文章编号:1004-0609(2016)-09-1886-07
显微组织对TC32钛合金高周疲劳性能的影响
李明兵,朱知寿,王新南,祝力伟,费 跃,商国强,李 静
(北京航空材料研究院 先进钛合金航空科技重点实验室,北京 100095)
摘 要:研究双态组织和网篮组织对TC32钛合金高周疲劳(HCF)性能的影响,并与TC4钛合金等轴组织和TC21钛合金网篮组织的高周疲劳性能进行对比分析。结果表明:TC32钛合金双态组织与网篮组织的高周疲劳强度分别为535.7MPa与537.5MPa,明显高于TC4钛合金等轴组织的,也高于TC21钛合金网篮组织的。TC32钛合金双态组织因原始β晶粒细小,且初生α相与β转变基体强度匹配性良好,不存在异常的平均应力敏感性;TC32钛合金网篮组织因存在较多的二次裂纹,且主裂纹扩展路径曲折,疲劳裂纹扩展速率较双态组织更缓慢。
关键词:TC32钛合金;高周疲劳;疲劳断口;显微组织
中图分类号:TG146.2+3 文献标志码:A
钛及钛合金因比强度与比刚度高、可焊接、耐高温、耐蚀等优异的综合性能,一直受到航空航天工业的极大重视与青睐[1-2]。而随着新一代飞机和航空发动机的不断发展,对钛合金材料的综合性能要求也越来越高[3],高用量、高性能与低成本将是我国航空用钛合金材料在21世纪所面临的主要挑战[4]。
材料长期在交变载荷作用下表现为疲劳断裂[5],其断裂过程可分为疲劳微裂纹的萌生(微裂纹萌生区)、稳定扩展(稳定扩展区)以及失稳扩展断裂(快速扩展区)3个阶段。文献表明[6-7],在大多数金属材料中,疲劳过程第一阶段的损伤程度由微裂纹行为所控制,微裂纹的萌生阶段占整个疲劳寿命的80%。材料的疲劳裂纹主要在驻留滑移带(PSB)、晶界以及缺陷等位置萌生[5]。由于疲劳断裂具有隐蔽性和突然性,一旦发生断裂,便会造成不可逆的严重后果。有资料显示,机械构件中疲劳失效占50%~90%,而航空构件中疲劳失效占80%以上[8],例如航空史上几次重大的飞行安全事故也与金属的疲劳破坏有关[9],因此,研究钛合金材料的疲劳性能对于提升飞机构件的安全性能具有重大的工程意义。
TC32钛合金是由北京航空材料研究院研制的综合性能优于TC4的新型高性能低成本钛合金[10-13],本文主要研究TC32钛合金双态组织与网篮组织的高周疲劳性能与损伤特性,并与中等强度TC4钛合金与中高强韧TC21钛合金的高周疲劳性能相对比,为TC32钛合金的工程化应用与选材提供一定的数据支持。
1 实验
1.1 实验原料
实验所用3种不同钛合金牌号的原材料均经过3次真空自耗电弧熔炼制备出铸锭,后经开坯、锻造等工序加工成棒材。两种实验用TC32钛合金棒材分别经两相区锻造与准β锻造后经双重退火处理。TC21钛合金棒材经准β锻造后再经双重退火处理。TC4钛合金棒材经两相区锻造后经普通退火处理。
1.2 实验方法
从棒材的边部取纵向高倍试样、室温拉伸试样及高周疲劳试样。采用LEICA DMI3000 M型倒立型光学显微镜观察合金显微组织,其中Kroll金相腐蚀剂体积比为V(HF):V(HNO3):V(H2O)=1:2:50。采用INSTRON5887型电子万能试验机测定合金的室温拉伸性能,检测标准为GB/T 228—2002。轴向应力疲劳试验在QBG-100型高频试验机上进行,检测标准为GB/T 228.1—2010,试验环境为室温与空气,试验频率为125 Hz,采用升降法得出材料的疲劳极限,通过三参数幂函数法拟合得到疲劳S-N曲线。采用FM-700型显微硬度计测定合金显微组织的硬度。采用JSM-5600LV型扫描电镜观察合金的疲劳断口形貌。
