DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2017.07.05
喷射沉积SiCp/ Al基复合材料致密化及其显微组织与力学性能
贺毅强1, 2,李俊杰2,周海生2,冯立超1, 2,陈志钢3
(1. 江苏省海洋资源开发研究院,连云港,222005;
2. 淮海工学院 机械工程学院,连云港 222005;
3. 湖南科技大学 机电学院,湘潭 411201)
摘 要:采用热压后多道次热轧制备喷射沉积SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si复合材料板材,研究热压、轧制工艺参数对复合材料显微组织、力学性能的影响。对热压后和轧制后的SiC颗粒的形状与分布、弥散粒子形貌、致密度与硬度进行研究,并分析与总结致密化过程中孔隙与沉积颗粒的变形。结果表明:在热压温度480 ℃、压力125 MPa,且当坯料直径略小于热压模内径时进行热压会产生一定程度的剪切变形,有利于SiC颗粒的均匀分布和孔洞的闭合;此时弥散粒子粒径为50~80 nm,晶粒粒径为600~900 nm,位错少,相对密度达98.8%,但仍残留孔隙。轧制过程中的大剪切变形促进了沉积颗粒的变形和颗粒之间冶金结合,有利于提高材料的致密度和力学性能。经480 ℃多道次热轧,沉积颗粒边界消失,弥散粒子钉扎位错,Al12(Fe,V)3Si约为100 nm、晶粒约为1 μm,无明显Al13Fe4相析出,材料相对密度达99.5%。当轧制总压下量低于20%时,SiC颗粒无序分布,孔隙减少,密度和硬度增加;当总压下量为20%~40%时,由于SiC颗粒相对基体转动和滑动产生孔隙引起密度和硬度下降。总压下量超过40%时,SiC颗粒的长轴方向平行于轧制方向,SiC颗粒与基体之间的间隙逐渐弥合,密度和硬度升高。当总压下量达到95%,相对密度达99.5%。
关键词:喷射沉积;颗粒增强;铝基复合材料;致密
文章编号:1004-0609(2017)-07-1352-09 中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
快速凝固Al-Fe-V-Si合金因在α(Al)基体上弥散分布高体积分数的细小近球状硅化物粒子,因此,其具有良好的室温和高温综合性能,从而获得了广泛研究[1-2]。SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料具有弹性模量、室温强度、高温强度高与抗应力腐蚀能力、耐磨性好的特点,在航空、航天、电子和卫星遥感系统上都有很高的应用价值,在世界范围内得到了广泛的研发[3-4]。喷射沉积因工艺简单和所沉积材料氧含量低、偏析程度小、组织均匀细小的特点,成为制备高性能铝基复合材料的有效方法之一[5-7]。国内喷射沉积的研究始于20世纪80年代,哈尔滨工业大学、北京科技大学和北京航空材料研究院对喷射沉积材料的组织凝固特征和工艺过程开展研究,上海钢铁研究所在制备复合轧辊方面取得较大进展;中南大学、上海交通大学、湖南大学等科研院所与高校在喷射沉积制备铝合金与铝基复合材料方面进行了深入研究[8-10]。但喷射沉积铝合金沉积颗粒表面存在轻微的氧化(含氧量(质量分数)一般为0.01%~0.05%),破坏了颗粒之间的完整冶金结合,且沉积坯中的孔隙率(体积分数)达15%~20%,降低了材料的性能。因此,喷射沉积铝基复合材料的后续致密化研究成为国内外众多学者共同关注的课题,采用的致密化方法主要为挤压、轧制、热等静压及旋压等[11-13]。采用挤压、热等静压、旋压等工艺进行致密化和塑性变形具有很多优势,但存在如下两个问题亟待解决:1) 产品规格受设备能力的限制和SiC颗粒的层状分布和偏聚问题,因此需要改善坯料致密化技术,确保显微组织的均匀性、工艺的简单可行性;2) 轧制大规格复合材料板材的预致密与工艺参数的选择。添加SiC后的SiCp/Al复合材料轧制工艺较合金材料更为苛刻,因此,优化轧制工艺对于制备高性能的复合材料板材尤为重要。
张昊等[14]采用陶粒轧制和外框限制轧制有效致密了喷射沉积SiCp/Al基复合材料,改善了复合材料的组织,提高了复合材料的力学性能。陈志钢等[15]采用楔形压制致密喷射沉积SiCp/Al基复合材料,获得了大尺寸环形件。孙有平等[16]研究了喷射沉积SiCp/Al基复合材料锭坯在楔形压制、等径角挤压过程中的致密化行为、SiC颗粒的破碎、运动及再分布规律。贺毅强等[17-19]采用多层喷射沉积制备了SiCp/Al基复合材料,并采用楔形压制进行致密,以使增强颗粒分布均匀,显微组织细小,力学性能较好。但采用陶粒轧制、外框限制轧制和楔形压制等致密沉积态铝基复合材料都存在塑性变形不充分的问题,难以实现沉积颗粒之间完全冶金结合。
