Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s722-s728
Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of Ti-B-N coatings deposited by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition
Jung Ho SHIN1,2, Kwang Soo CHOI2, Tie-gang WANG3, Kwang Ho KIM1, 2, Roman NOWAK4
1. National Core Research Center for Hybrid Materials Solution, Pusan National University, Busan 609-735, Korea;
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan 609-735, Korea;
3. State Key Laboratory of Corrosion and Protection, Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China;
4. School of Chemical Technology, Aalto University, Aalto 00076, Finland
Received 21 May 2012; accepted 24 September 2012
Abstract: Ternary Ti-B-N coatings were synthesized on AISI 304 and Si wafer by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) technique using a gaseous mixture of TiCl4, BCl3, H2, N2, and Ar. By virtue of X-ray diffraction analysis, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope, and high-resolution transmission electron microscope, the influences of B content on the microstructure and properties of Ti-B-N coatings were investigated systematically. The results indicated that the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-B-N coatings largely depend on the transformation from FCC-TiN phase to HCP-TiB2 phase. With increasing B content and decreasing N content in the coatings, the coating microstructure evolves gradually from FCC-TiN/a-BN to HCP-TiB2/a-BN via FCC-TiN+HCP-TiB2/a-BN. The highest microhardness of about 34 GPa is achieved, which corresponds to the nanocomposite Ti-63%B-N (mole fraction) coating consisting of the HCP-TiB2 nano-crystallites and amorphous BN phase. The lowest friction-coefficient was observed for the nanocomposite Ti-41%B-N (mole fraction) coating consisting of the FCC-TiN nanocrystallites and amorphous BN phase.
Key words: Ti-B-N coating; plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD); nanocomposite coating; hardness; friction coefficient
1 Introduction
Transitional metal (TM, such as Ti, Cr, and Mo) nitride coatings have been extensively studied due to their superior properties, such as high hardness, mechanical strength, chemical inertness, as well as good high- temperature stability [1]. Among them, titanium nitride (TiN) coatings have been widely applied to cutting tools, forming dies, bearings, etc [2-4]. To further improve its mechanical properties and high temperature stability, the addition of the third element in the TiN coating has been widely investigated, such as Ti-Al-N, Ti-Si-N, Ti-B-N and Ti-Al-Si-N coatings, which exhibits higher hardness, lower friction coefficient, and excellent wear resistance [5-8].
For the typical nanocomposite Ti-B-N coatings, GISSLER [9] reported their chemical compositions determined by EPMA (electron probe microanalysis) in the Ti-B-N phase diagram as shown in Fig. 1. By adjusting the mole ratios of B to N in the Ti-B-N coatings, the nanocomposite structures containing the nanocrystalline Ti(B,N) or/and TiB2 and amorphous TiB2, TiB or/and BN phases could be achieved, and hardness, high toughness, chemical inertness, and good thermodynamic stability at high temperatures [10-13].
In this work, the Ti–B–N coatings with various B and N contents were synthesized at a relatively low temperature of 600 °C by a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) technique. Through increasing the B content and decreasing the N content in the resulting coatings along the TiN-TiB2 tie line in Fig. 1, the microstructure and compositions of ternary Ti–B–N coatings were controlled. Moreover, their surface and cross-sectional morphologies, as well as mechanical and tribological properties were also investigated systematically.
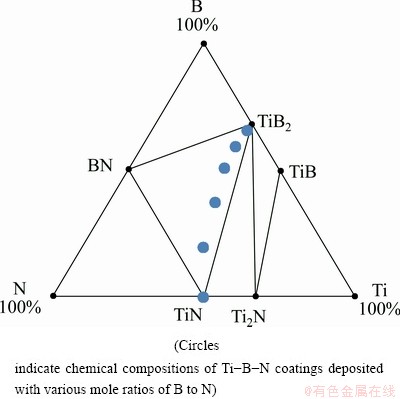
Fig. 1 Simplified phase diagram of Ti-B-N system
2 Experimental
Ternary Ti-B-N coatings were deposited on Si (100) wafers and AISI 304 stainless steel substrates by a PECVD technique using a gaseous mixture of TiCl4, BCl3, H2, N2, and Ar. A schematic diagram of our PECVD apparatus and its details were depicted in our previous work [14]. The gaseous mixture of TiCl4, BCl3, H2, N2, and Ar was passed downstream through a nozzle made of stainless steel. The flow rates of all the gases were individually controlled by mass flow controllers. Ti-B-N coatings with different B and N contents were deposited by varying the input gas mole ratio (R), R= n(BCl3)/n(N2+BCl3). The typical deposition conditions for the Ti-B-N coatings are listed in Table 1.
