Colonization of Penicillium oxalicum enhanced neutralizationeffects of microbial decomposition of organic matter in bauxite residue
来源期刊:中南大学学报(英文版)2019年第2期
论文作者:薛生国 廖嘉欣 张一帆 程庆宇 WU Hao吴昊 朱锋
文章页码:331 - 342
Key words:bauxite residue; alkalinity transformation; Penicillium oxalicum; soil formation in bauxite residue; column experiment
Abstract: Bauxite residue is a highly alkaline waste product from refining bauxite ore. Bioremediation driven by microbial activities has been evidently effective in lowering the alkalinity of bauxite residues, which is critical to the initiation of pedogenesis under engineered conditions. The present study investigated the changes of alkalinity and aggregation of bauxite residue at different depth in response to the colonization of Penicillium oxalicum in columns. The results demonstrated that the inoculation of P. oxalicum decreased the residue’s pH to about 7 after 30 d only at the surface layer, which was exposed to aerobic conditions. The formation of aggregates was improved overall in the organic matter treated bauxite residue. However, the EC of bauxite residue increased with time under the incubation condition, probably due to accelerated hydrolysis of sodium-rich minerals. The inoculation of P. oxalicum had no effects on urease activity, but increased cellulose enzyme activity at surface layer only.
Cite this article as: LIAO Jia-xin, ZHANG Yi-fan, CHENG Qing-yu, WU Hao, ZHU Feng, XUE Sheng-guo. Colonization of Penicillium oxalicum enhanced neutralization effects of microbial decomposition of organic matter in bauxite residue [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(2): 331–342. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771- 019-4005-y.

ARTICLE
J. Cent. South Univ. (2019) 26: 331-342
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-019-4005-y

LIAO Jia-xin(廖嘉欣), ZHANG Yi-fan(张一帆), CHENG Qing-yu(程庆宇),WU Hao(吴昊), ZHU Feng(朱锋), XUE Sheng-guo(薛生国)
School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
 Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2019
Central South University Press and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2019
Abstract: Bauxite residue is a highly alkaline waste product from refining bauxite ore. Bioremediation driven by microbial activities has been evidently effective in lowering the alkalinity of bauxite residues, which is critical to the initiation of pedogenesis under engineered conditions. The present study investigated the changes of alkalinity and aggregation of bauxite residue at different depth in response to the colonization of Penicillium oxalicum in columns. The results demonstrated that the inoculation of P. oxalicum decreased the residue’s pH to about 7 after 30 d only at the surface layer, which was exposed to aerobic conditions. The formation of aggregates was improved overall in the organic matter treated bauxite residue. However, the EC of bauxite residue increased with time under the incubation condition, probably due to accelerated hydrolysis of sodium-rich minerals. The inoculation of P. oxalicum had no effects on urease activity, but increased cellulose enzyme activity at surface layer only.
Key words: bauxite residue; alkalinity transformation; Penicillium oxalicum; soil formation in bauxite residue; column experiment
Cite this article as: LIAO Jia-xin, ZHANG Yi-fan, CHENG Qing-yu, WU Hao, ZHU Feng, XUE Sheng-guo. Colonization of Penicillium oxalicum enhanced neutralization effects of microbial decomposition of organic matter in bauxite residue [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(2): 331–342. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771- 019-4005-y.
1 Introduction
Approximately 200 million tons of bauxite residue with extreme of pH, particle size and low nutrient availability [1, 2] are generated globally each year by alumina processing and extracting activities [3, 4]. Over past decades, much attention has been paid to developing methods for eliminating the high alkalinity of bauxite residue [5, 6]. Reducing alkalinity of bauxite residue is the key to minimize environmental impacts and improve rehabilitation outcomes. The basic methods include inorganic acid neutralization, carbonization, amendment with gypsum [7], seawater neutralization [8] and bioremediation [9]. Among them, bioremediation has attracted extensive interest because of its moderate effects on the mineral structure of alluminosilicates, low cost and the sustainability of renewable biomass [10]. Bioremediation is targeted to reduce the pH, sodicity and salinity of bauxite residue, and microorganism plays a vital role in bioremediation. Microorganism contributes to remediation of residue through the process of metabolisms, such as produce organic acid, inorganic acid and carbon dioxide [11]. Organic wastes such as hay and woodchips were used as nutrients for the production of citric, acetic and lactic acid by microorganism [12], which makes the alkalinity of bauxite residue decrease during remediation. Some microorganism produces inorganic acids, such as H2SO4 [13], assisting in microbially-driven remediation of bauxite residue to neutralize pH. Mechanisms of neutralization by carbon dioxide could form carbonic acid and subsequently dissociate to produce H+ and HCO3– [14]. This method used in industry is costly because of the high demand for equipment. However, microorganism producing carbon dioxide through respiration makes a positive contribution to remediate bauxite residue by neutralizing pH [11].
