水土化学作用对土体抗剪强度的影响
王军1, 2,曹平1,赵延林1,柴红宝1
(1. 中南大学 资源与安全工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083;
2. 湖南工程学院 建筑工程学院,湖南 湘潭,411104)
摘 要:基于离子效应,以改良路基土体为目的,对土样、水样和粉煤灰的复合体进行室内水化学试验、土体物理力学常规试验和直剪试验,并从水化学的力学效应、水化学、指标线性回归和路基土的改良效果4个方面对土体抗剪强度的水土作用机制进行统计分析。研究结果表明:含水土体的Ca2+,HCO3-,K+和Na+等浓度对土体的原始黏结力和固有黏结力有明显的减弱效应,而NO3-和Cl-质量浓度对其影响较弱;内摩擦角随离子质量浓度的变化离散性很大;K+,Na+,Ca2+和HCO3-浓度以及总矿化度、硬度与黏结力有很好的线性相关性,然而,它们与内摩擦角的相关性较差;当粉煤灰掺入量为10%左右时,对路基土的改良有显著效应。
关键词:水土化学作用;离子效应;线性相关性;抗剪强度
中图分类号:TU431 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2010)01-0245-06
Influence of chemical action of water-soil on soil shear strength
WANG Jun1, 2, CAO Ping1, ZHAO Yan-lin1, CHAI Hong-bao1
(1. School of Resources and Safety Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. College of Architecture Engineering, Hunan Institute of Engineering, Xiangtan 411104, China)
Abstract: Based on the ion effect and the porpose of improved roadbed soil, samplings of soil, ground water and clays were obtained to observe and analyze the effect. The analysis on mechanics of water-soil interaction was carried out to find factors of shear strength, including mechanics effect of water chemical, analysis test on water chemical, linear correlation regress and effect of loadbed soil improvment. The results show the weakened effect occurs on soil cohesion and inner friction angle with Ca2+, HCO3-, K+ and Na+ consistency. But dispersed inner friction angle character is marked with ion consistency. There are correlation among cohesion and testing index including total salinity, hardness, and K+, Na+, Ca2+ and HCO3- concentration. The effect on roadbed improvement is remarkable with clays when the consistency is close to 10%.
Key words: chemical action of water-soil; ion effect; linear correlation; shear strength
