端淬冷却过程的实验及CFD研究
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第11期
论文作者:付佩 周萍 谢紫微 吴红宇 陈继光
文章页码:2440 - 2446
关键词:端淬实验;数值模拟;冷却速率;换热系数;镍基高温合金
Key words:end-quench test; numerical simulation; cooling rate; heat transfer coefficient; nickel-based superalloy
摘 要:合金的显微组织很大程度上受其冷却过程的影响。为了建立一种先进镍基高温合金材料的冷却速率及对应微观结构的关系,采用实验和数值模拟的方法研究其冷却过程。实验测量数据包含工件在端淬过程中的温度及其后的二次γ′相的尺寸。通过导热反问题方法确定模拟所需的端淬表面换热系数。结果表明,端淬表面换热系数超过1574 K/min。基于模拟所得的平均冷却速率和实验所得的二次γ′相的尺寸数据,建立两者间的双对数关系式,其可靠性通过特定冷却速率的实验得到验证。
Abstract: The microstructure of an alloy is affected intensively by the cooling process. To figure out the inherent relation between the cooling rate and microstructure of an advanced nickel-based superalloy, experimental and numerical studies on the cooling process were conducted. Specifically, the measurement was performed concerning both the temperature of the specimen during the end-quench test and the size of the secondary γ′ phase of the specimen after that. The heat transfer coefficient of the quenched surface was determined by the inverse heat transfer method for simulation. The results show that the cooling rate of the quenched surface exceeds 1574 K/min. Based on the averaged cooling rate obtained from the simulation and the measured size of the secondary γ′ phase, an empirical correlation in a double logarithmic relationship between them is proposed. The relationship is verified by the experiment with specified cooling rates.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 2440-2446
Pei FU1, Ping ZHOU1, Zi-wei XIE1, Hong-yu WU2, Ji-guang CHEN1
1. School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 19 February 2019; accepted 18 July 2019
Abstract: The microstructure of an alloy is affected intensively by the cooling process. To figure out the inherent relation between the cooling rate and microstructure of an advanced nickel-based superalloy, experimental and numerical studies on the cooling process were conducted. Specifically, the measurement was performed concerning both the temperature of the specimen during the end-quench test and the size of the secondary γ′ phase of the specimen after that. The heat transfer coefficient of the quenched surface was determined by the inverse heat transfer method for simulation. The results show that the cooling rate of the quenched surface exceeds 1574 K/min. Based on the averaged cooling rate obtained from the simulation and the measured size of the secondary γ′ phase, an empirical correlation in a double logarithmic relationship between them is proposed. The relationship is verified by the experiment with specified cooling rates.
Key words: end-quench test; numerical simulation; cooling rate; heat transfer coefficient; nickel-based superalloy
1 Introduction
The microstructure and mechanical performance of a metal material are significantly affected by the heat treatment, and the cooling rate is an important parameter during heat treatment process. Many heat treatment experiments have been performed to study the performance of metal subjected to different cooling rates [1-3], and the end-quench test was proposed in order to greatly reduce the test time and cost [4,5]. In the end-quench test, a cylindrical specimen is heated to the austenitizing temperature [6] and then cooled by projecting water against the quenched end of the specimen in order to induce the formation of the martensitic structure [7]. In this way, the cooling rate progressively decreases along the length direction of the specimen [8], and many samples with different properties can be obtained from a single test. The end-quench test changes the traditional “one sample, one experiment” approach to parallel processing [9] and provides a high-throughput method for studying heat treatment [10,11]. With this method, abundant experimental data from a single specimen can be obtained through the end-quench test, which meets the target of the Materials Genome Initiative [12].
Generally, the cooling rates at different positions of the specimen are fitted by linear interpolation based on the temperature recorded by thermocouples at only 2-4 points on the specimen. However, the thermocouples welded on the specimen may affect its heat transfer; thus, as few thermocouples as possible are used in the end-quench test, which makes it difficult to perform temperature fitting on the specimen. Second, the axial temperature of the specimen has a nonlinear distribution; thus, the use of linear interpolation to fit the temperature distribution of the specimen is inappropriate. In addition, the initial temperature distribution of the specimen has an important influence on the cooling process and is typically assumed to be uniform in previous works, which is not the correct assumption when induced heating is applied. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is therefore an effective method to obtain the overall temperature data of a specimen.