2 结果与分析
2.1 显微组织与室温拉伸性能
图1所示分别为TC32、TC4与TC21钛合金的金相显微组织,从图1中可知,经两相区锻造的TC32钛合金显微组织为双态组织(见图1(a)),其特征是β转变基体上分布着不连续的初生α相,含量约为24.5%,绝大多数的初生α相呈等轴状或椭圆状,尺寸约为5 μm,少量呈短棒状。经准β锻造的TC32钛合金与TC21钛合金显微组织均为网篮组织(见图1(b)与图1(c)),其特征是无原始β晶界,原始β晶粒内部的β转变组织编制成网篮结构,板条状α相厚度约为1.6 μm。经普通退火处理的TC4钛合金显微组织为等轴组织(见图1(d)),其特征是初生α相沿着原始β晶界析出长大,呈椭圆形,尺寸约为30 μm,含量约为67.5%,并且与周围其他初生α相接触连接。
表1所列分别为TC32、TC21与TC4钛合金的室温拉伸性能,Rm为抗拉强度,Rp0.2为屈服强度,A为伸长率,Z为断面收缩率。可以看到,双态组织状态下的TC32钛合金强度值明显高于其他合金的。而网篮组织状态下的TC32与TC21钛合金强度与塑性相当。等轴组织状态下的TC4钛合金强度值明显低于其他合金的,但塑性值最高。
2.2 高周疲劳性能
图2所示为TC32钛合金双态组织与TC4钛合金等轴组织在应力比R=-1下的S-N曲线。图3所示为TC32与TC21钛合金网篮组织在应力比R=-1下的S-N曲线。表2列出3种(α+β)型钛合金所对应的疲劳极限值,从中可以看出,在该应力比下,TC32钛合金双态组织与网篮组织的疲劳极限分别为σD=535.7 MPa与σD=537.5 MPa,相比TC4钛合金等轴组织的疲劳极限(σD=380 MPa),分别高出155.7 MPa与157.5 MPa。TC32钛合金与强度相当的TC21钛合金网篮组织相比,TC32钛合金的疲劳极限也相对较高,分别高出34.7 MPa与36.5 MPa。
一般地,当塑形和韧性等性能指标相当的情况下,金属材料的高周疲劳性能与强度水平密切相关,表现为金属的强度越高,其疲劳性能也就越好[14],因此,中等强度的TC4钛合金疲劳性能明显低于高强韧的TC32与TC21钛合金的。钛合金的高周疲劳性能反映了合金组织抵抗疲劳裂纹萌生的能力[15-17],对于钛合金的双态组织,影响其性能的最主要因素是由原始β晶粒控制的α集束尺寸[15],因为α集束尺寸直接决定了其有效滑移长度,有效滑移长度越短,疲劳裂纹萌生所需要的临界分切应力(CRSS)也就越大[17],疲劳性能也就越好,从图1(a)可以看出,TC32钛合金双态组织最典型的特点就是原始β晶粒细小,从而决定了该组织状态下的室温拉伸强度与疲劳性能最好。其次,从图1(d)可以看出,TC4钛合金等轴组织中初生α相沿着原始β晶界析出长大,并相互连接,这一特点不仅降低了材料的强度,而且互相连接的初生α相也容易萌生疲劳微裂纹,显著降低材料的疲劳裂纹萌生寿命,相比之下,TC32与TC21钛合金网篮组织具有小的滑移间距[18],从而使强度与疲劳性能也优于TC4钛合金的。
