纯电动汽车电液复合再生制动控制
刘志强1, 2,过学迅1
(1. 武汉理工大学 汽车工程学院,湖北 武汉,430070;
2. 长沙理工大学 汽车与机械工程学院,湖南 长沙,410114)
摘要:针对纯电动汽车电液复合再生制动过程机电制动力的动态分配问题,通过对制动动力学和ECE R13-H制动法规的分析,从理论上确定纯电动汽车电液复合再生制动的安全运行范围。在安全制动范围内,开发了以最大限度回收能量为目标,达到需求制动强度而前、后轴又不抱死的再生制动控制流程,生成机电制动力分配矩阵。以制动强度分别为0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5和0.6,初始车速为16.67 m/s,结合ECE-EUDC道路循环,构建新的仿真循环,将车辆参数、制动力分配矩阵、道路循环嵌入ADVISOR2002软件。研究结果表明:仿真运行1个道路循环后,电池荷电状态SOC(State of charge)相对原策略有较明显的提高,提高幅度达4.5%,较好地回收了制动能量,更重要的是保证了制动安全,表明开发的控制策略是有效的。
关键词:电动汽车;再生制动;安全制动;控制策略;道路循环
中图分类号:U461.3 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2011)09-2687-05
Electronic-hydraulic-compound regenerative braking control for electric vehicles
LIU Zhi-qiang1, 2, GUO Xue-xun1
(1. School of Automobile Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China;
2. School of Automobile and Mechanical Engineering, Changsha University of Science and Technology,
Changsha 410114, China)
Abstract: The braking force distribution of the compound brake system on small electric vehicles was studied. The safe range of braking force distribution was established by analyzing braking dynamics and the ECE R13-H rule. In the safe braking range, a strategy with optimal energy recovery was developed based on the concept, i.e. braking forces should be distributed on front and rear axles in such a way that the regenerated energy was maximized, as long as the commanded deceleration was reached and neither front nor rear axle was locked. The distribution matrixes of the regenerative braking forces, front and rear hydraulic braking forces were created. A driving cycle was established based on some different braking intensities and ECE-EUDC driving cycle. Simulation on this control strategy was performed in ADVISOR 2002 by establishing an embedded simulation model. The simulation results show that the state-of-charge is progressed by 4.5%, and the proposed control strategy on regenerative braking is effective.
Key words: electric vehicle; regenerative braking; safe braking; control strategy; driving cycle
