海相碎屑岩储层微观非均质性特征及其对高含水期剩余油分布的影响
孙廷彬1,林承焰1,崔仕提2,张曙振2,王平2,王玲3
(1. 中国石油大学(华东) 地球科学与技术学院,山东 青岛,266555;
2. 中国石油塔里木油田分公司 勘探开发研究院,新疆 库尔勒,841000;
3. 中石化中原油田博士后工作站,河南 濮阳,457001)
摘要:利用岩心精细描述、铸体薄片图像分析和X线衍射黏土矿物分析等手段,对TLM盆地A油藏石炭系下部海相碎屑岩储层的微观非均质性进行研究,并通过真实岩心水驱油实验研究微观非均质性对剩余油分布的影响。研究认为:基于孔隙与喉道类型、孔喉组合类型和微观结构类型3个层次内容,研究区储层的微观非均质性可划分为Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型3种类型。其中,Ⅰ型非均质具有均质粗粒结构,发育次生溶蚀型和原生孔隙型2种孔喉组合。在驱油过程中,非均质内绕流现象明显,剩余油呈斑块状富集;Ⅱ型非均质具有钙质斑块粗粒结构,发育次生溶蚀型和次生钙质斑块型孔喉组合。驱油过程中,受钙质斑块遮挡作用影响,非均质内剩余油呈斑块状富集;Ⅲ型非均质发育均质细粒结构和原生孔隙型孔喉组合,驱油效果差,剩余油呈连片状分布。3种非均质类型中,Ⅰ型非均质剩余油所占比例最大,Ⅱ型次之,Ⅲ型最小。在纵向上,油层非均质自下而上具有Ⅲ型—Ⅱ型—Ⅰ型的演化特点。在平面上,从研究区的西北部到东南部,Ⅰ型非均质剩余油所占比例逐渐增加,Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型非均质剩余油所占比例逐渐减少。
关键词:海相碎屑岩储层;微观非均质性;孔喉组合;微观结构;剩余油分布
中图分类号:TE343 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)08-3282-11
Microscopic heterogeneity characteristics of marine clastic reservoirs and effect to remaining oil distribution in high water cut stage
SUN Tingbin1, LIN Chengyan1, CUI Shiti2, ZHANG Shuzhen2, WANG Ping2, WANG Ling3
(1. School of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum, Qingdao 266555, China;
2. Exploration and Development Research Institute of Petrochina TarimOilfield Company, Korla 841000, China;
3. Postdoctoral Work Station of Zhongyuan Oil Company, SINOPEC, Puyang 457001, China)
Abstract: Using core fine description, cast thin section image analysis and X-ray diffraction of clay minerals and other means, the microscopic heterogeneity of marine clastic reservoir of lower Carboniferous reservoir in TLM basin was studied, and through the real core water flooding experiment the influence of micro-heterogeneity on the remaining oil distribution was analyzed. The study suggests that, depending on the type of pore throat, the pore throat portfolio type and microstructure type, microscopic heterogeneity of the reservoir can be divided into three types of type I, type II and III. Type I heterogeneous has homogeneous coarse-grained structure, and has the development of two pore throat combination types of secondary dissolution type and primary porosity type. In the Flooding process, the phenomenon of flow around is obvious, and it has a patchy remaining oil enrichment in this heterogeneous type. Type Ⅱ heterogeneity has calcium plaque coarse structure, and develops two pore throat combination types of secondary dissolution type and secondary calcium plaque-type. In the process of oil displacement, by effect of calcium plaque shelter, the remaining oil within heterogeneity was patchy enrichment. Type Ⅲ heterogeneous develops homogeneous fine-grained structure and primary porosity pore throat combination, and the remaining oil was even patchy distribution. Among the three heterogeneous types, type I heterogeneous has the largest residual oil ratio, type II followed, typeⅢ being minimum. Vertically, there is a evolution of type Ⅲ to typeⅡ to typeⅠ bottom-up, and the thickness is successively larger from type Ⅲ to typeⅠ. On the plane, the proportion of remaining oil of type I heterogeneity is gradually increased from the northwest to the southeast of the study area, and it is the opposite for type II and type Ⅲ heterogeneous.