The chemical compositions and bonding status of the Ti-B-N coatings were analyzed using an electron probe microanalyzer (EPMA 1600, Shimadzu) and X-ray photo electron spectroscopy (XPS, VG Scientifics, ESCALAB250), respectively. X-ray diffractometer (XRD, D8, Bruker) was utilized to investigate the phase constituents of the Ti-B-N coatings using the standard Bragg-Brentano geometry with Cu Kα radiation. The surface and cross-sectional morphologies of the coatings were observed using a field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM, S4800, Hitachi). The film thicknesses were determined from fractured cross-sectional SEM images. Cross-sectional transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images were obtained from a selected sample. A field emission transmission electron microscope (FE-TEM, JEOL, JEM-400FX) operated at an acceleration voltage of 400 kV was used. The sample was prepared by milling in a focused-ion-beam system. The hardness was evaluated using a microhardness tester with a Knoop indenter (Matsuzawa, MMT-7) under a load of 0.245 N. The friction coefficient was measured through sliding wear tests using a conventional ball-on-disk wear apparatus. A steel ball with a diameter of 6.34 mm (HV0.2700) was used as a counterpart material. The sliding tests were conducted with a sliding speed of 0.157 m/s under a normal load of 5 N at ambient temperature of around 24 °C and relative humidity (RH) of 25%-30%.
3 Results and discussion
The chemical compositions of the Ti-B-N coatings deposited at a temperature of 570 °C and radio frequency power of 180 W as a function of the gas mole ratio (R), n(BCl3)/n(TiCl4+BCl3) are summarized in Fig 2. It can be seen that the boron content in Ti-B-N coatings approximately linearly increased from 0 to 66% (mole fraction, the same below if not mentioned) with the increase of R value, whereas the nitrogen content in the coatings relatively decreased from 51% to 1%. At the same time, the titanium content in the coatings also varied slightly and decreased from 49% to 33%, and the residual chlorine content in all Ti-B-N coatings was maintained below 1%. This can be explained that the formation energy of BN is more favorable than that of TiN and TiB2. Consequently, the BN phase could be formed easily in the resulting coatings, and the excess nitrogen would react with Ti to generate TiN phase as the R value was low. With the increase of R value, more and more B began to react with Ti besides the formation of BN phase.
Table 1 Experimental conditions for preparation of ZnO samples


Fig. 2 Chemical compositions of Ti-B-N coatings affected by gas mole ratio of n(BCl3)/n(N2+BCl3)
Figure 3 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of the Ti-B-N coatings with various B and N contents. The titanium nitride of FCC phase with the preferred (200) orientation was only observed in the TiN coating. A shift of the TiN (200) peak appeared in the Ti-B-N coating when the B content was below 17%. As the B content in the Ti-B-N coatings was above 17%, no diffraction peaks for TiN phase were observed and HCP TiB2 phase with the diffraction peaks of (001), (100), (101) and (102) were detected. Also, the diffraction peak intensities corresponding to Ti(B,N) crystal gradually reduced and a peak-broadening phenomenon was observed in Fig. 3. The diffraction peaks for Ti(B,N) crystal almost disappeared at the B content of 41%. The similar XRD peak broadenings have also been reported for other ternary Ti-B-N coatings [15,16]. These phenomena were mainly attributed to the diminution of crystallite size. When the B content in the coatings was above 57%, the TiB2 phase of the diffraction peak intensities increased.
