利用高效降解菌株强化修复土壤中DBP及其细菌群落动态解析
吴学玲,代沁芸,梁任星,王洋洋
(中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:在实验室条件下,研究土壤中分别加入邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBP)和同时加入DBP及高效降解菌JDC13后,对土壤中DBP降解的影响以及土壤中细菌总数和细菌群落结构的动态变化。通过高效液相色谱(HPLC)检测土壤中DBP的残留含量。通过变性梯度凝胶电泳(DGGE)检测土壤细菌群落结构的变化。研究结果表明:只加入DBP的样品A中,DBP在14 d时被完全降解;加入DBP和JDC13的样品B中,DBP在9 d时被完全降解,说明JDC13有效加快了土壤中DBP的降解速度;土壤中细菌总数测定结果显示DBP会抑制土著细菌的生长,但加入JDC13后可以减少DBP的这种不利影响;只加入DBP和同时加入DBP与JDC13对土壤中细菌群落结构的影响十分明显;JDC13、放线菌和β变形菌在土壤DBP降解过程中成为优势种群;大部分优势菌与PAEs(邻苯二甲酸酯)降解菌具有同源性。
关键词:DBP;生物降解;生物强化;PCR-DGGE;细菌群落
中图分类号:Q938.1; X53 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)05-1188-07
Biodegradation of DBP contaminated soil by high-efficiency degrading strain and dynamics analysis of bacterial community
WU Xue-ling, DAI Qin-yun, LIANG Ren-xing, WANG Yang-yang
(School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: An experiment was conducted in lab by adding di-n-butyl phthalate (DBP) soil with DBP alone and DBP plus DBP degrader JDC13. Biodegradation of DBP in soil, and its effect of the inoculant JDC13 on soil bacterial population and structure of soil bacterial community were studied. The DBP remaining in soil was determined by HPLC. In Sample A, with the only addition of DBP, the DBP was completely degraded after 14 d. And in Sample B, with the addition of DBP and JDC13, the DBP in soil was absolutely degraded after 9 d. Changes in the bacterial community were monitored using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). The results show that JDC13 can enhance the biodegradation of DBP in soil. DBP can inhibit the growth of local soil bacteria, but inoculation with JDC13 can reduce the negative effect of DBP on local soil bacteria. DBP alone and DBP plus JDC13 substantially affect the structure of bacterial community in the soil. JDC13, Actinobacteria and Betaproteobacteria become the dominant bacteria in the DBP-contaminated soil. And most of them are homologous to the Phthalate esters (PAEs) degrader.