The heat transfer coefficient (HTC) of the quenched specimen is a key boundary condition that influences the calculation accuracy of the CFD simulation of the cooling process. The HTC is influenced by various factors, such as the specimen material, cooling conditions, and surrounding environment. When water is used as the cooling medium, the mechanism of heat transfer is very complex since the phase change of water and various mechanisms of heat transfer (e.g., conduction, radiation, and convection) occur simultaneously [13-15]. Thus, it is impossible to obtain the HTC of the quenched end directly by measurement or theoretical analysis. Instead, the inverse heat transfer method (IHTM) must be employed to determine the HTC [16-18]. This means that the HTC between the quenched end of the specimen and the cooling water is initially assumed, and the temperature in the specimen is then simulated by CFD. The HTC is not determined until the temperature difference between the simulated and measured results of the cooling process in the quench test meets the error allowance [19].
In this work, the end-quench test is conducted and the cooling process is simulated for an advanced polycrystalline nickel-based superalloy widely used in aircraft engine turbine disc components [20-22]. The relationship between its secondary γ′ phase and average cooling rate is obtained via a cost-efficient method, and then is helpful to optimize the heat treatment process of advanced materials.
2 End-quench test of nickel-based superalloy
2.1 End-quench test system
As shown in Fig. 1, the end-quench test system consists of two parts, namely, induction heating and end-quench cooling. The temperature of the specimen was controlled by induction heating with a power that was adjusted automatically by a programming controller. Specifically, the specimen was heated up to a temperature of 1423 K and then maintained at this temperature for 40 min for the solution treatment. The specimen was then cooled with the water jets at its bottom. Two S-type thermocouples were welded to the bottom of the specimen. The temperature measured by the first thermocouple was used as the feedback signal of the temperature controlled system during the heating process, and the second one was used to monitor the temperature during the heating and cooling processes.
In this way, the specimen with different cooling rates was obtained. The resulting microstructures with different cooling rates were then obtained using a scanning electron microscope with a procedure similar to that described in Refs. [23,24].
As illustrated in Fig. 2, the cylindrical end-quench specimen was 100 mm in length and 18 mm in diameter and was made of an advanced polycrystalline nickel-based superalloy. To prevent heat loss, the specimen was coated with ceramic fiber cotton. The cross-sectional microstructures of the specimen, 10, 25, 45, 65 and 95 mm away from the quenched end were recorded to study the effect of the cooling rate.
2.2 Measured temperature curve
As shown in Fig. 3, during the cooling process of the end-quench test, the quenched end of the specimen was cooled down to the ambient temperature in 2 s. The cooling curve measured by the monitor thermocouple at the quenched end provided important data for calculating the HTC.