因此,昆明理工大学的钟毅团队开发了喷射沉积连续挤压工艺,具有短流程、近净形、致密度高的特点,适于成形中小规格的管棒型材[20]。为克服以上致密化技术周期长、设备昂贵或塑性变形不充分等局限性,本文作者采用热压预致密喷射沉积SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料,再通过多道次热轧获得大尺寸致密板材。其工艺简单可行,且可实现沉积颗粒之间完全冶金结合。
本文作者研究了热压工艺参数对喷射沉积铝基复合材料致密化状况的影响和轧制工艺参数对复合材料成形性能、显微组织、力学性能的影响,且研究了热压后轧制过程中SiC颗粒的形状与分布、弥散粒子形貌、致密度与硬度的演变,并对致密过程中的物相进行了分析。旨在评估采用热压致密后再轧制的工艺制备组织均匀的SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料板材的可行性以及工艺优化的可行性,对于喷射沉积技术制备复合材料的产业化具有较为重要的指导意义,有望扩展喷射沉积多孔材料的应用前景。
1 材料与方法
1.1 原料及成分设计
本试验以名义成分为15%SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V- 1.7Si复合材料为研究对象,Fe和V以Al-40Fe和Al-40Fe-10V中间合金的形式加入。SiC颗粒为β-SiC,平均粒径约为10 μm,在复合材料中体积分数约为15%。通过多层喷射沉积设备实现SiC颗粒与Al-Fe-V-Si基体的共沉积。
1.2 塑性加工
将沉积锭坯车削成直径为155 mm的圆柱形坯料,然后在热压模内进行压制,热压模内径为160 mm。锭坯加热温度为430~500 ℃,保温1 h,模具及热压模加热温度为400 ℃,保温1 h。将一次热压得到的锭坯再车削成直径为155 mm的圆柱形坯料,在相同的工艺参数下进行第二次热压。将二次热压得到的坯料机加工成板坯进行多道次轧制,轧制温度为480~520 ℃,轧制前保温1 h,道次间退火保温时间20 min,采用石墨+机油润滑,轧速为0.43 m/s。
1.3 检测方法
常温拉伸试验在CSS-44100型电子万能试验机上进行,拉伸速率为0.5 mm/min,拉伸方向平行于板材轧制方向。金相样品在XJL-03金相显微镜(Optical Microscope, OM)下进行组织观察。采用H800和JEOL 3010透射电镜(Transmission electron microscope,TEM)观察弥散粒子及晶粒的变化,并用能谱(EDAX)分析各成分的相对含量。采用阿基米德法测量试样密度。X射线衍射物相分析在XD98全自动X射线衍射仪上进行,采用铜靶辐射,管压为36 kV,管流为30 mA,2θ为20°~80°。
2 结果与讨论
对于热敏感的SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料,变形温度和变形量是影响到复合材料的显微组织和最终力学性能的主要因素。
2.1 对显微组织与力学性能的影响
2.1.1 热压温度
SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料热变形抗力高,在较低的变形温度下难以致密。图1所示为热压轴向压力为125 MPa时,变形温度分别为430和480 ℃时SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si复合材料的显微组织。
当坯料变形温度为430 ℃时,Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si的变形抗力约为130 MPa。如图1(a)所示,由于轴向压力低于其变形抗力,坯料变形不充分,沉积颗粒之间的边界和孔隙仍较为明显,不利于材料的进一步成形。当变形温度提高至480 ℃时,基体合金的变形抗力约为100 MPa,轴向压力高于其变形抗力。如图1(b)所示,沉积坯变形充分,颗粒边界基本消失,颗粒间结合良好,有利于后续轧制。
2.1.2 轧制温度
图2所示对比了经480 ℃热压后的SiCp/Al基复合材料板坯分别在480℃和520℃下轧制后的弥散粒子。
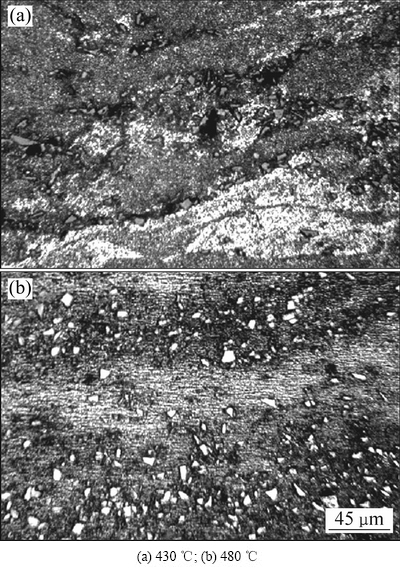

图1 不同变形温度下SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si复合材料热压致密后的显微组织
Fig. 1 Microstructures of SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si composite as hot-pressed at different temperatures