Soil structure plays a significant role in nutrient transport, soil moisture, gas exchange and establishment of habitat for living organisms. Soil aggregate is an important component of soil structure, which affects the physical, chemical and biological properties [15]. It is necessary to promote the formation of aggregate when establishing vegetation in bauxite residue for a long time [16]. Microorganism controls the content of soil organic matter and the stability of soil aggregates by direct transformation or physical intertwine, secretion of extracellular polymeric substances or changing the soil hydrophobic property [17]. There are many kinds of microorganisms, such as Aspergillus niger, Rhizopus stolonifer, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Beijerinckia indica, Cladosporium sphaerospermum, Cunninghamella blakesleeana, Mucor racemosus and Penicillium oxalicum, which can promote the soil aggregates formation [18]. P. oxalicum could facilitate the formation of stable mineral by secreting large amounts of oxalic acid [19]. Therefore, functional microbe inoculated in bauxite residue could accelerate the process of remediation and promote the soil formation by enhancing the contact with soil aggregates [20]. Besides, a critical element is organic matter in the process of soil formation, which improves the capacity of soil to hold water and nutrients, and allows them to release carbon slowly, thereby improving the conditions for plant growth [21]. However, the content of organic matter in bauxite residue was very low, in order to maintain or improve organic matter levels, new organic matter (from plant debris) is needed to accelerate the process of soil formation. In addition, microorganism cling to the surface of organic matter could form biofilms, resulting in a series of biorelated reactions in the soil, which leads to soil structure more stable than before [10]. Soil enzyme is an active participant in all soil biochemical processes such as soil organic degradation, mineralization and nutrient cycling. Almost all soil ecosystem degradation is accompanied by the decline of soil enzyme activity [22]. Some microorganisms produce enzymes to degrade polysaccharides, such as cellulose, resulting in the formation of aggregates structure [23]. Therefore, the assessment of soil enzyme should be taken into account for remediation of bauxite residue.
Previous remediation studies focus on techniques for vegetation establishment, while little attention has been paid to the alkalinity regulation of bauxite residue and the processes of soil formation. In particular, there was no study evaluating the effect of remediation at different depth of residue. The overall aim of this study was to develop and evaluate the effect of bioremediation on bauxite residue, and use organic waste as nutrients for P. oxalicum to produce acid, thereby reducing the alkalinity of residue. Meanwhile, a series of biochemical reactions between organic waste and fungus can improve the physical, chemical and biological properties of bauxite residue. Column methods have been used in this study to depict the effect of different depth on the properties of bauxite residue. Specific objectives of this study were to 1) determine the change of residues alkalinity at different depth; 2) analyze the change of organic matter and enzyme activity of residues during remediation; 3) investigate the chemical, biological and physical properties of bauxite residue under the different remediation.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Samples
Fresh bauxite residue (<3 years) was collected from Pingguo refinery, Aluminum Corporation of China, Guangxi province, China (23°18′N, 107°31′E). Organic matter (bagasse and barn) was also collected from Guangxi province nearby bauxite residue disposal areas (BRDAs). Samples were taken back to the laboratory in sterile polyethylene bags, and then air-dried for one week, subsequently sieved to retain the <2 mm fraction.
2.2 Leaching experiment apparatus
Three columns (95 cm in length and 12.6 cm in diameter) were used for the experiment. Each column was filled with 6 cm of quartz at the bottom to prevent the loss of bauxite residue. Control column (CK) was filled with 65 cm of bauxite residue, and biomaterial remediation (BR) of column was amended with organic matter, and it was filled with 40 cm of bauxite residue at bottom, the upper layer of 25 cm was filled with mixtures (organic matter and residue were mixed in a 1:10 ratio). Fungi-inoculated (FI) of column was filled with organic matter and bauxite residue as the same as BR column and inoculated with P. oxalicum every 5 d (Figure 1). The columns were fed with distilled water for 30 d to keep the residue moist and provided a suitable condition for microbe to reproduce. The residues were collected at the depth of 0, 5, 15, 25, 35, 45 cm on the 6th, 12th, 18th, 24th and 30th day, respectively. During this experiment process, temperature and moisture were stable at 25.2 °C and 70.4%, respectively.
