文章编号:1004-0609(2013)05-1331-07
ECAP及后续退火对Cu-Mg合金组织与性能的影响
朱承程1,马爱斌1, 2,江静华1, 2,宋 丹1, 2,李学斌3,陈建清1
(1. 河海大学 力学与材料学院,南京 210098;
2. 常州市河海科技研究院有限公司,常州 213164;
3. 中铁建电气化局集团 康远新材料有限公司,江阴 214521)
摘 要:采用等通道转角挤压(ECAP)和后续热处理对高铁接触导线用铜镁合金进行微观组织调控以获得优良的综合性能。结果表明:Cu-0.2%Mg(质量分数)和Cu-0.4%Mg合金在200 ℃下经多道次ECAP加工后,其晶粒组织明显细化,微观硬度和抗拉强度提高明显,同时仍保持了良好的导电率和伸长率。ECAP加工后Cu-Mg合金经不同温度退火后,其力学性能有较明显的下降,而导电率和伸长率有所提高。与Cu-0.2%Mg合金相比,Cu-0.4%Mg合金具有更好的抗高温软化能力。
关键词:Cu-Mg合金;高速铁路;ECAP;退火;力学性能;导电性能
中图分类号:TG379 文献标志码:A
Microstructure and properties of Cu-Mg alloys processed by ECAP and subsequent annealing
ZHU Cheng-cheng1, MA Ai-bin1, 2, JIANG Jing-hua1, 2, SONG Dan1, 2, LI Xue-bin3, CHEN Jian-qing2
(1. College of Mechanics and Materials, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China;
2. Hohai Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd, Changzhou 213164, China;
3. China Railway Construction Electrification Bureau Group Kang Yuan New Materials Co., Ltd, Jiangyin 214521, China)
Abstract: The microstructures of Cu-Mg alloys used for high-speed railway contact wire were changed and controlled to obtain excellent overall performance via equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) and subsequent annealing. The results show that multi-pass ECAP at 200 ℃ makes the grain size of Cu-0.2%Mg (mass fraction) and Cu-0.4%Mg alloys obviously refine, which significantly improves their micro-hardness and tensile strength while maintain their good electrical conductivity and elongation. After annealing at different temperatures, the mechanical properties of the ECAP Cu-Mg alloys are obviously declined but their electrical conductivity and elongation are increased. The Cu-0.4%Mg alloy has better resistance of high temperature softening than the Cu-0.2%Mg alloy.
Key words: Cu-Mg alloy; high-speed rail; ECAP; annealing; mechanical property; conductivity
