文章编号:1004-0609(2009)08-1480-08
Cu-Fe复合材料的形变对其力学性能及导电性能的影响
陆月娇,田若鸣,周 健,薛 烽
(东南大学 材料科学与工程学院,南京 211189)
摘 要:采用原位变形法制备Cu-8%Fe,Cu-12%Fe和Cu-16%Fe(质量分数)3种复合材料,利用金相显微镜和扫描电镜观察各材料的显微组织,利用拉伸试验和双臂电桥分别对力学性能和导电性能进行研究,并与经相同加工过程的纯铜材料进行对比。结果表明:在形变加工过程中,Cu-Fe复合材料中的Fe相由枝晶状逐渐变成沿形变方向的纤维状结构;随应变量逐渐增加,纤维逐渐增长,间距和宽度逐渐减小,分布趋于均匀,排列方向趋于一致;且随着应变量的增加,Cu-Fe复合材料的硬度和屈服强度呈上升趋势,塑性和导电性能呈下降趋势;退火后其屈服强度下降,导电性能增强。
关键字:Cu;Fe;复合材料;力学性能;导电性能
中图分类号:TG 146.1; TG 113 文献标识码: A
Influence of deformation processing on mechanical and conductivity properties of Cu-Fe composites
LU Yue-jiao, TIAN Ruo-ming, ZHOU Jian, XUE Feng
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing 211189, China)
Abstract: Cu-8%Fe, Cu-12%Fe and Cu-16%Fe (mass fraction) composites were prepared by in-situ synthesis technique and heavy deformation processing. Metallography microscope and scanning electron microscope were used to observe the microstructures of the Cu-Fe composites. The mechanical properties and electrical conductivity were studied by tensile test and double bridge, respectively. The three Gu-Fe composites were compared with pure copper treated in the same way. The results show that, during the deformation process, the primary and second dendritic arms of Fe phase are aligned along the drawing direction and elongated into filaments. With increasing drawing strains, the filaments become longer and thinner, and the space between them is shortened, and their orientations are gradually in good order. The improvement of hardness and yield strength results in heavy deformation, whereas the plasticity and electrical conductivity decrease. After annealing, the yield strength of Cu-Fe in-situ composites decreases, and the conductivity property increases.
Key words: Cu; Fe; composites; mechanical properties; conductivity property