Key words: DBP; biodegradation; bioaugmentation; PCR-DGGE; bacterial community
邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(di-n-butyl phthalate,DBP)是环境内分泌干扰物即邻苯二甲酸酯(Phthalate esters,PAEs)类化合物的一种[1]。PAEs具有环境激素作用,可在极低的浓度下干扰人类和动物的内分泌系统,目前已被多个国家列为优先控制的污染物[2]。近年来,由于DBP的广泛应用,土壤、河流、湖泊、海洋底质、饮用水、垃圾场甚至食品中都检测到DBP,对人类的身体健康造成了严重的威胁[3]。DBP在环境中的水解、光解速度非常缓慢,属于难降解物质。然而,利用一些微生物和淡水无脊椎动物可代谢DBP,半衰期仅为1~3 d,因此,微生物降解被认为是自然环境中DBP完全矿化的主要过程[4]。大量降解菌从各类环境中分离得到,主要包括变形菌门、放线菌门(高G+C革兰氏阳性菌)、厚壁菌门(低G+C革兰氏阳性菌)和绿菌门4个大类[5]。生物强化(Bioaugmentation)是接种具有特定降解能力的微生物来增强环境中的生物活性,以达到修复污染环境的目的[6]。研究结果表明:生物强化可以通过外源菌的引入改变原有的微生物群落结构,并且有可能改变原有的生化过程。因此,外源菌在自然环境中能否发挥降解作用,是生物能否强化的关键[7-8]。外源投入的微生物本身在环境中的行为和对环境的影响也成为研究的重要方向[9]。在此,本文作者以加入DBP的土壤为研究对象,考察利用DBP高效降解菌JDC13进行生物强化修复的效果,主要包括DBP在土壤中的降解情况和土壤中细菌总数的动态变化,并利用现代分子生物学手段即PCR-DGGE对土壤中细菌群落结构的变化进行监测,以便为生物强化技术的实际应用提供依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 样品来源
供试土壤采于长沙市岳麓山表层0~15 cm土壤。其基本性质如下:pH为6.2;黏粒(粒径≤2 μm) 含量为28.50%;有机质含量为86.5 g/kg,全氮含量为3.89 g/kg。土壤样品用无菌袋封存于温度为4 ℃的冰箱中。
1.2 降解菌的准备
从污染的河底污泥里分离得到的一株DBP高效降解菌JDC13,经16Sr RNA鉴定,JDC13 为Gordonia sp.。将筛选的JDC13于DBP培养基(K2HPO4 5.8 g/L, KH2PO4 4.5 g/L, (NH4)2SO4 2.0 g/L, MgCl2 0.16 g/L, CaCl2 0.02 g/L, Na2MoO4·2H2O 2.4 mg/L, FeCl3 1.8 g/L, MnCl2·2H2O 1.5 mg/L, DBP 0.4 g/L, pH=7.0)中培养至对数生长期后期,在转速10 000 r/min下离心5 min,用Na2HPO4-NaH2PO4 缓冲液洗涤3次,再用无菌水悬浮菌体,最终使菌液浓度为1×109 个/mL。
1.3 土壤中DBP的降解
取部分土壤样品,过150 μm筛滤除石头、植物等杂质,风干过夜。在土壤样品中加入DBP甲醇溶液(1 mL甲醇中含100 mg DBP)。于121 ℃灭菌60 min以上,置于无菌通风橱内风干甲醇。将原始土壤和上述处理过的土壤按质量比19:1的比例混合,充分混匀,最终土壤中DBP的含量为0.8 mg/g。
实验分为2组:第1组(样品A)取40 g实验土壤于500 mL三角瓶中;第2组(样品B)取40 g实验土壤于500 mL三角瓶中,加入降解菌JDC13的悬浮液至最终密度为1×107 个/g。将三角瓶置于30 ℃培养箱中避光培养,并定期加入适量无菌水以保持湿度。在第0,2,4,6,9,14和20天时取样分析。
土壤中残留DBP的含量使用高效液相色谱(HPLC)进行检测。取1 g土样,加入10 mL乙酸乙酯,充分振荡,于5 000 r/min转速下离心1 min,吸取上清液至烧杯中,重复3次。风干烧杯中的乙酸乙酯。将甲醇定容至5 mL用HPLC检测。HPLC使用Hyersil DBS C18柱(伊利特,大连)。流动相为甲醇和水(体积比为9?1),温度为35 ℃,流速为1 mL/min,吸收波长为228 nm。
1.4 土壤中细菌总数的测定
