文章编号: 1004-0609(2006)07-1177-07
高温、 高湿环境中时效时Sn-Zn基无铅焊点的显微组织演化
韦习成1, 2, 鞠国魁1, 孙 鹏2, 程兆年2, 上官东凯2, 3, 刘建影2
(1. 上海大学 材料科学与工程学院, 上海 200072;
2. 上海大学 新型显示与应用集成教育部重点实验室中瑞联合微系统集成技术中心, 上海 200072;
3. 美国伟创立公司 先进组装和环境技术部, San Jose, CA, USA)
摘 要: 研究Sn-Zn基焊料经高温和高湿环境时效后的显微组织演化。 在涂覆Au/Ni合金的PCB镀铜焊盘上焊接3种Sn-Zn基焊料的试样(Sn-9Zn合金、 Sn-8Zn-3Bi合金以及 Sn-7Zn-Al(30×10-6)合金), 然后在120℃, 100%相对湿度、 2.03×105Pa下分别时效96h和192h。 结果表明, Zn原子向表面和界面扩散, 形成富Zn相并长大。 粗大的Zn相易于导致O元素的富集, 使与β-Sn界面弱化, 从而降低在位移控制加载模式下的低周疲劳寿命。
关键词: Sn-Zn 基焊料; 时效; 湿度; 显微组织; 低周疲劳
中图分类号: TN406 文献标识码: A
Microstructure evolution of Sn-Zn based lead-free solder joints aged in humid atmosphere at high temperature
WEI Xi-cheng1, 2, JU Guo-kui1, SUN Peng2,
CHENG Zhao-nian2, SHANGGUAN Dong-kai2, 3, LIU Johan2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University,
Shanghai 200072, China;
2. Sino-Swedish Microsystem Integration Technology (SMIT) Centre,
Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072, China;
3. Advanced Assembly and Environmental Technologies,
Flextronics Corporate Technology Group, San Jose, California,USA)
Abstract: The Sn-Zn based lead free solder appears to be an attractive alternative with a melting temperature relatively close to eutectic Sn-Pb. The addition of bismuth in Sn-Zn alloy improves its wettability and aluminum is beneficial to improve the oxidation resistance. The degradation of Sn-Zn based solder joints after exposed in the temperature and humid atmosphere with high pressure was studied. Three kinds of Sn-Zn system solders (Sn-9Zn, Sn-8Zn-3Bi and Sn-7Zn-Al (30×10-6)) were soldered on copper pad with a layer of Au/Ni and the specimens were stored in a pressure cooker for 96 or 192h. The temperature and the relative humidity in the cooker were 120℃ and 100% respectively. The mechanical fatigue test was carried in a displacement-controlled mode to measure the low cycle fatigue of the joints. The results show that Zn diffuses to the surface and interface while coarsening at the same time, and the coarser Zn has weak interface with β-Sn matrix and oxides form. High temperature and high humidity exposure decreases the mean life of Sn-Zn solder joints when they are subjected to 120℃ and 100% relative humidity with 2.03×105Pa pressure for 192h.
