文章编号:1004-0609(2011)06-1348-11
铁酸镍基金属陶瓷的强化烧结与熔盐腐蚀行为
周科朝,陶玉强,刘宝刚,李志友
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:采用气氛烧结方法制备NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷材料,并进行960 ℃的铝电解腐蚀实验。通过分析烧结体的显微结构和物相组成、电解试样的表层形貌与成分以及电解质和阴极铝的杂质含量等,研究BaO、Yb2O3和CoO的添加以及金属相的组成对NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷烧结性能的影响;表征了该金属陶瓷强化烧结体作为铝电解惰性阳极的电解腐蚀性能;并对材料强化烧结机制和熔盐腐蚀行为进行探讨。结果表明:烧结过程中,BaO和Yb2O3与该金属陶瓷中的陶瓷相反应生成新的物相,CoO与陶瓷相形成固溶体,并加快烧结致密化进程;以Cu-Ni取代纯Cu和纯Ni作为金属陶瓷的金属相,可提高材料的相对密度;NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷的高致密度可抑制电解过程中金属相的流失和陶瓷相的腐蚀,阳极表层也转变为致密的NiFe2O4相。
关键词:惰性阳极;铝电解;金属陶瓷;NiFe2O4;电解腐蚀
中图分类号:TF 821 文献标志码:A
Enhanced sintering and molten salt corrosion behavior of nickel ferrite based cermets
ZHOU Ke-chao, TAO Yu-qiang, LIU Bao-gang, LI Zhi-you
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: NiFe2O4 based cermets were prepared by sintering method under controlled atmosphere, and their electrolysis corrosion in aluminum electrolysis at 960 ℃ was examined. Based on the studies of the microstructure and phase composition after sintering, surface morphology and composition after electrolysis, impurity content in electrolyte and cathode aluminum, the effects of BaO, Yb2O3 and CoO additive and metal composition on the sintering properties of NiFe2O4 based cermets were analyzed. The electrolysis corrosion property of highly sintered cermets as inert anode was characterized. The enhanced sintering mechanism and molten salt corrosion behavior were also discussed. The results show that the doped BaO, Yb2O3 and CoO react with the ceramic matrix, and then accelerate the process of sintering densification. The substituting of pure Cu and pure Ni by Cu-Ni as metal phase of cermets can increase the relative density of NiFe2O4 based cermets. The high relative density of NiFe2O4 based cermets is benefit to inhibit metal loss and ceramic-phase corrosion, and the anode surface will change to NiFe2O4 dense layer.
Key words: inert anode; aluminum electrolysis; cermets; NiFe2O4; electrolysis corrosion
现行铝电解是发生于940~960 ℃的强腐蚀性Na3AlF6-Al2O3熔体中的电化学反应过程,巨大的能源消耗和环境负荷严重制约铝工业的可持续发展。基于惰性电极的铝电解新工艺将彻底变革铝电解工业,实现电解过程温室气体零排放和大幅度节能目标[1-3]。自20世纪80年代以来,世界主要铝业公司都将基于惰性电极的铝电解新工艺视为21世纪铝电解工业进步的技术关键。美国能源部2003年将该工艺列为今 后20年最优先的研发课题,中国铝业公司将其列为10大核心研发技术之首。美国铝业公司[4-5]、瑞士Moltech公司[6-7]、俄罗斯铝业公司[8-9]、加拿大铝业公司[10]、美国阿贡国家实验室[11]、挪威科技大学[12-18]、新西兰奥克兰大学[19]、中南大学[20-24]和东北大学[25-27]等对惰性阳极、可润湿性阴极、低温电解质等关键材料及电解新工艺进行了系列研究。
