


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 768-772
Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-43Al-9V alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering
XU Li-juan1,2, XIAO Shu-long1,2, CHEN Yu-yong1,2, WANG Juan1
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China;
2. National Key Laboratory for Precision Hot Processing of Metals,Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
Received 9 August 2011; accepted 16 January 2012
Abstract: A fine-grained TiAl alloy with the composition of Ti-43Al-9V was prepared by mechanical milling and spark plasma sintering (SPS). The relationship among sintering temperature, microstructure and mechanical properties was studied. The results show that the morphology of mechanical milling powder is regular with size in a range of 5-30 μm. Main phases of γ-TiAl, α2-Ti3Al and few B2 phase are observed in the SPS bulk samples. For samples sintered at 1150 ℃, equiaxed crystal grain microstructure is achieved with size in a range of 300 nm-1 μm. With increasing SPS temperature to 1250 ℃, the size of equiaxed crystal grains obviously increases, the microhardness decreases from HV592 to HV535, and the bending strength decreases from 605 to 219 MPa. Meantime, the compression fracture strength also decreases from 2601 to 1905 MPa, and the strain compression decreases from 28.95% to 12.09%.
Key words: TiAl alloy; mechanical alloying; spark plasma sintering; microstructure; mechanical properties
1 Introduction
Recently, TiAl-based alloys have been developed as candidate materials in aerospace structural and engine applications due to their low density, high specific strength and attractive high-temperature properties [1,2]. However, their low room temperature ductility and elevated temperature formability limit the application of the alloys. The oxidation resistance of binary Ti-Al intermetallics is rather poor and other additives, such as Nb, Cr, V and Si, can improve the oxidation resistance and ductility [1,3]. Refining the microstructure is another current way investigated to attain well balanced and reproducible mechanical properties [4]. In attempt to improve the ductility, recent researches have focused on the production of ultrafine grained TiAl. Powder metallurgy (PM) is a favourable process for synthesizing ultrafine grained and nanostructured TiAl based alloys and forming near-net shaped components out of such alloys [4-6]. CALDERON et al [7] studied the mechanical properties of nanocrystalline TiAl-based alloys. YU et al [8] synthesized an ultrafine grained TiAl based alloy by subzero temperature milling and HIP. KAMBARA et al [9] obtained nano-structured intermetallic compound TiAl by the crystallization of mechanically alloyed amorphous TiAl. SURYANARAYANA et al [10] studied the characterization of alloyed nanocrystalline titanium aluminides. Spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique has already been successfully used by several groups of researchers in synthesizing bulk TiAl inermetallic based alloys, some of them are nanostructured or ultrafine structured. COURET et al [4] used the PM route coupled with the SPS process to produce TiAl alloys with refined microstructure. LU et al [11] prepared Ti-45Al-8.5Nb- 0.2B-0.2W-0.1Y and Ti-47.5Al- 2.0V-1.0Cr alloys by SPS with the average lamellar grain sizes of about 25 and 200 μm, respectively. CHEN et al [12] obtained ultrafine grained Ti-47Al alloy by SPS.
In the present work, a combination of high energy mechanical milling and SPS was used to produce TiAl-based alloy samples with a nominal composition of Ti-47Al-9V. The aim of this study is to determine the effect of SPS temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the TiAl-based alloy.
2 Experimental
A mixture of Ti (purity>99.9%, particle size<50 μm), Al (purity>99.9%, particle size<50 μm) and V (purity>99.9%, particle size<74 μm) powders was used as starting materials. The Ti, Al and V powders were mixed with a molar ratio of Ti-47Al-9V. The weighed powders were mixed and loaded in a stainless steel vial under argon atmosphere. Mechanical milling was carried out in a high-energy planetary ball mill. The mass ratio of ball to powder was 10:1 and 1% (mass fraction) stearic acid was added as a process control agent. The milling process included milling the powders for 20 h at a low rotation speed of 180 r/min to thoroughly mix the powders, and subsequently high energy mechanical milling the powder mixture for 60 h at a high rotation speed of 400 r/min.
The consolidation of the milled powder was done using a Dr. Sinter SPS-1050 furnace. Prior to the SPS process, the SPS furnace was evacuated and back-filled with argon for three times, and then evacuated to a vacuum of 2 Pa. The powder compact was heated through generating spark plasma in the furnace first to a temperature equal to (T -150) ℃ at a heating rate of 100 ℃/min, where T is the designated sintering temperature. It was then heated to T at a heating rate of 50 ℃/min. The furnace was held at the sintering temperature for 8 min, and then its power was switched off and the sample was cooled in the furnace. A uniaxial pressure of 50 MPa was applied to the powder compact in the whole duration of heating and sintering the powder compact. Three sintering temperatures of 1150, 1200 and 1250 ℃ were selected. The sintered samples were cylindrical disks with size of d30 mm×(6-7) mm.
