Mg-5Zn-1Mn-0.6Sn镁合金板材光纤激光焊接头的显微组织及液化行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2017年第4期
论文作者:佘庆元 严红革 陈吉华 苏斌 俞照辉 陈潮 夏伟军
文章页码:812 - 819
关键词:镁合金薄板;光纤激光焊;显微组织;液化现象;液化机理
Key words:magnesium alloy sheet; fiber laser welding; microstructure; liquation phenomenon; liquation mechanism
摘 要:采用光纤激光焊对厚度为2 mm的细晶Mg-5Zn-1Mn-0.6Sn镁合金板材进行焊接,研究焊接接头的成形特征、显微组织和半熔化区的液化行为。研究结果表明,随着焊接功率的降低及焊接速度的增大,焊接接头的宽度和深度减小;此外,当焊接速度过快时,焊缝中会出现气孔。在半熔化区中主要存在两种液化现象:一种是由基体熔化及偏析诱导液化导致的沿晶界的液化网络,另一种为由晶界上残余第二相液化导致形成的液化熔池现象。在本研究中,主要的液化机制为基体的熔化及偏析诱导液化。
Abstract: Fine-grained Mg-5Zn-1Mn-0.6Sn alloy sheets of 2 mm in thickness were welded by fiber laser welding. The appearance and microstructures of the welding joints and liquation behaviors in the partially melted zone (PMZ) were investigated. The results show that, with the lower welding power and higher welding speed, the width and depth of the joints decrease. Moreover, some pores are detected at a very high welding speed. There are two kinds of liquation phenomena in the PMZ. One is the liquation network along grain boundaries associated with the liquation of substrate and segregation-induced liquation, the other is the molten pool involved with the liquation of the residual second phases at the boundaries. However, the liquation of substrate and the segregation-induced liquation are the main liquation mechanism in the PMZ.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(2017) 812-819
Qing-yuan SHE1,2, Hong-ge YAN1,2, Ji-hua CHEN1,2, Bin SU1,2, Zhao-hui YU3, Chao CHEN1,2, Wei-jun XIA1,2
1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
2. Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Spray Deposition Technology & Application, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, China;
3. State Nuclear Power Plant Service Company, Shanghai 200233, China
Received 6 January 2016; accepted 7 July 2016
Abstract: Fine-grained Mg-5Zn-1Mn-0.6Sn alloy sheets of 2 mm in thickness were welded by fiber laser welding. The appearance and microstructures of the welding joints and liquation behaviors in the partially melted zone (PMZ) were investigated. The results show that, with the lower welding power and higher welding speed, the width and depth of the joints decrease. Moreover, some pores are detected at a very high welding speed. There are two kinds of liquation phenomena in the PMZ. One is the liquation network along grain boundaries associated with the liquation of substrate and segregation-induced liquation, the other is the molten pool involved with the liquation of the residual second phases at the boundaries. However, the liquation of substrate and the segregation-induced liquation are the main liquation mechanism in the PMZ.
Key words: magnesium alloy sheet; fiber laser welding; microstructure; liquation phenomenon; liquation mechanism
1 Introduction
With the rapid development of the transportation, aerospace and, national defense and military industry, magnesium alloys have received more and more attention because of the low density, high specific strength, excellent castability, outstanding vibration or shock energy absorption function, superior ability of resistance to electromagnetic interference, etc [1-3]. The AZ (Al-Mg-Zn) series, AM (Mg-Al-Mg) series, AS (Mg-Al-Sn) series, AE (Mg-Al-Re) series and ZK (Mg-Zn-Zr) series are the main commercial magnesium alloy systems. Among them, the ZK series especially ZK60 exhibit high strength, good corrosion resistance and heat-treatability [4]. The ZM (Mg-Zn-Mn) series have been the newly developed magnesium alloys in recent years. As compared with the ZK series, the relatively cheap Mn is used in the ZM series to replace the expensive Zr, and thus the cost is rather low. Moreover, the addition of Mn in magnesium alloy can refine grains, improve corrosion resistance and enhance mechanical properties at room temperature [5]. It is reported that the Mg-6Zn-1Mn alloy extruded at 350 °C and experienced solid solution and aging treatment exhibits the yield strength high up to 360 MPa [6].
