煤粉锅炉氮氧化物排放影响因素的数值模拟
夏小霞1,王志奇1, 2,徐顺生1
(1. 湘潭大学 机械工程学院,湖南 湘潭,411105;
2. 中南大学 能源科学与工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:针对1台35 t/h煤粉锅炉,应用数值模拟的方法,研究配风方式、煤粉粒径以及空气过量系数对NOx排放的影响。模拟结果表明:在计算的几种工况中,束腰型送风方式生成的NOx浓度最低,倒塔型的次之,而均匀型的最大;相比均匀型配风方式,束腰型配风方式的NOx排放浓度可降低15.6%;当三次风比例从20%增大到25%时,NOx排放浓度可降低20.5%;锅炉NOx排放随着煤粉粒径的减小而明显降低;与设计工况相比,当煤粉粒径由90 μm降低至50 μm时,NOx的排放浓度可降低14.3%;随着过量空气系数的减小,锅炉出口处的NOx浓度减小,合适的过量空气系数为1.1,此时NOx排放浓度可降低5.8%。
关键词:煤粉锅炉;数值模拟;NOx排放;配风方式
中图分类号:TK227 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2010)05-2046-07
Numerical simulation on influence factors of NOx emissions for
pulverized coal boiler
XIA Xiao-xia1, WANG Zhi-qi1, 2, XU Shun-sheng1
(1. Institute of Mechanical Engineering, Xiangtan University, Xiangtan 411105, China;
2. School of Energy Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The effects of air distribution, particle size and excess air rate on NOx emissions for a 35 t/h pulverized coal boiler were researched by numerical simulation. The results show that the concentration of NOx produced by girdled air distribution is the lowest, among the several combustion conditions, followed by the reverse-tower type, and the type of equal air distribution produces the highest concentration. There is a 15.6% decrease in NOx emissions of girdled air distribution compared with the equal type. When the rate of third air increases from 20% to 25%, concentration of NOx decreases by 20.5% compared with equal type. The concentration of NOx decreases obviously with the decrement of pulverized coal size. Compared with the original condition, it can decrease by 14.3% when the average diameter of pulverized coal is 50 μm. The concentration of NOx decreases with the decrement of excess air rate. The proper excess air ratio is 1.1 for the boiler. In this condition, the concentration of NOx can decrease by 5.8% compared with the original condition.