The microstructures and resultant phases of the powder particles and bulk SPS sintered samples were characterised using X-ray diffractometry (XRD, Philips X-Pert system with Cu Kα radiation) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Hitachi S-4700 SEM equipped with an energy dispersive spectrometer). For SEM examination, the polished surfaces of the sintered bulk solid samples were etched with Krool solution (5% HNO3+3% HF+92% H2O).
For compression test, the samples were cut into cylindrical samples with dimensions of 2.5 mm×3 mm. The three-point bending test samples were cut into rectangular shape with dimensions of 3 mm×4 mm× 26 mm. These sample surfaces were polished with 1200-grit SiC papers. For each data, three specimens were tested to record an average value. The compression and three-point bending tests were performed using an INSTRON mechanical testing machine. The cross-head speed for compression tests and three-point bending test were 0.18 and 0.5 mm/min, respectively. The Vickers micro-hardness tests were performed under a load of 4.9 N for loading time of 10 s. Five indentations were tested to record an average micro-hardness data.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Phase composition and micrograph of powders
Figure 1 shows the XRD pattern of Ti-47Al-9V powders after mechanical milling for 60 h and Fig. 2 shows the SEM micrograph of the powders after high energy mechanical milling. The XRD pattern shows Ti, Al and V peaks as major peaks after milling for 60 h at a high rotation speed of 400 r/min, suggesting the extent of the reaction between Al and Ti phases during milling is negligible. Meantime, the Al and Ti peaks exhibit shoulders, suggesting the milled powder particles contain Al(Ti) and Ti(Al) solutions formed by the interdiffusion between Al and Ti phases during milling. KAMBARA et al [9] indicated that increasing milling time resulted in a decrease of grain size of Ti and Al and the formation of Ti(Al) solid solution. FADEEVA et al [13] and BHATTACHARYA et al [5] separately reported that Ti(Al) solid solution was the only product of milling. The results show that the morphology of mechanical milling powder is regular with size in a range of 5-30 μm.
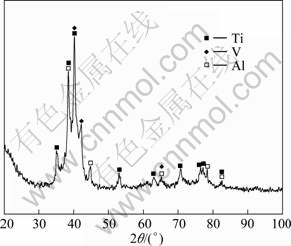
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of mechanical milling Ti-43Al-9V powders

Fig. 2 SEM morphology of mechanical milling Ti-43Al-9V powders
3.2 Phase composition and microstructure of bulk samples
Figure 3 shows the XRD patterns of the bulk samples prepared by SPS at different temperatures with Ti-47Al-9V composite powders milled for 60 h. It is clearly shown that at SPS temperature of 1150 ℃, the Al, Ti, Al(Ti) and Ti(Al) phases in the as-milled powders are completely reacted during SPS, resulting in the formation of γ-TiAl and α2-Ti3Al as the major phases, and B2 phase as the minor phase. Increasing the SPS temperature from 1150 to 1250 ℃ has little effect on the phase structure of the sintered samples, and only the fraction of the Ti3Al and B2 phases appears to increase slightly.
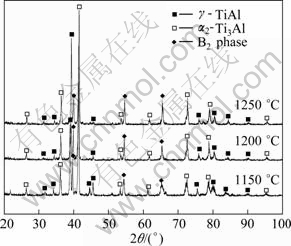
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of Ti-43Al-9V alloy bulk samples prepared by SPS
Microstructural examination by SEM (Fig. 4) clearly shows the effect of SPS temperature on the microstructure of the sintered samples. At SPS temperature of 1150 ℃, the sintered sample exhibits an equiaxed grain microstructure with grain size typically in the range of 300 nm-1 μm and some bright microstructure (Fig. 4(a)). At SPS temperature of 1200 ℃, the bright microstructure is also observed (Fig. 4(b)), which is the B2 phase. With increasing SPS temperature to 1250 ℃, the size of equiaxed crystal grain obviously increases. During SPS process, a small amount of α2 phase forms, which is related with two transformation mechanisms: 1) α phase nucleates and grows at the γ grain boundaries during the phase transformation of α→γ+α→γ+α2; and 2) α particles formed at γ grain boundaries in the course of prior powder consolidation grow into α2 during the SPS treatment [14].
