DOI:10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-39493
氯盐体系锡隔膜电沉积仿真模拟
汪文超,杨建广,陈 冰, 曾伟志
(中南大学 冶金与环境学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:采用COMSOL多场耦合计算机仿真软件对氯盐体系锡隔膜电沉积进行了仿真模拟,研究锡隔膜电积时电解槽内离子浓度、流体密度、流体速度、电流密度等的分布特征及其随时间的变化规律。结果表明:锡隔膜电积时槽内离子浓度分布受到入口流速、电流密度、电积时间、槽内离子互相作用的影响而发生变化。增加进液速度及降低HCl浓度有利于提高电解液平均密度及阴极表面Sn2+的最低浓度。电积时极板边缘发生离子对流,顶部对流速度高于边缘处对流速度,且流体密度梯度影响离子对流方式。极板周围电流密度分布呈非均匀分布,在电极边缘发生电流偏转。增加电流密度能降低阴极表面Sn2+最低浓度及流体的平均密度,同时也将增加阴极表面流体的平均流速,并使得阴极产物厚度不均匀。
关键词:锡;隔膜电积;仿真模拟;多场耦合
文章编号:1004-0609(2020)-01-0180-14 中图分类号:TF814 文献标志码:A
近年来,随着电子信息技术的迅猛发展和人们对物质文化生活更高水平的追求,我国电子电器产品更新换代速度明显加快,同时产生大量的含锡电子废弃物。目前,多数含锡废料的综合利用已经开发出多种湿法、火法冶金工艺[1-2],而针对这些含锡电子废弃物的处理,工业上通常采用“剪切-破碎-分选”的方式获得含铜40%~80%、含锡1%~8%等的铜锡多金属粉[3],之后再将其作为炼铜原料投入铜冶炼系统回收其中的铜[4-5]。但实践证明,该处理方式不仅不能高效回收铜锡粉中的锡,而且多金属粉中的锡还严重影响了主金属铜的冶炼。因此,对铜锡多金属粉进行预先脱锡,将有利于充分回收其中的锡,同时脱锡铜粉也可以直接投入铜精炼流程,这对电子废弃物中铜、锡的全量回收及资源再生时的节能减排有积极意义。
前期,杨建广等[6-7]提出了一种氯盐体系锡隔膜电积新工艺,并成功应用于含锡多金属铜粉中锡的高效分离提取。该工艺的实质是利用离子膜将阴、阳两极室分隔开进行电解反应,阳极室中的Sn2+在电流作用下转化成Sn4+,阴极室中的Sn2+则转化成Sn单质。反应结束后,阴极可直接得到99%以上的电锡产品,阳极产出Sn4+溶液则作为退锡剂返回退锡使用,实现了整个流程的闭路循环、无废水排放。前期研究结果表明,与其他锡回收技术相比,氯盐体系锡隔膜电积新工艺具有原料适应性强、效率高、能耗低、流程简单等突出优点,能充分实现对铜锡多金属粉的脱锡预处理。
陈冰等[8]、南天翔等[9]和彭思尧等[10]进一步开展了锡隔膜电积电化学机理、工艺优化等研究,初步形成了氯盐体系锡隔膜电沉积技术原型。多场耦合计算机仿真软件COMSOL Multiphysics广泛应用于地球化学[11]、物理学[12]、电化学分析[13]等多个领域[14-15]。为进一步阐明氯盐体系锡隔膜电沉积过程机理,本文采用COMSOL Multiphysics对锡隔膜电沉积过程进行仿真模拟,以揭示在电场、流体力场等多个物理场作用下氯盐体系隔膜电积时溶液中离子浓度、流体密度、流体速度、电流密度等物理量的分布特征及其随时间的变化规律,并通过建立氯盐体系锡隔膜电沉积模型,对该过程各物理量的变化进行可视化展示。本文仿真模拟研究得到的规律对于工业实践中调节电解液环境,促进锡更好地沉积有参考意义。
1 锡隔膜电积槽几何模型及网格划分
1.1 几何模型的建立
本研究锡隔膜电解槽的几何建模如图1所示,尺寸为0.12 m×0.09 m×0.064 m。电解槽左右分成阴极槽、阳极槽两部分,中间为阴离子交换膜。阳极尺寸65 mm×51.5 mm×4 mm,阴极尺寸70 mm×54 mm× 1 mm,极距0.06 m。阴、阳极除了正面之外设定均不发生化学反应。阴极槽、阳极槽分别设有进液管、出液管,进出液管外端设置为进出液口。
1.2 模型网格的划分