纯电动汽车由于其可以通过电机回收部分制动能量而具有明显的节能减排优势。然而,再生制动系统必须与液压制动系统共同作用,才能满足汽车较大制动强度下对制动系统的要求。若液压制动系统产生的前、后轮制动器制动力比例关系不可调,则在相同的制动踏板行程下,由于再生制动的影响,会使制动强度增大,容易突破法规限制,影响制动的平稳性和驾驶员对制动踏板的感觉。若液压制动系统产生的前、后轮制动器制动力比例关系可调,则可增加制动能量回收比例,但系统结构更加复杂,对软硬件的要求更高[1-3]。在此,本文作者针对前、后轮制动器液压制动力比例关系可调的电液复合再生制动系统[4-6],提出一种控制策略,在满足制动法规和制动稳定性的基础上,尽量将制动能量回收。把电机再生制动产生的地面制动力与制动强度和车速的关系制成二维查询表,建立新的再生制动控制模块,构建新的道路循环,把它们嵌入由美国可再生能源实验室NREL(National renewable energy laboratory)在Matlab和Simulink软件环境下开发的高级车辆仿真软件ADVISOR2002[7-9](Advanced vehicle simulator,高级车辆仿真器),并进行仿真分析。
1 纯电动汽车电液复合再生制动数学模型
1.1 安全制动范围
1.1.1 理想的前、后轮地面制动力分配曲线
同步附着时,前轮地面制动力Fxb1为:
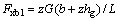 (1)
(1)
式中:z为制动强度;G为汽车重力,N;b为汽车质心至后轴中心线的距离,m;hg为汽车质心高度,m;L为前、后轴的距离,m。
理想的前、后轮地面制动力分配的关系曲线(本文按传统仍称之为I曲线[10-11]),用公式表示为:
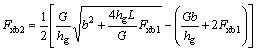 (2)
(2)
式中:Fxb2为后轮地面制动力,N。
1.1.2 后轮没有抱死、前轮抱死时前、后轮地面制动力关系曲线
后轮没有抱死、前轮抱死时,前、后轮地面制动力关系曲线称之为f线组,用公式表示为:
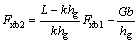 (3)
(3)
式中:k为轮胎与路面间的附着系数。
1.1.3 前轮抱死时后轮必须具有的最小制动力
制动法规明确要求:在车辆所有载荷状态下,当制动强度z处于0.15到0.80之间时,后轴附着系数利用曲线不应位于前轴上方;当附着系数k在0.2~0.8之间时,制动强度z≥0.1+0.85(k-0.2)。当前轮抱死时,为保持车辆稳定和制动效率,后轮必须具有一定的制动力。后轮的最小地面制动力与前轮地面制动力的关系曲线称为M曲线,用公式表示为:
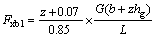 (4)
(4)
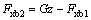 (5)
(5)
安全制动范围如图1中曲边四边形ABCDA所示。
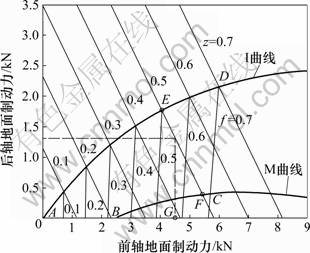
图1 汽车制动的安全范围及控制策略示意图
Fig.1 Sketch of safe range of braking and its control strategy
1.2 可充电功率
若再生制动电流充入动力电池,则电机制动功率不能超过电池可充电功率,以起到保护电池的作用。电池的内阻是电池荷电状态SOC(State of charge)和温度t的函数,当温度降低时,电池内阻显著增大,SOC增大,电池内阻也显著增大。在同一温度下,当SOC增大时,可充电功率明显减小,SOC又不能太小,否则电池放电功率减小[12]。考虑再生制动功率先用超级电容回收,则由于超级电容的内阻随充放电电流的增大而减小[13],使得其可以大电流充、放电,给制动能量回收带来了很大的方便。可以根据车速决定超级电容的SOC,吸收再生制动功率后,由车辆运行状态决定吸收的电能用于加速或向电池充电,使得电池的SOC保持较平稳状态[14]。
为集中考虑制动控制策略与制动力的分配,本文不研究超级电容的容量问题,假设其容量足够,不对可充电功率构成约束。
1.3 电机再生制动
驱动电机经过调速,具有较适合汽车要求的输出特性,即基速以下以恒转矩输出,基速以上以恒功率输出。电机再生制动时工作在发电机状态,其转矩输出特性与电动状态下的输出特性基本相同,用公式表示为:
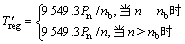 (6)
(6)
式中: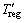 为电机再生转矩,N?m;Pn为电机额定功率,kW;nb为电机基速,r/min;n为电机转速,r/min。
为电机再生转矩,N?m;Pn为电机额定功率,kW;nb为电机基速,r/min;n为电机转速,r/min。
当汽车制动时,随着车速降低,电机转速降低,电枢反电动势降低,当电机转速降到500 r/min,再生制动力降为0 N,再生制动失效,进行以下修正:
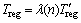 (7)
(7)
式中: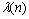 为与电机转速有关的修正因子。由此得到再生制动时电机能够提供的驱动轮处最大再生制动力为:
为与电机转速有关的修正因子。由此得到再生制动时电机能够提供的驱动轮处最大再生制动力为:
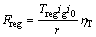 (8)
(8)
式中:ig为变速器传动比;i0为主减速器传动比;r为车轮半径,m;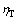 为传动系效率。
为传动系效率。
2 电液复合再生制动控制策略
在安全制动范围内,为最大限度地回收制动能量,建立如下控制策略流程。