2.3 Analytical methods
The pH and EC of samples were measured in a 1:5 of soil to water ratio extract after 2 h shaking and 30 min settling. Organic matter of samples was tested by potassium bichromate–sulfuric acid solution method [24]. The samples were air dried, and urease of residues was determined by TABATABAI et al [25]. The cellulose enzyme of bauxite residue was determined by colorimetry with 10 g samples of glucose consumed in 72 h. Soluble Na+, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations in bauxite residue were analyzed by a PerkinElmer Optima 5300 ICP-AES [26]. The residues micro- morphological features were adapted a scanning electron microscope equipped with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscope [27]. Au was required to support the conductivity during the experiment of scanning electron microscope. The BL08U1A beamline of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility was explored for distribution of Na experiment [5].
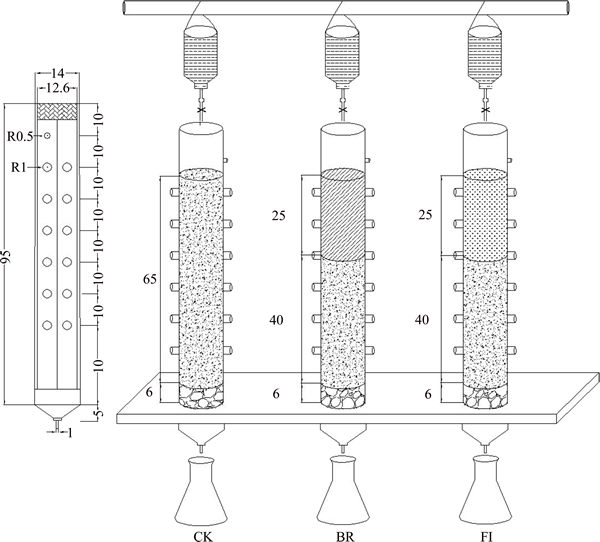
Figure 1 Experiment device of bauxite residue for different leaching column (FI: Fungi-inoculated)
2.4 Statistical analysis
The statistical analyses were performed using Origin 8 software. ANOVA was measured on residues properties at different depth of columns. The figure of Na distribution was analyzed by scanning transmission X-ray microscopy (STXM) technique.
3 Results
3.1 pH, EC and total alkalinity
The pH of bauxite residue in column FI generally decreased with time and reached the minimum after 30 d at the surface layer (Figure 2). However, the pH rose slightly on the 18th day, and then it declined until it its pH was stable around 7. P. oxalicum actually makes a considerable effect on the residue during 30 d, because there were distinct differences between the 6th day and 30th day for pH (P<0.05). The pH of bauxite residue in BR column has not changed over the time, holding the pH at 9 constantly. It is possible that the organic waste or leaching reduced alkalinity of the residue at some time but with no differences in the whole process. However, pH (10.42), EC (0.59 mS/cm) and total alkalinity (56.8 mg/kg) were stable in CK column. Therefore, this data were not shown in Figure 2. It was noticeable that the EC of bauxite residue in BR column declined with time. This may be due to the effect of leaching. It has been found that the EC of bauxite residue in FI column increased with time, and there was a significant difference between the 6th day and 24th day. The pH of bauxite residue in FI column was lower than that in BR column, nonetheless the EC of the residue in FI column was higher than that in BR column. Within FI column, pH was lower at the upper layer of 0 cm (6.66) than that at the bottom layer of 45 cm (8.65) after 30 d. Moreover, the EC of bauxite residue in FI column decreased from the upper layer of 0 cm (3.28 mS/cm) to the bottom of 45 cm (0.47 mS/cm) after 30 d. While the pH and EC had a little change with depth in BR column. The total alkalinity of bauxite residue in BR column was higher than that in FI column at the depth of 35–45 cm.

Figure 2 pH (a, d), EC (b, e) and total alkalinity (c, f) of bauxite residue (0–45 cm depth) from two different treatments during 30 d: (a, b, c) FI; (d, e, f) BR (Days marked with the same letter are not significantly different according to ANOVA)
3.2 Organic matter (OM), urease activity and cellulose enzyme
The organic matter has similar tendency both in FI and BR column, which means that P. oxalicum had no effect on OM during the short time (30 d). As shown in Figure 3, the concentration of OM rose with time. The OM concentration reached the maximum 4.27 g/kg on the 12th day, then it decreased slightly. The OM was higher at the 0–25 cm depth than that at the 35–45 cm depth. However, the OM in CK column was very low, with its value approximating to zero.