图2(a)所示为沉积板坯的TEM像和弥散粒子A的衍射图样,TEM像中深色弥散粒子A的EDAX分析结果如表1所列,x(Fe+V):x(Si)=3.03,白色区域为纯Al。综合分析可知,沉积态的板坯主要由α(Al)与BCC结构的Al12(Fe,V)3Si(a=1.260 nm)弥散粒子,Al12(Fe,V)3Si呈球状与近球状,直径为50~80 nm,均匀分布在α(Al)基体上。热压后经480 ℃热轧后,弥散粒子约为100 nm(见图2(b))。轧制温度提高到520 ℃时,粒子明显长大至200~300 nm(见图2(c))。有学者[21]研究发现,随着变形温度升高,Al12(Fe,V)3Si粗化,且逐渐聚集于晶界,对晶界的钉扎作用减弱,晶粒长大。高温滞留导致轧制过程中第二相粒子的粗大,这是因为在轧制过程中,变形热和摩擦热致使强烈剪切变形区金属产生区域温升,流动金属实际经历的温度要高于加热温度。在低于500 ℃进行轧制时,金属高温滞留时间短,温升的不良影响小,然而,在高于500 ℃进行轧制时,温升影响大, Al12(Fe ,V)3Si颗粒粗化,甚至产生有害相。因此,在高于500 ℃以上轧制,导致弥散粒子和晶粒的粗化。
将沉积态的SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si复合材料板坯经480 ℃、轴向压力为125 MPa下热压后,在不同变形温度条件下进行轧制,其他工艺参数一致,各温度下轧制出的板材力学性能如表2所列。
从表2可以看出,当轧制温度低于480 ℃时,轧制板材的室温强度和断后伸长率随着轧制温度的提高而提高;当轧制温度高于480 ℃后,室温强度和断后伸长率随着轧制温度的升高而下降。
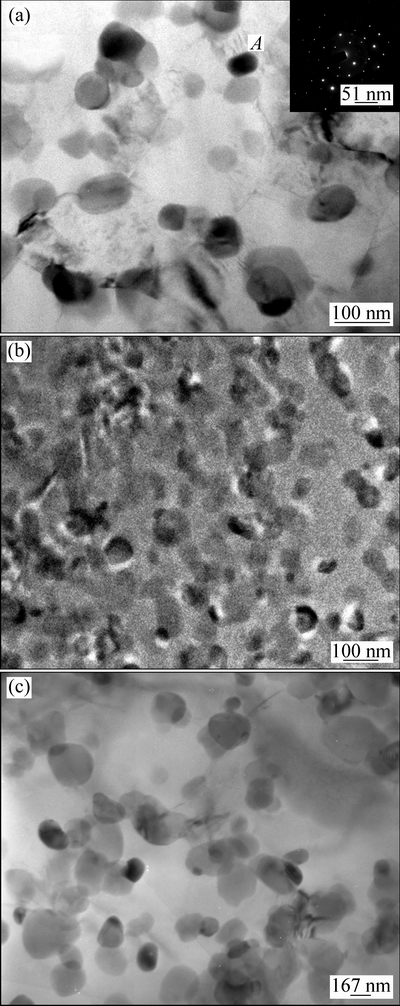
图2 复合材料板坯在不同温度下轧制板材的弥散粒子
Fig. 2 Dispersion particles of composite sheet as-deposited (a), as-rolled at 480 ℃ (b) and 520 ℃ (c)
表1 弥散相A的EDAX结果
Table 1 Results of dispersion A in as-deposited composite by EDAX

表2 SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si在不同温度下轧制板材的室温力学性能
Table 2 Ambient temperature mechanical properties of SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si rolled at different temperatures
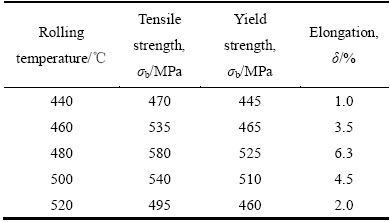
对于Al-Fe-V-Si合金而言,挤压或者轧制温度较低时,其室温强度就越高。但对SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料而言,变形温度在440 ℃到480 ℃之间时,基体与增强颗粒间变形协调能力差,成形过程中基体与颗粒间易出现微观裂纹,导致板材性能下降;当温度达到480 ℃时,复合材料成形能力较好,SiC颗粒与基体结合良好,微裂纹少,力学性能较好;轧制温度高于480 ℃时,由于高温导致材料晶粒与弥散强化相的长大,板材的力学性能下降。
2.2 热压后的显微组织与致密度
2.2.1 显微组织
图3所示为SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料热压后的SiC颗粒分布。从图3(a)可以看出, SiC颗粒的分布并没有出现分层的现象,仍保留着沿沉积颗粒表面分布的特点(见图3(b))。这是因为:喷射沉积时SiC颗粒主要粘附在沉积颗粒表面,而热压过程中SiC颗粒的流动较小,保留了沉积态下SiC颗粒分布的特点。SiC颗粒的均匀分布对防止因SiC颗粒聚集引起应力集中导致材料力学性能下降有利。圆柱坯料在压缩变形过程中,坯料直径略小于热压模内径,材料发生压缩变形和横向流动,孔洞同时受到静水压力和剪切应力的综合作用,静水压力使孔洞发生压缩变形,而且剪切变形作用使孔洞拉长、破碎,有利于孔洞的闭合。
2.2.2 热压后的致密度
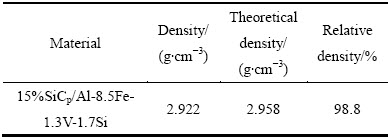
表2所列为15%SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si经二次热压后的密度及相对密度。从表2可知,由于二次热压较大的静水压力作用和一定的横向塑性流动,复合材料坯料的致密度显著提高,相对密度达98.8%,但由于剪切变形量小,沉积颗粒间仍残留孔隙。