3 Numerical simulation of gradient cooling process
3.1 Model description
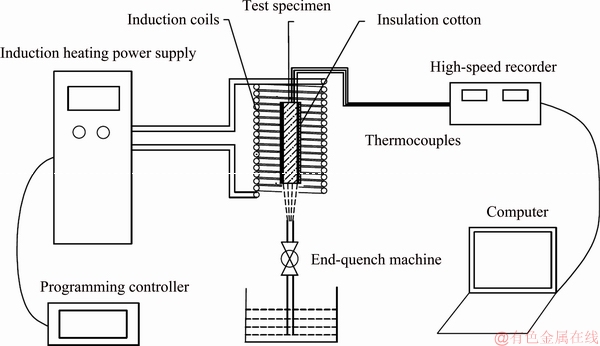
Fig. 1 End-quench test system
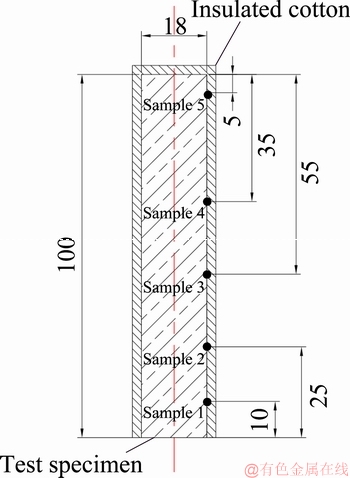
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of test specimen (Unit: mm)
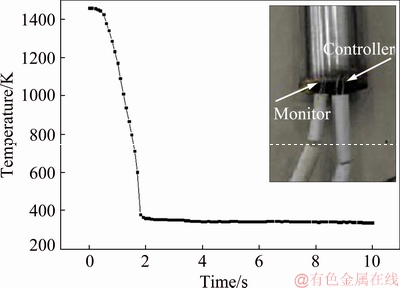
Fig. 3 Cooling curve at quenched end of specimen
All physical properties of the material are considered to be isotropic. The effect of the phase change of the low-content alloying components on the temperature is assumed to be negligible. The heat conduction in the end-quench process is assumed to be two-dimensional, and can be described in cylindrical coordinates as
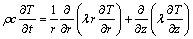 (1)
(1)
where T and t represent the temperature and time, respectively, r and z are the radial and axial coordinates, respectively, ρ is the density, λ denotes the thermal conductivity, and c denotes the specific heat capacity. The density of the nickel-based superalloy is 8256 kg/m3, as measured by drainage tests. The thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity, which depend on the temperature, are determined by using the Jmatpro software package and experimental results from Ref. [25]. The values at different temperatures are illustrated in Fig. 4.
Regarding the simulation, the initial temperature of the specimen is set to be 1423 K to match the experimental value at the end of the induction heating process [26]. During the calculation, the heat transfer coefficients of the top and side surfaces of the specimen are treated as constant values of 5 and 10 W/(m2·K), respectively. On the other hand, the HTC of the quenched end is determined via the IHTM.
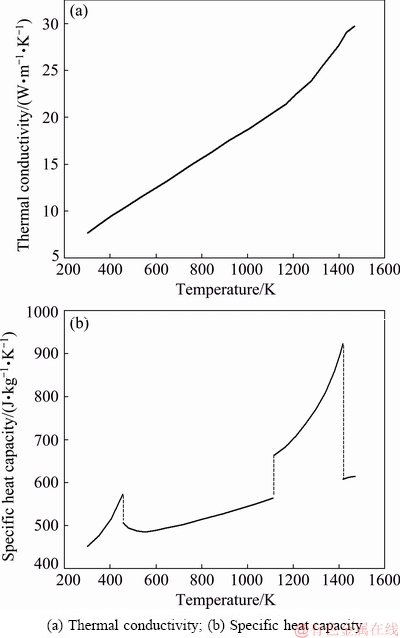
Fig. 4 Temperature-dependent thermal-physical properties of nickel-based superalloy
3.2 Calculation of HTC at quenched end via IHTM
The transient HTC, ht, of the quenched end of the specimen is calculated by the IHTM. The calculation procedure is shown in Fig. 5, where Te,t is the measured temperature in the end-quench test, and Ts,t is the simulated temperature at the same position. ht is not determined until the temperature difference at the quenched end between the simulated and measured results is within the error allowance.
The HTC curve is shown in Fig. 6. The HTC increases rapidly at first and then decreases, which is consistent with the theoretical analysis. Initially, the water quickly vaporizes when it contacts with the quenched end because of the high surface temperature, and then forms a layer of steam between the water and the quenched end, which is known as the film boiling stage. The thermal resistance of the steam film is so large that the HTC is small in this stage. Over time, the surface temperature decreases and the bubbles gradually leave the surface instead of coalescing such that the HTC increases continuously, which is known as the transition boiling stage. Next, the vaporization cores increase and secondary nucleation occurs, while the air bubbles are subject to strong turbulence, so the HTC increases sharply and reaches the peak, known as the nuclear boiling stage. Finally, the HTC decreases when the temperature of the quenched end is sufficiently low, which is known as the forced-convection heat transfer stage. HTC reaches a peak value of 120000 W/(m2·K) at 1.8 s and eventually approaches a stable value of 41000 W/(m2·K) at the end of the quenching process.
