DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.06.19
超声耦合隔膜电积锡电化学机理
南天翔,杨建广,陈冰,李树超,丁龙
(中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:采用超声耦合隔膜电积技术从氯盐体系(Sn(Ⅱ)-Cl--H2O)中电积锡,通过循环伏安法、线性扫描伏安法、计时电流法及计时电位法,对比研究有无超声耦合条件下锡隔膜电积的电化学机理。循环伏安曲线及线性扫描曲线分析表明,超声耦合可使锡隔膜电沉积的控制步骤由无超声耦合时的扩散控制转变为有超声耦合时的电化学控制;超声耦合条件下提高温度、酸度及超声功率有利于锡的电积;计时电流测试表明,超声耦合锡隔膜电积初始过程遵循扩散控制的三维成核和晶粒长大机制,超声波在此过程起到细化晶粒及加快反应进程的作用。超声耦合后,锡的沉积由高择优取向(易产生锡“晶须”)逐渐趋于无择优取向,阴极锡倾向于生成规则的网状结构,锡“晶须”得到遏制。同等条件下超声耦合更有利于获得结构更致密、形貌更平整的阴极锡。
关键词:超声波;隔膜电积;氯盐体系;电化学机理
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-06-1233-09 中图分类号:TF814;O646.541 文献标志码:A
锡因其具有许多优良的特性,如可焊性、可漆性、高耐蚀性及无毒性等,使其广泛应用于电器电子行业、食品包装、香水、涂料、油漆等领域。近几年有研究发现,电沉积的多孔锡膜能够有效地提高锂离子电池的电化学性能[1]。
锡的电沉积研究从19世纪中期开始兴起,所用到的电解液一般分为两种:碱性四价锡电解液和酸性二价锡。碱性电解液主要由锡酸钾或锡酸钠溶液组成,采用碱性电解液能够得到均匀的沉积物,但是要求较高的温度以及溶液稳定性;酸性电解液中主要有锡的硫酸盐[2-3]、磺酸盐[4-5]或氟硼酸盐[6]等,采用酸性电解液有利于避免氢氧化物的产生,但是必须添加有机添加剂如柠檬酸盐[7-8]、酒石酸盐[9]、葡萄糖酸盐[10-11]以及氯盐[12-13]等来抑制电沉积时锡“晶须”的生成,不仅增加了电解液的复杂性,而且随着电沉积时间的延长锡金属板形貌仍然逐渐恶化[14]。
近年来,超声波因其特殊的空化作用促进电积过程晶体生长、代替晶种成核[15]等特点,在电化学沉积、电镀、冶金,材料制备等领域得到广泛研究及应用。陈华茂等[16]研究了超声波对锡铋合金电镀层的影响,发现超声能使结晶更致密均匀,并能显著提高电沉积效率;常洪涛等[17]研究了超声波对溶剂萃取法分离镧铈元素的影响,发现施加超声波有利于实现镧、铈等相似元素的萃取分离;王建[18]研究了超声波对制备超细二氧化锡纳米材料的影响,得出超声波能够提高材料纯度、细化晶粒以及降低成本等结论。
近期,本团队将超声波引入隔膜电积体系,提出并研究了超声耦合锡隔膜电积提取新工艺,对超声耦合氯盐体系锡隔膜电积过程进行了试验研究[19-21]。前期研究结果表明,氯盐体系耦合超声隔膜电积提取锡,可以有效遏制传统锡电沉积过程锡“晶须”的产生,得到的锡结晶更细密、电流效率更高。本研究的目的,即是开展超声波耦合氯盐体系锡隔膜电积过程电化学机理研究,阐明超声波耦合条件下锡晶体成核及生长规律,对比研究有无超声波耦合时电化学曲线的异同,揭示超声耦合隔膜电积锡“晶须”的抑制机理。
1 实验
1.1 试验试剂、电解液制备及试验设备
试验所用试剂SnCl2·2H2O和HCl均为分析纯,电解液采用蒸馏水配置,阳极液Sn2+浓度100 g/L、HCl浓度3.5 mol/L;阴极液Sn2+浓度80 g/L、HCl浓度1.5~5.5 mol/L。