第1步:由制动意图识别模块判断制动工况是否低、中强度制动,若为紧急制动,则转入防抱制动控制。
第2步:由式(1)和(2)计算制动强度线与I曲线交点(如图1中的E点),其横坐标值和纵坐标值即为需求的前、后轴地面制动力。
第3步:由式(3)~(5)计算制动强度线与f线组或M曲线的交点(如图1中的F点)。
第4步:由式(6)~(8)计算电机能够提供的驱动轮处最大再生制动力Freg。
第5步:若最大再生制动力Freg在E和F 2点的横坐标范围内,如图1中的G点,则前轴制动力全部由电机再生制动提供,由G点作Fxb2轴的平行线与EF线相交,交点的纵坐标值即为后轴制动力控制点;若最大再生制动力小于E点的横坐标,则电机再生制动力控制在Freg,前轴液压制动补充一部分制动力以满足E点横坐标,E点的纵坐标为后轴制动力控制点;若制动需求较小,电机再生制动力可满足需求制动力,则液压制动不起作用。
第6步:防抱制动控制,不回收制动能量。
3 仿真分析
构建1辆电机前置、前驱动,有液压制动系的纯电动汽车,其整车参数如下:满载质量1 187 kg,质心高度0.5 m,轴距2.6 m,质心至前轴距离1.04 m,风阻系数0.335,迎风面积2.0 m2,滚动阻力系数0.009,车轮半径0.282 m;传动系参数为:主减速比3.24,变速器各档传动比分别为3.78,2.12,1.35,0.97和0.76;电机参数为:额定功率30 kW,额定转矩89.6 N?m,最高转速4 000 r/min,额定转速3 200 r/min。
ADVISOR2002中制动力分配方法的基本思路是:由车速确定总制动力,再把总制动力分配为前、后轮需求制动力。前轮的再生制动力比例随车速增大而增大,以一维查询表的形式嵌入模型中,未充分考虑制动强度和电机制动能力对能量回收的影响,且能否满足制动约束也是不确定的。
根据本文再生制动机电制动力分配方法,纯电动车电机制动产生的地面制动力与制动强度和车速的关系如图2所示,对应的电制动力占总制动力的比例和前轴液压制动力占总制动力的比例如图3和图4所示。把图3和图4制成二维查询表,嵌入ADVISOR2002,建立新的再生制动控制模块。以16.67 m/s为初始车速,制动强度分别为0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5和0.6构建道路循环,结合ECE-EUDC道路循环的一部分,组成新的仿真循环,如图5所示。该循环运行时间为660 s,运行里程为4.97 km,仿真结果如图6所示。由图6可知:根据ADVISOR2002的控制策略,车辆运行1个道路循环后,电池荷电状态SOC从1.00变到了0.84;而本文开发的再生制动控制策略,充分考虑了制动强度和电机制动能力对能量回收的影响,车辆运行1个道路循环后,SOC从1.00变到0.88,不但电池荷电状态SOC提高,更重要的是保证了制动安全。
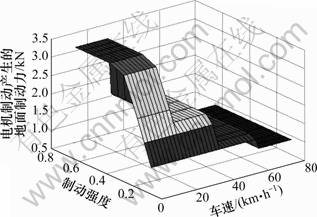
图2 电机制动产生的地面制动力与制动强度和车速的关系
Fig.2 Relationship among force on front wheels from motor and braking intensity and vehicle speed
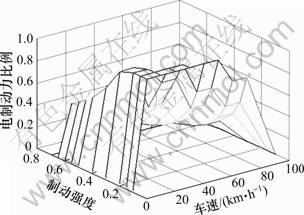
图3 电制动力比例与制动强度和车速的关系
Fig.3 Relationship among fraction of electric braking force and braking intensity and vehicle speed
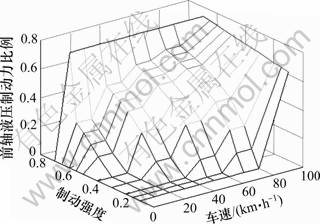
图4 前轴液压制动力比例与制动强度和车速的关系
Fig.4 Relationship of fraction of hydraulic braking force on front axle and braking intensity and vehicle speed
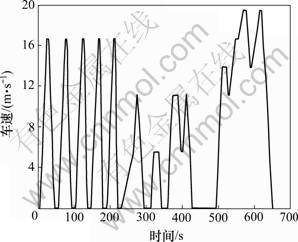
图5 用车速-时间表示的新的道路循环
Fig.5 Vehicle speed versus time in a new driving schedule
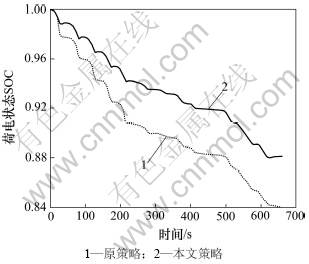
图6 电池荷电状态SOC随时间的变化历程
Fig.6 SOC-time profiles for new driving schedule
4 结论
(1) 通过对制动动力学和ECE R13-H制动法规的研究,从理论上确定了纯电动汽车电液复合再生制动的安全运行范围。
(2) 在安全制动范围内,开发了以最大限度回收制动能量为目标的再生制动控制策略。
(3) 构建了1种新的道路循环,把开发的再生制动控制策略嵌入ADVISOR2002软件进行仿真,结果表明:电动汽车的电池荷电状态得到提高,提高幅度达4.5%,控制策略是有效的。
参考文献:
[1] GAO Yi-min, CHEN Li-ping, Ehsani M. Investigation of the effectiveness of regenerative braking for EV and HEV[J]. SAE Paper, 1999-01-2910.