将该模型离散化成四面体网格元素。最大网格尺寸7.66 mm,最小网格尺寸2.33 mm,最大网格增长速率为1.2。由于该电沉积模型中阴极、阳极及阴离子交换膜附近区域为重点研究区域,需更精细的网格结构划分。因此本研究在4个面上(阴阳极对立面、隔膜双面)分别设置4个边界层结构,边界层拉伸系数为1.2(下一层厚度为前一层的1.2倍),第一层厚度为1.2 mm。这些较为精细的边界层网格被集成到四面体网格元中,网格划分如图2(a)所示。阳极、阴极和隔膜表面边界层网格如图2(b)所示。几何边界则离散成三角形元素,在模型中所有的边界网格中,最大网格尺寸为5.2 mm,最小网格尺寸为1.55 mm,最大网格增长速率为1.15。几何图形中的边和顶点分别离散化到边缘元素和顶点元素。
2 多场耦合模型描述
2.1 控制方程
锡隔膜电解过程各项理化数值以及溶液中离子的行为,需要多个控制方程进行描述。其中,电解液中离子的传输由能斯特普朗克方程控制,电解液-隔膜界面由Donnan平衡控制,电极-电解液界面遵循Butler-Volmer方程,流速场由连续动量方程控制。
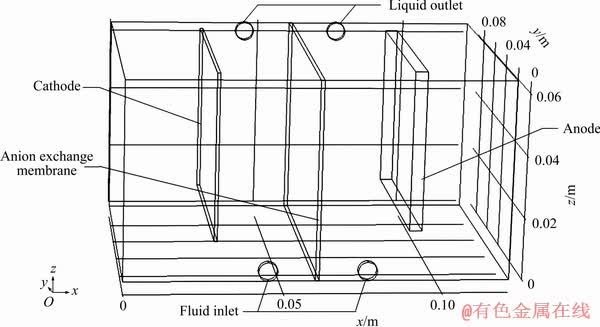
图1 锡隔膜电解槽COMSOL模型示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of COMSOL model of tin membrane electrolytic cell
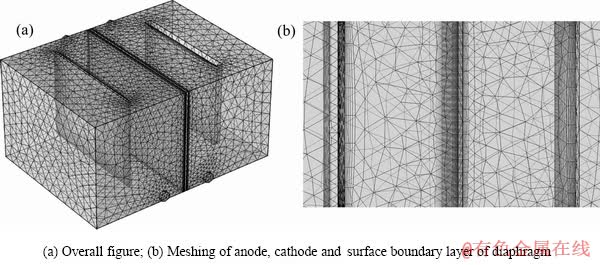
图2 隔膜电解槽网格划分示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of mapped meshing of membrane electrolytic cell
锡隔膜电积时,电极主反应如下:
Sn2+(aq)+2e→Sn(s), 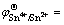 0.15 V (1)
0.15 V (1)
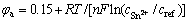 (2)
(2)
Sn2+(aq)→Sn4+(aq)+ 2e, 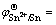 -0.1375 V (3)
-0.1375 V (3)
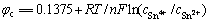 (4)
(4)
式中: 、
、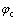 、n、T、R分别表示阳极电势、阴极电势、迁移电子数、温度及摩尔气体常数。在电解液中,离子传输的控制方程为Nernst-Planck方程:
、n、T、R分别表示阳极电势、阴极电势、迁移电子数、温度及摩尔气体常数。在电解液中,离子传输的控制方程为Nernst-Planck方程:
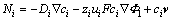 (5)
(5)
式中:Ni、zi、ui、ci、Di分别表示物种i的通量密度、核电荷数、迁移率、离子浓度及扩散系数;F为法拉第常数;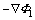 为电场强度;
为电场强度;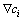 为浓度梯度;v为速度向量。
为浓度梯度;v为速度向量。
电解液-隔膜界面由Donnan平衡来描述,界面上的Donnan电位偏移根据界面两侧载体离子的浓度自动计算:
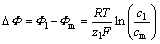 (6)
(6)
式中: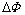 为Donnan电势;
为Donnan电势;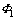 为隔膜-电解液界面处电解液电势;
为隔膜-电解液界面处电解液电势;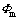 为隔膜-电解液界面处隔膜电势;zl为电荷载体带电荷数,该模型载体为Cl-,核电荷数-1;F为法拉第常数;cl为隔膜-电解液界面处电解液中电荷载体的浓度,该模型中为Cl-浓度
为隔膜-电解液界面处隔膜电势;zl为电荷载体带电荷数,该模型载体为Cl-,核电荷数-1;F为法拉第常数;cl为隔膜-电解液界面处电解液中电荷载体的浓度,该模型中为Cl-浓度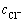 ;cm为隔膜-电解液界面处隔膜中电荷载体的浓度。