惰性阳极材料技术是铝电解新工艺的核心与技术难点。作为惰性阳极材料,应能耐受电解质的腐蚀、新生态氧的渗蚀,具有良好导电性和抗热震性强,易于加工成型及与金属导电连杆连接。典型材料包括氧化物陶瓷[17]、金属/合金[8, 12-13]和金属陶瓷[15-16]等。金属陶瓷兼顾氧化物陶瓷的耐腐蚀性、良好热稳定性、抗氧化性和金属的良好导电性及抗热冲击性等优点,认为是最具应用前景的惰性阳极材料。典型的金属陶瓷材料是尖晶石型氧化物陶瓷与合金的复合材料,陶瓷相有NixFe3-xO4、NiFe2O4+NiO、ZnFe2O4+ZnO、NixFe2yZnzO(3y+x+z)和NiAl2O4等氧化物,金属相有Cu、Ni、Fe及其合金。其中,NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷由于具有陶瓷相在电解质熔体中的溶解度低、电解温度下良好的导电性能、陶瓷相与金属相相容性好的优点,一直是国内外的研究重点[15-16, 20-23, 26-27]。美国铝业公司和雷诺兹金属公司等机构对该类材料进行了25 d的6 kA级电解试验[28];中南大学和中国铝业股份有限公司进行28 d的4 kA级960~980 ℃电解试验。大型电解试验也存在一些问题,如电流效率低于碳素阳极、阳极腐蚀严重、阳极预热-更换和电解过程中易开裂、惰性阳极与金属导杆间稳固连接困难而导致阳极脱落、阳极电流分布不均匀、原铝中杂质含量偏高,其中阳极腐蚀问题尤为关键。本文作者重点研究烧结助剂和金属相组成对NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷的烧结和耐腐蚀性能的影响,并探讨材料的强化烧结机制和熔盐腐蚀行为。
1 实验
1.1 NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷的制备
以Fe2O3和NiO为原料,采用热反应合成方法 (1 200 ℃煅烧6 h)制备NiFe2O4基陶瓷。破碎后的合成产物混入一定量的金属、掺杂剂和成型剂,采用模压和冷等静压成型。压坯在氧分压1×10-4~5×10-4的N2气氛中,于1 150~1 350 ℃下进行烧结。
1.2 结构与性能检测方法
XJP-6A型金相显微镜、JSM-6360LV型扫描电镜进行显微组织和微观形貌分析,JSM-6360LV型扫描电镜和 EDX-GENESIS型能谱仪进行显微组织和微区成分分析,利用德国莱兹公司HZG4/B-PC型X衍射仪分析物相组成。ASTM C373-88(1999)测定密度,四端电极法测试在空气和Ar气氛下的电阻率,测试温度范围为25~1 100 ℃。电解实验所用电解质组成为78.07%Na3AlF6-9.5%AlF3-5.0%CaF2- 7.43%Al2O3 (质量分数),电解质分子比Rc(电解质中NaF与AlF3的摩尔比)为2.3,初晶温度为947 ℃,电解温度960 ℃,圆柱形阳极底部面积为2.5 cm2、电流密度为1.0 A/cm2。采用Philips8424 TW2424型X射线荧光分析(XRF)检测电解质和原铝中的杂质含量。
2 结果与分析
以Cu/Ni为金属相的NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷是一类较特殊的材料体系,不像WC-Co合金那样可通过WC在Co相的溶解析出实现烧结致密化,也不像Al2O3/Ni那样可在真空或还原气氛进行烧结。NiFe2O4基金属 陶瓷的烧结过程既要防止陶瓷相过度失氧导致的还原,又要避免金属相的氧化,而且两相之间不存在类似溶解析出的烧结反应。NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷的烧结 需在严格控制气氛氧分压下,通过陶瓷相烧结完 成。烧结致密度是铝电解惰性阳极材料NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷的核心参数,直接影响材料的力学、导电和耐腐蚀性能。NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷的高致密度烧结是解决电解过程中电解质沿孔洞溶渗、以及由此带来阳极肿胀和表层脱落问题的有效方法。
2.1 添加BaO进行NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷的活化烧结
添加烧结助剂是强化烧结的常用手段。NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷的烧结助剂的选择需保证其腐蚀溶解产物只进入电解质而不进入阴极铝液,且能与陶瓷相进行一定程度的反应,加强陶瓷相本身或烧结体系的扩散传质能力。1 273 K下BaO的分解电压(2.224 V)稍高于Al2O3的(2.188 V)[29],且热力学上能与Fe2O3生成系列产物。研究发现,添加1%的BaO可得到较好的烧结效果。表1所列为经1 200 ℃烧结4 h后试样密度的对比。添加1%的BaO使xCu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO)金属陶瓷的相对密度提高显著;金属相含量为5%、10%和17%时,金属基陶瓷掺杂1%BaO样品的相对密度分别为97.42%、97.50%和96.06%,而未掺杂样品其相对密度分别只有91.45%、90.52%和89.62%,分别提高了5.97%,6.98%和6.44%。
表1 1 200 ℃烧结时Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO)金属陶瓷的相对密度