Key words: Sn-Zn based solder; aging; humidity; microstructure; low cycle fatigue
过去十几年间, 欧盟出台了一系列新的法规, 迫使电子制造业在封装互连中逐步减少对含铅焊料的使用。 截止于2006年7月, 凡进入欧盟市场的电子产品必须无铅化。 Sn-Pb共晶焊料中锡与铅的比例为63∶37, 共晶温度183℃。 随着无铅化的日期日益迫近, 无铅焊料的发展受到广泛关注。 例如, 含3%~4%Ag的Sn-Ag-Cu, 熔点高达217℃, 比Sn-37Pb熔点高34℃, 因此Sn-Ag-Cu焊料的回流温度高达250℃。 为满足较高的回流温度, 待焊器件及基板需要更好的耐热性。 因此考虑到封装设备的兼容性, 急需发展低熔点的无铅焊料。
Sn-Zn焊料由于其与Sn-Pb相近的共晶温度, 理所当然地是二元Sn-Pb合金焊料的理想替代品[1]。 但尚有不少问题有待攻克, 如, Zn是还原性较高的元素, 在高温下极易氧化, 提高其抗氧化性的途径之一是加入某种合适元素。 Al元素是一种可能的选择。 研究表明[2-4], 在合金制备过程中, Al会在液态Sn-9(Zn-5Al)合金表面生成致密氧化膜, Al氧化膜的形成抑制了Sn与Zn的进一步氧化, 提高了合金的抗氧化性能。 实验已证实[5-12], 在Sn-Zn共晶合金中加入少量的Bi, 可以提高焊料在电子封装中的焊接性能, 同时降低回流温度。 典型的Sn-Zn基焊料替代品(替代Sn-Pb)包括二元合金Sn-9Zn以及三元合金Sn-Zn-Bi, Sn-Zn-Al, Sn-Zn-Ag 和 Sn-Zn-Cu等。 目前NEC公司已经研制出Sn-8Zn-3Bi合金, 并应用于个人电脑产品上。 Fujitsu公司也于2002年6月研制出Sn-Zn-Al无铅焊料[13]。 但有关Sn-Zn基焊料在高温高湿环境下组织和性能变化的研究很少。 本文作者对Sn-Zn基焊点在120℃, 100%、 2.03×105Pa湿度下分别时效96h和192h后的微观组织演变及其低周疲劳性能进行了研究, 以探讨这些因素对焊点可靠性的影响。
1 实验
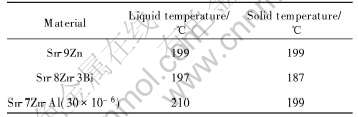
实验采用法国Avantec化学公司提供的Sn-9Zn、 Sn-8Zn-3Bi 和Sn-7Zn-Al(30×10-6)焊膏。 在涂覆Au/Ni合金的PCB(Printed circuit board)印刷电路板的铜焊盘上, 将两片FR-4板(玻璃纤维板)的焊点对中夹持, 采用回流焊形成焊点。 制造过程采用传统的SMT(Surface mount technology)工艺。 Sn-Zn基焊料的回流温度曲线的最高温度为230℃, 总的回流时间为6min, 熔点以上保温时间约1min。 然后试样取出空冷至室温, 再将其保存于2.03×105Pa、 120℃, 100%相对湿度的Hirayama PC-242 高压釜中分别时效96h和192h。 随后在室温下采用Instron 5548型微应变机械疲劳测试仪对试样进行低周疲劳测试(LCF)。 LCF实验采用的是位移控制加载模式, 实验波形为三角波(R=-1), 加载应变幅为40μm。 低周疲劳测试后的试样用金刚石刀片切割成小片, 制成金相实验试样。 组织腐蚀采用2%HCl+4%HNO3 +94%C2H5OH的溶液, 在光学显微镜和扫描电镜下观察其内部微观组织的变化, 通过SEM线扫描研究焊点中各元素的分布。 所用焊料合金列于表1。
表1 研究所用焊料合金性能
Table 1 Properties of solder alloys investigated
2 实验结果
2.1 焊点的微观结构
回流焊后空冷试样经50℃退火24h以消除残余应力[3]。 图1(a)~(c)所示分别为Sn-9Zn, Sn-8Zn-3Bi和Sn-7Zn-Al (30×10-6)的显微组织。 3种焊料中富Zn相形态随化学成分不同而变化。 图1(a)所示Sn-9Zn合金晶粒较大, 两相共晶凝固组织分布均匀, 较亮基体相是β-Sn, 暗针状是富Zn相[14]。 Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊料的微观组织由胞状混合相和粗针状相组成。 Sn-7Zn-Al (30×10-6)的微观组织主要是大胞状结构。
