准噶尔盆地乌夏地区二叠系碎屑岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化
牛海青1,陈世悦1,张鹏2,鄢继华1
(1. 中国石油大学 地球资源与信息学院,山东 东营,257061;
2. 中国石化股份胜利油田分公司 物探研究院,山东 东营,257022)
摘 要:对岩芯进行观察,并对薄片进行电镜扫描和物性分析及鉴定,对储层成岩作用过程进行研究。研究结果表明:乌夏地区二叠系砂岩经历了机械压实作用、胶结作用、交代作用、溶蚀作用、破裂作用等多种成岩作用,目前已达到中成岩期A 亚期—晚成岩期;储层的孔隙演化与成岩作用密切相关;机械压实作用、化学胶结作用是导致砂岩孔隙度降低、储集性能变差的主要因素,孔隙损失分别达23.65%和4.30%;长石颗粒、火山岩岩屑、钠长石、沸石、碳酸盐胶结物的溶蚀及刚性颗粒的破裂作用是形成次生孔隙的主要因素,明显提高了乌夏地区二叠系砂岩储集性能,孔隙增生量达4.90%。
关键词:准噶尔盆地;乌夏地区;二叠系;成岩作用;孔隙演化
中图分类号:TE122.2;P588.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2010)02-0749-10
Diagenesis and porosity evolution of Permian reservoir in
Wu-Xia Area, Junggar Basin
NIU Hai-qing1, CHEN Shi-yue1, ZHANG Peng2, YAN Ji-hua1
(1. Faculty of Geo-Resources and Information, China University of Petroleum, Dongying 257061, China;
2. Geophysical Research Institute, Shengli Oilfield Company of SINOPEC, Dongying 257022, China)
Abstract: Core was observed, and the thin section was analyzed through SEM observation and reservoir property analysis. The results show that the Permian reservoirs in Wu-Xia Area are primarily in A-substage of middle diagenesis and late diagenesis, which mainly undergoes compaction, cementation, dissolution and fracturing processes. The porosity evolution of reservoir is closely related with the diagenesis types. Mechanical compaction and chemical cementation are the main reasons for destroying primary pores, which contribute 23.65% and 4.30% to the loss of primary porosity respectively. The dissolution of feldspar, volcanic fragments, clay mineral, zeolite, calcite and the fracturing of rigid particle are the main factors for forming secondary pores, which obviously improves the reservoir property for increasing reservoir porosity by 4.90%.