;cm为隔膜-电解液界面处隔膜中电荷载体的浓度。
电极-电解液界面遵循Butler-Volmer方程。电极附近电解液的电流密度与Butler-Volmer局部电流密度有如下关系:
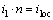 (7)
(7)
式中:il为电极附近电解液的电流密度;n为电极表面单位法向量;iloc为局部电流密度。由于电解过程中的Sn离子浓度、Cl-、H+浓度的变化会引起密度的变化,这种因密度差而产生的自然对流由以下连续动量方程控制:
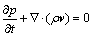 (8)
(8)
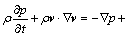
 (9)
(9)
式中: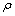 为流体密度;v为流体速度向量;p为压力;
为流体密度;v为流体速度向量;p为压力;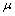 为动力黏度;I为特性张量;F为作用于流体的力矢量(单位体积)。
为动力黏度;I为特性张量;F为作用于流体的力矢量(单位体积)。
2.2 边界条件
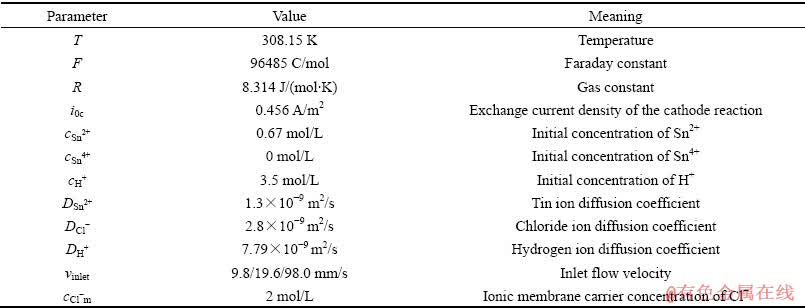
本研究通过实验初始设定(温度、各离子浓度、进液口流速等)、查阅文献(电极平衡常数、H+、Cl-离子扩散系数等)和实验测定(交换电流密度、Sn离子扩散系数、流体密度、流体黏度等) 3种方式,建立了如下表1所示的边界条件。在该边界条件下模拟电沉积过程,分别考察了溶液入口流速、电流密度、电解液Sn2+浓度和盐酸浓度等条件对隔膜电沉积锡过程电化学行为的影响。表2所列为模型主要参数,包括隔膜电沉积参数、流场以及阴离子交换膜的各项参数等。
表1 仿真边界条件
Table 1 Simulative boundary conditions
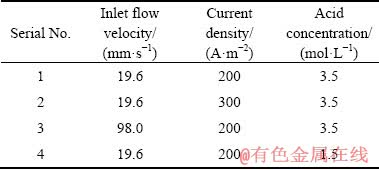
表2 模型主要参数
Table 2 Main model parameters
3 模拟仿真结果与分析
本研究采用多场耦合计算机仿真软件COMSOL Multiphysics对锡膜电沉积过程进行仿真模拟,并以时间依赖型方法进行求解。经0~1000 s计算发现,60 s后隔膜电解槽内电场、流场的变化较小,可认为t=1000 s时为稳态解。因此,下述研究中对不同边界条件下氯盐体系隔膜电沉积均进行0~1000 s的时间依赖型求解,获得氯盐体系锡隔膜电积槽内离子浓度、流体密度、流体速度、电流密度等的分布特征及其随时间的变化规律。
3.1 离子浓度分布
电解槽内离子浓度分布显著影响电解效果,因此有必要通过模拟仿真,分析氯盐体系下锡隔膜电沉积过程槽内主要离子的分布规律及其随时间的变化规律。图3所示为根据仿真计算结果绘制的在入口流速19.6 mm/s、电流密度200 A/m2、3.5 mol/L HCl的边界条件下,隔膜电沉积1000 s时电解槽中Sn2+、Sn4+浓度的分布情况。
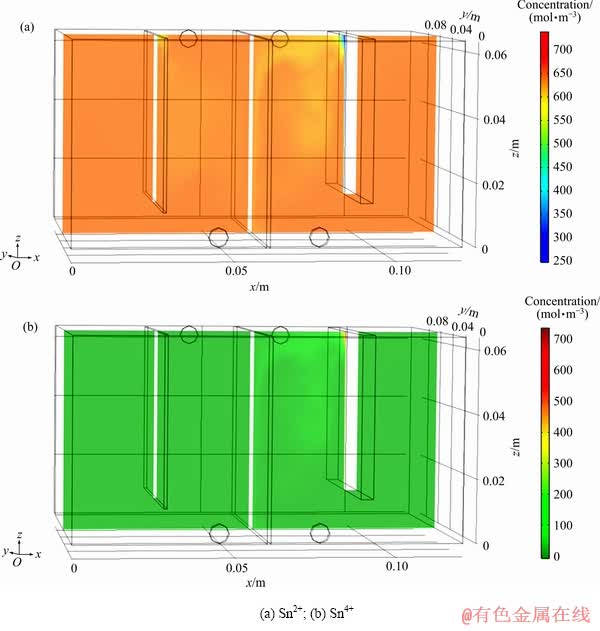
图3 锡隔膜电解离子浓度分布剖面图
Fig. 3 Ion concentration distribution profile in tin membrane electronic cell
由图3(a)可以看出,在阴、阳极表面附近,Sn2+浓度水平明显低于溶液本体平均Sn2+浓度,这是因Sn2+离子在电极表面发生电化学反应的结果:Sn2+在阴极发生还原反应生成Sn,在阳极表面发生氧化反应生成Sn4+。而且此条件下溶液中离子扩散速率不够高,不足以将Sn2+从溶液本体通过扩散层迅速转移到电极表面。导致Sn2+在电极附近耗尽而与溶液本体Sn2+出现浓度差异。对比阴、阳极附近Sn2+浓度差异也可看出,阳极附近Sn2+变化较阴极更明显,原因分析为阳离子在电场作用下发生趋近阴极、远离阳极的电迁移现象,而阴极附近的Sn2+更容易由溶液本体补充,阳极则反之。图3(b)所示为隔膜电积1000 s时Sn4+的浓度分布。由图3(b)可知,阳极表面生成的Sn4+不足以从扩散层转移到溶液本体,而是在阳极表面聚集导致阳极表面Sn4+浓度升高。
