铬铁精矿球团烧结工艺与机理
朱德庆1,熊守安2,仉宏亮1,潘建1
(1. 中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 武钢程潮铁矿,湖北 鄂州,436000)
摘 要:对铬铁精矿球团烧结新工艺以及球团烧结矿冶金性能和固结机理进行研究。研究结果表明:铬铁精矿粒度粗,成球差,必须经过球磨机细磨,使其比表面积达到1 700 cm2/g,才具有良好的成球性;在膨润土配比为1.5%(质量分数)、造球水分为9.0%(质量分数)、造球时间为12 min的条件下,生球落下强度5次/(0.5 m),抗压强度11 N/个,爆裂温度480 ℃。优化的球团烧结工艺参数为:焦粉用量7%(质量分数)(内配比例30%),烧结混合料水分为9.5%,料层高度为650 mm,干燥温度为300~350 ℃,干燥负压为4 kPa,干燥时间为3 min,点火温度为1 100 ℃,点火负压为5 kPa,点火时间为1.5 min,烧结负压为8 kPa,取得了良好的指标:烧结矿产量为3.01 t/(m2?h),转鼓强度为89.33%,固体燃耗为79.19 kg/t。铬铁精矿球团烧结矿在900 ℃时很难还原,但还原膨胀率只有5%~6%,还原粉化率RDI+3.15大于94%,还原过程将具有较好的强度;在烧结料层的中上部,烧结矿的宏观结构以单个散状球团为主;在烧结料层下部以葡萄状烧结矿为主。铬铁精矿球团烧结矿矿物组成以铁铬尖晶石和硅酸盐矿物为主,单颗粒的球状烧结矿以固相固结为主,葡萄状烧结矿中液相量占30%左右,由固相固结和液相黏结共同维持烧结矿强度。
关键词:铬铁精矿;球团烧结;球磨预处理;固相固结;液相黏结
中图分类号:TF046.4 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2010)05-1658-10
Pellets sintering process of chromite concentrate and
mechanism of consolidation
ZHU De-qing1, XIONG Shou-an2, ZHANG Hong-liang1, PAN Jian1
(1. School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Chencao Iron Ore Mine, WISCO Minerals, Erzhou 436000, China)
Abstract: Pellets sintering of finely ground chromite concentrates was conducted, metallurgical performance and consolidation mechanism of sinter were examined. The results show that the tested chromite concentrate possesses poor pelletability due to coarser size and lower specific surface areas, which can be significantly improved by finely grinding the chromite concentrate up to 1 700 cm2/g through wet ball milling. Good green pellets are manufactured from the finely ground chromite concentrate under the following conditions: 1.5% bentonite (mass fraction), 9.0% moisture (mass fraction) of pellet feed and balling for 12 min, and drop number of 5 times from 0.5 m height, compressive strength of 11 N per pellet and cracking temperature of 480 ℃ are achieved. The operation parameters of pellets sintering process are optimized as follows: 7% coke breeze (mass fraction) (30% of it added into pellet feed before balling), 9.5% moisture, 650 mm bed height, drying at 300-350 ℃ and 4 kPa suction for 3 min, ignition at 1 100 ℃ and 5 kPa suction for 1.5 min, and sintering at 8 kPa, and the excellent sintering indexes are attained as follows: unit productivity of 3.01 t/(m2?h), tumble index of 89.33%, and solid fuel consumption of 79.19 kg/t. Chromite sinter is difficult to reduce at 900 ℃ due to chromium spinel occurring, and has high strength during reduction because of reduction swelling of 5%-6% and reduction degradation index RDI+3.15 over 94%. The consolidation mechanism of pellet sintering of chromite is demonstrated that macrostructure of sinter is classified into two groups, the first is individual fired pellets in the middle and top layers of sinter bed, and the second is racemose sinter in the bottom of sinter bed. The main minerals of chromite sinter comprise chromohercynite and silicate. The individual fired pellets are hardened by solid phase diffusion and the racemose sinter are consolidated by both solid phase diffusion and liquid phase bonding, the latter is 30% in sinter.
Key words: chromite concentrate; pellet sintering process; wet ball milling; solid diffusion consolidation; liquid phase bonding
铬铁矿是生产铬铁合金的重要原料。但是,我国铬矿资源贫乏,保有储量仅占世界储量的0.15%,95% 铬铁矿依靠进口,进口量达302万t/a。目前,世界铬矿开采量约为2 000万t/a,其中粉矿(粒径小于8 mm)约占80%[1]。虽然粉矿品位高,价格低,但在冶炼高碳铬铁过程中粉矿过多会使炉料透气性变差,炉况恶化、翻渣,严重影响各项技术经济指标[2-3]。因此,如何利用廉价粉矿,加强铬矿粉的造块是降低我国铬系铁合金生产成本、提高铬系铁合金市场竞争力的有效措施之一。目前,铬铁矿主要的造块方法有压团法、球团法和烧结法[4-6]。压团法生产的是生团块,加入无机黏结剂量大、降低铬品位及团块热稳定性差[6]。球团法所处理的铬精矿粒度要小,其比表面积要求达到 1 700~1 900 cm2/g以上,所需设备为链箅机-回转窑或带式焙烧机,投资大[7-9]。烧结法则具有烧结矿强度高、粒度均匀等优点,使电炉透气性改善,烧结矿结构疏松,高温电阻率比块矿和冷压团块大得多,冶炼产品单位电耗降低幅度为200~300 (kW·h)/t。但是,铬矿粉烧结温度高、产量低及能耗高,尤其是铬精矿粉制粒性能差,烧结过程透气性差[2, 10-11]。由于铬矿粉烧结在世界上的生产实践很少,开展铬精矿球团烧结新工艺研究,提高铬矿烧结矿产量和降低能耗,为电炉冶炼高碳铬铁提供优质炉料,具有重要的理论意义和应用价值。
1 实验
1.1 原料
1.1.1 铬铁精矿
所用原料主要包括一种铬铁精矿、膨润土和焦粉,其化学成分见表1。从表1可见:Cr2O3含量高,达到47.10%,w(MgO)/w(Al2O3)比低,只有0.69。此外,该矿石硫、磷含量低,有利于减少铬铁合金冶炼时的脱硫脱磷成本,提高产品质量。
表1 铬铁精矿的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical composition of chromite concentrate %

