文章编号: 1004-0609(2005)05-0751-06
纤维相强化Cu-12%Ag合金的组织和力学性能
张 雷, 孟 亮
(浙江大学 材料与化学工程学院, 杭州 310027)
摘 要: 通过冷变形拉拔结合中间热处理制备了纤维相增强的Cu-12%Ag(质量分数)合金, 研究了变形过程对组织形态和力学性能的影响。 随着变形程度的增加, 不连续分布的原始共晶体演变成细密的纤维束结构, 合金强度和硬度升高。 在一定变形程度范围内或当共晶纤维束间距约大于150nm时, 抗拉强度随共晶纤维束间距的变化类似于Hall-Petch关系, 强化效应与位错塞积机制有关; 当拉拔变形超过一定程度或共晶纤维束间距小于约150nm后, 合金强化速率降低并偏离Hall-Pecth关系, 强化效应可认为与界面障碍机制有关。
关键词: Cu-Ag合金; 纤维组织; 强度; 硬度; 应变率 中图分类号: TB331; TG146.3
文献标识码: A
Microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-12%Ag filamentary composite
ZHANG Lei, MENG Liang
(College of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering,
Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China)
Abstract: Cu-12%Ag filamentary composite was prepared by cold drawing and intermediate heat treatments. The evolution of filamentary microstructure and mechanical properties were investigated for the alloy at different draw ratio. With the increasing draw ratio, the as-cast eutectic colonies with a discontinuous distribution develop into fine fibrous bundles to result in the increase of the strength and hardness. As the draw ratio is in a certain strain range or the spacing of eutectic fibrous bundles greater than is 150nm, the ultimate tensile strength dependent on the spacing of eutectic fibrous bundles is similar to the Hall-Petch relationship. The mechanism of pile-up of dislocation can be suggested to be responsible for the strengthening benefit. As the draw ratio is over a certain degree or the spacing of eutectic fibrous bundles is less than 150nm, the strength increase becomes slow and deviates from the Hall-Petch relationship. The mechanism of athermal obstacles at the interfaces can be suggested to be responsible for the strengthening benefit.