此外,对表1四组边界条件下阴极表面Sn2+浓度最小值随时间的变化关系作图,可获得阴极表面Sn2+浓度最小值随时间的变化关系如图4所示。由图4可以看出,随着电沉积反应开始,阴极表面Sn2+逐渐消耗,浓度逐渐降低,同时由于扩散、对流的存在,Sn2+由溶液本体向电极表面逐渐补充,60 s后消耗和补充基本达到了平衡,其浓度随时间变化不大。在溶液流速19.6 mm/s、电流密度300 A/m2、3.5 mol/L HCl的边界条件下,隔膜电积20 s时,阴极表面Sn2+浓度出现了一个极低的值。这是电流密度过大造成的,20 s之后由于溶液本体和极板表面存在大的浓度梯度,通过扩散进行补充,Sn2+浓度回升并保持稳定。比较4组边界条件,在19.6 mm/s、200 A/m2、1.5 mol/L的HCl以及98.0 mm/s、200 A/m2、3.5 mol/L HCl的两组的边界条件下,阴极表面Sn2+浓度最小值经隔膜电积60 s后几乎不再下降,故认为这两组边界条件下隔膜电积60 s后Sn2+浓度更加稳定。
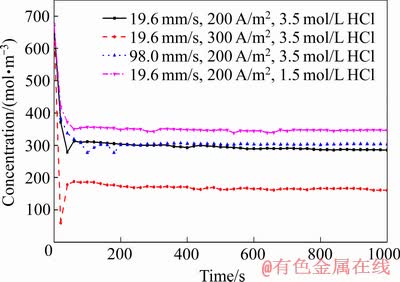
图4 阴极表面Sn2+浓度最小值随时间的变化
Fig. 4 Change of minimum concentration of Sn2+ on cathode surface over time
图5所示为四组边界条件下隔膜电积1000 s时阴极表面Sn2+浓度最小值的对比图。由图5可知,在4组边界条件中仿真计算所得的Sn2+浓度存在一些差异。在19.6 mm/s、300 A/m2、1.5 mol/L HCl的边界条件下阴极表面Sn2+浓度相对最低,显然这是由于该条件下电极反应消耗速度更快造成的。也即是说,电流密度越高,表面Sn2+浓度越低。其次是19.6 mm/s、200 A/m2、3.5 mol/L HCl和98.0 mm/s、200 A/m2、3.5 mol/L HCl边界条件下的阴极表面Sn2+浓度。在19.6 mm/s、200 A/m2、1.5 mol/L HCl的条件下阴极表面Sn2+浓度相对最高。当入口流速从19.6 mm/s增加到98.0 mm/s时,电极之间的对流增大,阴极表面Sn2+得以补充而浓度降低更少。当HCl浓度由3.5 mol/L降低到1.5 mol/L时,带电离子的减少使得Sn2+承担了更多的电解液的电荷转移,在电迁移作用下,溶液本体中的Sn2+也能更快的向阴极表面补充。
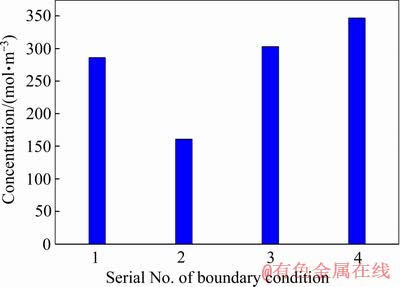
图5 1000 s时不同边界条件下阴极表面Sn2+浓度最小值
Fig. 5 Minimum concentration of Sn2+ on cathode surface under different boundary conditions at 1000 s
在所设定的参数范围内,锡隔膜电积时溶液中Cl-、H+不参与电极反应,局部浓度变化不大。但本研究为更直观地研究H+、Cl-的变化规律,以溶液流速19.6 mm/s、电流密度200 A/m2、3.5 mol/L HCl的边界条件为例,对y=0.5 m,z=0.015 m、0.035 m、0.060 m位置处阴、阳极板之间的Cl-、H+浓度分布情况作图,结果如图6所示。
从图6(a)中Cl-分布曲线可以看出,除阴极表面(x=0 m)、阳极表面(x=0.0612 m)、隔膜(x=0.030~0.0312 m)表面外,Cl-浓度受流场影响略有波动。在电场作用下,Cl-从阴极区域向阳极区域迁移,使得阴极表面附近Cl-浓度远低于本体浓度,阳极表面附近Cl-浓度远高于本体浓度。在阴离子隔膜附近,Cl-作为阴离子隔膜的载体,从隔膜左侧(阴极侧)向右侧(阳极侧)迁移,左侧离子浓度降低,右侧离子浓度升高,因此在隔膜两侧出现了较大的Cl-浓度差;图6(b)为H+浓度分布曲线,H+在电场作用下由阳极向阴极移动,阳极扩散层H+浓度降低,阴极扩散层H+浓度升高。H+由右向左从阳极向阴极方向移动,由于H+不能通过隔膜,故其在隔膜右侧累积浓度升高,在隔膜左侧发生向左的迁移浓度降低。