铬铁精矿的粒度组成见表2。原始矿粉的比表面积为390 cm2/g,细磨矿粉的比表面积为1 700 cm2/g。铬铁精矿的粒度较小,小于150 μm粒级矿粉含量占75%左右,不适于烧结。但相对于球团工艺要求,其粒度又太大,小于75 μm粒级矿粉含量只有22.3%,小于45 μm粒级矿粉含量仅9.3%,而球团生产中通常要求原料粒度小于75 μm矿粉含量在85%以上。另外,其比表面积仅390 cm2/g,远低于球团生产对原料比表面积1 700~900 cm2/g的要求。因此,必须对其进行细磨预处理,才能保证有较好质量的合格生球用于烧结。
表2 铬铁精矿的粒度组成
Table 2 Size distribution of chromite concentrate

表3 膨润土的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 3 Chemical composition of bentonite %

表4 膨润土物理性能
Table 4 Physical properties of bentonite

1.1.2 膨润土
膨润土是国内外球团厂广泛采用的黏结剂。其主要成分是蒙脱石,并含有一定数量的其他黏土矿物和非黏土矿物(如石英、长石、方英石等)[9]。本研究所用膨润土化学成分见表3。可见:主要组成为SiO2和Al2O3,将降低烧结矿的铬品位。因此,原料中尽量少加膨润土。膨润土的物理性能见表4,该膨润土蒙脱石含量为65.61%,2 h吸水率高达404.8%,胶质价为100%,是一种优质膨润土。
1.1.3 焦粉
焦粉的工业分析结果及灰分化学成分分别见表5和表6。可见:焦粉固定碳较低,只有76%,而灰分含量较高,达到19.70%,硫含量为0.3%左右,属于较低硫含量燃料。
表5 焦粉工业分析(质量分数)
Table 5 Industry analysis of coke %