Urease activity experiments showed that there was no difference between FI and BR column (Figure 4). The results presented the same tendency that they all increased with time in the whole process. This indicated that fungus was not able to activate urease in bauxite residue, but there were markedly distinctions at different depth. The urease activity was higher at the 0–25 cm depth than that at the 35–45 cm depth, and there were significant differences between them (P<0.01). This illustrated that biomaterial addition leads to the increase of urease activity. However, the cellulose enzyme in FI column was higher than that in BR column, which means that P. oxalicum considerably boosts the cellulose enzyme activity. The cellulose enzyme was higher at the 0–5 cm depth (about 0.8 mg/g), lower at the 35–45 cm depth, and moderate at 15–25 cm depth. At the depth of 0–5 cm, the cellulose enzyme reaches the maximum on the 30th day. Urease activity and cellulose enzyme were below detection limits in CK column and therefore not shown in Figure 4.
3.3 Change of soluble cations at different depth
Bauxite residue showed the lowest pH on the 30th day in preliminary tests. Based on this discovery, the concentration of soluble cations at different depth was investigated in different column on the 30th day. The main element in residues was Na+ and there were also significant amounts of Ca2+, K+ and Mg2+ (Figure 5). Soluble Na+ of the total soluble cations in FI, BR and CK column accounts for 86%, 90% and 91%, respectively. The cationic contents of FI column were always higher than those of BR column. The concentrations of soluble cations in FI column increased in the order: Na+ > Ca2+ > K+ > Mg2+. Although the pH of residues in FI column was lower than that in BR column, the concentration of Na+ was higher than that in BR column. This may be due to the acid that was metabolized by P. oxalicum, which could accelerate the dissolution of Na from bonding alkali in bauxite residue. Within FI column, the concentration of Na+ decreased from the extremely high value (5069 mg/kg) on the surface to the very low value (65.56 mg/kg) in the bottom. Soluble Na+ in the BR column has the similar tendency with FI column, but the value at surface (1044 mg/kg) was significantly lower than that in FI column. The concentration of Ca2+ in FI column decreased from 263.6 mg/kg to 72.28 mg/kg with depth, and there were significant differences between BR and FI column on the soluble Ca2+ (P<0.05). The concentration of soluble K+ in FI column was higher at 0–25 cm depth than that at 35–45 cm depth; especially its value reaches to the maximum (316.1 mg/kg) at the surface (0 cm). Soluble Mg2+ in residue was extremely low, but there was still extremely high value in FI column on the surface.
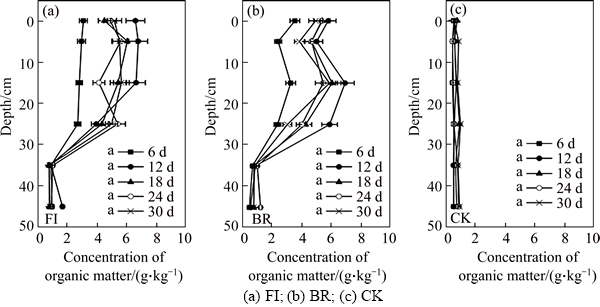
Figure 3 Concentration of organic matter in bauxite residue (0–45 cm depth) from three treatments during 30 d:(Days marked with the same letter are not significantly different according to ANOVA)

Figure 4 Concentrations of urease and cellulose enzyme in bauxite residue from different two treatments:(Days marked with the same letter, are not significantly different according to ANOVA)
3.4 Distribution of Na in bauxite residue
According to the preliminary tests, Na was the main element in bauxite residue, which can influence the alkalinity regulation, especially at surface in the column. Based on this discovery, distribution of Na in residue on the surface of the column was investigated. Distribution of Na obviously discriminated between FI and BR column (Figure 6). The distributions of Na in BR column were dense in size, and the color was clear. This indicated that abundant Na exists in BR column. However, distribution of Na in FI column was diluted in size, which influenced the reduction on alkalinity of bauxite residue. Na STXM imaging highlights that P. oxalicum significantly reduces the alkalinity of residues.
