吐哈盆地台北凹陷西缘油气成藏过程主控因素及成藏模式
肖冬生,杨占龙
(中国石油勘探开发研究院 西北分院,甘肃 兰州,730020)
摘要:从多元地质条件及其配置关系出发,分析吐哈盆地台北凹陷西缘油气成藏过程主控因素。研究结果表明:区域盖层与断裂共同控制着油气垂向运移的距离及层位;古构造背景、不整合面、输导断裂与储层砂体的配置关系控制着油气侧向运移的方向、通道和距离;基准面旋回、沉积微相类型与现今构造配置关系控制着油气的垂向聚集层位及平面分布规律。在此基础上,结合构造发育史、油源条件及沉积微相研究成果,总结出研究区4种主要成藏模式:源内为自生自储式和下生上储式;近源为短距离垂向—侧向运移—断层或局部构造成藏模式;远源为长距离侧向运移—不整合面上下成藏模式;油气再次分配运聚成藏模式。
关键词:吐哈盆地;台北凹陷;成藏模式;主控因素
中图分类号:TE122.31 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2013)02-0679-08
Controlling factors and accumulation model of hydrocarbon accumulation in western Taibei Sag, Turpan-Hami Basin
XIAO Dongsheng, YANG Zhanlong
(Northwest Branch, Research Institute of Petroleum Exploitation and Development, Lanzhou 730020, China)
Abstract: In order to further clarify the role of different geological conditions in hydrocarbon accumulation process, the main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation in western Taibei Sag, Turpan-Hami Basin were researched based on the angle of diverse geological conditions and their relationship in space-time. The results show that the distance and layer of hydrocarbon migrated upward are controlled by regional caprocks and faults. The direction, pathway and distance of the migrated oil-gas are controlled by palaeostructure and the relationship between unconformity, transport faults and reservoir. Vertical and lateral distributions of oil and gas are controlled by the factors of base level, sedimentary microfacies and recent tectonic. Based on the analysis of factors mentioned above coupled with structural history, oil sources conditions, sedimentary microfacies, four kinds of hydrocarbon accumulation models are summarized, i.e. inside source-lower source upper reservoir model and self-generating and self-preserving model, near source-short distance vertical and lateral migration-faults or local structures screened model, far source-long distance lateral migration-up, and down of unconformity model and secondary migration and accumulation model.