Although the ZM series have excellent mechanical properties, these alloys with high Zn content are difficult to be welded because of the high hot cracking susceptibility including solidification crack and liquation crack associated with the wide melting range just like ZK60 [7]. There are many studies on liquation cracking. MAYAR and EDWARDS [8] found that some low melting point compounds in AZ91 magnesium alloys promote the formation of liquation in the PMZ. YANG et al [9] studied the liquation behavior of the laser welded joint of AZ91 and have indicated that limiting the size and the number of Mg17Al12 can reduce the liquation in the PMZ effectively. YU et al [10] studied the liquation cracking mechanism of ZK60 and have indicated that the liquation cracks initiated from the cavities and spread along GBs. CHEN et al [11] have studied the effect of grain size on liquation cracking of AZ61 and have found that grain refinement can limit the liquation cracks. The high hot cracking tendency has seriously limited the applications of the Mg-Zn-Mn system. Therefore, it is important to find a good way to solve the problem. Fiber laser beam welding, which has low input energy, narrow heat-affected zone (HAZ), high welding precision and large depth-to-width ratio, is suitable for welding the alloy sheets with the thickness below 1 mm. In this work, microstructure and liquation mechanism of the fine- grained Mg-Zn-Mn alloy joints welded by fiber laser welding were investigated in detail.
2 Experimental
The as-rolled Mg-5Zn-1Mn-0.6Sn (mass fraction, %) alloy sheets with dimensions of 76 mm × 44 mm × 2 mm were used in this experiment. Before welding, the surface of each sheet was cleaned by abrasive paper to remove oxidation film, and then washed by acetone to clear oil stain. The welding was conducted by fiber laser beam with the following parameters: mode, TEM00; wavelength, 1070 nm; divergence, <0.15 rad; spot diameter, 0.4 mm. The laser powers of 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 1.2 kW and the welding speeds of 50, 60, 70, 80 mm/s were adopted. The welding direction was perpendicular to the rolling direction. During the welding, the high purity argon (99.9%) with the flow rate of 12 L/min on the face and 9 L/min on the back was used to protect the weld line. The defocusing amount of 0 was adopted. The welding process is shown in Fig. 1. After welding, the samples were cut along the cross section and polished, and then etched with picric acid reagent (0.3 g picric acid + 1 mL glacial + 1.5 mL water + 10 mL alcohol) and tartaric acid reagent (5 g tartaric acid + 100 mL water) for microstructural examination. Microstructural examination was conducted on the optical microscopy (OM, Leitz, MM-6) and the scanning electron microscopy (SEM, FEI QUANTA- 2000). The picric acid was used for the FZ and the PMZ and the tartaric acid was used for the HAZ and base metal.
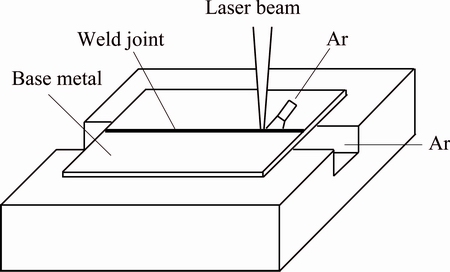
Fig. 1 Sketch map of welding process
3 Result and discussion
3.1 Microstructure of base metal
The base metal in the experiment is the high-performance wrought magnesium sheet prepared by high strain rate rolling at 350 °C with the reduction in pass of 80%. As shown in Fig. 2, the sheets with the thickness of 2 mm can be obtained and the grains are uniform with the average size of 5 μm.