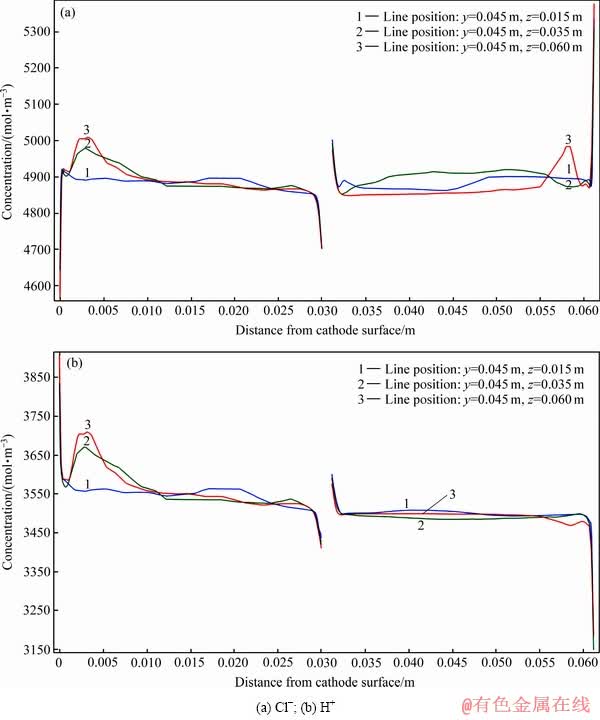
图6 锡隔膜电沉积阴极(左侧)与阳极(右侧)之间浓度离子浓度分布曲线
Fig. 6 Distribution curves of ion concentration between cathode (left) and anode (right) during tin membrane electrodeposition
3.2 流体密度分布
电解槽中的流体密度分布主要由各离子浓度的分布确定,而阴极表面的流体密度分布可以影响到阴极表面Sn2+的供给及其电化学反应,也显著影响阴极表面附近的流体流动。
图7所示为根据仿真计算结果绘制的在溶液入口流速19.6 mm/s、电流密度200 A/m2、HCl 3.5 mol/L的边界条件下,隔膜电积1000 s时电解槽内稳态流体密度分布情况。图7(a)中阴极板以外的区域(即阴极与电解槽左侧、右侧以及底部内壁之间存在的间隙)几乎呈同一种颜色,此部分为溶液本体密度;而极板表面大部分区域由于Sn2+消耗,因此流体密度较低。极板边缘虽然也有消耗,但从各个方向溶液中得到补充相对较多,因此此区域流体密度较中心区域高;顶部则出现了小区域的密度升高,原因分析可能与H+的聚集有关;图7(b)所示为阴极底部(z=0.010 m)、中部(z=0.035 m)和顶部(z=0.060 m)处阴极板左、右边缘之间流体密度分布曲线,该曲线更直观的反映了极板边缘与中部的密度差异,且电极表面z方向也存在密度梯度。
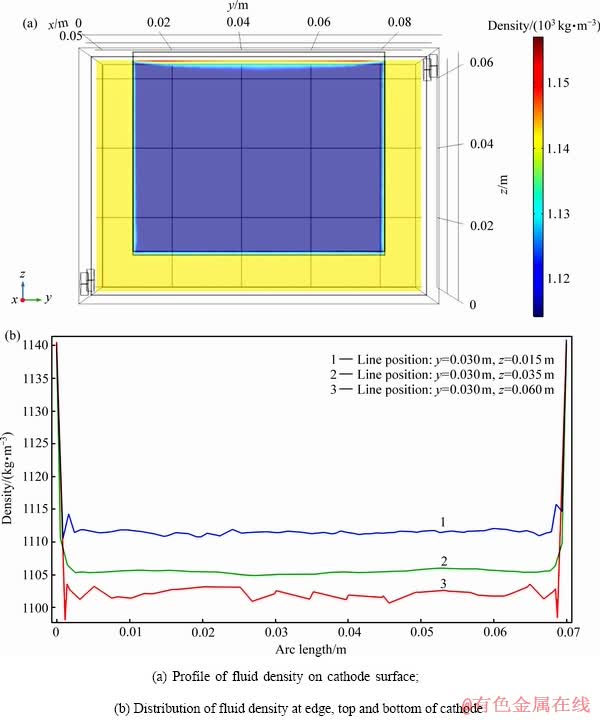
图7 隔膜电解槽内溶液流体密度分布
Fig. 7 Distribution of solution fluid density in membrane electrodeposition cell
电极表面与电解液本体的流体之间存在密度梯度是驱动电解槽内流循环的主要原因之一。同时,阴极顶部流体的密度梯度大于阴极边缘的密度梯度,意味着顶部由密度梯度驱动的对流速度快于边缘。
图8所示为4种不同边界条件下隔膜电积1000 s时阴极表面平均流体密度情况。由图8可知,4组不同边界条件下阴极表面平均流体密度分布略有不同。边界条件19.6 mm/s、200 A/m2、HCl 3.5 mol/L与边界条件98.0 mm/s、200 A/m2、HCl 3.5 mol/L时的阴极表面密度差异不大,说明较高的溶液流速对表面平均流体密度的影响较小。当电流密度增加到300 A/m2,平均流体密度则下降较大,这主要是由于增加电流密度扩散层需要消耗的Sn2+量增多。当HCl浓度由3.5 mol/L下降至1.5 mol/L时,密度的变化值有所减小,如之前所讨论的,较低的HCl浓度将有助于Sn2+的电迁移,减少浓度差异,导致较小的平均流体密度梯度。
3.3 流体速度分布
电解槽中的流体速度场是由进液口流入速度和电解液的密度梯度共同驱动的。图9所示为入口流速19.0 mm/s、电流密度200 A/m2、HCl 3.5 mol/L的边界条件下,隔膜电积1000 s时电解槽内的稳态流体速度场。
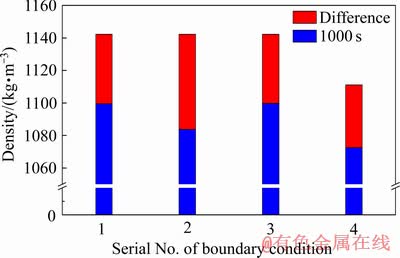
图8 1000 s时4组边界条件下阴极表面流体平均密度及与初始密度的差值
Fig. 8 Average density of cathode surface fluid and difference between initial density and average density under four different boundary conditions at 1000 s