地下水是地质环境中最活跃的因素,它是一种成分复杂的化学溶液。自然界中,土体中水呈液态、固态和气态分布,并且水是造成地质环境损害的一个重要因素,有时它比力学效应造成的损害更严重。工程实践证明,水对土体的强度与变形有很大的影响。目前,很多学者对含水岩石的强度进行了研究,如:汤连生等[1-3]开展了水岩化学作用的岩石宏观力学效应试验,揭示水对岩体断裂强度和裂纹面上剪切强度的研究;冯夏庭等[4]就化学环境侵蚀下的岩石破裂特性进行了试验,揭示了水化学作用下裂纹变化特性;马水山等[5]基于水岩作用对边坡变形机理进行了研究,指出了滑体变形的全过程;Karfakis等[6]考虑化学作用对岩石进行断裂求解;Feucht等[7]总结了化学影响下的砂岩剪切效应。然而,人们就水化学作用对土体抗剪强度的研究较少。目前,路基、岸坡、土坝、引水隧道等工程因水化学作用引发的灾害处处可见,必须加强治理研究[8]。在此,本文作者以武(汉)广(州)高速铁路路基为试验背景,在不同里程处采取水样和土样进行分析,测试其溶液的化学性质对土体抗剪强度参数c(黏结力)和φ(内摩擦角)的影响,探讨其力学效应及其机理,以便为软弱路基改良提供一种新的途径。
1 水效应的力学分析
路基土体介质在含有复杂离子成分的地下水中浸泡,必将发生一系列的诸如水解、溶解和碳酸化等化学反应,从而导致介质的结构发生破坏,减弱其强度指标。土体介质孔隙中的水化学溶液与矿物颗粒或晶体发生化学反应,使原生矿物分解并生成新的次生矿物,而新生成物质常具有高度的分散性,同时,水化学作用产生的易溶矿物容易随水流失,导致介质中的孔隙增大,含水量增加,有效应力降低,强度减小,给工程带来安全隐患。
原生矿物中最普遍的成分是长石,是一种空间结构带负电荷的硅酸盐矿物。由于阳离子的交换作用,配位数目增多,使开放式结构与单元间成键强度降低,经水化学作用生成高岭石、伊利石和胶体,可塑性和压缩性强,强度低。相应的化学反应方程式为:
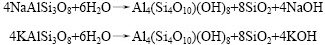
次生矿物分子间的吸引力由下式计算[9]:
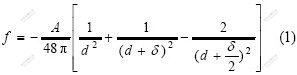
式中:f为分子间的吸引力;d为颗粒薄片间距的一半;A为范德华常数;δ为薄片厚度。取δ为9.68×10-10 m,d为1.16×10-10 m,A为1×10-21 J,经计算可得分子间的引力为4.62×10-4 J/m2,比原生矿物分子间的引力小1~2个数量级。颗粒黏结力主要由受电分子吸引的原始黏结力和受分子结构控制的固有黏结力组成。次生矿物的颗粒粒径一般比原生矿物颗粒粒径小,致使颗粒之间面与面的接触变为点与点、点与面的接触,土颗粒间的表面摩擦和颗粒间的连锁作用减弱,这充分表明水化作用对内摩擦角和黏结力的减弱效应,致使土体强度降低。
2 化学分析试验
2.1 指标测试
通过机动地质钻探,分别钻取路基技术孔和标贯孔,并从中采取土样(试验段主要为粉质黏土)和水样,分析其阴、阳离子质量浓度,并进行统计分析研究。为满足研究的需要,对不同里程段的试样加以提取,并对水进行化学分析,具体试验结果见表1。
表1 地下水成分分析结果
Table 1 Results of chemical analysis of groundwater

从表1可看出:该段路基地下水中含有的化学成分具有很大的离散性,其中变化最大的是HCO3-的质量浓度,其次是总矿化度和Ca2+的质量浓度;Cl-和NO3-的质量浓度相对稳定;K+,Na+和Mg2+的质量浓度相对比较集中,分别在某值附近波动。土中碳酸盐物质遇游离CO2的水化学溶液,易生成溶解度更大的重碳酸盐,使矿物变得更加容易侵蚀,破坏其结构。其方程式为:
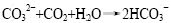
土样的pH值变化范围为6.60~7.46,靠近地表处pH值较小,主要受降雨或地表水的补给,显弱酸性和中性,而在地层深处显弱碱性。这里主要研究离子效应对路基土体强度的影响。
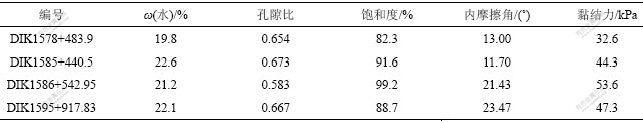
土的物理力学参数见表2。从表2可以看出:该粉质黏土的物理力学某些参数值变化不大,水溶液的化学成分对土颗粒密度几乎不产生影响;同时,土的密度对抗剪强度指标c(黏结力)和φ(内摩擦角)影响较小,但是,饱和度和孔隙比对抗剪强度的影响比较大;若孔隙比越大,则内摩擦角越小,但对黏结力的影响很小;饱和度越大,则黏结力较大,对内摩擦角的影响较小。结合表1还可看出溶液的pH值与土的黏结力c关系也不大,但随着pH值升高,内摩擦角φ逐渐降低;总矿化度和硬度越小,则黏结力越大,然而,对内摩擦角影响不大。