表6 焦粉灰分化学成分(质量分数)
Table 6 Chemical composition of braize ash %

焦粉粒度组成见表7。焦粉粒度均小于3 mm。与普通铁矿烧结对燃料粒度要求相比(80%左右小于 3 mm),此次球团烧结试验中要求燃料粒度偏小。
表7 焦粉粒度组成
Table 7 Size distribution of coke

1.2 试验研究方法
湿式球磨预处理。球磨机直径×高为460 mm×620 mm,钢球质量及钢球粒度组成可调,钢球填充率为15%~18%(体积分数)。湿式球磨矿浆质量分数为75%,每次磨45 kg矿样。
造球试验是在圆盘造球机中进行的。其主要技术参数为:直径1 000 mm,转速28 r/min,边高150 mm,倾角47°。生球取样测定其抗压强度、落下强度、爆裂温度和水分。
生球爆裂温度测定是参照美国AC公司的动态测定法[12],在直径×高为650 mm×1 000 mm的竖式管炉中进行。每次取50个合格生球装入干燥杯中,将干燥杯放入风速为1.8 m/s(冷态)的竖式管中,生球在炉膛内停留5 min后取出,以生球破裂4%所能承受的最高温度(AC公司生球裂10%)为爆裂温度。
球团烧结试验流程包括:配料、混合、造球、外滚焦粉、布料、干燥、点火、烧结、冷却、落下、筛分等环节。采用质量配料法,在配料计算时,铬铁矿粉、焦粉、返矿内配,水和膨润土外配。原料混匀后,在圆盘造球机内造球;生球置于直径×高为600 mm× 1 400 mm圆筒混合机内外滚焦粉,圆筒混合机转速为15 r/min,滚动时间为1.5 min。采用人工布料方式将生球装入直径为165 mm烧结杯中,使用1 kg粒度为15~25 mm成品烧结矿做铺底料,铺底料高度为40 mm。
在球团烧结工艺中,干燥是非常重要的一个工艺环节[11]。以点火器废气为热源,调节废气温度和时间控制干燥效果。
采用液化气点火,点火时间为1.5 min,点火温度 为(1 100±50) ℃,点火负压为5 kPa。烧结负压为8~10 kPa。到达烧结终点时,抽风负压调低至4 kPa,冷却5 min后卸料,烧结矿经单齿辊破碎机破碎,然后进行落下、分级及转鼓强度检测等。成品烧结矿取样用于化学分析及矿相鉴定。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 铬铁精矿造球
2.1.1 膨润土添加量对生球性能的影响
在球团烧结工艺中,生球质量直接影响球团烧结矿产量和质量。生球质量包括生球强度和爆裂温度。膨润土添加量对生球性能的影响见表8。铬铁精矿无论润磨与否,随膨润土用量增加,生球落下强度稍有提高,生球抗压强度几乎没有提高,与不添加膨润土时基本一致,只有4 N/个左右,远远达不到相关要求。由表8可见:铬铁精矿的成球性很差,这主要是其粒度偏粗,比表面积偏小所致。
2.1.2 润磨时间对生球性能的影响
为了提高生球强度,延长润磨时间对生球性能的影响如表9所示。从表9可见:随润磨时间的延长,造球原料的比表面积有所提高,生球的落下强度也有较明显提高,但润磨时间大于6 min后,生球落下强
表8 膨润土用量对铬铁精矿生球性能的影响
Table 8 Effect of bentonite dosage on properties of green pellets from chromite concentrate
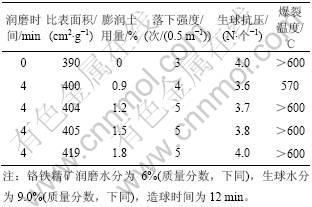
表9 润磨时间对铬铁精矿生球性能的影响
Table 9 Effect of damp milling time on properties of green pellets from chromite concentrate
度反而下降。但生球的抗压强度并无多大变化,仍达不到基本要求(>10 N/个)。可见,润磨不适于预处理该种铬铁精矿。
2.1.3 球磨对生球性能的影响
铬铁精矿比表面积对生球性能的影响如表10所示。从表10可见:湿式球磨提高了铬铁精矿比表面积;随其比表面积增加,生球落下强度增加,抗压强度也显著提高;在比表面积达到1 700 cm2/g时,生球的抗压强度达到11 N/个,生球落下强度也达到5次/(0.5 m)。随比表面积增加,生球的爆裂温度降低,但仍有480 ℃左右。
表10 细磨铬铁精矿比表面积对生球性能的影响
Table 10 Effect of specific surface area of ball-milled chromite concentrate on properties of green pellets

