广西大厂锡多金属矿田侵入岩地球化学特征:岩石成因及地球动力学意义
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2015年第1期
论文作者:成永生1$ 2$ 3
文章页码:284 - 292
关键词:地球化学;岩石成因;构造背景;岩浆演化;大厂矿田;广西
Key words:geochemistry; petrogenesis; tectonic setting; magma evolution; Dachang ore field; Guangxi
摘 要:对广西大厂矿田的侵入岩体开展主量元素、微量元素以及稀土元素的分析。结果表明,岩石中斑晶和基质主要由石英、钾长石以及斜长石组成,其中,斑晶约占15%,基质约占85%。岩石中硅含量偏低,Al2O3含量偏高;另外,Ca、Fe2O3、Na以及TiO2等含量也较低。侵入岩体中碱含量中等,属于富钾型岩石;稀土元素含量中等至偏低,其中,轻稀土元素和重稀土元素高度分馏,显示出Ce微弱负异常、Eu负异常特征。岩体富集轻稀土元素,Rb、Sr以及U等大离子亲石元素也较富集,而Nb、Th等高场强元素则相对亏损。稀土元素球粒陨石标准化分布型式总体表现出较好的一致性,大体上表明各岩体具有相似的特点、来源以及演化等,侵入岩体主要形成于碰撞时期以及板内构造时期。
Abstract: The major element, trace element and rare earth element (REE) of the intrusion rock from the Dachang ore field in Guangxi, China, were analyzed. The results show that the phenocryst (about 15%) and matrix (about 85%) mainly consist of quartz, K-feldspar and plagioclase. The rock is composed of low content of Si and high content of Al2O3, low contents of Ca, Fe2O3, Na, TiO2, etc. The intrusion rock has the medium alkali content, attributing to K-rich type rock; and contains medium to low REE contents, of which light rare earth elements (LREEs) and heavy rare earth elements (HREEs) are highly fractionated, showing a weak negative Ce anomaly and a negative Eu anomaly. These rocks are enriched in LREE, and the large ion lithophytes elements (LILE) are rich in Rb, Sr, and U; the high-field-strength elements (Nb, Th, etc) are relatively depleted. The REE chondrite-normalized patterns are consistent with the overall, roughly indicating their similar characteristics, sources and evolution. The intrusion rock mainly formed during the collisional and within-plate periods.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25(2015) 284-292
Yong-sheng CHENG1, 2, 3
1. Key Laboratory of Metallogenic Prediction of Nonferrous Metals, Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. School of Geosciences and Info-Physics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Ore Deposit Geochemistry, Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guiyang 550002, China
Received 26 December 2013; accepted 30 June 2014
Abstract: The major element, trace element and rare earth element (REE) of the intrusion rock from the Dachang ore field in Guangxi, China, were analyzed. The results show that the phenocryst (about 15%) and matrix (about 85%) mainly consist of quartz, K-feldspar and plagioclase. The rock is composed of low content of Si and high content of Al2O3, low contents of Ca, Fe2O3, Na, TiO2, etc. The intrusion rock has the medium alkali content, attributing to K-rich type rock; and contains medium to low REE contents, of which light rare earth elements (LREEs) and heavy rare earth elements (HREEs) are highly fractionated, showing a weak negative Ce anomaly and a negative Eu anomaly. These rocks are enriched in LREE, and the large ion lithophytes elements (LILE) are rich in Rb, Sr, and U; the high-field-strength elements (Nb, Th, etc) are relatively depleted. The REE chondrite-normalized patterns are consistent with the overall, roughly indicating their similar characteristics, sources and evolution. The intrusion rock mainly formed during the collisional and within-plate periods.
