DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.06.031
剪切荷载下岩体结构面-浆体-锚杆相互作用机理宏细观研究
王刚1, 2, 3,袁康1, 3,蒋宇静1, 3,吴学震1, 2, 3
(1. 山东科技大学 矿山灾害预防控制省部共建国家重点实验室培育基地,山东 青岛,266590;
2. 山东科技大学 山东省土木工程防灾减灾重点实验室,山东 青岛,266590;
3. 山东省矿山灾害预防控制重点实验室,山东 青岛,266590)
摘要:基于PFC中FISH语言,采用双线性锚杆本构模型对岩体加锚节理面在剪切荷载作用下的力学行为进行数值模拟研究,通过变化锚杆刚度和浆体强度,深入研究岩体结构面-浆体-锚杆相互作用下锚固体系宏细观力学响应。结果表明:加锚节理面的力学响应与锚固结构的力学性质密切相关。锚杆刚度越大,节理面宏观抗剪强度越高;随着锚杆刚度的增加,岩体和浆体中的裂纹也越来越多,锚杆对浆体和岩体的损伤逐渐增加。岩体结构面-浆体-锚杆相互作用,裂纹的产生首先起于节理面上和锚杆与节理面交叉处,随着剪切位移的不断增加,节理面上的裂纹在接触力集中的地方继续产生,而在锚杆周围则由锚杆与节理面交叉处向锚杆两端继续扩展,且裂纹集中在锚固体系的受压侧,主要为由“压致拉”机理导致的张拉裂纹。浆体的强度过小或过大都可能导致锚固体系中裂纹数量的增多,且裂纹以张拉裂纹为主。当浆体强度较低时,裂纹主要集中在浆体中,而当浆体强度较高时,裂纹主要集中在岩体中。因此,在对节理岩体进行加固的过程中,应综合考虑节理面宏观上的抗剪强度和细观上锚固体系的损伤,以实现锚固体系的宏细观耦合支护。分析结论对于节理岩体的锚固支护设计具有参照价值。
关键词:颗粒流;岩石节理面;锚杆;直剪试验;宏细观耦合
中图分类号:TD 353 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2015)06-2207-09
Macro-micro mechanical on joint -grout-bolt interaction in rockmass subjected to shear loading
WANG Gang1, 2, 3, YUAN Kang1, 3, JIANG Yujing1, 3, WU Xuezhen1, 2, 3
(1. State Key Laboratory of Mining Disaster Prevention and Control Co-founded by
Shandong Province and the Ministry of Science and Technology,
Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China;
2. Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Civil Engineering Disaster Prevention and Mitigation,
Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China;
3. Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Mining Disaster Prevention and Control, Qingdao 266590, China)
Abstract: The mechanical behavior of bolted rock joints was researched by using bilinear constitutive model of bolt in virtue of the inner-embed FISH language of PFC based on DEM. Through a variation of the bolt’s elastic modulus and the strength of grout, their influence on macroscopic mechanical response and microscopic mechanical response of anchoring system were studied under the bolt-grout-rock interaction. The results show that there is a clear relationship between the mechanical response of bolted rock joint and the mechanical property of anchoring structures. Macroscopic aspect: the stiffer the bolt the more shear strength of bolted rock joint has. Microscopic aspect: the quantity of cracks in grout and rock increase with the increase of bolt’s stiffness so as to result in more damage to anchoring system. Cracks will appear in the joint and the intersection of bolt and joint initially. With the increase of shear displacement, the cracks in joint will be generated at the place whose compressive contact force is very concentrated while the cracks around the bolt will propagate from the intersection of bolt and joint to the two ends of bolt. Besides, the cracks are mainly concentrated on the compression side. Most of the cracks are tension cracks which are induced by compression among particles. The number of cracks in rock and grout will increase when the strength of grout is much larger or smaller. The cracks are mainly tension cracks which are result from the compression among the particles. When the strength of grout is much smaller, the cracks are mainly concentrated on the rock otherwise the cracks will be mainly distributed in grout. Therefore, the shearing strength of bolted rock joint in macroscopic aspect and the damage of anchoring system resulting from anchoring structure in microscopic aspect should be considered comprehensively while reinforcing jointed rock mass so as to realize the macroscopic-microscopic coupling support. It has a certain guiding significance for the bolt supporting design of joint rock mass.