Key words: marine clastic reservoirs; microscopic heterogeneity; pore throat combination; heterogeneity structure; residual oil distribution
剩余油分布受构造特征、储层特征等地质因素以及开发井网、注水方式等开发因素共同影响,其中地质因素是根本因素,特别是储层的非均质性。在陆相油藏中,剩余油分布主要受平面[1-2]和层间强非均质性[3-4]影响,表现为层间差异大[5]、平面分布极不均匀[2]。而海相碎屑岩储层往往具有岩性单一、厚度大、平面连续性好、垂向上隔夹层少的特点,表现出较弱的平面和层间非均质性。但是,受多种成岩作用影响,其微观非均质性比较突出。在油层开发过程中,微观非均质性控制了油层中油、水的渗流特征,对水驱剩余油分布具有重要影响。TLM盆地A油藏石炭系底部油层于1990年被发现,为一套海相沉积的厚度碎屑岩段,目前处于水驱开发特高含水阶段。目前,相关的公开发表文献主要是对地层[6-8]、沉积[9-11]、储层[11]和成岩作用[12-16]方面的研究,且多为盆地规模或区域规模,没有针对研究区目的油层的细致研究,尤其在开发地质及剩余油分布方面,研究比较薄弱。作者综合分析研究区内钻遇油层顶部的检查井岩心分析化验资料、水淹解释结果及油藏数值模拟结果后认为,该油层目前整体高水淹,剩余油分布高度分散。油藏内高水淹层位剩余油的微观赋存状态、分布规律认识不清,严重阻碍了下一步的剩余油挖潜。因此,本文作者通过铸体薄片资料、压汞曲线测试资料和岩心分析化验资料的综合分析,对储层微观非均质的特征、类型和分布特征进行研究。并结合真实储层岩心水驱油实验,总结剩余油分布规律和剩余油潜力,为下一步剩余油挖潜奠定基础。
1 油藏概况
图1所示为研究区概况。图2所示为J3井综合柱状图。A油藏位于西部TLM盆地的中央隆起带上,为构造-底水块状油气藏,含油面积19.7 km2(见图1)。目的油层归属一直存有争议,有学者认为,从古生物学的角度讲为油层应属于晚泥盆系[6],有学者从盆地演化的角度属于石炭纪初期海侵底部沉积[10]。本次研究对地层不做讨论,将油层归为石炭系Ⅲ油组下部6~12小层(见图2)。油层为海相滨岸环境沉积的厚层均质砂岩段[9],顶界埋深3 500~3 700 m,平均厚度大于100 m,平面连续性好。油层岩石类型单一,以细砂岩、中砂岩为主,平均孔隙度17.5%,平均渗透率256×10-3 μm2。油层1995年进入整体开发阶段,目前含水大于90%,处于停产状态。
前人研究认为,目的油层在沉积埋藏过程中,经历过2次大规模的次生溶蚀和多期次钙质胶结[10, 12],目前处于成岩演化中的晚成岩A期[11]。受多期次生溶蚀作用和钙质胶结作用影响,油层中石英次生加大[14]、石英与长石等颗粒溶蚀现象[12]以及多世代钙质胶结等现象非常普遍,显示了较强的微观非均质性。
2 岩石学特征
储层岩石表现为接触式胶结,颗粒间线接触为主。颗粒多为次圆状、圆状、次棱角状,分选较好,结构成熟度高。岩石矿物组分中石英含量高,平均为70.5%,最高可达97%,岩屑平均含量20.2%,长石含量小于10%,成分成熟度高。储层中胶结物含量低,平均为5.65%,主要成分为泥质、钙质和云质。其中,泥质占76%,呈薄膜状分布在颗粒边缘。钙质和云质胶结物合占23%,呈斑点状分布。
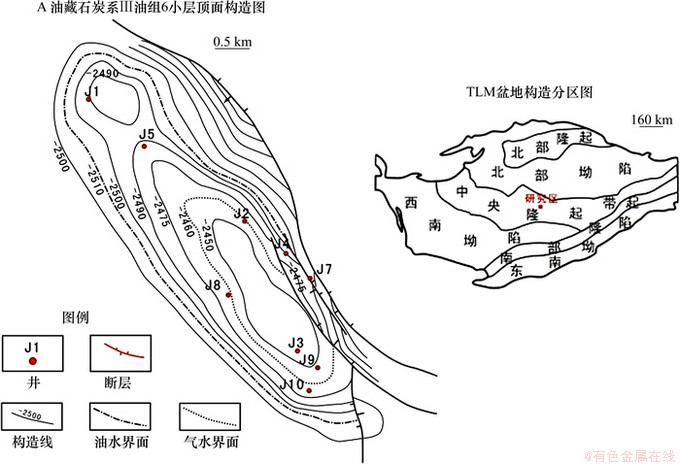
图1 研究区概况
Fig. 1 Location map of study area
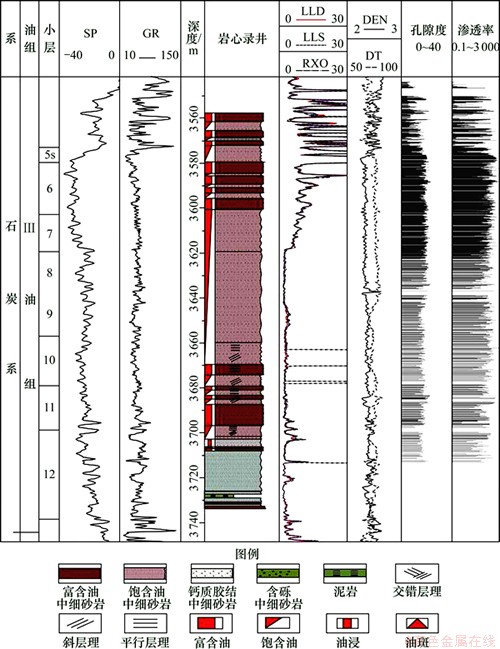
图2 J3井综合柱状图
