there is an obvious increase in AER value of the specimens when the wind speed is higher than 24 m/s. Consequently, saline soil specimens undergo three times wetting and drying. The reduction of the wind erosion resistance of the earthen materials caused by the increase of the salt content is in evidence. And increase in wind speed, especially higher than 24 m/s, significantly magnifies this reduction.
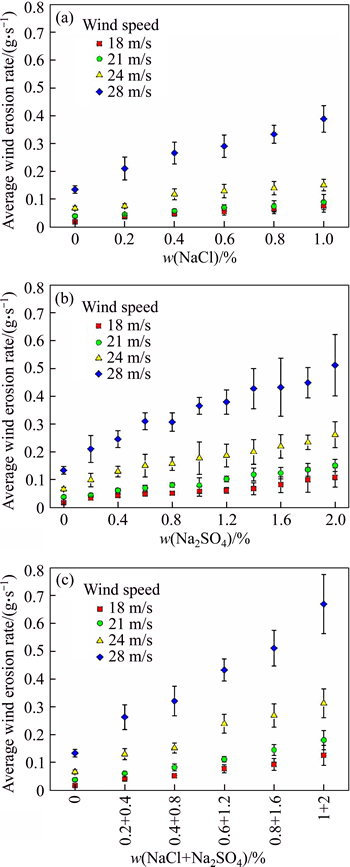
Fig. 6 Variation of average wind erosion rate of specimens mixed with different salt contents after three dry-wet cycles at different wind speeds
5 Discussion
5.1 Crystallisation behaviours of Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O system during humidity cycling
Salt is widely recognized as a major cause of the damage of porous construction material. In this study, after one wet-dry cycle, whatever the salt category, the samples suffer damage from crystallisation. Furthermore, repeated wetting and drying results in an accumulation of damage to the soil structure. According to the result of ultrasonic test, there is no doubting that this damage is attributed to the formation of crystallisation pressure and hydration pressure in the confinement pores when the relative humidity changes. The crystallisation behaviour of salts should be characterized to interpret the deterioration mechanism during the wetting (or deliquescence) and evaporation. Therefore, the result of calculated phase diagram of the system Na2SO4-NaCl- H2O at 25 °C is depicted in Fig. 7, using the model adopted from STEIGER et al [15]. For sodium sulphate, one thermodynamically stable mirabilite (Na2SO4·10H2O) and three metastable phases, thenardite, phase III (Na2SO4) and heptahydrate (Na2SO4·7H2O) present in Fig. 7(a). All phase states are able to be formed during drying in this case as they have been observed in the laboratory experiments [19, 24, 38, 39]. Furthermore, theoretical results show that both of them can produce pressure sufficient to induce tensile stresses exceeding the tensile strengths of most materials, resulting in tensile failure [40]. However, in general, only anhydrate sodium sulphate can exist at the end of drying (RH=15%). When the relative humidity goes up, anhydrous crystals dissolve until complete deliquescence since 95% RH is above the deliquescence relative humidity of all phase states. From previous researches, mirabilite might crystallize in this process [41, 42]. Therefore, crystallisation pressure could appear in either the drying or wetting process. In contrast, for sodium chloride, the other single salt in the ternary system, only dissolution and recrystallisation have to be considered because no different hydrated states could be formed. In the case of Na2SO4-NaCl solution (xNaCl=0.5), mirabilite, thenardite, phase III or heptahydrate would crystallize out upon evaporation. The precipitation of sulphate changes the composition of the remaining solution which becomes more enriched with chloride. In continuous evaporation and crystallisation, the solution composition moves until reaching the drying point (thenardite-halite coexistence point) of the solution. During wetting process, thenardite and halite re-dissolve, while mirabilite may precipitate, but eventually they will completely dissolve.