Key words: geochemistry; petrogenesis; tectonic setting; magma evolution; Dachang ore field; Guangxi
1 Introduction
The genesis of granite has been one of the most important topics in geology. It is not only the basic problem of petrology, but also has a close relationship with the geological structure, ore genesis and stratigraphy [1,2]. In 1979, PITCHER [3] proposed granite typology, which classified the types of granites, guided by plate tectonics and combined the theory of geological environment and melting system. From the perspective of development, the genesis of granite should combine material resource, formation mechanism and tectonic setting, aiming to make new breakthroughs on some unsettled basic geological questions [2]. DONG et al [4] put forward the granite topology concept, which was defined as: the granite topology mainly studying the granite genesis and its relationship with tectonic environment, reflecting the source and evolution of granite natural system as a whole, and revealing the relationship between the granite formation and tectonic evolution. The concept emphasized the viewpoint that the granite formation was related to some certain stages of tectonic evolution, and moreover, they further developed PITCHER’s ideas about granite tectonic setting. XIAO et al [5] pointed out that the granite the scientific frontiers primarily are the relationship among the granite formation, continent growth and the deep process in lithosphere; the relationship between the granite anatexis and the heat source in the granite formation; and the relation of genetic type of granite to the tectonic environment [5,6].
The Danchi metallogenic belt is a NW trending tin polymetallic metallogenic region, located in Nandan-Hechi of the northwest Guangxi, China, and there are four ore fields including Mangchang, Dachang, Beixiang and Wuxu from north to south. As one of the most important ore fields, the Dachang ore field is featured with rich resources, large scale, concentrated reserve, complex ore-type [7-9], and the production of Sn, Zn, Pb, Sb, Cu, W, Ag, In, S, As, and so on, among which the main content is composed of cassiterite- sulfide deposit followed by skarn zinc-copper deposit and quartz vein type Sb-W deposit [10-12]. Based on the mineral resource distribution, structural assemblage and occurrence of Longxianggai intrusion, the Dachang ore field is divided into three ore belts: the west belt, central belt, and east belt (Fig. 1). Tin-polymetallic ore is the typical deposit in the west and east ore belts, whereas Zn-Cu-Sb-W ore is the typical deposit in the central ore belt. Tongkeng-Changpo deposit is the most typical ore and its form is the most complete. For a long time, the relation between the mineralization and magmatic rock has been the debate [11,13-16], which not only relates to the ore genesis, but also affects the current prospecting exploration, being considered one of the key scientific problems in the Dachang ore field in Guangxi, China.

Fig. 1 Mineralization zoning of Dachang ore field, China
In recent years, about Dachang rock genesis, it has made some new progresses, which is favorable to promoting the theory research and practice exploration. CAI et al [17] analyzed the major element, trace element and REE of magmatic rock from Dachang ore field in Guangxi, China, and pointed out that different granite stages formed in the transshipment period of the post-orogenic and within-plate tectonics, mainly in the stable regional extensional tectonic environment. Recently, CHENG [18] has been found that the magmatic rock is not the unique material source, and some other material sources exist.
Based on the previous academic results, in the current study some representative samples of the recently developed area and newly found ore body were supplemented, and the geodynamic background based on the chemical analysis was discussed, which provided new materials for understanding the genesis of Dachang tin ore deposit in Guangxi, China. Most importantly, these research results have practical significance for deep geological prospecting in Dachang area, Guangxi, China.
2 Petrography
According to the thin section and field observation, the intrusion rock is characterized by porphyritic texture and massive structure. Phenocryst and matrix, accounting for 15% and 85% respectively, mainly consist of quartz, K-feldspar and plagioclase. The features and contents of the minerals are as follows:
1) Quartz: It is in the form of phenocryst and matrix, and the quartz phenocryst mainly consists of a xenomorphic granular usually corroded that are round or harbor-shaped with dimensions of 0.2 mm×0.3 mm in shape. The quartz matrix is of xenomorphic fine grains with a size of 0.02 mm and a content of 35%.