Key words: pulverized coal boiler; numerical simulation; NOx emissions; air distribution type
目前,氮氧化物的排放问题越来越引起社会的重视。煤粉燃烧是氮氧化物排放的主要来源,而我国的产煤主要用于火力发电。据统计,2005年我国发电用煤约占总产煤量的53.6%[1]。火电厂中,除大型煤粉锅炉外,我国还运行着大量的中小型燃煤锅炉。2005年,我国中小型煤粉锅炉的燃煤量约占锅炉总消耗量的25%[2]。这些锅炉一般不考虑排烟脱硝,从而造成NOx排放浓度高、控制困难。因此,降低中小型煤粉锅炉的NOx排放对缓解我国日益严峻的环境问题具有重要意义。为降低煤粉锅炉NOx排放量,近年来,国内外学者从分级燃烧、煤粉再燃及三次风优化等方面对炉内NOx的生成情况进行了模拟研究,并提出一些改进措施[3-7]。然而,这些研究工作主要针对大型燃煤锅炉,难以在中小型燃煤锅炉中推广应用。目前,关于降低中小型煤粉锅炉NOx排放的报道较少。本文作者以一台35 t/h的煤粉锅炉为研究对象,运用CFD方法针重点研究锅炉配风方式、过量空气系数及煤粉粒径对NOx排放的影响,为降低中小型燃煤锅炉的NOx排放提供理论依据。
1 物理模型
1.1 研究对象及操作参数
以1台35 t/h的燃煤锅炉为研究对象。炉膛横截面面积为4 200 mm×4 200 mm,燃烧设备为四角布置切向燃烧,在炉膛内形成直径为400 mm的假想切圆。燃烧器由2层一次风喷口、3层二次风喷口、1层三次风喷口组成,燃烧器的布置如图1所示。锅炉燃用的
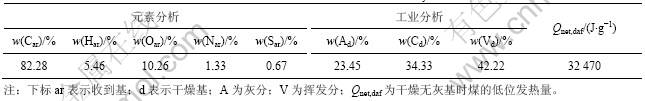
是挥发分较高的烟煤,其平均粒径为90 μm,煤的工业分析及元素分析结果如表1所示。
1.2 网格划分
网格是数值计算的基础,网格质量直接影响数值解的计算精度。在对锅炉进行网格划分时,需要重视计算时产生的伪扩散问题。二维流动时,伪扩散系数的表示式为[8]:
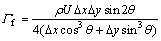 (1)
(1)
式中:?x和?y分别表征网格x方向和y方向的长度;ρ为流体密度;U为合速度;θ为合速度与网格线方向之间的夹角。从式(1)可知:当流动方向与网格线方向夹角为45°时,伪扩散最大;当流动和网格线成1条直线时,伪扩散最小。
当采用Paving方法对燃烧器部分的炉膛横截面划分网格时,能降低伪扩散对计算准确性的影响[9]。在生成炉膛横截面网格后,再将网格沿着高度方向延伸,生成体网格。锅炉横断面及整体网格划分如图2所示,网格数约为25万。从图2可以看出:Paving方法生成的辐射状网格线与四角射流的气流轨迹基本平行,减小了网格线与流线的夹角,有助于降低伪扩散。

(a) 锅炉结构;(b) 燃烧器布置
图1 锅炉结构及燃烧器布置(单位: mm)
Fig.1 Sketch of boiler and burners
表1 煤的元素分析及工业分析
Table 1 Fuel elemental and industrial analysis

(a) 锅炉横断面网格;(b) 锅炉网格划分
图2 锅炉网格划分
Fig.2 Mesh of boiler
2 数学模型及边界条件
2.1 数学模型
采用三维稳态和Simple算法进行模拟计算。将气相作为连续相介质,采用标准k-ε湍流模型模拟气相湍流,用混合分数-概率密度函数模拟气相燃烧,用P-1辐射模型对空间的辐射传热进行模拟[10-11]。将煤粉颗粒看作离散相物质,颗粒相采用拉格朗日颗粒轨道模型,颗粒直径分布遵循Rosin Rammler分布。采用单步反应模型模拟挥发分的析出,煤粉颗粒的表面燃烧采用动力/扩散反应速率模型模拟[12-14]。
锅炉内三维气相流动、能量平衡的控制方程可写成如下统一形式:

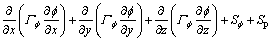 (2)
(2)
式中: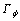 为扩散系数;
为扩散系数;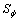 为气相引起的源项;Sp为固体颗粒引起的源项;
为气相引起的源项;Sp为固体颗粒引起的源项;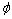 为通量,分别代表速度u,v和w以及湍流动能k、湍动能耗散率ε、时均混合分数
为通量,分别代表速度u,v和w以及湍流动能k、湍动能耗散率ε、时均混合分数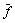 、混合分数脉动均方值g、焓h和i组分的质量分数Yi。当