Key words: Junggar Basin; Wu-Xia Area; Permian; diagenesis; porosity evolution
在准噶尔盆地以往的沉积储层研究中,目的层多集中在侏罗系。而对于二叠系的研究,研究者大多对不整合与油气成藏、断裂活动及其沉积响应进行研究,对其储层特征、评价及分布没有进行系统研究。近年来,随着准噶尔盆地石油勘探开发与综合地质研究的深入,勘探层位主要有浅层的侏罗系、三叠系逐渐拓展到二叠系,目前,二叠系已累计探明石油2.759× 107 t,天然气达8.28×108 m3,成为乌夏地区勘探主力层系之一,但探明率仅为21.90%,勘探潜力巨大。在此,本文作者在沈英等[1-4]研究的基础上,系统研究乌夏地区二叠系储层成岩作用及其对储层孔隙演化的影响,以期为进一步勘探和开发提供依据。
1 地质背景
乌夏地区是准噶尔盆地西北缘十分重要的勘探领域之一,西起百口泉油田,东至红旗坝区,北以哈拉阿拉特山为界,南与艾里克湖毗连(图1),内部包括乌尔禾区、风城区、夏子街区3个探区,东西长70 km,南北宽约30 km,面积约2×103 km2。构造上乌夏地区位于准噶尔盆地西部隆起东北部,断裂发育,褶皱形态复杂,主要发育乌兰林格断裂、夏红北断裂及百乌断裂等一系列北东向、北东东向大断裂。
在石炭纪晚期,受哈萨克斯坦板块、西伯利亚板块与准噶尔地块强烈碰撞拼合运动影响,准噶尔盆地边界断裂大规模活动,同时伴随较广泛的火山活动。而哈拉阿拉特山以南稳定区持续下沉进入前陆盆地发育期,处于盆地西北缘前陆坳陷区的乌夏地区,接受了巨厚的上、下二叠统沉积,早二叠世发育了一套由火山-火山碎屑岩和正常碎屑岩沉积,中晚二叠世主要发育冲积扇相、扇三角洲相和湖泊相(图2)。冲积扇相、扇三角洲相砂砾岩体及滨浅湖滩坝砂体构成二叠系主要的碎屑岩储集体。乌夏地区二叠系自下而上发育佳木河组、风城组、夏子街组和下乌尔禾组,各层位碎屑岩储层发育,乌尔禾组和风城组储层物性明显比佳木河组和夏子街组的物性好。乌夏地区二叠系储层为低孔、中低渗储层,其物性受沉积相和成岩作用的共同控制[5],沉积相通过控制储集岩的碎屑成分、颗粒粒度等控制储集物性,而成岩作用对储层物性的控制则表现为随储层埋藏深度不同,储层所受的成岩作用类型和强度存在明显差异。
2 储层基本特征
2.1 储层岩石学特征
乌夏地区二叠系碎屑岩储层主要分布在夏子街组和下乌尔河组,岩性不等粒岩屑砂岩、砂砾岩和砾岩总体表现为成分成熟度低、结构成熟度低-中等、火山岩岩屑含量高的岩石学特征。石英和长石碎屑在二叠系储层中含量(质量分数)普遍很低,其平均含量分别为2%~8%和5%~8%;而岩屑含量普遍很高,平均为85%~91%。岩屑组分以凝灰岩、安山岩、流纹岩、霏细岩等火山岩岩屑为主,其中:凝灰岩岩屑含量较高,各层系凝灰岩岩屑平均含量为30%~50%,其次为硅质岩及浅变质岩岩屑。砂岩的结构成熟度为低~中等,碎屑颗粒呈次圆~次棱角状,分选较差~中等,碎屑颗粒间以点-线、线-凹凸接触为主,胶结类型主要为孔隙-压嵌式,泥质含量较低,平均为1.7%~3.3%。胶结物主要为碳酸盐、硅质、沸石类、石膏及钠长石。
2.2 储集空间类型
通过铸体薄片和扫描电镜观察发现:研究区碎屑岩原生孔隙含量(即其孔隙面积与总孔隙面积之比)很少,原生粒间孔几乎不发育,储集空间类型以次生孔隙为主,其中粒内溶孔最发育,含量占整体储集空间类型的41.77%;其次为微裂缝、填隙物内溶孔和界面缝,含量分别为14.43%,12.84%和11.51%,晶间孔、粒间溶孔及剩余粒间孔含量较小,均小于10% (表1)。
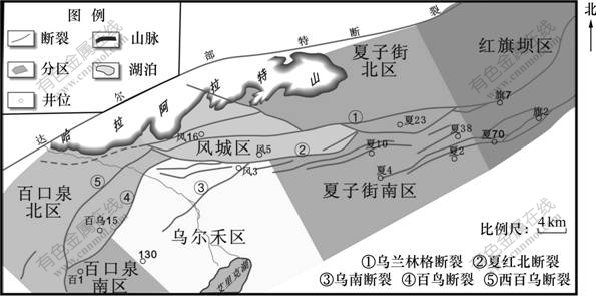
图1 乌夏地区探区划分
Fig.1 Division of exploration area in Wu-Xia Area

图2 乌夏地区二叠系沉积充填序列
Fig.2 Permian sedimentary sequences in Wu-Xia Area
表1 乌夏地区二叠系碎屑岩储集空间类型
Table 1 Types of reservoir space in Permian clastic rock in Wu-Xia Area