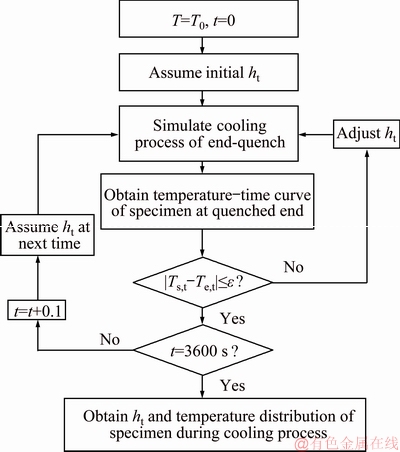
Fig. 5 Iteration flow of HTC calculation with IHTM
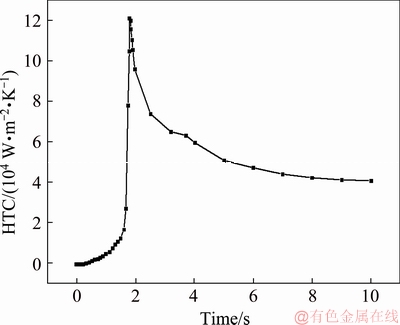
Fig. 6 Plot of HTC vs time
3.3 Simulation results
3.3.1 Temperature distribution
The simulated cooling curve is shown in Fig. 7. It is revealed that the cooling rate at the quenched end is much greater than that at the other end. Sample 1, which is near the quenched end, cools quickly to 700 K in 2 s. Meanwhile, Sample 5, which is far away from the quenched end, cools more slowly than Sample 1 and takes 1218 s to reach 700 K. The maximum temperature difference between Sample 5 and Sample 1 is 930 K, which occurs at 179 s.
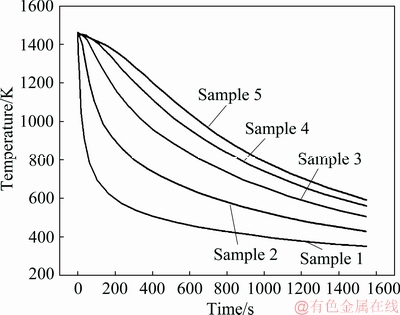
Fig. 7 Simulated profiles of temperature vs time for samples
3.3.2 Average cooling rate
The microstructure of the nickel-based superalloy depends on the secondary γ′ phase precipitation, and the temperature range in which the precipitation occurs is defined as the sensitive temperature range [27]. Therefore, the average cooling rate is calculated:
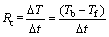 (2)
(2)
where Tb and Tf are the starting and final temperatures of the secondary γ′ phase precipitation, respectively. △T is the temperature difference between Tb and Tf, and △t is the duration of the precipitation process.
The simulated average cooling rate along the length of the specimen is shown in Fig. 8. Obviously, it decreases abruptly with increasing distance from the quenched end. The average cooling rates of samples 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 (shown in Fig. 2) are 1574, 279, 99, 61 and 51 K/min, respectively.