试验所用电化学测试设备为上海辰华CHI660C电化学工作站。自制三电极隔膜电解槽置于昆山美美KM-100FBD超声波发生器内,工作电极(7.068 mm2)为316L不锈钢电极,辅助电极(1.5 cm2)为铂片电极,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极(SCE)。全套电化学测试装置示意图如图1所示。

图1 电化学测试装置示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of electrochemical testing
1.2 电化学试验
电化学测试前,工作电极用1200号及3500号的金相砂纸打磨抛光,再用乙醇溶液和蒸馏水清洗干净。电解槽通过鼓入氮气使电解液隔绝氧气。
循环伏安曲线在35℃、扫描速率20 mV/s、超声波功率0~100 W条件下测定;线性极化曲线在扫描速率20 mV/s、温度25~55 ℃、酸浓度1.5~5.5 mol/L及0~100 W功率40 kHz超声波的条件下测定,分析施加超声波后温度、酸度及超声功率对锡还原和析氢电化学行为的影响;考察不同阶跃电势下的计时电流曲线,以研究超声波耦合对锡沉积初期成核和长大机制的影响规律;研究不同电流密度下的计时电位曲线,探究超声耦合条件下锡沉积晶核的生长趋势。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 超声耦合循环伏安测试
在温度35 ℃、HCl浓度3.5 mol/L、阴极Sn2+质量浓度80 g/L、扫描速率为20 mV/s,超声频率为40 kHz、超声波功率分别为0、20、40、60、80及100 W条件下的循环伏安曲线如图2所示。
线性伏安曲线表明,未施加超声波,电位负向扫描至-0.53 V时,电流开始迅速增加,表明阴极液中的锡开始还原沉积;在-0.58 V左右时电流出现峰值,表明此时阴极表面附近的Sn(Ⅱ)离子基本已耗尽,此时扩散速度远不及化学反应速度,锡的沉积形核受扩散控制,反应以式(1)为主。随着电位继续负扫,阴极表面消耗的Sn(Ⅱ)离子的速度过快,溶液中Sn(Ⅱ)离子来不及补充,则还原电流有所下降;当电位扫至-0.64 V时,还原电流又急剧升高,开始发生析氢反应,反应以式(2)为主。反向扫描至-0.4 V时,出现一阳极峰,表明此时阴极生成的锡开始返溶。
Sn2++2e=Sn (1)
2H++2e=H2 (2)
改变施加的超声功率分别为20、40、60、80及100 W时,循环伏安曲线形态与未施加超声波的曲线形态基本类似,但峰值显著增加;扫描至-0.52 V时,电流开始增加,相比于未施加超声时还原电位提前约0.01 V,表明施加超声后锡离子更有利于成核沉积;相比于未施加超声的情况,在-0.58 V左右的阴极还原沉积峰明显消失,电流无明显下降,保持平稳,说明施加超声促进了溶液中Sn(Ⅱ)离子的传递,阴极表面附近不再缺少Sn(Ⅱ)离子,即此时锡的沉积形核受电化学控制;当电位扫至-0.64 V时,还原电流急剧上升,相比于未施加超声时,其电流直线斜率明显增加,且随着超声功率的增加,直线斜率也略有增加,表明在-0.64 V后,随着超声功率的增加,阴极析氢越来越剧烈。电位负向扫描时,相比于未施加超声波时,其电流的斜率明显增加,通过欧姆定律可计算出溶液中总电阻明显减小,且超声功率越大溶液中总电阻越小,说明耦合超声波能够减小溶液电阻促进反应进行,这对提高锡隔膜电积时的电流效率有显著意义;反向扫描时阳极峰出现的位置明显后移,在-0.35 V左右时,出现阳极峰,即为返溶峰,20~100 W功率的阳极峰值电流相比未施加超声时的峰值电流分别下降0.5、0.6、0.7、0.8及1.3 A,说明耦合超声后电沉积的锡含量较未施加超声时有明显提高,即超声波有利于提高锡电沉积效率。

图2 不同超声波功率下循环伏安曲线
Fig. 2 Cyclic voltammograms curves under different ultrasonic powers
2.2 超声耦合线性扫描测试