、混合分数脉动均方值g、焓h和i组分的质量分数Yi。当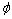 =1时,式(2)即为连续性方程。
=1时,式(2)即为连续性方程。
采用单步反应模型来模拟挥发分的析出,该模型假设挥发分析出速率与颗粒中保持的挥发分含量呈一次幂的关系,可用下式表示:
 (3)
(3)
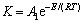 (4)
(4)
式中:mp为煤粉颗粒质量,kg;fv0为煤粉颗粒初始挥发分的质量分数;mp0为煤粉颗粒的初始质量,kg;K为反应速率常数;A1为指前因子,A1=492 000;E为活化能,E=7.4×107 kJ/mol。
NOx的生成机理有3种:热力型NOx,快速型NOx和燃料型NOx。一般地,在煤粉燃烧炉内生成的快速型NOx的量很少,可以忽略不计。热力NOx可根据广义的Zeldovich机理计算[15],NO的变化率为:
 (5)
(5)
式中:Mi为i种组分的物质的量;Yi为i种组分的质量分数;k1为反应常数,为1.8×108 e38 370/T;x(NO)为NO的摩尔分数;x(O)为氧原子的摩尔分数; 为NO的密度,kg/m-3。
为NO的密度,kg/m-3。
燃料型NOx生成机理如图3所示。热解中间产物为HCN,挥发分中的氮首先转化为HCN,HCN可以被O2氧化成NO,也可以被NO还原为N2;焦炭中的氮直接转化为NO[16]。NOx采用后处理方法,用PDF模型求解湍流下NOx的生成特性,即在整个炉膛流动、传热和燃烧过程计算出收敛结果后再进行计算。

图3 NOx生成机理
Fig.3 NOx emission mechanisms
2.2 边界条件
2.2.1 入口条件
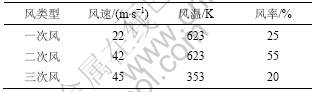
对于连续相,其入口边界条件为燃烧器各层喷口的速度和温度,各层喷口的操作参数如表2所示。对于离散相,煤粉颗粒由一次风喷口喷入炉膛,假定喷口处颗粒的速度和温度与一次风的一致。
表2 燃烧器喷口参数
Table 2 Parameters of burner injectors
2.2.2 出口条件
假定出口平面的流动为充分发展流,即所有变量在流动方向上的梯度为0。
2.2.3 壁面边界条件
对于气相,将炉膛壁面处理为无滑移和无质量渗透条件,对近壁面区域采用标准壁面函数处理。对于煤粉颗粒,假定颗粒与壁面之间为弹性碰撞。
3 计算结果及分析
3.1配风方式对NOx排放的影响
表3列出了不同工况下的配风方式,其中:工况Ⅰ为设计工况,采用均匀型的配风方式。在不同工况下,煤粉锅炉内不同截面的平均温度、O2浓度、CO浓度及NOx浓度随高度的变化情况如图4~7所示。
从图4可以看出:在不同配风方式下,截面平均温度随炉膛高度的变化规律基本相同。沿炉膛高度方向,当一次风和煤粉喷入时(y=1.2 m),炉内的温度迅速增高。随着燃尽风的喷入,煤粉得到充分燃烧,炉膛的温度进一步升高,截面平均最高温度出现在中二次风喷口处(y=1.9 m)。随着炉膛高度的升高,燃烧逐
表3 不同工况下的配风方式
Table 3 Air distribution rate for boiler under different conditions


1—工况Ⅰ;2—工况Ⅱ;3—工况Ⅲ;4—工况Ⅳ;5—工况Ⅴ
图4 截面平均温度随炉膛高度的变化
Fig.4 Average temperature on different sections along height of boiler
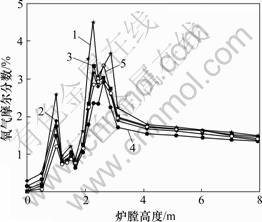
1—工况Ⅰ;2—工况Ⅱ;3—工况Ⅲ;4—工况Ⅳ;5—工况Ⅴ
图5 截面平均O2摩尔分数随炉膛高度的变化
Fig.5 Average O2 mole fraction on different sections along height of boiler

1—工况Ⅰ;2—工况Ⅱ;3—工况Ⅲ;4—工况Ⅳ;5—工况Ⅴ
图6 截面平均CO摩尔分数随炉膛高度的变化
Fig.6 Average CO mole fraction on different sections along height of boiler
1—工况Ⅰ;2—工况Ⅱ;3—工况Ⅲ;4—工况Ⅳ;5—工况Ⅴ
图7 截面平均NOx浓度随炉膛高度的变化