3.5 Micromorphological features in bauxite residue
Preliminary tests showed that chemical and biological properties of FI column varied at the surface. Based on this discovery, micromorphological features were investigated in different columns at the surface. The chemical and biological properties of CK column were stable during the whole process; therefore, it was not considered in this experiment. In FI column, the number of pores was decreased among microaggregates; the distribution of surface particle became uniform and microaggregate structure turn into dense (Figure 7). There were lots of mini particles with poor crystallinity in microaggregates which were relatively dispersed and disordered distribution in BR column. Calcium and sodium contents varied significantly between BR and FI column at the surface. The contents of total calcium (6.65%) in BR column were lower than those in FI column (24.21%), whilst the contents of total sodium in BR column were higher than those in FI column. These results illustrated that P. oxalicum could improve the microaggregates of residues, decline the contents of Na+ and increase the contents of Ca2+ in bauxite residue.

Figure 5 Change of solution cations (Na, K, Ca and Mg) at different depth extracted from three treatments after 30 d: FI; BR; CK is as a control experiment (Days marked with the same letter, are not significantly different according to ANOVA)

Figure 6 Na STXM imaging by two-dimensional scan mode for FI (a) and BR (b)

Figure 7 Morphological structures (a, b) and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis spectra (c, d) obtained from macroaggregates (0.25 mm):
4 Discussion
4.1 Different factors effect on alkalinity of bauxite residue
High alkalinity of bauxite residue is a potential threat to the environment which influences the surrounding plants growth of its disposal areas. This study aimed to create a similar condition with BRDAs, and to investigate the effects of inoculated with P. oxalicum on residues alkalinity. Due to the fact that plant roots were always distributed on the topsoil, this work only remedies the residue at 0– 25 cm depth via the column experiment. The pH of residue in FI column was lower than that in BR column, which means that the organic acids secreted by P. oxalicum could neutralize the alkalinity of residue. KRISHNA et al [28] reported that Aspergillus tubingensis was able to reduce the pH values of bauxite residue by using the nutrient medium. VALARIE [29] also reported that it would be possible to reduce the pH of residue after being inoculated with indigenous bacteria and nutrients in bauxite residue. HAMDY et al [30] found that residue pH reduced from 13 to about 7.0 by inoculating with various nutrients and different microbes that could produce organic acids. They all used microbe to reduce the alkalinity of bauxite residue, but their studies were only at the experimental stage. In this study, we investigated the alkalinity of bauxite residue at different depth, which reflected the actual condition at the BRDAs. The total alkalinity in FI column was similar with BR column at 0–25 cm depth, but that in FI column was lower than that in BR column at 35–45 cm depth. This result dedicated that P. oxalicum was able to influence the alkalinity of residue in the deeper depth. From a macroscopic perception of view, our study provides a promising method to remediate bauxite residue. Besides, specific monitor of alkalinity change in bauxite residue should be considered more stable in the long term than short term.
A lot of studies show that EC was positively correlated to pH in bauxite residue [6]. But in this study, EC was negatively correlated to pH in FI column. Measuring EC is an effective method to know how many cations exist in the soil and the concentration of cations was positively correlated to EC. Compared to BR column, soluble cations increased in FI column, which means that P. oxalicum producing acid could accelerate the dissolution of cations. Nitrohumic acid was used to neutralize the alkalinity of bauxite residue according to by research REN et al [31] and the results showed that the concentration of cations increased under this condition. In this study, the residue in FI column at surface (0 cm) was possessed with the properties of lower pH, higher EC and higher soluble cations, and the experiment of Na distribution showed that there were few contents of Na in FI column. Inoculating with P. oxalicum in bauxite residue could promote the dissolution of Na from alkaline cancrinite due to the effect of organic acids produced by P. oxalicum. According to by research GRAFE et al [32], removal of Na was the first step to reduce the alkalinity of residue. KONG et al [5] also highlighted that the removal of Na could improve the physical, chemical and biological properties on bauxite residue.