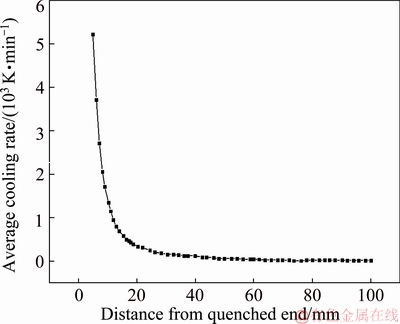
Fig. 8 Average cooling rate along length direction of specimen
3.3.3 Relationship between cooling rate and size of secondary γ′ phase
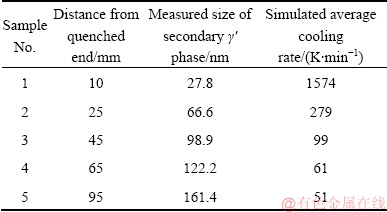
To establish the inherent relation between the average cooling rate and the size of the secondary γ′ phase, five cross-sectional samples, whose locations are shown in Fig. 2, were cut from the end-quenched specimen. The size of the secondary γ′ phase was measured using a field emission scanning electron microscope (FEI Quanta 650 FEG). The corresponding data for the samples are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Measured sizes of secondary γ′ phase and simulated average cooling rates of samples
The relationship between the size of the secondary γ′ phase and the cooling rate can be described by a double logarithmic function [28-30]. Therefore, the data in Table 1 are drawn and fitted in Fig. 9.
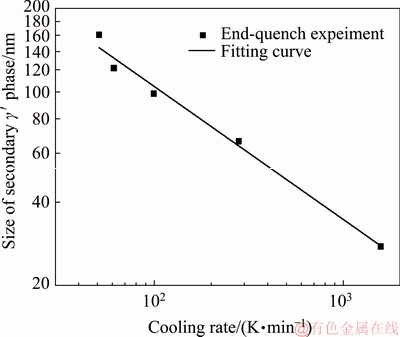
Fig. 9 Relationship between size of secondary γ′ phase and cooling rate
The fitting curve is described by
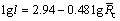 (3)
(3)
where l is the size of the secondary γ′ phase (nm), and 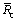 is the average cooling rate (K/min). This empirical correlation can be used to design the heat treatment technique based on the grain size.
is the average cooling rate (K/min). This empirical correlation can be used to design the heat treatment technique based on the grain size.
4 Model verification
The temperature measured by the thermocouple in the end-quench test was applied to calculating the HTC between the specimen and the cooling water and thus cannot be used to directly verify the model for simulating the end-quench process. Therefore, the dilatometry test is used to indirectly verify the simulation model.
A DIL805A dilatometer was used, and the sample was made of the same material in the end-quench test. A rod sample of 10 mm in length and 4 mm in diameter was heated to the solid-solution temperature of 1423 K and then cooled at constant cooling rates of 20, 70 and 120 K/min. The grain sizes of the samples with three different cooling rates were obtained using a field emission scanning electron microscope. The grain sizes at these three cooling rates were predicted using Eq. (3), and the results are given in Table 2.
Table 2 Measured and predicted grain size
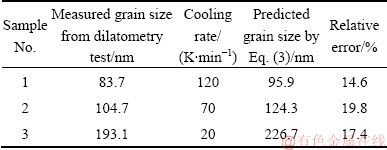
By comparing the predicted grain size with the measured grain size, the cooling rate has a similar influence on the grain size with a relative error of less than 20%. The main reason for the error is that the cooling rate in the end-quench test varies in a nonlinear type, while in the dilatometry test it is a constant.
5 Conclusions
(1) An end-quench test system with automatically controlled induction heating was established to treat a specimen made of an advanced nickel-based superalloy. An unsteady two-dimensional model was developed to study the temperature distribution of the specimen in the gradient cooling process.
(2) The HTC of the quenched end was determined via the IHTM. The HTC increases sharply at first and then decreases when water is used as the cooling medium. The maximum value of the HTC in the quenching process is 120000 W/(m2·K) at 1.8 s.
(3) The cooling curve along the length of the specimen was numerically simulated. The cooling rate at the quenched end exceeds 1574 K/min, which is much greater than that of 51 K/min observed at the opposite end, which is physically farther away.
(4) A double logarithmic relationship between the size of the secondary γ′ phase and the average cooling rate was established through an efficient high-throughput method. This correlation is verified by the experiment with specified cooling rates. This empirical correlation can contribute to the databases of the Materials Genome Initiative.