[2] GAO Yi-min, Ehsani M. Electronic braking system of EV and HEV … integration of regenerative braking, automatic braking forces control and ABS[J]. SAE Paper, 2001-01-2478.
[3] Walker A M, Lampérth M U, Wilkins S. On friction braking demand with regenerative braking[J]. SAE Paper, 2002-01-2581.
[4] Ahn J K, Jung K H, Kim D H, et al. Analysis of a regenerative braking system for hybrid electric vehicles using an electro- mechanical brake[J]. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2009, 10(2): 229-234.
[5] Ye M, Bai Z, Cao B. Robust control for regenerative braking of battery electric vehicle[J]. IET Control Theory Appl, 2008, 2(12): 1105-1114.
[6] PENG Dong, YIN Cheng-liang, ZHANG Jian-wu. An investigation into regenerative braking control strategy for hybrid electric vehicle[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University: Science, 2005, E-10(4): 407-412.
[7] 曾小华, 王庆年, 李胜, 等. 正向仿真模型与反向软件ADVISOR的集成开发[J]. 汽车工程, 2007, 29(10): 851-854.
ZENG Xiao-hua, WANG Qing-nian, LI Sheng, et al. Development of forward simulation model in ADVISOR[J]. Automobile Engineering, 2007, 29(10): 851-854.
[8] 高辉松, 张莹, 朱思洪. 基于ADVISOR的电动拖拉机仿真系统开发与应用[J]. 计算机仿真, 2009, 26(20): 282-285.
GAO Hui-song, HANG Ying, ZHU Si-hong. Development and application of electrictractor simulation system based on ADVISOR[J]. Computer Simulation, 2009, 26(20): 282-285.
[9] 赵国柱. 电动汽车再生制动稳定性研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学能源与动力学院, 2006: 58-59.
ZHAO Guo-zhu. Research on braking stability of regenerative braking system in EV and HEV[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics. College of Energy and Power Engineering, 2006: 58-59.
[10] 余志生. 汽车理论[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2002: 87-95.
YU Zhi-sheng. Automobile theory[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2002: 87-95.
[11] 石庆升. 纯电动汽车能量管理关键技术问题的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学控制科学与工程学院, 2009: 87-88.
SHI Qing-sheng. Key technologies in pure electric vehicles energy management problems[D]. Jinan: Shandong University. School of Control Science and Engineering, 2009: 87-88.
[12] 羌嘉曦, 敖国强, 何建辉, 等. 电动汽车动力电池特性仿真系统[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2009, 43(8): 1196-1200.
QIANG Jia-xi, AO Guo-qiang, HE Jian-hui, et al. Research on the battery simulation system of electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2009, 43(8): 1196-1200.
[13] 邓隆阳, 黄海燕, 卢兰光, 等. 超级电容性能试验与建模研究[J]. 车用发动机, 2010(1): 28-32.
DENG Long-yang, HUANG Hai-yan, LU Lan-guang, et al. The performance experiment and modeling of ultracapacitor[J]. Vehicle Engine, 2010(1): 28-32.
[14] 李贵远, 陈勇. 动力电池与超级电容混合驱动系统设计与仿真[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2007, 19(1): 101-105.
LI Gui-yuan, CHEN Yong. Design and simulation of hybrid-drive system with battery pack and capacitors[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2007, 19(1): 101-105.
(编辑 陈灿华)
收稿日期:2011-04-18;修回日期:2011-06-25
基金项目:湖南省教育厅重点项目(10A005)
通信作者:刘志强(1970-),男,湖南湘乡人,博士研究生,副教授,从事内燃机节能及电动汽车研究;电话:0731-85258630;E-mail: lzq0228@126.com