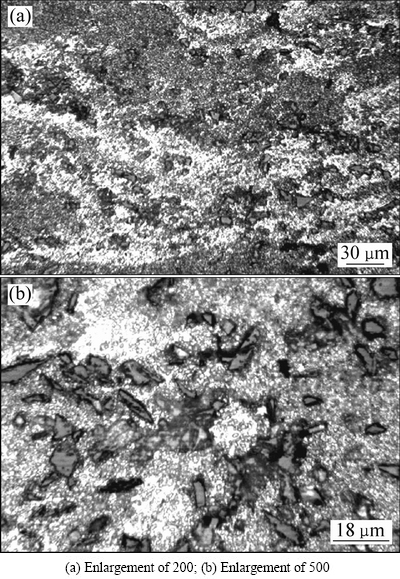
图3 热压态SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料的SiC颗粒分布
Fig. 3 SiC particle distribution of SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si as-hot pressed
表2 15%SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si热压后的密度以及相对密度
Table 2 Density and relative density of 15%SiCp/Al-8.5Fe- 1.3V-1.7Si as-hot pressed
2.3 轧制过程中的显微组织与力学性能
2.3.1 SiC颗粒、孔隙
将喷射沉积SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料锭坯在480 ℃下进行热压致密。因未经大的塑性变形,板坯保留了喷射沉积态下由于扫描形成的SiC颗粒层状分布,沉积颗粒间结合较沉积态有改善,但仍存在孔隙,SiC颗粒主要沿沉积颗粒表面分布,未出现明显的SiC颗粒聚集现象(见图4(a))。通过后续的多道次热轧后,SiC颗粒层与层之间的距离减小,逐渐实现SiC颗粒的均匀分布。当轧制总压下量为20%时,沉积颗粒间的残留孔隙减少,颗粒边界消失,SiC颗粒分布均匀且无方向性(见图4(b))。当轧制总压下量为40%时,SiC颗粒分布更均匀,SiC颗粒长轴方向平行于轧制方向,SiC颗粒与基体金属之间存在间隙(见图4(c))。总压下量增大至60%时, SiC颗粒分布呈明显方向性,且SiC颗粒与基体间隙消失(见图4(d))。
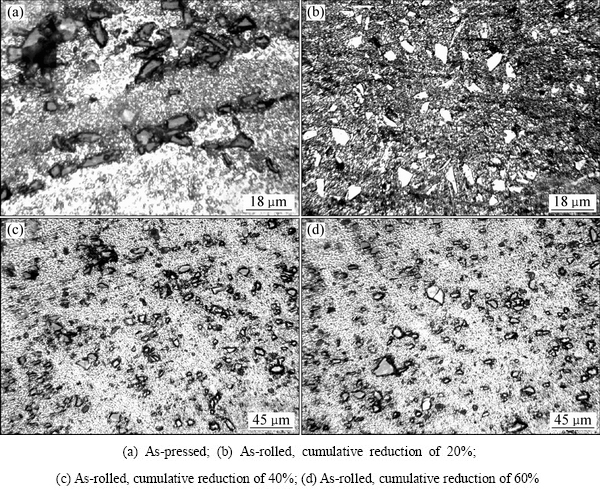
图4 SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si复合材料坯料经480 ℃热压后轧制过程中板材显微组织演变
Fig. 4 Microstructure evolution of SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si composites
从图4可以看出,轧制过程中SiC颗粒发生转动与滑动,经多道次轧制后,SiC颗粒长轴方向平行于轧制方向。有研究认为[22],SiC增强颗粒转动的宏观原因是金属的不均匀流动。在SiC增强颗粒和其周围不均匀流动的基体中,如果存在速度梯度,则SiC增强颗粒会以长轴的中点为转动轴进行转动,由此可见,金属不均匀流动导致SiC增强颗粒周围金属不同方向的流动,使SiC增强颗粒产生了转动的力矩。且金属流动越不均匀,增强颗粒所受转动力矩越大,增强颗粒越易转动;增强颗粒长轴与金属流动方向夹角越大,增强颗粒所受的转动力矩越大,增强颗粒越易转动。在热压与轧制过程中主要发生孔洞变形、沉积颗粒间的结合与SiC颗粒的转动。
1) 孔洞变形
孔洞变形由孔隙的形状变化和体积变化两部分组成,通过基体材料的塑性变形实现,基体材料与孔隙的变形相互影响。多孔材料的塑性泊松比小于0.51,正比于材料的相对密度[23]。孔洞的闭合方式有[24]:由静水压力引起的孔洞收缩;垂直压应力与剪切力共同作用使孔洞延长、崩塌。孔洞的变形不但与变形过程有关,且受应力状态的影响。
静水压力可以使孔洞体积缩小,但难以完全消除孔洞。且在无剪切变形的情况下,孔洞内表面的氧化物和污染层阻碍了内表面的冶金结合。SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si圆柱体坯料在热压过程中,压坯直径应小于压模内径,使压坯在压缩过程中同时产生横向剪切变形,有利于孔洞的闭合。且剪切力会使压扁孔洞的相对面之间发生相对摩擦,破坏氧化膜并形成新鲜表面,使部分己被压扁孔洞的内界面形成牢固的冶金结合。
2) 沉积颗粒间的结合与SiC颗粒的转动
喷射沉积过程中在沉积表面形成氧化膜,阻碍颗粒之间的结合,热压的剪切作用小,需通过后续的轧制来破碎氧化膜。轧制过程中产生的剪切力可使沉积颗粒发生剪切变形,破坏颗粒的原始边界,形成新鲜表面并相互结合,实现颗粒间良好的冶金结合[25]。
在喷射沉积颗粒增强铝基复合材料的致密化过程中,随着成形压力继增加,沉积颗粒间出现机械啮合和冶金结合,孔隙减少,沉积颗粒特性逐渐消失,材料密度与硬度升高。随着变形量的继续增大,由于增强颗粒周围基体金属的不均匀流动,增强颗粒相对基体发生转动与滑动,二者之间产生微裂纹,材料密度与硬度下降。随着变形量的进一步增大,增强颗粒转动至长轴方向平行于最大变形方向,且分布更均匀。增强颗粒与基体之间的孔洞弥合,材料密度与硬度增加。