References
[1] YANG Lin, FENG Hui, QIU Ke-qiang, CHEN Li-jia, LIU Zheng. Effect of cooling rate on microstructure and compressive performance of AZ91 magnesium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(s3): 1698-1702.
[2] SIM G C, TUN X H, TAN Xing-he, WENG C K J, ONN K W R, MANOJ G, KHENG L K. Effect of cooling rate on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-Y alloys [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 597: 135-139.
[3] MAJI S, SUBHANI A R, SHOW B K, JOYDEEP M. Effect of cooling rate on microstructure and mechanical properties of eutectoid steel under cyclic heat treatment [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering & Performance, 2017, 26(7): 1-13.
[4] JOMINY W E, BOEGEHOLD A L. A hardenability test for carburizing steel [J]. Trans of ASM, 1938, 26: 574-599.
[5] LI Pei-yue, XIONG Bai-qi, ZHANG Yong-an, LI Zhi-hui, ZHU Bao-hong, WANG Feng, LIU Hong-wei. Quench sensitivity and microstructure character of high strength AA7050 [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 268-274.
[6] YUAN Lu, SISSON R D Jr, RONG Yi-ming, MOCSARI J. Critical heat transfer coefficient test for gas quench steel hardenability [C]// Proceedings of the 28th ASM Heat Treating Society Conference. Detroit: AMS International, 2015: 490-494.
[7] NUNURA, CESAR R N, DOS SANTOS C A, SPIM J A. Numerical-experimental correlation of microstructures, cooling rates and mechanical properties of AISI 1045 steel during the Jominy end-quench test [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 76: 230-243.
[8] YAZDI A Z, SAJJADI S A, ZEBARJAD S M, MOOSAVI NEZHAD S M. Prediction of hardness at different points of Jominy specimen using quench factor analysis method [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 199(1-3): 124-129.
[9] WANG Hai-zhou, WANG Hong, DING Hong, XIANG Xiao-dong, XIANG Yong, ZHANG Xiao-kun. Progress in high-throughput materials synthesis and characterization [J]. Science and Technology Review, 2015, 33(10): 31-49. (in Chinese)
[10] WU Hong-yu, LI Jia, LIU Feng, HUANG Lan, ZENG Xin, FANG Hong-qi, HUANG Zai-wang, JIANG Liang. A high-throughput methodology search for the optimum cooling rate in an advanced polycrystalline nickel-based superalloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2017, 128: 176-181.
[11] JAIN A, HAUTIER G, MOORE C J, ONG S, FISCHER C C, MUELLER T, PERSSON K A, CEDER G. A high-throughput infrastructure for density functional theory calculations [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2011, 50(8): 2295-2310.
[12] JAIN A, ONG S P, HAUTIER G, CHEN Wei, RICHARDS W, DACEK S, CHOLIA S, GUNTER D, SKINNER D, CEDER G, PERSSON K A. Commentary: The Materials Project: A materials genome approach to accelerating materials innovation [J]. APL Materials, 2013, 1(1): 001001.
[13] LAING Gang-tao, MUDAWAR I. Review of spray cooling. Part 2: High temperature boiling regimes and quenching applications [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 6: 1-17.
[14] MASSON P L, LOULOU T, ARTIOUKHINE E. Estimations of a 2D convection heat transfer coefficient during a metallurgical “Jominy end-quench” test: Comparison between two methods and experimental validation [J]. Inverse Problems in Engineering, 2004, 12(6): 595-617.
[15] AGRAWAL C, KUMAR R, GUPTA A, CHATTERJEE B. Rewetting and maximum surface heat flux during quenching of hot surface by round water jet impingement [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(17-18): 4772-4782.
[16] PRICE R F, FLETCHER A J. Determination of surface heat-transfer coefficients during quenching of steel plates [J]. Metals Technology, 1980, 7(1): 203-211.
[17] ZHOU Jian-hua, ZHANG Yu-wen. CHEN J K, FENG Zai-chun. Inverse estimation of surface heating condition in a three- dimensional object using conjugate gradient method [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2010, 53(13-14): 2643-2654.