Key words: PFC; rock joint; rock bolt; direct shear test; macroscopic-microscopic coupling
节理普遍存在于岩体中,节理岩体中块体常常沿着节理面发生剪切滑移或错动,导致节理岩体的稳定性和整体性降低。锚杆可以限制块体的层间错动或滑移,提高岩体的稳定性,现已广泛用于节理岩体锚固领域,如图1所示。然而,由于岩体的各向异性和节理面发育的复杂性,锚杆加固节理岩体的机制非常复杂,因此,国内外学者对此进行了大量的研究和探索。

图1 锚杆在节理岩体锚固中的应用
Fig. 1 Application of bolt in jointed rock mass
国外方面,Spang和Egger[1]研究了剪切过程中锚杆的变形,发现了变形后锚杆中2个奇异点,一个在锚杆与节理面交叉处,另一个在节理面两侧的塑性铰处。Pellet等[2]根据加锚节理剪切过程中的轴力和剪力特征以及锚杆的变形特征,提出了一种新的锚杆失效机制的分析模型,建立了锚杆倾角、锚杆的力学性质岩石强度等与锚固节理抗剪强度的关系。Aziz等[3]通过室内双剪试验装置和ANSYS有限元软件研究了围岩强度对全长锚固锚杆的剪切行为的影响。Aziz等[4]又在原来研究成果的基础上研究了灌浆体厚度对锚杆-浆体-混凝土基体相互作用的影响和对锚杆弯曲行为的影响。Jalalifar 等[5]通过室内双剪试验和有限元模拟研究了锚杆形状、围岩强度和锚杆预应力对全长锚固锚杆弯曲变形行为的影响。后来,Jalalifar等[6]采用5种不同类型的锚杆进行了双剪试验和数值模拟,研究了锚杆的受力和破坏机制。我国学者在加锚节理剪切方面也进行了很多的研究,并取得了不少研究成果。刘波[7]对加锚节理锚杆横向作用进行了系统的物理试验,对锚杆的横向效应和剪切过程中的综合抗力进行了研究。杨松林等[8]提出了定量评价锚杆对节理加固作用的理论公式,并利用提出的公式研究了影响锚杆加固作用的一些重要因素。伍佑伦等[9]采用线弹性断裂力学的方法,分析了拉剪综合作用下锚杆对裂纹尖端应力强度因子产生的贡献,发现锚杆能够加固节理岩体的重要原因就是锚杆明显降低了对岩体破坏产生主要作用的应力强度因子。温进涛等[10]对含结构面岩体的锚索锚固机理做了室内模拟实验研究,并监测了锚索加载过程中的受力变化情况。Song[11]利用数值分析软件ANSYS研究了锚杆的横向作用机理,分析了加锚非连续岩体与锚杆的错动变形和受力规律。刘爱卿等[12]通过FLAC3D软件着重研究了围岩强度、锚杆以及预应力对节理面抗剪性能的影响。由此可见:现有的成果中很少有人对岩体结构面-浆体-锚杆之间的相互作用进行系统的研究,但是锚固体系中各种介质的相互作用却是真实存在的,如图2所示,是一个典型的锚固体系受剪之后岩体结构面-浆体-锚杆相互作用示意图。研究锚固体系中结构面-浆体-锚杆的相互作用对指导锚杆支护设计是有意义的。本文作者在现有研究成果的基础上,采用离散元软件颗粒流程序PFC2D对锚固节理中岩体结构面-浆体-锚杆相互作用进行探索,研究了锚杆的刚度、浆体的强度等对锚固系统的影响。
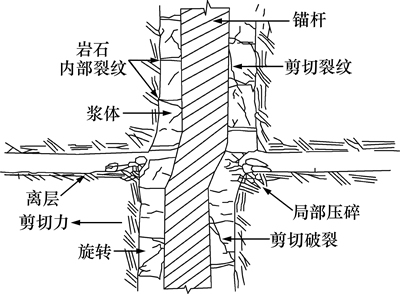
图2 岩体-浆体-锚杆相互作用示意图
Fig. 2 Illustration of interaction among rock-grout-bolt
1 颗粒流程序简介与平行黏结模型