Key words: Cu-Ag alloy; filamentary microstructure; strength; hardness; draw ratio
对确定Ag含量的Cu-Ag合金进行强烈冷拉拔变形可以获得纳米纤维相复合强化效果, 使得这种先进导体材料能够表现出高强度和高电导率的综合性能[1]。 由于其显著优于普通导体材料的高强高导特性可以被用于抵抗强洛仑兹力和避免产生高焦耳热[2-4], 因而目前纤维相复合强化Cu-Ag合金的一个重要应用领域是作为强磁场磁体线圈绕组材料。
Cu-Ag合金组织由富Cu的α基体和富Ag的β相组成。 根据合金Ag含量及形成条件的不同, β往往以次生相或共晶体相形式存在。 经较大冷拉拔应变后, 两相组织可演变成纳米尺寸的纤维, 应变强化程度明显超过用复合材料各相强度叠加原则预测的水平[5-14]。 文献[8]研究了原始共晶体组织连续分布的高Ag含量Cu-25%Ag(质量分数, 下同)合金的应变强化规律, 认为合金强度取决于组织中各相比例和尺寸在应变过程中的变化, 而合金原始组织和应变程度决定了各相最终尺寸, 同时在冷变形及中间热处理过程中Cu基体内的次生相析出行为也对强化效果有一定影响。 文献[9]对高Ag含量的Cu-24%Ag合金的研究发现, 较大的拉拔变形使纤维组织界面的比表面积显著增大, 界面间距接近位错亚结构尺寸时导致位错亚结构无法稳定存在而易被界面吸收, 反而使得合金中的位错密度减小, 强化机制可能由加工硬化转变为无热障碍(athermal obstacle)。 文献[10-12]研究了共晶体数量较少而原始基体连续分布的低Ag含量Cu-6%Ag和Cu-10%Ag合金, 表明应变程度对合金强度与电导率的影响规律与高Ag含量合金有一定区别, 即在相同的应变条件下, 低Ag含量合金强度水平较低而导电性能较高。 在此基础上, 本文作者研究了具有一定数量原始共晶体组织但呈不连续分布状态的纤维相复合强化的中等Ag含量的Cu-12%Ag合金冷变形过程中组织和性能的变化规律, 讨论了不同变形阶段的强化机理。
1 实验
用给定配比的电解铜、 高纯银在真空感应炉中熔炼成分为Cu-12%Ag的合金, 氩气保护下在铜模中浇注成直径为23.0mm的棒状铸锭, 分别于700及720℃均匀化退火各2h。 对铸锭表面进行车削加工后在室温下经多道次拉拔, 拉拔的变形程度用η=ln(A0/A)表示(A0和A分别表示拉伸前后合金线材的横截面积), 合金最终变形η=9.3, 截面收缩率达到99.99%。 在拉拔过程中, 当η=1.3, 2.0及2.8时, 分别进行400, 380及360℃退火1h的中间热处理。
在CMT5205型电子万能试验机上测定试样的抗拉强度。 用HITACHI S-570扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和JEM-2010透射电子显微镜(TEM)观察试样显微组织。 将合金线材机械减薄至70μm后再进行离子减薄制备TEM试样。
2 实验结果
2.1 显微组织
与低Ag含量合金仅包含次生α相而不存在共晶体以及高Ag含量合金中存在连续网状共晶体的原始组织不同, 试验合金铸态组织的α基体上分布着有一定连续性的岛状共晶组织, 其中应有一部分是不平衡共晶(图1(a))。 由于共晶区域较小, 难以分辨出α+β两相层叠结构, 基本表现为离异共晶形态。 在均匀化退火时, 不平衡共晶部分溶入基体, 使原共晶区域进一步分离成不连续的岛状形态, 间距约10~20μm(图1(b))。
Cu和Ag两相的协同变形可使一定应变量范围内的合金在横截面上始终保持加工前Cu相基体包围岛状共晶体的形态(图2(a)), 纵截面则显示出α基体及共晶体均沿拉伸方向变形, 共晶体由两相层叠结构演变成α+β纤维束(图2(b))。 在更大变形程度下, 共晶纤维束的束径和束间距均随变形程度增大而减小(图2(c)), 内部组织形态用SEM已难以清楚分辨(图2(d))。
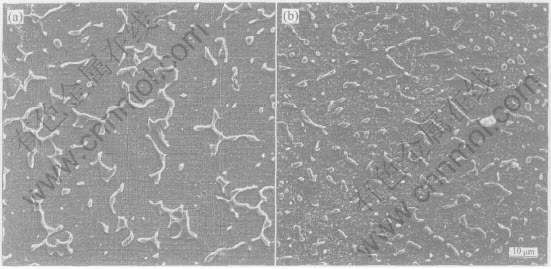