为进一步考察超声波对隔膜电积锡电化学行为的影响,采用线性扫描伏安法分别对温度25~55 ℃、H+浓度1.5~4.5 mol/L、超声波功率0~100 W下的阴极极化曲线进行了测定。
2.2.1 不同超声功率对电积锡的影响
在扫描速率20 mV/s、HCl浓度3.5 mol/L、温度为35 ℃、阴极Sn2+质量浓度80 g/L、超声波频率为40 kHz的条件下,获得的超声功率分别0、20、40、60、80及100 W的阴极极化曲线如图3所示。分析不同超声功率下的阴极极化曲线规律可发现,超声对锡的隔膜电沉积有显著影响。未施加超声时,还原电位在-0.58 V时电流有明显下降,随着超声功率的增加,在-0.58 V左右电流的下降逐渐减小,最终趋于直线。这是因为超声波的存在使得溶液中Sn(Ⅱ)扩散得到促进,扩散的加快使得控制步骤发生改变,由扩散控制逐渐转变为扩散和电化学混合控制。同时由于Sn(Ⅱ)的扩散增强,其争夺电子能力变强使得溶液中H+争夺电子的能力减弱,说明超声耦合促进了锡的电沉积。

图3 不同超声功率电积锡阴极极化曲线
Fig. 3 Cathode polarization curves under different ultrasonic powers
2.2.2 超声耦合条件下温度对电积锡的影响
在扫描速率20 mV/s、HCl浓度3.5 mol/L、阴极Sn2+质量浓度80 g/L、超声波频率为40 kHz、超声功率为100 W、温度分别为25、35、45、55 ℃条件下的阴极极化曲线如图4所示。由图4可以看出,随着温度的升高,Sn(Ⅱ)离子初始还原电位基本没有变化,为-0.52 V;还原电流曲线略有上升。反应初期阴极首先进行锡沉积过程,阴极附近的Sn(Ⅱ)离子逐渐减少,温度较低时,Sn(Ⅱ)离子无法及时补充至阴极附近,H+开始争夺电子,导致电流上升缓慢并出现阴极析出峰,随着温度升高,溶液中Sn(Ⅱ)离子转移加快,及时补充阴极附近损失的Sn(Ⅱ)离子,H+失去争夺能力,故曲线电流逐渐上升,反应加快。控制步骤逐步由扩散控制转变为扩散及电化学混合控制。

图4 不同温度下超声电积锡阴极极化曲线
Fig. 4 Cathode polarization curves under ultrasonic at different temperatures
2.2.3 超声耦合条件下酸度对电积锡的影响
在扫描速率20 mV/s、温度35 ℃、阴极Sn2+质量浓度80 g/L、超声波频率为40 kHz、超声功率为100 W、HCl浓度分别为1.5、2.5、3.5、4.5、5.5 mol/L条件下的阴极极化曲线如图5所示,同等条件下未施加超声的阴极极化曲线如图6所示。
不同酸度条件下超声耦合电积锡阴极极化曲线表明,随着酸度的增加锡初始还原电位及析氢电位发生明显变化,酸度为1.5~5.5 mol/L初始还原电位分别为-0.48、-0.52、-0.53、-0.55及-0.58 V;析氢电位分别为-0.62、-0.63、-0.64、-0.65及-0.67 V。表明酸度增加不利于锡的电沉积发生,因为溶液中的锡能与氯形成多种配合物(SnCl+、SnCl2、SnCl3-、SnCl42-),H+浓度的升高使带负电荷的锡-氯配合物物种增多,考虑到静电作用的影响,阴极液中Sn(Ⅱ)物种离子扩散速率将降低。但酸度过低电积过程中锡会发生水解反应,故较为理想的酸度为2.5~4.5 mol/L之间。
不同酸度条件下未施加超声耦合的电积锡阴极极化曲线如图6所示,对比施加超声耦合曲线(见图5),相同酸度下两者阴极锡沉积还原电位基本相同,表明超声对锡析出电位无明显影响;低酸度(1.5 mol/L)时的超声耦合与未超声耦合曲线形状基本相同,酸度升高(2.5~5.5 mol/L)未超声耦合曲线析出电位负移时,还原电流先有明显下降再上升,表明低酸度下超声耦合与未超声耦合对电积锡成核无明显影响,酸度增加超声对锡成核促进效果明显,因为酸度增加,H+浓度增加,未施加超声时,H+在阴极附近争夺电子能力逐渐增强,抑制了锡成核的形成,施加超声后,超声促进了离子间的交流使得H+及Sn(Ⅱ)在阴极附近的浓度均保持稳定,Sn(Ⅱ)得电子能力一直强于H+的,故有利于锡的析出。