由图9(a)可以看出,流体以设定的速度从入口进入电解槽后迅速分散,一部分沿着y方向流动,一部分受到电解液密度的影响改变方向与电解槽内自发形成的对流混为一体难以区分。相比于流体流入带来的对流,由密度梯度驱动的流体速度主要沿z方向。以阴极区域为例,根据离子浓度、密度的分布规律可知,阴极表面即隔膜左侧流体由于密度相对较低故受到向上浮力而上升,到达电解槽顶部后,一部分流体随后又从极板和隔膜之间的空隙下降而形成环流,另一部分则从出口流出。阳极区域由于阳极表面密度变化较小,没有规律的对流路径。但值得指出的是,真实情况下宏观流体流速受多种因素共同作用,其流体速度分布将更加复杂。图9(b)所示为y=0.045 m处流场的分布剖面二维图,由此能够更明确地观察到该剖面处流场速度分布及阴极表面、隔膜附近流体的流通路径。在隔膜附近,由于阴离子隔膜的作用,Cl-、H+等离子在右侧累积,左侧消耗,因此在离子浓度、密度的分布规律作用下,隔膜左侧由于密度低皆受到向上浮力上升,到达电解槽顶部后,一部分流体随后又从极板和隔膜中间的位置下降,形成环路。阳极(右侧)和阴极(左侧)之间流体速度z方向分量曲线(见图9(c))量化了这种变化。除此之外还发现,随着z的增加(位置的升高),隔膜右侧流体沿z轴的流速vz也呈增加的趋势。
图10所示为溶液入口流速19.6 mm/s、电流密度200 A/m2、HCl 3.5 mol/L的边界条件下,隔膜电积 1000 s时阴极前表面100 μm处的速度场剖面。由图10可以看出,在此剖面处阴极左右两侧、底部与电解槽壁之间的间隙处,流体速度相对较小,尤其是底部方向各异。而在阴极板正前方,大多数流体速度向量几乎是垂直的,且均沿着z分量方向而非x和y分量流动,并且在阴极边缘附近流速大于阴极中间部分的流体流速,这显然是由两区域间密度梯度差异引起的。此外,与图9(c)有类似的规律,流体速度的z分量沿正z方向逐渐变大,这可能与流速方向末端流体受到更多作用力有关。
图11所示为4组边界条件下(见表1)阴极表面100 μm处平均流体速度对照图。由图11可知,在流体速度19.6 mm/s、电路密度200 A/m2、HCl 3.5 mol/L的边界条件下阴极表面的平均流速最小。而当入口流速增加到98.0 mm/s,由于流体流动的强化,阴极表面流速增加。当HCl浓度从3.5 mol/L降到1.5 mol/L时,由于电解液黏度降低,阴极表面流速增加。当电流密度从200 A/m2提高到300 A/m2时,由于密度梯度较大,流速继续增加,这也意味着电流密度对阴极表面流速影响最大。
3.4 电流密度分布
电流密度的分布不仅决定了电解液中离子所受电场力的大小和方向,也决定了阴极表面沉积物的数量。因此,对电流密度分布的考察有助于说明阴极产物的分布和阴极产物的平整度。
图12所示为入口流速19.6 mm/s、电流密度200 A/m2、HCl 3.5 mol/L的边界条件下,隔膜电积1000 s时,y=0.045 m处电流密度分布的剖面图(颜色表示电流密度的大小,红色箭头表示电流密度矢量)。由图13可知,在电解槽内溶液上部分区域电流密度分布均匀,且方向与阴、阳极表面垂直。但在极板的边缘处出现有一个电流极大的区域,这个区域附近的电流方向呈现出有弧度的偏转,这符合电场分布的理论,也与实际电解经验相符合。
图13所示分别为阴极表面x、y、z方向ix、iy、iz分布及总电流大小itot的分布。在电场力的作用下,阴极板底部边缘附近总电流方向发生偏转,x轴方向的分电流减小,ix在靠近极板底部的区域较小,在极板其它处分布则较均匀;由于电力线呈弧状,iy在极板一侧集中;iz只在靠近底部的地方有所分布。总电流分布如图13(d),itot在阴极板底部较小,在其他区域分布则相对均匀。
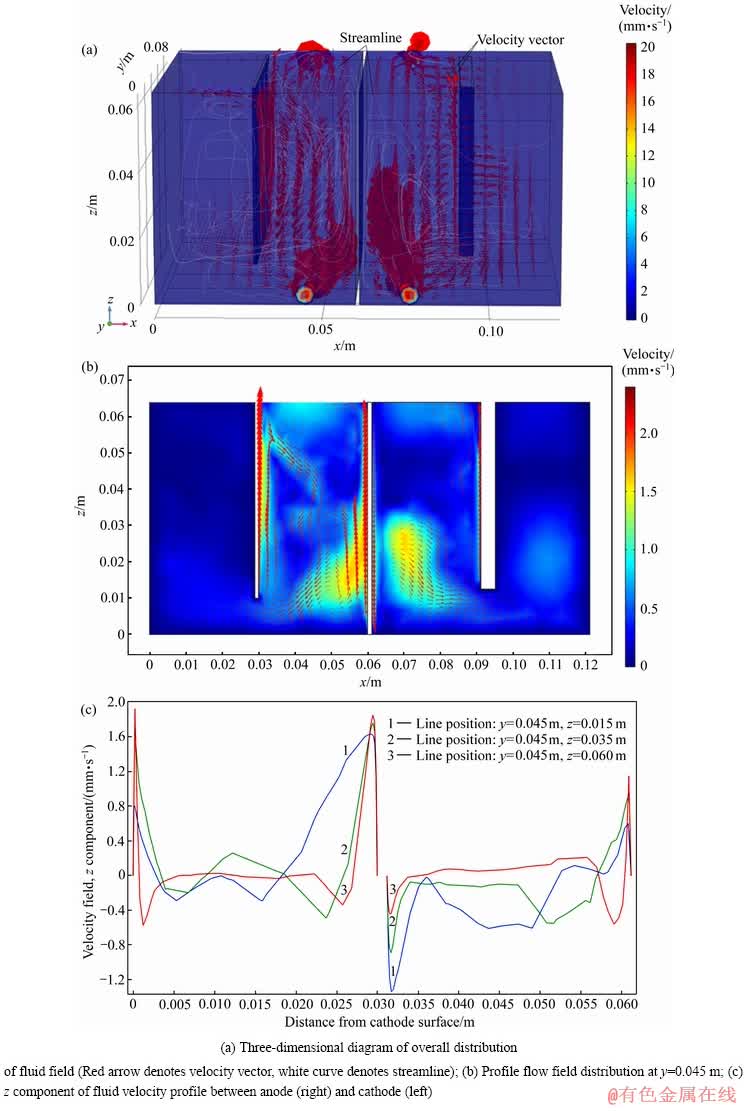
图9 隔膜电解槽内流体流速场分布
Fig. 9 Distribution of fluid velocity field in membrane electrodeposition cell
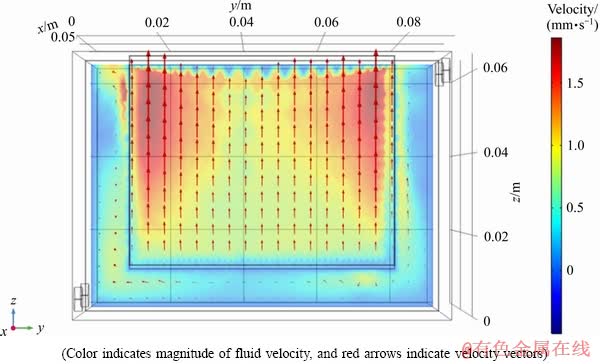
图10 阴极表面100 μm处流体流速剖面图
Fig. 10 Fluid velocity profile at 100 μm of cathode surface
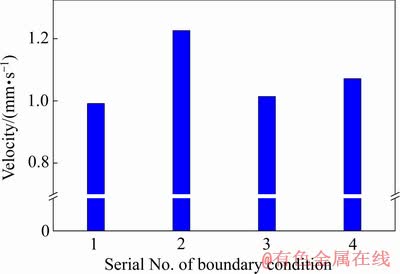
图11 4组边界条件下阴极表面100 μm处的平均流体速度
Fig. 11 Average fluid velocity at 100 μm on cathode surface under four different boundary conditions
3.5 阴极产物
在仅考虑阴极沉积物与电流密度的关系,不考虑锡的形核与长大过程的前提下,阴极表面沉积物厚度可由下式计算[8]:
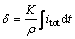 (10)
(10)
式中:δ为沉积层厚度;K为电化当量;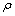 为锡的密度。
为锡的密度。
在入口流速19.6 mm/s、200 A/m2、HCl 3.5 mol/L的边界条件下,1000 s时,仿真模拟阴极产物图如图14所示,颜色代表厚度,可以看出产物与上述电流密度分布图呈现相同的规律。
为了验证COMSOL的模拟结果,本研究还开展了实际电沉积实验。由于仿真模拟1000 s沉积层厚度仅10-5数量级,沉积层很薄,在实验中不容易观察到。因此在同等条件下进行锡隔膜电沉积验证实验时,时间延长至8 h,得到的阴极电沉积产物如图15所示。可以看出中部区域电沉积厚度比较均匀,厚度约为0.0008 m。左右两侧及下边缘厚度较大,同时出现了结瘤的现象,其外观形貌与图14模拟仿真计算结果呈现大致相同的规律。沉积物左右边缘距离较极板宽度0.070 m多0.004 m,这是由于实际实验中边缘产物晶核形核与生长不会严格按照x方向所导致的。
图16所示为4组边界条件下隔膜电积1000 s时,阴极沉积层厚度对比图。由图16可以看出,在19.6 mm/s、300 A/m2、HCl 3.5 mol/L的边界条件下,阴极沉积物厚度出现最大值和最小值,且最大值与最小值的差值也相较其他组大,表明在此边界条件下所得阴极产物厚度分布最不均匀。由此可知,在只考虑电流密度分布情况下,阴极产品厚度主要受平均电流密度影响,电流密度过大阴极表面趋于不平整。而入口流速、HCl浓度对阴极沉积层影响则相对较小。
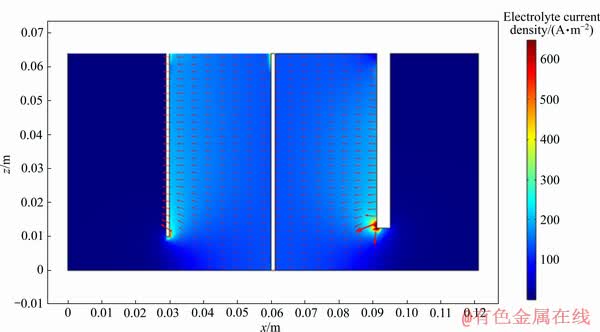
图12 锡隔膜电解槽电流密度分布剖面图
Fig. 12 Profile of current density distribution in tin membrane electrolytic cell
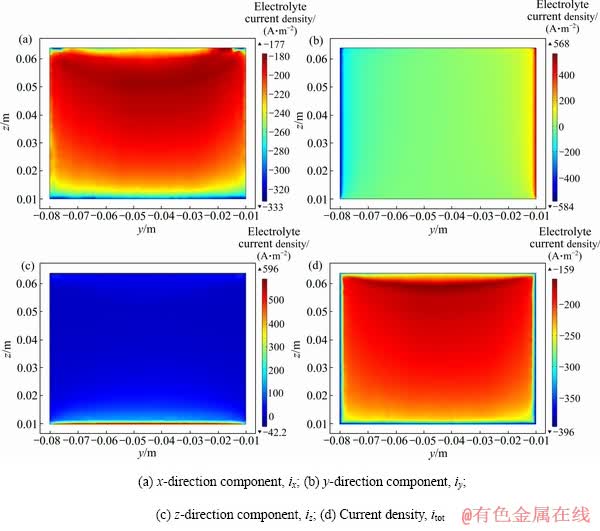
图13 锡隔膜电解槽阴极表面电流密度分布
Fig. 13 Current density distribution on cathode surface in tin membrane electrolytic cell (color represents current density value)
图14 阴极沉积物厚度分布图
Fig. 14 Thickness profile of cathode deposits

图15 同等电解条件下隔膜电积8 h所得到的阴极沉积物光学图
Fig. 15 Optical picture of cathode deposits obtained by membrane electrodeposition for 8 h under same electrolytic condition
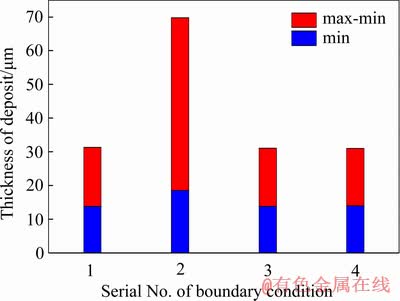
图16 隔膜电积1000 s时4组边界条件下阴极沉积物厚度对比
Fig. 16 Thickness comparison of membrane electrodeposited over 1000 s under four different boundary conditions
4 结论
1) 在阴、阳极表面附近,Sn2+浓度水平明显低于溶液本体平均Sn2+浓度。
2) 极板顶部流体密度高于边缘,极板周围流体与本体溶液间存在密度差;极板周围流体与本体溶液之间的密度差异是引起电解槽内流循环的一个主要原因。
3) 电解槽中流体速度分布受到进液口流入速度和电解液密度共同影响,电解液密度的影响更大;流体在两极板中间的流动速度高于其他地方。
4) 电流分布在两极板中间,越接近极板下端,电流越受到电场影响向下发生弯折。
5) 考察阴极产物厚度的分布。对比模拟阴极产物与同等条件下8 h电积实物的厚度分布可知:模拟与真实电积的阴极产物均在中部区域分布均匀,在左右两侧及下边缘厚度较大。
REFERENCES
[1] 雷 霆, 杨志鸿, 余宇楠, 张报清. 锡冶金[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2013: 19-23.