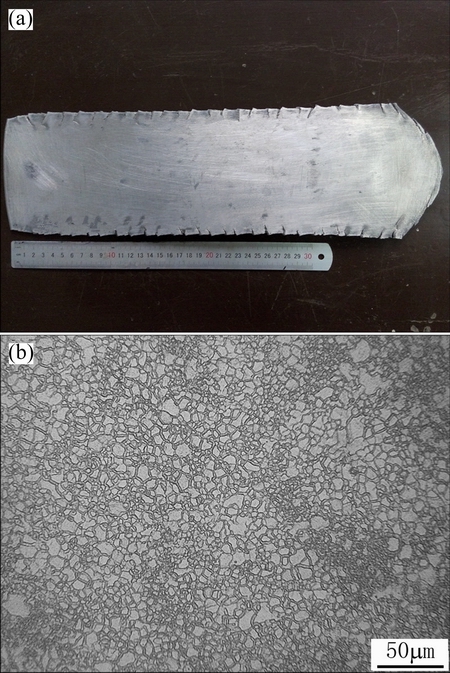
Fig. 2 Photograph of as-rolled sheet (a) and OM image of sheet (b)
3.2 Appearance of welding joints
The ZM51-0.6Sn sheets were jointed under various process conditions. The cross-sections of the fiber laser beam welded ZM51-0.6Sn joints under different power inputs and various welding speeds are shown in Fig. 3. The joints have high depth-to-width ratios and present the characteristic of laser deep penetration welding. At the same time, no obvious crystallization cracks are found in the weld joints, indicating that the fiber laser beam welding joints have low crack sensitivity. Although there are no obvious cracks in the joints, concavity on the upper surface of the welding joints is found in most joints and more depressions are detected with the increase of welding power and the decrease of welding speed. Although the fiber laser beam welding power is very low, the temperature of the molten pool is very high, some alloying elements which have a high saturated vapor pressure will evaporate and depression of the welding joints appears due to the lack of enough supplement. The welding parameters have great influence on the shape and the size of the welding joints. The width and the depth of the welding joints increase with the increase of the welding power. Generally speaking, the joints with larger dimensions will cause higher residual stress and larger deformation and thus reduce the manufacturing precision of the as-welded components. The welding speed has great influence on the welding joints, as can be seen from Fig. 3, too fast welding speed will lead to incomplete penetration with other conditions constant, and at the welding speed higher than 70 mm/s, some pores are visible in the welding joints when the welding power is constant. Some researchers regard these pores as the oxygen- induced pores [12] or the evaporation of Mg and Zn [13], but more researchers regard them as the hydrogen- induced pores [13,14]. The solubility of hydrogen decreases with the lower temperature. When the welding speed is too fast, the dissolved hydrogen has no time to float out and thus pores are formed.
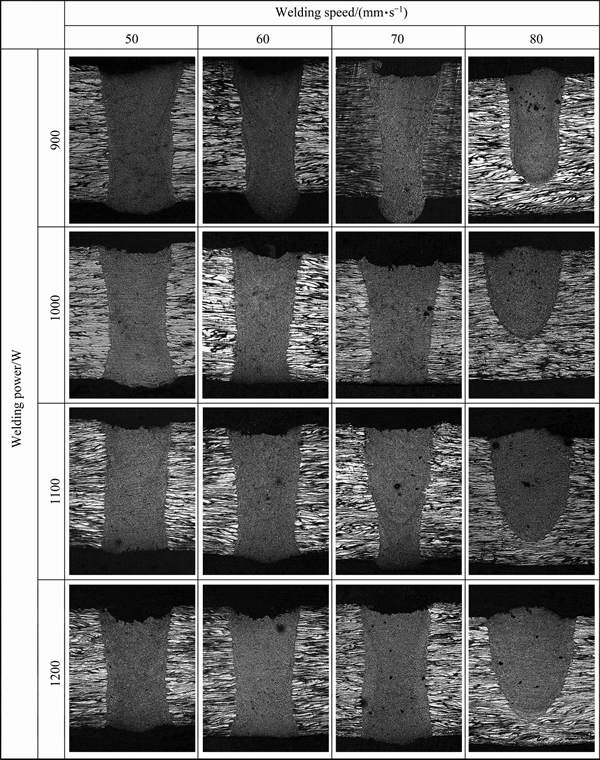
Fig. 3 Cross-section images of welding joints
3.3 Microstructure of welding joints
The microstructures of the welding joints are shown in Fig. 4. The welding joints include three areas: fusion zone (FZ), partially melted zone (PMZ) and heat-affected zone (HAZ). The center area of the fusion zone is shown in Fig. 4(a), and the area near the fusion boundary is offered in Fig. 4(d). As shown in Figs. 4(a) and (d), the microstructure of the fusion zone consists of three kinds of grains, in turn for cellular, columnar dendritic and equiaxed dendritic from the fusion line to the middle of the fusion zone. According to the theory of welding metallurgy [15], the crystal shape is decided by the solute concentration C0, crystallization velocity R and temperature gradient G. When the C0 is