5.2 Damage patterns of salt mixture and single salts
In a large number of laboratory experiments in which the effects of different salts were compared, NaCl crystallisation produced little damage, whereas Na2SO4 always showed high damage potential that attributed to the volume expansion when the mirabilite was formed [19, 22]. This state is confirmed in this study. For the same salt content, the sample treated with the sodium sulphate represented the lower mechanical strength than the one mixed with sodium chloride. However, the compression strength of the samples loaded with salt mixture is the lowest among them while it has the highest shear resistance. Such unexpected result may arise from the different damage patterns during repeated wetting and drying cycles, as depicted in Fig. 8. In general, after the wetting and drying procedure, the low relative humidity promotes rapid evaporation, driving the flow through the pores to the surface, resulting in an accumulation of salt crystallisation close to the interface. For example, either sodium chloride or sodium sulphate presents efflorescence, as shown in Fig. 8(b) and Fig. 8(c), respectively. However, in Fig. 8(d), it can be seen that relatively little efflorescence develops on the soil surface, although it has the maximum amount of salt. According to the solubility in the system Na2SO4-NaCl- H2O (Fig. 7(b)), the solubility of the various Na2SO4 phases decreases with increasing NaCl molality, indicating that in the presence of NaCl, the Na2SO4 precipitation is earlier than the pure sodium sulphate solution with the same concentration. Moreover, as a general trend, the evaporation of sodium sulphate solution is slower than that of sodium chloride solution under the similar conditions [19]. Then, sodium chloride precipitates prior on the surface, somehow preventing the crystallisation of sodium sulphate. In conclusion, salts crystallisation takes place deeper in the soil, resulting in more deterioration of the intact specimen but less damage occurring close to the surface of the specimen.
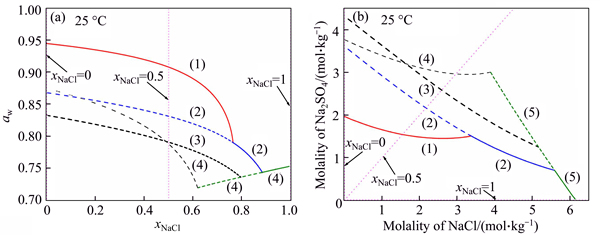
Fig. 7 Equilibrium water activity (a) and solubility (b) in system Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O at 25 ° (aw is the water activity and xNaCl is the mole fraction NaCl. Solid and dashed curves denote stable and metastable equilibria, respectively, of mirabilite (1), thenardite (2), phase III (3), heptahydrate (4) and halite (5). Dotted line represents the composition of the salt solutions used in this experiment)
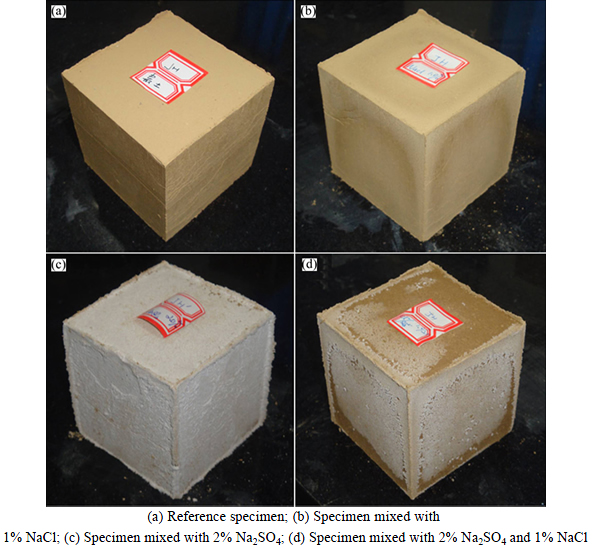
Fig. 8 Damage patterns of specimens mixed with salts after three dry-wet cycles:
5.3 Effect of salt content on soil deterioration under wet-dry cycles
It is clear that all results, including ultrasound velocity, mechanical strength and wind erosion resistance, indicate that more decay occurs when increasing salt content within the soil. With the increasing salt content, the pore filling ratio gradually increases and generates higher macroscopic stress to the soil. On the other hand, the soil used in this experiment contains more than 10% clay. The physicochemical interactions between clay particles caused by salt solution also influence the fabric of the soil [14]. The thickness of double layer of clay particles decreases with increasing salt concentration, thus ion diffusion into the fluid causes decrease of osmotic repulsion and consequently increases the interparticle forces among clays [43, 44]. As indicated by the previous studies [45, 46], the interpaticle bond stresses among the soil particles can be reduced by a series of physical weathering process, such as the disintegration of mudstone by wetting and drying. Therefore, it is reasonable to understand experimental results of this study, from the sense of salt crystallisation aggregating in the pores and loose soil structure caused by wet-dry cycles. Although this mechanism has not been comprehensively understood, based on the experimental results, the interpaticle bond stresses of saline soils may be sufficiently affected by the wetting and drying processes. Furthermore, salts precipitate in the pores can increase the roughness of the contact surface between adjacent particles, while crystallisation pressure decreases the compactness of the soil. Hence, when the salt content is smaller, the friction angle increases due to the filling of the pores with growing salt crystals, whereas in the case with larger salt contents, the angle of internal friction is primarily determined by the reduction of the compactness.