PFC[13]是由Itasca公司开发的商业离散元软件,现已被广泛用于岩石力学问题的研究。PFC采用颗粒集合体表征介质,以牛顿第二定律和力与位移的关系为基础,可以模拟圆形颗粒的运动与相互作用问题,也可以通过2个或多个颗粒与其直接相邻的颗粒连接形成任意形状的组合体来模拟块体结构问题。颗粒单元被视为刚性体,它们之间的相互作用是通过接触产生的,其相互作用的本构模型包含3种:接触刚度模型、滑动模型和黏结模型。黏结模型又分为2种:接触黏结模型和平行黏结模型。
平行黏结填充在颗粒接触点邻近区域,可以视为一组弹簧均匀设置在以接触点为中心的2个接触颗粒邻近区域上,既具有法向刚度和切向刚度,也具有法向抗拉强度和切向抗剪强度[13-14]。平行黏结模型中黏结的受力遵循力与位移的关系。平行黏结的受力-位移关系由法向及切向刚度 和
和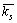 ,抗拉及抗剪强度
,抗拉及抗剪强度 和
和 ,黏结半径因子
,黏结半径因子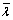 等参数得到。作用于平行黏结上的合力和合力矩可以用
等参数得到。作用于平行黏结上的合力和合力矩可以用 和
和 表示。合力和合力矩又由法向和切向方向的分量组成,可以表示为如下:
表示。合力和合力矩又由法向和切向方向的分量组成,可以表示为如下:
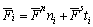 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
其中: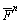 和
和 分别为作用在黏结上的轴向力和切向力,
分别为作用在黏结上的轴向力和切向力, 和
和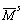 分别为作用在黏结上的轴向弯矩和切向弯矩。
分别为作用在黏结上的轴向弯矩和切向弯矩。
平行黏结一旦形成, 和
和 将会被初始化为零。随后的相对位移增量和相对转动增量所引起的弹性力和力矩将会被叠加到当前数值,由相对位移增量和相对转动增量所产生的弹性力和力矩的表达式如下:
将会被初始化为零。随后的相对位移增量和相对转动增量所引起的弹性力和力矩将会被叠加到当前数值,由相对位移增量和相对转动增量所产生的弹性力和力矩的表达式如下:
 (3)
(3)
 (4)
(4)
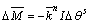 (5)
(5)
式中:A和I分别为平行黏结横截面的面积和惯性矩。在PFC2D中其计算公式如下:
 ,t=1 (6)
,t=1 (6)
 ,t =1 (7)
,t =1 (7)
作用在平行黏结上的最大拉伸应力和剪切应力是由梁弯曲理论得到的,如下式所示:
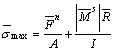 (8)
(8)
 (9)
(9)
当作用在黏结上的最大拉伸应力超过了黏结本身的极限抗拉强度时,黏结就会断裂,并产生张拉裂纹;当作用在黏结上的最大剪切应力超过了黏结本身的极限抗剪强度时,黏结也会断裂,产生剪切裂纹。黏结的破裂过程如图3所示[15]。PFC可以通过内置FISH语言实现对计算过程中裂纹的监测。
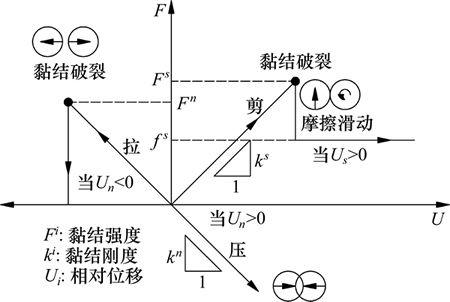
图3 平行黏结破裂机理分析图
Fig. 3 Illustration of yielding process for parallel bond
2 加锚节理岩体的颗粒流直剪模拟
2.1 岩石材料细观参数的选取