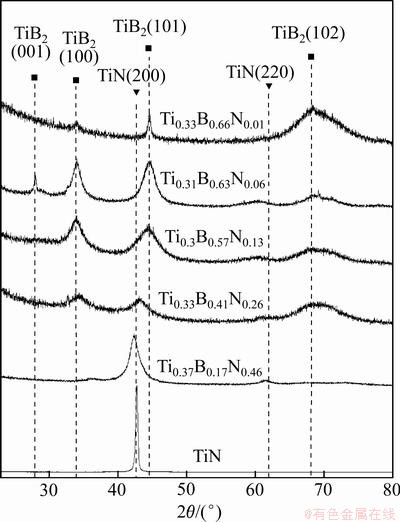
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of Ti–B–C–N coatings with various B and N contents
The chemical bonding status of the Ti, B, and N elements in the Ti-B-N coatings were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The binding energies were calibrated using the C 1s peak at 284.5 eV as a reference. Figure 4 shows the XPS spectra near the binding energies of B 1s and N 1s in the Ti-41%B-N coating (Figs. 4(a) and 4(b)) and Ti-63%B-N coating (Figs. 4(c) and 4(d)). The binding energies of N 1s and B 1s peaks were observed to be TiB2 (187.5 eV), BN (190.5 eV and 398.1 eV) and TiN (396.9 eV) in the Ti-41%B-N coating (Figs. 4(a) and 4(b)), respectively [17,18]. In the case of B 1s for the Ti-63%B-N coating (Fig. 4(c)), the TiB2 and BN phase peaks corresponding to 187.5 eV and 190.5 eV were observed, respectively [19]. As shown in Fig. 4(d), only one peak corresponding to 398.1 eV was also observed, which is in good agreement with that of the BN phase [17,18]. No peak corresponding to TiN was detected. The XRD and XPS results in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4 indicate that a crystalline Ti(B,N) solid-solution, a crystalline TiB2 phase and an amorphous BN phase exist in coatings by varying B and N contents in the Ti-B-N coatings.
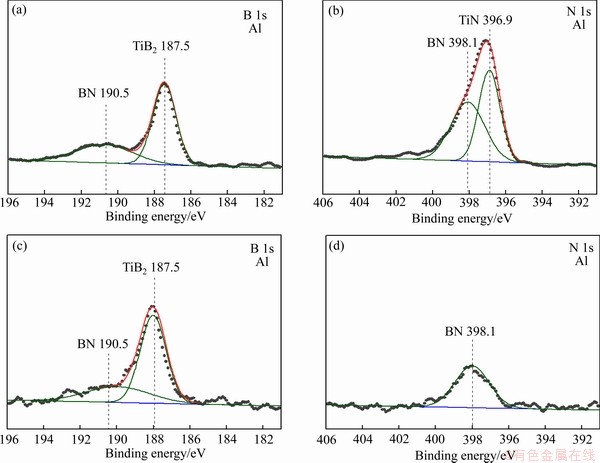
Fig. 4 XPS spectra near binding energy of N 1s and B 1s for Ti-41%B-N coating (a, b) and Ti-63%B-N coating (c, d)
Figures 5 and 6 show the FE-SEM morphologies of the surfaces and fractured cross-sections of the Ti-B-N coatings with various B contents, respectively. With the increase of the B contents in the coatings, the grain size was reduced and microstructures became denser. In the B-free TiN coatings, apparent columnar grains with faceted tops were observed (Fig. 5(a) and Fig. 6(a)). The B-containing Ti-B-N coatings exhibited much finer columnar microstructures with an increase of B content (Figs. 5(b-e) and Figs. 6(b-(e)). On the surfaces of the coatings when the B content was higher than 66%, peaked grains were observed (Fig. 5(f) and Fig. 6(f)).