3 成岩作用类型及特征
利用偏光显微镜、扫描电镜等对岩石铸体薄片中各种成岩组构、孔隙类型和自生矿物组合等特征进行观察发现:研究区砂岩储层主要经历了压实作用、绿泥石黏土膜形成、石英次生加大、长石及火成岩屑溶蚀和晚期含铁碳酸盐胶结、交代作用的叠加改造[6-8]。
3.1 压实作用
研究区压实作用分为机械压实作用和化学压溶作用。机械压实作用表现为颗粒紧密接触,多为线接触,塑性颗粒(云母片、泥岩岩屑等)弯曲变形,有的进入孔隙中形成假杂基,刚性颗粒发育裂纹、边缘破裂(图3(a))。压溶作用主要表现在石英、长石和酸性火山岩岩屑纵向上的压溶,石英颗粒横向增生,使储集物性降低。该区压实作用受岩性和碳酸盐胶结的影响较大,在杂基、塑性颗粒以及塑性岩屑含量低的部位,由于碳酸盐胶结物大量形成,增加了岩石的抗压强度,压实作用不强烈,相反,在杂基、塑性颗粒以及塑性岩屑含量较高部位,由于软岩屑、塑性矿物颗粒以及杂基很容易被挤压变形,压实作用比较强烈[9-10]。
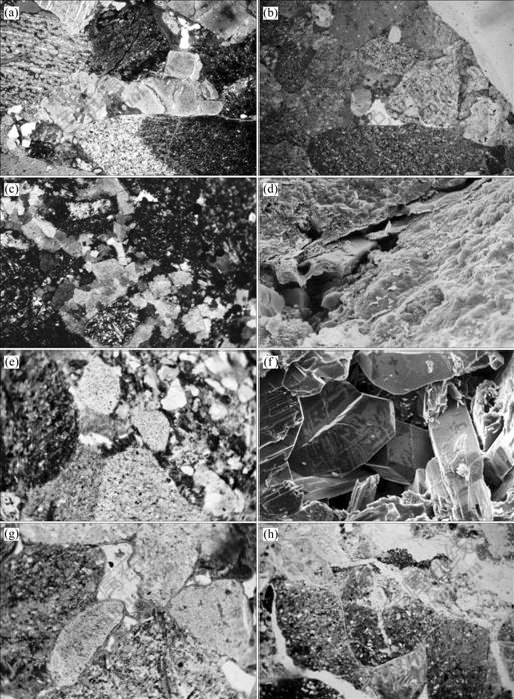
(a) 夏70井,深度为2.793 44 km,夏子街组,砂砾岩,颗粒接触紧密,压裂缝, 蓝色铸体,单偏光;(b) 乌001井,深度为2.072 48 km,下乌尔禾组,方解石胶结物、方解石溶孔,蓝色铸体,单偏光;(c) 风南1井,深度为4.442 km,风城组,不等粒长石岩屑砂岩,菱形白云石胶结物,正交光;(d) 玛003井,深度为3.635 97 km, 下乌尔禾组,粒间石英晶体与粒表弯曲片状伊利石,扫描电镜;(e) 乌8井,深度为3.001 35 km,夏子街组,砂质砾岩,片沸石胶结物并交代颗粒,单偏光;(f) 玛003井,深度为3.658 92 km,下乌尔禾组,板条状钠长石及钠长石晶间孔,扫描电镜;(g) 风南1井,深度为4.004 09 km,夏子街组,砂砾岩,绿泥石包膜,粒间钠长石晶间孔,红色铸体,单偏光;(h) 风504井,深度为0.885 26 km,下乌尔禾组,砂质砾岩,颗粒部分溶解孔隙,蓝色铸体,单偏光
图3 乌夏地区二叠系储层成岩作用类型
Fig.3 Main diagenetic types of Permian sandstones in Wu-Xia Area
3.2 胶结作用
3.2.1 碳酸盐胶结物
研究区碳酸盐胶结物分布广泛,在二叠系各层位均有分布,胶结物类型主要包括方解石、铁方解石、白云石、含铁白云石及菱铁矿。(铁)方解石胶结物多为中-细晶,不均匀地充填于颗粒孔隙间(图3(b)),或以交代其他组分产出。白云石、(含)铁白云石胶结物常沿碎屑颗粒周围呈断续的薄膜式胶结,或分散充填于孔隙中,晶体自形程度较高,个别晶体为菱形(图3(c))。菱铁矿胶结物主要发育在侏罗系和三叠系,在二叠系中较少,经薄片观察,发现仅在风503井的夏子街组存在,呈微晶粒状不均匀分布于颗粒之间。
3.2.2 硅质胶结物
本区硅质胶结物常见石英次生加大及自生石英(图3(d))。石英颗粒常具不规则窄边状或锯齿状次生加大,在扫描电镜下发现自生石英多呈集合体状。
3.2.3 沸石胶结物
沸石类胶结物常见于富含火山碎屑和长石的砂岩中,是火山碎屑和长石与地下水相互作用的产物,研究区常见的类型有方沸石、片沸石和浊沸石。方沸石常沿着颗粒向粒间孔隙中呈马牙状生长,常与方解石共生形成粒间胶结物堵塞孔隙,但后期遭受溶蚀形成次生孔隙,从而提高储集性能[11]。片沸石多包含铁离子而呈橘红色,呈板条状晶体分散在孔隙中,或沿颗粒周围向粒间孔隙中呈马牙式生长(图4(e))。浊沸石一般呈柱状、纤维状充填于孔隙中,二叠系岩屑类型多为火山碎屑和凝灰质,富含硅和钙,可蚀变形成浊 沸石。
3.2.4 长石胶结物
研究区长石胶结物类型主要为钠长石,多呈小的自形晶体产出,呈细的板条状或粒状充填于孔隙中(图3(f)),常具双晶。
3.2.5 黏土矿物胶结物