2.3.2 弥散粒子与晶粒
图5所示为复合材料经过致密化后弥散粒子的形貌与分布和晶粒。图5(a)所示为沉积态复合材料的显微组织,弥散粒子均匀细小,粒径为50~80 nm,呈近球状,晶粒粒径约为300 nm。谭敦强等[26]研究了冷却速率对Al-Fe-V-Si合金相组成的影响。研究发现:当冷却速率大于102K/s时,合金中出现大量的Al12(Fe,V)3Si粒子;当冷却速率大于103K/s时,合金中不会存在Al13Fe4相;当冷却速率大于104K/s时,合金中主要存在Al12(Fe,V)3Si粒子。喷射沉积过程中,微小熔滴依靠与气体的对流热交换可以达到104~106K/s的冷却速率,而在与沉积基体碰撞时也可以获得较高的冷却速率。因此,沉积坯中弥散粒子主要为Al12(Fe,V)3Si[26]。Al12(Fe,V)3Si弥散粒子是由α(Al)过饱和固溶体在凝固后高温滞留和再辉温升效应作用下脱溶分解而成,或是在溶质分配凝固过程中在溶质富集而析出。480 ℃热压后弥散粒子粒径仍为50~80 nm,晶粒粒径为600~900 nm。由于热压过程中材料塑性变形小,基体中位错密度低,晶内位错少(见图5(b))。通过后续480 ℃下热轧,弥散粒子粒径略长大至100 nm,晶粒粒径约为1 μm(见图5(c)),并形成亚晶。从图5可以看出,经过塑性变形后,弥散粒子大多分布在晶界上。 等[27]认为在晶界被弥散粒子钉扎以前有轻微移动,因此,晶内位错和弥散粒子少,晶粒在加热过程中因晶界受到弥散粒子的钉扎而不易长大。铝基体的堆垛层错能高,使位错易于交滑移,在热轧过程中,加工硬化与动态回复软化同时发生,螺位错交滑移和刃位错攀移导致同号位错重排及异号位错对消,从而使位错密度降低;另一方面,由于多边形化形成等轴亚晶。此外,弥散分布的Al12(Fe,V)3Si粒子阻碍位错重排、晶界滑动与迁移,位错在弥散粒子附近产生缠结。
等[27]认为在晶界被弥散粒子钉扎以前有轻微移动,因此,晶内位错和弥散粒子少,晶粒在加热过程中因晶界受到弥散粒子的钉扎而不易长大。铝基体的堆垛层错能高,使位错易于交滑移,在热轧过程中,加工硬化与动态回复软化同时发生,螺位错交滑移和刃位错攀移导致同号位错重排及异号位错对消,从而使位错密度降低;另一方面,由于多边形化形成等轴亚晶。此外,弥散分布的Al12(Fe,V)3Si粒子阻碍位错重排、晶界滑动与迁移,位错在弥散粒子附近产生缠结。

图5 复合材料不同加工状态下的弥散粒子
Fig. 5 Dispersions of composite

图6 SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si经热压后轧制过程的密度和硬度变化
Fig. 6 Density and hardness evolution SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si during rolling
2.3.3 致密度与硬度
图6所示为热压态复合材料在轧制过程中硬度和密度的变化过程。如图6(a)所示,因复合材料在热压过程中未经历充分的塑性变形,沉积颗粒之间的孔洞边界未完全消除。在轧制初始阶段,沉积颗粒间的孔隙在轧制压力和剪切力作用下发生变形和弥合,材料密度升高。当轧制总压下量低于20%时,密度和硬度随着压下量增加。当总压下量大于20%时,由于SiC颗粒相对基体产生转动和滑动,SiC颗粒与基体之间产生孔隙导致密度和硬度下降。总压下量约为40%时,密度与硬度值最低。当总压下量超过40%时,SiC颗粒长轴方向平行于轧制方向,SiC颗粒与基体之间的间隙逐渐弥合,密度和硬度升高。当总压下量达到95%,密度和硬度基本稳定,相对密度达99.5%。
2.4 X射线衍射物相分析
图7所示为在沉积态、热压态和轧制态SiCp/ Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si复合材料的XRD谱。从图7可以看出,喷射沉积复合材料经过480 ℃热压、480 ℃热轧后,其衍射峰并没有发生明显变化,沉积态复合材料的衍射峰主要由α-SiC、α(Al)、Al12(Fe,V)3Si的衍射峰组成。此外,在热变形过程中,Al12(Fe,V)3Si衍射峰的峰强增加,这说明在热变形过程中过饱和的α(Al)继续析出Al12(Fe,V)3Si相。经过后续的热加工,其衍射峰中未出现该耐热铝合金中在高温加热过程中易出现的Al13Fe4相衍射峰,这说明在后续热致密过程中Al12(Fe,V)3Si保持稳定,未发生明显的向Al13Fe4相的转变,与图5所反映的显微组织一致。
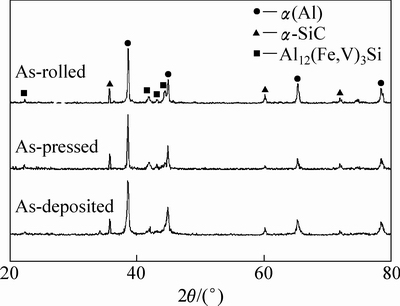
图7 复合材料在沉积态、挤压态和经热轧轧薄后的XRD谱