Key words: Turpan-Hami Basin; Taibei Sag; hydrocarbon accumulation model; key controlling factors
吐哈盆地台北凹陷西缘位于喀拉乌成山和博格达山西段交汇部位的南侧,西部紧邻布尔加凸起,东接胜北生油洼陷,北到北部山前带,南至托克逊凹陷的北部,可划分为北部山前带、中央凹陷带和南部斜坡带3个构造区带[1],面积约1 800 km2(见图1)。研究区油气主要来自胜北洼陷中下侏罗统水西沟群煤系烃源岩和湖相泥岩烃源岩,油气主要分布在侏罗系三间房组、七克台组、西山窑组上部、白垩系和第三系鄯善群[2-3],目前在台北凹陷西缘已经发现了胜南-雁木西、神泉、葡萄沟、葡北、七泉湖、玉果等油气田。然而,经过20多年的勘探开发,现今台北凹陷西缘油气勘探开发面临2方面难题:一是剩余探明储量动用困难;二是空白区油气勘探进展缓慢。其原因主要是储层横向变化快、非均质性强、油水关系复杂、构造型油气藏勘探程度较高,导致对该区油气成藏主控因素及成藏模式认识不够,严重制约了下步勘探与开发。陈凤来等[4-7]对研究区油气成藏条件及成藏模式进行研究和探讨,取得了丰富成果,但大多讨论的是某一地质条件对油气成藏的控制作用,而对各种成藏要素及其配置关系对油气成藏过程的控制作用的综合研究较少。因此,本文作者对台北凹陷西缘多元地质条件及其配置关系进行综合分析,确定油气成藏过程主控因素,并以此为基础总结了该区油气成藏模式,这对指导该区下步勘探和开发、丰富陆相盆地油气成藏理论具有一定的理论和生产意义。

图1 研究区平面位置图
Fig.1 Location of study area
1 油气成藏过程主控因素
台北凹陷西缘油气主要来自胜北洼陷中下侏罗统水西沟群,而油气分布于中侏罗统七克台组、三间房组及白垩系和第三系鄯善群,且在远离生油洼陷区聚集成藏[8]。这种烃源岩和油气藏的分布特征必然伴随着油气的垂向、侧向运移过程,因此,下面从油气垂向、侧向运移和聚集3个方面讨论油气成藏过程的主要控制因素。
1.1 油气垂向运移过程控制因素——区域盖层与断裂共同控制油气垂向运移的距离及层位
台北凹陷水西沟群发育烃源岩,上覆三间房组、七克台组及白垩系和第三系为主要油气藏发育层段,表明必然存在油气垂向运移过程。区域盖层及断裂或断裂组合对“垂向运移”过程具有重要控制作用。
台北凹陷西缘主要发育6套区域盖层和局部盖层。其中白垩系中上部、鄯善群中上部、七克台组二段及齐古组为分布稳定的区域盖层,西山窑组中上部煤系泥岩、三工河组中上部泥岩和八道湾组中上部煤系地层为局部盖层。七克台组二段及齐古组发育了累计厚度600 m左右的泥岩盖层,南北向主要分布在火焰山断裂上盘到北部山前带,东西向主要分布在葡萄沟—葡北构造带及以东地区。当油源断裂未断穿该区域盖层时,油气通过断裂垂向运移至七克台组一段以后,受该套盖层遮挡在七克台组一段聚集成藏;白垩系及第三系鄯善群中上部区域盖层全区分布,主要控制西缘浅层白垩系及第三系鄯善群油气垂向运移;局部盖层厚度薄、连续性差,对油气垂向运移控制作用不大。
根据断裂与烃源岩接触关系,研究区控制油气“垂向运移”的断裂可分为2类:一类是在有效烃源岩范围内直接与烃源岩接触的断裂或断裂组合;另一类是烃源岩范围以外,与不整合面或含油砂体相接触的断裂或断裂组合。这些断裂或断裂组合控制着油气“垂向运移”的距离。
有效烃源岩范围内控制油气“垂向运移”的断裂主要包括火焰山断裂及其伴生断裂和葡北构造带七克台组、三间房组与水西沟群烃源岩连通的层间断裂。其中,火焰山断裂及其主要伴生断裂断穿了侏罗系、白垩系及第三系,直接控制着火焰山构造带油气纵向分布,紧邻火焰山断裂的神泉油田和葡萄沟油田从中侏罗统三间房组到第三系鄯善群均为含油层系,为复式油气田,含油层系明显多于远离火焰山断裂的胜南、葡北等油田;另外,葡北构造带七克台组、三间房组油气藏多依附于层间断裂分布,这些层间断裂与下伏水西沟群烃源岩连通,层间断裂向上断穿距离控制着油气垂向运移距离,进而控制着葡北构造带含油层系(见图2)。