constant, the crystal habit is dependent on the G/R value. With the decrease of the G/R value, the crystal shape varies from cellular to columnar dendritic and finally to equiaxed dendritic. In the middle of the fusion zone, the temperature gradient is large and the crystallization speed is slow, so the G/R value is low and equiaxed dendritic grains are dominant in the central area. From the center of the fusion zone to the fusion line, the temperature gradient increases and the crystallization velocity decreases, and thus the G/R value increases and the crystal shape becomes cellular and columnar dendritic. As seen from Figs. 4(a) and (d), the cellular and the columnar dendritic grains only locate in a very narrow zone near the fusion line and the equiaxed denritic grains are dominant in the fusion zone.
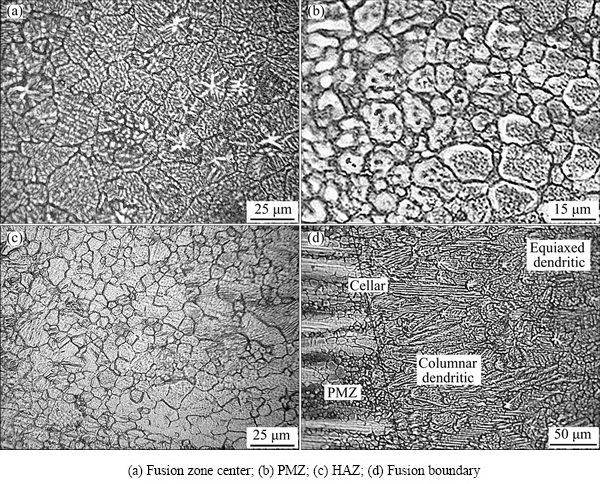
Fig. 4 Microstructure (OM images) evolution of welding joints
The PMZ is the area between the fusion zone and the heat-affected zone. As shown in Fig. 4(b), the grains in the PMZ are characteristic of apparent recrystallization and are featured with the equiaxed dendritic. Moreover, the grain interior appears gray and the grain boundary appears black under the erosion of tartaric. It is worth noting that a circle of the white substrate appears around most grains, indicating that the liquation occurs at the grain boundary. At the same time, with the decrease of distance from the fusion line, the white substrate becomes thicker and some precipitated phases are detected within the grains, indicating that the liquation also occurs in the grain interior near the fusion line. In addition, some resolidified structures are also detected, which are generated by the liquation of the large second phase in Fig. 5(a). During the liquation of the second phase, some grains around the second phase also melt and therefore the shape of the molten pool becomes ellipse or roundness. The SEM image of the resolidified structure is shown in Fig. 5(b). It shows that the white net-like structure and some black island-like substrates are surrounded by the net. The microstructure of the HAZ is shown in the Fig. 4(c). As compared with the base metal, the grains in the HAZ are uniform and fine, and exhibit a slight growth. Since the heat input of fiber laser beam is low, the base metal is less affected by the heat and the welding speed is very quick, and thus the grains do not have enough time to grow up [16].
3.4 Mechanism of liquation in PMZ
The liquation phenomena near the fusion line and the EDS analysis results are shown in Fig. 6. The SEM image of the PMZ near the fusion line is shown in Fig. 6(a). Many fine and dispersed white particles are found in the grain interior and the segregation of alloying elements at the grain boundary is also observed. The EDS analysis results of the fine and dispersed second phase (point A), the substrate (point B) and grain boundary (point C) are shown in Figs. 6(b), (c) and (d), respectively.