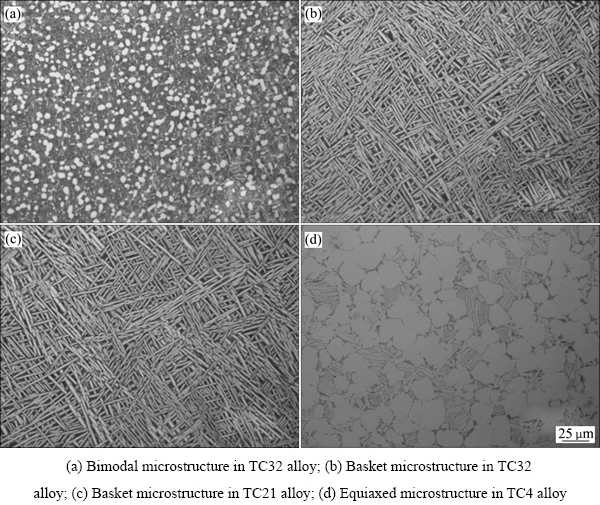
图1 TC32、TC21、TC4钛合金的金相显微组织
Fig. 1 Metallographs of TC32, TC21 and TC4 alloys
表1 TC32、TC21、TC4钛合金的室温拉伸性能
Table 1 Room temperature tensile properties of TC32、TC21 andTC4 alloys
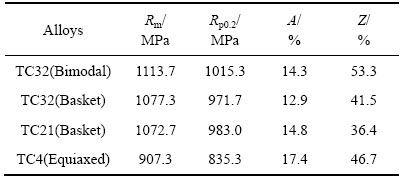
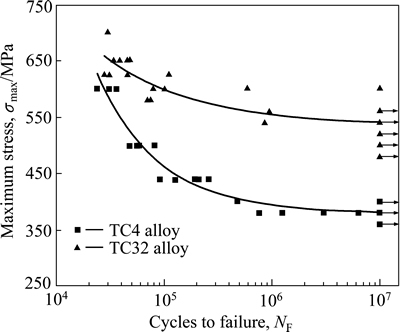
图2 TC32钛合金双态组织与TC4钛合金等轴组织在应力比R=-1时的S-N曲线
Fig. 2 Maximum stress as function of number of cycles to failure (S-N curve) of bimodal microstructure in TC32 and equiaxed microstructure inTC4 alloys at a stress ratio of -1
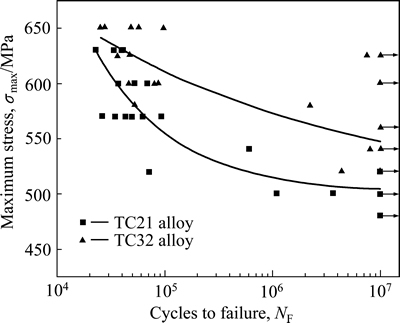
图3 TC32与TC21钛合金网篮组织在应力比R=-1时的S-N曲线
Fig. 3 Maximum stress as a function of number of cycles to failure (S-N curve) of basket microstructure in TC32 and TC4 alloys at a stress ratio of -1
表2 TC32、TC21、TC4钛合金在应力比R=-1的高周疲劳极限
Table 2 Fatigue limits of TC32, TC21 and TC4 alloys at a stress ratio of -1
研究表明[19-21],(α+β)型钛合金双态组织和等轴组织常常表现出异常的平均应力敏感性(AMSS)这通常与组织强度匹配程度和疲劳裂纹形核机制有关。双态组织由初生α相及β转变基体组成,而β转变基体则是由β残余相及与β转变基体具有伯根斯位向关系的板条状次生α相组成。经测定,TC32钛合金双态组织中β转变基体显微硬度值为301.54 HV,初生α相的为376.41 HV,这说明在交变载荷条件下β转变基体要先于初生α相变形。而疲劳裂纹的萌生是一个损伤累积的过程[22-24],双态组织疲劳裂纹萌生的位置主要集中在β转变基体的次生α相之间或者与初生α相晶界处[15-16],这主要是因为存在元素分配效应[15],使得双态组织中β转变基体的强度明显低于初生α相,在循环载荷条件下,β转变基体的次生α相优先变形,滑移首先沿着具有较低的临界分切应力(CRSS)的基面(0002)及棱柱面 开始滑移[25-27],进而形成驻留滑移带(PSB),由于滑移的不可逆性,位错容易在次生α相之间或者初生α相晶界处净塞积[24, 27-28],使弹性应变能增加,引起应力集中,因而容易萌生疲劳裂纹,降低高周疲劳性能。