图1 铸态和均匀化退火后Cu-12%Ag合金的SEM形貌
Fig.1 SEM images of as-cast(a) and homogenized(b) Cu-12%Ag alloy
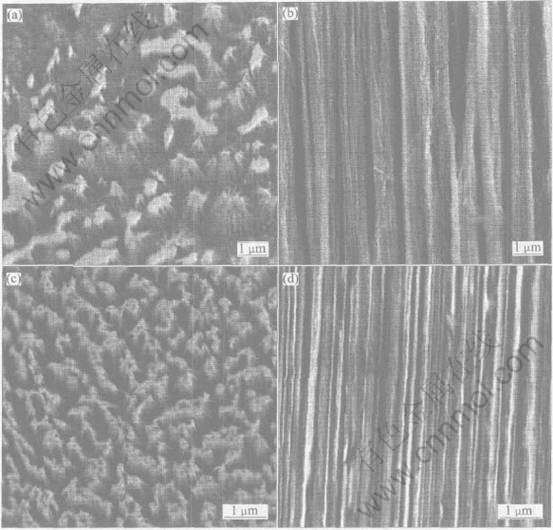
图2 Cu-12%Ag合金变形至η=4.1的横截面(a)和纵截面(b)及
η=7.1的横截面(c)和纵截面(d)的SEM组织
Fig.2 SEM images of Cu-12%Ag alloy drawn to η=4.1 on transverse section(a),η=4.1 on longitudinal section(b), η=7.1 on transverse section(c) and η=7.1 on longitudinal section(d)
η=4.1的合金横截面在TEM观察下, 容易分辨出由两相共晶体演变而来的纤维束结构。 α基体晶粒直径减小到500~600nm, 晶粒内部可以观察到位错胞壁和小角晶界, 上面存在一些单根纤维相, 直径在10~30nm之间(图3(b))。 这些纤维相应该是由均匀化退火和中间热处理时析出的次生Ag相在随后的拉拔过程中演变而成, 与共晶纤维束相比, 次生Ag相纤维数量相对较少, 因此在后面关于组织和性能之间关系的讨论中不考虑次生Ag相的作用。
当η=7.1时, 共晶纤维束的束径减小到60nm左右, 内部包含若干排列更紧密的纤维, 每根直径约为5~20nm(图4(a)), 出现了清晰平直的Moiré纹(图4(b)), 表明内部位错已经很少。 这说明在这种应变程度下, 纤维晶体的直径和间距已小于胞状位错亚结构稳定存在的临界尺寸, 使得位错亚结构失稳而被比表面积迅速增大的晶界和相界吸收。
2.2 力学性能
合金抗拉强度及显微硬度随变形程度的变化如图5所示。 抗拉强度和硬度随变形程度的关系前者为线性关系而后者为指数关系, 两者可分别拟合为
σ(Cu-Ag)=200+130η(1)
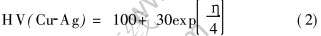
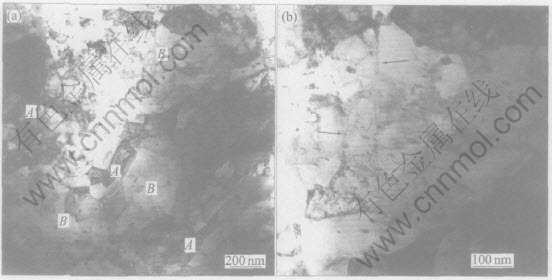
图3 变形程度η=4.1时Cu-12%Ag合金的横截面TEM组织中的
共晶区域和α基体(a)及α基体中的小角晶界(b)
Fig.3 TEM microstructures of Cu-12%Ag alloy drawn to η=4.1 on transverse section for eutectic regions marked by “A”, α matrix marked by “B”(a) and some Ag precipitates pointed by arrows at low angle grain boundaries inside α matrix(b)
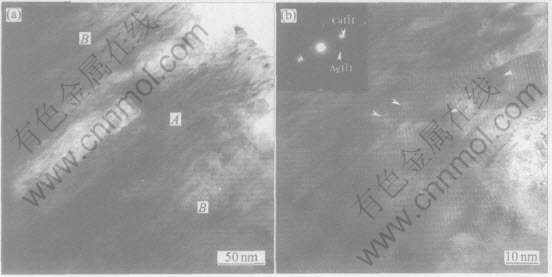
图4 变形程度η=7.1时Cu-12%Ag合金的纵截面TEM组织中的
共晶纤维束(a)和α基体及纤维相中的Moiré条纹(b)
Fig.4 TEM microstructure(a) of Cu-12%Ag alloy drawn to η=7.1 on longitudinal section for
fiber bundle of eutectic structure marked by “A” and α matrix marked by
“B” and Moiré fringes in fibrous phases(b)
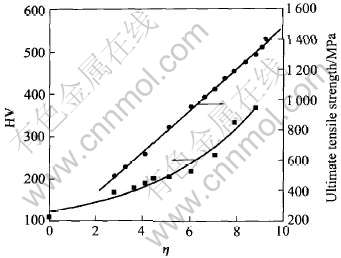
图5 Cu-12%Ag合金抗拉强度及显微硬度随变形程度的变化
Fig.5 Ultimate tensile strength and vickers hardness as function of
draw ratio of Cu-12%Ag alloy