Table 1 Relative density of Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) based cermets sintered at 1 200 ℃

图1所示为金属相含量17%试样的断口形貌。未掺杂试样陶瓷相的晶粒尺寸不到10 ?m,孔洞连通状态明显;1% BaO的添加使晶粒长大到20 ?m左 右,残留的孔洞主要以孤立的闭孔形式位于陶瓷相的晶界处。这表明试样中添加1% BaO可明显提高材料的烧结性能。
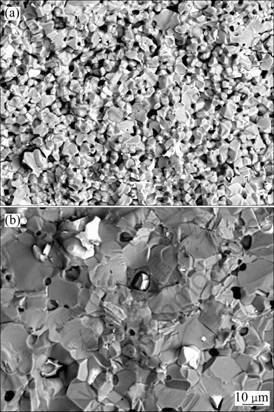
图1 1 200 ℃烧结金属陶瓷的断口SEM像
Fig.1 SEM images on fracture surface of cermets samples sintered at 1 200 ℃: (a) 17Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO); (b) 1BaO- 17Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO)
为揭示烧结过程中可能发生的反应,制备出BaO与NiFe2O4-10NiO的扩散偶,并经历与金属陶瓷烧结相同的过程。NiFe2O4-10NiO陶瓷基体与BaO界面X射线衍射分析表明(见图2),界面出现了BaFe2O4、Ba2Fe2O5和NiBa3O4等新物相。活化烧结效果可能来源于这些新物相的产生及其导致的NiFe2O4相和NiO相结构的变化。该类金属陶瓷中的NiFe2O4相和NiO相实际上是非化学计量化合物,分别为含Fe2+的Ni(1-x)FexFe2O4和同时含Fe2+和Fe3+的Ni(1-x)Fex′O (x>x′)(见表5的能谱分析结果),少量添加的BaO可能易与二者发生以下反应,生成缺Fe3+和O的Ni(1-x)FexFe(2-2y)O(4-3y)、缺Ni和O的Ni(1-x-y)Fex′O(1-y),其中x ?1,y?1(下同)。
Ni(1-x)FexFe2O4+yBaO=
Ni(1-x)FexFe(2-2y)O(4-3y)+yBaFe2O4 (1)
Ni(1-x)FexFe2O4+2yBaO=
Ni(1-x)FexFe(2-2y)O(4-3y)+yBa2Fe2O5 (2)
Ni(1-x)Fex′O+3yBaO=Ni(1-x-y)Fex′O(1-y)+yNiBa3O4 (3)
根据Fe2O3-BaO和NiO-BaO二元相图,3种新物相在本实验的烧结温度下均为固相,烧结体系中不存在液相烧结现象,烧结性能的改善可能源于NiFe2O4相和NiO相颗粒中空位浓度的提高。NiFe2O4相为反尖晶石结构,Ni2+占据晶体中的B位,Fe3+占据晶体中的A位和部分B位。NiFe2O4和NiO晶体承受空位能力极强,1 300 ℃左右其空位浓度高达几个百分点时仍不会发生结构上的分解。反应(1)和(2)均可使得晶体中的A、B和O位的空位浓度同时提高,无论是体扩散还是表面扩散,高空位浓度促进各类离子依照相应的空位扩散机制进行的扩散迁移,加快NiFe2O4相颗粒烧结进程,即孔洞的球化与消失、晶粒的长大。类似现象同样出现在NiO相颗粒中。实验同时发现,进一步提高BaO的含量,由于BaFe2O4、Ba2Fe2O5和NiBa3O4等新物相颗粒的空间位阻作用加强和钉扎NiFe2O4相的晶界迁移,对烧结的负面效果逐步加强。
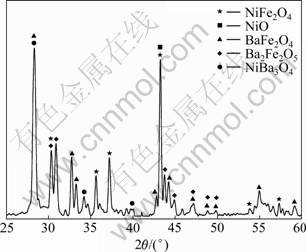
图2 BaO与NiFe2O4-10NiO界面层XRD谱
Fig.2 XRD pattern of interface of BaO and NiFe2O4-10NiO composite ceramics
图3和4所示分别为两组试样960 ℃电解10 h后的纵向形貌。图中显示,添加1%BaO使试样中的金属流失层的厚度分别由300~350 ?m降低到100~ 200 ?m(含10%Cu样品如图3所示)、400~500 ?m 降低到约300~400 ?m(含17%Cu样品如图4所示)。该结果表明,金属陶瓷烧结致密度的提高可防止内部金属相颗粒与电解质熔体的直接接触,有效抑制电解过程中金属相的选择性溶解腐蚀,从而阻止由于金属相的流失导致的电解质溶渗以及由此带来的阳极肿胀现象。
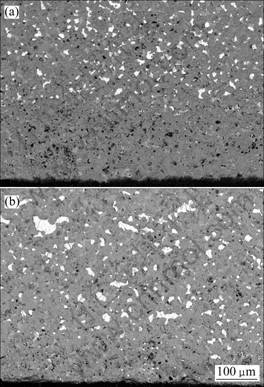
图3 金属陶瓷960 ℃电解10 h后的纵向SEM像
Fig.3 SEM backscattered images of cermets after electrolyzed at 960 ℃ for 10 h: (a) 10Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO); (b) 1BaO- 10Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO)
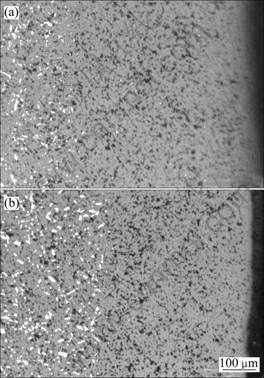
图4 金属陶瓷960 ℃电解10 h后的纵向金相照片
Fig.4 OM images of cermets after electrolyzed at 960 ℃ for 10 h: (a) 17Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO); (b) 1BaO-17Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO)
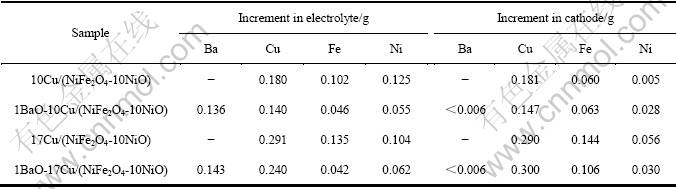
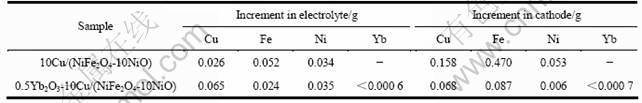