图5 不同酸度下超声耦合电积锡阴极极化曲线
Fig. 5 Cathode polarization curves under ultrasonic at different acidities

图6 不同酸度下无超声耦合电积锡阴极极化曲线
Fig. 6 Cathode polarization curves at different acidities
2.3 超声耦合计时电位测试
在温度35 ℃、HCl浓度3.5 mol/L、阴极Sn2+质量浓度80 g/L、扫描速率为20 mV/s、超声频率为40 kHz、超声功率为100 W的条件下,研究施加超声后锡电积过程中电势和时间的关系。
超声耦合计时电位测试所得曲线如图7所示。从图7中可知,在低电流密度下(100~300 A/m2),电势缓慢上升,Sn2+开始进行还原沉积;5 s后逐渐趋于平稳,不再随时间而变化,此时电势趋于平稳并缓慢上升,说明低电流密度下超声能促进锡电积的稳定进行同时具有细化晶粒的作用,因为超声波的振动作用使得在阴极成核过程形成的较大晶核被振动落下,而较小的晶核则继续生长,从而形成致密锡板。但是当电流密度大于400 A/m2时,电势趋势改变,逐渐下降,这是因为当电流密度较大时,阴极表面Sn2+消耗逐渐增加;损失极快,而后发生析氢反应,氢气产生的气泡在超声波存在的条件下产生空化作用,破裂释放巨大能量,使阴极表面溶液不稳定,消除Sn2+离子耗尽层,不利于电沉积锡的发生,故在工业生产过程中超声锡电积过程中电流密度不宜超过300 A/m2[22]。
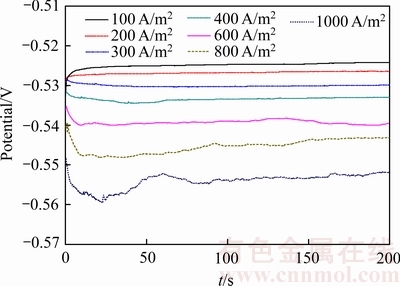
图7 超声耦合条件下锡电沉积过程不同电流密度的计时电位曲线
Fig. 7 Chronopotentiogram curves under ultrasonic at different electrical current densities

图8 无超声耦合条件下锡电沉积过程不同电流密度的计时电位曲线
Fig. 8 Chronopotentiogram curves under ultrasonic at different electrical current densities
对比无超声耦合计时电位曲线(见图8),有超声耦合时计时电位曲线稳定后电位均小于相同电流密度下无超声耦合计时电位曲线稳定电位,说明无超声耦合时开始还原沉积锡所需电势大于有超声耦合时,即有超声耦合有利于降低槽电压、节能[23]。
2.4 超声耦合计时电流测试
雷杰[24]研究了无超声耦合条件下隔膜电积锡成核机理,发现锡在该体系下成核长大遵循的是三维半球形成核(瞬时成核)模型。本研究则在该研究的基础上进一步耦合超声波,研究超声耦合条件下锡电沉积初期的成核和生长机制,采用计时电流法得到电流与时间的暂态曲线(见图9)。图9表明,当阶跃电位在-0.52~-0.59 V变化时,锡在阴极上电沉积的电流-时间(I-t)曲线。在初始0.05 s内电流急剧减小,这是由于电极双电层充电所引起的。随后,由于Sn2+离子放电形核和长大使电流开始上升至最大值Im,而后出现平稳曲线并略有上升,这是由于随着还原反应的不断进行,虽然阴极电极表面Sn2+离子的浓度降低,不足以维持电化学反应的持续进行,但是超声的存在使得溶液中Sn2+离子迅速补充到阴极附近。故电流将保持平稳并略有上升,此时电极表面Sn2+离子的扩散与电化学反应即处于动态平衡状态。同时还可观察到,随着阶跃电位越负,电流上升至最大值(Im)所需的时间(tm)越短。

图9 超声条件下锡电沉积过程的计时电流曲线
Fig. 9 Chronoamperometric curves under ultrasonic