据薄片鉴定、电镜扫描和X线衍射分析结果,该区黏土矿物类型包括伊利石(I)、绿泥石(C)、伊蒙混层(I/S)及少量的高岭石。在显微镜下,高岭石常呈分散质点状孔隙充填,伊利石、绿泥石常呈薄膜状孔隙衬垫状产出(图3(g));在扫描电镜下,高岭石呈蠕虫状充填于孔隙或分布于颗粒表面,伊利石呈弯曲片状充填于孔隙或分布于颗粒表面(图3(d)),绿泥石呈不规则片状、绒球状充填于孔隙中。自生黏土矿物来源于孔隙水的沉淀作用,碎屑岩中不稳定组分的蚀变作用以及上覆黏土岩中黏土转化为自生黏土矿物的形成提供了物质来源,伊利石、伊蒙混层黏土则是在富K+的碱性条件下形成的[12-13]。
3.2.6 黄铁矿胶结物
黄铁矿也是本区较常见的胶结物类型,分布比较广泛,是强还原介质条件下的产物。在单偏光下不透明,在反射光下具金属光泽,常呈分散状或集合体呈凝块状分布。
由于压实作用高峰期发生在胶结作用之后,胶结作用也减小了压实作用对孔隙的影响,同时为次生孔隙的形成提供了物质基础。
3.3 交代作用
研究区交代作用分布广泛,二叠系各层位均有发育,常见的交代作用有碳酸盐矿物交代碎屑颗粒、沸石交代碎屑颗粒(图3(e))、黏土矿物交代碎屑颗粒以及自生矿物之间的相互交代。
3.3.1 碳酸盐矿物交代颗粒
常见有方解石、菱铁矿、铁方解石或铁白云石交代石英、长石、岩屑颗粒边缘或完全交代碎屑,使这些颗粒的边缘形状不规则或交代物中残留有被交代矿物包体或交代物呈被交代矿物的外形,偶见菱铁矿交代云母颗粒的现象。
3.3.2 沸石交代颗粒
多见片沸石交代碎屑颗粒,主要表现为:延斜长石的双晶纹或解理缝进行交代,或者交代碎屑颗粒的边缘呈港湾状、锯齿状(图3(e))。
3.3.3 黏土矿物交代颗粒
主要表现为绿泥石交代石英、长石边缘、颗粒表面的绿泥石化,高岭石、伊利石、伊利石/蒙皂石的混层黏土矿物、绿泥石/蒙皂石混层黏土矿物附着于颗粒表面生长。
3.3.4 自生矿物之间的交代作用
在显微镜下可观察到晚期生成的方解石对早期形成的浊沸石的交代,方解石、浊沸石对绿泥石环边的交代,以及碳酸盐矿物之间的相互交代,表现为菱铁矿与方解石相互交代、铁方解石交代方解石、铁白云石交代铁方解石。
3.4 溶解作用
通过普通显微镜、扫描电镜、阴极发光、铸体薄片观察发现:本区被溶蚀的物质主要是岩屑、长石等不稳定的颗粒及少量方解石、浊沸石、钠长石和硅质填隙物。岩屑颗粒的溶解通常有3种特征:粒内仅部分矿物或局部发生溶解,形成斑点状、蜂窝状、条纹状粒内溶孔(图3(h));颗粒发生强烈溶解仅剩部分残余或整体溶解形成铸模孔;颗粒边缘溶解呈不规则状,或向粒间扩展形成粒间扩大溶孔。长石常沿解理面或边缘溶解,也会扩大粒间孔。除此之外,粒间填隙物及方解石、浊沸石、钠长石等胶结物也存在少量的溶蚀,形成填隙物溶孔及晶间孔(图3(b),(g)和(f))。研究区次生孔隙发育的砂岩主要是岩屑和长石发生溶蚀所致,岩屑颗粒中大量存在的火山岩屑物质是次生溶蚀孔隙发育的物质基础;在方解石胶结强烈的砂岩中,溶蚀作用较弱。在强烈溶蚀带中,碳酸盐岩胶结物和部分不稳定矿物长石或岩屑同时溶解,并有少量残余斑点残存。这表明溶蚀事件发生在大规模胶结作用 之后[14]。
4 成岩阶段划分
乌夏地区二叠系深度变化范围大,大多为0.70~
4.89 km。由于处于前陆盆地演化背景,构造活动强烈且伴随有多期间歇式火山活动爆发,致使二叠系储层所处的成岩阶段晚,变化范围大。根据新成岩阶段划分标准,综合镜质体反射率、伊蒙混层中混层蒙脱石含量、自生矿物等资料认为:研究区二叠系储层处于中成岩A亚期—晚成岩期(见图4)。各成岩阶段的特征主要表现如下。
4.1 中成岩期A亚期
进入中成岩A 阶段,蒙脱石向伊利石转变,伊利石/蒙皂石中蒙皂石的含量为35%~50%,镜质体反射率为0.5%~1.3%,形成晚期亮晶方解石和铁白云石胶结,石英次生加大属Ⅱ级,还可见其他自生矿物如钠长石、浊沸石、片沸石、方沸石等。
在有机酸的作用下,长石、岩屑等碎屑颗粒及粒间填隙物发生溶解,部分碳酸盐也开始发生溶解,孔隙类型除少部分保留的原生孔隙外,以次生孔隙为主。碎屑颗粒溶解释放出的Al,Fe,Mg,SiO2和Ca等元素加入到孔隙水中导致自生石英、石英次生加大,方沸石及高岭石、伊利石等新的自生矿物形成[15]。随着这些自生矿物的沉淀,孔隙水由酸性变为弱碱性,有利于CaCO3沉淀。由于在该阶段有机质所提供的CO2较充分,孔隙水中又富含Ca2+及Fe2+,与CO2结合形成大量(含)铁方解石充填在原生孔隙或次生溶孔中,又使孔隙度降低。