由表2可见:铬铁精粉经过球磨机细磨后,细粒级含量明显增加,尤其小于45 μm粒级粉末含量 (<37 μm和37~45 μm 2个粒级粉末含量之和)由9.30%提高到88.68%,相应比表面积也明显升高,这从扫描电镜照片(图1)可得到证实。因此,选定比表面积1 700 cm2/g的细磨铬铁矿为原料进行后续试验。
2.2 铬铁精矿球团烧结工艺参数优化
2.2.1 干燥温度
球团烧结过程与普通烧结比较,必须增设干燥工
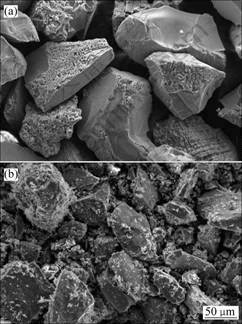
(a) 细磨前; (b) 细磨后
图1 铬铁精矿颗粒形貌
Fig.1 Particle morphologies of chromite concentrate
艺[9]。因为烧结点火温度远远高于生球爆裂温度,如果不设干燥工艺,点火时将造成生球大量爆裂,严重影响烧结料层透气性。
干燥温度对细磨铬铁精矿球团烧结性能的影响如表11所示。从表11可见:当干燥温度为300~350 ℃时,烧结的产质量指标比较高。这是由于低温干燥或不干燥时,表层生球干燥效果不好,在点火时导致表层生球爆裂,使烧结料层透气性下降,故垂直烧结速度较慢,最终影响烧结矿产量和强度;当干燥温度太高时,有一部分球团干燥时爆裂,同样也影响烧结矿产量和强度。
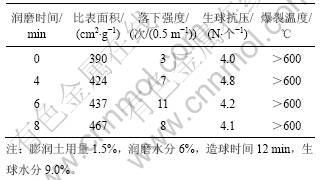
2.2.2 焦粉添加量及添加方式
焦粉用量对铬铁精矿球团烧结矿性能的影响见表12。从表12可见:随着焦粉配比升高,烧结矿产量和强度升高,但当配入的焦粉质量分数高于7%时,烧结矿强度和产量反而下降,因此,适宜的焦粉配比为7%时效果最好,烧结矿产量为2.42 t/(m2?h),转鼓强度为85.24%,固体燃耗为79.98 kg/t。
焦粉在造球前和造球后加入的比例(分别称为内配和外配)对铬铁精粉球团烧结性能的影响如表13所示。
表11 干燥温度对球团烧结指标的影响
Table 11 Effect of drying temperature on pellets sintering indexes