土壤中细菌总数采用活菌平板计数法测定[10]。称取1 g土壤样品置于灭菌三角瓶中,加入100 mL质量分数为0.85%的无菌NaCl水溶液,于转速250 r/min下振荡30 min。取1 mL上清液稀释10倍涂布于牛肉膏蛋白胨琼脂平板上,于30 ℃倒置培养2 d,再进行平板计数。
1.5 土壤中细菌群落结构的PCR-DGGE分析
土壤基因组DNA的提取参考Zhou等[11]的提取方法。提取的基因组经1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳、切胶回收纯化后,置于-20 ℃保藏备用。
细菌PCR扩增引物选用16Sr RNA基因V3区域通用引物对GC341F(5′-CGCCCGCCGCGCGCGGCG GGCGGGGCGGGGGCACGGGGGGCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′)和534R(5′-A TTACCGCGGCTGCTGG- 3′)[12]。扩增体系为:10×PCR buffer 5 μL,10 mmol/L dNTPs 1 μL,25 mmol/L MgCl2 5 μL, 5 U/μL Taq酶 1 μL,10 pmol/μL引物各1 μL,DNA模板3 μL,加H2O补齐50 μL。扩增程序采用降落式PCR:于95 ℃延伸5 min,于94 ℃解链1 min,于65 ℃退火1 min,循环20次,每次循环退火温度降低0.5 ℃;于72 ℃延伸1 min;于94 ℃解链1 min,于55 ℃退火1 min,循环15次;于72 ℃延伸1 min;于72 ℃延伸10 min,于4 ℃保存。扩增产物用1.5%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳 检验。
DGGE使用美国C.B.S公司的DGGE-2401电泳槽。电泳使用质量分数为7.5%的聚丙烯酰胺凝胶(m(丙烯酰胺)/m(甲叉双丙烯酰胺)=37.5),变性胶浓度梯度为45%~65%(100%的变性剂中含7 mol/L的尿素和40%的去离子甲酰胺)。使用TAE为电泳缓冲液,上样15 μL PCR产物。电泳条件为:在60 ℃恒温下,于200 V时电泳6 h。然后,用溴乙锭染色30 min。在紫外凝胶成像系统下分析电泳结果,对20个不同位置的较亮条带进行切胶。DNA溶解,再使用不带GC链的F341和R534引物对进行PCR扩增。产物送上海桑尼生物公司测序。
DGGE图谱采用Bio-rad公司的Quantity one软件分析,将图像信息转化为数字信息后用Microsoft公司的SPSS软件进行聚类分析。将测序所得序列在GenBank核酸序列数据库中进行序列比较,下载相似序列,用clustalx1.8软件进行序列比对,并采用邻接法(Neighbor joining, NJ)构建系统发育树[13]。
2 分析
2.1 土壤中DBP的降解和动力学分析
土壤样品中DBP的降解结果如图1所示。从图1可以看出:样品A中的土著微生物在14 d内可将DBP彻底降解;当土样中加入高效DBP降解菌JDC13作为外源菌后,DBP的降解速度明显加快,仅在9 d内就将DBP完全降解;样品B与不接种外源菌的样品A相比,降解时间缩短了5 d,这表明土壤中接种外源菌后可以迅速启动DBP的生物降解,并加快其降解速
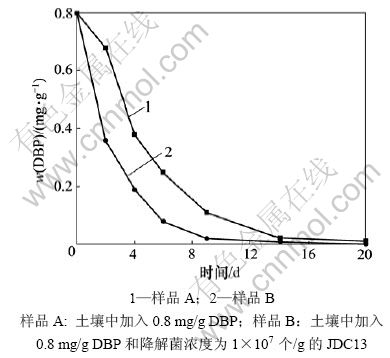
图1 土壤样品A和B中DBP的生物降解曲线
Fig.1 Biodegradation of DBP in soil for samples A and B
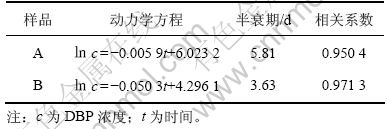
度。根据Numerous模型[14]进行降解动力学分析,其降解动力学方程和相关系数(表1)表明样品A和B对DBP的生物降解符合一级动力学反应模型。
表1 样品A和B对DBP生物降解动力学方程
Table 1 Kinetic equation of DBP degradation in soil
2.2 土壤中细菌总数的动态变化