表2所列为电解10 h后电解质和阴极铝中阳极腐蚀元素的增加量。BaO虽可溶解进入电解质,但未在阴极析出。其添加显著降低Fe、Ni和Cu元素进入电解质和阴极的总含量,即有效地抑制金属陶瓷中各物相的电解腐蚀。
表2 金属陶瓷电解10 h后电解质和阴极铝中阳极腐蚀元素的增加量
Table 2 Net increments of elements of anode distributed in electrolyte and aluminum cathode after electrolyzed at 960 ℃ for 10 h
2.2 稀土氧化物强化陶瓷相晶界结构
相对陶瓷相晶粒而言,其晶界是易腐蚀区域。球化、减小甚至消除晶界气孔,强化界面结合,可有效提高金属陶瓷材料的耐蚀性能。许多研究证实在陶瓷材料中添加稀土氧化物可发送材料的烧结性能。经过分解电压[29]、溶解于电解质中的金属态Al对稀土氧化物和氟化物的反应热力学分析,选取CeO2、Y2O3、Yb2O3 3种氧化物进行NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷的掺杂研究。结果发现,添加0.5%~1.0% Yb2O3可显著改善材料的烧结和腐蚀性能。
图5所示为1 300 ℃烧结的未掺杂与2.0% Yb2O3掺杂17Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO)样品抛光后的SEM像。Yb2O3掺杂使孔洞尺寸减小,NiFe2O4相(深灰色)的晶界、NiFe2O4相与NiO相(浅灰色)的相界变得更平 直。图5(a)显示,NiFe2O4相的晶界处出现亮色的点状粒子,某些区域呈现由点状连成条的迹象;在Cu相和NiO相颗粒边缘,这些粒子的尺寸变大、亮度加强。这说明亮色粒子与NiFe2O4相的界面相容性好,能沿NiFe2O4相晶界铺展;而与Cu相和NiO相的相容性 差,团聚成较大颗粒。为避免新生物相在界面处团聚成膜,以致对材料力学和导电性能造成太大影响,Yb2O3的掺杂应适量。
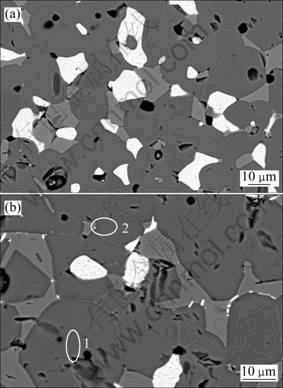
图5 1 300 ℃烧结未掺杂与2.0%Yb2O3掺杂17Cu/ ( NiFe2O4-10NiO)样品的SEM像
Fig.5 SEM images of 17Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) samples sintered at 1 300 ℃: (a) Without Yb2O3; (b) With 2.0% Yb2O3
对图5(a) 的能谱分析表明,Cu、NiO、NiFe2O4 3相中没有检测出Yb元素,图5(b)中亮色粒子1和2中含有一定量的Yb元素(见图6(b)),2点的Yb含量稍高,这可能是能谱分析时选区的影响。

图6 图5(b)中新生物相的EDX谱
Fig.6 EDX analysis of product in Fig.5(b): (a) Point 1; (b) Point 2
图7所示为1 300 ℃烧结的掺杂3.0%Yb2O3样品的XRD谱。分析表明:样品中除Cu、NiO、NiFe2O4 3相外,还出现了新物相。为清晰地表征新生物相,制备了高掺杂含量的试样,XRD结果显示,除原来的3个物相外,只出现正铁氧体化合物YbFeO3这一种新相(见图8)。这说明图7的新物相为YbFeO3相,这由Yb2O3、NiFe2O4和NiO相通过反应(4)和(5)生成。YbFeO3相的生成不可避免地使NiFe2O4相和NiO相中阴、阳离子的空位浓度增加,这与添加BaO的作用相似,Yb2O3的添加同样加速了材料的烧结致密化过程。
Ni(1-x)FexFe2O4+yYb2O3=
Ni(1-x)FexFe(2-2y)O(4-3y)+2yYbFeO3 (4)
Ni(1-x)Fex′O+yYb2O3=Ni(1-x)Fe(x′-2y)O(1-y)+2yYbFeO3 (5)
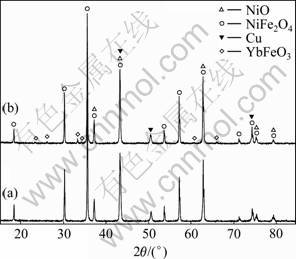
图7 未掺杂与掺杂3.0%Yb2O3的10Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) XRD谱
Fig.7 XRD patterns of 10Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) samples sintered at 1 300 ℃: (a) Without Yb2O3; (b) With 3.0%Yb2O3
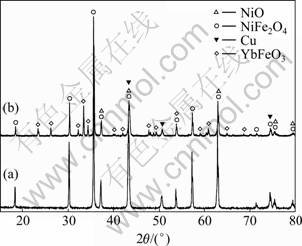
图8 未掺杂与掺杂10%Yb2O3 10Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO)的XRD谱
Fig.8 XRD patterns of 10Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) samples: (a) Without Yb2O3; (b) With 10%Yb2O3
图9所示为对比电解10 h后样品底部的SEM像。
由图9可知:未掺杂样品出现了一个厚度100~120 μm的Cu损失层;0.5% Yb2O3掺杂样品只在局部出现30~50 μm的无Cu层,一些区域没有明显的金属相颗粒流失的迹象。这表明0.5%Yb2O3的掺杂有效抑制了金属陶瓷的金属相电解过程中的流失。电解实验对电解质和阴极铝中杂质含量分析显示(见表3),0.5%Yb2O3掺杂与未掺杂样品相比,Cu、Ni和Fe的总杂质增量均减少1倍以上,尤其是Fe总杂质增量由未掺杂时的0.522 g(电解质和阴极铝中增量之和)降低到掺杂后的0.111 g。这表明,掺杂0.5%Yb2O3不仅抑制了金属陶瓷中金属相在电解过程中的流失,而且显著提高陶瓷相尤其NiFe2O4相的耐蚀性能。这是因为掺杂剂与陶瓷基体的反应生成物YbFeO3出现在晶/相界面,既提高了致密度(见图9),也强化了陶瓷相(尤其NiFe2O4相)晶粒界面结合,消除了晶界连通气孔,抑制了金属相的氧化与溶解和陶瓷相的晶界腐蚀。