表12 焦粉添加量对烧结指标的影响
Table 12 Effect of coke dosage on pellets sintering indexes
从表13可见:适宜的焦粉添加方式为内配30%~45%,对应的烧结矿强度和产量最高。烧结矿产量为2.42~3.56 t/(m2?h),转鼓强度为82.55%~85.24%,固体燃耗为78.73~79.98 kg/t。
2.2.3 混合料水分
表14所示为混合料水分对细磨铬铁精矿球团烧结性能的影响。可见:随着烧结混合料水分增加,制粒效果改善,烧结速度加快,烧结矿利用系数增加,转鼓强度升高,固体燃耗下降,水分质量分数9.5%为最适宜值。当水分质量分数超过9.5%,烧结各项指标变差。
2.2.4 烧结负压
烧结负压对铬铁精矿球团烧结性能的影响如表15所示。可见:当烧结负压为8 kPa时,烧结矿成品率、转鼓强度、利用系数均较理想。由于烧结负压增大,通过料层的风量加大,垂直烧结速度变快,在适宜范围内,增加负压能提高烧结矿产量。但当烧结负压过大时,高温保持时间短,表层冷却快,此外料层中细粒焦粉在高负压下向下迁移,导致料层热量分布更加不合理,从而降低烧结矿质量。
2.2.5 料层高度
烧结料层高度与烧结指标的关系见表16。适宜的料层高度为650 mm,利用系数为3.01 t/(m2?h),转鼓强度为89.33%,固体燃耗为79.19 kg/t。料层进一步升高,烧结矿强度和产量下降。该工艺所得烧结矿产量和质量远高于普通烧结工艺的产量和质量,铬铁矿粉普通烧结的烧结矿产量1.3 t/(m2?h),转鼓强度为58%,固体燃耗为112 kg/t[11-12]。
一般而言,料层高度增加,由于蓄热作用,烧结矿的产量和质量都会提高,固体燃耗降低。但料层过高,料层下部过湿加剧,热态透气性变差,表现在垂直烧结速度下降,燃料燃烧不充分,烧结料层中温度下降,从而导致产量和强度下降。
2.3 烧结矿冶金性能
2.3.1 铬铁精矿球团烧结矿化学成分
表17所示为铬铁精矿球团烧结矿化学成分,球团烧结矿中w(Cr2O3)/w(FeO)为3.61,可用来生产高铬铁合金。从其粒度组成(表18)可见:主要粒度范围为5~ 16 mm,表明以球团为主,普通烧结矿粒度为5~ 40 mm[11],两者有显著差别。
2.3.2 铬铁精矿球团烧结矿冶金性能
铬铁精矿球团烧结矿冶金性能[11]如表19所示。反映烧结矿冶金性能的指标包括还原性指数(RI)、还原膨胀率(RSI)、低温还原分化率(RDI)。从表19可见:成
表13 焦粉添加方式对烧结指标的影响
Table 13 Effect of adding method on pellets sintering indexes
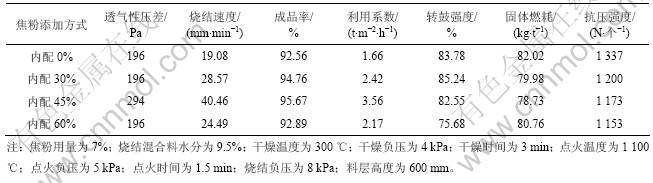
表14 混合料水分对球团烧结指标的影响
Table 14 Effect of moisture content in mixture on pellets sintering indexes

表15 烧结负压对球团烧结指标的影响
Table 15 Effect of sintering suction pressure on pellets sintering indexes

表16 料层高度对烧结指标的影响
Table 16 Effect of bed height on pellets sintering indexes
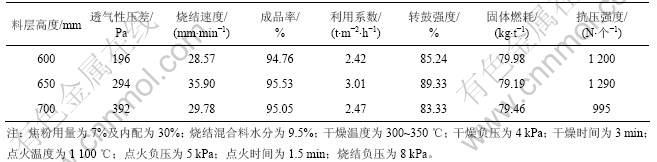
表17 细磨铬铁精矿球团烧结矿化学成分(质量分数)
Table 17 Chemical composition of pellet sinter using ball-milled chromite concentrate %

表18 球团烧结矿粒度组成
Table 18 Size distribution of pellet sinter using ball-milled chromite concentrate

表19 细磨铬铁精矿球团烧结矿冶金性能
Table 19 Metallurgical properties of pellet sinter using ball-milled chromite concentrate
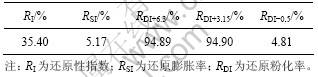
品球团的还原性指数仅35%左右,表明球团矿中只有部分铁氧化物发生了还原,而含铬氧化物在900 ℃的低温还原条件下很难还原。因此,铬铁矿熔炼温度远高于普通铁矿的熔炼温度[2]。但球团还原膨胀率只有5%~6%左右,而且还原粉化率RDI+3.15大于94%,还原过程将具有较高的强度。
2.4 铬铁精矿球团烧结矿固结机理
2.4.1 矿物组成
铬铁精矿球团烧结矿经光学显微镜鉴定及扫描电镜能谱图(见图2)证实矿物组成如下:铁铬尖晶石为主的铬尖晶石(FeCr2O4),三氧化二铬(Cr2O3),硅酸盐多成分液相,钛铁矿(FeTiO3),镁铁尖晶石(Mg,Fe)(AlFe)O4及玻璃质等,其含量见表20。可见:液相量(硅酸盐液相与玻璃质含量之和)占28.81%,比常规工艺所得烧结矿少[12]。
表20 铬铁精矿球团烧结矿矿物组成(质量分数)
Table 20 Mineral composition of pellet sinter using ball-milled chromite concentrate %