2) K-feldspar: It is usually in the form of phenocrysts and matrix, and the K-feldspar phenocryst mainly consists of a subhedral tabular shape of roughly 0.2 mm×0.4 mm. The K-feldspar matrix is approximately dimensions of 0.02 mm×0.05 mm and is of fine tabular shape with a content of 40%.
3) Plagioclase: It mainly consists of plagioclase phenocryst and plagioclase matrix. The plagioclase phenocryst mainly has a subhedral tabular shape, with dimensions of 0.2 mm×0.4 mm. The plagioclase matrix is roughly 0.03 mm×0.06 mm, with a fine-grained tabular shape and a content of approximately 25%.
3 Samples and analytical methods
All of rock samples were collected from Tongkeng mine area of Dachang ore field in Guangxi, China. In order to ensure the freshness of the samples, the alteration of rocks has been avoided to the greatest extent. The samples showed typical features and could reflect the general characteristics of intrusive rock in this area. No. Y014 sample emplaced in Liujiang group. No. Y030 sample was characterized by massive structure, and emplaced in Luofu group. No.Y031-1 sample was also the rock intruded into Luofu group, but with porphyritic texture and massive structure, of which phenocryst and matrix are composed of quartz, K-feldspar and plagioclase. Both No.Y035 and No.Y037 samples were granite, collected from drill hole No. ZK39-1, which was characterized by porphyritic texture and massive structure, and both phenocryst and matrix consist of quartz, K-feldspar and plagioclase.
The analysis of the samples was completed in ALS Laboratory Group (Guangzhou) Co., Ltd, China. Using ME-XRF06 method, through the fusion of lithium borate or lithium metaborate and X fluorescence quantitative analysis, 13 element oxides and LOI were detected. The major elements consist of SiO2, Al2O3, CaO, Cr2O3, Fe2O3, K2O, MgO, MnO, Na2O, P2O5, TiO2, BaO and SrO. The trace element and rare earth element were analyzed by the method of alkali fusion (ME-MS81 method), and through the fusion of LiBO2 and mass spectrometry quantitative analysis, 38 elements were detected.
4 Analytical results
The major elements, trace elements and REEs compositions of the intrusion rock from Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China, are listed in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. They are characterized by low content of Si (w(SiO2)=49.48%-71%, with average of 60.67%) and high content of Al2O3 (13.89%-15.12%; average, 14.33%), low contents of Ca (w(CaO)=3.86%-7.03%; average, 4.88%) and Fe2O3 (w(Fe2O3)=1.01%-8.66%; average, 4.46%), and low content of Na (w(Na2O)= 0.07%-2.58%; average, 0.97%), and TiO2 (w(TiO2)= 0.1%-1.51%; average, 0.67%), K2O (w(K2O)=3.08%- 3.94%; average, 3.58%). The intrusion has a medium alkali content (w(K2O+Na2O)=3.7%-6.1%; average, 4.55%), being K-rich type rock, and the ratios of w(K2O)/w(Na2O) are relatively high. The values of A/NK range from 2.48 to 3.87, with an average value of 3.25. The ratios of A/CNK range from 0.726 to 1.292, being averaged 1.046.