2.2 低周疲劳测试
表2列出了Sn-8Zn-3Bi和Sn-7Zn-Al (30×10-6)在控制位移(40μm)加载条件下焊点的平均疲劳寿命。 结果显示, Sn-8Zn-3Bi和Sn-7Zn-Al (30×10-6)焊料在经受高温和高湿环境时效后, 焊点可靠性严重下降。 在高压釜中时效96h试样的疲劳寿命是标准试样的32%~47%。 同时, 在高压釜中时效192h试样的疲劳寿命仅为标准试样的6%~10%, 说明随着时效时间的延长, 焊点的可靠性下降愈加显著。
2.3 高温、 高湿度环境下试样显微结构的演变
图2和图3所示为Sn-8Zn-3Bi 和Sn-7Zn-Al (30×10-6)焊点在高压釜中时效处理后疲劳测试失效焊点的光学显微照片。 可以发现, 在高压釜中, 试样的显微组织发生了显著变化。 时效192h后的试样基体中的黑色析出相明显比时效96h后的大[CM(22]而且多。 另外, 从图中还可以发现, 所有试样的疲劳裂纹都是沿着焊点与焊盘的界面形成并扩展(而此前的一些研究中, 焊料内部也曾发现过裂纹), 同时在焊点裂纹附近还发现了一些细微的黑色析出相。
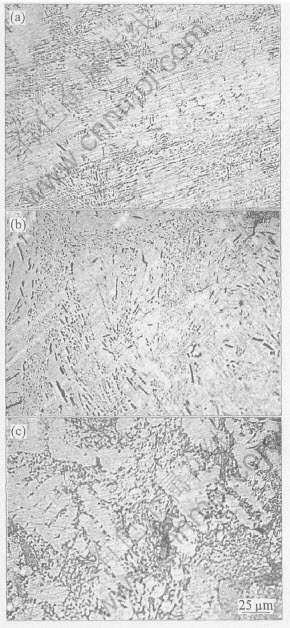
图1 Sn-9Zn, Sn-8Zn-3Bi和Sn-7Zn-0.03Al合金的显微组织
Fig.1 Microstructures of Sn-9Zn(a),Sn-8Zn-3Bi(b) and Sn-7Zn-0.03Al(c) alloys
表2 Sn-Zn基焊点的疲劳寿命
Table 2 Fatigue lifetime for Sn-Zn system solder joints
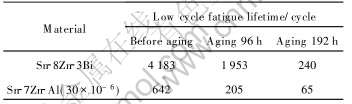
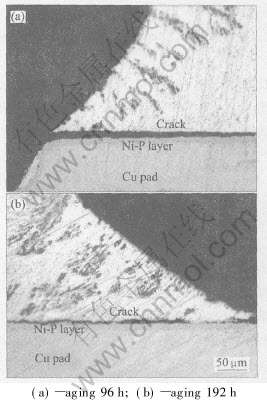
图2 Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊点试样经120℃, 100%相对湿度高压釜中时效并经LCF的失效组织
Fig.2 Failures in solder joints of Sn-8Zn-3Bi after 120℃, 100% relative humidity aging in pressure cooker and LCF testing
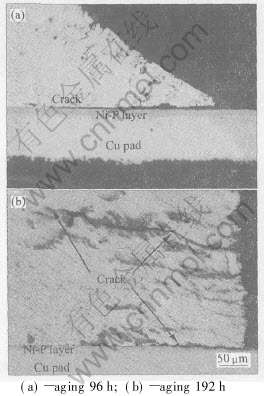
图3 Sn-7Zn-Al (30×10-6)焊点试样经120℃, 100%相对湿度高压釜中时效并经LCF后的失效组织
Fig.3 Failures in solder joints of Sn-7Zn-Al (30×10-6) after 120℃, 100% relative humidity aging in pressure cooker and LCF testing
比较图2(a)与3(a)发现, Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊点中的析出相比Sn-7Zn-Al(30×10-6)中的更加明显。 随着焊点在高压釜中时效时间的延长, Sn-7Zn-Al (30×10-6)焊料中的析出相逐渐长大并聚集, 经192h后的焊料基体中形成了大范围的暗褐色条纹状相。
2.4 线扫描结果分析
为了分析失效后焊点中及焊点与焊盘接触面的析出相和各元素的分布情况, 采用SEM线扫描对焊点基体和裂纹处界面的成分进行了进一步分析。 图4和图5分别为Sn-9Zn共晶焊料和Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊料的焊点在高压釜中时效96h后失效焊点的横截面检测结果。
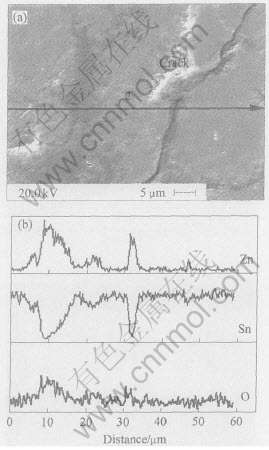
图4 Sn-9Zn焊点在120℃, 100%相对湿度,2.03×105Pa条件下时效96h后的SEM像和EDS线扫描成分分布