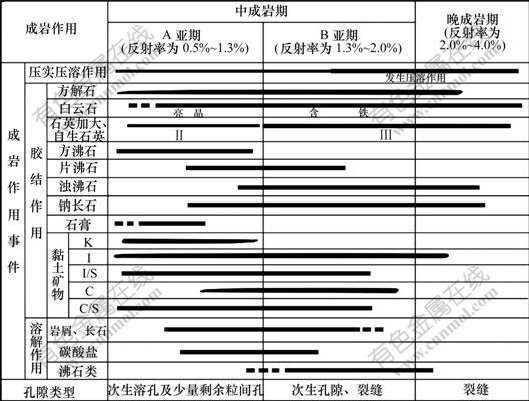
K为高岭石;I 为伊利石;S为蒙皂石;C为绿泥石;I/S为伊利石/蒙皂石的混层黏土矿物(简称I/S混层);
C/S为绿泥石/蒙皂石的混层黏土矿物(简称C/S混层)
图4 乌夏地区二叠系成岩阶段划分
Fig.4 Diagenesis evolution stages of Permian sandstones in Wu-Xia Area
4.2 中成岩期B亚期
中成岩阶段B亚期I/S中蒙皂石的含量为15%~35%,I/S为有序层,镜质体反射率为1.3%~2.0%,石英次生加大为Ⅲ级;岩石致密,有裂缝发育,晚期含铁碳酸盐类胶结物发育,其他自生矿物如钠长石、浊沸石、片沸石、方沸石发育;溶解作用发育,次生孔隙及裂缝发育。
由于脱羧基酸性水的进入,长石溶解作用继续发生,黏土矿物之间相互转化,主要是蒙脱石在有机酸的作用下向伊利石转变。在温压不断增加时,黏土中的分散有机质和分散碳酸盐质分解出来的CO2使砂层再次呈现酸性至弱酸性的成岩环境[9],造成砂岩的晚期溶蚀,使次生孔隙发育,同时,砂岩本身由于胶结作用影响,被自生石英和次生伊利石进一步充填,孔隙度在整体上略降低。随着深度的再次增加,强烈的压实作用造成云母和塑性岩屑变形,堵塞粒间孔,从而导致储层储集性变差,非均质性变强,但由于构造运动、压实作用和矿物转化的成岩收缩作用产生了一系列微裂缝,在一定程度上增强了储层的储集物性。
4.3 晚成岩期
主要发育在风城组,镜质体反射率为2.0%~4.0%,砂岩中可见晚期碳酸盐类矿物以及钠长石、榍石等自生矿物,砂岩和泥岩中代表性黏土矿物为伊利石和绿泥石,并有绢云母、黑云母,混层已基本消失,石英加大属Ⅳ级。岩石极致密,颗粒呈缝合接触及有缝合线出现,孔隙极少,而裂缝发育。
5 成岩作用与孔隙演化
研究表明:除沉积条件外,成岩作用也是影响储层物性的重要因素之一,其中压实、溶蚀和胶结是最重要的3个因素[16];孔隙演化与成岩作用密切相关。乌夏地区二叠系经过一系列成岩阶段,受各种成岩作用的影响,填隙物不断改变,孔隙也随之演化[7]。
5.1 原始孔隙度
恢复砂岩初始孔隙度是定量评价不同成岩作用类型对原生孔隙丧失和次生孔隙产生影响的基本前 提[17]。砂质沉积物的原始孔隙度与颗粒粒径和分选程度密切相关,Scherer等[18-19]根据Beard和Weyl提供的孔隙度与分选系数资料,建立了原始孔隙度与分选系数之间的函数关系式:
 (1)
(1)
其中: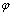 为原始孔隙度;
为原始孔隙度;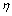 为分选系数。
为分选系数。
通过对普通薄片和铸体薄片的详细观察和统计,研究区分选系数多在2.0~3.4之间, 研究区砂岩分选较差~差。这主要是因为乌夏地区二叠系沉积时期为冲积扇、扇三角洲沉积, 经河流搬运的沉积物运移距离较近, 砂质载荷未得到充分分选改造。根据研究区22口井73块砂岩样品的粒度分析资料统计,二叠系砂岩的平均分选系数为2.612,按式(1)计算的平均原始孔隙度为31.9%。
5.2 孔隙损失量的计算
5.2.1 压实作用损失的孔隙度
在沉积物进入埋藏期后, 压实作用往往是原生孔隙损失的最主要原因, 这时,上覆沉积物静压力、孔隙水压力以及沉积物颗粒的物理性质如刚性、塑性和半塑性、填屑物成分和含量等因素综合制约原生孔隙的消亡方式。因此,恢复剩余粒间孔隙也是定量评价后期化学胶结作用、交代作用对孔隙破坏以及次生孔隙增长对整体孔隙度增加程度的前提[9]。
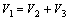 (2)
(2)
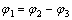 (3)
(3)
其中:V1为压实后粒间剩余孔隙体积;V2为粒间孔隙体积;V3为胶结物体积;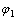 为压实作用损失的孔隙度;