上述分析表明,锡电沉积过程的初期受扩散控制,并遵循典型的三维半球型成核和晶粒长大机制。为了确定锡电沉积的成核类型(瞬时成核或连续成核),SCHARIFKER等[25]建立了一种理论模型用于分析电流与时间的暂态曲线数据。由该模型可知,瞬时成核和连续成核过程中电流与时间分别符合关系式(3)和式(4)。
 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
式中:Im和tm分别为电流-时间暂态曲线的最大电流及所对应的时间。
因此,通过将暂态电流-时间的试验数据绘制成(I/Im)2与(t/tm)两个无量纲参数的关系曲线,随即与式(3)和式(4)的理论曲线相比较,从而确定锡电沉积的成核类型。由图10所示,阶跃电位对(I/Im)2-(t/tm)曲线有一定影响,-0.53 V时开始成核,实验数据的上升部分在理论瞬时成核与理论连续成核之间,更趋近于瞬时成核。电位下降后曲线上升部分更趋近于理论瞬时成核曲线;但当t/tm≥1时,试验数据和理论曲线出现了明显的偏差,这说明SCHARIFKER的理论模型并不能完全解释该体系中锡的电沉积形核过程,其结果更接近于瞬时成核。同时由于超声波的存在使得控制步骤偏向于扩散及电化学反应同时控制。不仅如此还有可能是因为析氢导致曲线偏差[26]。
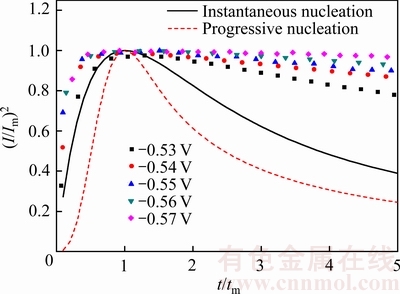
图10 不同电位无量纲(I/Im)2-(t/tm)曲线
Fig. 10 Nondimensional curves (I/Im)2-(t/tm) in different potentials
2.5 超声耦合锡隔膜电积试验验证
在温度35 ℃、HCl浓度3.5 mol/L、阴极Sn2+质量浓度80 g/L的条件下分别开展有无超声耦合(超声频率为40 kHz,功率为100 W)的锡隔膜电积试验,考察有无超声耦合条件下阴极电流效率、电锡板的宏观形貌、物相结构及微观形貌的变化。
2.5.1 阴极锡形貌对比
表1 所列为有无超声耦合锡隔膜电积试验结果对照。试验结果表明,有超声耦合比无超声耦合锡隔膜电积的电流效率及平均槽电压都有显著改善,超声耦合后电流效率由无超声耦合的85.84%提高到95.11%,平均槽电压由1.725 V降低至1.660 V,说明超声波在隔膜体系电积锡时有提高电流效率,降低平均槽电压的作用。图11所示为有无超声耦合所得电沉积锡的表观形貌,图11表明,超声耦合锡隔膜得到的电锡板平整致密,而同等条件下未施加超声波进行电积时,阴极锡表明生长出大量晶须,长时间电积时“晶须”甚至触及阴阳极之间的离子膜,妨碍隔膜电积的正常进行。图12所示为有无超声耦合所得电沉积锡的SEM像,由图12可以发现,当超声存在时所得到的电积锡表面较为平整,呈较为规则的网状结构,观察不到明显的锡“晶须”或“晶须”胚芽,晶粒排列致密,晶粒尺寸也较细小;而无超声耦合时,所得电锡板可明显观察到锡“晶须”及“晶须”胚芽,锡晶粒呈不规则形貌。
表1 有无超声耦合锡隔膜电积试验结果
Table 1 Technological parameters of tin membrane electro- deposition under ultrasonic
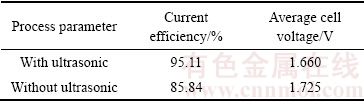

图11 施加超声波前后电沉积锡的表观形貌
Fig. 11 Surface morphology photomicrographs of tin electrodeposition under different conditions
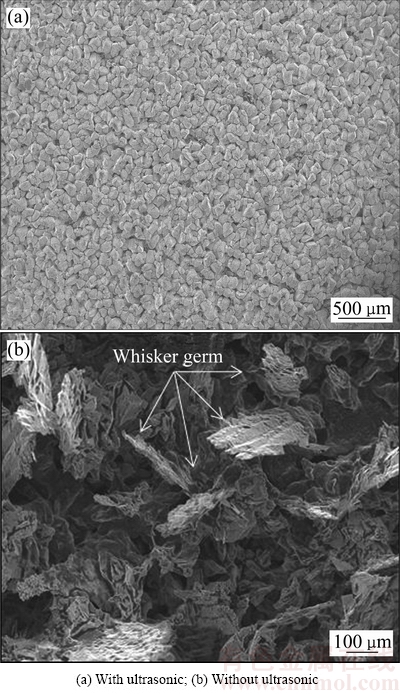

图12 施加超声波前后电沉积锡的SEM像
Fig. 12 SEM images of tin electrodeposition under different conditions
2.5.2 阴极锡XRD对比