Fig.7 Average NOx concentration on different sections along height of boiler
渐减弱,同时,由于水冷壁的吸热,炉膛温度逐渐降低。配风方式对炉内温度有一定影响。几种方式中,均匀型送风的截面平均温度最高,最高平均温度为 1 645 K;束腰送风及倒塔型送风的最高截面平均温度分别为1 542 K和1 582 K。此外,三次风率也会对炉内温度造成一定影响。当三次风率增加时,炉膛内的截面最高平均温度有所降低。工况Ⅳ和工况Ⅴ对应的最高平均温度分别为1 532 K和1 563 K。
从图5可以看出:沿炉膛高度方向,炉内各截面的平均O2浓度明显出现了2个峰值,一个位于下二次风截面(y=1.0 m),另一个位于上二次风截面 (y=2.27 m)。在一次风喷入的区域,由于煤粉燃烧消耗了大量的氧气,因此,出现一个低氧区。在这5种工况中,工况Ⅰ的氧气浓度最高,因此,煤粉燃烧充分,炉膛温度高。在燃烧器区域,由于送入的中二次风率较少,束腰型送风的氧气浓度低于倒塔型送风的氧气浓度。
从图6可以看出:CO浓度沿高度方向出现1个明显的峰值,峰值位于上一次风喷口处的低氧区(y=1.5 m)。在主燃烧区域,工况Ⅰ的CO浓度最低,而其他几种工况下的CO浓度都比较高;随着三次风率的增加,不同送风方式下的最高CO浓度有所增大。
从图7可以看出:NOx的低浓度区位于燃烧器区域(y=1.5 m)。这主要是由于该区域O2浓度低,CO浓度高,形成了还原性气氛,抑制了燃料型NOx的生成。而随着燃尽风的喷入,炉内的O2含量迅速增加,NOx浓度也迅速增加。其原因可能是温度急剧升高,高温促进热力型NOx的生成。在采用均匀送风的设计工况下,炉膛出口处的NOx浓度为1 017.8×10-6,这与文献[17]中的结果一致。对于工况Ⅱ和工况Ⅲ,出口截面的平均NOx浓度分别为858.8×10-6和906.1×10-6。可以看出:配风方式对NOx排放浓度有较大影响。3种送风方式中,均匀型送风生成的NOx浓度最高,这与O2含量高是对应的,倒塔型送风次之,而束腰型送风最低;与均匀型送风相比,束腰型送风的NOx排放浓度可降低15.6%。
当三次风率从20%增加到25%时,工况Ⅳ和工况Ⅴ对应的NOx浓度分别为808.5×10-6和864.4×10-6,锅炉的NOx排放进一步降低。这主要是由于三次风率增加时,膛燃烧温度降低,减少了热力型NOx的生成;同时,燃烧器区域的O2浓度降低,降低了燃料型NOx的生成。相比均匀型配风方式(工况Ⅰ),倒塔型(工况Ⅴ)和束腰型配风方式(工况Ⅳ)的NOx排放浓度分别降低了15.1%和20.5%。
3.2 煤粉粒径对NOx排放的影响
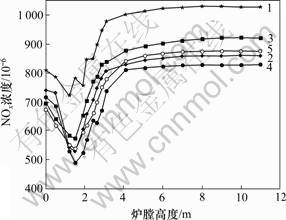
锅炉出口NOx浓度随煤粉粒径的变化规律如图8所示。
从图8可以看出:煤粉粒径对生成的NOx浓度有较大的影响。随着煤粉粒径的减小,锅炉NOx的排放浓度明显降低。当煤粉粒径从130 μm减小到50 μm时,NOx的排放浓度从1.12×10-3降低至0.87×10-3,降低了22.3%。相比设计工况所采用的90 μm煤粉,当粒径降低至50 μm时,NOx的排放浓度可降低14.3%。这主要是由于随着煤粉颗粒的细化,其燃烧速率提高,O2的消耗加速,使颗粒表面附近的氧气分
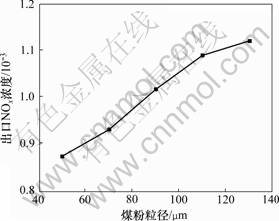
图8 NOx排放与煤粉粒径的关系
Fig.8 Effects of particle size on NOx emissions
压力迅速降低,有效抑制了燃料型NOx的生成。另一方面,燃烧速率提高增加了挥发分的析出量,使单位质量焦炭参与化学反应的比表面积增大,NO与焦炭间的还原过程增强。
3.3 过量空气系数对NOx排放的影响
采用不同过量空气系数时,锅炉出口处的NOx浓度及CO浓度如图9所示。
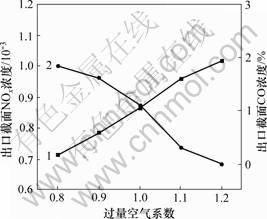
1—出口截面NOx浓度;2—出口截面CO浓度
图9 出口截面平均NOx及CO浓度随过量空气系数变化情况
Fig.9 Average NOx and CO concentration at outlet versus excess air rate
从图9可以看出:过量空气系数对NOx的生成产生了明显的影响;随着过量空气系数的减小,炉膛出口处的NOx浓度明显减小;当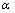 =1.2时,出口处NOx的浓度为1.02×10-3;当