6 Conclusions
The wetting and drying experiments showed that crystallisation pressure is responsible for the stress. The ultrasonic test results demonstrated that the overall wave velocities of the specimens decrease with the increase of wet-dry cycle times, indicating that more damage is likely to be caused by salts after repeated wet-dry cycles. The results presented in this work have also shown that the dependence of the degree of deterioration on the salt content is obvious. With increasing salt content, the pore filling ratio gradually increases and generates higher macroscopic stress to the soil. Moreover, the interpaticle bond stresses of saline soil may be sufficiently affected by the wetting and drying processes. Therefore, ultrasound velocity, mechanical strength and wind erosion rate decrease with the increase of salt content. On other hand, salt precipitations in the pores cause more roughness and less compactness of the soil. Thus, the internal friction angle increases firstly followed by a gradual reduction with the increase in salt content added to the specimens.
The extent of salt damage in porous material due to crystallisation pressure appears to be largely dependent on the salt category. Based on the experiments presented here, sodium sulphate showed higher damage potential and less damage produced by sodium chloride crystallisation, consisting with the previous research results. This can be explained that NaCl is the salt that cannot cause hydration pressure during wetting and drying. For salt mixture, the existence of sodium chloride has an important influence on the damage pattern. First, the solubility of the Na2SO4 is directly related to the NaCl molality. Second, the precipitation of sodium chloride on the surface directly affects the crystallisation location of sodium sulphate. Thus, more deterioration of the intact specimen but less damage occurs close to the surface comparing with the soil contaminated with the respective single salts, as observed from the experiment results.
Nevertheless, the results demonstrated in this work play a solid foundation to develop a more detailed understanding of salt damage in soil, especially for the salt mixture with sodium sulphate and sodium chloride. Future work will allow for different damage behaviours under varying experimental conditions, such as mixed salt solution in different proportions at higher/lower temperatures. It is also necessary to extend this work to other types of substrates as well as other salts.
Acknowledgement
We appreciate to Dr Michael Steiger for his generous help on the calculation of phase diagram of the Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O system. We are also grateful to wind tunnel laboratory technicians for preparing experiment instruments. The authors want to thank all the members who helped us and cooperated with us.
References
[1] BARTON J. 3D laser scanning and the conservation of earthen architecture: A case study at the UNESCO World Heritage Site Merv, Turkmenistan [J]. World Archaeology, 2009, 41: 489-504.
[2] SHAO Ming-shen, LI Li, WANG Si-jing, WANG En-zhi, LI Zui-xiong. Deterioration mechanisms of building materials of Jiaohe ruins in China [J]. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 2013, 14: 38-44.
[3] FUJII Y, FODDE E, WATANABE K, MURAKAMI K. Digital photogrammetry for the documentation of structural damage in earthen archaeological sites: The case of Ajina Tepa, Tajikistan [J]. Engineering Geology, 2009, 105: 124-133
[4] ZHAO Hai-ying, LI Zui-xiong, HAN Wen-feng, WANG Xu-dong, CHEN Wen-wu. Main diseases and their causes of earthen ruins in arid region of northwestern China [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(2): 2875-2880. (in Chinese)
[5] FODDE E. Structural faults in earthen archaeological sites in Central Asia: Analysis and repair methods [C]// The Sixth International Conference on Structural Analysis of Historic Construction. London: Taylor & Francis, 2008: 1415-1422.