为了把岩石的宏细观性质联系在一起,进行剪切试验数值模拟前,需要对细观参数进行校核,获取符合岩石宏观特性的细观参数。为此,通过一系列双轴压缩数值模拟试验来反演模拟岩石细观参数。双轴压缩模型中试样尺寸为50 mm×100 mm,采用的数值试样细观力学参数见表1[16]。
采用上述细观校核参数,分别在围压为0,2,4和6 MPa下进行压缩试验。图4所示为压缩之后的试件的破坏情况,白色的区域是裂纹产生后形成的破裂带。图5所示为该参数下试件的莫尔圆及其强度包络线。由图5可知:该参数下试件的内聚力为10.51 MPa,内摩擦角为25.3°,单轴抗压强度经计算可知为33 MPa。
表1 岩石试样细观参数
Table 1 Micro-parameters of rock sample


图4 不同围压下压缩后的试件
Fig. 4 Samples after biaxial test simulations under different confining pressures
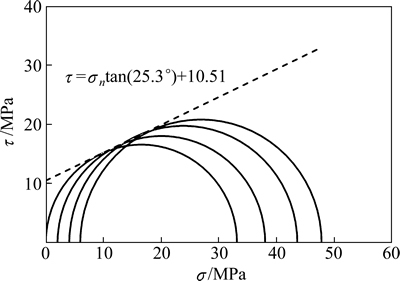
图5 压缩试验的莫尔圆及强度包络线
Fig. 5 Mohr circles corresponding to biaxial test simulations at different confining pressures
2.2 双线性锚杆本构模型
在PFC中锚杆可以用一串相互外切的颗粒组成,锚杆颗粒之间由平行黏结相连,黏结的受力满足力与位移的关系。平行黏结模型既可以传递力,也可以传递弯矩,这一点与实际中锚杆的受力是相一致的,尤其是在节理岩体锚固中,锚杆的受力状态时非常复杂的,一般处于拉力、剪力以及弯矩的共同作用之下。图6(a)所示为未经修改的表示锚杆线弹性变形的本构模型,它的缺点是在与实际中锚杆抗拉强度和弹性模量相联系时,锚杆断裂时伸长率不符合实际要求,只能表示锚杆等金属介质在弹性阶段的特性,不能表示金属介质屈服之后的塑性大变形特征。因此,基于PFC内置FISH语言进行对锚杆本构模型进行修正,将使其既满足实际锚杆的刚度要求,又满足较大的可变形能力要求。如图6(b)所示为修改的锚杆双线性模型,对锚杆设置一个屈服强度,在屈服强度之前,锚杆的应力-应变关系处于线弹性阶段,而当锚杆轴向的应力超过屈服强度后,黏结不会破裂,仍能有一定的承载能力,只不过应力增加的速率降低了。当轴向应力超过黏结的极限抗拉强度时,也就是到达锚杆本身的应变极限时,黏结才破裂,失去承载能力。此外,锚杆与周围介质之间也是有黏结的,当锚杆颗粒与周围介质颗粒之间的黏结破裂而自身的黏结未破裂时,由于颗粒之间存在摩擦因数,锚杆与浆体之间也存在摩擦,这一点也是与实际中的锚杆也是一致的。
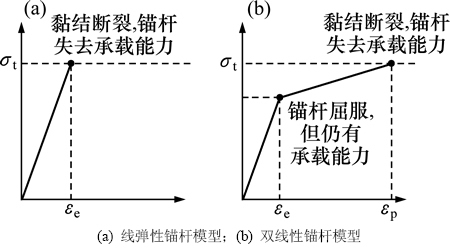
图6 锚杆本构模型示意图
Fig. 6 Illustration of bolt’s constitutive model
2.3 加锚节理岩石直剪试验模型
加锚节理岩石剪切数值模型采用PFC2D程序进行。模型尺寸为100 mm×50 mm,包含上下部岩石、灌浆体以及节理面和锚杆,总计2 921个颗粒。岩石选用压缩试验确定的参数,灌浆体在原来岩石参数的基础上将平行黏结强度变为40 MPa,节理面是由未经黏结的圆形颗粒通过软件自身的命令生成,其平行黏结刚度和平行黏结强度设置为0。锚杆采用平行黏结模型,因为平行黏结模型既可以传递力也可以传递弯矩。模型外部的剪切盒由wall单元组合构成,其中5号墙体作为剪切加载墙,而1号、5号和6号墙体单元共同构成下部主动剪切盒,使得模型在水平方向运动。上部剪切盒水平方向固定,只有2号墙体可以上下运动,而且2号墙体作为伺服墙体,对模型施加恒定的法向荷载。完整模型如图7所示:浅灰色细颗粒代表岩体,中间10个互相外切的浅灰色颗粒代表锚杆,锚杆周围的深灰色颗粒代表灌浆体,黑色的颗粒代表节理面。