高强高导铜合金可广泛应用于大规模集成电路引线框架、电气工程开关触桥、连铸机结晶器内衬、高脉冲磁场导体、大功率异步牵引电动机转子和电气化铁路接触导线等[1]。尽管当前合金化及常规塑性加工仍是提高铜合金强度的主要手段,但是这些强化方法会在晶体内引入大量的微观缺陷(如点缺陷、位错、第二相等)而导致其导电性能下降[2]。如Cu-Cr系合金经冷加工后具有较高的抗拉强度,但导电率很低,只有经过较高温度的退火后才能获得良好的导电性能,故此加工工艺十分烦琐[3-4]。国内外学者正尝试用特殊的加工手段以兼顾铜合金高强度、高导电性这两种重要性能[5-6],但这些方法离商业化生产还有很长的距离。目前,我国已有厂家借助Conform后再经冷加工的方法获得了高强度的Cu-0.4%Mg(质量分数)合金,其抗拉强度达到了522 MPa,但是导电率只有68.6%IACS(国际退火铜标准规定:17.241 nΩ·m被定义为100%IACS)[7]。尽管该合金已成功应用于我国高速铁路接触线,但要满足高铁进一步提速的要求还需提升其综合性能。可见,如何兼顾铜合金的高强度和高导电性是当前一项极具研究价值的课题。
等通道转角挤压(ECAP)加工技术被研究人员认为是最有希望获得高强、高韧和良好物理性能金属块体材料的手段之一,近年来备受材料学界的重视[8]。已有研究表明,商业纯铜材料经高道次ECAP加工后获得了超细晶组织,而且具有高比例的大角度晶界、低的晶格应力和低的位错密度等微观特征[9],故而使铜材在提高强度的同时还能保持良好的韧性。利用ECAP加工及后续热处理组合工艺有望开发出高强高导铜合金,目前尚无相关报道。本文作者基于合作企业现有基础,以Conform态Cu-Mg系合金为研究对象,在200 ℃下进行ECAP加工细化其组织,而后进行不同温度的退火处理,利用现代测试手段研究ECAP加工及后续退火对试样微观组织、力学性能和导电性能的影响,旨在为提升国有产品质量及其商业化生产提供理论依据和技术支持。
1 实验
实验原材料是由中铁建电气化局集团康远新材料有限司提供的Conform态Cu-0.2%Mg(以下简称为0.2Mg)和Cu-0.4%Mg(以下简称为0.4Mg)合金杆坯。利用线切割将合金杆坯加工成19.5 mm×19.5 mm×40 mm的块状样品, 采用自制的ECAP模具(Ф=90°,Ψ=0°,如图1所示)进行多道次挤压加工。选用石墨润滑剂涂在试样表面,以减小试样在挤压过程中与模具之间的摩擦力。将样品随模具一起加热到200 ℃并保温10 min,然后开始挤压。完成1道次挤压之后,将试块倒置,并沿中心轴线旋转180°,然后进入下一道次加工。将部分ECAP试样放置在箱式电阻炉中分别经200和300 ℃退火,保温时间均为2 h。其中300 ℃为测定电气化铁路接触导线耐热性的软化温度点。
利用Olympus BX51M光学显微镜和JEN-2000EX透射电子显微镜观察ECAP后试样的显微组织形貌,所观察的面与挤压方向平行。用HXD-1000TC维式硬度计测试其微观硬度,荷载质量为100 g,加载时间为15 s。用RGM-4050型电子拉伸仪测试应力—应变曲线,拉抻试样的横截面为3 mm×3 mm,标距为15 mm。用HITACHI S-3400N扫描电子显微镜观察拉伸试样的断口形貌。用QJ36S型四端式直流低电阻测试仪测量试样的导电率。

图1 ECAP示意图[10]
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of ECAP[10]
2 结果及分析
2.1 ECAP及后续退火对Cu-Mg微观组织的影响
图2所示为0.2Mg和0.4Mg合金在ECAP加工前后的金相组织。由图2可以看出,试样经4道次ECAP加工后,最初的等轴状晶粒在强烈的剪切力作用下被细化拉长,形成带状组织;经16道次ECAP加工后,利用光学显微镜已无法清楚地分辨晶粒的形貌特征,只能观察到细密的塑性变形流纹。
图3所示为0.2Mg合金经16道次ECAP加工后的TEM像。从图3(a)以及右上角均匀分布的环状电子衍射花样图可以看出,经16道次加工后,晶粒细化至500 nm以下,同时含有高比例的大角度晶界。图3(b)为区域放大图,从中可以看出晶粒内部的位错密度较低。这主要是由两方面原因造成的:1) 当晶粒细化至纳米级别时,晶粒的内部位错更容易扩散到晶界上,被晶界所吸收,或形成自由位错胞,这是一个能量降低的过程;2) 试样在ECAP加工的过程中,晶粒会发生动态回复再结晶的行为,导致晶粒内的部分位错被湮灭[9-11]。从图3(c)可以看到,晶粒内部有孪晶的形成,这是晶界处产生的不完全位错交互作用的结果。因为在ECAP加工的过程中,试样受到很高的外界应力而发生剧烈的剪切应变,导致在晶界处不断的有位错产生,并在晶界和孪晶界处发生位错反应而生成孪晶,最终形成了一系列相平行的孪晶[12]。