=1.2时,出口处NOx的浓度为1.02×10-3;当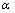 =0.8时,NOx的浓度为 0.71×10-3,降低了30.4%。此外,当过量空气系数降低时,炉膛出口处的CO浓度逐渐增大,不完全燃烧损失增大,将降低锅炉的燃烧效率。合适的过量空气系数可取1.1。此时,NOx浓度为0.96×10-3,比设计工况(
=0.8时,NOx的浓度为 0.71×10-3,降低了30.4%。此外,当过量空气系数降低时,炉膛出口处的CO浓度逐渐增大,不完全燃烧损失增大,将降低锅炉的燃烧效率。合适的过量空气系数可取1.1。此时,NOx浓度为0.96×10-3,比设计工况(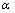 =1.2时)降低了5.8%。
=1.2时)降低了5.8%。
4 结论
(1) 配风方式对NOx生成有较大影响。3种配风方式中,束腰型配风方式炉内温度和生成的NOx浓度最小,倒塔型配风方式次之,而均匀型配风方式生成的NOx浓度最大。与均匀型配风方式相比,束腰型配风方式可有效减小NOx排放浓度。
(2) 适当增大三次风的送风比例能降低NOx的排放浓度。当三次风比例从20%增大到25%时,与均匀型配风方式相比,束腰型配风方式的NOx排放浓度可降低20.5%。
(3) 煤粉粒径对NOx排放浓度产生明显的影响。与设计工况相比,当粒径降低至50 μm时,NOx的排放浓度可降低14.3%。
(4) 随着过量空气系数的减小,炉内整体温度降低,NOx的排放浓度减小。对所研究的锅炉,合适的过量空气系数为1.1,此时,煤粉燃烧较充分,NOx的排放可降低5.8%。
参考文献:
[1] WANG H, Nakata T. Analysis of the market penetration of clean coal technologies and its impacts in China’s electricity sector[J]. Energy Policy, 2009, 37(1): 338-351.
[2] YU Zhao, WANG Shu-xiao, LEI Duan, et al. Primary air pollutant emissions of coal-fired power plants in China: Current status and future prediction[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(36): 8442-8452.
[3] 苟湘, 周俊虎, 周志军, 等. 三次风对四角切圆锅炉燃烧和NOx排放的影响[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2008, 28(8): 7-12.
GOU Xiang, ZHOU Jun-hu, ZHOU Zhi-jun, et al. Tertiary-air effects on combustion and NOx emission in tangentially fired furnace[J]. Proceeding of the CSEE, 2008, 28(8): 7-12.
[4] Srdjan B, Miroslav S, Dragan T, et al. A numerical study of a utility boiler tangentially-fired furnace under different operating conditions[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(15): 3353-3361.
[5] 贾艳艳, 毕明树, 柳智. 煤种对超细煤粉再燃脱硝效率影响的数值研究[J]. 热能动力工程, 2007, 22(5): 542-548.
JIA Yan-yan, BI Ming-shu, LIU Zhi. A numerical study of the influence of coal ranks on reburning based denitration efficiency of superfine pulverized coal[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy & Power, 2007, 22(5): 542-548.