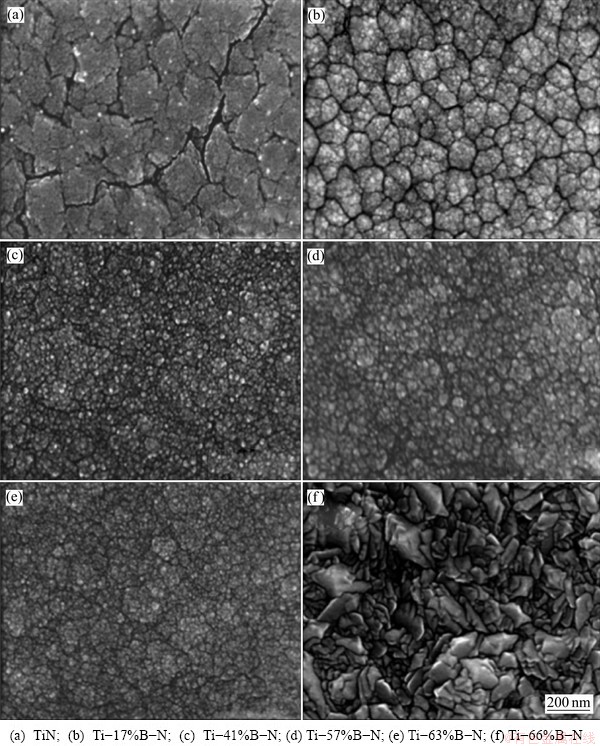
Fig. 5 Surface FE-SEM images of Ti-B-N coatings with various B contents
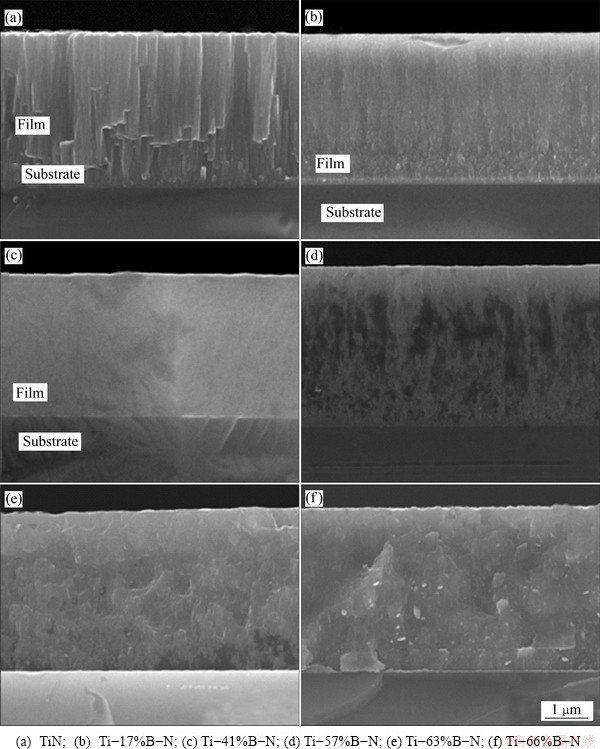
Fig. 6 Fractured cross-sectional SEM micrographs of Ti-B-N coating with various B contents
Microstructural evolutions of Ti-B-N coatings with B addition were also investigated by TEM and high- resolution TEM (HR-TEM) analyses. Figure 7 shows the cross-sectional dark-field TEM images, selected area diffraction patterns (SADP), and HRTEM images of Ti–41%B-N coating and Ti-63%B-N coating. The SADP in Fig. 7(a) clearly indicated continuous diffraction rings and diffraction points of (100) and (101) of the HCP TiB2 phases and (200) of FCC TiN phases. The fine grains with size of 3–4 nm were uniformly distributed in the matrix. The HR-TEM image in Fig. 7(b) clearly shows the nano-compostie microstructure containing lattice fringes of the nanocrystals and the amorphous matrix phase. The SADP of the Ti-63%B-N coating in Fig. 7(c) clearly indicated continuous diffraction rings and diffraction points of (100), (101), (110) and (102) of the HCP TiB2 phases. No TiN phase was identified in the Ti-63%B-N coating. The crystallites in Ti-63%B-N coatings (Fig. 7(d)) were found to have an irregular and ellipsoidal shape of structure with relatively small crystal sizes ranging from 8 to 10 nm, and those were surrounded by amorphous phase distinguished from crystallites by a lattice fringe contrast.