图7 加锚节理剪切数值模型
Fig. 7 Numerical shear model of bolted joint
模型试验过程中采用伺服加载、应变控制的方式进行:在剪切过程中,通过对2号墙体采用伺服机制进行对整个模型施加恒定的法向荷载,并把其竖直方向的位移作为法向位移。通过对模型下部右端的5号墙体单元施加恒定的加载速率并将其水平位移作为剪切位移来实现对模型的剪切。以5号和6号墙体单元受到的水平方向不平衡力除以节理面的水平投影面积作为平均剪切应力,当试件的剪切位移达到预设值时试验终止,在剪切过程中动态记录试件的剪切应力、法向位移、锚杆的受力、锚杆颗粒的位移变化以及裂纹的位置、类型和数目等情况。
3 结果分析
3.1 锚杆刚度的影响
3.1.1 锚固体系宏细观分析
在节理岩体锚固中,对支护构件的锚固效果进行评价,往往采用单一的节理面抗剪强度,这种方法有很大的局限性,不能完整地反映锚杆的支护效果。因此,在对支护效果进行评价的时候,本文既采用了宏观上节理面的抗剪强度,还考虑到了锚固体系的细观损伤,对锚固体系进行宏细观分析。人们已经知道,节理锚固中锚杆可以发挥阻滑抗剪的“销钉作用”[1],而销钉作用的发挥在很大程度上就是依靠的锚杆自身的弹性模量,因此,为了突出锚杆本身弹性模量在锚固节理剪切过程中的影响,且忽略锚杆断裂时节理面直接剪切的影响,采用不同刚度的锚杆研究锚杆刚度对锚固体系宏细观行为的影响,锚杆强度设置一样并保证在一定的剪切位移下不会发生断裂失效。根据金属的剪切模量与弹性模量的关系,计算出相应的剪切模量,并给模型中相应参数赋值。设置锚杆的抗拉强度为380 MPa,屈服强度为266 MPa。按以上条件,使模型发生7 mm的剪切位移,监测剪切过程中的裂纹数量和节理面剪切强度。
图8所示为不同锚杆弹模下节理面峰值剪切强度和裂纹数量关系。由图8可以看出:随着锚杆刚度的逐渐增大,裂纹数量虽然有些不稳定,但总体趋势上是随着锚杆弹模的增加而逐渐增多的。当锚杆弹性模量小于15 GPa时,节理面峰值剪切强度的增长速率大,而当锚杆的弹性模量超过15 GPa时,峰值剪切强度虽然有所增加,但是增加的速率越来越小。这表明,锚杆本身的刚度对锚固系统的行为有着显著的影响,单纯地增加锚杆的刚度虽然会导致节理面抗剪强度的增加,但是也会对锚固体系造成越来越大的损伤,而锚固体系的局部损伤有可能导致新的破裂带的产生,进而导致整体的失稳。因此,在对节理岩体进行锚杆支护的时候,不能无限制的增加锚杆的刚度,还应该考虑锚杆对岩体的损伤,达到既能提高节理面的抗剪强度又能保证锚杆对锚固体系的损伤程度较低的目的,实现宏细观耦合支护。

图8 不同锚杆弹模下节理面峰值剪切强度和裂纹数量
Fig. 8 Peak shear stress and number of cracks under different elastic modulus of bolt
3.1.2 细观裂纹分析