[6] Luis D, Cristobal C, Javier P. Numerical investigation of NOx emissions from a tangentially-fired utility boiler under conventional and overfire air operation[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(7): 1259-1269.
[7] Mana C, Gibbinsa J R, Witkamp J G, et al. Coal characterisation for NOx prediction in air-staged combustion of pulverised coals[J]. Fuel, 2005, 84(17): 2190-2195.
[8] 王志刚, 禚玉群, 陈昌和, 等. 四角切圆锅炉流场伪扩散效应网格的研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2007, 27(5): 22-28.
WANG Zhi-gang, ZHUO Yu-qun, CHEN Chang-he, et al. Mesh investigation about crossflow diffusion of computational flow dynamics in tangential combustion flow field[J]. Proceeding of the CSEE, 2007, 27(5): 22-28.
[9] 刘向军, 徐旭常. 采用不同网格比较伪扩散对四角切圆型炉膛流场计算的影响[J]. 燃烧科学与技术, 1997, 3(2): 114-117.
LIU Xiang-jun, XU Xu-chang. Comparison of the influence of pseudo diffusion on the numerical simulation of flow field in a tangential firing furnace with different grid systems[J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 1997, 3(2): 114-117.
[10] Srdjan B, Miroslav S, Simeon O, et al. Three-dimensional modeling of utility boiler pulverized coal tangentially fired furnace[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2008, 51(7): 1970-1978.
[11] 张家元, 周孑民, 闫红杰. 煤粉锅炉膜法富氧局部助燃技术[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(5): 857-862.
ZHANG Jia-yuan, ZHOU Jie-min, YAN Hong-jie. Technology of local supporting-combustion by membrane oxygen- enrichment for pulverized coal boiler[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(5): 857-862.
[12] 阎维平, 刘亚芝, 黄景立. 300 MW四角切圆煤粉锅炉燃烧和NOx排放的数值模拟[J]. 电站系统工程, 2007, 23(2): 11-13.
YAN Wei-ping, LIU Ya-zhi, HUANG Jing-li. Numerical simulation of combustion and NOx generation process in a 300 MW tangentially pulverized coal fired boiler[J]. Power System Engineering, 2007, 23(2): 11-13.
[13] SU Sheng, XIANG Jun, SUN Lu-shi, et al. Application of gaseous fuel reburning for controlling nitric oxide emissions in boilers[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2008, 90(3): 1-7.
[14] 刘泰生, 周武, 叶恩清. 燃尽风对炉内流动和燃烧过程影响的数值模拟[J]. 动力工程, 2006, 26(1): 116-120.
LIU Tai-sheng, ZHOU Wu, YE En-qing. Numerical simulation of the effect of over-Fire air on flow and combustion in furnaces[J]. Power Engineering, 2006, 26(1): 116-120.
[15] LI Kang, Steve T, PENG Jian-xun. Modeling and prediction of NOx emission in a coal-fired power generation plant[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2004, 12(6): 707-723.
[16] 张颉, 吴少华, 孙锐, 等. 350 MW燃煤锅炉燃烧过程和NOx排放的数值研究[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2004, 36(9): 1239-1244.
ZHANG Jie, WU Shao-hua, SUN Rui, et al. Numerical study on combustion process and NOx emissions in a 350 MW pulverized coal fired boiler[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2004, 36(9): 1239-1244.
[17] 柳智. 超细煤粉再燃技术降低NOx的数值模拟[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学化工学院, 2006: 65-66.
LIU Zhi. The numerical simulation on micronized coal reburning technology for reducing NOx emission[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology. College of Chemical Engineering, 2006: 65-66.
(编辑 赵俊)
收稿日期:2010-01-03;修回日期:2010-04-15
基金项目:湖南省教育厅科研基金资助项目(07C749);湖南省自然科学基金资助项目(07JJ5069);湖南省自然科学市州联合基金资助项目(09JJ9011)
通信作者:夏小霞(1980-),女,湖南常德人,讲师,从事热工设备的仿真与优化;电话:15897323160;E-mail: xxx620@xtu.edu.cn