Table 1 Major element compositions of intrusion rock in Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China
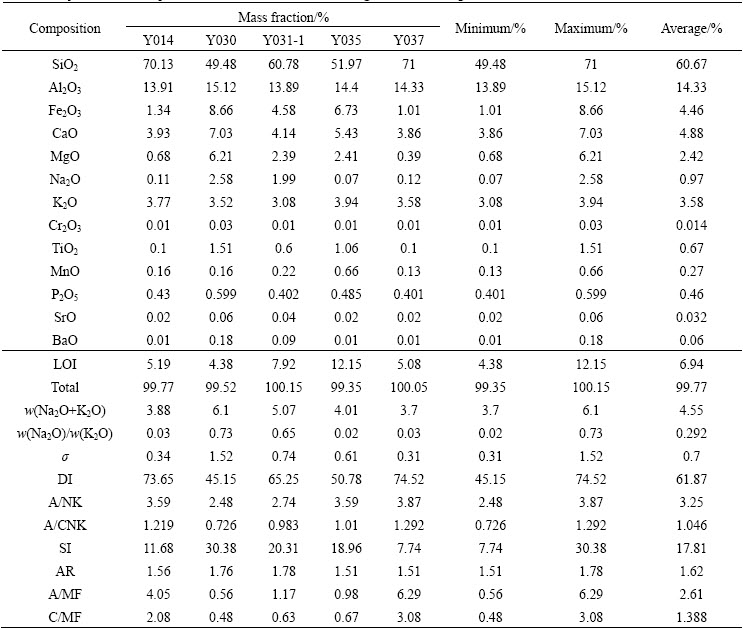
Table 2 Trace element and REE compositions of intrusion rock in Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China

The rock contains medium to low REE contents (w(ΣREE)=32.53×10-6-318.77×10-6; average 139.94× 10-6). The contents of LREE and HREE range from 28.25×10-6 to 298.13×10-6 and 4.28×10-6 to 20.64×10-6, respectively. In general, LREEs and HREEs are obviously fractionated, with w(LREE)/w(HREE)=6.22- 14.44 (average, 9.88) and [w(La)/w(Yb)]N=6.63-24.17. However, most of the samples show a weak negative Ce anomaly (δ(Ce)=0.92-0.97) and a negative Eu anomaly (δ(Eu)=0.29-0.76, with an average value of 0.584). The rocks are enriched in LREEs, and have a slightly negative Eu anomaly, and low contents of Y and Yb. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns show that LREEs slope to the right and that HREEs are relatively flat, with low HREE contents.
The contents of the large ion lithophilte elements Sr and Ba are 108×10-6 to 613×10-6 and 58.8×10-6 to 1570×10-6, respectively. The ratio of w(Sr)/w(Ba) is low, ranging from 0.37 to 1.83. The Nb content ranges from 69.3×10-6 to 106×10-6. The trace element shows that the large ion lithophile elements (LILE) are rich in Rb, Sr, and U; however, the high-field-strength elements (HFSE), such as Nb and Th, are relatively depleted.
The ratios of w(Gd)/w(Lu) are from 11.53 to 21.67, with an average value of 15.4, indicating the tensional tectonic environment possibly in period of the magma intrusion [19].
5 Discussion
5.1 Magma characteristics
As early as 1990, MA [20] put forward that the study based on the magma dynamics theory can not only deepen the understanding of magmatic origin and evolution mechanism, but also solve the problems of emplacement mechanism, tectonic environment and prospecting, etc. In various stages of tectonic evolution, the chemical composition of granite rock exhibits the orderly evolution trend, which can be reflected by the major element, trace element and REE contents [19]. The variation of intrinsic energy of the lithosphere results in the formation and subduction of rocks. The evolution of three kinds of rocks that constitute the lithosphere has different effects on the earth surface [21].
Based on w(K2O)-w(SiO2) diagram (Fig. 2), three samples project in the high-K calc-alkaline zone, indicating that they have low pH values compared with the similar rocks. The Al2O3 content is high and ranges from 13.89% to 15.12%, with an average value of 14.33% (Table 1). The Rittman index σ ranges from 0.31 to 1.52, with an average value of 0.7 (Table 1), which conforms to calcium rock type.
The alkalinity ratio (AR) ranges from 1.51 to 1.78, with an average value of 1.62 (Table 1). The differentiation index (DI) ranges from 45.15 to 74.52, with an average value of 61.87 (Table 1), indicating that the fractional crystallization of the intrusion rock is pretty complete. The solidification index (SI) ranges from 7.74 to 30.38, with an average value of 17.81 (Table 1). The aluminum saturation index (A/CNK) ranges from 0.726 to 1.292, with an average value of 1.046 (Table 1), corresponding to the peraluminous and strongly peraluminous rock type.