铜因具有优异的导电、导热、耐腐蚀性而被广泛应用于社会生产的各个领域。但纯的铜强度和硬度较低,即便是通过加工硬化,强度和硬度仍不能满足人们的使用要求。自20世纪70年代以来,在冶金、电子等行业快速发展的背景下,国内外学者相继研制出一批强度和导电性都较高的铜合金,在制造连铸结晶器内衬、集成电路引线框架、高速列车架空导线等方面得到广泛应用[1?3]。随着科学技术的高速发展,对高强高导电材料的性能也提出了越来越高的要求,因此,开发新的高强高导铜合金材料成为目前铜合金领域的研究热点之一。
合金元素的固溶会提高铜的强度,但显著降低铜的电导率[4?5],因此,对高强高导铜合金而言,需控制固溶合金元素的总量,通常难以采用添加固溶元素方式强化合金。在实际应用中,一般都采用在铜基体中形成具有强化效果的第二相强化的方法,常见的有析出强化(如Cu-Ni-Si系[6])和弥散强化(如Cu-Al2O3系[7])等,而原位形变法则是近年来发展出的一种新方法,可保持较高的导电率和强度综合匹配[8],同时制备方法简单,已成为高导电铜基材料的一个重要研究方向。
目前,原位形变铜基复合材料的研究主要集中于Cu-Ag[9]和Cu-Nb[8?9]系,这主要是因为Ag和Nb在铜中都具有很低的室温溶解度,大形变量原位形变后,形成的在接近纯铜的基体中所均匀分布的纤维状Ag或Nb纤维能起到显著的强化作用,同时又不显著恶化其导电性能。与Cu-Ag和Cu-Nb相比,对Cu-Fe系材料的研究尚不系统,但由于其低廉的成本引起了研究者的广泛兴趣,同时,Cu-Fe还有更突出的优点:1) Fe的熔点比较低,液态Fe与Cu的溶混间隙小,应用普通工业熔炼设备即可制备合金坯料;2) Fe和Cu的密度比较接近,熔铸法制备材料时,比重偏析小,可以制备尺寸较大的坯料[10?11]。因此,在工业规模制备和应用方面,Cu-Fe原位复合材料更具潜力。
本文作者采用原位变形法制备了4种成分的Cu-Fe基材料,对材料的组织、力学性能和导电性能进行了研究,分析了成分、形变及热处理对Cu-Fe复合材料综合性能的影响。
1 实验
根据Cu-Fe二元相图[12],两组元液相时可相互混熔,凝固后Fe在高温下能部分溶于Cu中形成α固溶体,1 000 ℃时,Fe在Cu中的溶解度约为4.1%(质量分数),随着温度的下降,溶解度急剧下降;到635 ℃左右时,溶解度降为0.15%;室温下时,溶解度接近于零。
根据高强高导铜合金性能的要求,本实验选择了纯Cu、Cu-8%Fe、Cu-12%Fe和Cu-16%Fe进行研究。考虑到杂质元素对铜合金导电性的影响,原材料采用高纯度(99.98%)的标准阴极铜和电工纯铁(DT4)。4种材料均在ZG101?10B型真空中频感应电炉中熔炼,所有原材料均随炉加入,升温至1 400 ℃,待原料熔清后保温5 min,随后采用铸铁模浇注成直径62 mm的圆锭坯。锭坯在780 ℃热挤压至直径20 mm的棒坯,经固溶(1 000 ℃, 20 min,炉冷)、时效处理(500 ℃, 4 h,主要目的是降低固溶在铜基体中的过饱和铁含量)后,进行一系列的连续冷拉拔至0.8 mm,得到试验用Cu-Fe原位形变复合材料,其中部分试样在最终变形后进行了退火处理。冷拔过程的应变量ε=ln(A0/A),其中A0和A分别为原始和拉拔态横截面积。
室温拉伸试验在CMT5105型电子万能试验机上进行,拉伸应变速率为5×10?2 s?1;硬度测试在HV?10型维氏硬度计上进行;通过QJ36型双臂电桥测量试样的导电率;显微组织采用Olympus金相显微镜和Sirion 200型扫描电镜(SEM)观察分析。所有测试用试样均在铸锭或形变样相似部位截取。
2 结果与分析
2.1 形变对复合材料显微组织的影响
实验研究的各材料铸态下的金相组织如图1所示。由图1可见,纯铜呈单相组织,晶粒非常粗大。而Cu-Fe材料呈两相组织,其中铜基体的晶粒较纯铜小得多,第二相呈较为粗大的树枝状,基本处于晶内,但分布并不十分均匀,随着铁含量增加,组织中的枝晶数量也相应增加。

图1 各材料铸态的光学及SEM组织
Fig.1 Optical and SEM micrographs of as-cast materials: (a) Pure copper; (b) Cu-8%Fe; (c) Cu-16%Fe; (d) Cu-16%Fe