表2 土的物理力学参数
Table 2 Parameters of physical mechanics of soil
2.2 离子分布特征
图1所示为样品中K+,Na+,Ca2+,Mg2+,Cl-,SO42-和HCO3-的质量浓度与黏结力c的关系,可以看出:阳离子中,Ca2+质量浓度最高,与CO2的水溶液生成了碳酸氢钙,矿物更加容易受到侵蚀,破坏土体结构,生成较少胶结物,水膜厚度增大,电分子吸引减弱,原始黏结力和固有黏结力降低;但当Ca2+质量浓度足够高时,Ca2+与SO42-和CO32-发生反应,有大量胶结物生成,黏结力增大;Mg2+质量浓度较小,但质量浓度较低的Mg2+也能与CO2的水溶液发生反应,生成胶结物,固有黏结力有所提高;阴离子中HCO3-质量浓度最高,离散性最大,很容易与大量的Ca2+发生反应,矿物容易受到侵蚀,使土体黏结力降低;NO3-和Cl-质量浓度较低,但分布很稳定,很难生成胶结物,对黏结力影响很小。K+和Na+的质量浓度也对黏结力有影响,能吸收大量的水分,水膜增厚,电分子引力减弱,随着K+和Na+质量浓度增大,黏结力逐渐减小。
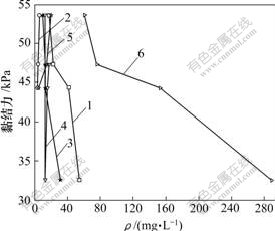
1—Ca2+; 2—Mg2+; 3—K+, Na+; 4—Cl-; 5—SO42-; 6—HCO3-
图1 阴、阳离子质量浓度与黏结力c的关系
Fig.1 Relationship among concentration of cation and anion and cohesion
图2所示为样品中K+,Na+,Ca2+,Mg2+,Cl-,SO42-和HCO3-的质量浓度与内摩擦角φ的关系。可以看出:离子质量浓度对内摩擦角的影响弱于对黏结力的影响;内摩擦角随离子质量浓度的变化离散性很大,主要表现在离子交换对土体的体积变化不明显,孔隙比在小范围内波动,使得颗粒表面间的摩擦和连锁作用平稳。若次生矿物中蒙脱石质量浓度较高,则压缩性增强,可塑性提高,势必对内摩擦角产生很大影响。
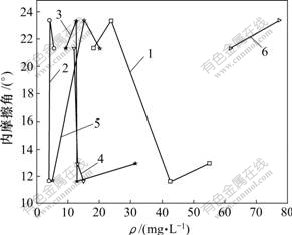
1—Ca2+; 2—Mg2+; 3—K+, Na+; 4—Cl-; 5—SO42-; 6—HCO3-
图2 阴、阳离子质量浓度与内摩擦角φ的关系
Fig.2 Relationship among concentration of cation and anion and inner friction
3 回归分析
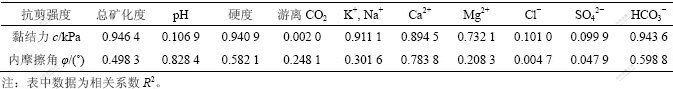
从表1、表2和图1、图2可以看到:K+,Na+,Ca2+和 HCO3-等离子质量浓度以及总矿化度、硬度与路基土体的抗剪强度有一定的线性相关性。作者通过相关系数R2(线性回归值和实际值之比)和直线拟合函数,得出具体相关系数见表3。相关系数越大,说明数据之间的线性相关性越好[10-11],离子效应越显著。根据线性拟合,由表3所示的各指标与黏结力c和内摩擦角φ的相关系数,R2范围为 0.002 0~0.946 4,离散性很大。其中,大于0.800 0的组合有6组,即:土的黏结力c与总矿化度(相关系数为0.946 4),c与硬度(0.940 9),c与K+和Na+(0.911 1),c与Ca2+(0.894 5);c与HCO3-(0.943 6),土的内摩擦角φ与pH值(0.828 4)。游离的CO2,Cl-和SO42-与c和φ的线性相关性较差。可见,各指标对黏结力c有很好的相关性,对内摩擦角的相关性较小。从分析试验结果也可知:受水化学作用,各指标对土体黏结力产生的效应要大于内摩擦角所产生的效应。这里只列举几种指标与黏结力c和内摩擦角φ的相关系数线性回归关系,见图3。
表3 抗剪强度参数c和φ的离子质量浓度线性相关系数R2
Table 3 Linear correlation coefficient R2 between reinforced shear strength index and different ingredients
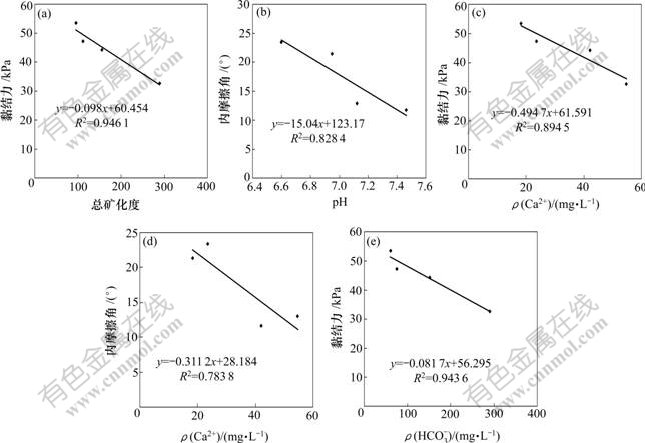
(a) 总矿化度与黏结力的关系;(b) pH值与内摩擦角的关系;(c) Ca2+与黏结力的关系;(d) Ca2+与内摩擦角的关系;(e) HCO3-与黏结力的关系