有效烃源岩范围以外,与不整合面或含油砂体相接触的断裂或断裂组合主要包括神泉及胜南-雁木西构造带连通白垩系顶底不整合面与中侏罗统、白垩系或第三系鄯善群砂、砾岩层的断裂。神泉地区油气在中侏罗统连通砂体内部侧向运移的同时,沿这些断裂或断裂组合发生垂向运移;雁木西构造带油气沿沟通白垩系顶底的垂向断裂向上运移,在第三系鄯善群形成油气藏(图2)。
1.2 油气侧向运移过程控制因素
水西沟群烃源岩生成的油气垂向向上运移进入储层之后,在浮力作用下沿被断裂沟通的储层砂体和不整合面发生侧向运移,并在有利的圈闭条件下聚集成藏[9]。从已发现油气田的分布状况看,在有效烃源岩范围之外有大量油气分布(图1),证实了油气侧向运移过程的存在,而在这一地质过程中古构造背景、不整合面与储层砂体配置关系起到了重要的控制作用。
1.2.1 古构造背景控制着油气侧向运移的方向
勘探实践表明,区域构造演化控制了油气的二次运移,古构造是诱导油气运聚的有利场所,油气运移期的古构造形态对油气运聚成藏具有重要的控制作 用[10]。对台北凹陷西缘而言,来自中下侏罗统水西沟群的油气通过油源断裂进入上覆三间房组、七克台组或白垩系和鄯善群储层以后,在浮力作用下将由构造低部位向构造高部位发生侧向运移,而油气运移时期古构造背景控制着油气侧向运移的方向。生排烃史研究表明,研究区主要含油层系侏罗系主成藏期为第三纪早期[11]。本文以“体积平衡”理论为指导[12],以压实、剥蚀恢复等方法为手段,恢复了主要成藏期对油气运、聚有重要控制作用的七克台组及三间房组顶面古构造形态。油气运移、成藏期,七克台及三间房组顶面古构造特征总体一致:古构造深陷区与生排烃中心基本重合,油气侧向运移的主要方向为生排烃中心西部及南部构造高部位。另外,在深陷区西南方向的神泉、胜南-雁木西地区具有鼻隆构造背景,这成为神泉、胜南-雁木西构造带远源成藏的主控因素之一。具体侧向运移方向取决于生排烃中心与相应构造之间的相对位置,即受控于油气运移期古构造背景(见图3)。
1.2.2 不整合面、输导断裂与储层砂体的有效配置构成油气侧向运移的良好通道
油气从胜北洼陷向台北凹陷西缘运移,运移通道主要有3种类型:不整合面、输导断裂和砂体[13]。
台北凹陷西缘对油气侧向运移贡献最大的不整合面为侏罗系与白垩系间不整合及白垩系与第三系间不整合,分别受燕山II和III幕区域构造运动影响,在凹陷西缘广泛发育,尤其胜南—雁木西构造带,不整合面缺失风化黏土层,其输导能力更佳[14]。
输导断裂主要包括火焰山、七泉湖—玉果及吐鲁番等较大规模断裂。火焰山断裂形成于第四纪中后期[14],说明在侏罗系油气藏成藏期,白垩纪末—早第三纪火焰山构造尚未形成,因此既不存在火焰山构造阻碍油气向西缘运移,也不存在火焰山断裂作为油源通道向西输送油气的过程,但火焰山断裂对白垩系和第三系鄯善群油气藏形成具有重要控制作用。这些油气藏成藏期为早第三纪末—第四纪[15],该时期火焰山断裂与不整合面衔接起来,共同作为良好的油气运移通道。七泉湖—玉果断裂对北部山前带油气运聚具有重要控制作用,作为油源断裂直接控制着七泉湖—玉果构造带的油气运移和聚集[5]。吐鲁番断裂形成于早燕山期,大规模活动于中燕山期,是神泉—胜南构造带油气运移的主要通道。
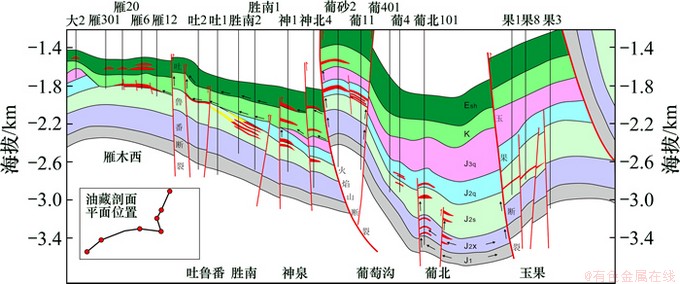
图2 台北凹陷西缘油气运移、聚集过程示意图
Fig.2 Sketch map of migration and accumulation of oil-gas in western Taibei Sag

图3 主要成藏期含油层系顶面古构造图
Fig.3 Palaeostructure of oil-bearing series’top in main accumulation periods
雁木西地区鄯善群在不整合面之上发育了分布较为稳定的砂、砾岩,而油气显示及成藏位于砂砾岩上部,下部含油气性较差,说明该区以连通砂体的侧向运移为主;另外,神泉—胜南地区侏罗系七克台组底部发育砂泥岩频繁互层的湖相滩砂,单层砂岩厚度一般在10 m以下,但连续性较好,且有断裂沟通,是油气从神泉运移至胜南的主要通道[14]。
1.2.3 古构造背景、不整合面、输导断裂与储层砂体的配置关系控制着油气侧向运移方向、通道和距离