3 讨论
3.1 共晶体间距在变形过程中的变化
在拉拔变形过程中, 共晶体平均间距λeut不断减小, 在η达到一定值后, 共晶体被拉长成纤维束, λeut即成为共晶纤维束的束间距(为讨论方便, 后面将λeut均称为共晶体间距)。 由于α和β均属于面心立方结构, 且具有相近的变形能力, 因此可以认为两相在变形过程中能够协调一致[13]。 假设共晶体间距的减小正比于试样宏观直径D的减小, 应有

式中 λeut0和D0分别为初始共晶体间距和试样原始直径。 根据变形程度的定义:
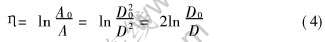
可得

图6给出了λeut随η变化的实际测量结果和用式(5)表达的结果, 两者符合较好。
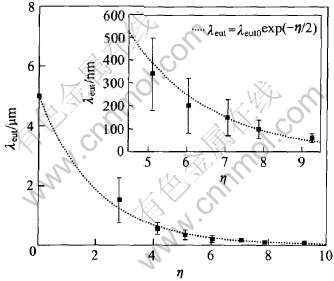
图6 Cu-12%Ag合金中共晶体间距随变形程度的变化
Fig.6 Spacing of eutectic structure as
function of draw ratio of Cu-12%Ag alloy
3.2 变形对力学性能的影响
与高Ag含量合金及低Ag含量合金不同, 中等Ag含量的Cu-12%Ag合金中共晶体呈不连续分布, 在演变成纤维束过程中, 将α基体分隔成更窄的条带(图2), 共晶纤维束与α基体的界面成为位错运动的主要障碍。 因此, 共晶体间距λeut的减小是合金强化的重要原因之一。 将合金抗拉强度与实测和由式(5)估算的λ-1/2eut值的对应关系用图7表示后可见, 当λ>150nm(即约η〈7)时, 抗拉强度与λeut之间近似为线性关系, 即可以表示为
σCu-Ag=σ0+kλ-1/2eut(6)
由此可见, 在一定变形程度范围内, 合金强度与共晶体间距之间的关系类似于Hall-Petch关系。 这种现象也曾在共晶成分(Cu-71.9%Ag)的合金中被发现[15]。 与Hall-Petch 关系不同的是, 式(6)中的λeut代表的是共晶体间距而非晶粒尺寸, 根据Hall-Petch关系表明的是晶粒细化时位错在晶界塞积而产生的强化规律[16]及图7结果可以推断, Cu-12%Ag合金在一定变形程度内的强化主要来自于共晶体和α基体的界面对位错运动的阻碍, 并且这种界面对强化的贡献与基体中α晶粒之间的晶界或亚晶界的贡献相比, 更占主要地位。
当η>7以后, 抗拉强度开始偏离线性关系, 结合显微组织观察结果分析其原因为: 合金组织在变形过程中逐渐纤维化, 当纤维直径减小到接近位错亚结构尺寸时, 亚结构便无法稳定存在而汇聚于纤维相界面, 或者在强烈应变条件下, 亚结构胞壁中的位错超过临界密度而失稳演变为大角晶界。 因此当变形程度超过一定值后, 纤维相内位错密度反而下降(图4(b)), 使合金强化规律偏离以位错在界面塞积强化为主要机制的Hall-Petch关系。
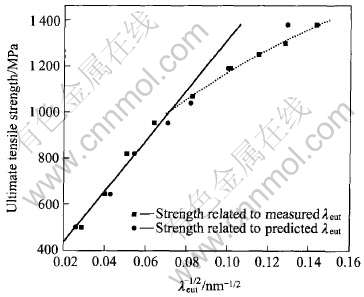
图7 合金抗拉强度与共晶体间距的关系
Fig.7 Relationship between spacing of eutectic structure and ultimate tensile
strength in Cu-12%Ag alloy
4 结论
1) Cu-12%Ag合金中不连续分布的铸态共晶体组织经强烈冷拉拔应变演变为共晶纤维束结构。 随变形程度增加, 共晶纤维束间距减小, 合金抗拉强度和硬度上升。
2) 应变过程中当共晶纤维束间距大于约150nm时, 抗拉强度与共晶纤维束间距之间的关系类似于Hall-Petch关系, 材料冷变形强化效应可认为主要由位错塞积机制引起; 当共晶体纤维束间距小于约150nm时, 抗拉强度随变形程度的升高速率减弱并偏离Hall-Petch关系, 材料冷变形强化效应可认为主要由界面障碍机制引起。
REFERENCES
[1]张雷, 颜芳, 孟亮. 高强高导Cu-Ag合金的研究现状与展望[J]. 材料导报, 2003, 17(5): 15-17.