锚固节理在剪切的过程中,由于锚杆的弯曲变形,加载侧锚杆处于受压状态,非加载侧则为受拉状态;而由于浆体和锚杆之间很好的黏结,导致相邻近的浆体和岩体的应力状态在加载侧和非加载侧分别为受压和受拉状态,如图9所示。随着剪切位移的不断增加,锚杆会发生弯曲变形,裂纹也会由于颗粒之间的挤压和滑移而不断产生。在受压区域,由于颗粒之间的相互挤压,产生了大量的裂纹,且裂纹的类型以张拉裂纹为主,这符合压制拉裂纹产生的机理,如图10所示。图11所示为锚固体系中裂纹的扩展过程示意图。从图11可以看出:当剪切位移较小的时候,锚杆与周围颗粒之间的接触或挤压还不剧烈,锚杆弯曲变形很小,周围裂纹很少,裂纹最初主要产生于节理面上;而随着剪切位移的不断增加,节理面和锚杆周围的裂纹逐步扩展,尤其是锚杆周围的裂纹扩展速度最快,裂纹开始主要集中在锚杆与节理面的交叉处,然后向锚杆的两端扩展。最后,当剪切位移很大时,裂纹主要集中在节理面上和锚杆周围,且锚杆周围以受压区域为多。图12所示为锚固体系中粒间接触力的分布。由图12可以看出,在剪切过程初期,粒间接触力主要集中在节理面上,随着剪切过程的继续,粒间接触力主要集中在锚杆周围。裂纹的分布区域与接触力集中的区域吻合。

图9 锚固体系应力状态图
Fig. 9 Stress state of bolted rock joint system

图10 压致拉裂纹产生的机理示意图
Fig. 10 Illustration of compression induced tension cracks mechanism

图11 岩体结构面-浆体-锚杆相互作用产生裂纹扩展过程
Fig. 11 Crack propagation under interaction among rockmass joint-grout-bolt

图12 岩体结构面-浆体-锚杆相互作用粒间接触力扩展过程
Fig. 12 Intergranular contact force under interaction among rockmass joint-grout-bolt
3.1.3 锚杆受力分析
锚固体系中锚杆的受力情况对于评价锚固效果以及防止锚固体系中锚杆的屈服破坏有一定的参考意义,在剪切过程中监测锚杆最大轴向应力和最大剪切应力随剪切位移的变化情况。
锚杆的最大轴向应力变化情况如图13所示。在剪切过程中,随着剪切位移的不断增加,锚杆所受的轴向应力大致可以分为3个阶段。当剪切位移较小的时候,由于锚杆与周围介质之间接触的不是很密实,锚杆开始并没有充分发挥横向的抗剪作用,轴向应力较小,随着剪切位移的不断增加,锚杆的横向抗剪作用开始发挥,导致其轴向应力急剧增加,从图13可以看出:锚杆刚度的不同,轴向应力的增加速率也是不一样的。刚度越大,轴向应力增长的越剧烈,在很小的剪切位移下锚杆就已经发生屈服。而当锚杆的轴向应力超过其屈服强度时,轴向应力的增加速率就变得很缓慢了且具有小幅震荡的特征这主要是由于离散元方法造成了模型体系存在一定的不均匀性,但由监测到的数据显示,在相同的剪切位移下,锚杆刚度越大,轴向应力也越大。最后,锚杆由于本身的应变率超过其应变极限时而发生断裂,因此,在实际应用中,应该使用大变形高强锚杆,防止其较快地屈服并保证其在大变形条件下仍然具有足够的承载力。
锚杆最大剪切应力变化情况如图14所示,锚杆的刚度越大,越能在较短的剪切位移下达到最大值,而刚度较小的时候,其最大剪应力在剪切过程中会有些浮动,这是由于锚固体系不是由各向同性介质构成,而是由离散的颗粒组成导致的。当锚杆屈服后,剪切应力基本上维持不变。

图13 不同弹性模量下锚杆最大轴向应力趋势
Fig. 13 Tendency of maximum axial stress in bolt with different elastic modulus
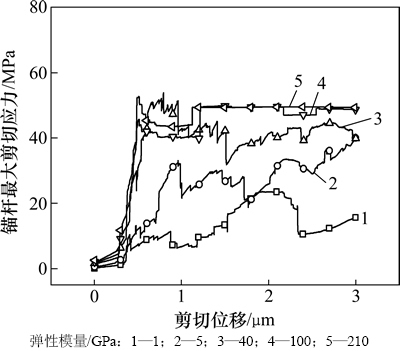