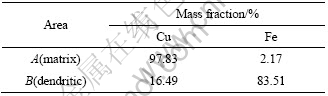
图1(d)所示为铸态Cu-16%Fe试样的SEM像。图中第二相的枝晶结构更为清晰,枝晶臂直径在5 μm左右,对图中基体和树枝晶部位(分别为A和B)的能谱分析结果如表1所列,可见基体基本由铜构成,而第二相树枝晶为溶有一定量铜元素的铁相,这也与Cu-Fe二元相图吻合;Cu-8%Fe和Cu-12%Fe的组织与Cu-16%Fe相似,仅第二相含量有所不同。
表1 Cu-16%Fe复合材料铸态组织的微区成分分析
Table 1 Component analysis of microareas of as-cast Cu- 16%Fe
各材料经热挤压后,沿挤压方向的显微组织形貌如图2所示。由图2可以看出,纯铜晶粒沿挤压方向伸长,呈条带状,晶粒仍然较大;而Cu-Fe材料中铜基体沿挤压方向也呈带状,晶粒明显比纯铜的晶粒小,而且随着Fe含量的增加不断细化,铸态组织中部分树枝晶状第二相也出现沿挤压方向破碎拉长的趋势,沿形变方向其宽度约在5 μm,这从图2(d)可以明显看出。
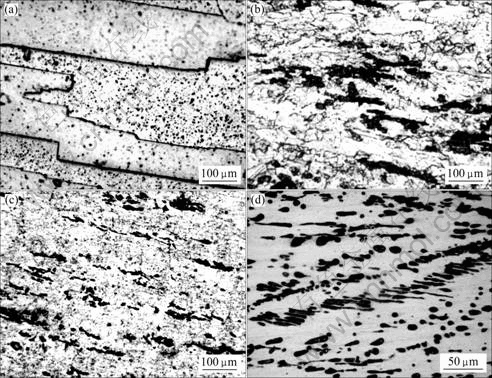
图2 挤压态试样的光学组织
Fig.2 Optical micrographs of as-extruded materials: (a) Pure copper; (b) Cu-8%Fe; (c) and (d) Cu-16%Fe
在连续冷拉拔加工过程中,分别观察了材料应变量(ε)为1.39、2.77、3.79、4.61、5.39和6.44时的金相组织。图3所示为ε=1.39时各Cu-Fe材料的金相组织。从图3可以看出,由于此时应变量较小,虽然大部分Fe相已开始向纤维状转变,但分布不均匀,并且仍有少量尺寸较大的Fe相变形不大,还保持着接近颗粒状的形貌。

图3 拉拔态(ε=1.39)试样的光学组织
Fig.3 Optical micrographs of as-drawn (ε=1.39) materials: (a) Cu-8%Fe; (b) Cu-12%Fe; (c) Cu-16%Fe
随着应变量ε的增加,Fe相沿拉拔方向的变形程度相应增加,逐渐呈纤维状,尺寸不断变细,间距逐渐减小,分布也趋于均匀。这可以从图4所示的Cu-8%Fe复合材料金相显微组织的变化中明显看出,而Cu-12%Fe和Cu-16%Fe在拉拔过程中组织的变化情况类似,只是纤维间距更小。图5所示为Cu-8%Fe复合材料的冷拔态(ε=6.44)SEM像。由图5可知,其中Fe相纤维宽度在200 nm左右,其它两种合金Fe相纤维宽度基本相同,只是随着Fe含量的增加,纤维间距逐渐减小。
style="PAGE-BREAK-BEFORE: auto; mso-break-type: section-break" clear=all>

图4 不同应变量时Cu-8%Fe拉拔态纵截面的光学组织
Fig.4 Optical micrographs of as-drawn Cu-8%Fe material at different strains: (a) ε=1.39; (b) ε=2.77; (c) ε=4.61; (d) ε=6.44
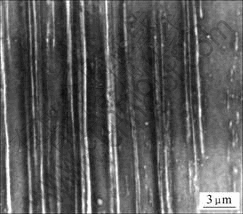
图5 Cu-8%Fe复合材料冷拔态(ε=6.44)的SEM像
Fig.5 SEM image of as-drawn Cu-8%Fe material (ε=6.44)
2.2 形变对复合材料力学性能的影响
表2所列为各材料在铸态、挤压态和时效态下的硬度值。由表2可见,随着Fe含量的增加,Cu-Fe系材料各状态的硬度都呈增加趋势;而相同Fe含量材料挤压态硬度稍高于铸态,时效退火处理后则显著降低。
表2 试样的维氏硬度
Table 2 Vickers hardness of materials at different states
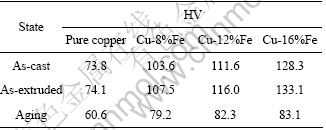
图6所示为各材料拉拔态硬度随应变量的变化曲线。由图6可看出,随着拉拔应变量的增大,各材料拉拔态的硬度值也不断提高,但当应变量超过3.79以后,纯铜试样的硬度基本保持在HV120左右,而其它Cu-Fe系材料的硬度随应变量的增加不断增加。