(a) 扫描电镜;(b) 能谱分析
图2 球团烧结矿扫描电镜能谱分析结果
Fig.2 SEM energy spectrum analysis of pellet sinter
2.4.2 微观结构
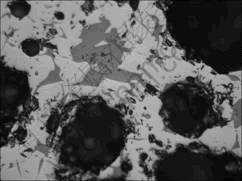
烧结矿宏观结构:在烧结料层的中上部,烧结矿大多数为单颗粒的球团,但在烧结料层底部,有一些球团相互黏结在一起形成葡萄状。在显微镜下观察,葡萄状烧结矿中铁铬尖晶石结晶良好,晶粒粗大互连成整体(见图3)。对这些晶粒进行点扫描时发现大部分晶粒中都夹杂着少量的Mg和Al元素(见图4)。散状球团数量远多于葡萄状烧结块,而普通烧结矿呈现 块状。

铁铬尖晶石—浅棕灰色,互连状;硅酸盐液相—灰色,嵌布状;孔洞—黑色,不规则
图3 葡萄状烧结矿中铁铬尖晶石结晶的分布
Fig.3 Distribution of chromohercynite crystal in racemose pellet sinter

(a) 扫描电镜;(b) 能谱分析
图4 铁铬尖晶石扫描电镜能谱分析结果
Fig.4 SEM energy spectrum analysis of chromohercynite
在铁铬尖晶石的间隙中充填着大量的硅酸盐液相,将铁铬尖晶石紧紧胶结在一起(见图5),维持这种球团烧结矿的机械强度。该液相化学成分见图6。
硅酸盐液相—灰色,嵌布状;铬铁尖晶石—浅棕灰色,互连状;孔洞—黑色,不规则
图5 硅酸盐液相嵌布状况
Fig.5 Distribution of silicate liquidoid

(a) 扫描电镜;(b) 能谱分析
图6 液相扫描电镜能谱分析结果
Fig.6 SEM energy spectrum analysis of silicate liquid phase
在烧结料层中上部,由于烧结温度低,烧结矿大多数呈单颗粒球团状(12~13 mm),球团中液相量比下部葡萄状烧结矿少得多,主要以固相固结为主,浅白色的三氧化二铬结晶明显(见图7),呈线条状或细粒状,在孔洞周围分布较多。烧结矿细小孔洞较多,一般孔径为0.11~0.13 mm,配碳量越多,孔隙率越大,对还原性有利,但对提高强度不利。