Fig. 2 J3 well integrated histogram
3 微观非均质性特征
通过显微镜下观察发现,储层中存在一些细小尺度的非均质结构,如颗粒尺寸及排列方式差异造成的孔喉差异分布、局部钙质胶结形成的钙质斑块结构、差异溶蚀作用形成的次生孔隙发育区与原生孔隙发育区的交互分布等。这类非均质结构在非均质尺度上处于宏观岩心级别与微观孔隙级别之间,肉眼难以识别,且通过宏观的孔隙度、渗透率等参数以及传统的层内非均质性描述等研究手段都难以对其进行准确表征。此外,目前公开发表的文献中,也无这方面内容的系统研究和评价。本次研究将其定为微观非均质的研究内容,并将其划分孔喉组合和微观结构2个层次。最终,将微观非均质性的研究内容分为孔隙与喉道、孔喉组合和微观结构3个层次。
3.1 孔隙与喉道
3.1.1 孔隙特征
表1所示为A油藏石炭系底部油层孔隙类型参数。图3所示为孔隙和喉道类型。镜下铸体薄片观察结果表明,目的油层发育原生孔隙、次生孔隙2个大类(表1和图3)。
(1) 原生孔隙为经过压实作用后储层内剩余的粒间孔隙。多呈规则的三角形、四边形,边缘规则。孔隙直径小,连通性差,分布较广,在研究区平均占51.3%。
(2) 次生孔隙这在次生溶蚀、钙质胶结等作用改选后形成的孔隙空间。孔隙形状多不规则,孔隙直径大,在目的油层中平均占48.7%。根据成因,研究区内次生孔隙可划分为溶蚀次生孔隙、压实变形次生孔隙2种类型。
溶蚀次生孔隙是经过次生溶蚀改造形成的孔隙空间。根据溶蚀部位和溶蚀程度的不同,研究区内溶蚀次生孔隙可分为粒间扩大溶孔、铸模孔、粒内溶孔和石英次生加大溶孔4种类型。粒间扩大溶孔是由原始粒间孔隙向外扩大溶蚀骨架颗粒后形成的粒内孔隙空间,形态不规则,平均孔隙半径大,连通性最好,平均占42%,是研究区内分布最为广泛的一种次生孔隙类型;铸模孔隙为单个骨架颗粒整体溶蚀后留下的孔隙空间,形状规则、孔壁圆滑,平均占2.3%;粒内溶孔为长石、岩屑等颗粒发生差异溶蚀后形成的粒内孔隙空间,为不规则小孔,连通性差,平均占1.6%;石英次生加大溶孔是石英颗粒边缘次生加大边差异溶蚀形成的孔隙空间,多呈锯齿状、港湾状,在研究区平均占1.8%。
压实变形次生孔隙是长石、云母等解理矿物在压实作用下沿解理缝张裂形成的孔隙空间,孔隙空间小,连通性中等,平均占1%。
3.1.2 喉道特征
喉道是孔隙之间的相对狭窄部分,在研究区内共识别出孔隙缩小型、缩颈型、片状或弯片状3种喉道类型(图3)。
孔隙缩小型喉道:为大孔隙内的缩小部分,具有喉道宽度大、毛细管阻力小、连通性好的特点。该类喉道有2种成因,一种是先期钙质胶结抑制了压实作用,后期钙质发生溶解形成;另外一种是储层经历强烈的溶蚀作用后,细喉道发生扩大溶蚀形成。在研究区所占比例较小,平均为7.7%。
表1 A油藏石炭系底部油层孔隙类型参数
Table 1 Pore type parameter of reservoir lower Carboniferous reservoir
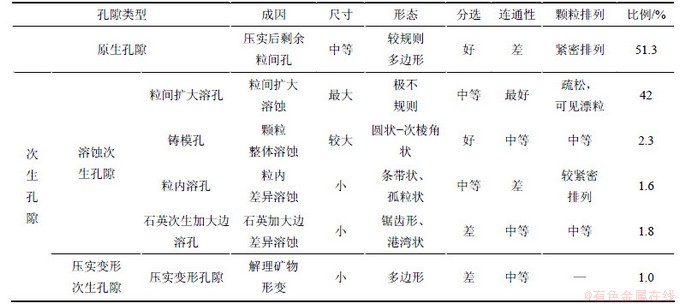
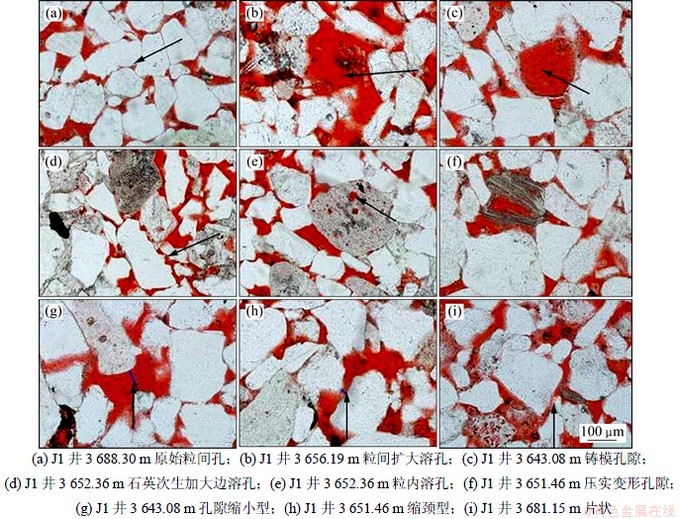
图3 孔隙和喉道类型
Fig. 3 Different pore and throat types
缩颈型喉道:喉道较细,具有一定的毛细管力,连通性中等。缩颈型喉道的成因有2种:一种是局部欠压实保留的细小喉道,另外一种为压实后颗粒边缘局部溶蚀形成的宽喉道。该类喉道类型分布广泛,是研究区的主要喉道类型,平均占89.8%。
片状、弯片状喉道:喉道为狭窄的片状、弯片状,毛细管阻力大,连通性差,平均占2.5%。这种喉道与强压实后的局部溶蚀作用有关。