图3 各成分与抗剪强度指标(黏结力和内摩擦角)的相关性
Fig.3 Linear correlation between shear strength index and different ingredients
4 工程应用
4.1 路基土改良分析
路基工程是铁路、公路、城市道路等工程建设的主要组成部分。目前,改良路基土的主要措施是水泥灰、石灰以及采取换填和复合地基等方法[12-14]。然而,粉煤灰作为一种复合材料,来源广泛,颗粒结构比较致密,干缩性小,抗震性较强,物理力学性能远比原状土的物理力学性能优,其低钙粉煤灰Ca2+质量浓度小,经化学反应,HCO3-质量浓度也较小,对提高软弱路基土体黏结力c和内摩擦角φ效果显著,且后期强度可以达到甚至超过普通水泥土的强度[15]。
提高土的强度主要是增加土颗粒之间的吸引力和减小土颗粒之间的排斥力,龚晓南[9]推导了颗粒间的排斥力,计算式为:
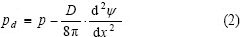
式中:pd为x=d处的排斥力;p为随x变化的水压力;ψ为电位势;D为介电常数。通常,黏土颗粒表面带有负电荷,Al3+和Ca2+与颗粒具有很好的亲合性,使得电位势减小,排斥力增大;但随着Ca2+质量浓度的增大,电位势又增加,排斥力减小,对改良土性能有利。可见,在粉煤灰改良路基土工程中,控制粉煤灰的掺入量非常关键。
4.2 对土体强度的影响
在路堤的分层填筑中,软弱路基的破坏主要表现为沿滑动面的塑性剪切破坏。依据Mohr-Coulomb强度理论:

土体的抗剪强度与黏结力c和内摩擦角φ有关。式(3)中:τ为抗剪强度;σ为正应力。
另一方面,在国内常用的Duncan-Chang模型中,应力水平的表达式为:
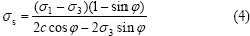
式中:σs为应力;σ1和σ3分别为最大、最小主应力。可见:随着内摩擦角φ增大,应力也增大。
4.3 试验结果分析
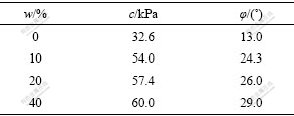
为验证粉煤灰改良路基土的优越性,研究粉煤灰的掺入量对试验段(DIK1578+483.9)土体强度的影响,试验中掺灰量w为0,10%,20%和40%(掺灰量w指的是掺入粉煤灰的质量与原料土的质量比,龄期为 28 d),在这里粉煤灰的烧失量为3.13%,细度为15.8%,需水量为95%。养护至规定龄期之后,在基于应变控制式的直剪仪上进行直剪试验,其强度参数c和φ见表4。
从表4可知:当掺灰量从0增加至40%时,路基改良土的黏结力c和内摩擦角φ分别为原状土的1.84倍和2.23倍,增加效果显著;当掺灰量q为10%左右时,路基改良土的黏结力和内摩擦角增幅梯度最大,抗剪强度满足规范要求;随着掺灰量q的继续增加,改良效果增缓,这与机理分析结果比较吻合。因此,建议工程建设中掺灰量控制在10%左右。
表4 粉煤灰改良路基土的直剪试验结果
Table 4 Testing results of loadbed improvement
5 结论
(1) 含水土体受水化学作用,生成高度分散性的次生矿物,电分子结构发生变化,导致介质中的孔隙增大,含水量增加,有效应力减小,抗剪强度减小。
(2) 水中离子质量浓度差异显著,其中:HCO3-和Ca2+质量浓度最高,Mg2+和NO3-质量浓度较低;pH值变化范围为6.6~7.46,表层显弱酸性和中性,深层显弱碱性。Ca2+质量浓度越高,土体原始黏结力和固有黏结力越低,但当Ca2+质量浓度足够高时,黏结力提高,Mg2+有利于黏结力提高;HCO3-质量浓度越大,黏结力越小。NO3-和Cl-对黏结力影响很小。然而,离子质量浓度对内摩擦角的影响弱于对黏结力的影响。内摩擦角随离子质量浓度的变化离散性很大。
(3) 总矿化度、硬度和Ca2+与黏结力的相关系数都大于0.900 0,表明土体抗剪强度受水化学的影响较大。一些指标对内摩擦角产生的效应线性相关性较小,其影响较弱。
(4) 粉煤灰改良路基土中,存在1个最佳掺灰量,使改良土强度增加梯度最大。
参考文献:
[1] 汤连生, 张鹏程, 王思敬. 水岩化学作用的岩石力学宏观力学效应的试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2002, 21(4): 526-531.