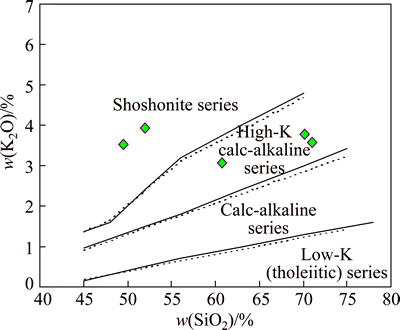
Fig. 2 w(K2O) vs w(SiO2) diagram of intrusion rock in Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China
REE is a group of elements very similar in geochemistry properties, but some tiny differences still exist between them essentially. With the change of geochemical conditions, REE can produce some degree of fractionation, which is the cause for being used as the geochemistry indicator. REEs have achieved remarkable achievements in solving the genesis, material sources, formation mechanism, differentiation and evolution, etc [22].
REEs of the intrusion rock in Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China, were chondrite-normalized [23]. The chondrite-normalized REE patterns exhibit a gently right-dipping V-type curve with a slight depletion in Eu (Fig. 3).
The ratios of w(LREE)/w(HREE) are usually larger than 1, ranging from 6.22 to 14.44, suggesting the enrichment of LREE and the obvious loss of HREE. [w(La)/w(Yb)]N=6.63-24.17 (Table 2), indicating the high fractionation between LREE and HREE. As can be seen in Fig 3, chondrite-normalized REE patterns of the intrusion rock are generally consistent, roughly indicating their similar characteristics, sources and evolution, etc.
The trace elements play an important role in studying the ore genesis, metallogenic regularity, and metallogenic prognosis. Their contents, distribution, and ratios with the similar elements can be used as sensitive indicators of the physical and chemical conditions of the rock. CAI et al [17] pointed out that different stages of granite in Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China, formed in the conversion stage from post-orogenic to within-plate environment, and the long-term and stable regional extension environment was dominated, which was also the favorable condition for the mineralization of super large-scale ore deposit. In Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China, the vein rocks supplied a part of metallogenic material or the filled fracture was the migration channel of ore fluid and was filled after the mineralization, which had important significance for deposit. And, the vein rock was also the ore source. Quartz diorite porphyrite was characterized by adakitic rocks, which might be from the underplating basaltic lower crust and involved in the mineralization of the polymetallic deposit near the dykes [24].

Fig. 3 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of intrusion rock in Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China [23]
5.2 Geodynamic background
The divergence of the material composition, temperature, pressure and tectonism led to different manifestations, such as the formation mechanism, the contamination degree, the differentiation style, migration process, emplacement way, metamorphism and deformation, which were the primary cause of close relationships between the granite and the tectonic environment [19]. Based on the viewpoint that different granite genetic types represent different active belts, according to the theory of plate tectonics, combining granites of different genetic types and tectonic setting, PITCHER [1] raised the classification of tectonic setting, and divided granite into the following five types: ocean island (M-type), active continental plate margin (cordillera I-type), post-orogenic uplift (caledon I-type), craton fold belt and continental collision belt (S-type), stable fold belt and craton uplift rift (A-type). XIAO et al [5] pointed out that studying granite can not only get the information about the material sources and tectonic setting, but also know the state, process and dynamics of crust-mantle material movement, and the transmission and transformation of deep energy, which plays very important role in understanding the growth of continent. It is also the key to solve geological evolution and establish dynamic system of continent. Nowadays, it is seen as the beginning of the third milestone of granite study, thus, it is of great strategic importance. WANG and SHU [2] proposed the concept of granite tectono- magmatic assemblages to reflect the relation between the granite type and tectonic environment, which emphasized that the space distribution of granite was related to plate convergent boundary, including the granite resulted from the oceanic crust subduction and intercontinental collision. However, the granite formed in divergent plate boundary has no such a strong connection.