古构造背景决定了油气侧向运移的方向,不整合面、输导断裂和砂体的有效配置构成了油气侧向运移的良好通道,因此,古构造背景(即油气侧向运移方向)、不整合面分布、输导断裂走向与储层砂体展布方向的配置关系必然控制着油气侧向运移距离。当油气侧向运移方向、输导断裂走向与储层砂体展布方向三者一致且发育不整合面时,具有良好的空间配置关系,最有利于油气的侧向运移,其运移距离可达几十km;当不整合面发育,油气侧向运移方向与输导断裂走向或储层砂体展布方向中的某一项一致,而与另一项垂直或斜交时,具有较好的空间配置关系,但由于受到一方因素的阻挡,油气侧向运移距离稍小;而当油气侧向运移方向与输导断裂走向和砂体的展布方向均垂直,且不整合面不发育时,侧向运移受阻,以原地生储特征为主。
图4所示为台北凹陷西缘沉积相与断裂叠合图。由图3和4可知:七泉湖—玉果及葡萄沟—葡北构造带油气侧向运移方向、输导断裂走向与储层砂体展布在空间具有良好的配置关系,因此在七克台组及三间房组油气富集。胜南—雁木西—神泉构造带不整合面
之上砂、砾岩主要发育在神泉和雁木西地区,不整合面之下砂岩主要发育在胜南地区,储层砂体与不整合面的有效配置形成侧向运移的良好通道[14],而油气侧向运移方向、输导断裂走向与储层砂体展布的有效配置决定了该构造带远源成藏特征。
1.3 油气聚集过程控制因素
烃源岩生成的油气经过上述运移过程,在储层砂体发育的有利构造聚集成藏;而储层砂体发育程度在垂向上主要受控于基准面旋回及其伴随的可容纳空间变化所引起的沉积环境的变化,在平面上则体现为沉积微相类型的差异,因此基准面旋回、沉积微相类型与现今构造配置关系共同控制着油气聚集规律。
1.3.1 基准面旋回控制着油气的垂向聚集层位
基准面旋回及其伴随的可容纳空间变化的动力学系统控制着地层的结构与沉积特征,不同级次的基准面旋回对应着不同级次的地层旋回[16]。识别不同级次的基准面旋回有助于认清基准面旋回时期沉积地层的结构与沉积特征,进而准确把握储层砂体在垂向上的分布规律。
在高分辨率层序地层学理论指导下,综合钻测井、二维和三维地震资料,建立了研究区高分辨率层序地层格架,将侏罗系、白垩系及第三系鄯善群划分为9个长期基准面旋回及14个中期基准面旋回(见图5)。对基准面旋回及其伴随的可容纳空间变化所引起的沉积环境的变化分析可知:SC1~SC5期构造整体沉降、气候温湿、沉积地貌平缓,以准平原化沉积背景下的河泛平原及湖相沼泽沉积为主,为烃源岩发育期;SC6~SC8期构造挤压、隆升强烈、物源供给充足、沉积地貌分异较大,以湖泊-辫状河三角洲沉积为主,为储层集中发育期;SC6~SC8旋回为油气藏及油气显示最富集层段;SC9对应二级层序最大洪泛期,与SC1一起沉积了近600 m厚的泥岩,是较好的区域盖层。
1.3.2沉积微相类型与现今构造配置关系控制着油气聚集的平面分布
在油气来源充足的条件下,油气的平面分布规律主要取决于储层砂体分布状况及其与构造条件的有效配置;储层砂体的分布则与沉积微相类型密切相关。七克台组、三间房组及西山窑组上部沉积期研究区主要发育滨浅湖-辫状河三角洲沉积体系;白垩系三十里大墩组和第三系鄯善群沉积期发育冲积扇-冲积平原沉积体系。前人研究表明:该时期台北凹陷是一个极浅水的平坦洼地,呈“碟状”构造背景[17],具有“湖弱河强”的沉积特征,不发育席状砂、河口坝,砂体主要为三角洲平原辫状河道、前缘水下分流河道、湖相滩砂及冲积扇水道等微相沉积[18]。
在沉积微相划分基础上,统计了全区94口探井含油层系试油结论与沉积微相之间的关系(见图6)。由图6可知:油气主要分布于辫状河三角洲前缘水下分流河道及滨浅湖相滩砂微相砂体中,少数分布于冲积扇水道和辫状河道微相砂体中,分流间湾和其他微相类型的砂体中几乎不含油气,这说明沉积微相类型对储层有效砂体具有重要的控制作用。此外,从各含油层系已发现油气分布范围来看,油气主要聚集在现今构造的有利部位,如火焰山大型鼻状构造带、葡北断鼻带及胜南—雁木西背斜带等继承性构造高部位。上述分析表明,沉积微相类型与现今构造格局配置关系共同控制着油气聚集的平面分布规律。

图4 台北凹陷西缘沉积相与断裂叠合图
Fig.4 Overlay of sedimentary facies and faults in western Taibei Sag

图5 台北凹陷西缘层序地层格架
Fig.5 Sequence stratigraphy frame in western Taibei Sag
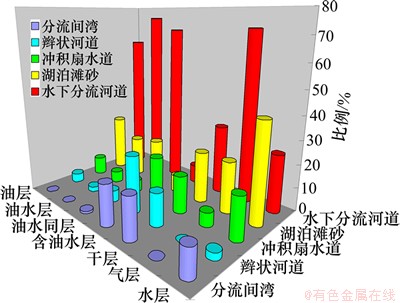
图6 含油气状况与沉积微相关系图
Fig.6 Cartogram of relationship between oil-gas and microfacies
综上所述,基准面旋回、沉积微相类型与现今构造格局的配置关系控制着油气的垂向聚集层位及平面分布规律。