为压实作用损失的孔隙度;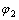 为原始孔隙度;
为原始孔隙度;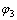 为压实后粒间剩余孔隙度。
为压实后粒间剩余孔隙度。
据式(2)和(3),研究区二叠系储层压实后粒间剩余孔隙为7.35%,由压实作用损失的孔隙度平均为23.65%,平均视压实率为74.10%,为较强~强压实,且视压实率与岩石孔隙度呈明显的线性负相关关系(图5(a))。
5.2.2 胶结作用损失的孔隙度
研究区发育的碳酸盐矿物、硅质、沸石、长石及黏土矿物的胶结使原生孔隙进一步减少。胶结作用损失的孔隙度指在各个成岩期内胶结作用消除的原始孔隙,可以通过岩石薄片中胶结物的含量来估计由胶结作用损失的孔隙度。二叠系储层胶结物平均含量为4.30%,平均视胶结率高达36.83%,胶结程度强。通过薄片鉴定与统计发现:由胶结作用损失的孔隙度为4.30%,研究区视胶结率与孔隙度呈较明显的负相关关系,随着胶结作用的增强,岩石孔隙度呈对数关系降低(图5(b))。
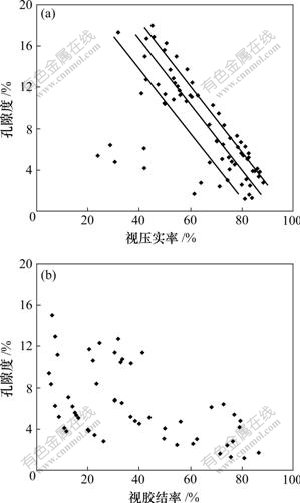
(a) 视压实率与孔隙度关系;(b) 视胶结率与孔隙度关系
图5 成岩作用与岩石孔隙的关系
Fig.5 Relationship between diagenesis and porosity
5.3 孔隙增生量计算
砂岩经受不同程度的溶解作用改造形成多种类型的次生孔隙,导致孔隙度增加,主要包括生成的粒间溶孔、粒内溶孔、填隙物溶孔、晶间孔及因溶蚀作用而使原有孔隙加大所形成的孔隙。强烈的机械压实导致岩屑、石英等刚性颗粒破裂产生的压裂缝和成岩收缩产生的界面缝,使孔隙度增加,也对提高砂岩的储集性能起积极作用。孔隙增生量可以认为是铸体薄片中次生孔隙和裂缝的面孔率(即铸体薄片中次生孔隙和裂隙的面积与总孔隙面积之比),经统计,本研究区孔隙增生量平均为4.90%。其中:长石、岩屑颗粒内部的溶解作用对孔隙增量的贡献最大,达44.50%,压裂缝和界面缝贡献分别为15.40%和12.30%,粒间填隙物被溶解形成的孔隙对孔隙增生量的贡献为13.69%。
5.4 孔隙演化模式
根据上述各成岩阶段的成岩作用特征及其对孔隙度的影响分析,可总结出乌夏地区二叠系储层成岩作用与孔隙演化的模式,见图6。
乌夏地区二叠系储层处于中成岩A亚期—晚成岩期,进入中成岩A 阶段,晚期含铁碳酸盐类胶结物、钠长石及沸石类胶结物发育,在有机酸的作用下,长石、岩屑等碎屑颗粒及粒间填隙物发生溶解,部分碳酸盐也开始发生溶解,孔隙类型除少部分保留的原生孔隙外,以次生孔隙为主;在中成岩B期,除晚期含铁碳酸盐类胶结物外,钠长石、浊沸石、片沸石、方沸石等自生矿物胶结物溶解作用发育,储集空间类型主要为次生孔隙及裂缝。在晚成岩期,岩石极致 密,颗粒呈缝合接触及有缝合线出现,孔隙极少而裂缝发育。
以原始孔隙度31.90%计,经强烈的机械压实作用和化学压溶作用后,孔隙度为7.35%,再经方解石、硅质、晚期含铁碳酸盐胶结物及钠长石、浊沸石、片沸石、方沸石等自生矿物充填后为3.35%。在有机酸的溶解作用下产生次生孔隙,强烈的压实作用形成的压裂缝及成岩收缩形成的界面缝使得孔隙回升到7.95%。
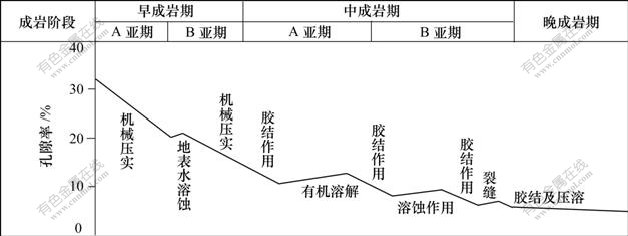
图6 乌夏地区二叠系储层孔隙演化模式
Fig.6 Pore evolution pattern of Permian sandstones in Wu-Xia Area
6 结论
(1) 冲积扇相、扇三角洲相砂砾岩体、滨浅湖及滩坝砂体构成二叠系主要的碎屑岩储集体。储集岩岩性以不等粒岩屑砂岩、砂砾岩和砾岩为主,岩石具有较低的结构成熟度和成分成熟度。
(2) 乌夏地区二叠系储集空间类型以次生孔隙为主,其中粒内溶孔最发育,含量占整体储集空间类型的41.77%,其次为微裂缝、填隙物内溶孔和界面缝;原生剩余粒间孔含量很少;原生粒间孔几乎不发育。
(3) 乌夏地区二叠系砂岩经历了压实、胶结、交代和溶蚀作用的改造,砂岩储层中含大量的碳酸盐胶结物,目前储层所处的成岩阶段变化范围大,成岩强度强,处于中成岩A亚期—晚成岩期。