Based on the results from XRD, XPS, and TEM analyses, it is clear that the B addition into Ti-B-N coatings resulted in crystal size refinement and the Ti-B-N coatings had a fine composite microstructure consisting of nano-sized Ti(B, N) crystallites surrounded by amorphous phase of BN. The formation of the nanocomposite in the Ti-B-N coatings was related to the spinodal phase segregation due to immiscibility between crystal (TiN and/or TiB2) and amorphous phase (BN) [20].
Figure 8 shows the microhardness of the Ti-B-N coatings as a function of the B content. The hardness values were obtained from samples with the thickness of about 3 μm. It can be seen that the Ti-63%B-N coating possessed the highest microhardness value of about 34 GPa. This can be explained by the grain boundary hardening created by a strong cohesive energy of interphase boundaries between nano-scale TiB2 crystals with a higher hardness than that of TiN crystals and amorphous BN phase, which restrains grain boundary sliding [20], and by a Hall-Petch relation derived from crystal size refinement [21]. On the other hand, the microhardness value rebounded to about 27 GPa at B content of 66%, which is related to the increase of grain boundary sliding by absence of the a-BN phase.
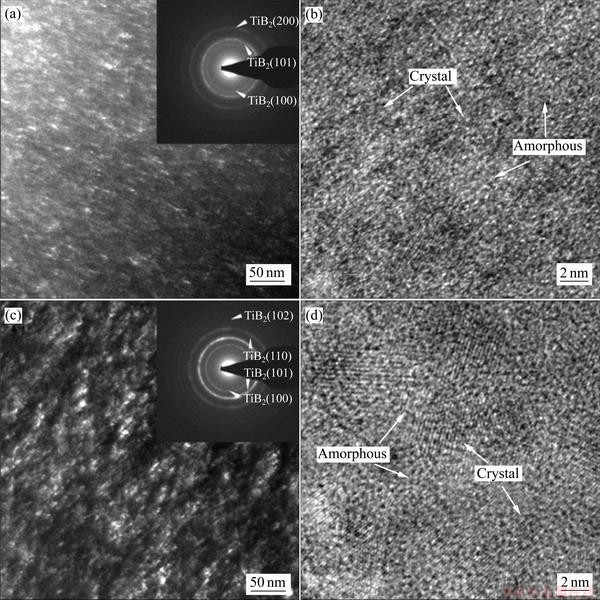
Fig. 7 Cross-sectional HRTEM images, selected area diffraction patterns (SADP), and dark-field TEM images of Ti-41%B-N coating (a, b) and Ti-63%B-N coating (c, d)

Fig. 8 Microhardness of Ti-B-N coatings as function of B content
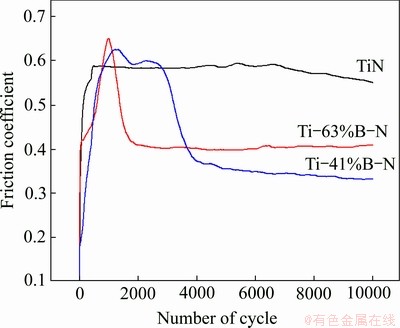
Fig. 9 Friction coefficients of TiN and Ti-B-N coatings as function of B content
Figure 9 shows the friction coefficients of TiN, Ti-41%B-N and Ti-63%B-N coatings against coated steel ball (ball-on-disc) as a function of the B content under a normal load of 5 N at room temperature and a relatively humidity of 25%-30%. With increasing the B content in the coatings, the average friction coefficient of the Ti-B-N coatings was reduced from 0.56 for the B-free TiN coating to 0.36 for the Ti-41%B-N coating, and then rebounded to 0.44 for the Ti-63%B-N coating. The Ti-41%B-N coating with FCC-TiN and amorphous BN phase revealed lower friction coefficient than that of the Ti-63%B-N coating with HCP-TiB2 and amorphous BN phase.