开始滑移[25-27],进而形成驻留滑移带(PSB),由于滑移的不可逆性,位错容易在次生α相之间或者初生α相晶界处净塞积[24, 27-28],使弹性应变能增加,引起应力集中,因而容易萌生疲劳裂纹,降低高周疲劳性能。
图4所示为TC32钛合金双态组织在不同应力比下的S-N曲线。在应力比R=0.1与R= -1的条件下,两者疲劳极限相差226.8MPa,说明TC32钛合金双态组织不表现出异常的平均应力敏感性,这证明了双态组织中β转变基体与初生α相两者强度匹配良好(差值为74.87 HV),从而降低了双态组织在低应力比下疲劳微裂纹沿着β转变基体萌生的概率。
由前面可知,网篮组织状态下的TC32与TC21钛合金室温拉伸性能相当,显微硬度测试结果表明,两者的显微硬度也彼此接近(前者为373.62 HV;后者为374.58 HV),但前者的高周疲劳极限相对较高,这表明TC32钛合金网篮组织抗疲劳裂纹萌生的能力更高。
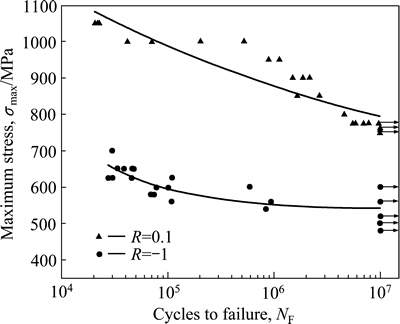
图4 TC32钛合金双态组织在不同应力比下的S-N曲线
Fig. 4 Maximum stress as function of number of cycles to failure (S-N curve) of bimodal microstructure in TC32 alloy at different stress ratios
2.3 断口分析
为了进一步分析TC32钛合金不同组织的高周疲劳损伤特性,利用扫描电镜(SEM)观察了其疲劳断口形貌。图5与图6所示分别为双态组织与网篮组织在应力比为R=-1下的扫描断口形貌。从图5和6中可以看出,TC32钛合金的高周疲劳断口形貌按照断裂的过程可以分为疲劳源区、扩展区与瞬断区3部分。
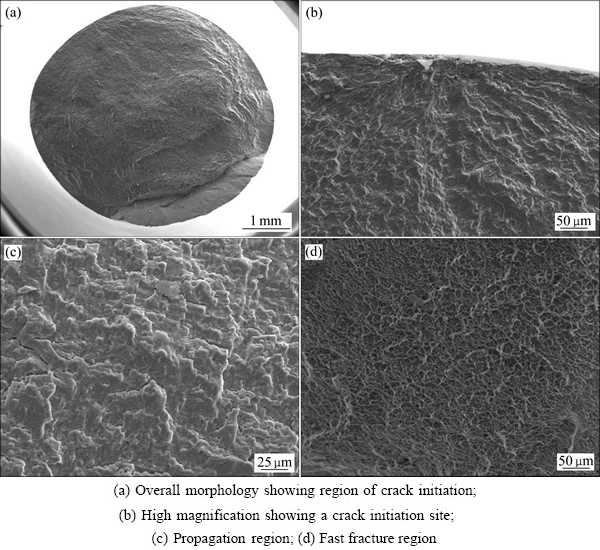
图5 TC32钛合金双态组织的高周疲劳断口形貌
Fig. 5 SEM images of high cycle fatigue fracture surface of bimodal microstructure at a stress ratio of -1 in TC32 alloys
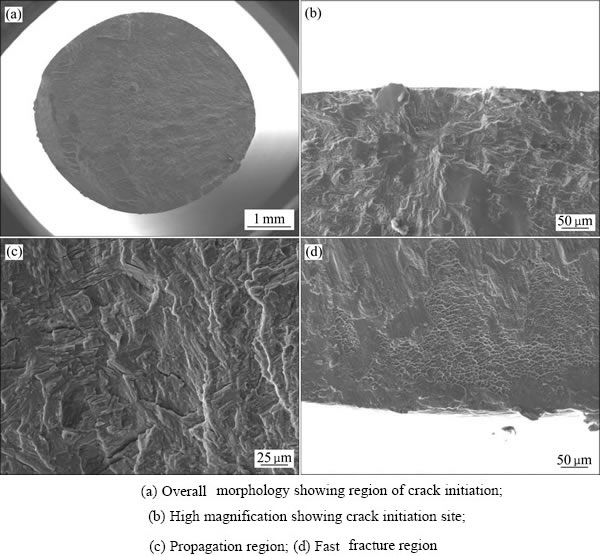
图6 TC32钛合金网篮组织的高周疲劳断口形貌
Fig. 6 SEM images of high cycle fatigue fracture surface of basket microstructure at stress ratio of 0.1 in TC32 alloys
图5(a)与图6(a)所示分别为双态组织与网篮组织的宏观断口形貌,观察发现,疲劳裂纹源均萌生于试样近表面,且为单一疲劳源。图5(b)与图6(b)所示分别为双态组织与网篮组织的疲劳源区放大图。由于疲劳源区裂纹的扩展速率较慢,裂纹在循环载荷的不断作用下反复张开与闭合所造成挤压磨损,同时在不同高度起始的裂纹扩展中相遇,汇合成辐射状台阶或形成放射棱线。