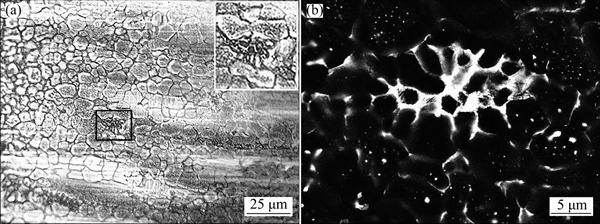
Fig. 5 OM image (a) and SEM image (b) of resolidified structure
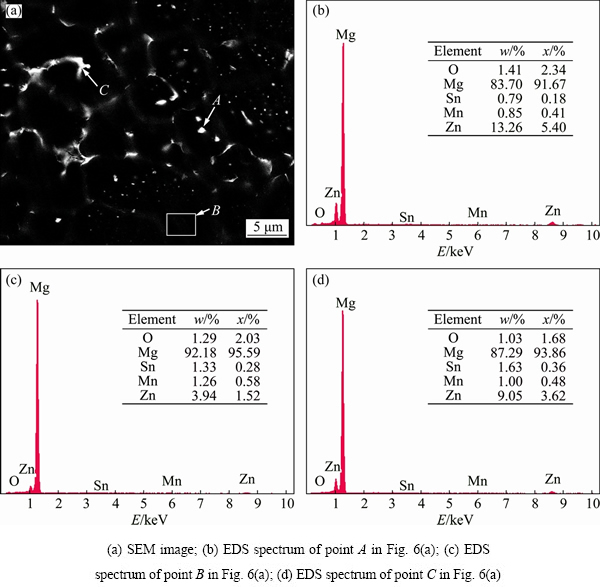
Fig. 6 SEM image and EDS spectra of PMZ near fusion line
As seen from Figs. 6(b), (c) and (d), the mass fractions of Zn in the second phase (13.26%) and grain boundary (9.05%) are more than that of the substrate (3.94%), indicating that fine second phases are the Zn-rich phases and the segregation of Zn at the grain boundary appears.
Because there are no apparent fine second phase particles distributed in the substrate, according to the welding metallurgy [15], the reason for this phenomenon may be the melt of the substrate and the fine, dispersed second phase particles and the solute-enriched grain boundary formed in the subsequent solidification process of the substrate when the temperature is under the solidus temperature TS. During the welding, when the temperature is below TS, the substrate is in a stable state. During the welding proceeding, the temperature rises quickly, and the substrate begins to melt into liquid when the temperature of the substrate near the fusion line exceeds TS. In the subsequent solidification process, the α-Mg will solidify into the crystal firstly due to its higher liquidus temperature. Because the content of Zn in α-Mg which is firstly solidified is low, the residual Zn is excluded into the surrounding liquid and the content of Zn element in the residual liquid increases constantly as the solidification proceeds. When the temperature is under TS, the residual liquid is completely solidified and Zn is enriched at the grain boundaries. Meanwhile, many Zn-enriched second phase particles are separated out in the grain interiors. Similar liquation phenomena are also found in the PMZ of Al-4.5Cu alloy [17]. This phenomenon mainly occurs near the fusion line. As the distance from the fusion line increases, it decreases gradually and disappears at last. This is because the welding temperature near the fusion line is high enough to melt the substrate.