Fig. 7 XRD patterns of Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si/SiC composite as-deposited, as-pressed, and as-rolled
3 结论
1) 在本实验条件下,热压温度480 ℃、热压压力125 MPa,且当坯料直径略小于热压模内径时静水压力有利于喷射沉积复合材料中孔隙的缩小,而横向流动产生一定程度的剪切变形有利于SiC颗粒的均匀分布和孔洞的闭合,相对密度达98.8%,位错少,弥散粒子粒径为50~80 nm,晶粒粒径为600~900 nm;
2) 轧制温度为480 ℃有利于保持复合材料中弥散粒子与晶粒的细小,轧制过程中沉积颗粒变形,颗粒之间实现冶金结合,有利于提高材料的致密度和力学性能。经480 ℃多道次热轧,沉积颗粒边界消失,材料相对密度达99.5%,弥散粒子粒径约为100 nm、晶粒粒径约为1 μm,无明显Al13Fe4相析出,弥散粒子阻碍位错运动并产生位错缠结;轧制温度低于480 ℃,增强颗粒与基体间协调能力差而出现微裂纹,导致性能下降;当轧制温度高于于480 ℃时,弥散粒子与晶粒粗化,力学性能下降。
3) 当轧制总压下量低于20%时,SiC颗粒无序分布,密度和硬度增加;当总压下量为20%~40%时,由于SiC颗粒相对基体转动和滑动产生孔隙引起密度和硬度下降;总压下量超过40%时,SiC颗粒长轴方向平行于轧制方向,SiC颗粒与基体之间的间隙逐渐弥合,密度和硬度升高;当总压下量达到95%,相对密度达99.5%。
REFERENCES
[1] KORAMAN E,  M, SAYILGAN S, KALKANLI A. Dry sliding wear behaviour of Al-Fe-Si-V alloys at elevated temperatures[J]. Wear, 2015, 322/323: 101-107.
M, SAYILGAN S, KALKANLI A. Dry sliding wear behaviour of Al-Fe-Si-V alloys at elevated temperatures[J]. Wear, 2015, 322/323: 101-107.
[2] SUN S B, ZHENG L J, PENG H, ZHANG H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Fe-V-Si aluminum alloy produced by electron beam melting[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 659: 207-214.
[3]  K, ZHU S J. Creep behaviour of an Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si-15Si/SiCp composite at temperatures ranging from 873 to 948K[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 328(1/2): 283-290.
K, ZHU S J. Creep behaviour of an Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si-15Si/SiCp composite at temperatures ranging from 873 to 948K[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2002, 328(1/2): 283-290.
[4] PENG L M, ZHU S J, MA Z Y, BI J, WANG F G, CHEN H R, NORTHWOOD D O. High temperature creep deformation of Al18B4O33 whisker-reinforced 8009 Al composite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1999, 265(1/2): 63-70.
[5] CHEN X, YANG C X, GUAN L D, YANB. TiB2/Al2O3 ceramic particle reinforced aluminum fabricated by spray deposition[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 496(1/2): 52-58.