[18] KANG Lei, ZHAO Gang, TIAN Ni, ZHANG Hai-tao. Computation of synthetic surface heat transfer coefficient of 7B50 ultra-high-strength aluminum alloy during spray quenching [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 989-997.
[19] OSMAN A M, BECK J V. Investigation of transient heat transfer coefficients in quenching experiments [J]. Journal of Heat Transfer (Transactions of the ASME, Series C), 1990, 112(4): 843-848.
[20] REED R C. The superalloys: Fundamentals and applications [M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2006.
[21] POLLOCK, TRESA M. Alloy design for aircraft engines [J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(8): 809-815.
[22] JIA Chen-chang, TIAN Gao-feng. Powder metallurgy superalloy [J]. Metal World, 2011(2): 19-25. (in Chinese)
[23] CHEN Yi-qiang, PRASATH B R, SLATER T J A, BAI Ming-wen, MITCHELL R, CIUCA O, PREUEE M, HAIGH S J. An investigation of diffusion-mediated cyclic coarsening and reversal coarsening in an advanced Ni-based superalloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 110: 295-305.
[24] ANTONOV S, DETROIS M, ISHEIM D, SEIDMAN, HELMINK R C, GOETZ R L, SUN E, TIN S. Comparison of thermodynamic database models and APT data for strength modeling in high Nb content γ–γ′ Ni-base superalloys [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 86: 649-655.
[25] DAI Xian-chaung, LI Zhen-feng, CHEN Ji-guang, DING Han-hui, WU Hong-yu, LIU Feng, JIANG Liang. Gamma prime phase evolution rule during end quench cooling in nickel-based superalloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(2): 258-264. (in Chinese)
[26] CHEN Ji-guang, DENG Wen-kai, ZHOU Ping, JIANG Liang. Numerical simulation of transient temperature field during thermomechanical fatigue of IN718 alloy [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(2): 265-271. (in Chinese)
[27] MOU Gang, CHE Yun, JIANG Yu, ZHANG Zhong-ke, MAO Jian-gang. Water-quenching hardenability of 211Z high strength and toughness heatproof aluminum alloy [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2015, 44: 2847-2851. (in Chinese)
[28] OSORIO W R, GOULART P R, GARCIA A, SANTOS G, NETO C M. Effect of dendritic arm spacing on mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Al 9 Wt Pct Si and Zn 27 Wt Pct Al alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006, 37(8): 2525-2538.
[29] MAO Jian, CHANG K M, YANG Wan-hong, RAY K, VAZE S P, FERRER D U. Cooling precipitation and strengthening study in powder metallurgy superalloy U720LI [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2001, 32(10): 2441-2452.
[30] SEMIATIN S L, ZHANG F, TILEY J S, FURRER D U. A comparison of the precipitation behavior in pm γ–γ′ nickel-based superalloys [J]. High Temperature Technology, 2016, 33(4-5): 301-309.
付 佩1,周 萍1,谢紫微1,吴红宇2,陈继光1
1. 中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,长沙 410083
摘 要:合金的显微组织很大程度上受其冷却过程的影响。为了建立一种先进镍基高温合金材料的冷却速率及对应微观结构的关系,采用实验和数值模拟的方法研究其冷却过程。实验测量数据包含工件在端淬过程中的温度及其后的二次γ′相的尺寸。通过导热反问题方法确定模拟所需的端淬表面换热系数。结果表明,端淬表面换热系数超过1574 K/min。基于模拟所得的平均冷却速率和实验所得的二次γ′相的尺寸数据,建立两者间的双对数关系式,其可靠性通过特定冷却速率的实验得到验证。
关键词:端淬实验;数值模拟;冷却速率;换热系数;镍基高温合金
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Project (2016YFB0700300) supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China; Project (2019zzts262) supported by the Postgraduate Independent Exploration and Innovation Program of Central South University, China
Corresponding author: Ping ZHOU; Tel: +86-13975804856; E-mail: zhoup@csu.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)65150-2