Except for the melt of the substrate, there is another liquation phenomenon called segregation-induced liquation. The SEM image of PMZ far away from the fusion line is shown in Fig. 7. Different from Fig. 6(a), no white particles are detected in the PMZ and the liquid films along the PMZ grain boundaries are either extremely thin or almost invisible. Obviously, this liquation phenomenon is generated by a segregation mechanism. LIPPOLD et al [18] have put forward the segregation-induced liquation mechanism according to the study of austenitic and duplex stainless steels. This mechanism indicates that some alloying elements and the impurities can reduce the melting point of grain boundaries by segregation through diffusion and thus lead to the liquation of grain boundaries. Different from the viewpoints of other researchers, the segregation is formed at first and then it leads to the liquation. According to the theory in Ref. [18], the segregation at grain boundaries follows three reasons: 1) zinc atoms diffuse to the grain boundaries because of the severe thermal motion of atoms during the welding process; 2) in the process of grain growth, zinc atoms are pushed to the grain boundaries by the movement of grain boundaries; 3) zinc atoms in the fusion zone access to the PMZ by crossing over the boundary of fusion zone continuously through diffusion channel. In the present study, the reasons for this segregation are mainly the former two, since the PMZ is far away from the FZ and Zn is hardly to diffuse from the FZ to the PMZ.
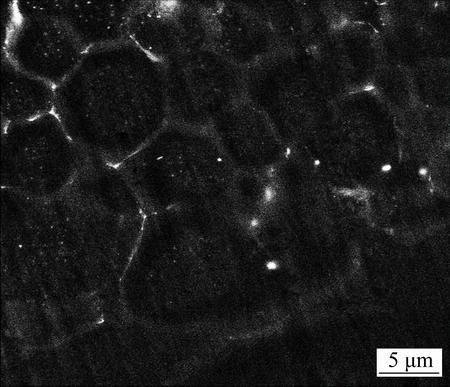
Fig. 7 SEM image of PMZ far away from fusion line
As mentioned above, in the PMZ there exist two kinds of liquation phenomena. One is the uniform liquefied network along the grain boundary, the other is molten pool produced by the liquation of large second phases at the boundaries.
The SEM image of the as-rolled ZM51-0.6Sn sheet is shown in Fig. 8. Some white residual second phases along the rolling direction are found in the substrate. The EDS analysis results show that the white residual second particles are the MgZn phases.
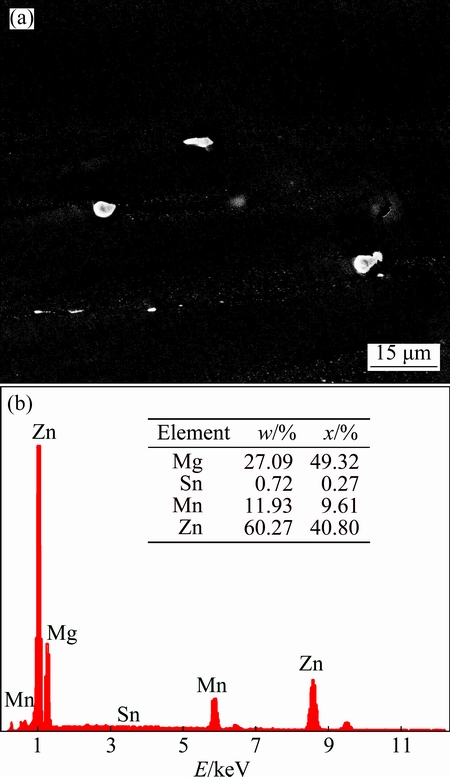
Fig. 8 SEM image (a) and EDS analysis spectrum (b) of as-rolled sheet
According to the Mg-Zn binary phase diagram, the melting point of MgZn is 347 °C, only 6 °C higher than the eutectic temperature (341 °C). During the welding process, because of the quick heating rate, the residual large second phases reach the melting point and melt too quickly to have enough time to react with the surrounding substrate, or just the surface of the residual second phase reacts with a small amount of the substrate. The process of the liquefaction of the large residual MgZn is shown in Fig. 9 [19]. As seen from Fig. 9, when the temperature rises to the melting point, MgZn melts quickly. Meanwhile, with the temperature increasing, the surrounding α-Mg dissolves constantly, the component of the melt ranges from MgZn to hypoeutectic and the shape of the molten pool becomes circular or ellipse at last. In the subsequent process of solidification, the Zn-depleted α-Mg grows from the boundary to the center in the form of planar crystal at first. When the welding heat source is removed, the temperature of melt decreases and the content of Zn increases gradually, and the form of the melt growth ranges from planar crystal to cellular crystal. At the same time, some α-Mg nucleus also form in the melt and grow up. At the end of solidification, the remaining spaces between grains are filled by the Mg7Zn3 phase. Mg7Zn3 is a kind of unstable phase and it will decompose into MgZn at a slow cooling rate; however, during welding, Mg7Zn3 has not enough time to decompose to MgZn because of the high cooling rate.