[6] SU B, YAN H G, CHEN G, SHI J L, CHEN J H, ZENG P L. Study on the preparation of the SiCp/Al-20Si-Cu functionally graded material using spray deposition[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(24/25): 6660-6665.
[7] LI W, CHEN Z H, CHEN D, TENG J, FAN C H. Low cycle fatigue behavior SiCp/Al-Si composites produced by spray deposition[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(29/30): 7631-7637.
[8] 李 超, 彭超群, 余 琨, 王日初, 杨 军, 刘 溶. 喷射沉积70%Si-Al合金电子封装材料的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009, 19(2): 303-307.
LI Chao, PENG Chao-qun, YU Kun, WANG Ri-chu, YANG Jun, LIU Rong. Microstructure and properties of spray deposition 70%Si-Al alloy for electronic packaging applications[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(2): 303-307.
[9] 蔡元华, 梁瑞光, 苏占培, 张济山. 喷射成形Al-22Si-5Fe合金的热变形行为及组织稳定性[J]. 金属学报, 2010, 46(7): 814-820.
CAI Yuan-hua, LIANG Rui-guang, SU Zhan-pei, ZHANG Ji-shan. Hot deformation behavior and microstructural stability of spray formed Al-22Si-5Fe alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(7): 814-820.
[10] 李 微, 陈振华, 陈 鼎, 滕 杰. 喷射沉积SiCp/Al-7Si复合材料的疲劳裂纹扩展[J]. 金属学报, 2011, 47(1): 102-108.
LI Wei, CHEN Zhen-hua, CHEN Ding, TENG Jie. Crowth behavior of fatigue crack in spray-formed SiCp/Al-7Si composite[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2011, 47(1): 102-108.
[11] YU H C, WANG M P, Jia Y L, XIAO Z, CHEN C, LEI Q, LI Z, CHEN W, ZHANG H, WANG Y G, CAI C Y. High strength and large ductility in spray-deposited Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 601(15): 120-125.
[12] GUO Biao, GE Chang-chun, XU Yi. Flow behavior and numerical simulation of spray-formed FGH 95 superalloy under hot compression[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2013, 20(12): 69-74.
[13] MAZZER E M, AFONSO C R M, BOLFARINI C, KIMINAMI C S. Microstructure study of Al 7050 alloy reprocessed by spray forming and hot-extrusion and aged at 121 ℃[J]. Intermetallics, 2013, 43: 182-187.
[14] ZHANG Hao, CHEN Ding, CHEN Zhen-hua. Densification of spray deposited aluminum composite sheets via ceramic rolling technique[J]. Materials and Manufacturing Process, 2008, 23(5): 479-483.
[15] CHEN Zhi-gang, CHEN Zhen-hua, TANG Gun-ning. Processing, microstructure, and mechanical properties of large spray- deposited hypoeutec TiC Al-Si alloy tubular preform[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2011, 20(2): 238-243.
[16] SUN Y P, YAN H G, CHEN Z H, CHEN D, CHEN G. Effect of a novel sequential motion compaction process on the densification of multi-layer spray deposited 7090/SiCp composite[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2008, 43(8): 6200-6205.
[17] HE Y Q, TU H, QIAO B, FENG L C, YANG J M, SUN Y P. Tensile fracture behavior of spray deposited SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si composite sheet[J]. Advanced Composite Materials, 2013, 22(4): 227-237.
[18] 贺毅强. 多层喷射共沉积制备SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si复合材料[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(2): 109-114.
HE Yi-qiang. SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si composites prepared by multi-layer spray co-deposition[J]. Acta Material Composite Sinica, 2012, 29(2): 109-114.
[19] 贺毅强, 胡建斌, 张 奕, 陈志钢, 冯立超, 陈振华. 喷射沉积SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si板坯楔形压制后轧制的显微组织与断裂行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(8): 2035-2043.
HE Yi-qiang, HU Jian-bin, ZHANG Yi, CHEN Zhi-gang, FENG Li-chao, CHEN Zhen-hua. Microstructure and fracture behaviour of spray-deposited SiCp/Al-Fe-V-Si sheet as-rolled after wedge pressing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2014, 24(8): 2035-2043.
[20] 汪创伟, 尹建成, 周静波, 刘英莉, 高 鹏, 李明瀚, 钟 毅. 喷射沉积连续挤压制备2A12铝合金[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(4): 957-963.
WANG Chuang-wei, YIN Jian-cheng, ZHOU Jing-bo, LIU Ying-li, GAO Peng, LI Ming-han, ZHONG Yi. 2A12 aluminum alloy produced by spray forming conform[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2013, 23(4): 957-963.
[21] 肖于德, 钟 掘, 黎文献, 马正青. 快速凝固Al-Fe-V-Si合金喷射沉积坯的显微组织与力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(11): 1869-1875.
XIAO Yu-de, ZHONG Jue, LI Wen-xian, MA Zheng-qing. Microstructure features and mechanical properties of spray deposited billets of rapidly solidified Al-Fe-V-Si aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(11): 1869-1875.