4.2 Variation of biological properties in bauxite residue
Temperature and moisture are important for soil formation, they can affect the soil biota activities by determining the rate of physiological activity such as enzyme activity, and meanwhile they can also affect physicochemical properties such as diffusion and solubility of nutrients, mineral weathering and the rate of evaporation. Moisture can change the oxygen consumption in the soil, thereby the quantity of microorganism was changed according to by research JOHAN et al [33]. Therefore, the temperature and moisture were also considered in this experiment. During this experiment process, temperature and moisture were stable at 25.2 °C and 70.4%, respectively, which supported a suitable condition for P. oxalicum to reproduce. Soil microorganisms have an essential role in soils, because it can transform organic matter into plant available nutrients through mineralization. Therefore, it is important to maintain high microbial activity in bauxite residue. Decomposition of organic matter served two functions for the microorganisms, providing energy for growth and supplying carbon for the formation of new cells. In this study, organic matter at remediation layer (0–25 cm) was extremely higher than that at bottom layer (35–45 cm). It is because the input of biomaterial rapidly changed the storage of organic matter in residues. However, there was no difference between FI and BR column in terms of organic matter experiment. This may be due to the reason that P. oxalicum would not change the concentration of organic matter in the short term. SANTINI et al [11] pointed out that organic matter has a critical role in the physical, chemical and biological properties of bauxite residue. Therefore, adding biomaterial in bauxite residue is a feasible method to improve the biological properties of residues. SANTINI et al [34] used glucose to offer nutrient for microbe, and the results showed that microorganisms not only survived in bauxite residue but also reduced the alkalinity of the residue. HAMDY et al [30] reported that the injured bacterial cells were activated by adding hay into bauxite residue.
Urease activity was related to the content of organic matter and the quantity of microorganisims in soil, which also reflects the nitrogen cycle. In this study, the urease activity showed a decreasing pattern with depth and the bottom layer (35–45 cm) was basically undetectable. This result was similar to DAS’s research [35]. Cellulose is the most abundant polysaccharide in plant cell walls, which represents a significant component of soils. P. oxalicum is a strong cellulose-decomposer microorganism, which could produce cellulose- enzyme. In this study, bagasse and barn were added in residue as nutrient for P. oxalicum, because bagasse and barn were able to provide cellulose.
4.3 Effects on micromorphological properties of residue
Physicochemical properties and aggregate stability of bauxite residue were important to establish vegetation, and plays a key role in soil formation [36]. In this study, inoculating with P. oxalicum significantly increased the content of Ca while reduced the Na content. The reason is that organic acids produced by P. oxalicum could dissolve andradite from the residue. Ca content was beneficial to stable aggregate in bauxite residue [37], because calcium ions are regarded as ion bridges to form microaggregates [27]. ZHU et al [16] discovered that the physical condition would be improved after added gypsum and vermicompost into bauxite residue, and the content of Ca increased. This illustrated that Ca is critical for aggregates formation in bauxite residue.
5 Conclusions
This study indicated that waste biomaterial associated with P. oxalicum could achieve an excellent effect of remediation. The organic matter and enzyme activities were strikingly increased at 0–25 cm depth of residue. The alkalinity of the residue was reduced significantly, and the microaggregates become uniform. Moreover, a large amount of the alkaline cations in bauxite residue was dissolved due to the effect of acid produced by P. oxalicum. And P. oxalicum has effect on the distribution of Na in the mesoporous range.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility for use of the synchrotron facilities at beamlines BL08U. The authors sincerely acknowledge HUANG Long-bin and WANG Yan-hong to further improve the quality of the manuscript.
References
[1] XUE Sheng-guo, ZHU Feng, KONG Xiang-feng, WU Chuan, HUANG Ling, HUANG Nan, HARTLEY W. A review of the characterization and revegetation of bauxite residues (red mud) [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23: 1120–1132. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-015- 4558-8.
[2] LI Yi-wei, JIANG Jun, XUE Sheng-guo, MILLAR G, KONG Xiang-feng, LI Xiao-fei, LI Meng, LI Chu-xuan. Effect of ammonium chloride on leaching behavior of alkaline anion and sodium ion in bauxite residue [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 2125–2134. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64857-5.
[3] XUE Sheng-guo, LI Meng, JIANG Jun, GRAEME J M, LI Chu-xuan, KONG Xiang-feng. Phosphogypsum stabilization of bauxite residue: Conversion of its alkaline characteristics [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 77: 1–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.05.016.
[4] LI Xiao-fei, YE Yu-zhen, XUE Sheng-guo, JIANG Jun, WU Chuan, KONG Xiang-feng, HARTLEY W, LI Yi-wei. Leaching optimization and dissolution behavior of alkaline anions in bauxite residue [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 1248–1255. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64763-6.
[5] KONG Xiang-feng, LI Meng, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, CHEN Cheng-rong, WU Chuan, LI Xiao-fei, LI Yi-wei. Acid transformation of bauxite residue: Conversion of its alkaline characteristics [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 324: 382–390. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.073.
[6] KONG Xiang-feng, GUO Ying, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, WU Chuan, YE Yu-zhen, CHENG Qin-yu. Natural evolution of alkaline characteristics in bauxite residue [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 143: 224–230. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.125.