对样品A和B细菌总数的变化情况进行研究。加入DBP 2 d后,未加降解菌的土壤样品A中DBP降解了10.4%,细菌数量由5.3×107 个/g减少到4.5×107 个/g,说明土壤细菌对DBP有一定降解能力,但菌数减少说明外加DBP对土壤细菌有一定的抑制作用。而同时加入降解菌JDC13的土壤样品B中在2 d内DBP降解了51.8%,细菌数量由6.9×107 个/g增加到1.02×108 个/g,说明接种外源降解菌可以加快DBP的降解并减少DBP对土著细菌的抑制作用。样品A中的细菌在被抑制2 d左右后开始繁殖生长,细菌数量增加,在第6天时达到最高菌数1.79×108 个/g,然后,缓慢下降,在第9天之后趋于稳定。样品B中的细菌数量在第4天时达到最大值2.19×108 个/g,然后,逐渐下降,在第6天后趋于稳定。在趋于稳定之后,样品A和B中的细菌总数接近,表明在大部分DBP被降解后,降解菌JDC13对土壤中细菌总数无明显影响。因此,与样品A相比,样品B中加入了外源降解菌JDC13,在培养初期土壤菌群就能够更好地适应DBP,在含DBP的土壤中快速生长繁殖,直至DBP被完全降解为止。
2.3 土壤中细菌群落结构分析
以样品A和B不同时间点所提取的基因组DNA为模板,利用16Sr RNA V3区域引物进行PCR扩增,对PCR产物进行DGGE分析(图2)。DGGE图谱中的条带类型显示了样品A和B不同时期优势细菌群落结果的变化情况。A0~A20及B0~B20分别为样品A和样品B在第0天到第20天所取样品。
通过Quantity one软件对土壤样品A和B的细菌群落结构进行分析,结果见图2。图2(a)表明样品A和B在不同时期的细菌基因组DNA共存在46个不同条带类型,其中样品A和B分别拥有35个和38个不同位置的条带,并且样品A和B的DGGE图谱存在明显差异。加入DBP 2 d后,只加入DBP的样品(A2)中出现了6个新的条带,5个已有条带消失;而加入DBP和降解菌JDC13的样品(B2)中出现了5个新的条带,3个消失,并且其条带较亮的优势菌在样品A和B中也存在明显差异。样品A在随后的2~6 d条带变化较小,第9天后又有5个新的条带出现,已有条带的亮度也有明显变化,说明DBP的大量降解后细菌群落结构发生了较大变化。样品B在每个时间段里都有一定变化,说明不同细菌之间的竞争比较明显,但是,加入的降解菌JDC13的DNA条带始终很亮,说明JDC13在土壤DBP降解过程中一直是优势种群之一。
采用组平均法对DGGE图谱进行聚类分析。由图2(b)可见:在聚类重新标定距离为25的水平上,样品
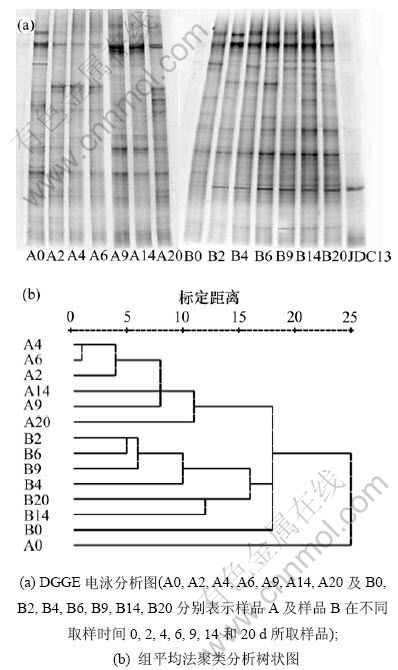
图2 土壤样品A和B的细菌群落结构分析
Fig.2 Structure of bacterial community in sample A and B
A和B各取样时间点分别聚为两大类,且与第0天时的样品(A0和B0)距离较远。样品A中,A2,A4和A6在标定距离小于4时聚为一类,其细菌群落差异较小,A14,A6和A9在标定距离为8~10时才与A2,A4和A6聚为一大类。样品B中,B2,B6和B9在标定距离5左右聚为一类,B14和B20在标定距离为12时聚为一类,样品B的所有取样点在标定距离为16时聚为一大类。说明只加入DBP与同时加入DBP和JDC13对土壤细菌群落结构的影响均十分明显,而样品A和B之间的细菌群落变化也存在明显差异。
对DGGE图谱中20个不同位置较亮的条带(YL1~YL20)进行切胶测序,将所得序列提交到Genbank数据库,登录号为GQ863464~GQ863483。 用Blaste软件在Genebank数据库中进行比对,并与相似序列通过邻接法构建系统发育树,见图3。从系统发育树可以看出:20个条带可分为8大类群。YL4~YL11和YL14属于β变形菌纲(Betaproteobacteria),共包含9个条带,是最具优势的一大类;YL19和YL20属于α变形菌纲(Alphaproteobacteria);YL1属于δ变形菌纲(Deltaproteobacteria);YL12属于γ变形菌纲(Gammaproteobacteria);YL13属于黄杆菌纲(Flavobacteria);YL18属于酸杆菌纲(Acidobacteria);YL12和YL15~YL17属于放线菌纲(Actinobacteria),是第二大类优势菌;YL3属于芽孢杆菌纲(Bacilli)。β变形菌纲中与YL14和YL4相似的有Delftia sp.,γ变形菌纲中与YL12相似的有Pseudomonas sp.,黄杆菌纲中与YL13相似的有Flavobacteria sp.,放线菌纲中与YL2相似的Mycobacterium sp.,芽孢杆菌纲中与YL3相似的有Bacillus sp.,从各类环境样品中分离得到,可以有效降解PAEs类化合物[15-19]。样品A在加入DBP后,其优势细菌种群发生了明显的变化。