Fig.4 SEM image of Sn-9Zn solder after exposure to 120℃, 100% relative humidity, 2.03×105Pa condition for 96h(a) and composition distribution from EDS-test with line scanning on cross section of Sn-9Zn solder joint(b)
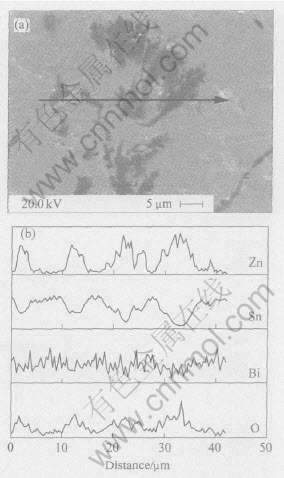
图5 Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊点在120℃, 100%相对湿度,2.03×105Pa条件下时效96h后的SEM像和EDS线扫描的成分分布
Fig.5 SEM image of Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder joint after exposure to 120℃, 100% relative humidity, 2.03×105Pa condition for 96h(a) and composition distribution from EDS-test with line scanning on cross section of Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder joint(b)
图4(a)所示为Sn-9Zn共晶焊点照片。 可见基体中存在两种条纹, 暗褐色区域“1”, 亮区“2”, 二者都有Sn元素和Zn元素。 图4(b)示出了成分沿图4(a)中箭头方向的分布。 “1”区成分为较多的Zn和少量Sn, 而“2”区正好相反。 比较图中裂纹和成分分布发现, 裂纹界面处的Zn含量比共晶成分的Zn偏高, 而Sn偏低, 这与“1”区成分分布结果类似。 结果表明, 焊点中粗化的和析出的富Zn相与疲劳裂纹方向一致。
EDS线扫描的半定量结果(表3)表明, Sn-9Zn中的“2”区含Sn 60.12%, Zn 10.25%(摩尔分数), 而暗褐色的“1”区含Zn高达20.13%, 是“2”区含Zn量的2倍。 焊点中大范围的暗褐色条纹的形成可能是晶粒粗化和形成扩散型析出相的结果, 从而弱化了两相界面的强度。
表3 Sn-9Zn焊点试样经120℃, 100%相对湿度, 2.03×105Pa时效96h后的EDS线扫描结果
Table 3 Result of EDS-test with line scanning on Sn-9Zn solder joint after exposure in 120℃,100% relative humidity, 2.03×105Pa for 96h
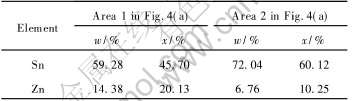
图5(a)所示为Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊料在120℃, 100%相对湿度条件下时效96h后的典型基体照片。 图5(a)中也存在一些与图4(a)完全相同的富含Zn的黑色区域(图5(b))。 从线扫描的分布曲线可知, Zn元素和O元素的含量在同一点达到峰值, 而且Zn与O的成分分布趋势相同。 为了进一步分析成分分布对性能的影响, 对焊点与Cu焊盘界面处的成分也进行了分析。
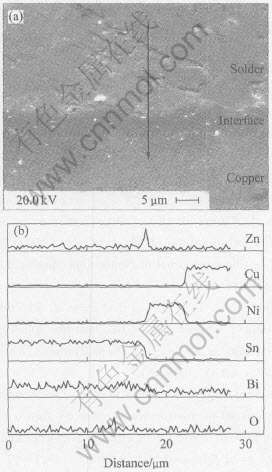
图6 未时效处理的Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊料与焊盘界面的SEM像和EDS线扫描的成分分布
Fig.6 SEM image of interface between Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder joint and copper pad without aging(a) and composition distribution from EDS-test with line scanning on cross section(b)