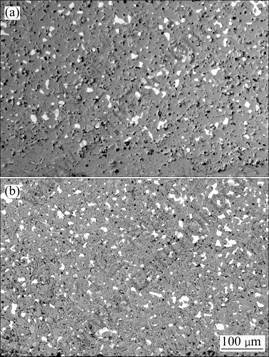
图9 电解10 h后样品底部的SEM像
Fig.9 SEM images of 10Cu/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) samples after electrolyzed for 10 h: (a) Without Yb2O3; (b) With 0.5%Yb2O3
表3 经1 300 ℃烧结金属陶瓷在960 ℃电解10 h后电解质和阴极铝中阳极腐蚀元素的增加量
Table 3 Net increments of elements from anode distributed in electrolyte and aluminum cathode after electrolyzed at 960 ℃ for 10 h of ceramic sintered at 1 300 ℃
2.3 CoO掺杂对NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷性能的影响
Ba2+和Yb3+的离子半径远远大于Ni2+和Fe3+的离子半径,以BaO和Yb2O3作为添加剂,两者并不能与基体中的NiFe2O4相和NiO相形成固溶体,而是在烧结过程中与其反应生成新的物相。Co2+与Ni2+的离子半径相近,以CoO作为添加剂,能与基体中的陶瓷相形成固溶体。图10所示为1 300 ℃烧结的未掺杂和掺杂10%CoO金属陶瓷的XRD谱,从图10可以看出, 掺杂10%CoO的15(20Ni-Cu)/(10CoO-NiFe2O4)金属陶瓷中并没有出现新的物相,这说明掺杂的CoO完全与NiFe2O4和NiO相形成了固溶体。
图11所示为1 300 ℃烧结的15(20Ni-Cu)/ [10(CoO-NiO)-NiFe2O4]金属陶瓷的相对密度随不同CoO掺杂量的变化曲线。从图11可以看出, 样品的相对密度随着CoO掺杂量的增加而不断增大,掺杂10%CoO的样品相对密度达到97.8%,与未掺杂样品的相对密度相比增加了0.7%,这说明掺杂CoO有利于该材料的烧结致密化。
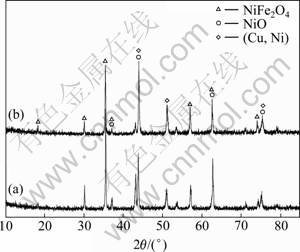
图10 1 300 ℃烧结的10%CoO金属陶瓷的XRD谱
Fig.10 XRD patterns of samples sintered at 1 300 ℃: (a) 15(20Ni-Cu)/(10NiO-NiFe2O4); (b) 15(20Ni-Cu)/(10CoO- NiFe2O4)
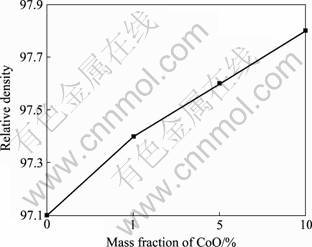
图11 CoO掺杂量对15(20Ni-Cu)/(NiO-NiFe2O4)金属陶瓷相对密度的影响
Fig.11 Effect of CoO content on relative densities of 15(20Ni-Cu)/(NiO-NiFe2O4)cermets
图12所示为CoO掺杂15(20Ni-Cu)/(NiO-NiFe2O4)金属陶瓷的电导率随温度的变化曲线。从图12可以看出,各成分金属陶瓷电导率均随温度升高而增大,符合半导体导电规律。且在同一温度下,随着CoO掺杂量的增加,样品的电导率不断增大。在960 ℃下,掺杂10%CoO金属陶瓷的电导率达到了53.04 S/cm,比未掺杂CoO样品电导率的43.35 S/cm提高了22%。这主要是由于空穴在Co2+和Co3+间跳跃的几率大于其在Ni2+和Ni3+间跳跃的几率引起的;另外,掺杂后样品相对密度的提高减小了电子和空穴的扩散阻力,进一步提高了样品的电导率。
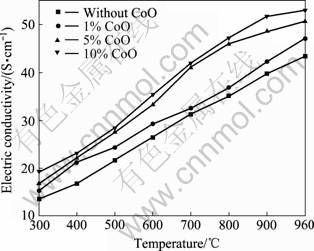
图12 CoO掺杂15(20Ni-Cu)/(NiO-NiFe2O4)金属陶瓷的电导率与温度的关系
Fig.12 Relationship between electric conductivity of CoO doped 15(20Ni-Cu)/(NiO-NiFe2O4) and temperature
图13所示为不同CoO掺杂量的15(20Ni-Cu)/ (NiO-NiFe2O4)金属陶瓷在960 ℃下电解12 h后阳极底部的SEM像。图13中均匀弥散的白色块状体为(Cu,Ni)复合金属相。未掺杂CoO样品的底部有一个约100 μm的腐蚀层,该腐蚀层内金属相已被完全腐蚀,留下较多孔洞,材料变得明显疏松。掺杂1.0%CoO的样品底部腐蚀层厚度约有80 μm,腐蚀后仍有较多的孔洞产生,这说明掺杂1%CoO由于含量较低,还未能有效抵挡电解质的侵蚀,样品的耐腐蚀性能仍然较差。掺杂5%CoO样品电解后存在一个厚度约40 μm的金属相损失层,该层内孔洞较样品芯部减少,比较致密,金属相的流失并未使材料出现严重腐蚀。这可能是由于CoO掺杂后,样品烧结相对密度提高,金属相与陶瓷相的润湿性有所改善,腐蚀后残留较小的二次孔洞,NiFe2O4吞噬NiO相的过程中体积膨胀,容易填补小孔洞形成的致密层,可以有效抵挡电解质对金属陶瓷的进一步腐蚀。当掺杂量为10%时,试样底部存在一个厚度约为130 μm的金属相损失层,该层疏松多孔,能谱分析表明,电解质通过这些孔洞已渗入阳极内部。这说明掺入过多的CoO会导致材料的耐腐蚀性能下降。