对比分析结果表明:原生孔隙发育区以缩颈型为主,而次生孔隙发育区以孔隙缩小型、缩颈型2种类型为主。
3.2 孔喉组合特征
孔喉组合是指在一定范围内同类孔隙、喉道的集中分布。这种组合反映了局部范围内孔隙与喉道类型、二者配置及连通关系的特殊性。其大小为几百微米到几毫米,在非均质的研究内容中比单个孔隙高一个级别。
研究区的孔喉组合根据成因和孔喉组合形式可分为次生溶蚀型、次生钙质斑块型和原生孔隙型3种类型,见图4。
(1) 次生溶蚀型:孔隙类型主要为粒间扩大溶孔,还包括少量的铸模孔隙、粒内溶孔和石英次生加大边溶蚀孔隙,平均孔隙半径大,配位数高。喉道类型多为孔隙缩小型和缩颈型,毛细管阻力小,连通性最好。该类孔喉组合多呈连片状、枝状分布,平均占53.4%。
(2) 原生钙质斑块型:是由次生钙质胶结作用形成的孔喉组合类型,大小从几百微米到几毫米级,在研究区占15.9%。钙质胶结呈斑块状,内部孔隙90%被钙质充填,10%为半充填或是为充填状态,边缘孔隙为单侧充填后向外开口的盲端孔隙,配位数低,连通性差。
(3) 始孔隙型:孔隙类型以原始粒间孔隙为主,次生孔隙较少,平均孔隙半径小,配位数低。喉道类型多为缩颈型,毛细管阻力大,连通性差。该类孔喉组合分布较广,平均占30.6%。
3.3 微观结构特征
微观结构是由一种或是多种孔喉组合按照一定方式组合而成的特殊结构,比孔喉组合高一个层次,为毫米到厘米级。这种微观结构与颗粒的粒度和排列方关系密切。
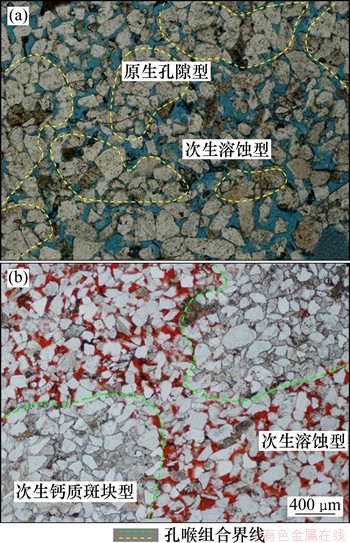
图4 同孔喉组合类型分布示意图
Fig. 4 Distribution diagram of different pore throat combination type
研究区内共识别出均质粗粒结构、钙质斑块粗粒结构和均质细粒结构3类微观结构,见图5。
(1) 均质粗粒结构是一种颗粒粗、分选好的均质结构,表现为孔隙大、喉道粗,渗透性好,在研究区分布最广,平均占42%。该结构中次生孔隙十分发育,具有次生溶蚀型和原生孔隙型2种孔喉组合类型。其中,次生溶蚀型孔喉组合呈网、枝状和不规则片状分布,平均占70%,原生孔隙型孔喉组合呈不规则的片状、椭圆状或条带状分布,平均占30%。
(2) 钙质斑块粗粒结构是局部发生斑状钙质胶结后形成的非均质结构。该类结构颗粒较粗,分选较好,局部的钙质胶结斑块直径为0.4~2 mm,造成超大颗粒假象。该类微观结构中发育次生钙质斑块型和次生溶蚀型2种孔喉组合类型。其中,次生钙质斑块型主要呈斑点状分散分布,所占比例在35%~75%之间,平均60%。次生溶蚀型孔喉组合呈网状、枝状分布,平均占40%。钙质斑块粗粒结构在研究区分布较广,平均占35.5%。
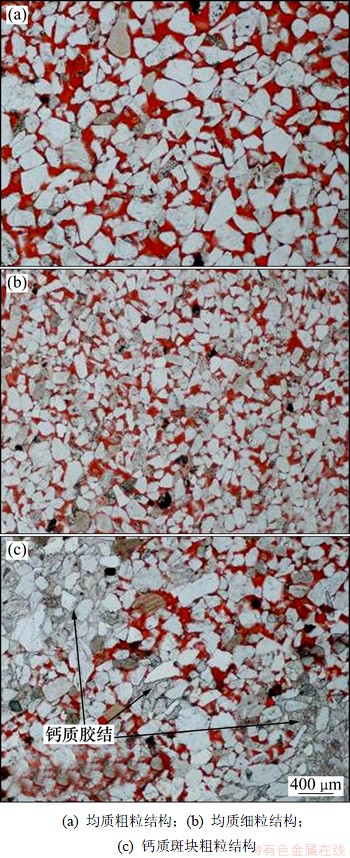
图5 微观结构类型示意图
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of microscopic structure type
(3) 均质细粒结构是一种颗粒较细、分选较好的均质结构。孔隙类型以原生孔隙为主,孔隙小、配位数低,渗透性差。孔喉组合类型为原生孔隙型和次生溶蚀型2种,其中原生孔隙型占90%,次生溶蚀型占10%。均质细粒结构在研究区分布最少,平均仅占22.6%。
3.4 微观非均质类型及分布特征
研究区井网稀且不规则,钻穿目的层的仅有3口探井,其他井仅钻遇油层顶部。本次研究充分利用3口探井的连续取芯资料,根据岩心精细描述和铸体薄片观察结果,建立非均质类型与不同岩性段之间对应关系。在此基础上,结合铸体薄片图像分析结果得到的孔隙类型含量及碳酸盐岩含量数据对单井非均质类型进行划分。最终,通过纵向演化和横向对比分析,研究了储层微观非均质的空间展布规律。