图14 不同弹性模量下锚杆最大剪切应力趋势
Fig. 14 Tendency of maximum shear stress in bolt with different elastic modulus
3.2 浆体强度的影响
浆体颗粒之间的黏结的强度对锚固体系中细观裂纹的分布影响很大,宏观影响主要表现在节理面抗剪强度上,而对锚杆的力学行为影响不是很大,因此,将浆体颗粒的黏结强度分别设置为20,40,60,80和100 MPa,研究浆体强度对锚固体系中宏细观行为的影响。
由图15可以看出:随着浆体强度的增加,裂纹的数量先减小后增加,而峰值剪切强度的值随着浆体强度的增加开始是逐渐增加的,而当增加到一定的程度后有小幅度的下降然后保持不变。裂纹主要集中在浆体和岩石中,2个界面上的裂纹数量有限,锚固剂中裂纹的数量是随着浆体强度的增加而逐渐降低的,岩石中的裂纹数量却是一直增加的,且裂纹以张拉裂纹为主,如图16所示。这说明,仅增加浆体的强度也不一定是有利的,强度过高可能导致岩体局部损伤的增加,甚至导致岩体的失稳,应该实现岩体的强度和浆体强度的耦合支护。

图15 不同浆体强度下峰值剪切强度和裂纹数
Fig. 15 Peak shear stress and number of cracks under different grout strengthes

图16 不同浆体强度下裂纹分布特征
Fig. 16 Distribution characteristic of cracks under different grout strengthes
4 结论
1) 锚杆本身的弹性模量对节理面的抗剪强度有很大的影响,锚杆刚度越大,节理面抗剪强度越高;但与此同时,弹性模量越大的锚杆对锚固体系的损伤也越来越大,导致浆体和岩体中大量裂纹的产生,影响了锚固体系的整体性和稳定性。因此,节理锚固中应综合考虑抗剪强度和锚杆对岩体及浆体的损伤,实现锚固体系“宏细观耦合支护”。
2) 锚杆刚度的不同,轴向应力的增加速率也是不一样的。刚度越大,轴向应力增长的越剧烈。当锚杆的轴向应力超过其屈服强度时,轴向应力的增加值就很缓慢了,在相同的剪切位移下,锚杆刚度越大,轴向应力也越大。因此,在实际应用中,应该使用高强锚杆,防止其较快地屈服。此外,锚杆的剪切应力增长速率较慢,当锚杆轴向屈服时,剪切应力远未屈服,一般不会发生剪切屈服。但是,轴向应力的增加在很大程度上是由于锚杆受剪之后的弯曲导致的,因此,提高锚杆的抗剪刚度对于减小锚杆轴向的应力也是很有意义的。
3) 锚固节理面在剪切荷载作用下,岩体结构面-浆体-锚杆相互作用,裂纹的产生首先起于节理面上和锚杆与节理面交叉处,随着剪切位移的不断增加,节理面上的裂纹在接触力集中的地方继续产生,而在锚杆周围则由锚杆与节理面交叉处向锚杆两端继续扩展,且裂纹集中在锚固体系的受压侧,主要为由压制拉机理导致的张拉裂纹。
4) 节理锚固中,浆体的强度过小或过大都可能导致锚固体系中裂纹数量的增多,且裂纹以张拉裂纹为主。当浆体强度较低时,裂纹主要集中在浆体中,而当浆体强度较高时,裂纹主要集中在岩体中,因此,节理锚固中浆体的强度选择应适中,以减少对锚固体系的损伤。
参考文献:
[1] Spang K, Egger P. Action of fully-grouted bolts in jointed rock and factors of influence[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 1990(23): 201-229.