The relationship between the granite formation and tectonic setting reflects the tectonic evolution and crust- mantle interaction in a certain stage. WU [19] investigated the granite REE patterns in the extension and compression environments, and pointed out that the ratio of w(Gd)/w(Lu) of the granite generally ranged from 15 to 20 in a tensile environment and was from 8 to 12 in a compression environment. The ratio of w(Gd)/w(Lu) of the granite in Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China, ranges from 11.53 to 21.67 (Table 2), which is greater than that in the compression environment but close to that of the extensional environment, suggesting that the granite of Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China, mainly formed in a extensional tectonic environment possibly.
In recent years, the genesis of the ore deposit in Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China, has been discussed frequently and the achievements have been very abundant [25-29]. Specifically, concerning the tectonic system of Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China [30], CAI et al [31] thought that the conversion of regional tectonic system obviously lagged behind its eastern area, which might relate to the stress transference from the collision of eastern pacific plate, and result the conversion of regional tectonic system and the diagenesis and mineralization. The trace elements are effective instructors for judging tectonic setting. Four samples of intrusion rock in Fig. 4(a) project in syn-COLG zone. Three samples in Fig. 4(b) project in syn-COLG zone, and the other two samples project in WPG area. However, all samples in Fig. 4(c) project in WPG zone. Three samples in Fig. 4(d) project in WPG area, and the other two samples project in VAG+syn-COLG area. On the whole, the trace elements mainly project in the within-plate and syn-collision granite zones, indicating that the intrusion rock mainly formed during the collisional and within-plate periods, or maybe in conversion time from collision to within-plate.

Fig. 4 Tectonic setting discriminating diagrams of trace elements of intrusion rock in Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China
6 Conclusions
1) The rock is characterized by low content of Si and high content of Al2O3, low contents of Ca and Fe2O3, and low contents of Na and TiO2, K2O and high ratio of w(K2O)/w(Na2O). The medium alkali content (w(K2O+ Na2O)=3.7%-6.1% with average of 4.55%) indicates the K-rich type rock. The values of A/NK and A/CNK range from 2.48 to 3.87 and 0.726 to 1.292, respectively.
2) The rock contains medium to low REE contents (average of 139.94×10-6). LREE and HREE are obviously fractionated. A weak negative Ce anomaly and a negative Eu anomaly exist. The rock is enriched in light REEs (LREEs) and has low contents of Y and Yb. The chondrite-normalized REE patterns show that LREE slope is to the right and that heavy HREEs are relatively flat. Overall, the quite similar REE chondrite- normalized pattern implies the similar characteristics, sources and evolution possibly.
3) The ratio of w(Sr)/w(Ba) is low, ranging from 0.37 to 1.83. The large ion lithophyte elements (LILE) are rich in Rb, Sr, and U. The high-field-strength elements (HFSE) are relatively depleted. The ratio of w(Gd)/w(Lu) (average of 15.4) indicates the tensional tectonic environment possibly during the mineralization. The intrusion rock mainly formed in period of the collisional and within-plate phase, being the conversion period of tectonic environment more likely.
References
[1] PITCHER W S. The nature and origin of granite [M]. London: Blackie Academic & Professional, 1993: 231-279.
[2] WANG De-zi, SHU Liang-shu. On granitic tectono-magmatic assemblages [J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 13(3): 362-370. (in Chinese)
[3] PITCHER W S. The nature, ascent and emplacement of granitic magmas [J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1979, 136: 627-662.