(4) 储层的孔隙演化与成岩作用密切相关。早成岩期的压实作用以及方解石、硅质、沸石、含铁碳酸盐、黏土矿物等胶结作用,使二叠系砂岩孔隙度由原来的31.90%变为中成岩初期的3.35%,进入中成岩演化阶段,有机质成熟,有机酸溶解产生次生孔隙,裂缝形成,使总孔隙度回升到7.95%。
参考文献:
[1] 沈英, 王斌. 准噶尔西北缘车排子—小拐地区二叠系储层及含油性研究[J]. 岩相古地理, 1999, 19(2): 47-49.
SHEN Ying, WANG Bin. The Permian reservoir rocks and their hydrocarbon potential in the Chepaize—Xiaoguai region along the northwestern margin of the Junggar Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeography, 1999, 19(2): 47-49.
[2] 李嵘. 准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠系储层特征及分类[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2001, 22(1): 79.
LI Rong. Characteristics and classification of Permian reservoirs in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2001, 22(1): 79.
[3] 门相勇, 赵文智, 胡素云, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部二叠系、三叠系储层特征及烃类侵位对深部储层物性的影响[J]. 石油探勘与开发, 2006, 33(2): 208-211.
MEN Xiang-yong, ZHAO Wen-zhi, HU Su-yun, et al. Characteristics of deep-buried fragmental reservoirs in central Junggar Basin and the effect of hydrocarbon emplacement on reservoirs’ Diagenetic mineral evolution[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(2): 208-211.
[4] 邹才能, 侯连华, 匡立春, 等. 准噶尔盆地西缘二叠-三叠系扇控成岩储集相成因机理[J]. 地质科学, 2007, 42(3): 587-601.
ZOU Cai-neng, HOU Lian-hua, KUANG Li-chun, et al. Genetic mechanism of diagenesis-reservoir facies of the fan-controlled Permo-Triassic in the western marginal area, Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2007, 42(3): 587-601.
[5] 杨晓萍, 赵文智, 邹才能, 等. 低渗透储层成因机理及优质储层形成与分布[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(4): 57-60.
YANG Xiao-ping, ZHAO Wen-zhi, ZOU Cai-neng, et al. Origin of low permeability reservoir and distribution of favorable reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(4): 57-60.