第0天时原有较亮条带属于酸杆菌纲的YL18和属于δ变形菌纲的YL1从第2天起消失。与此同时,一些优势细菌种群产生,如属于芽孢杆菌纲的YL3、属于放线菌纲的YL2以及Delftia sp. YL14等在第2天后出现,且条带较亮。而属于β变形菌纲的YL5~YL11和属于黄杆菌纲的YL13一直都有条带。样品B在加入DBP和降解菌JDC13后,JDC13的条带一直很亮,属优势种群。另外,属于放线菌纲的YL15、属于β变形菌纲的YL7~YL11以及属于酸杆菌纲的YL18在样品B中条带一直较亮。在第2天后新出现的优势细菌包括属于α变形菌纲的YL19和YL20以及属于放线菌纲的YL17和YL17等,而消失的条带包括属β变形菌纲的YL5和YL6以及属于δ变形菌纲的YL1等。
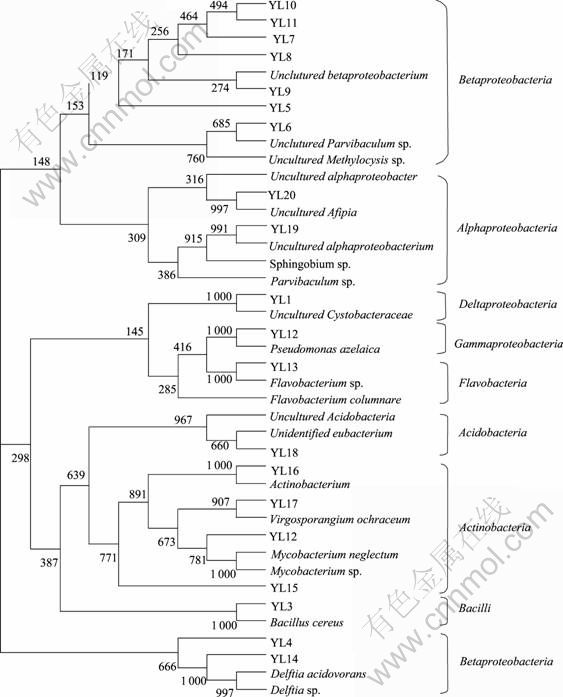
图3 用邻接法构建的样品A和B中优势细菌16Sr RNA系统发育树
Fig.3 Phylogenetic tree of 16Sr RNA sequence of dominant bacteria from samples A and B determined by NJ methods
3 讨论
在受污染土壤中接种外源微生物进行生物强化,是生物修复过程中的一种重要手段。生物强化的研究主要有以下几个方面[20]:(1) 与其他生物修复技术的降解效果相比较;(2) 研究接种的微生物演变情 况;(3) 研究接种微生物对土著微生物群落结构的影响。本文研究从环境中筛选出的一株DBP高效降解菌JDC13进行生物强化的效果,主要从以下几个方面进行分析:(1) 土壤中DBP残留含量;(2) 土壤中细菌总量的动态变化;(3) 土壤中细菌群落结构的变化(包括接种外源细菌的变化情况)。
JDC13是从污染的河底污泥里分离得到的一株DBP高效降解菌。在无机盐培养基中,它能够在30 h内完全降解8 mg DBP。选用JDC13作为外源降解菌接种到含0.8 mg/g DBP的土壤中,并与未加入JDC13的样品进行对比培养,研究JDC13的生物强化效果。在培养进行的前2 d,只含有DBP的样品A中细菌总数下降,DBP的降解速率十分缓慢(图1);而含有等量DBP并同时加入了降解菌JDC13的样品B中细菌的总数量缓慢上升,DBP的残留含量迅速下降。因此,DBP对土壤中的土著细菌有一定的抑制作用,使得样品A中DBP降解缓慢。而加入了高效降解菌JDC13后,通过JDC13 对DBP的快速降解,大大降低了DBP对土著细菌的最初抑制,使得在最初2 d内DBP的残留量迅速下降。经过前期适应后,样品A和B中的细菌开始快速繁殖生长,加入的DBP也被迅速利用,样品A和B中的细菌分别在第14天和第9天时几乎将DBP 完全降解。加入JDC13的样品B将DBP完全降解的时间提前了5 d。因此,接入JDC13进行生物强化修复具有很好的效果。
PCR-DGGE技术广泛应用于土壤微生物群落结构的研究。处于不同位置的每条DNA带及其相对浓度(亮度)代表群落中某一种特定微生物及其在群落中的相对丰度[21]。一般认为PCR-DGGE只能分辨土壤中丰度为1%以上的微生物,因此,PCR-DGGE数据更适用于解释土壤中优势细菌群落结构[22]。在土壤中加入DBP后,由于特殊碳源的富集作用,会明显改变土壤中细菌的优势种群构成[23]。样品A和B在DBP加入后,其细菌群落结构与土壤原有细菌群落相比发生了显著的变化,且A和B之间的细菌群落变化也有明显的差异(图2)。DGGE条带测序结果表明:样品A中放线菌、β变形菌等在培养过程中处于优势地位,而原有的酸杆菌、δ变形菌等被淘汰;样品B中,由于JDC13是一株DBP高效降解菌,进入土壤后它可以迅速利用DBP生长,在降解过程中成为土壤中的优势种群。另外,放线菌、α-变形菌以及部分β变形菌也为土壤中优势种群,δ变形菌、部分β变形菌等被淘汰。将土壤中优势细菌的测序结果与已报道的细菌来源进行追索,发现大部分优势细菌与PAEs降解相关,且部分为PAEs高效降解菌。因此,DBP的加入对土壤中能够耐受和利用DBP的细菌类群起了选择性富集作用。
4 结论
(1) 接种外源降解菌JDC13有利于土壤中DBP的降解,与直接用土壤中的土著微生物降解DBP相比,其完全降解0.8 mg/g DBP的时间提前了5 d。
(2) 在土壤中加入DBP, 在最初的一段时间内会抑制土著微生物的生长。接种外源降解菌可以有效减少这种不利影响。
(3) 只加入DBP与同时加入DBP和外源降解菌JDC13都会显著影响土壤中细菌群落的构成,且二者的细菌群落变化也有明显差异。