2 油气成藏模式
油气成藏模式是油气藏形成和赋存状态的高度概括[19],也是对生、储、盖、运、圈、保多种地质要素综合作用的系统总结。在上述油气成藏过程主控因素分析的基础上,结合构造发育史、油源条件及沉积微相研究成果,将研究区油气成藏模式概括为以下4 种类型(图2)。
2.1 源内——自生自储式和下生上储式
此类型成藏模式平面上位于水西沟群烃源岩范围内,依据纵向上成藏层系与烃源岩的关系分为自生自储式和下生上储式,研究区该类型成藏模式主要分布在葡萄沟构造带和葡北构造带。自生自储式如葡北油田西山窑组煤系地层内部砂岩油藏,煤系烃源岩既为生油层又为盖层,在局部构造高部位聚集成藏,油藏类型以低幅背斜或断鼻油藏为主;下生上储式如葡北油田三间房组和七克台组油藏,下伏水西沟群烃源岩生成油气在浮力作用下沿断裂垂向运移至三间房或七克台组有利构造聚集成藏,油藏类型以断块和断鼻型为主,或沿砂体短距离侧向运移形成上倾尖灭型岩性油气藏。
2.2 近源——短距离垂向—侧向运移—断层或局部构造成藏模式
此类型成藏模式平面上位于烃源岩范围以外,距离烃源岩较近,以短距离侧向运移和垂向运移为主,如玉果油田和葡萄沟油田三间房组和七克台组油藏,下伏水西沟群烃源岩生成油气在浮力作用下沿有利构造背景向上倾方向运移至输导断裂,沿输导断裂发生垂向运移进入储层砂体,在断块或局部构造聚集成藏,油藏类型以断块和断鼻型为主。
2.3 远源——长距离侧向运移-不整合面上下成藏模式
此类型成藏模式平面上位于烃源岩范围以外,距离烃源岩较远,以长距离侧向运移为主,如吐鲁番油田、胜南—雁木西油田白垩系和第三系鄯善群油气藏。胜北洼陷水西沟群烃源岩生成油气侧向运移至输导断裂(主要是火焰山断裂、吐鲁番断裂)后,沿输导断裂垂向运移,在不整合面或孔渗条件较好砂、砾岩层继续向构造高部位侧向运移,在不整合面上下有利构造圈闭聚集成藏,或沿局部断裂再次垂向运移至有利构造聚集成藏。
2.4 油气再次分配运聚成藏模式
早期构造由于与烃源岩的生排烃期匹配关系良好而捕获油气聚集并成藏,后期由于构造运动引起构造形态的剧烈变化,导致原生油气藏遭受破坏,而在受破坏的早期油气藏上方形成次生油气藏。此类型油气藏多发育于白垩系及第三系鄯善群地层中,具有晚期成藏的特征,如七泉湖地区油气藏形成较晚,为晚喜山期玉果地区油气藏遭到破坏、再次运移-分配而形成的次生油气藏。从油气成藏过程主控因素分析可知,除前述垂向、侧向及聚集控制因素外,此类型成藏模式多与“早期开启、晚期封闭”的大断裂活动有关。
3 结论
(1) 多元地质条件及其配置关系控制着油气成藏过程:区域盖层与断裂共同控制着油气垂向运移的距离及层位;古构造背景、不整合面、输导断裂与储层砂体的配置关系控制着油气侧向运移的方向、通道和距离;基准面旋回、沉积微相类型与现今构造配置关系控制着油气的垂向聚集层位及平面分布规律。
(2) 台北凹陷西缘主要存在4种类型油气成藏模式,即源内为自生自储式和下生上储式;近源为短距离垂向—侧向运移—断层或局部构造成藏模式;远源为长距离侧向运移-不整合面上下成藏模式;油气再次分配运聚成藏模式。
参考文献:
[1] 卫延召, 戴金星, 赵长毅. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷西部油源浅析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2001, 23(2): 191-194.
WEI Yanzhao, DAI Jinxing, ZHAO Changyi. Preliminary analysis on the oil sources of the west Taibei Sag in the Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 2001, 23(2): 191-194.
[2] 柳波, 黄志龙, 涂小仙, 等. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷北部山前带构造样式与油气成藏[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011, 38(2): 152-157.