TANG Lian-sheng, ZHANG Peng-cheng, WANG Si-jing. Testing study on macroscopic mechanics effect of chemical action of water on rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 21(4): 526-531.
[2] 汤连生, 张鹏程, 王洋. 水作用下岩体断裂强度探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2002, 21(增1): 2154-2158.
TANG Lian-sheng, ZHANG Peng-cheng, WANG Yang. On fracture strength of rocks with cracks under water pressure and chemical damage[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 21(S1): 2154-2158.
[3] 汤连生, 张鹏程, 王思敬, 等. 水-岩土化学作用与地质灾害防治[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1999, 10(3): 61-69.
TANG Lian-sheng, ZHANG Peng-cheng, WANG Si-jing, et al. Mechanical properties of rock and soil influenced by hydrochemical action and geological hazard control[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1999, 10(3): 61-69.
[4] 冯夏庭, 赖户政宏. 化学环境侵蚀下的岩石破裂特性(第一部分): 试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2000, 19(4): 403-407.
FENG Xia-ting, Seto M. Rock fracture behaviors under chemical corrision (Part 1): Experiment study[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 19(4): 403-407.
[5] 马水山, 雷俊荣, 张保军, 等. 滑坡体水岩作用机制与变形机理研究[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2005, 22(5): 37-39.
MA Shui-shan, LEI Jun-rong, ZHANG Bao-jun, et al. Study on rock-water interaction and deformation mechanism of landslide[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2005, 22(5): 37-39.
[6] Karfakis M G, Askram M. Effects of chemical solutions on rock fracturing[J]. Int J Rock Mech Sci & Geomech Abstr, 1993, 37(7): 1253-1259.
[7] Feucht L J, Logan M. Effects of chemically active solutions on shearing behavior of a sandstone[J]. Tectonophysics, 1990, 175(1): 159-176.
[8] 阮波, 张向京. 武广客运专线路基改良填料的试验研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2008, 5(1): 64-67.
RUAN Bo, ZHANG Xiang-jing. Experiment study on filling material Improvement for the embankment of Wuhan-Guangzhou railway passenger line[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2008, 5(1): 64-67.
[9] 龚晓南. 高等土力学[M]. 杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 1996: 33-34.
GONG Xiao-nan. Advanced soil mechanics[M]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press, 1996: 33-34.
[10] 邵光辉, 刘松玉, 杜广印, 等. 海相黏土孔压静力触探试验指标与离子化学特性的关系[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007, 29(10): 1582-1586.
SHAO Guang-hui, LIU Song-yu, DU Guang-yin, et al. Correlation between cone penetration tests index characteristics and ion chemistry of marine clay[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(10): 1582-1586.
[11] Kurup P U, Voyiadjis G Z, Tumay M T. Calibration chamber studies of piezocone test in cohesive soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1994, 120(1): 81-101.
[12] 贺建清, 张家生. 石灰改良软土路基填料饱水强度特性研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2004(4): 4-7.
HE Jian-qing, ZHANG Jia-sheng. Improving the strength properties of water-saturated packings for soft roadbed using lime—A study[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2004(4): 4-7.
[13] 赵明华, 张玲, 刘敦平. 散体材料桩复合地基桩土应力比分析[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 38(3): 555-560.
ZHAO Ming-hua, ZHANG Ling, LIU Dun-ping. Bearing capacity calculating method of discrete material pile composite foundation[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2007, 38(3): 555-560.
[14] 王贻明, 吴爱祥, 左恒, 等. 微粒渗滤沉积作用对铜矿排土场渗流特性的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(12): 2074-2078.
WANG Yi-ming, WU Ai-xiang, ZUO Heng. Effect of particles sedimentation during leaching on seepage characteristic of copper dumps[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2007, 17(12): 2074-2078.
[15] 庄心善, 王功勋, 朱瑞赓, 等. 粉煤灰炉渣加固土的室内无侧限抗压强度试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2005, 27(8): 965-969.
ZHUANG Xin-shan, WANG Gong-xun, ZHU Rui-geng, et al. Experimental study on unconfined compressive strength of clays stabilized with fly ash and slag[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2005, 27(8): 965-969.
收稿日期:2008-12-05;修回日期:2009-03-05
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(50774093);高等学校博士学科点专项科研基金资助项目(20060533071)
通信作者:王军(1978-),男,湖南澧县人,博士研究生,从事岩土工程数值计算和设计研究;电话:13787420570;E-mail: wjinlin@126.com
(编辑 陈灿华)