(4) 由于DBP对土壤中能够耐受和降解DBP细菌的富集作用,JDC13以及放线菌、β变形菌等在DBP土壤降解过程中成为优势种群,大部分优势细菌测序序列与PAEs降解菌序列相似。
(5) 接种的外源降解菌JDC13可以促进DBP 的生物降解,因此,接种JDC13进行生物强化修复具有较好的效果。
参考文献:
[1] Sung H H, Kao W Y, Su Y J. Effects and toxicity of phthalate esters to hemocytes of giant freshwater prawn, macrobrachium rosenbergii[J]. Aquatic Toxicol, 2003, 64(1): 25-37.
[2] Gu J D, Li J X, Wang Y Y. Biochemical pathway and degradation of phthalate ester isomers by bacteria[J]. Water Sci & Technol, 2005, 52(8): 241-248.
[3] 骆祝华, 黄翔玲, 叶德赞. 环境内分泌干扰物——邻苯二甲酸酯的生物降解研究进展[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2008, 14(6): 890-897.
LUO Zhu-hua, HUANG Xiang-ling, YE De-zhan. Advances in research of biodegradation of environmental endocrine disruptors-phthalate esters[J]. Chin J Appl Environ Biol, 2008, 14(6): 890-897.
[4] Staples C A, Peterson D R, Parkerton T F, et al. The environmental fate of phthalate esters: A literature review[J]. Chemosphere, 1997, 35(4): 667-749.
[5] LIANG Da-wei, ZHANG Tong, Herbert H P, et al. Phthalates biodegradation in the environment[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2008, 80(2): 183-198.
[6] Bent F M., Camargo F A, Okeke B C, et al. Comparative bioremediation of soils contaminated with diesel oil by natural attenuation, biostimulation and bioaugmentation[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2005, 96(9): 1049-1055.
[7] Boon N, Top E M, Verstraete W, et al. Bioaugmentation as a tool to protect the structure and function of an activated sludge microbial community against a 3-chloroaniline shock load[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 2003, 69(3): 1511-1520.
[8] 许育新, 李晓慧, 滕齐辉. 氯氰菊酯污染土壤的微生物修复及对土著微生物的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2008, 45(4): 695-698.
XU Yu-xin, LI Xiao-hui, TENG Qi-hui. Microbial remediation of cypermethrin-contaminated soil and effect on soil microbial communities[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008, 45(4): 695-698.