LIU Bo, HUANG Zhilong, TU Xiaoxian, et al. Structural styles and hydrocarbon accumulation of the northern piedmont belt in the Taibei Sag, Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(2): 152-157.
[3] 袁明生, 牛仁杰, 焦立新, 等. 吐哈盆地前陆冲断带地质特征及勘探成果[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2002, 23(5): 376-379.
YUAN Mingsheng, NIU Renjie, JIAO Lixin, et al. Geology characteristic and exploration of foreland thrust belt in Tuha Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2002, 23(5): 376-379.
[4] 陈凤来, 漆万珍, 何燕清. 台北凹陷西部油气运移和勘探方向分析[J]. 吐哈油气, 2006, 11(2): 127-133.
CHEN Fenglai, QI Wanzheng, HE Yanqing. Analysis for hydrocarbon migration and exploration target in west of Taibei Sag[J]. Tuha Oil & Gas, 2006, 11(2): 127-133.
[5] 蒋明亮, 刘护创, 靳继坤, 等. 七泉湖构造带成藏条件分析[J]. 吐哈油气, 2008, 13(1): 5-8.
JIANG Mingliang, LIU Huchuang, JIN Jikun, et al. Analysis on condition of hydrocarbon accumulation in Qiquanhu structural belt[J]. Tuha Oil & Gas, 2008, 13(1): 5-8.
[6] 张振英, 邵龙义, 张世焕, 等. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷西部弧形构造带混源原油特征[J]. 石油学报, 2005, 26(2): 15-20.
ZHANG Zhenying, SHAO Longyi, ZHANG Shihuan, et al. Distribution of mixed crude in western arc structural belt of Taibei Depression in Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2005, 26(2): 15-20.
[7] 杜宏宇, 梁桂宾, 徐桂芳, 等. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷西部原油“混源”分析[J]. 中国西部油气地质, 2006, 2(1): 79-83.
DU Hongyu, LIANG Guibin, XU Guifang, et al. Mixed sources analysis on crude oil of the west Taibei Sag of the Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. West China Petroleum Geosciences, 2006, 2(1): 79-83.
[8] 刘洪林, 王红岩, 赵群, 等. 吐哈盆地低煤阶煤层气地质特征与成藏控制因素研究[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(1): 133-137.
LIU Honglin, WANG Hongyan, ZHAO Qun, et al. Geological characteristics of coalbed methane and controlling factors of accumulation in the Tuha Basin[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2010, 84(1): 133-137.