3.4.1 微观非均质类型
根据微观孔隙类型、孔喉组合以及微观结构3个方面特征,研究区的微观非均质可分为Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型3种类型,见表2。
图6所示为储层微观非均质分布。Ⅰ型非均质表现为大孔粗喉,次生孔隙所占比例高,孔隙性、渗透性好。该类非均质具有均质粗粒结构,发育次生溶蚀型和原生孔隙型两种孔喉组合类型。Ⅰ型非均质分布在2种岩性段中:一种是块状富含油或饱含油中细砂岩段,碳酸盐胶结物含量为0或接近于0,分布在目的层的上部(图6)。Ⅰ型非均质在该岩性段中占100%;另一种是无钙质胶结的平行层理、斜层理及交错层理砂岩段,分布在研究区下部(图6)。其中,Ⅰ型非均质对应其中的粗粒纹层段。该层理砂岩段中粗、细粒纹层段为近似等厚互层,粗粒纹层段中夹有50%的细粒薄夹层。Ⅰ型非均质在该层段中占25%。
Ⅱ型非均质的突出特征在于钙质胶结比较发育,孔隙性、渗透性较好。此类非均质具有钙质斑块粗粒结构,且发育次生溶蚀型和次生钙质斑块型2种孔喉组合类型。Ⅱ型非均质分布在2种岩性段中,一种是斑点状钙质胶结细砂岩段(图6,典型岩性特写),碳酸盐胶结物含量为5%~30%不等,呈白色斑点状均匀分布,位于目的油层的中部和下部(图6);一种是发育钙质胶结的平行层理、斜层理及交错层理中细砂岩段。其中,Ⅱ型非均质对应其中的粗粒纹层段,在该岩性段中占25%,碳酸盐胶结物含量为5%~30%。Ⅱ型非均质中钙质团块的形态及特征因碳酸盐胶结物含量的不同而有所差别。当碳酸盐胶结物含量在8%以上时,钙质斑点直径在1~4 mm之间,可肉眼观察。当碳酸盐胶结物含量小于8%时,钙质斑点小,最小直径可达0.2 mm,需要凭借显微镜进行观察。
Ⅲ型非均质以原生孔隙为主,次生孔隙较少,孔隙性和渗透性较差。该类非均质具有均质细粒结构,且主要发育原生孔隙型孔喉组合,次生溶蚀型较少。在研究区,Ⅲ型非均质分布在平行层理、斜层理及交错层理细砂岩段(图6,典型岩性特写)中,对应其中的细粒纹层段,分布在目的油层下部(图6)。Ⅲ型非均质在“层理细砂岩段”中占75%。
3.4.2 微观非均质分布特征
在研究区的不同井、不同层位,储层微观非均质性分布各有特点,且不同微观非均质、微观结构、孔喉组合类型所占比例也不相同。本次研究根据岩心描述得到的各井岩性序列及各岩性段所占比例,经过计算可以得到各岩性段在各井中所占比例及纵向分布特征(表2)。然后,根据不同层次非均质性间的比例关系(表2),经过计算可以得到各层次非均质在整个研究区分布特征。
结果表明,研究区内Ⅰ型非均质所占比例最高,为42%,Ⅱ型非均质次之,为35.5%,Ⅲ型非均质最少,为22.6%。微观结构类型与微观非均质类型为一一对应关系,其中,均质粗粒结构所占比例最高,钙质斑块粗粒结构次之,细粒均质结构最低。研究区各类孔喉组合中,次生溶蚀型最多,占53.4%,原生孔隙型次之,占30.6%,次生钙质斑块型最少,占15.9%。
表2 微观非均质性参数
Table 2 Parameters of microscopic heterogeneity types
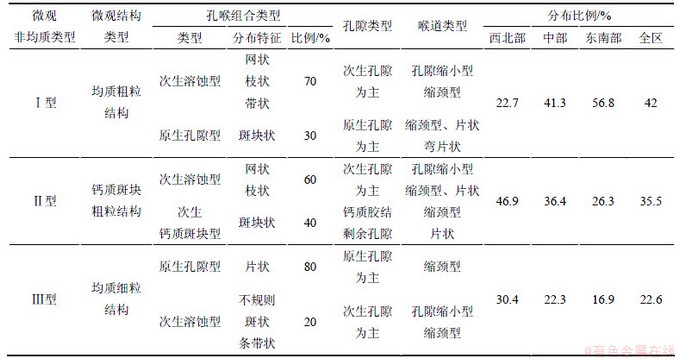
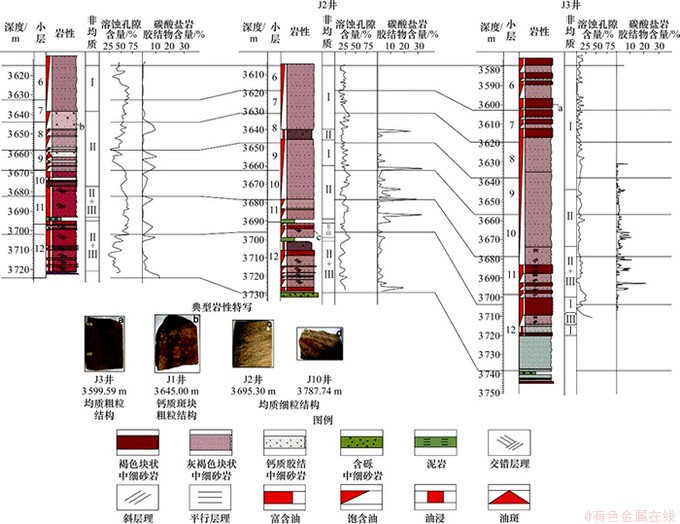
图6 储层微观非均质分布
Fig. 6 Microscopic reservoir heterogeneity distribution map