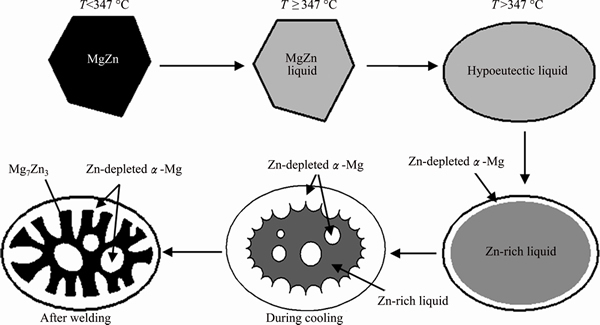
Fig. 9 Mechanism of liquation of residual second phase [19]
Although obvious liquation phenomenon exists in the PMZ, there is no obvious liquation cracking in the PMZ. The high hot cracking sensitivity is a serious problem in the welding of magnesium alloys. Liquation cracking always takes place at grain boundaries and the large residual second phases are also mainly distributed at grain boundaries. Thus, liquation cracking caused by the residual second phases with low melting point also takes place at grain boundaries. As for the as-cast magnesium alloys or magnesium alloy sheets produced by conventional rolling, the hot cracking sensitivity is higher because of the larger low-melting second phases and coarser grains, while the high strain-rate rolled magnesium sheets have lower hot cracking sensitivity due to the finer, more dispersive second phases and finer grains.
4 Conclusions
1) The welding power and the welding speed have great influence on the macrostructure of the welding joint. With higher welding speed and lower welding power, the width and the depth of the joint decrease. When the speed is beyond 70 mm/s, incomplete penetration occurs and many pores are found in the joint.
2) There are no obvious cracks in the FZ and PMZ because of the finer grains in the base metal and the lower welding power and the grains of the HAZ do not grow severely compared with the base metal.
3) Two kinds of liquefaction phenomena are detected in the PMZ. One is the liquation network along grain boundaries, the other is molten pool. The former is associated with the liquation of substrate and the segregation-induced liquation, whereas the latter is the liquation of the residual second phases. However, the liquation of substrate and the segregation-induced liquation are dominant.
References
[1] HUANG Zhen-hua, QI Wen-jun, XU Jing. Effects of Gd on microstructure and mechanical property of ZK60 magnesium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 2568-2576.
[2] YAN Hong-ge, ZHAO Qiang, CHEN Ping, CHEN Ji-hua, SU Bin. Microstructures and mechanical properties of laser welded wrought fine-grained ZK60 magnesium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25: 389-396.
[3] ZHAO Zu-de, CHEN Qiang, CHAO Hong-ying, HUANG Shu-hai. Microstructure evolution and tensile mechanical properties of thixoforged ZK60-Y magnesium alloys produced by two different routes [J]. Materials & Design, 2010, 31(4): 1906-1916.
[4] AVEDESIAN M M, BAKER H. ASM specialty handbook: Magnesium and magnesium alloys [M]. Ohio: ASM International, 1999: 16-19.
[5] ZHANG Ding-fei, SHI Guo-liang, ZHAO Xia-bing, QI Fu-gang. The evolution and effect of Mn element in Mg-Zn-Mn alloy [J]. Materals Review, 2011, 25(9): 1-10. (in Chinese)
[6] ZHANG Ding-fei, QI Fu-gang, SHI Guo-liang, DAI Wei-qing. Effects of Mn content on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Mn wrought alloys [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2010, 39(12): 2205-2210. (in Chinese)
[7] KEARNS W H. Welding handbook [M]. Miami: American Welding Society, 1982: 396.