随着裂纹的持续扩展,疲劳断裂过程进入了扩展区。组织因素对疲劳裂纹萌生与扩展寿命的影响往往是一对矛盾的关系,钛合金双态组织的抗疲劳裂纹萌生能力高于网篮组织的,这往往与有效滑移长度有关,但抗裂纹扩展能力却低于网篮组织的,本实验中,TC32钛合金网篮组织的高周疲劳极限值并不低于双态组织的极限值,这也能从扩展区的断口形貌中找到依据。结合图5(a)与图6(a)可以看出,网篮组织的扩展区面积要大于双态组织,这说明网篮组织的裂纹扩展寿命要高于双态组织的。图5(c)与图6(c)所示分别为双态组织与网篮组织的扩展区放大图,可以发现两者均存在不连续的疲劳条带,但网篮组织中的二次裂纹数量要多于双态组织的,二次裂纹数量越多,并且主裂纹扩展路径更曲折[29],所消耗的能量也就越多,裂纹扩展速率也就越缓慢。
当疲劳裂纹扩展至临界尺寸时,疲劳断裂过程进入了瞬断区。图5(d)与图6(d)所示分别为双态组织与网篮组织的瞬断区放大图,从图中可以发现,瞬断区表面由许多相互连接的凹坑组成,表现为韧窝断裂,但相比于网篮组织,双态组织的韧窝断裂特征更明显,这主要是取决于材料的断裂韧度与载荷方式。
3 结论
1) TC32钛合金双态组织与网篮组织的高周疲劳强度分别为535.7 MPa与537.5 MPa,明显高于TC4钛合金等轴组织的,也高于TC21钛合金网篮组织的。
2) TC32钛合金双态组织原始β晶粒细小,初生α相与β转变基体强度匹配性良好,不表现出异常的平均应力敏感性。
3) 从断口形貌分析可知,TC32钛合金双态组织与网篮组织的高周疲劳断口呈现典型的疲劳断裂特征,网篮组织中因存在较多的二次裂纹,且主裂纹扩展路径更曲折,疲劳裂纹扩展速率较双态组织更缓慢。
REFERENCES
[1] BANERJEE DIPANKAR, WILLIAMS J C. Perspectives on titanium science and technology[J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(3): 844-879.
[2] 朱知寿, 王新南, 童 路, 商国强. 航空用损伤容限型钛合金研究与应用[J]. 中国材料进展, 2010, 29(5): 14-24.
ZHU Zhi-shou, WANG Xin-nan, TONG Lu, SHANG Guo-qiang. Research and application of damage tolerance titanium alloys for aeronautical use[J]. Materials China, 2010, 29(5): 14-24.
[3] 朱知寿. 航空结构用新型高性能钛合金材料技术研究与发展[J]. 航空科学技术, 2012: 5-9.
ZHU Zhi-shou. Research and development of advanced new type titanium alloys for aeronautical applications[J]. Aeronautical Science and Technology, 2012: 5-9.
[4] 曹春晓. 我国航空用钛合金面临的21世纪的挑战[J]. 钛工业进展, 1999, 5: 1-5.
CAO Chun-xiao. Challenges of Chinese aviation titanium alloy in the 21st century[J].Titanium Industry Progress, 1999, 5: 1-5.