表4所列为未掺杂试样和掺杂5%CoO试样电解12 h后电解质和阴极铝中阳极腐蚀元素的增加量。从表4中可以看出,掺杂5%CoO试样电解后电解质和阴极铝中的Cu、Ni、Fe杂质含量明显降低,这表明添加适量的CoO可以有效抑制金属陶瓷中各物相的电解腐蚀。
2.4 金属相对NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷耐蚀性能的影响
NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷中金属相的引入是为了提高材料的导电和热震性能。金属相对材料性能的影响差异主要体现在烧结和腐蚀性能两个方面。烧结时,熔融态的纯Cu相颗粒易团聚和溢出,并导致二次孔洞的产生,固态Ni相颗粒虽能均匀地分布在陶瓷基体中,但其形状不会因陶瓷相颗粒烧结需要进行相应的调整,同样不利于材料的烧结致密化。在电解过程中,Cu相的耐蚀性能优于Ni相的,次表层的Cu相先转变为氧化物再腐蚀,Ni 相从外向内一直进行选择性溶解[30]。因此,优化金属相的Cu/Ni配比可获得较好的综合结构与性能。
图14所示为一组金属含量为17%、金属粉末初始平均粒度相当(约8 μm)经1 300 ℃烧结试样的金相照片。17%Ni的样品制备过程中出现金属相颗粒团聚成条片状的现象,孔洞多为球形闭孔,说明烧结过程一直为固相的Ni颗粒存在不利于陶瓷基体的烧结,孔洞难以消除。17%Cu样品孔洞也较多,较多孔洞密集分布在Cu颗粒附近,这说明烧结过程中Cu相迁移团聚产生二次孔洞,不利于材料的致密化。在以Cu、Ni混合粉为金属相的样品中,金属颗粒附近同样出现较大孔洞。以Ni包Cu粉的形式加入时,样品烧结结构明显改善,孔洞的尺寸和数量较其它样品有所降 低,这表明在Cu相中加入与多种陶瓷润湿性好的Ni元素可改善Cu相与NiO及NiFe2O4相的润湿性,抑制烧结过程中熔融金属相颗粒的流动迁移,减少二次孔洞的形成,同时熔融金属相颗粒形貌的易调整,对陶瓷基体烧结的负面影响程度降低。陶瓷基体的良好烧结预期将有良好的耐蚀性能。

图13 金属陶瓷电解试样底部腐蚀区域的SEM像
Fig.13 SEM images of electrolyzed samples: (a) Without CoO; (b) With 1.0% CoO; (c) With 5.0% CoO; (d) With 10.0% CoO
表4 1 300 ℃烧结金属陶瓷960 ℃电解10 h后电解质和阴极铝中阳极腐蚀元素的增加量
Table 4 Net increments of elements from anode distributed in electrolyte and aluminum cathode after electrolysis at 960 ℃ for 10 h
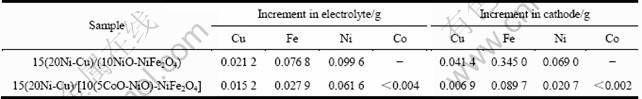
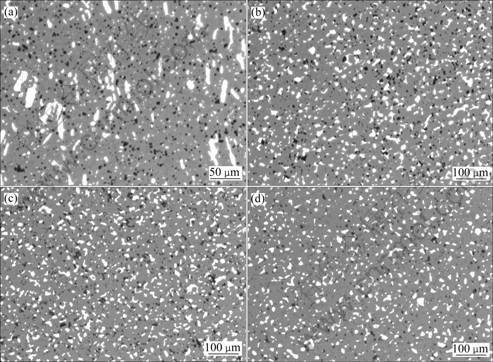
图14 金属相含量为17%时10NiO-NiFe2O4金属陶瓷的金相照片
Fig.14 OM photographs of 10NiO-NiFe2O4 cermets with 17% metal phase added by Ni(a), Cu(b), Cu-10Ni mixture(c) and 10Ni coated Cu(d)
从17(10Ni-Cu)(10NiO-NiFe2O4)经960 ℃电解40 h后的剖面SEM像中(见图15)可以看出,尽管在阳极底面及电解质浸渍的侧面边缘分别出现约140 μm和60 μm的金属相流失层,且NiO相也消失了,但该层已转变为较致密的、3种物相中最耐腐蚀的NiFe2O4相,对材料的耐电解腐蚀性能更有利。
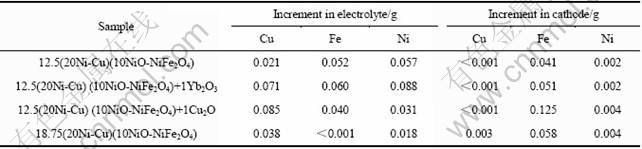
鉴于金属相为Cu-Ni合金的NiFe2O4相金属陶瓷电解时能在表面形成致密的NiFe2O4相层,在960 ℃下进行一组样品10 h电解实验,分析电解过程中阳极组元的腐蚀情况。表5所列为电解质和阴极在电解过程中新增杂质含量。与表2和3的数据相对比,当金属相为Cu-Ni合金时,电解过程Cu进入电解质和阴极的总量,尤其进入阴极的量显著降低。同时,进入阴极的Ni含量也明显减少、Fe含量有一定程度的降低。由此可见,不仅金属相的选择性溶解受到良好的抑制,陶瓷相的溶解速率也有不同程度的降低,这应归结于金属陶瓷烧结性能的提高。

图15 17(10Ni-Cu)/(NiFe2O4-10NiO)金属陶瓷960 ℃下电解40 h后的SEM像
Fig.15 SEM images of 17(10Ni-Cu)/(NiFe2O4-10NiO) cermets after electrolyzed at 960 ℃ for 40 h: (a) Bottom; (b) Side face
表5 Cu-Ni金属相样品经960 ℃电解10 h后电解质和阴极铝中阳极腐蚀元素的增加量
Table 5 Net increments of elements in electrolyte and aluminum cathode after electrolyzed at 960 ℃ for 10 h
3 结论
1) NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷体系添加适量的BaO或Yb2O3时,烧结过程中添加剂与陶瓷基体相反应生成新物相BaFe2O4、Ba2Fe2O5、NiBa3O4或YbFeO3,新物相的生成提高了陶瓷相的烧结活性,加速了金属陶瓷的烧结致密化进程。
2) NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷体系添加适量的CoO,可与陶瓷基体形成固溶体,加速金属陶瓷材料的烧结致密化进程,有效提高材料的导电性能和耐腐蚀性能。
3) 相对于Cu、Ni金属相,以Cu-Ni合金作NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷的金属相组元时,金属相颗粒流动迁移的抑制、相界面润湿性的提高、颗粒形貌易于调整等因素有助于减少烧结过程中二次孔洞的形成,易获得高致密度的烧结体。
4) 高致密度烧结的NiFe2O4基金属陶瓷电解过程中表面可生成由高耐蚀物相NiFe2O4组成的致密层,抑制因金属相颗粒优先溶解所带来的电解质熔体的渗透,减缓各物相的腐蚀速率。
REFERENCES
[1] KENIRY J. The economics of inert anodes and wettable cathodes for aluminum reduction cells[J]. JOM, 2001, 53(5): 43-47.
[2] SADOWAY D R. Inert anodes for the Hall-Héroult cell: The ultimate materials challenge[J]. JOM, 2001, 53(5): 34-35.
[3] LI Jie, LAI Yan-qing, ZHOU Ke-chao, LI Zhi-you, LIU Ye-xiang. Preparation and preliminary testing of cermet inert anode for aluminum electrolysis[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2003, 13(3): 663-670.
[4] ROBERT L K, SIBA P R, ROBERT K D, ALFRED F L. Corrosion of cermet anodes during low temperature electrolysis of alumina[R]. Washington: Alcoa technical center, 1997.
[5] JOHN Y. Inert anode metal life in low temperature aluminum reduction process[R]. Washington: Goldendale Aluminum Company, 2003.
[6] PAWLEK R P. Inert anodes: an update[C]//Wolfgang Schneider. Light Metals 2002. Warreudale PA. USA: TMS, 2002: 449-456
[7] PAWLEK R P. Inert anodes: an update[C]//ALTON T. Tabereaux. Light Metals 2004. Warreudale PA. USA: TMS, 2004: 283-287.
[8] ANTIPOV E V, BORZENKO A G, DENISOV V M, FILATOVET A Y, IVANOV V V, KAZAKOV S M, MAZIN P M, MAZIN V M, SHTANOV V I, SIMAKOV D A, TSIRLINA G A, VASSILIEV S Y, VELIKODNY Y A. Electrochemical behavior of metals and binary alloys in cryolite-alumina melts[C]// TRAVIS J G. Light Metals 2006. Warreudale PA: TMS, 2006: 403-408.
[9] PAWLEK R P. Aluminum wettable cathodes: An update[C]// PETERSON R D. Light Metals 2000.Warrendale PA: TMS, 2000: 449-454
[10] CHIN P C, SIDES P J, KELLER R, The transfer of nickel, iron, and copper from Hall cell melts to molten aluminum[J]. Canada Metall Q, 1996, 35: 61.
[11] YANG Y H, JOHN N H, GREG K K. Aluminum electrolysis tests with inert anodes in KF-AlF3-based electrolytes[C]//Travis Galloway. Light Metals 2006. Warrendale PA. USA: TMS, 2006: 421-424
[12] NGUYEN T, DE NORA D V. Oxygen evolving inert metallic anode[C]//TRAVIS J. Galloway, Light Metals 2006. Warrendale PA, USA: TMS, 2006: 385-390.
[13] KAENEL R, NORA D V. Technical and economical evaluation of the de NORA inert metallic anode in aluminum reduction cells[C]//TRAVIS J. Light Metals 2006. Warrendale PA, USA: TMS, 2006: 397-402.