[8] MARYA M, EDWARDS G R. The laser welding of magnesium alloy AZ91 [J]. Welding World, 2000, 44(2): 31-37.
[9] YANG Zi-mei, YAN Hong-ge, CHEN Ji-hua, SU Bin, ZHANG Guang-hao. Microstructural characterization and liquation behavior of the laser welded joint of fine-grained AZ91 magnesium alloy thin sheets [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2015, 20(1): 27-34.
[10] YU Zhao-hui, YAN Hong-ge, YIN Xu-yu, LI Ying, YAN Guo-hua. Liquation cracking in laser beam-welded joint of ZK60 magnesium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 2891-2897.
[11] CHEN Xiao-ling, YAN Hong-ge, CHEN Ji-hua, SU Bin, YU Zhao-hui. Effects of grain size and precipitation on liquation cracking of AZ61 magnesium alloy laser welding joints [J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2013, 18(6): 458-465.
[12] LIU Li-ming, SONG Gang, LIANG Guo-ji, WANG Ji-feng. Pore formation during hybrid laser-tungsten inert gas arc welding of magnesium alloy AZ31B-mechanism and remedy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 390(1-2): 76-80.
[13] ZHANG Fu-quan, WANG Xiang-qun, CHEN Zhen-hua, QUAN Ya-jie, LI Mei. Researches on gas pore in fusion zone of gas tungsten arc welding magnesium alloy AZ31 sheets [J]. Welding and Joining, 2006, 50(3): 36-39. (in Chinese)
[14] SHAN Ji-guo, ZHANG Jing, ZHENG Shi-qing, LEI Xiang, CHEN Wu-zhu, REN Jia-lie. Experimental study on porosity in laser welding of magnesium alloy [J]. Raremetal Materials and Engineering, 2009, 38(S3): 234-239. (in Chinese)
[15] KOU S. Welding metallurgy [M]. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2002: 263-430.
[16] MIN Dong, SHEN Jun, LAI Shi-qiang, CHEN Jie, XU Nan, LIU Hui. Effects of heat input on the low power Nd: YAG pulse laser conduction weldability of magnesium alloy AZ61[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2011, 49(1): 89-96.
[17] KOU S. Welding metallurgy [M]. Hoboken: Wiley-Interscience, 2002: 155-206.
[18] LIPPOLD J C, BASELACK W A, VAROL I. Heat-affected zone liquation cracking in austenitic and duplex stainless steels [J]. Welding Journal, 1992, 71(S): 1-14.
[19] YU Zhao-hui. The research of the laser welding of high strength ZK series magnesium alloy [D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2011: 82-85. (in Chinese).
佘庆元1,2,严红革1,2,陈吉华1,2,苏 斌1,2,俞照辉3,陈 潮1,2,夏伟军1,2
1. 湖南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410082;
2. 湖南大学 喷射沉积技术及应用湖南省重点实验室,长沙 410082;
3. 国家核电站运行服务技术公司,上海 200233
摘 要:采用光纤激光焊对厚度为2 mm的细晶Mg-5Zn-1Mn-0.6Sn镁合金板材进行焊接,研究焊接接头的成形特征、显微组织和半熔化区的液化行为。研究结果表明,随着焊接功率的降低及焊接速度的增大,焊接接头的宽度和深度减小;此外,当焊接速度过快时,焊缝中会出现气孔。在半熔化区中主要存在两种液化现象:一种是由基体熔化及偏析诱导液化导致的沿晶界的液化网络,另一种为由晶界上残余第二相液化导致形成的液化熔池现象。在本研究中,主要的液化机制为基体的熔化及偏析诱导液化。
关键词:镁合金薄板;光纤激光焊;显微组织;液化现象;液化机理
(Edited by Wei-ping CHEN)
Foundation item: Project (51274092) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Corresponding author: Hong-ge YAN; Tel: +86-731-88664005; E-mail: yanhg68@163.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60093-1