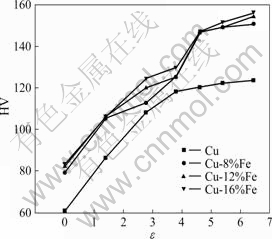
图6 试样硬度随应变量的变化曲线
Fig.6 Changing curves of HV with ε for materials
图7所示为Cu-Fe系复合材料在拉拔态下的屈服强度随应变量的变化曲线。图8所示为Cu-Fe系复合材料在拉拔态下的伸长率随应变量的变化曲线。由图7和8可见,Cu-Fe系复合材料在经过大量的拉拔变形后,屈服强度显著提高,而伸长率则急剧下降,如应变量从1.39增加到6.44时,Cu-16%Fe拉拔态强度从486.9 MPa增加到970.3 MPa,几乎增大一倍。虽然各材料的屈服强度随应变量增加而增加的情况与硬度值的变化相似,但两者随应变量的变化规律却有所差别。在本试验范围内,除纯铜的屈服强度随应变量的变化几乎呈线性关系外,其它材料的屈服强度随应变量的变化曲线基本分为两段。当应变量小于4.61时,与纯铜类似;而变形量大于4.61时,材料的强度迅速增加。从图8中还可看出,随着铁含量增加,材料的强度也相应增加。
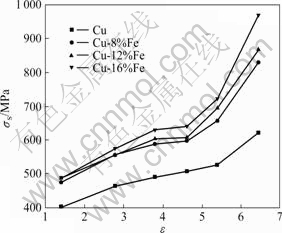
图7 试样的屈服强度随应变量的变化曲线
Fig.7 Changing curves of σs with ε of materials
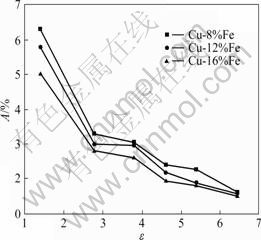
图8 试样的伸长率随应变量的变化曲线
Fig.8 Changing curves of A with ε for materials
2.3 形变对复合材料导电性能的影响
图9所示为Cu-Fe系复合材料在拉拔态下的电导率随应变量的变化曲线。从图9中看出,Fe的加入使复合材料的电导率明显低于纯铜的,而Fe含量的增加对其影响相对较小,如应变量为1.39时,纯铜的电导率为97.8%(IACS),而Cu-8%Fe仅为56.9%(IACS),Cu-12% (Fe)仅为55.7%(IACS),Cu-16%(Fe)仅为51.9%(IACS)。由图9中还可看出,各材料的电导性都随应变量的增加而降低,但下降不显著。
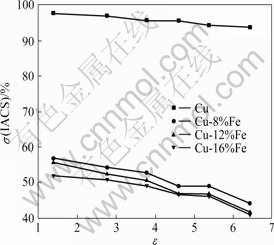
图9 试样电导率随应变量的变化曲线
Fig.9 Changing curves of σ with ε for materials
2.4 退火对各材料导电性能的影响
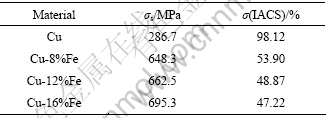
考虑到高强高导铜合金在实际应用中对强度与导电性匹配的要求多样,本文作者初步探讨了退火对Cu-Fe原位变形复合材料室温拉伸性能和电导率的影响。分别将各材料最终拉拔态(ε=6.44)试样在350 ℃下退火1 h后测试其性能。表3和4中所列分别为Cu-Fe复合材料在最终拉拔态及退火后的强度与导电性能。
将表3和4中相应数据进行比较,发现Cu-Fe复合材料在退火后,电导率升高近20%,而屈服强度却降低20%左右。另外,从表4可看出,Fe元素含量越高,则复合材料经相同温度退火相同时间后的屈服强度越高,电导率越低,这和在铸态及形变态时的情况类似。
表3 试样的拉拔态强度和导电性能(ε=6.44)
Table 3 Yield strength and electrical conductivity of as-drawn materials (ε=6.44)
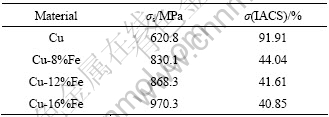
表4 试样退火后强度和导电性能
Table 4 Yield strength and electrical conductivity of materials after anneal (350 ℃, 1 h)
3 讨论
3.1 拉拔过程中Cu-Fe复合材料相尺寸的变化规律及其对力学性能的影响
由于ε=ln(A0/A),假设Cu-Fe合金中Fe相和Cu相拉拔变形程度相同,有ε=2ln(D0/D),式中,D0和D分别为形变前后Fe相纤维的平均宽度。在D0已知的情况下,形变后的Fe纤维相平均宽度D可以通过计算得到(见表5)。在ε=0时,即挤压态时,Fe相纤维的平均宽度为5 μm。在拉拔终态ε=6.44时,计算值与本试验结果吻合非常好,这也说明合金中Fe相和Cu相的延伸变形确实基本同步的。