图13所示为同等条件下有无超声耦合隔膜电积所得阴极锡的XRD谱对比,曲线(a)所示为未施加超声波时的电积锡XRD表征,曲线(b)所示为施加超声波后的电积锡XRD表征。由图13可知,在无超声情况下,电积锡主要以(101)晶面生长,其强度最强,达到1400左右,表现出极强的取向(“晶须”生长面)。相比于无超声状态下,在超声波作用下(101)晶面的织构系数降低,其他各个晶面织构系数都有显著提高,这表明超声波作用下缩小了各个晶面之间的表面扩散活化能的差距,从而使得电积出的锡由高择优取向(锡“晶须”现象明显)逐渐趋于无择优取向(无锡“晶须”),也间接证明超声波具有强烈的去浓差极化作用,有效抑制了阴极的氢析出反应及氢原子的表面吸附[27-28]。
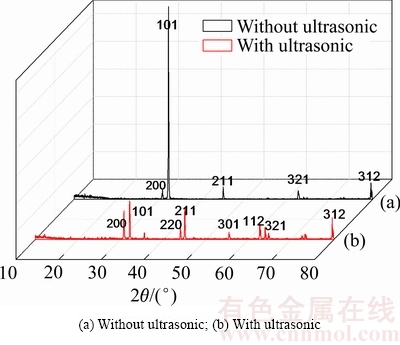
图13 施加超声波前后的电沉积锡的XRD谱
Fig. 13 XRD patterns of tin electrodeposition under different conditions
3 结论
1) 超声耦合后氯盐体系锡隔膜电沉积反应控制步骤由扩散控制逐步转变为电化学控制。增加超声功率有利于加快反应扩散,也有利于反应由扩散控制转变为电化学反应控制,提高温度及增加酸度能加快反应的进行。
2) 超声施加对细化晶粒有显著效果,锡初始电积遵循扩散控制的三维半球型成核和晶粒长大机制,但由于超声的存在及析氢反应存在使得成核不明确,更接近于连续成核。
3) 超声耦合场的施加使得溶液浓差极化降低,抑制了阴极的氢析出反应及氢原子的表面吸附,阴极表面金属锡的析出由高择优取向逐渐趋于无择优取向,锡“晶须”现象得到抑制,晶粒生长致密,防止了电积过程中产生气泡等不良特征。
REFERENCES
[1] WANG Fei, CHEN Lin, DENG Chen-fang, YE Hai-tao, JIANG Xue-fan, YANG Gang. Porous tin film synthesized by electrodeposition and the electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 149: 330-336.
[2] BARRY F J, CUNNANE V J. Synergistic effects of organic additives on the discharge, nucleation and growth mechanisms of tin at polycrystalline copper electrodes[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2002, 537(1/2): 151-163.
[3] BAKKALI S, TOUIR R, CHERKAOUI M, TOUHAMI M E. Influence of S-dodecylmercaptobenzimidazole as organic additive on electrodeposition of tin[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2015, 261: 337-343.
[4] BENGOA L N, TUCKART W R, ZABALA N, PRIETO G, EGLI W A. Tin coatings electrodeposited from sulfonic acid-based electrolytes: Tribological behavior[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering & Performance, 2015, 24(6): 2274-2281.