[9] 刘江涛, 黄志龙, 王海. 吐哈盆地西部弧形带油气远距离运移成藏主控因素[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 34(2): 24-30.
LIU Jiangtao, HUANG Zhilong, WANG Hai. Dominant control factors of hydrocarbon distance accumulating in western arc-like zone of Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2010, 34(2): 24-30.
[10] 董福湘, 刘立, 何兴华, 等. 松辽盆地南部十屋断陷古构造对营城组扇三角洲发育的控制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2003, 33 (4): 464-468.
DONG Fuxiang, LIU Li, HE Xinghua , et al. Constrains on the development of fan deltas of Yingcheng formation by the Shiwu fault depression, southern Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2003, 33(4): 464-468.
[11] 苏传国, 黄卫东, 白喜俊, 等. 吐哈盆地天然气成藏地质条件与富集因素分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(1): 50-56.
SU Chuanguo, HUANG Weidong, BAI Xijun, et al. Natural gas accumulation conditions and controlled factors in Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(1): 50-56.
[12] 漆家福, 杨桥, 王子煜. 编制盆地复原古构造图的若干问题的讨论[J]. 地质科学, 2003, 38(3): 413-424.
QI Jiafu, YANG Qiao, WANG Ziyu. Some problems about compiling a restored paleo-structural map of basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2003, 38(3): 413-424.
[13] 秦长文, 庞雄奇, 李宏伟. 台北凹陷侏罗系油气输导体系分析[J]. 天然气工业, 2005, 25(3): 11-19.
QIN Changwen, PANG Xiongqi, LI Hongwei. Hydrocarbon transport system of Jurassic in Taibei Sag[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2005, 25(3): 11-19.
[14] 刘江涛, 黄志龙, 涂小仙, 等. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷西部弧形带油气远距离运聚规律[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 41(5): 18881893.
LIU Jiangtao, HUANG Zhilong, TU Xiaoxian, et al. Distant migration and accumulation of oil and gas in western arc-like zone of Taibei Sag in Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2010, 41(5): 1888-1893.
[15] 袁明生, 梁世君, 燕列灿, 等. 吐哈盆地油气地质与勘探实践[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2002: 198-203.
YUAN Mingsheng, LIANG Shi-jun, YAN Lie-can, et al. Hydrocarbon geology and exploration practice[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2002: 198-203.
[16] 邓宏文, 王洪亮, 李熙喆. 层序地层地层基准面的识别、对比技术及应用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1996, 17(3): 177-184.
DENG Hongwen, WANG Hongliang, LI Xizhe. Identification and correlation techniques of sequence stratigraphic base-levels and their application[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 1996, 17(3): 177-184.
[17] 张尚锋, 张昌民, 李志军, 等. “碟状”盆地沉积充填特点及油气聚集特征: 以吐哈盆地台北凹陷侏罗系为例[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2007, 29(3): 8-10.
ZHANG Shangfeng, ZHANG Changmin, LI Zhijun, et al. Filling features and hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics of dish-like basin: Jurassic in Taipei Sag in Tuha Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2007, 29(3): 8-10.
[18] 吴青鹏, 杨占龙, 李红哲, 等. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷西缘侏罗系层序划分及沉积体系演化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(3): 348-359.
WU Qingpeng, YANG Zhanlong, LI Hongzhe, et al. Sequence division, distribution and evolution of sedimentary facies of Jurassic, western Taibei Sag, Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(3): 348-359.
[19] 张雷, 卢双舫, 张学娟, 等. 松辽盆地三肇地区扶杨油层油气成藏过程主控因素及成藏模式[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2010, 40(3): 491-502.
ZHANG Lei, LU Shuangfang, ZHANG Xuejuan, et al. Controlling factors and accumulation model of hydrocarbon accumulation of the Fuyang oil units in Sanzhao region of the Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2010, 40(3): 491-502.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2012-01-30;修回日期:2012-04-11
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划(“973”计划)项目(2007CB209503)
通信作者:肖冬生(1982-),男,蒙古族,辽宁朝阳人,博士,从事地震地质综合研究;电话:13677596028;E-mail:xdsh1982@126.com