根据Cu-Fe材料中Fe的含量以及Fe相纤维的宽度,还可以通过计算获得相应的纤维平均间距D1(见表5)。
表5 Cu-Fe复合材料的组织特征参数
Table 5 Characteristic parameters of Cu-Fe materials
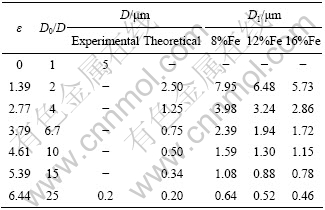
图10所示为本研究的3种Cu-Fe基材料的屈服强度与(D+D1)?1/2关系曲线。由图10可见,3种Cu-Fe复合材料的屈服强度(R)随(D+D1)?1/2的变化规律大致相同,基本符合Hall-Patch关系[13]:

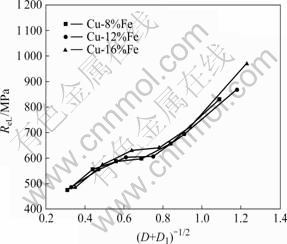
图10 Cu-Fe材料的屈服强度与(D+D1)?1/2的关系
Fig.10 Relationship between ReL and (D+D1)?1/2 of Cu-Fe composites
对上述关系曲线作线性拟合后所得的k值分别为412、419和460 MPa·m1/2左右,表明影响材料强度的主要因素是Fe纤维尺寸D及其间距D1之和,而在相同应变量的情况下,Fe含量的影响不大。因此采用较低Fe含量的复合材料,通过较大形变量后形成的复合材料可能获得更好的综合性能。
3.2 影响Cu-Fe基复合材料导电性的因素分析
Cu-Fe基复合材料中,由于Cu和Fe的电导率差异较大,无氧铜为的102%(IACS),纯铁为17%(IACS),因此,起导电作用的主要是Cu相。根据复合材料导电性能的复合原理[14],Cu-Fe基纤维复合材料纵向导电率理论上可由Cu相和Fe相导电率经加权平均计算获得,即
σFe-Cu=φ(Fe)σFe+φ(Cu)σCu (2)
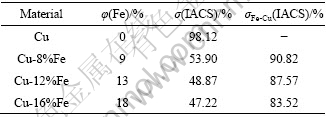
式中:σFe-Cu、σFe和σCu分别为复合材料、Fe和Cu的电导率;φ(Fe)和φ(Cu)为复合材料中Fe和Cu的体积分数。表6所列为按上式计算出的σFe-Cu理论值。其中由于Fe纤维的电导率较低,对复合材料影响较小,因此以纯铁计,铜基体导电率以本研究纯铜实验值 代入。
由表6可见,复合材料的导电性基本由Cu相含量决定,Fe纤维对导电率贡献极低,基本可以忽略。同时还可以发现,实验值明显小于理论值(仅为理论值的55%~60%左右),本文作者认为这主要是以下原因引起:1) Cu基体中溶入了微量Fe。Fe是对铜合金的导电性能影响最大的元素之一,根据文献[15]报道,溶入0.1%Fe后,退火铜的导电率可从98%(IACS)几乎线性降低到约65%(IACS),这主要是铁在铜中的溶解使铜基体晶格产生畸变,从而自由电子被散射的几率增大的结果,铁原子在铜晶格中的浓度越大,铜的晶格畸变程度越大,合金的电导率越低;2) 大应变量变形导致材料中缺陷增加。尽管经过350 ℃退火处理1 h,但材料中仍存在包括位错、晶界以及相界等缺陷,都会导致晶格畸变,从而影响材料的导电性,但总体来看,这方面的影响相对较小。
表6 退火态Cu-Fe材料电导率理论值与实验值的比较
Table 6 Comparison of theoretical and experimental electrical conductivity of materials annealed
4 结论
1) Cu-Fe材料铸态组织为等轴状富Cu相基体上分布树枝状富Fe相,不同Fe含量材料中枝晶臂尺寸均为5 μm左右。经过热挤压和冷拉拔加工后,Fe相逐渐变成沿形变方向的纤维状结构。随应变量增加,纤维长度增加,同时间距和宽度减小,分布趋于均匀、排列方向趋于一致。
2) 在相同加工状态下,Cu-Fe材料的硬度、强度明显高于纯铜的,但导电性能也下降较多。在Cu-Fe材料中增加Fe含量后,相同应变量时,材料的硬度和屈服强度增大,电导率和塑性降低。
3) 3种Cu-Fe基材料的屈服强度与铁纤维及其间距符合Hall-Patch关系,铁含量的影响相对较小;材料的电导率基本由其中Cu相的导电能力决定。
REFERENCES
[1] 隋晓红, 李昊涵. 连铸结晶器用Cr-Zr-Cu合金抗氧化性能分析[J]. 物理测试, 2007, 25(5): 24?26.