[7] XUE Sheng-guo, YE Yu-zhen, ZHU Feng, WANG Qiong-li, JIANG Jun, W HARTLEY. Changes in distribution and microstructure of bauxite residue aggregates following amendments addition [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences. 2019, 78: 276–286. DOI: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.10.010.
[8] XUE Sheng-guo, WU Yu-jun, LI Yi-wei, KONG Xiang-feng, ZHU Feng, HARTLEY W, LI Xiao-fei. Industrial wastes applications for alkalinity regulation in bauxite residue: A comprehensive review [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(2): 268–288.
[9] ZHU Feng, HOU Jing-tao, XUE Sheng-guo, WU Chuan, WANG Qiong-li, HARTLEY W. Vermicompost and gypsum amendments improve aggregate formation in bauxite residue [J]. Land Degradation and Development. 2017, 28: 2109– 2120. DOI: 10.1002/ldr.2737.
[10] LIAO Jia-xin, JIANG Jun, XUE Sheng-gue, CHENG Qing-yu, WU Hao, MANIKANDAN R, HARTLEY W, HUANG Long-bin. A novel acid-producing fungus isolated from bauxite residue: The potential to reduce the alkalinity [J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2018, 35: 840–847. DOI: 10.1080/01490451.2018.1479807.
[11] SANTINI T C, KERR J L, WARREN L A. Microbially- driven strategies for bioremediation of bauxite residue [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 293: 131–157. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.024.
[12] SAUER M, PORRO D, MATTANOVICH D, BRANDUARDI P. Microbial production of organic acids: Expanding the markets [J]. Trends in Biotechnology, 2008, 26: 100–108. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2007.11.006.
[13] SCHIPPERS A, SAND W. Bacterial leaching of metal sulfides proceeds by two indirect mechanisms via thiosulfate or via polysulfides and sulfur [J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65: 319–321. DOI: 10.1002/abio. 370190413
[14] POWER G, GRAFE M, KLAUBER C. Bauxite residue issues: I. Current management, disposal and storage practices [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 108: 33–45. DOI: 10.1016/ j.hydromet.2011.02.006.
[15] TISDALL J M, OADES J M. Organic matter and water- stable aggregates in soils [J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 33: 141–163. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1982. tb01755.x.
[16] ZHU Feng, XUE Sheng-guo, W HARTLEY, HUANG Ling, WU Chuan, LI Xiao-fei. Novel predictors of soil genesis following natural weathering processes of bauxite residues [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2016, 23: 2856–2863. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-015-5537-9.
[17] JIANG Yu-ji, SUN Bo, JIN Chen, WANG Feng. Soil aggregate stratification of nematodes and microbial communities affects the metabolic quotient in an acid soil [J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2013, 60: 1–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.01.006.
[18] KABIR Z, KOIDE R T. The effect of dandelion or a cover crop on mycorrhiza inoculum potential, soil aggregation and yield of maize [J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2000, 78: 167–174. DOI: 10.1016/s0167-8809(99)00121-8.
[19] TIAN Da, WANG Wen-chao, SU Mu, ZHENG Jun-yi, WU Yuan-yi, WANG Shi-mei, LI Zhen, HU Shui-jin. Remediation of lead-contaminated water by geological fluorapatite and fungus Penicillium oxalicum [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25: 21118–21126. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-018-2243-4.
[20] SANTINI T C, FEY M V. Assessment of Technosol formation and in situ remediation in capped alkaline tailings [J]. Catena, 2016, 136: 17–29. DOI: 10.1016/j.catena.2015. 08.006.
[21] ZANUZZI A, AROCENA J M, MOURIK J M V, CANO A F. Amendments with organic and industrial wastes stimulate soil formation in mine tailings as revealed by micromorphology [J]. Geoderma, 2009, 154: 69–75. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.09.014.
[22] CHANG E H, CHUANG R S, TSAI Y H. Effect of different application rates of organic fertilizer on soil enzyme activity and microbial population [J]. Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, 2010, 53: 132–140. DOI: 10.1111/j.1747-0765.2007.00122.x.
[23] MAKI M, LEUNG K T, QIN W. The prospects of cellulase- producing bacteria for the bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass [J]. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2009, 5: 500–516. DOI: 10.1007/BF00373654.