ZHANG Lei, YAN Fang, MENG Liang. Prospect and current status of research on Cu-Ag alloys with high strength and conductivity[J]. Materials Review, 2003, 17(5): 15-17.
[2]Grünberger W, Heilmaier M, Schultz L. Development of high-strength and high-conductivity conductor materials for pulsed high-field magnets at dresden[J]. Physica B, 2001, 294-295: 643-647.
[3]Maeda H, Inoue K, Kiyoshi T, et al. Present status and future plan of the tsukuba magnet laboratories[J]. Physica B, 1996, 216: 141-145.
[4]Wood J T, Embury J D, Ashby M. An approach to materials processing and selection for high-field magnet design[J]. Acta Mater, 1997, 45: 1099-1104.
[5]Sakai Y, Inoue K, Asano T, et al. Development of high-strength, high-conductivity Cu-Ag alloys for high-field pulsed magnet use[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 1991, 59(23): 2965-2967.
[6]Sakai Y, Schneider-Muntau H J. Ultra-high strength high conductivity Cu-Ag alloy wires[J]. Acta Mater, 1997, 45: 1017-1023.
[7]Benghalem A, Morris D G. Microstructure and strength of wire-drawn Cu-Ag filamentary composites[J]. Acta Mater, 1997, 45: 397-406.
[8]Han K, Vasquez A A, Xin Y, et al. Microstructure and tensile properties of nanostructured Cu-25wt%Ag[J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51: 767-780.
[9]Hong S I, Hill M A. Mechanical stability and electrical conductivity of Cu-Ag filamentary microcomposites[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 1999, A264: 151-158.
[10]Zhang L, Meng L. Microstructure and properties of Cu-Ag, Cu-Ag-Cr and Cu-Ag-Cr-RE alloys[J]. Mater Sci Tech-Lond, 2003, 19: 75-79.
[11]张雷, 孟亮. 合金元素对Cu-Ag合金组织、 力学性能和电学性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(6): 1218-1223.
ZHANG Lei, MENG Liang. Effects of the alloying elements on microstructure, mechanical and electrical properties of the Cu-Ag based alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(6): 1218-1223.
[12]张晓辉, 宁远涛, 李永年, 等. 大变形Cu-10Ag原位纤维复合材料的结构和性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(1):115-119.
ZHANG Xiao-hui, NING Yuan-tao, LI yong-nian, et al. Microstructure and properties of heavily deformed Cu-10Ag in-situ filamentary composite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2002, 12(1):115-119.
[13]Zhang L, Meng L. Microstructure, mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of Cu-12wt.% Ag wires annealed at different temperature[J]. Materials Letters, 2004, 58: 3888-3892.
[14]张雷, 孟亮. 应变程度对Cu-12%Ag合金纤维相形成及导电性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2005, 41(3): 255-259.
ZHANG Lei, MENG Liang. Effect of drawing strain on formation of filamentary structure and conductivity for Cu-12wt.%Ag alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2005, 41(3): 255-259.
[15]Frommeyer G, Wassermann G. Microstructure and anomalous mechanical properties of in situ-produced silver-copper composite wires[J]. Acta Metall, 1975, 23: 1353-1360.
[16]Kumar K S, van Swygenhoven H, Suresh S. Mechanical behavior of nanocrystalline metals and alloys[J]. Acta Mater, 2003, 51: 5743-5774.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金资助项目(50371076); 高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助项目(20020335014)
收稿日期: 2004-06-14; 修订日期: 2005-01-27
作者简介: 张 雷 (1978-) , 男, 博士研究生.
通讯作者: 孟 亮, 教授; 电话: 0571-87951523, 传真: 0571-87951171, E-mail: mengliang@zju.edu.cn
(编辑龙怀中)