[2] Pellet F, Egger P. Analytical model for the mechanical behavior of bolted rock joints subjected to shearing[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 1996, 29(2): 73-97.
[3] Aziz N, Hossein J, Hadi M S N. The effect of rock strength on shear behavior of fully grouted bolts[C]//Proceedings Fifth International Symposium on Ground Support in Mining and Underground Construction. Perth, 2004: 243-251.
[4] Aziz N, Hossein J, Hadi M S. The effect of resin thickness on bolt-grout-concrete interaction in shear[C]//Proceedings 6th Australasian Coal Operators Conference. Brisbane, 2005: 3-9.
[5] Jalalifar H, Aziz N, Hadi M. The effect of surface profile, rock strength and pretension load on bending behavior of fully grouted bolts[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2006(24): 1203-1227.
[6] Jalalifar H, Aziz N. Experimental and 3D numerical simulation of reinforced shear joints[J]. Rock Mech Rock Eng, 2010(43): 95-103.
[7] 刘波. 锚杆横向效应及综合抗力研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学研究生部, 1998: 20-50.
LIU Bo. Research on the lateral behavior of a bolt and its global resistance[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology. Graduate Department, 1998: 20-50.
[8] 杨松林, 徐卫亚, 朱焕春. 锚杆在节理中的加固作用[J]. 岩土力学, 2002, 23(5): 604-607.
YANG Songlin, XU Weiya, ZHU Huanchun. Reinforcement of bolt in joints[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2002, 23(5): 604-607.
[9] 伍佑伦, 王元汉, 许梦国. 拉剪条件下节理岩体中锚杆的力学作用分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2003, 22(5): 769-772.
WU Youlun, WANG Yuanhan, XU Mengguo. Effect of bolt in jointed rock mass under mixed loading of tension and shearing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(5): 769-772.
[10] 温进涛, 朱维申, 李术才. 锚索对结构面的锚固抗剪效应研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2003, 22(10): 1699-1703.
WEN Jintao, ZHU Weishen, LI Shucai. Research on anchoring and shearing effect of anchoring cable[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003(10): 1699-1703.
[11] SONG Hongwei, DUAN Yanyan, YANG Jing. Numerical simulation on bolted rock joints shearing performance[J]. Mining Science and Technology, 2010, 20(3): 460-465.
[12] 刘爱卿, 鞠文君. 预应力全长锚固锚杆抗剪作用分析[J].煤矿开采, 2012, 17(1): 45-48.
LIU Aiqing, JU Wenjun. Analysis of shear resisting action of full-length anchored bolt with pre-stress[J]. Coal mining Technology, 2012, 17(1): 45-48.
[13] Itasca Consulting Group Inc. Manual of particle flow code in 2-dimension (Version 3.10)[M]. Minneapolis: Itasca Consulting Group Inc, 2005: 16-50.
[14] Potyondy D O, Cundall P A. A bonded-particle model for rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2004, 41(8): 1329-1364.
[15] Cho N, Martin C D, Sego D C. A clumped particle model for rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Science, 2007, 44(7): 997-1010.
[16] ZHANG Xiaoping, Louis Ngai Yuen Wong. Cracking processes in rock-like material containing a single flaw under uniaxial compression: A numerical study based on parallel bonded-particle model approach[J]. Rock Mech Rock Eng, 2012, 45(5): 711-737.
(编辑 陈爱华)
收稿日期:2014-04-13;修回日期:2014-07-20
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51279097,51479108,51379117,51009086);山东科技大学研究生创新基金资助项目(YC140357)(Projects (51279097, 51479108, 51379117, 51009086) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (YC140357) supported by Graduate Innovation Foundation of Shandong University and Science and Technology)
通信作者:王刚,博士,副教授,从事岩石力学与工程方面的研究;E-mail:25499829@qq.com