[5] LOW C T J, WALSH F C. The influence of a perfluorinated cationic surfactant on the electrodeposition of tin from a methanesulfonic acid bath[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2008, 615(2): 91-102.
[6] HUANG Xian-qiu, CHEN Yu, ZHOU Jian-qi, ZHANG Zhao, ZHANG Jian-qing. Electrochemical nucleation and growth of Sn onto double reduction steel substrate from a stannous fluoborate acid bath[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2013, 709(22): 83-92.
[7] SHARMA A, BHATTACHARYA S, DAS S, DAS K. Influence of current density on surface morphology and properties of pulse plated tin films from citrate electrolyte[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 290(1): 373-380.
[8] HAN Chun-fen, LIU Qi, IVEY D G. Kinetics of Sn electrodeposition from Sn(Ⅱ)-citrate solutions[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53(28): 8332-8340.
[9] TORRENT-BURGUES J, GUAUS E. Electrodeposition of tin from tartrate solutions[J]. Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta, 2005, 23(4): 471-479.
[10] SURVILA A, MOCKUS Z, KANAPECKAITE S, STALNIONIS G. Kinetics of Sn(Ⅱ) reduction in acid sulphate solutions containing gluconic acid[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2012, 667(1): 59-65.
[11] RUDNIK E, WLOCH G. Studies on the electrodeposition of tin from acidic chloride-gluconate solutions[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 265(1): 839-849.
[12] RIMASZEKI G, KULCSAR T, KEKESI T. Investigation and optimization of tin electrorefining in hydrochloric acid solutions[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2012, 42(8): 573-584.
[13] RIMASZEKI G, KULCSAR T, KEKESI T. Application of HCl solutions for recovering the high purity metal from tin scrap by electrorefining[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 125-126(8): 55-63.
[14] 雷 霆, 杨志鸿, 余宇楠, 张报清. 锡冶金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2013: 19-23.
LEI Ting, YANG Zhi-hong, YU Yu-nan, ZHANG Qing-bao. Tin metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013: 19-23.
[15] 彭万金. 超声波在冶金中的应用研究[J]. 上海有色金属, 2008, 29(3): 135-139.
PENG Wan-jin. Application research of ultrasonic wave in metallurgy[J]. Shanghai Nonferrous Metals, 2008, 29(3): 135-139.
[16] 陈华茂, 吴华强. 超声波对锡铋合金电镀层的影响[J]. 材料保护, 2004, 37(8): 24-25, 59.
CHEN Hua-mao, WU Hua-qiang. The influence of ultrasonic on tin bismuth alloy plating[J]. Journal of Materials Protection, 2004, 37(8): 24-25, 59.
[17] 常宏涛, 季尚军, 李 梅, 柳召刚, 张福顺. 超声波作用下溶剂萃取法分离镧铈元素[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(1): 169-186.
CHANG Hong-tao, JI Shang-jun, LI Mei, LIU Zhao-gang, ZHANG Fu-shun. Separation of lanthanum and cerium elements by solvent extraction under the effects of ultrasonic[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2014, 33(1): 169-186.
[18] 王 建. 超声波-溶胶-凝胶法制备超细二氧化锡粉体的研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2002.
WANG Jian. Research on preparation of ultrafine SnO2 power sol-gel method combined with ultrasonic wave[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2002.
[19] 彭思尧, 杨建广, 陈 冰, 李树超, 雷 杰, 李焌源. 含锡二次资源隔膜电积回收锡新工艺试验[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(12): 2656-2667.
PENG Si-yao, YANG Jian-guang, CHEN Bing, LI Shu-chao, LEI Jie, LI Jun-yuan. Novel process for tin recovery from stannous secondary resources based on membrane electrodeposition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(12): 2656-2667.
[20] 杨建广, 李焌源, 雷 杰, 杨声海, 何 静, 唐朝波, 陈永明. 一种基于盐酸-锡盐体系的退锡水及从废退锡水中回收锡的方法: 中国, CN103741142A[P]. 2014-04-23.
YANG Jian-guang, LI Jun-yuan, LEI Jie, YANG Sheng-hai, HE Jing, TANG Chao-bo, CHEN Yong-ming. A kind of tin-fading liquid based on the hydrochloric acid-tin salt system and the process of Recycling tin from the spent tin-fading liquid: China, CN103741142A[P]. 2014-04-23.