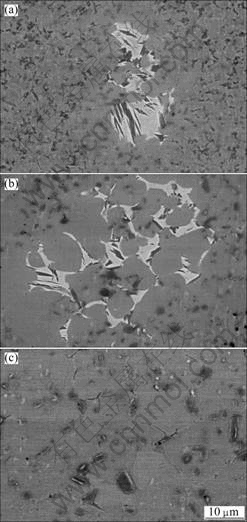
Fig. 4 SEM images of Ti-43Al-9V alloy bulk samples prepared by SPS at different temperatures: (a) 1150 ℃; (b) 1200 ℃; (c) 1250 ℃
3.3 Mechanical properties of bulk samples
Figure 5 shows the typical compression stress—strain curves of specimens cut from the samples produced by SPS at different temperatures. All the specimens show a substantial amount of plastic deformation and work hardening prior to fracture. The changes of compression fracture strength, compression strain, bending strength and micro-hardness of the samples with SPS temperature are listed in Table 1. With increasing SPS temperature from 1150 to 1250 ℃, the compression fracture strength decreases from 2601 to 1905 MPa, and the compression strain decreases from 28.95% to 12.09%. At the same time, the bending strength also decreases from 605 to 219 MPa, and the micro-hardness decreases from HV592 to HV535.
SEM examination of the bulk alloy samples shows that increasing of SPS temperature from 1150 to 1250 ℃ causes a significant increase of the size of TiAl equiaxed grains. This increase of the grain size of TiAl should cause a clear decrease in the compression yield strength according to the Hall-Petch relationship between
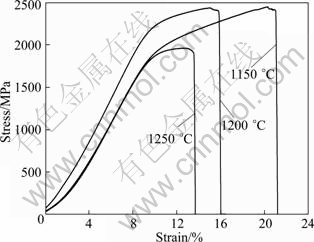
Fig. 5 Compression stress—strain curves of Ti-43Al-9V alloy samples prepared by SPS at different temperatures
strength and grain size [13]. The SPS temperature increase has more significant effect than the grain coarsening on the strength of the alloy. As shown in the typical compression strain—stress curves in Fig. 5, the finer grains of the bulk TiAl alloy sample produced at an SPS temperature of 1150 ℃ facilitates substantial compression plasticity and work hardening. Since the bending half of the specimen is in tension, it is expected that the bending strength of a sample is sensitive to grain coarsening. Based on this consideration, it is not surprising to observe that the bending strength of the bulk samples produced at SPS temperature of 1250 ℃ is fairly low.
Table 1 Mechanical properties of Ti-43Al-9V alloy bulk samples prepared by SPS at different temperature
Figure 6 shows the bending fracture morphologies of Ti-43Al-9V alloy samples prepared by SPS at different temperatures. The fractured surfaces for the sample prepared by SPS at 1150 ℃ are shown in Figs. 6(a) and (b). Fine cleavage facets are observed in the fracture surface of this sample, together with some terrace-type morphology. As shown in Figs. 6(c) and (e), at SPS temperatures of 1200 and 1250 ℃, coarse cleavage facets are observed in the fracture surfaces of these samples, which contain a lamellar microstructure. A combination of interlamellar cracking and intergranular fracture leads to brittle fracture of the lamellar structure. At higher magnification in Figs. 6(d) and (f), the lamellar morphology is more obvious. In these samples, delamination of the lamellar appears to be the principal mechanism for the nucleation of microcracks within the grains. When these microcracks propagate and reach the lamellar grain boundaries, the cracks are deflected and follow the grain boundaries, causing the intergranular fracture [15]. The cleavage fracture is the extreme brittleness of these samples.
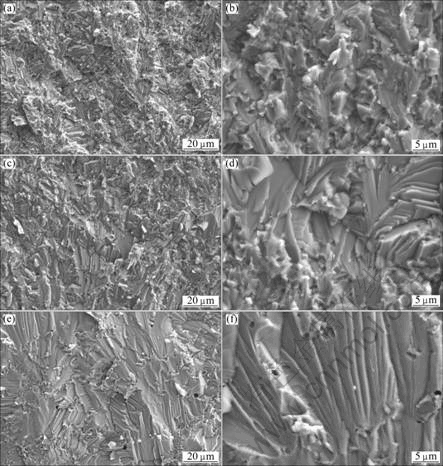
Fig. 6 Bending fracture morphologies of Ti-43Al-9V alloy samples prepared by SPS at different temperatures: (a), (b) 1150 ℃; (c), (d) 1200 ℃; (e), (f) 1250 ℃
4 Conclusions
1) The morphology of mechanical milling powders is regular with size of 5-30 μm. The main phases γ-TiAl, α2-Ti3Al and few B2 phase are observed in the Ti-43Al-9V alloy.
2) The sintered Ti-43Al-9V alloy exhibits an equiaxed grain microstructure. With increasing SPS temperature from 1150 to 1250 ℃, the size of equiaxed crystal grain obviously increases.
3) The samples show a substantial amount of plastic deformation and work hardening prior to fracture. The mechanical properties of Ti-43Al-9V alloy prepared at SPS temperature of 1150 ℃ are better than those prepared at 1200 and 1250 ℃. The bending fracture mode of the SPS Ti-43Al-9V alloy is cleavage fracture.