铁铬尖晶石—浅棕灰色,互连状;硅酸盐液相—灰色,嵌布状;三氧化二铬—浅白色,条粒状;孔洞—黑色,不规则
图7 单颗粒球团烧结矿中三氧化二铬结晶状况
Fig.7 Distribution of chromium trioxide crystal in granular pellet sinter
3 结论
(1) 铬铁精矿粒度大,成球性差,仅通过润磨预处理,生球强度只为4 N/个,远达不到要求,必须经过球磨机细磨,使其比表面积达到1 700 cm2/g,才具有良好的成球性。在膨润土配比为1.5%,造球水分为9.0%,造球时间为12 min的条件下,细磨铬铁精矿制备的生球落下强度为5 次/(0.5 m),抗压强度为11 N/个,爆裂温度为480 ℃。
(2) 优化的球团烧结工艺参数为:焦粉用量7%(内配比例30%),混合料水分9.5%,料层高度650 mm,干燥温度300~350 ℃、干燥负压4 kPa、干燥时间3 min,点火温度1 100 ℃,点火负压5 kPa,点火时间1.5 min,烧结负压8 kPa。在此工艺条件下,取得良好的烧结指标:烧结矿产量3.01 t/(m2?h),转鼓强度89.33%,固体燃耗为79.19 kg/t。
(3) 铬铁精矿球团烧结矿在900 ℃很难还原,但球团还原膨胀率只有5%~6%,还原粉化率RDI+3.15大于94%,还原过程将具有较好的强度。
(4) 在烧结料层的中上部,烧结矿的宏观结构以单个散状球团为主,在烧结料层下部以葡萄状烧结矿为主。铬铁矿球团烧结矿矿物组成以铁铬尖晶石和硅酸盐矿物为主,单颗粒的球团烧结矿以固相固结为主,葡萄状烧结矿中液相量占30%左右,由固相固结和液相黏结共同维持烧结矿强度。
参考文献:
[1] 方实. 国外铬矿概况与顿斯克铬矿山[J]. 地质与勘探, 1998, 34(2): 16-18.
FANG Shi. Foreign chromite survey and DUNCEK Chromite Mine[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1998, 34(2): 16-18.
[2] 戴维, 舒莉. 铁合金冶金工程[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1999: 121-122.
DAI Wei, SU Li. Ferroalloy metallurgy engineering[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1999: 121-122.
[3] 张启轩. 我国铁合金工业的现状及加快实施创新对策[J]. 铁合金, 2000(2): 33-39.
ZHANG Qi-xuan. Present situation of China ferroalloy industry and countermeasures to innovate quickly[J]. Ferroalloy Metallurgy, 2000(2): 33-39.
[4] 朱德庆, 李建, 范晓慧, 等. 铬铁矿粉造块方法综述[J]. 烧结球团, 2004, 29(2): 27-30.
ZHU De-qing, LI Jian, FAN Xiao-hui, et al. Literature review of the agglomeration of chromite fines[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2004, 29(2): 27-30.
[5] 贾振海. 粉状铬矿的预处理技术[J]. 铁合金, 1989(3): 39-40.
JIA Zhen-hai. Techniques for chromite ore fines processing[J]. Ferroalloy Metallurgy, 1989(3): 39-40.
[6] 邱伟坚. 铁合金矿粉冷压球团成球机理及固结[J]. 铁合金, 2003(3): 7-9.
QIU Wei-jian. Balling-up mechanism and consolidation of briquetting from fine ores[J]. Ferroalloy Metallurgy, 2003(3): 7-9.
[7] 冯志明. 印度粉铬矿球团及生产高碳铬铁的应用实践[J]. 铁合金, 2003(4): 32-33.
FENG Zhi-ming. Pelleting of India chrome-ore fines and its application to high-carbon ferrochrome production[J]. Ferroalloy Metallurgy, 2003(4): 32-33.
[8] 张明俊, 刘福泉. 铬矿烧结工艺研究[J]. 铁合金, 1994(3): 7-10.
ZHANG Ming-jun, LIU Fu-quan. The study of chromite sintering[J]. Ferroalloy Metallurgy, 1994(3): 7-10.
[9] 傅菊英, 朱德庆. 铁矿氧化球团基本原理、工艺及设备[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2005: 43, 234-236,
FU Ju-ying, ZHU De-qing. Theory, techniques and equipment of iron concentrate oxidized pellet[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2005: 43, 234-236.
[10] 朱德庆, 李建, 潘建, 等. 铬矿粉烧结试验研究[J]. 钢铁, 2007, 42(8): 7-11.
ZHU De-qing, LI Jian, PAN Jian, et al. Study on sintering of chromite fines[J]. Iron and Steel, 2007, 42(8): 7-11.
[11] 傅菊英, 姜涛, 朱德庆. 烧结球团学[M]. 长沙: 中南工业大学出版社, 1996: 38, 210-216.
FU Ju-ying, JIANG Tao, ZHU De-qing. Sintering and pelletizing[M]. Changsha: Central South University of Technology Press, 1996: 38, 210-216.
[12] ZHU De-qing, LI Jian, PAN Jian, et al. Sintering behaviours of chromite fines and the consolidation mechanism[J]. Int J Miner Process, 2008, 86(1/4): 58-67.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2009-11-02;修回日期:2010-03-30
基金项目:高校青年教师教学科研奖励基金资助项目(教人司2000[26])
通信作者:朱德庆(1964-),男,湖南安乡人,博士,教授,博士生导师,从事烧结球团、直接还原及资源综合利用等方面研究;电话:0731-88836942;E-mail: dqzhu@mail.csu.edu.cn