[14] SEKHAR J A, NORA V, LIU J, WANG X. TiB2/colloidal alumina carbon cathode coating in Hall-Heroult and drained cells [C]//WELCH B. Light Metals 1998. Warrendale PA, USA: TMS, 1998: 605-615.
[15] OLSEN E, THONSTAD J. The behaviour of nickel ferrite cermet materials as inert anodes[C]//HALE W. Light Metals 1996. Warrendale PA, USA: TMS, 1996: 249-257.
[16] OLSEN E, THONSTAD J. Nickel ferrite as inert anodes in aluminum electrolysis (PartⅠ): Material fabrication and preliminary testing[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 29(3): 293-299.
[17] ISSAEVA L, YANG Jian-hong, HAARBERG G M, THONSTAD J, AALBERG N. Electrochemical behavior of tin species dissolved in cryolite-alumina melts[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1997, 42(6): 1011-1018.
[18] THONSTAD J, SOLHEIM A. The use of strongly acid low melting bath in aluminium electrolysis[J]. Aluminium, 1986, 12: 938-941.
[19] MARK G, MARGARET H. Cu-Al alloy as an anode for aluminum electrowinning[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48: 2457-2469.
[20] 赖延清, 张 勇, 张 刚, 李 劼, 贺跃辉, 黄伯云, 刘业翔. CaO掺杂对10NiO-NiFe2O4复合陶瓷烧结致密化的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(8): 1355-1360.
LAI Yan-qing, ZHANG Yong, ZHANG Gang, LI Jie, HE Yue-hui, HUANG Bai-yun, LIU Ye-xiang. Effect of CaO doping on densification of 10NiO-NiFe2O4 composite ceramics[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(8): 1355-1360.
[21] LAI Yan-qing, TIAN Zhong-liang, LI Jie, YE Shao-long, LI Xin-zheng, LIU Ye-xiang. Results from 100 h electrolysis testing of NiFe2O4 based cermet as inert anode in aluminum reduction[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16: 970-974.
[22] HE Han-bing, ZHOU Ke-chao, LI Zhi-you, HUANG Bai-yun. Effect of BaO addition on electric conductivity of xCu/10NiO-NiFe2O4 cermets[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(5): 1134-1138.
[23] 张 雷, 周科朝, 李志友, 张晓泳. 气氛对NiFe2O4陶瓷烧结致密化的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(6): 1002-1006.
ZHANG Lei, ZHOU Ke-chao, LI Zhi-you, ZHANG Xiao-yong. Effect of atmosphere on densification in sintering nickel ferrite ceramic for aluminum electrolysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(6): 1002-1006.
[24] LI Jie, L? Xiao-jun, LAI Yan-qing, LI Qing-yu, TIAN Zhong-liang, FANG Zhao. Effect of carbon fibre on properties of TiB2/C composite cathode coating for aluminum electrolysis[J]. Jounal of Central South University of Technology, 2008, 15: 526-530.
[25] 石忠宁, 徐君莉, 邱竹贤, 舒方霞. 低温铝电解用Cu-Ni-Cr金属阳极性能研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2004, 24(6): 45-47.
SHI Zhong-ning, XU Jun-li, QIU Zhu-xian, SHU Fang-xia. Research on the properties of Cu-based metal anodes for aluminum electrolysis cell at low temperature[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2004, 24(6): 45-47.
[26] 焦万丽, 张 磊, 姚广春, 刘宜汉. NiFe2O4及添加TiO2的尖晶石的烧结过程[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2004, 32(9): 1150-1153.
JIAO Wan-li, ZHANG Lei, YAO Guang-chun, LIU Yi-han. Sintering process of NiFe2O4 spinel with and without TiO2 adding[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2004, 32(9): 1150-1153.
[27] 席锦会, 姚广春, 刘宜汉. 添加物对镍铁尖晶石惰性阳极微观结构和性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 26: 574-577.
XI Jin-hui, YAO Guang-chun, LIU Yi-han. Effect of additives on microstructure and properties of inert anode of NiFe2O4 spinel[J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 2005, 26: 574-577.
[28] ALCORN T R, TABEREAUX A T, RICHARDS N E. Operational results of pilot cell test with cermet "inert" anodes[C]//CHRISTIAN M B. Light Metals 1993. Warrendale PA. USA: TMS, 1993: 433-445.
[29] 朱元保, 沈子琛, 张传福. 电化学数据手册[M]. 长沙: 湖南科学技术出版社, 1985: 338-339.
ZHU Yuan-bao, SHEN Zi-chen, ZHANG Chuan-fu. Electrochemical data handbook[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 1985: 338-339.
[30] STRACHAN D M, KOSKI O H, MORGAN L G, WESTERMAN R E, PETERSON R D, RICHARDS N E, TABEREAUX A T. Results from a 100-hour electrolysis test of a cermet anode: material aspects[C]//CHRISTIAN M B. Light Metals 1990. Warrendale PA, USA: TMS, 1990: 395-401.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家高技术研究发展计划资助项目(2008AA030501);国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2005CB623703);国家自然科学创新团队资助项目(51021063)
收稿日期:2010-06-18;修订日期:2010-09-20
通信作者:周科朝,教授,博士;电话:0731-88836264;E-mail: zhoukechao@mail.csu.edu.cn