[4] DONG Shen-bao, HONG Da-wei, XU Bao-liang. A prospect on granite topology [J]. Geological Review, 2001, 47(4): 356-360. (in Chinese)
[5] XIAO Qing-hui, XING Zuo-yun, ZHANG Yu, WU Guang-ying, TONG Jin-song. The major frontiers of the recent studies of granite [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(3): 221-229. (in Chinese)
[6] XIAO Qing-hui, QIU Rui-zhao, XING Zuo-yun, ZHANG Yi, WU Guang-ying, TONG Jin-song. Major frontiers on studies of granite formation [J]. Geological Review, 2007, 53: s17-s27. (in Chinese)
[7] CHEN Yu-chuan. Geology of Dachang tin deposit [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993: 15-39. (in Chinese)
[8] HUANG Wei-hong, FAN Sen-kui, CHEN Chun-wen, BI Zhong-min. Application of metallogenic regularity to study of skarn zinc-copper deposits in Dachang orefield: A case study of Heishuigou-Dashujiao and Yangjiaojian skarn zinc-copper deposits [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2012, 31(3): 535-544. (in Chinese)
[9] TANELLI G, LATTANZI P. The cassiterite-polymetallic sulfide deposits of Dachang, Guangxi, People’s Republic of China [J]. Mineral Deposita, 1985, 20: 102-106.
[10] LI Hua-qin, WANG Deng-hong, MEI Yu-ping, LIANG Ting, CHEN Zhen-yu, GUO Chun-li, YING Li-juan. Lithogenesis and mineralization chronology study on the Lamo zinc-copper polymetallic ore deposit in Dachang orefield, Guangxi [J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2008, 82: 912-920. (in Chinese)
[11] FAN D, ZHANG T, YE J,  J, KRIBEK B, DOBES P, VARRIN I, ZAK K. Geochemistry and origin of tin-polymetallic sulfide deposits hosted by the Devonian black shale series near Dachang, Guangxi, China [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2004, 24: 103-120.
J, KRIBEK B, DOBES P, VARRIN I, ZAK K. Geochemistry and origin of tin-polymetallic sulfide deposits hosted by the Devonian black shale series near Dachang, Guangxi, China [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2004, 24: 103-120.
[12] LIANG Ting, WANG Deng-hong, CAI Ming-hai, CHEN Zhen-yu, GUO Chun-li, HUANG Hui-min. Sulfur and lead isotope composition tracing for the sources of ore-forming material in Dachang tin-polymentallic orefield, Guangxi [J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2008, 82(7): 967-977. (in Chinese)
[13] LATTANZI P, CORAZZA M, CORSINI F, TANELLI G. Sulfide mineralogy in the polymetallie cassiterite deposits of Dachang, P.R. China [J]. Mineral Deposita, 1989, 24: 141-147.
[14] JIANG Shao-yong, HAN Fa, SHEN Jian-zhong, PALMER M R. Chemical and Rb-Sr, Sm-Nd isotopic systematics of tourmaline from the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore deposits, Guangxi Province, P.R. China [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 157: 49-67.
[15] CAI Ming-hai, MAO Jing-wen, LIANG Ting, FRANCO P, HUANG Hui-lan. The origin of the Tongkeng-Changpo tin deposit, Dachang metal district, Guangxi, China: Clues from fluid inclusions and He isotope systematics [J]. Miner Deposita, 2007, 42: 613-626.
[16] CHENG Yong-sheng, HU Rui-zhong.Lead isotope composition and constraints on origin of Dafulou ore deposit, Guangxi, China [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(6): 1766-1773.
[17] CAI Ming-hai, LIANG Ting, WU De-cheng, HUANG Hui-min. Geochemical characteristics of granites and their tectonic setting of Dachang ore field in Guangxi [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2004, 23(2): 57-62. (in Chinese)
[18] CHENG Yong-sheng. REE geochemistry of Devonian stratum, in the Dachang ore district, Guangxi, south China [J]. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 2011, 2: 104-108.
[19] WU Tai-ran. Granites and their tectonic setting [J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium, 1995, 31(3): 358-365. (in Chinese)
[20] MA Chang-qian. The study of magma dynamics and granite [J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1990(6): 37-41. (in Chinese)
[21] CHEN Guo-neng. Pondering over the genesis of rocks and the evolution of lithosphere [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(1): 1-8. (in Chinese)
[22] LUO Ting-chuan. The significance of rare earth element geochemistry in the study of granitoids [J]. Geological Science and Technology, 1986, 5(2): 140-146. (in Chinese)
[23] SUN S S, MCDONOUGH W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes [C]//Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society Special Publication, 1989: 313-345.