[5] SURESH S. 材料的疲劳[M]. 王中光, 译. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1993.
SURESH S. Fatigue of material[M]. WANG Zhong-guang, transl. Beijing: Defense Industrial Press, 1993.
[6] 洪友士, 方 彪. 疲劳短裂纹萌生及发展的细观过程和理论[J]. 力学进展, 1993, 23(4): 468-486.
HONG You-shi, FANG Biao. Microscopic process and description for the initiation and propagation of short fatigue cracks[J] Advances in Mechanics, 1993, 23(4): 468-486.
[7] 洪友士, 顾子晏, 方 彪. 疲劳短裂纹萌生的损伤特征和计算机模拟[J]. 机械强度, 1995, 17(3): 88-93.
HONG You-shi, GU Zi-yan, FANG Biao. Damage characteristics and computer simulation of short fatigue cracks[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 1995, 17(3): 88-93.
[8] 赵少汴. 抗疲劳设计[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1994.
ZHAO Shao-bian. Anti-fatigue design[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1994.
[9] SCHIJVE J. Fatigue of aircraft materials and structures[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 1994, 16(1): 21-32.
[10] 朱知寿, 商国强, 王新南, 费 跃, 李 军. 低成本高性能钛合金研究进展[J]. 钛工业进展, 2012, 29(16): 1-5.
ZHU Zhi-shou, SHANG Guo-qiang ,WANG Xin-nan, FEI Yue, LI Jun. Research and development of low cost and high performance titanium alloys[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2012, 29(16): 1-5.
[11] 王新南, 费 跃, 刘 洲, 商国强, 李 军, 祝力伟, 朱知寿. 航空用新型低成本钛合金显微组织与损伤容限性能关系研究[J]. 钛工业进展, 2013, 30(2): 7-10.
WANG Xin-nan, FEI Yue, LIU Zhou, SHANG Guo-qiang, LI Jun, ZHU Li-wei, ZHU Zhi-shou. Research of the relationship between microstructure and damage-tolerance property of new low cost titanium alloy in aviation applications[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2013, 30(2): 7-10.
[12] 商国强, 王新南, 费 跃, 李 军, 祝力伟, 朱知寿. 新型低成本钛合金高周疲劳性能和断裂韧度[J]. 失效分析与预防, 2013, 8(2): 74-78.
SHANG Guo-qiang, WANG Xin-nan, FEI Yue, LI Jun, ZHU Li-wei, ZHU Zhi-shou. High-cycle fatigue properties and fracture toughness of new low cost titanium alloy[J]. Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2013, 8(2): 74-78.
[13] 费 跃, 朱知寿, 王新南, 李 军, 商国强, 祝力伟. 锻造工艺对新型低成本钛合金组织和性能影响[J]. 稀有金属, 2013, 37(2): 186-191.
FEI Yue, ZHU Zhi-shou, WANG Xin-nan, LI Jun, SHANG Guo-qiang, ZHU Li-wei. Influence of forging process on microstructure and mechanical properties of a new low-cost titanium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2013, 37(2): 186-191.
[14] SMITH J O. The effect of range of stress on the fatigue strength of metals[J]. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, College of Engineering Experiment Station, 1942, 26: 19-27.
[15] L TJERING G. Influence of processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of (α+β) titanium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 243: 32-45.
TJERING G. Influence of processing on microstructure and mechanical properties of (α+β) titanium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1998, 243: 32-45.
[16] PETERS J O, L TJERING G. Comparison of the fatigue and fracture of α+β titanium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 32: 2805-2818.
TJERING G. Comparison of the fatigue and fracture of α+β titanium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2001, 32: 2805-2818.
[17] BASAK YAZGAN KOKUOZ, YOJI KOSAKA, RACK H J. High-cycle fatigue crack initiation and growth in TIMETAL LCB[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2005, 14(6): 773-777.
[18] 朱知寿. 新型航空高性能钛合金材料技术研究与发展[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2013.
ZHU Zhi-shou. Research and development of new-brand titanium alloys of high performance for aeronautical applications[M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2013.