从空间分布上看,研究区不同地区各类非均质的比例和分布特征有所差别。在研究区西北部,油层上部为Ⅰ型非均质,中部为Ⅱ型非均质,下部为Ⅱ型与Ⅲ型非均质的组合。其中,Ⅱ型非均质所占比例最高,为46.9%,Ⅲ型非均质次之,为30.4%,Ⅰ型非均质最低,为22.7%。在研究区中部,目的油层上部与中部为Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型非均质,二者呈交互式分布,下部为Ⅱ型与Ⅲ型非均质的组合。其中Ⅰ型非均质所占比例最高,为41.3%,Ⅱ型非均质次之,为36.4%,Ⅲ型非均质为22.3%。在研究区东南部,油层上部为Ⅰ型非均质,中部为Ⅱ型非均质,下部为Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型与Ⅲ型非均质的组合。其中,Ⅰ型非均质所占比例最高,为56.8%,Ⅱ型非均质次之,占26.3%,Ⅲ型非均质仅为16.9%。总体来看,在纵向上,由下而上具有Ⅲ型非均质—Ⅱ型非均质—Ⅰ型非均质的演化规律;在横向上,由研究区西北部到东南部,Ⅰ型非均质所占比例逐渐增加,Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型非均质所占比例逐渐减少。
4 微观非均质性控油特征
在储层微观非均质性类型划分的基础上,针对3种微观非均质分别进行了真实岩心可视化模型水驱油实验,实验参数见表3。
表3 真实岩心可视化模型水驱油实验参数
Table 3 Real reservoir water flooding experiment parameter

4.1 非均质控油特征
由图7和表4可见:Ⅰ型非均质整体驱油效果好,剩余油富集程度较高,但不同孔喉组合中剩余油分布差异较大。其中,次生溶蚀型孔喉组合的毛细管阻力相对较小,在驱油过程中,驱替液优先进入,驱油速度大,驱油效率高。剩余油富集程度低,多呈孤立油珠状、膜状分布,局部呈半饱和状态分散分布在小孔隙或细喉道中。在原生孔隙型孔喉组合中,由于孔喉毛细管阻力大,驱替液发生绕流,驱油效率较低。剩余油富集程度高,在连续的孔隙、喉道中呈饱和、半饱和状态,表现为一种局部“油包水”的斑块状剩余油。
Ⅱ型非均质渗透性较好,整体驱油效果好,剩余油富集程度较高,但不同的孔喉组合之间具有差异性。其中,次生溶蚀型孔喉组合的毛细管阻力相对较小,驱替液优先进入,驱油效果最好。剩余油分布比较分散,多在孔喉中呈孤立油滴状、膜状分布,局部呈半饱和状态分布在小孔隙或细喉道中;在次生钙质斑块型孔喉组合中,驱替液绕流现象明显,驱油效果较差,剩余油呈斑块状富集。具体来讲,在钙质斑块的背水一侧,剩余油富集程度高,表现为连续多个孔隙内饱和、半饱和状态,整体呈斑块状;在钙质斑块的迎水面,剩余油富集程度低,多为盲端剩余油;在钙质斑块的侧面剩余油富集程度较低,多呈孔壁膜状及边角油滴状分布。
Ⅲ型非均质由于孔隙小,喉道细,毛细管阻力大,渗透性较差,驱油效果较差,剩余油富集程度高。在实际生产中,该非均质易受油层中高渗透区的屏蔽,注水波及系数低。实验结果表明,该非均质驱油效果相对较差,剩余油富集程度高,呈连片分布,在孔隙中多呈半饱和、饱和状态,少量呈孔内油珠状和孔壁膜状分布。
4.2 剩余油潜力
Ⅰ型非均质厚度最大,剩余油富集程度较高,具有较大剩余油潜力。此外,Ⅰ型非均质渗透性好,驱替液波及程度高,分布在油层顶部,井网相对较完善,具备良好的基础地质和井网条件。因此,该类非均质剩余油挖潜难度小,风险小,经济效益最高,是下一步提高采收率工作的首选目标。建议采用加密水平井挖潜、加密井网实现面积注水和3次采油3种主要方式进行剩余油挖潜。
Ⅱ型非均质厚度较大,其剩余油富集程度较高,具有较大剩余油潜力。但由于Ⅱ型非均质分布在油层中下部,埋深较大,钻遇井数少,剩余油挖潜难度大,经济风险大。钻水平井进行剩余油挖潜是一种经济、有效的方式。
Ⅲ型非均质不仅处于油层下部,埋深大,而且钻遇井少,驱替液波及系数小,挖潜难度大,经济风险最大,可以通过局部井3次采油方式进行试探性挖潜。