References
[1] KUMARAN S, CHANTAIAH B, RAO S T. Effect of niobium and aluminium additions in TiAl prealloyed powders during high-energy ball milling [J].Mater Chem Phys, 2008, 108(1): 97-101.
[2] FOROUZANMELU N, KARIMZADEH F, ENAYATI M H. Study on solid-state reactions of nanocrystalline TiAl synthesized by mechanical alloying [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2009, 471(1-2): 93-97.
[3] YOSHIHARA M, KIM Y W. Oxidation behaviour of gamma alloys designed for high temperature applications [J]. Intermetallics, 2005, 13(9): 952-958.
[4] COURET A, MOLENAT G, GALY J, THOMAS M. Microstructures and mechanical properties of TiAl alloys consolidated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Intermetallics, 2008, 16(9): 1134-1141.
[5] BHATTACHARYA P, BELLON P, AVERBACK R S, HALES S J. Nanocrystalline TiAl powders synthesized by high-energy ball milling: effects of milling parameters on yield and contamination [J]. J Alloys Compd, 2004, 368(1-2): 187-196.
[6] MOON K I I, LEE K S. A study of the microstructure of nanocrystalline Al-Ti alloys synthesized by ball milling in a hydrogen atmosphere and hot extrusion [J]. J Alloys Compd, 1999, 291(1-2): 312-321.
[7] CALDERON H A, GARIBAY-FEBLES V, UMEMOTO M, YAMAGUCHI M. Mechanical properties of nanocrystalline Ti-Al-X alloys [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 329-331: 196-205.
[8] YU H B, ZHANG D L, CHEN Y Y, CAO P, GABBITAS B. Synthesis of an ultrafine grained TiAl based alloy by subzero temperature milling and HIP, its microstructure and mechanical properties [J].J Alloys Compd, 2009, 474(1-2): 105-112.
[9] KAMBARA M, UENISHI K, KOBAYASHI K F. Nano-structured intermetallic compound TiAl obtained by crystallization of mechanically alloyed amorphous TiAl, and its subsequent grain growth [J]. J Mater Sci, 2000, 35(11): 2897-2905.
[10] SURYANARAYANA C, KORTH G E, FROES F H. Compaction and characterization of mechanically: Alloyed nanocrystalline titanium aluminides [J]. Metall Mater Trans, 1997, 28(2): 293-302.
[11] LU X, HE X B, ZHANG B, QU X H, ZHANG L, GUO Z X, TIAN J J. High-temperature oxidation behavior of TiAl-based alloys fabricated by spark plasma sintering[J].J Alloys Compd, 2009, 478(1-2): 220-225.
[12] CHEN Y Y, YU H B, ZHANG D L,CHAI L H. Effect of spark plasma sintering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of an ultrafine grained TiAl intermetallic alloy [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, 525(1-2): 166-173.
[13] FADEEVA V I, LEONOY A V, SZEWCZAK E, MATYJA H. Structural defects and thermal stability of Ti(Al) solid solution obtained by mechanical alloying [J].Mater Sci Eng A, 1998, 242(1-2): 230-234.
[14] WANG Y H, LIN J P, HE Y H, WANG Y L, CHEN G L. Fabrication and SPS microstructures of Ti-45Al-8.5Nb-(W, B, Y) alloying powders [J]. Intermetallics, 2008, 16(2): 215-224.
[15] SEETHARAMAN V, SEMIATIN S L. Microstructures and tensile properties of Ti-45.5Al-2Nb-2Cr rolled sheets [J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2001, 299(1-2): 195-209.
放电等离子烧结Ti-43Al-9V合金显微组织和力学性能
徐丽娟1,2,肖树龙1,2,陈玉勇1,2,王 娟1
1. 哈尔滨工业大学 材料科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001;
2. 哈尔滨工业大学 金属精密热加工国家级重点实验室,哈尔滨 150001
摘 要:采用机械合金化和放电等离子烧结工艺制备细晶Ti-43Al-9V合金,研究不同烧结温度与显微组织和力学性能之间的关系。结果表明:机械球磨后粉末形状规则,尺寸在5~30 μm之间,烧结所得块体材料主要由γ-TiAl、 α2-Ti3Al 和少量 B2相组成。烧结温度为1150 ℃时,获得的等轴晶粒尺寸为300 nm~1 μm。烧结温度升高到1250 ℃时,等轴晶粒的尺寸明显增大,显微硬度从HV592降低到HV535, 抗弯强度从605降低到219 MPa,压缩断裂强度从2601降低到1905 MPa, 压缩率从28.95%降低到12.09%。
关键词:TiAl合金;机械合金化;放电等离子烧结;显微组织;力学性能
(Edited by FANG Jing-hua)
Foundation item: Project (51001040) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: XIAO Shu-long; Tel/Fax: +86-451-86418802; E-mail: xiaoshulong@hit.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61243-0