[19] ADACHI S, WAGNER L, L TJERING G. Influence of mean stress on fatigue strength of Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Strength of Metals and Alloys(ICSMA.7), 1986: 2117-2122.
TJERING G. Influence of mean stress on fatigue strength of Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Strength of Metals and Alloys(ICSMA.7), 1986: 2117-2122.
[20] LINDEMANN J, WAGNER L. Mean stress sensitivity in fatigue of α,(α+β) and β titanium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 234/236: 1118-1121.
[21] LINDEMANN J, WAGNER L. Microtextural effects on mechanical properties of duplex microstructures in (α+β) titanium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 263: 137-141.
[22] BACHE M R. A review of dwell sensitive fatigue in titanium alloys: the role of microstructure, texture and operating conditions[J]. International Journal of Fatigue 2003, 25: 1079-1087.
[23] PILCHAK A L, WILLIAMS J C. Observation of facet formation in near-α titanium and comments on the role of hydrogen[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42(4): 1000-1027.
[24] SZCZEPANSKI C J, JHA S K, SHADE P A, WHEELER R, LARSEN J M. Demonstration of an in-situ microscale fatigue testing technique on a titanium alloy[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2013, 57: 131-139.
[25] WILLIAMS J C, BAGGERLY R G, PATON N E. Deformation behavior of HCP Ti-Al alloy single crystals[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2002, 33: 837-850.
[26] BRIDIER F, VILLECHAISE P, MENDEZ J. Slip and fatigue crack formation process in an α/β titanium alloy in relation to crystallographic texture on different scales[J]. Acta Meterialia, 2008, 56: 3951-3962.
[27] GUO Y, BRITTON T B, WILKINSON A J. Slip band-grain boundary interaction in commercial-purity titanium[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 76: 1-12.
[28] ZHANG K, YANG K V, HUANG A, WU X, DAVIES C H J. Fatigue crack initiation in as forged Ti-6Al-4V bars with macrozones present[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2015, 80: 288-297.
[29] 王新南, 朱知寿, 童 路, 周 宇, 周晓虎, 俞汉清. 锻造工艺对T4-DT和TC21损伤容限型钛合金疲劳裂纹扩展速率的影响[J]. 稀有金属快报, 2008, 27(7): 12-16.
WANG Xin-nan, ZHU Zhi-shou, TONG Lu, ZHOU Yu, ZHOU Xiao-hu, YU Han-qing. The influence of forging processing on fatigue crack propagation rate of damage-tolerant titanium alloy[J]. Rare Metals Letters, 2008, 27(7): 12-16.
Influence of microstructure on high cycle fatigue properties of TC32 titanium alloy
LI Ming-bing, ZHU Zhi-shou, WANG Xin-nan, ZHU Li-wei, FEI Yue, SHANG Guo-qiang, LI Jing
(Aviation Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Advanced Titanium Alloys,
Institute of Aeronautical Materials, Beijing 100095, China)
Abstract: The high cycle fatigue(HCF) properties were investigated on TC32 titanium alloy with the bimodal and basket microstructures, compared with the HCF properties of TC4 titanium alloy with the equiaxed microstructure and TC21 alloy with the basket microstructure. The results show that TC32 titanium alloy with bimodal and basket microstructures has a much higher HCF strength level compared to that of TC4 titanium alloy with the equiaxed microstructure and has a better HCF strength level than that of TC21 titanium alloy with the basket microstructure, which is 535.7MPa and 537.5MPa, respectively. TC32 alloy with the bimodal microstructure does not show anomalous mean stress sensitivity (AMSS) since its better matching strength between primary α and β phase, and its small grain size. TC32 alloy with the basket microstructure has a greater crack propagation resistance due to main crack deflection and more secondary cracks in propagation region.
Key words: TC32 titanium alloy; high cycle fatigue; fatigue fracture; microstructure
Received date: 2015-11-10; Accepted date: 2016-01-24
Corresponding author: ZHU Zhi-shou; Tel: +86-010-62496635; E-mail: zszhu@163.com
(编辑 王 超)
收稿日期:2015-11-10;修订日期:2016-01-24
通信作者:朱知寿,研究员,博士;电话:010-62496635;E-mail: zszhu@163.com