图6(a)所示为Cu焊盘上的Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊点 (未时效)经低周疲劳后界面处的SEM像。 图7(a)所示为Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊点经高压釜时效后, 低周疲劳后焊点界面处的SEM像。 可以看出, 暗色针状物为富Zn相。 另外, 图6(b)所示的EDS成分分布曲线表明, 在焊料与Cu焊盘的接触面附近存在Zn元素的富集。 Duan等[15]也发现, 经回火时效后, Zn原子向Cu盘界面的扩散现象, 而且在此界面上未见氧的峰值。
从图7(a)可以看出, 横截面上分布着暗褐色团状富Zn相, 因为在120℃, 100%相对湿度, 2.03×105Pa高压釜中时效后, 针状富Zn相长大为团状, 同时也形成了Zn的析出相。 根据“Zn含量的变化相应地引起氧化物的变化”这种观点, 可以说明实验过程中有Zn氧化物的形成。
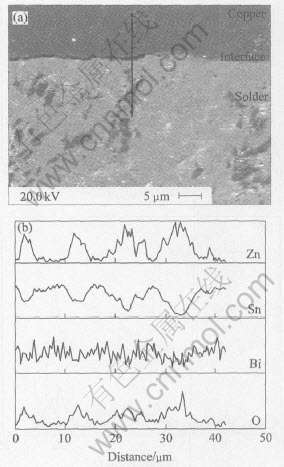
图7 Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊点在120℃, 100%相对湿度,2.03×105Pa条件下时效96h后的界面SEM像和 EDS线扫描的成分分布
Fig.7 SEM image of interface between Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder joint and copper pad after exposure to 120℃, 100% relative humidity, 2.03×105Pa condition for 96h(a) and composition distribution from EDS-analysis with line scanning on cross section between Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder joint(b)
2.5 氧化物富集
图4, 5和7的结果都表明了焊点中氧成分的变化与Zn的变化趋势基本一致。 为了更好地说明该结果, 绘制成图8。 图8(a)和(b)所示分别为图5和图7中线扫描的Zn、 O的成分分布的对比。 从图8(a)和(b)的结果可以看出, 氧当量与锌当量的比率约28%, 表明焊料中富Zn区发生了氧元素的严重富集。 结合图2~4的结果, 说明Zn、 O元素的富集或偏聚促进了焊点中显微组织各相间的结合力降低, 容易诱发裂纹的早期形成, 从而降低焊点的可靠性。
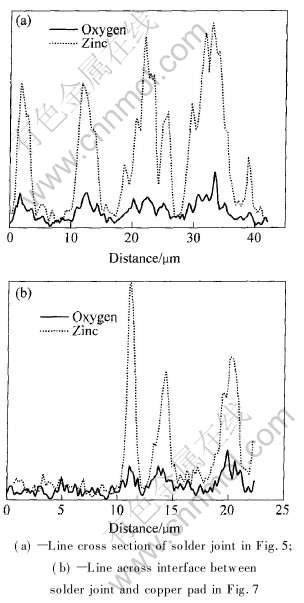
图8 Sn-8Zn-3Bi焊点经120℃,100%相对湿度,2.03×105Pa时效96h后的EDS线扫描的成分分布
Fig.8 Composition distribution from EDS analysis on line scanning of Sn-8Zn-3Bi solder joint after exposure of 120℃, 100% relative humidity, 2.03×105Pa for 96h
3 结论
高温、 高压环境下的时效显著影响Sn-Zn基无铅焊点的显微组织, 而且时效时间促进Zn相析出或富Zn相长大。 富Zn相促进界面裂纹形成, 降低焊点的低周疲劳性能。 焊点中富Zn相出现促进了O元素的吸附, 恶化焊点组织中两相的界面结合力, 从而降低焊点的可靠性。
REFERENCES
[1]Mulugeta A, Guna S. Lead-free solders in microelectrinics[J]. Materials Science and Engineering Review, 2000, 27: 95-141.