表4 不同微观非均质剩余油分布特征
Table 4 Residual oil distribution statistics table of different microscopic heterogeneity types
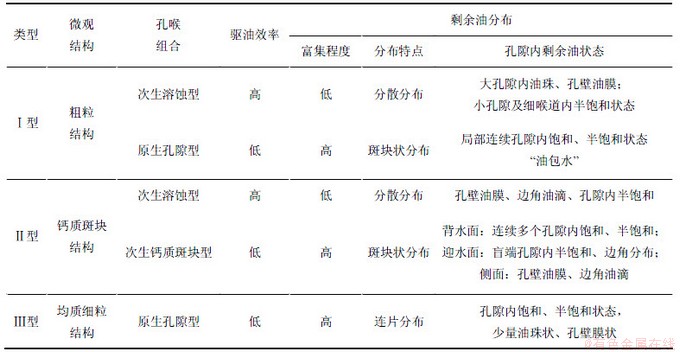
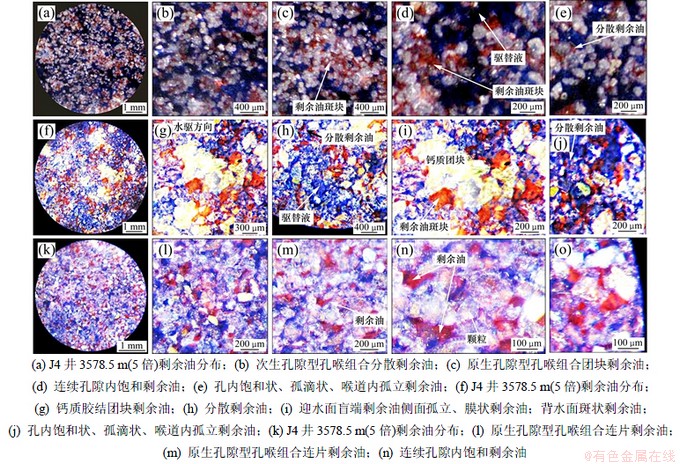
图7 不同微观非均质剩余油分布特征
Fig. 7 Residual oil distribution of different microcosmic heterogeneous types
5 结论
(1) 研究区微观非均质分为Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型3种类型。其中,Ⅰ型非均质分布在油层上部,厚度最大,剩余油呈斑块状富集;Ⅱ型非均质分布在油层中部和下部,厚度次之,剩余油呈斑块状富集;Ⅲ型非均质分布在研究区下部,厚度最小,剩余油呈连片状分布。从研究区的西北部到东南部,Ⅰ型非均质剩余油所占比例逐渐增加,Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型非均质剩余油所占比例逐渐减少。
(2) Ⅰ型非均质剩余油潜力最大,是剩余油挖潜的首选目标,其剩余油挖潜方式有加密水平井挖潜、加密井实现面积注水和3次采油3种;Ⅱ型非均质剩余油潜力相对较高,但其井网条件差,具有一定的风险型,可以通过加密水平井进行剩余油挖潜。Ⅲ型非均质剩余油潜力较小,挖潜难度最大,风险最大,可以通过局部井3次采油方式进行试探性挖潜。
(3) 提出的孔喉组合和微观结构介于传统的层内非均质性与微观非均质性之间,不仅丰富了储层非均质研究内容,还可以更好地为储层内流体渗流规律和剩余油分布特征研究奠定地质基础。
参考文献:
[1] 赵彬, 侯加根, 张国一, 等. 哥伦比亚Velasquez油田始新统Guaduas组沉积微相与剩余油分布[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(5): 1384-1392.
ZHAO Bin, HOU Jiagen, ZHANG Guoyi, et al. Sedimentary microfacies and remaining oil distribution of the Eocene Guaduas formation in Velasquez Oilfield, Columbia[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2011, 42(5): 1384-1392.
[2] 李阳, 王瑞平, 刘建民. 陆相水驱油藏剩余油富集区研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(3): 91-96.
LI Yang, WANG Duanping, LIU Jianmin. Remaining oil enrichment areas in continental water flooding reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(3): 91-96.
[3] 温立峰, 吴胜和, 王延忠, 等. 河控三角洲河口坝地下储层构型精细解剖方法[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 42(4): 1072-1078.