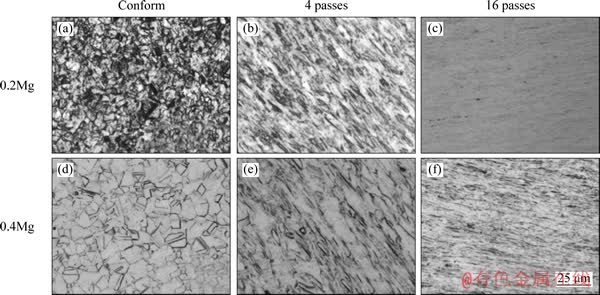
图2 铜镁合金在ECAP加工前后的金相组织
Fig. 2 OM micrographs of Cu-Mg alloy before and after ECAP processing

图3 0.2Mg合金经16道次ECAP加工后的TEM像
Fig. 3 TEM images of 0.2Mg alloy processed by 16 passes of ECAP processing

图4 ECAP试样经退火后的金相组织
Fig. 4 OM micrographs of ECAP samples after annealing
图4所示为0.2Mg和0.4Mg合金经16道次ECAP加工后在200和300 ℃退火的金相组织。由图4(a)和(c)可见,试样经200 ℃退火后,微观组织没有发生明显的变化。因为在200 ℃的退火温度下,微观组织的变化仍处回复阶段,不发生大角度晶界的迁移,所以晶粒的形状和大小与变形态相同,仍保持带状组织。从图4(b)和(d)可以看到,试样经300 ℃退火后,微观组织有了较明显的变化,晶粒由带状组织开始向等轴状演变。说明在300 ℃的退火温度下,微观组织发生了再结晶的行为,但是由于退火时间较短,限止了晶粒的继续长大。
2.2 ECAP加工以及后续退火对Cu-Mg合金力学性能的影响
2.2.1 微观硬度
图5所示为Cu-Mg合金经ECAP加工以及后续退火后的微观硬度随加工道次的变化曲线。从图5中可以得到以下几个规律:1) 与Conform态0.2Mg合金相比,Conform态0.4Mg合金的微观硬度较低。这主要与试样的晶粒尺寸有关,从图2可以看到,Conform态0.4Mg合金的晶粒更粗大一些,所以硬度也较低。2) 不同Mg含量的Cu-Mg合金的微观硬度随着挤压道次的增加而增加,尤其在前几个道次,微观硬度的增加幅度较大。这是因为经低道次的ECAP加工时,晶粒在剧烈剪切力的作用下产生大量的位错,导致试样产生了明显的加工硬化现象;而经更高道次的ECAP加工时,晶粒逐渐细化,位错容易在晶界处被吸收,使晶粒内部的位错密度趋于饱和,其时硬度的增加主要是晶粒细化的结果[13-14]。3) ECAP试样经退火后,微观硬度有不同程度的降低,而且随着退火温度的升高,下降的幅度增大。这是因为在200 ℃的退火温度下,晶体内部会发生点缺陷以及位错的运动和重新分布的现象,部分位错被湮灭;而在300 ℃退火时,晶粒发生了再结晶的行为,晶体内的缺陷密度明显降低,导致硬度下降较大。4) 与0.2Mg合金相比,0.4Mg合金的ECAP试样经退火后,其微观硬度下降的幅度较小。这是由于Mg含量的增加,阻碍了退火过程中位错的滑移和晶界的迁移,提高了合金的回复再结晶温度点,从而降低了回复和再结晶的速率[15]。

图5 ECAP加工道次以及后续退火对合金微观硬度的影响
Fig. 5 Effect of passes of ECAP and annealing after ECAP on microhardness
2.2.2 应力—应变结果与分析
图6和7所示为Cu-Mg合金经ECAP加工以及后续退火后的应力—应变曲线。从图6可知:1) 与Conform态0.2Mg合金试样相比,Conform态0.4Mg合金试样具有更高的抗拉强度,但伸长率较之下降。这是因为镁含量的增加使溶质原子与位错及晶界的交互作用增强,提高了位错滑移的阻力,使加工硬化的速率增大,从而在提高合金强度的同时降低了合金的塑性。2) 0.2Mg和0.4Mg合金经4道次ECAP加工后,其屈服强度和抗拉强度都明显提高,但伸长率有较大程度的降低。这是因为试样经低道次的ECAP加工后,产生的加工硬化现象在提高合金强度的同时损害了合金的塑性变形的能力。3) 0.2Mg和0.4Mg合金经16道次ECAP加工后,其最大抗拉强度和断裂伸长率分别达到了566.3 MPa和12.8%及589.1 MPa和14.3%。可见,与4道次ECAP试样相比,经16道次ECAP加工后的试样具有更高的抗拉强度,而伸长率却相差不大。这是由于高道次的ECAP加工使晶粒更加细小,晶体内的位错密度降低,导致合金的变形机制由最初的位错滑移向晶界滑移转变,从而使合金在提高强度的同时仍具有较好的塑性变形能力[16]。同时,经高道次ECAP加工后,部分孪晶的生成也有利于提高合金的抗拉强度和塑性,而且在ECAP加工的过程中,镁含量的增加使试样晶体内部的形变应力增大,这也有利于变形孪晶的萌生[15]。

图6 Cu-Mg合金经ECAP加工后的应力—应变曲线