[2]Lin K L, Liu T P. High temperature oxidation of a Sn-Zn-Al solder[J]. Oxidation of Metals, 1998, 50: 255-267.
[3]何鹏, 冯吉才, 周恒. 不同钎料对Ti3Al 基合金钎焊接头强度及界面微观组织的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(1): 24-32.
HE Peng, FENG Ji-cai, ZHOU Heng. Microstructure and strength of brazed joints of Ti3Al base alloy with different filler metals[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(1): 24-32.
[4]陈晶阳, 关绍康, 林敦文, 等. Al3Ti4B中间合金对Mg27Al20.4Zn20.2Mn合金显微组织和性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(3): 478-484.
CHEN Jing-yang, GUAN Shao-kang, LIN Dun-wen, et al. Effects of Al3Ti4B master alloy on microstructure and properties of Mg27Al20.4Zn20.2Mn alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(3): 478-484.
[5]Shiue R K, Tsay L W, Lin C L, et al. The reliability study of selected Sn-Zn based lead-free solder on Au/Ni-P/Cu substrate[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2003, 43(3): 453-463.
[6]Akio H, Hiroto Y, Eiichi I, et al. Joint Strength and interfacial microstructure between Sn-Ag-Cu and Sn-Zn-Bi solders and Cu substrate[J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2004, 5(1-2): 267-276.
[7]Wang M C, Yu S P, Chang T C, et al. Kinetics of intermetallic compound formation at 91Sn-8.55Zn-0.45Al lead-free solder alloy/Cu interface[J]. Alloys & Compounds, 2004, 381(1-2): 162-167.
[8]Chang T C, Hon M H, Wang M C. Intermetallic compounds formed at the interface between Cu substrate and an Sn-9Zn-0.5Ag lead-free solder[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2003, 38(5): 909-916.
[9]Yu D Q, Xie H P, Wang L. Investigation of interfacial microstructure and wetting property of newly developed Sn-Zn-Cu solders with Cu substrate[J]. Alloys & Compounds, 2004, 385(1-2): 119-125.
[10]Lin K L, Liu P C, Song J M. Wetting Interactions between Pb-free Sn-Zn Series Solders and Cu, Ag Substrates[A]. ECTC 04 Proceedings of Electronic Components and Technology[C]. IEEE, 2004. 1310-1313.
[11]Lee H T, Chen M H, Jao H M, et al. Influence of interfacial intermetallic compound on fracture behavior of solder joints[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 358(1-2): 134-141.
[12]Suganuma K. Low Temperature Lead-Free Soldering JIEP Project (SnZnBi etc)[A]. Proceedings of International Conference on Lead Free Electronics “Towards implementation of the RHS Directive”[C]. Brussels, Belgium, 2003. 97-104.
[13]Yuki F, Michael G P, Kota F, et al. Lead-Free Soldering in the Japanese Electronics Industry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Components and Packaging Technologies, 2003, 26(3): 616-624.
[14]Kim K S, Yang J M, Yu C H, et al. Analysis on interfacial reactions between Sn-Zn solders and the Au/Ni electrolyti-plated Cu pad[J]. Alloys & Compounds, 2004, 379(1-2): 314-318.
[15]Duan L L, Yu D Q, Han S Q, et al. Microstructural evolution of Sn-9Zn-3Bi solder/Cu joint during long-term aging at 170℃[J]. Alloys & Compounds, 2004, 381(1-2): 202-207.
(编辑陈爱华)
基金项目: 上海市科委国际合作资助项目(045107006, 035007031); 欧盟“Flex-Eman”资助项目(COOP-CT-2003-507983)
收稿日期: 2005-11-28; 修订日期: 2006-04-02
通讯作者: 韦习成, 副研究员; 电话: 021-56331462; 传真: 021-56331977; E-mail: wxc1028@staff.shu.edu.cn