[22] 张文龙. SiCW/Al复合材料的大应变变形和再结晶[J]. 材料导报, 2000, 14(12): 43-48.
ZHANG Wen-long. Large strain deformation and recrystallization of SiCW/Al composite[J]. Materials Review, 2000, 14(12): 43-48.
[23] 黄培云. 粉末冶金原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2000: 342-346.
HUANG Pei-yun. Powder metallurgy theory[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000: 342-346.
[24] KUHN H A. Effects of porosity in materials processing[J]. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1976, 16: 171-188.
[25] 田荣璋. 铝合金及其加工手册[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2000: 328-332.
TIAN Rong-zhang. Aluminium alloy andits processing manual[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2000: 328-332.
[26] 谭敦强, 唐建成, 黎文献, 肖于德, 王日初, 陈 伟. 冷却速度对Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si合金主要相组成的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(8): 1226-1230.
TAN Dun-qiang, TANG Jian-cheng, LI Wen-xian, XIAO Yu-de, WANG Ri-chu, CHEN Wei. Effect of cooling rate on primary phase constitutes of Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(8): 1226-1230.
[27]  F, TORRALBA M, EDDAHBI M, RUANO O A. Elevated temperature creep behavior of three rapidly solidified Al-Fe-Si materials containing Cr, Mn, or Mo[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 230(1/2): 116-123.
F, TORRALBA M, EDDAHBI M, RUANO O A. Elevated temperature creep behavior of three rapidly solidified Al-Fe-Si materials containing Cr, Mn, or Mo[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1997, 230(1/2): 116-123.
Densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of spray deposited SiCp/Al-matrix composites
HE Yi-qiang1, 2, LI Jun-jie2, ZHOU Hai-sheng2, FENG Li-chao1, 2, CHEN Zhi-gang3
(1. Jiangsu Marine Resources Development Research Institute, Lianyungang 222005, China;
2. College of Mechanical Engineering, Huaihai Institute of Technology, Lianyungang 222005, China;
3. College of Electromechanical Engineering, Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan 411201, China)
Abstract: SiCp/Al-8.5Fe-1.3V-1.7Si composite prepared by spray deposition were densified by hot pressing, and then were rolled into sheets. Effects of hot pressing parameters and rolling parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties were investigated. Shape and distribution of SiC particles, shape of dispersoids, density and hardness of the composite as-hot pressed and as-rolled were studied separately. Evolution of pores and deposited particles during densification process were discussed and summarized. The results show that hot pressing temperature of 480 ℃ and 125 MPa, and smaller diameter of the billet than the inner diameter of the hot die are benefit for homogeneous distribution of SiC particles and void closing. Dispersoids of the composite as-pressed is 50-80 nm in diameter, and grain is 600~900 nm in diameter with few dislocation in the grains. Relative density of the composite as-pressed is up to 98.8% with residual pores remaining. Large plastic shear strain of multi-pass hot rolling contributes to deformation of deposited particles and metallurgical bonding between the particles, subsequently benefits to densification and mechanical properties of the composites. After multi-pass hot rolling at 480 ℃, boundaries among deposited particles disappear, and dislocations are pinned by dispersoids in the matrix with Al12(Fe,V)3Si dispersoids of about 100 nm, and grains are about 1 μm in diameter without Al13Fe4 forming. Relative density of the composite as-rolled is up to 99.5%. SiC particles distribute randomly, and density and hardness increase because of pore reducing and eliminating when cumulative reduction is below 20%. Then density and hardness decrease because of pores resulted from rotation and sliding between SiC particles and the matrix when cumulatie reduction is 20%-40%. Long axis of SiC particle becomes parallel to rolling direction, pores between SiC particles and the matrix disappear, and density and hardness increase when cumulative reduction is over 40%. Relative density of the composite is up to 99.5% with cumulative reduction of 95%.
Key words: spray deposition; particle reinforcement; Al-matrix composite; densification
Foundation item: Projects(BK20141250, BE2015100) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China; Project(14KJB430005) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Colleges and Universities, China; Projects(51004050, 51301044) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects(CG141, CXY1404) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Lianyungang, China; Project (JSIMR201222) supported by the Marine Resources Development Institute of Jiangsu Foundation, China; Project (PPZY2015C214) supported by the Top-notch Academic Programs of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, China
Received date: 2015-12-28; Accepted date: 2017-04-03
Corresponding author: HE Yi-qiang ; Tel.: +86-518-85895330; E-mail: ant210@126.com
(编辑 何学锋)
基金项目:江苏省自然科学基金资助项目(BK20141250,BE2015100);江苏省高校自然科学研究面上项目(14KJB430005);国家自然科学基金资助项目(51004050,51301044);连云港市科技计划资助项目(CG141,CXY1404);江苏省海洋资源开发研究院开放基金资助项目(JSIMR201222);江苏高校品牌专业建设工程资助项目(PPZY2015C214)
收稿日期:2015-12-28;修订日期:2017-04-03
通信作者:贺毅强,教授,博士;电话:0518-85895330;E-mail:ant210@126.com