[21] 杨建广, 雷 杰, 彭思尧, 李焌源, 何 静, 杨声海, 唐朝波, 陈永明. 一种从锡阳极泥中回收锡的工艺: 中国, CN104630826[P]. 2015-05-20.
YANG Jian-guang, LEI Jie, PENG Si-yao, LI Jun-yuan, HE Jing, YANG Sheng-hai, TANG Chao-bo, CHEN Yong-ming. A process of tin recovery from the tin anode slime: China, CN103741142A[P]. 2015-05-20.
[22] 郭志超, 王静康, 李 鸿, 陈 巍, 张 缨, 潘 杰, 李 斌. 超声波对结晶过程部分热力学和动力学性质的影响[J]. 河北化工, 2003(2): 1-4.
GUO Zhi-chao, WANG Jing-kang, LI Hong, CHEN Wei, ZHANG Yin, PAN Jie, LI Bin. The effect of ultrasound on some thermodynamic and kinetic properties in crystallization process[J]. Hebei Chemical Engineering and Industry, 2003(2): 1-4.
[23] 陈国军. 低频脉冲磁场金属凝固晶粒细化机理研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2015.
CHEN Guo-jun. Study on the mechanism of grain refinement under low frequency pulsed magnetic field during solidification[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2015.
[24] 雷 杰. 铜锡多金属粉氯盐体系隔膜电积新工艺研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2016.
LEI Jie. Study on a new process of membrane electrowinning for recovery of tin from the copper-tin polymetallic powders in the chloride system[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2016
[25] SCHARIFKER B R, MOSTANY J. Three-dimensional nucleation with diffusion controlled growth: Part Ⅰ. Number density of active sites and nucleation rates per site[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1984, 177: 13-23.
[26] BARD A J, FAULKNER L R. Electrochemical methods: Fundamentals and applications[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2001: 669-676.
[27] 方小红. 超声波电镀镍基金刚石钻头工艺与机理研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2008.
FANG Xiao-hong, Study on technique and mechanism of ultrasound-assisted electroplating of nickel-based diamond bit[D].Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2008.
[28] GUO Z, ZHANG M, LI H, WANG J, KOUGOULOS E. Effect of ultrasound on anti-solvent crystallization process[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2005, 273: 555-563.
Electrochemical mechanism of tin membrane electrodeposition in ultrasonic field
NAN Tian-xiang, YANG Jian-guang, CHEN Bin, LI Shu-chao, DING Long
(School of Metallurgy and Environmental, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Tin was electrodeposited from chloride solutions by using a membrane cell in ultrasonic field. Cyclic voltammetry(CV), linear sweep voltammetry(LSV), chronoamperometry (CHR) and chronopotentiometry were applied to investigate the electrochemical mechanism of tin electrodeposition under ultrasonic field. Cyclic voltammetry and linear sweep voltammetry diagrams analysis shows that the application of ultrasound can change the tin membrane electro-deposition reaction from diffusion control to electrochemical control, and the increasing of temperature, acidity and ultrasonic power is beneficial to tin electrodeposition. Chronoamperometry curves show that the initial process of tin electrodeposition follows the diffusion controlled three-dimensional nucleation and grain growth mechanism. The coupling ultrasonic field plays a role in refining the grain and accelerating the electro-deposition reaction in this process, and the high preferential orientation of tin (tin whisker) tends to be no preferred orientation. The tin deposition tends to form regular network structure, and the tin whisker can be restrained. The ultrasonic coupling is more favorable to obtain the more compact and more smooth cathode tin under the same condition.
Key words: ultrasonic; membrane electrodeposition; acid chloride electrolyte; electrochemical mechanism
Foundation item: Project(51574294) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2015CX001) supported by the Plan of Innovation-driven of Central South University, China
Received date: 2017-05-03; Accepted date: 2017-06-28
Corresponding author: YANG Jian-guang; Tel: +86-731-88830470; E-mail: jianguang_y@163.com
(编辑 王超)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51574294);中南大学创新驱动计划(2015CX001)
收稿日期:2017-05-03;修订日期:2017-06-28
通信作者:杨建广,教授,博士;电话:0731-88830470;E-mail: jianguang_y@163.com