[24] BARANCIKOVA G, JERZYKIEWICZ M, GOMORYOVA E, TOBIASOVA E, LITAVEC T. Changes in forest soil organic matter quality affected by windstorm and wildfire [J]. Journal of Soils & Sediments, 2018, 18: 2748–2748. DOI: 10.1007/s11368-018-1979-2.
[25] TABATABAI M A, BREMNER J M. Assay of urease activity in soils [J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 1972, 4: 479–487. DOI: 10.1016/0038-0717(72)90064-8.
[26] KONG Xiang-feng, JIANG Xing-xing, XUE Sheng-guo, HUANG Ling, HARTLEY W, WU Chuan, LI Xiao-fei. Migration and distribution of salinity in bauxite residue during water leaching [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28: 534–541. DOI: 10.1016/S1003- 6326(18)64686-2.
[27] ZHU Feng, LIAO Jia-xin, XUE Sheng-guo, HARTLEY W, ZHOU Qi, WU Hao. Evaluation of aggregate microstructures following natural regeneration in bauxite residue as characterized by synchrotron-based X-ray micro-computed tomography [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 573: 155–163. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.108.
[28] KRISHNA P, REDDY M S, PATNAIK S K. Aspergillus Tubingensis reduces the pH of the bauxite residue (red mud) amended soils [J]. Water Air and Soil Pollution, 2005, 167: 201–209. DOI: 10.1007/s11270-005-0242-9.
[29] VALARIE E. The bioremediation of bauxite residue (red mud) using indigenous bacteria [D]. Perth: Murdoch University, 1999.
[30] HAMDY M K, WILLIAMS F S. Bacterial amelioration of bauxite residue waste of industrial alumina plants [J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2001, 27: 228–233. DOI: 10.1038/sj.jim.7000181.
[31] REN Jie, LIU Ji-dong, CHEN Juan, LIU Xiao-lian, LI Fa-sheng, DU Ping. Effect of ferrous sulfate and nitrohumic acid neutralization on the leaching of metals from a combined bauxite residue [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 24: 1–12. DOI: 10.1007/s11356- 017-8605-5.
[32] GRAFE M, KLAUBER C. Bauxite residue issues: IV. Old obstacles and new pathways for in situ residue bioremediation [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 108: 46–59. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2011.02.005.
[33] SCHNURER J, CLARHOLM M, BOSTROM S, ROSSWALL T. Effects of moisture on soil microorganisms and nematodes: A field experiment [J]. Microbial Ecology, 1986, 12: 217–230. DOI: 10.1007/BF02011206.
[34] SANTINI T C, MALCOLM L I, TYSON G W, WARREN L A. pH and organic carbon dose rates control microbially driven bioremediation efficacy in alkaline bauxite residue [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50: 11164–11173. DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.6b01973.
[35] DAS S, GANGULY D, MUKHERJEE A, CHAKRABORTY S, DE T K. Soil urease activity of sundarban mangrove ecosystem, India [J]. Advances in Microbiology, 2017, 7: 617–632. DOI: 10.4236/aim.2017.78048.
[36] JONES B E H, HAYNES R J, PHILLIPS I R. Effect of amendment of bauxite processing sand with organic materials on its chemical, physical and microbial properties [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2010, 91: 2281–2288. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.06.013.
[37] COURTNEY R, HARRINGTON T, BYRNE K A. Indicators of soil formation in restored bauxite residues [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2013, 58: 63–68. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013. 06.022.
(Edited by YANG Hua)
中文导读
草酸青霉强化有机质的分解实现赤泥碱中和
摘要:赤泥是氧化铝工业生产过程中产生的强碱性固体废弃物,而生物修复是降低赤泥碱性的有效方法。针对赤泥高碱性问题,通过土柱实验开展草酸青霉调控赤泥碱性,探究不同深度的赤泥碱性变化。结果发现应用草酸青霉能显著降低赤泥碱性并形成稳定的团聚体结构;赤泥表层的pH值在30天内降低至7左右,而电导率则上升。草酸青霉对赤泥中的有机质和脲酶活性无明显影响,但能增加纤维素酶的活性。
关键词:赤泥;碱性调控;草酸青霉;土壤化;土柱实验
Foundation item: Projects(41877511, 41842020) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2018zzts421) supported by the Innovative Project of Independent Exploration of Central South University, China
Received date: 2018-10-19; Accepted date: 2018-11-27
Corresponding author: XUE Sheng-guo, PhD, Professor; Tel: +86-13787148441; E-mail: sgxue70@hotmail.com, sgxue@csu.edu.cn; ORCID: 0000-0002-4163-9383