Fig. 6 Stress—strain curves of Cu-Mg alloy subjected to ECAP process
从图7可以看出,16道次ECAP态0.2Mg和0.4Mg合金经200和300 ℃退火后,其抗拉强度随着退火温度的升高而降低,而伸长率随着温度的升高而提高。与ECAP态0.2Mg合金相比,ECAP态0.4Mg合金经退火后的抗拉强度值下降幅度降小,具有更好的抗软化能力。这一结果与ECAP试样经退火后的微观硬度的变化趋势一致。
2.2.3 断口形貌分析
图8所示为0.2Mg合金ECAP前后以及退火后的拉伸断口形貌。从图8可以看到很明显的圆锥形韧窝和拉长的韧窝,可以判定试样属于韧性断裂。从图8(a)可以看出,Conform态拉伸试样的断口形貌中,其韧窝的尺寸大小均匀,呈等轴状,韧窝有较大的深度,说明Conform态试样的塑性很好。从图8(b)可以看出,经4道次ECAP加工后,试样断口中的韧窝尺寸明显减小,均匀度和深度有所减弱,这主要是晶粒细化的结果。从图8(c)可以看出,试样断口形貌主要是以拉长形状的韧窝为主。这是因为经16道次ECAP加工后,其晶粒已细化至500 nm以下,当试样受到外加的拉力时,其晶粒更容易与外加拉力形成45 ℃的剪切面,从而形成晶界滑移,所以Conform态试样经ECAP多道次加工后,仍具有较好的塑性变形能力[17]。从图8(d)可看出,16道次的ECAP试样经300 ℃退火后,其断口形貌发生了明显的变化。与未经退火的16道次ECAP试样的断口相比,其韧窝尺寸变大,而且均匀度较差。这主要是ECAP试样在退火的过程中,晶粒发生了回复再结晶的行为,导致部分晶粒长大的结果。

图7 ECAP态Cu-Mg合金经退火后的应力—应变曲线
Fig. 7 Stress—strain curves of Cu-Mg alloy subjected to annealing after ECAP process

图8 不同加工态的Cu-0.2%Mg试样的拉伸断口SEM 像
Fig. 8 SEM images of fracture surface of Cu-0.2%Mg samples after different processes
2.3 ECAP加工以及后续退火对Cu-Mg合金导电性能的影响
图9所示为Cu-Mg合金经ECAP加工及后续退火后导电率的变化。从图9可知:1) Mg含量的增加显著降低了合金的导电性能。因为材料的电阻率与晶体结构中的缺陷(如空位、间隙原子、位错、晶界等)密切相关,而且点缺陷对电子的散射作用比位错引起的更为强烈,所以对材料的导电性能损害较大[15]。2) 合金试样经1道次ECAP加工后,导电率下降较快,这主要是位错密度增加结果;而经4~12道次ECAP加工后,其导电率趋于稳定甚至有所恢复,因为经高道次ECAP加工后,晶体内的位错密度开始下降[18]。3) 试样经16道ECAP加工后,导电率又出现了下降,因为经16道次加工后,晶界增多,尤其是大角度晶界比例的提高对金属导电率的损害较大[19]。如图9所示,0.2Mg和0.4Mg合金经16道次ECAP加工后,其导电率分别为85.2%IACS和79.4%IACS,而Conform态0.2Mg和0.4Mg合金经常规塑性加工后其导电率分别只有78.4%IACS和68.6%IACS。

图9 不同退火温度时Cu-Mg合金导电率与ECAP加工道次的关系
Fig. 9 Relationship between conductivity of Cu-Mg alloy and number of ECAP passes at different annealing temperatures
ECAP试样经退火后,导电率随退火温度的升高而升高。因为退火后,晶体内部的位错密度降低,微观组织的回复和再结晶使晶体点阵的畸变程度减弱,而且其回复的程度随着退火温度的升高而增加,所以退火后合金的导电率会相应的提高。
3 结论
1) Cu-Mg合金经16道次的ECAP加工后,晶粒组织细化至500 nm以下,晶粒内部的位错密度较低,晶粒内部有部分孪晶生成。
2) Cu-Mg合金的微观硬度和抗拉强度随着ECAP加工道次的增加而增加,而导电率则随着加工道次的增加而逐渐降低。合金经多道次的ECAP的加工后,仍保持了较好的塑性变形能力。
3) ECAP加工后的Cu-Mg经不同温度退火后,其微观硬度和抗拉强度有所下降,而导电率有所提升。
REFERENCES
[1] 尹志民, 张生龙. 高强高导铜合金研究热点及发展趋势[J]. 矿冶工程, 2002, 22(2): 1-5.