[6] GOUDIE A, VILES H. Salt weathering hazards [M]. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 1997.
[7] SCHERER G W. Crystallisation in pores [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1999, 29: 1347-1358.
[8] FLATT R J. Salt damage in porous materials: How high supersaturations are generated [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2002, 242: 435-454.
[9] PU Tian-biao, CHEN Wen-wu, LV Hai-min, DU Yu-min. Analysis on function of deterioration of typical earthen ruins under the coupling of salinized and freezing and thawing in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2016, 47(4): 1420-1426. (in Chinese)
[10] LAVALLE J. Research on the slow formation of crystals at ordinary temperature [J]. Compte Rend Acad Sci(Paris), 1853, 36: 493-495. (in French)
[11] ANGELI M, BIGAS J P, BENAVENTE D, MENENDEZ B, HEBERT R, DAVID C. Salt crystallization in pores: Quantification and estimation of damage [J]. Environmental Geology, 2007, 52(2): 205-213.
[12] BENAVENTE D, MA G D C. Durability estimation of porous building stones from pore structure and strength [J]. Engineering Geology, 2004, 74(1): 113–127.
[13] CORRENS C W. Growth and dissolution of crystals under linear pressure [J]. Discuss Faraday Soc, 1949, 5(5): 267-271.
[14] MORI R. Some problems on the chemical stability of soils [R]. Tokyo: Committee of Soil Chemistry, Association of Electrochemistry, 1964.
[15] STEIGER M, KIEKBUSCH J, NICOLAI A. An improved model incorporating Pitzer’s equations for calculation of thermodynamic properties of pore solutions implemented into an efficient program code [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2008, 22: 1841-1850.
[16] LIN Qing-tao. Research on the survey and distribution of salt in the wall of Suoyang ruins in Gansu Province [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2010. (in Chinese)
[17] HUANG Si-ping, LI Yu-hu, ZHAO Yu-jie. Preliminary study on migration of soluble salts in simulated earthen site [J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2010, 38 (5): 51-55. (in Chinese)
[18] CUI Kai, CHEN Wen-wu, SHEN Yun-xia, WANG Xu-dong, HAN Wen-feng. Experimental study on response of intensity on earthern ruin’s soil undergoing recombination process of salinized and dry-wet in arid and semi-arid regions [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2012, 43(11): 4451-4456. (in Chinese)
[19] RODRIGUESZ-NAVARRO C, DOEHNE E. Salt weathering: influence of evaporation rate, supersaturation and crystallisation pattern [J]. Earth Surf Process Landforms, 1999, 24: 191-209.
[20] TSUI N, FLATT R J, SCHERER G W. Crystallisation damage by sodium sulfate [J]. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 2003, 4: 109-115.
[21] LINNOW K, JULING H, STEIGER M. Investigation of NaCl deliquescence in porous substrates using RH-XRD [J]. Environmental Geology, 2007, 52: 317-327.
[22] ESPINOSA-MARZAL R M, SCHERER G W. Crystallisation of sodium sulfate salts in limestone [J]. Environmental Geology, 2008, 56: 605-621.
[23] STEIGER M, ASMUSSEN S. Crystallisation of sodium sulfate phases in porous materials: The phase diagram Na2SO4-H2O and the generation of stress [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72: 4291-4306.
[24] SAIDOV T, PEL L, van der HEIJDEN G. Crystallisation of sodium sulfate in porous media by drying at a constant temperature [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 83: 621-628.
[25] CHEN Wen-wu, LV Hai-min, CUI Kai, WU Guo-peng, DU Yu-min. Comparative study of the influence of chlorine and sulfate slat on grain size distribution and limit moisture content in site soils [J]. Journal of Lanzhou University: Natural Science, 2015, 51(3): 334-338. (in Chinese)
[26] CHEN Yu, WANG Xu-dong, YANG Shan-long, GUO Qing-lin, LIN Bo, LI Feng-jie. A preliminary study of the freeze-thaw cycle on the structure of earthen sites with different salts [J]. Dunhuang Research, 2013(1): 98-107. (in Chinese)
[27] CHEN Wei-tao, LI Shu, WANG Ying. Influence of shearing strength of salt-bearing-soil from salt content and salt sort [J]. Railway Construction Technology, 2005(6): 54-56. (in Chinese)
[28] GROSSI C M, ESBERT R, DEL RIO L S, MONTOTO M, LAURENZI-TABASSO M. Acoustic emission monitoring to study sodium sulphate crystallisation in monumental porous carbonate stones [J]. Studies in Conservation, 1997, 42: 115-125.