[24] FAN Sen-kui, LI Xiu-dan, CHENG Yong-sheng, CHEN Cheng-zhen, HUANG Wei-hong. Geochemical features of vein rocks and their significance to structure and mineralization in the Dachang ore district, Guangxi province [J]. Geology and Exploration, 2010, 46(5): 828-835. (in Chinese)
[25] CHENG Yong-sheng, HU Rui-zhong, WU Yong-tian. Geology and geochemistry of Dafulou tin-polymetallic ore deposit in Dachang ore field, Guangxi, China [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(3): 751-760. (in Chinese)
[26] CAI Ming-hai, MAO Jing-wen, LIANG Ting, HUANG Hui-lan. Fluid inclusion studies of Tongkeng-Changpo deposit in Dachang polymetallic tin orefield [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2005, 24(3): 228-241. (in Chinese)
[27] WANG Deng-hong, CHEN Yu-chuan, CHEN Wen, SANG Hai-qing, LI Hua-qin, LU Yuan-fa, CHEN Kai-li, LIN Zhi-mao. Dating the Dachang giant tin-polymetallic deposit in Nandan, Guangxi [J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2004, 78(1): 132-138.
[28] ZHAO Kui-dong, JIANG Shao-yong, XIAO Hong-quan, NI Pei. Origin of ore-forming fluids of the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore deposit: Evidence from helium isotopes [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(12): 1041-1045.
[29] FU M, KWAK T, MERNAGH T P. Fluid inclusion studies of zoning in the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field, People’s Republic of China [J]. Economic Geology, 1993, 88: 283-300.
[30] CHENG Yong-sheng, HU Rui-zhong. Lead isotope geochemistry of Dafulou tin-polymetallic deposit, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2012, 43(11): 4381-4387. (in Chinese)
[31] CAI Ming-hai, LIANG Ting, WU De-cheng, HUANG Hui-min. Structural feature and its control of mineralization of the Nandan-Hechi metallogenic belt in Guangxi Province [J]. Geology and Exploration, 2004, 40(6): 5-10. (in Chinese).
成永生1, 2, 3
1. 中南大学 有色金属成矿预测教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 地球科学与信息物理学院,长沙 410083;
3. 中国科学院 地球化学研究所 矿床地球化学国家重点实验室,贵阳 550002
摘 要:对广西大厂矿田的侵入岩体开展主量元素、微量元素以及稀土元素的分析。结果表明,岩石中斑晶和基质主要由石英、钾长石以及斜长石组成,其中,斑晶约占15%,基质约占85%。岩石中硅含量偏低,Al2O3含量偏高;另外,Ca、Fe2O3、Na以及TiO2等含量也较低。侵入岩体中碱含量中等,属于富钾型岩石;稀土元素含量中等至偏低,其中,轻稀土元素和重稀土元素高度分馏,显示出Ce微弱负异常、Eu负异常特征。岩体富集轻稀土元素,Rb、Sr以及U等大离子亲石元素也较富集,而Nb、Th等高场强元素则相对亏损。稀土元素球粒陨石标准化分布型式总体表现出较好的一致性,大体上表明各岩体具有相似的特点、来源以及演化等,侵入岩体主要形成于碰撞时期以及板内构造时期。
关键词:地球化学;岩石成因;构造背景;岩浆演化;大厂矿田;广西
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (41202051) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project ([2014]76) supported by the Platform of Scientific and Technological Innovation for Hunan Youth, China; Project (2014T70886) supported by the Special Program of the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China; Project (2012M521721) supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
Corresponding author: Yong-sheng CHENG; Tel: +86-13017386868; E-mail: cys968@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63603-2