YIN Zhi-min, ZHANG Sheng-long. Hotspots and developing tendency on high-strength and high-conductivity copper alloys[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2002, 22(2): 1-5.
[2] LU K, LU L, SURESH S. Strengthening materials by engineering coherent internal boundaries at the nanoscale[J]. Science, 2009, 324(16): 349-352.
[3] HE W X, YU Y, WANG E D, SUN H F, HU L X, CHEN H. Microstructures and properties of cold drawn and annealed submicron crystalline Cu-5% Cr alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2009, 19(1): 93-98.
[4] OLOFINJANAA A O, TAN K S. Achieving combined high strength and high conductivity in re-processed Cu-Cr alloy[J]. Journal of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering Selected, 2009, 35(1): 14-20.
[5] LU L, SHEN Y, CHEN X, QIAN L, LU K. Ultrahigh strength and high electrical conductivity in copper[J]. Science, 2004, 304(4): 422-426.
[6] HAN K, WALSH R P, ISHMAKU A, TOPLOSKY V, BRANDAO L, EMBURY J D. High strength and high electrical conductivity bulk Cu[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2004, 84(34): 3705-3716.
[7] 赵大军, 唐丽, 管桂生. 我国电气化铁道用接触线的现状和发展趋势[J]. 铁道机车车辆, 2008, 28(5): 74-77.
ZHAO Da-jun, TANG Li, GUAN Gui-sheng. Current situation and development tendency of Chinese contact wires for electric railway[J]. Railway Locomotive & Car, 2008, 28(5): 74-77.
[8] VALIEV R Z, ISLAMGALIEV R K, ALEXANDROV I V. Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2000, 45(2): 103-189.
[9] DALLA T F, LAPOVOK R, SANDLIN J, THOMSON P F, DAVIES C H J, PERELOMA E V. Microstructures and properties of copper processed by equal channel angular extrusion for 1-16 passes[J]. Acta materialia, 2004, 52(16): 4819-4832.
[10] XU S, ZHAO G, REN G, REN G, MA X. Numerical simulation and experimental investigation of pure copper deformation behavior for equal channel angular pressing/extrusion process[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2008, 44(2): 247-252.
[11] CARLTON C E, FERREIRA P J. What is behind the inverse Hall-Petch effect in nanocrystalline materials?[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007, 55(11): 3749-3756.
[12] ZHU Y T, NARAYAN J, HIRTH J P, MAHAJAN S, WU X L, LIAO X Z. Formation of single and multiple deformation twins in nanocrystalline fcc metals[J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57(13): 3763-3770.
[13] SHAARBAF M, TOROGHINEJAD M R. Nano-grained copper strip produced by accumulative roll bonding process[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 473(1/2): 28-33.
[14] HABIBI A, KETABCHI M, ESKANDARZADE M. Nano-grained pure copper with high-strength and high-conductivity produced by equal channel angular rolling process[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2011, 211(6): 1085-1090.
[15] 胡赓祥, 蔡 珣, 戎咏华. 材料科学基础[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2006: 80-212.
HU Geng-xiang, CAI Xun, RONG Yong-hua. Fundamentals of materials science[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 2006: 80-212.
[16] ZHU Y T, LIAO X. Nanostructured metals: Retaining ductility[J]. Nature Materials, 2004, 3(6): 351-352.
[17] YAMASHITA A, YAMAGUCHI D, HORITA Z, LANGDON G. Influence of pressing temperature on microstructural development in equal-channel angular pressing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2000, 287(1): 100-106.
[18] MOLODOVA X, GOTTSTEIN G, WINNING M, HELLMIG R. Thermal stability of ECAP processed pure copper[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 460(1): 204-213.
[19] DANNENBERG R, KING A H. Behavior of grain boundary resistivity in metals predicted by a two-dimensional model[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2000, 88(5): 2623-2633.
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51141002);常州市科技支撑(工业)计划资助项目(CE20110061)
收稿日期:2012-07-12;修订日期:2012-09-30
通信作者:马爱斌,教授,博士;电话:025-83787239;E-mail:aibin-ma@hhu.edu.cn