[29] GB/T50123—1999. Standard for soil test method. (in Chinese)
[30] MOORE D M, REYNOLDS R C. X-ray Diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals [M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1989.
[31] JIANG Yao, CHEN Wen-wu, WANG Gong-hui, SUN Guan-ping, ZHANG Fan-yu. Influence of initial dry density and water content on the soil–water characteristic curve and suction stress of a reconstituted loess soil [EB/OL]. [2016-05-13]. http://link.springer. com/article/10.1007/s10064-016-0899-x.
[32] KAHRAMAN S. Estimating the direct P-wave velocity value of intact rock from indirect laboratory measurements [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2002, 39: 101-104.
[33] ZHANG J, SHAO Y, HUANG N. Measurements of dust deposition velocity in a wind-tunnel experiment [J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2014, 14: 8869-8882.
[34] CHEPIL W. Factors that influence clod structure and erodibility of soil by wind: IV. sand, silt, and clay [J]. Soil Science, 1955, 80: 155-162.
[35] VAN PELT R S, ZOBECK T M. Validation of the wind erosion equation (WEQ) for discrete periods [J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2004, 19: 199-203.
[36] HAN Lin. Experiment research on the destroyed mechanism of the saline soil in the Great Wall in Shandan County [D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2010. (in Chinese)
[37] CHEPIL W. Properties of soil which influence wind erosion: V. Mechanical stability of structure [J]. Soil Science, 1951, 72: 465-478.
[38] HAMILTON A, HALL C, PEL L. Sodium sulfate heptahydrate: direct observation of crystallisation in a porous material [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2008, 41: 212002.
[39] SCHIRO M, RUIZ-AGUDO E, RODRIGUEZ-NAVARRO C. Damage mechanisms of porous materials due to in-pore salt crystallization [J]. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 109: 265503.
[40] STEIGER M. Crystal growth in porous materials—I: the crystallisation pressure of large crystals [J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2005, 282: 455-469.
[41] SHAHIDZADEH N, DESARNAUD J. Damage in porous media: role of the kinetics of salt (re) crystallization [J]. The European Physical Journal Applied Physics, 2012, 60: 24205.
[42] DESARNAUD J, BERTRAND F, SHAHIDZADEH-BONN N. Impact of the kinetics of salt crystallisation on stone damage during rewetting/drying and humidity cycling [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2013, 80: 020911.
[43] BARBOUR S, FREDLUND D. Mechanisms of osmotic flow and volume change in clay soils [J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1989, 26: 551-562.
[44] MITCHELL J K, SOGA K. Fundamentals of Soil Behavior [M]. 3rd ed., Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley& Sons, 2005.
[45] BJERRUM L. Progressive failure in slopes of over consolidated plastic clay and clay shales [C]// Terzaghi Lectures. ASCE, 1967: 77-78.
[46] ZHANG Hu-yuan, YAN Geng-sheng, ZHAO Tian-yu. Durability of earthen architecture ruins under cyclic wetting and drying [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(2): 347-355. (in Chinese)
(Edited by YANG Hua)
Cite this article as: SHEN Yun-xia, CHEN Wen-wu, KUANG Jing, DU Wei-fei. Effect of salts on earthen materials deterioration after humidity cycling [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(4): 796-806. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-017-3482-0.
Foundation item: Projects(2010BAK67B16, 2013BAK08B11, 2014BAK16B02) supported by the National Science and Technology Support Program of China during the 12th Five-year Plan Period
Received date: 2016-07-27; Accepted date: 2016-11-10
Corresponding author: CHEN Wen-wu, Professor, PhD; Tel: +86-931-8914308; E-mail:sungp@lzu.edu.cn