LEI Ting, YANG Zhi-hong, YU Yu-nan, ZHANG Bao-qing. Tin metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013: 19-23.
[2] 孔 霞, 李沪萍, 罗康碧, 胡 创. 锡废料综合利用的研究进展[J]. 化工科技, 2011, 19(2): 59-63.
KONG Xia, LI Hu-ping, LUO Kang-bi, HU Chuang. Research advance on comprehensive utilization of the tin scraps[J]. Science & Technology in Chemical Industry, 2011, 19(2): 59-63.
[3] KIDDEE P, NAIDU R, MING H W. Electronic waste management approaches: An overview[J]. Waste Management, 2013, 33(5): 1237-1250.
[4] CUI Ji-rang,ZHANG Li-feng. Metallurgical recovery of metals from electronic waste: A review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 158(2): 228-256.
[5] 赵跃民, 王全强, 焦红光, 温雪峰, 曹亦俊. 废弃电路板选择性破碎基础研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2005, 34(6): 683-687.
ZHAO Yue-min, WANG Quan-qiang, JIAO Hong-guang, WEN Xue-feng, CAO Yi-jun. Selectivity crushing of discarded printed circuit boards[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2005, 34(6): 683-687.
[6] 杨建广, 唐朝波, 唐谟堂, 何 静, 杨声海. 一种铋或锑湿法清洁冶金方法: 中国, CN101775619A[P]. 2010-07-14.
YANG Jian-guang, TANG Chao-bo, TANG Mo-tang, HE Jing, YANG Sheng-hai. A cleaning hydrometallurgy method of bismuth or antimony: China, CN101775619A[P]. 2010-07-14.
[7] 杨建广, 李焌源, 雷 杰,杨声海,何 静,唐朝波,陈永明. 一种基于盐酸-锡盐体系的退锡水及从废退锡水中回收锡的方法: 中国, CN103741142A[P]. 2014-04-23.
YANG Jian-guang, LI Jun-yuan, LEI Jie, YANG Sheng-hai, HE Jing, TANG Chao-bo, CHEN Yong-ming. A method for tin recovery from waste tin water based on hydrochloric acid-tin salt system: China, CN103741142A[P]. 2014-04-23.
[8] 杨建广, 陈 冰, 雷 杰, 李树超. 废弃电路板铜锡多金属粉隔膜电积回收锡实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 38(11): 1648-1653.
YANG Jian-guang, CHEN Bing, LEI Jie, LI Shu-chao. Experimental study on tin recovery based on membrane electrodeposition from metal fractions of waste printed circuit boards[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Nature Science), 2017, 38(11): 1648-1653.
[9] NAN Tian-xiang, YANG Jian-gaung, CHEN Bing. Electrochemical mechanism of tin membrane electrodeposition under ultrasonic waves[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2018, 42(4): 731-737.
[10] 彭思尧, 杨建广, 陈 冰, 李树超, 雷 杰, 李焌源. 含锡二次资源隔膜电积回收锡新工艺试验[J]. 中国有色属学报, 2016, 26(12): 2656-2667.
PENG Si-yao, YANG Jian-guang, CHEN Bing, LI Shu-chao, LEI Jie, LI Jun-yuan. Novel process for tin recovery from stannous secondary resources based on membrane electrodeposition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2016, 26(12): 2656-2667.
[11] NARDI A,IDIART A, TRINCHERO P, VRIES L M, MOLINERO J. Interface COMSOL-PHREEQC (iCP), an efficient numerical framework for the solution of coupled multiphysics and geochemistry[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2014, 69(8): 10-21.
[12] WEI Z, WEAVERS L K. Combining COMSOL modeling with acoustic pressure maps to design sono-reactors[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2016, 31(7): 490-498.
[13] DESHPANDE K B. Numerical modeling of micro-galvanic corrosion[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(4): 1737-1745.
[14] LABAIR H, TOUHAMI S, TILMATINE A, HADJERI S,MEDLES K, DASCALESCUL. Study of charged particles trajectories in free-fall electrostatic separators[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2017, 88(4): 10-14.
[15] SALVI D, BOLDOR D, AITA G M, SABLIOV C M. COMSOL multiphysics model for continuous flow microwave heating of liquids[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2011, 104(3): 422-429.
Simulation of tin membrane electrodeposition in chloride system
WANG Wen-chao, YANG Jian-guang, CHEN Bing, ZENG Wei-zhi
(School of Metallurgy and Environment, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: ACOMSOL multi-field coupled computer simulation software was used to simulate tin membrane electrodeposition in the chloride system, and the distribution characteristics of ion concentration, fluid density, fluid velocity, current density and other physical quantities in the cell were studied, as well as the variation law with time. The results show that the ion concentration distribution is affected by the inlet velocity, current density, reaction time and the interaction between the ions. The way of increasing the inlet velocity and decreasing the HCl concentration can improve the average density of electrolyte and the lowest concentration of Sn2+ on the cathode surface. The velocity of the top convection is higher than that of the edge, and the fluid density gradient affects the ion convection mode. The current density distribution around the plate is non-uniform and current deflection occurs at the edge of the electrode. The increase of current density can reduce the lowest concentration of Sn2+ on the cathode surface and the average density of the fluid. It also increases the average flow rate of the fluid on the cathode surface and makes the thickness of the cathode products uneven.
Key words: tin; membrane electrodeposition; simulation; multi-field coupling
Foundation item: Project(51574294) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Received date: 2019-01-20; Accepted date: 2019-04-25
Corresponding author: YANG Jian-guang; Tel: +86-731-88830470; E-mail: jianguang_y@163.com
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51574294)
收稿日期:2019-01-20;修订日期:2019-04-25
通信作者:杨建广,教授,博士;电话:0731-88830470;E-mail:jianguang_y@163.com