SUI Xiao-hong, LI Hao-han. Analysis on property of oxidiation resistance of Cr-Zr-Cu alloy for continuous crystallizer[J]. Physics Examination and Testing, 2007, 25(5): 24?26.
[2] 黄国杰, 谢水生, 程镇康, 李华清. 引线框架用铜合金冷轧板材鱼鳞状缺陷[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(2): 353?356.
HUANG Guo-jie, XIE Shui-sheng, CHENG Zhen-kang, LI Hua-qing. Fish defects of cold rolling copper alloys applie to lead frame[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(2): 353?356.
[3] JIA S G, LIU P, REN F Z, TIAN B H, ZHENG M S, ZHOU G S. Sliding wear behavior of copper alloy contact wire against copper-based strip for high-speed electrified railways[J]. Wear, 2007, 262(7/8): 772?777.
[4] XIAO G H, TAO N R, LU K. Effects of strain, strain rate and temperature on deformation twinning in a Cu-Zn alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia,2008, 59(9): 975?978.
[5] LU Hai-bo, LI Ying, WANG Fu-hui. Corrosion behavior and porous structure formation of sputtered Cu-Zr nanostructured films[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 465(1/2): 139?144.
[6] 张旦闻, 赵冬梅, 董企铭, 刘 平, 刘宏昭. Cu-Ni-Si合金二次时效时的再结晶行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2004, 14(7): 1241?1245.
ZHANG Dan-wen, ZHAO Dong-mei, DONG Qi-ming, LIU Ping, LIU Hong-zhao. Recrystallization behaviour of Cu-Ni-Si alloy during two-step aging[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2004, 14(7): 1241?1245.
[7] LIU Rui-hua, SONG Ke-xing, JIA Shu-guo, XU Xiao-feng, GAO Jian-xin, GUO Xiu-hua. Morphology and frictional characteristics under electrical currents of Al2O3/Cu composites prepared by internal oxidation[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2008, 21(3): 281?288.
[8] HONG S I, HILL M A. Strength and ductility of heavily drawn bundled Cu-Nb filamentary micro composite wires with various Nb contents[J]. Metal Mater Trans A, 2000, 31: 2457?2473.
[9] HERINGHUAS F, SCHNEIDER-MUNTAU H J, GOTTSTEIN G. Analytical modeling of the electrical conductivity of metal matrix composites: application to Ag-Cu and Cu-Nb[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 347: 9?20.
[10] KOZESCHNIK E. Thermodynamic prediction of the equilibrium chemical composition of critical nuclei: BCC Cu precipitation in α-Fe[J]. Scripta Materialia,2008, 59(9): 1018?1021.
[11] MIURA H, TSUKAWAKI H, SAKAI T, JONAS J J. Effect of particle/matrix interfacial character on the high-temperature deformation and recrystallization behavior of Cu with dispersed Fe particles[J]. Acta Materialia,2008, 56(17): 4944?4952.
[12] 刘 平, 任凤章, 贾淑果. 铜合金及其应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007.
LIU Ping, REN Feng-zhang, JIA Shu-guo. Copper alloys and their application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2007.
[13] 胡赓祥, 蔡 珣. 材料科学基础[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2000.
HU Geng-xiang, CAI Xun. Basic of material sience[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University Press, 2000.
[14] CEN Shu-chuan. Physical property of material[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University Press, 1999.
[15] WEST E G. Copper and its alloys[M]. Chichester, West Sussex, England: Horwood E; New York: Halsted Press, 1982.
基金项目:华南理工大学博士后创新科学基金资助项目(20080212)
收稿日期:2008-11-05;修订日期:2009-03-12
通讯作者:薛 烽,教授;电话:025-52090689;E-mail: xuefeng@edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)