WEN Lifeng, WU Shenghe, WANG Yanzhong, et al. An accurate method for anatomizing architecture of subsurface reservoir in mouth bar of fluvial dominated delta[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2011, 42(4): 1072-1078.
[4] 李国永, 徐怀民, 路言秋, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘八区克下组冲积扇高分辨率层序地层学[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 41(3): 1124-1131.
LI Guoyong, XU Huaimin, LU Yanqiu, et al. High-resolution sequence stratigraphy for alluvial fan on lower Karamay formation in 8th zone of northwestern Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2010, 41(3): 1124-1131.
[5] 刘建民, 徐守余. 河流相储层沉积模式及对剩余油分布的控制[J]. 石油学报, 2003, 24(1): 58-62.
LIU Jianmin, XU Shouyu. Reservoir sedimentary model of fluvial facies and it’s control to remaining oil distribution[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2003, 24(1): 58-62.
[6] 廖卫华. 论东河塘组的时代[J]. 新疆地质, 1995, 13(3): 195-201.
LIAO Weihua. On the age of Donghetang formation in Tarim basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 1995, 13(3): 195-201.
[7] 朱怀诚, 张师本, 罗辉. 塔里木盆地泥盆系-石炭系界线研究新进展[J]. 地质学杂志, 2000, 24(增): 370-372.
ZHU Huaicheng, ZHANG Shiben, LUO Hui. New advances in the study of the devonian-carboniferous boundary in the tarim basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2000, 24(S): 370-372.
[8] 朱筱敏, 张强, 马立驰. 塔里木盆地东河砂岩层序地层分析[J]. 海相油气地质, 1999, 4(4): 13-17.
ZHU Xiaomin, ZHANG Qiang, MA Lichi. The sequence stratigraphic analysis of East River sandstone in Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleun Geology, 1999, 4(4): 13-17.
[9] 顾家裕. 塔里木盆地石炭系东河砂岩沉积环境分析及储层研究[J]. 地质学报, 1996, 70(2): 153-161.
GU Jiayu. Sedimentary environment and reservoir characters of the carbonniferous Donghe sandstone in the Tarim basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1996, 70(2): 153-161.
[10] 顾家裕, 张兴阳, 郭彬程. 塔里木盆地东河砂岩沉积和储层特征及综合分析[J]. 古地理学报, 2006, 8(3): 285-294.
GU Jiayu, ZHANG Xingyang, GUO Bincheng. Characteristics of sedimentation and reservoir of the Donghe Sandstone in Tarim Basin and their synthetic analysis[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2006, 8(3): 285-294.
[11] 钟大康, 朱筱敏, 周新源, 等. 塔里木盆地中部泥盆系东河砂岩成岩作用与储集性能控制因素[J]. 古地理学报, 2003, 5(3): 378-390.
ZHONG Dakang, ZHU Xiaomin, ZHOU Xinyuan, et al. Diagenesis and controlling factors of reservoir quality of devonian Donghe sandstones in centralTarim basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2003, 5(3): 378-390.
[12] 翟永红, 刘生国, 郭建华, 等. 塔中石炭系碎屑岩成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 石油与天然气学报, 1995, 16(3): 252-258.
ZHAI Yonghong, LIU Shengguo, GUO Jianhua, et al. Diagenesis and pore evolution of carboniferous clastic rocks in central Tarim[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1995, 16(3): 252-258.
[13] 王招明, 王清华, 孙丽霞, 等. 东河砂岩钙结成岩作用的主要特征[J]. 地质科学, 2004, 39(4): 517-522.
WANG Zhaoming, WANG Qinghua, SUN Lixia, et al. Main features of calcic-diagenesis in the Donghe sandstones[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2004, 39(4): 517-522.
[14] 苏娟, 郭建华, 蔡习尧. 塔中地区泥盆系东河砂岩段成岩作用研究[J]. 中国西部油气地质, 2006, 2(3): 267-271.
SU Juan, GUO Jianhua, CAI Xiyao. Study of Diagenesis of Devonian Donghe Sandstone in Tazhong Area[J]. West China Petroleum Geosciences, 2006, 2(3): 267-271.
[15] 郭建华, 朱锐, 周小康. 塔河地区西南缘东河砂岩的成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 37(3): 572-578.
GUO Jianhua, ZHU Rui, ZHOU Xiaokang. Diagenesis and porosity evolution of Donghe sandstone in southwest of Tahe area[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2006, 37(3): 572-578.
[16] 刘清俊, 于炳松, 周芳芳, 等. 阿克库勒凸起东河砂岩成岩作用与成岩相[J]. 西南石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2011, 33(5): 54-62.
LIU Qingjun, YU Bingsong, ZHOU Fangfang, et al. Diagenesis and diagenesis facies of Donghe sandstone of akekule upliftin Tarim basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Science & Technology Edition, 2011, 33(5): 54-62.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2012-10-08;修回日期:2012-12-23
基金项目:国家科技重大专项(2011ZX05009-003);中国石油天然气股份有限公司重大科技专项资助项目(2010E-2111);中央高校基本科研业务费专项(11CX06005A)
通信作者:孙廷彬(1985-),男,山东省临朐人,博士研究生,从事油藏描述和剩余油分布规律方向研究;电话:18953248353;E-mail:stbchina@126.com