[6] 应凤祥, 罗平, 何东博, 等. 中国含油气盆地碎屑岩储层成岩作用与成岩数值模拟[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004: 142-231.
YING Feng-xiang, LUO Ping, HE Dong-bo, et al. Diagenesis and diagenetic simulation of clastic reservoirs in China petroliferous basins[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004: 142-231.
[7] Sullivan K B, McBride E F. Diagenesis of sandstones at shale contacts and diagenetic heterogeneity, Frio Formation, Texas[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1991, 75(1): 121-138.
[8] 王琪, 禚喜准, 陈国俊, 等. 鄂尔多斯西部长6砂岩成岩演化与优质储层[J]. 石油学报, 2005, 26(5): 17-23.
WANG Qi, ZHUO Xi-zhun, CHEN Guo-jun, et al. Diagenetic evolution and high-quality reservoir in Chang 6 sandstone in the western Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2005, 26(5): 17-23.
[9] 胡宗全, 朱筱敏. 准噶尔盆地西北缘侏罗系储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 26(3): 17-20.
HU Zong-quan, ZHU Xiao-min. Diageneses and pore evolution of Jurassic reservoir in northwestern edge of Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of University of Petroleum, 2006, 26(3): 17-20
[10] 况军, 唐勇, 朱国华, 等. 准噶尔盆地侏罗系储层的基本特征及其主控因素分析[J]. 石油探勘与开发, 2002, 29(1): 52-56.
KUANG Jun, TANG Yong, ZHU Guo-hua, et al. Basic characteristics and main controlling factors of Jurassic reservoirs in Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2002, 29(1): 52-56.
[11] 韩守华, 余和中, 斯春松, 等. 准噶尔盆地储层中方沸石的溶蚀作用[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(3): 51-52.
HAN Shou-hua, YU He-zhong, SI Chun-song, et al. Corrosion of analcite in reservoir of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(3): 51-52.
[12] 李壮福, 郭英海, 李熙哲, 等. 王府凹陷储层成岩作用及对储集性能的影响[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2001, 30(1): 94-98.
LI Zhuang-fu, GUO Ying-hai, LI Xi-zhe, et al. Diagenesis and its influence on property of reservoirs in Wangfu Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2001, 30(1): 94-98.
[13] 张金亮, 刘宝军, 毛凤鸣, 等. 苏北盆地高邮凹陷北斜坡阜宁组成岩作用及储层特征[J]. 石油学报, 2003, 24(2): 43-49.
ZHANG Jin-liang, LIU Bao-jun, MAO Feng-ming, et al. Clastic diagenesis and reservoir characteristics of Funing Formation in north slope of Gaoyou Depression in Subei Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2003, 24(2): 43-49.
[14] 朱剑兵, 陈丽华, 纪友亮, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘逆冲带上古生界孔隙发育影响因素[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(3): 37-41.
ZHU Jian-bing, CHEN Li-hua, JI You-liang, et al. Influence factors for development of the Upper Paleozoic pore in thrust belt of western Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(3): 37-41.
[15] 肖丽华, 孟元林, 牛嘉玉, 等. 歧口凹陷沙河街组成岩史分析和成岩阶段预测[J]. 地质科学, 2005, 40(3): 346-362.
XIAO Li-hua, MENG Yuan-lin, NIU Jia-yu, et al. Diagenetic history and diagenetic stages’prediction of Shahejie formation in the Qikou Sag[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2005, 40(3): 346-362.
[16] 艾华国, 朱宏权, 张克银, 等. 伦坡拉盆地下第三系储层成岩作用和储集性能的成岩控因[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(1): 100-105.
AI Hua-guo, ZHU Hong-quan, ZHANG Ke-yin, et al. The diagenetic controlling factors of reservior property and diageneses of reservoir of lower-tertiary in Lunpola Basin, Tibet[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(1): 100-105.
[17] 杨仁超, 樊爱萍, 韩作振, 等. 姬塬油田砂岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 37(4): 626-629.
YANG Ren-chao, FAN Ai-ping, HAN Zuo-zhen, et al. Succession of diagenesis and pore in sandstone reservoirs in Jiyuan Oilfield[J]. Journal of Northwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2007, 37(4): 626-629.
[18] Scherer M. Parameters influencing porosity in sandstones a model for sandstone porosity prediction[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1987, 71(5): 485-491.
[19] Beard D C, Weyl P K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1973, 57(2): 349-369.
收稿日期:2009-04-30;修回日期:2009-06-15
基金项目:中国石油科技攻关项目(B20060104)
通信作者:牛海青(1982-),女,山东聊城人,博士研究生,从事层序地层、沉积学及储层地质学的研究;电话:0546-8391321;E-mail: upc_nhq@163.com
(编辑 陈灿华)