[9] 叶央芳, 闵航. 代谢指纹评估苯噻草胺对水稻土微生物群落的短期影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2006, 43(2): 287-294.
YE Yang-fang, MIN Hang. Monitoring of short-term impact of mefenacet treatment on paddy soil microbial communities with metabolic fingerprinting[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2006, 43(2): 287-294.
[10] 李慧, 张颖, 苏振成, 等. 沈抚石油污水灌区稻田土壤细菌遗传多样性: 16Sr DNA-PCR-DGGE分析[J]. 土壤学报, 2006, 43(6): 972-980.
LI Hui, ZHANG Yin, SU Zhen-cheng, et al. Analysis of bacterial genetic diversity in paddy soil in Shenfu irrigation zone irrigated with wastewater from petroleum industry: By denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and sequencing of PCR-amplified 16S ribosomal DNA fragments[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2006, 43(6): 972-980.
[11] ZHOU Ji-zhong, Bruns M A, Tiedje J M. DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1996, 62(3): 16-22.
[12] Muyzer G, de Waal E C, Uitterlinden A G. Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16Sr RNA[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1993, 59(3): 695-700.
[13] Thompson J D, Gibson T J, Plewniak F, et al. The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1997, 25(24): 4876-4882.
[14] ZENG Feng, CUI Kun-yan, LI Xiang-dong, et al. Biodegradation kinetics of phthalate esters by Pseudomonas fluoresences FS1[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2004, 39(9): 1125-1129.
[15] Patil N K, Kundapur R, Shouche Y S, et al. Degradation of a plasticizer, di-n-butyl phthalate by Delftia sp. TBKNP-05[J]. Curr Microbiol, 2006, 52(3): 225-230.
[16] Shailaja S, Ramakrishna M, Mohan S V, et al. Biodegradation of di-n-butyl phthalate (DnBP) in bioaugmented bioslurry phase reactor[J]. Bioresour Technol, 2007, 98(8): 1561-1566.
[17] Tanaka T, Yamada K, Iijima T, et al. Complete degradation of the endocrine-disrupting chemical phthalic acid by Flavobacterium sp[J]. J Health Sci, 2006, 52(6): 800-804.
[18] Nakamiya K, Hashimoto S, Ito H, et al. Microbial treatment of bis (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in polyvinylchloride with isolated bacteria[J]. J Biosci Bioeng, 2005, 99(2): 115-119.
[19] Chang B V, Wang T H, Yuan S Y. Biodegradation of four phthalate esters in sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 69(7): 1116-1123.
[20] Coppotelli B M, Ibarrolaza A, Del M T, et al. Effects of the inoculant strain Sphingomonas paucimobilis 20006FA on soil bacterial community and biodegradation in phenanthrene- contaminated soil[J]. Microb Ecol, 2008, 55(2): 173-183.
[21] 钟文辉, 蔡祖聪, 尹力初, 等. 用PCR-DGGE研究长期施用无机肥对种稻红壤微生物群落多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(10): 4011-4018.
ZHONG Wen-hui, CAI Zu-cong, YIN Li-chu, et al. The effects of the long-term application of inorganic fertilizers on microbial community diversity in rice-planting red soil as studied by PCR-DGGE[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(10): 4011-4018.
[22] 吴宇澄, 骆永明, 滕应, 等. 多氯联苯污染农田土壤的细菌群落结构差异及其影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(5): 854-859.
WU Yu-chen, LUO Yong-ming, TENG Ying, et al. Variation of microbial communities in PCBS-contaminated agricultural soils and influencing factions[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(5): 854-859.
[23] 任随周, 郭俊, 邓穗儿. 石油降解菌的分离鉴定及石油污染土壤的细菌多样性[J]. 生态学报, 2005, 25(12): 3314-3322.
REN Shui-zhou, GUO Jun, DENG Sui-er. Isolation and identification of petroleum degrading strains and the diversity of microbes in petroleum-contaminated soils[J]. Acta Ecollgical Sinica, 2005, 25(12): 3314-3322.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2010-02-15;修回日期:2010-05-21
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(30770388)
通信作者:吴学玲(1965-),女,湖南常德人,博士,副教授,从事环境微生物学及生物冶金研究;电话:0731-88804873;E-mail: xueling0714@yahoo.com.cn