4 Conclusions
(1) The chemical compositions of the Ti-B-N coatings are close to the TiB2-BN tie line in the Ti-B-N phase diagram. As a function of B and N contents, the FCC-TiN and HCP- TiB2 phases are identified in the XRD patterns.
(2) By controlling the B and N contents in the coatings, a nanocomposite microstructure consisting of Ti(B, N) nanocrystals surrounded and supported by amorphous BN phase is achieved. The coating microstructure evolves gradually from FCC-TiN/a-BN to HCP-TiB2/a-BN via FCC-TiN+HCP-TiB2/a-BN with increasing the B content.
(3) With the increase of B content, the Ti-B-N coating hardness first increases, and then rebounds. The highest microhardness of about 34 GPa is achieved as the B content is 63%, which corresponds to a nanocomposite microstructure, namely the HCP-TiB2 nanocrystallites are embedded in amorphous BN phase. The lowest friction-coefficient is observed in the Ti-41%B-N coating, which corresponds to a nanocomposite microstructure consisting of the FCC-TiN nanocrystallites and amorphous BN phase.
Acknowledgments
It was also funded by a grant from the National Core Research Center (NCRC) Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 2012-0000-957) and by a grant from the Fundamental R&D Program for Core Technology of Materials funded by the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Republic of Korea.
References
[1] KIM K H. Hybrid functional multi-component composite films for hard coating applications [J]. Journal of Ceramic Processing Research, 2009, 10: 1-9.
[2] KAWANA A, ICHIMURA H, IWATA Y, ONO S. Development of PVD ceramic coatings for valve seats [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 1996, 86-87(1-3): 212-217.
[3] HILTON M R, NARASIMHAN L R, NAKAMURA S, SALMERON M, SOMORJAI G A. Composition, morphology and mechanical properties of plasma-assisted chemically vapor-deposited tin films on M2 tool steel [J]. Thin Solid Films, 1986, 139(3): 247-260.
[4] MAKABE R, NAKJIMA S, TABATA O. Dependence of the hardness of titanium nitride prepared by plasma chemical vapour deposition on the gas flow rate and the r.f. power [J]. Thin Solid Films, 1986, 137(1): 49-50.
[5] SUSZKO T,  W, JAGIELSKI J. The role of surface oxidation in friction processes on molybdenum nitride thin films [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2005, 194(2-3): 319-324.
W, JAGIELSKI J. The role of surface oxidation in friction processes on molybdenum nitride thin films [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2005, 194(2-3): 319-324.
[6] MURRAY S F, CALABRESE S J. Low speed sliding behavior of metal-ceramic couples at temperatures up to 800 °C [J]. Lubrication Engineering, 1993, 49(5): 387-397.
[7] LYO I W, AHN H S, LIM D S. Microstructure and tribological properties of plasma-sprayed chromium oxide–molybdenum oxide composite coatings [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2003, 163-164: 413-421.
[8] RUDNIK P J, GRAHAM M E, SPROUL W D. High rate reactive sputtering of MoNx coatings [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 1991, 49(1-3): 293-297.
[9] GISSLER W. Structure and properties of Ti-B-N coatings [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 1994, 68-69: 556-563.
[10] KARVANKOVA P, VEPREK-HEIJMAN M G J, ZINDULKA O, BERGMAIER A, VEPREK S. Super hard nc-TiN/a-BN and nc-TiN/a-TiBx/a-BN coatings preparedby plasma CVD and PVD:A comparative study of their properties [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2003, 163-164: 149-156.
[11] KARVANKOVA P, VEPREK-HEIJMAN M G J, AZINOVIC D, VEPREK S. Properties of superhard nc-TiN/a-BN and nc-TiN/ a-BN/a-TiB2 nanocomposite coatings prepared by plasma induced chemical vapor deposition [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2006, 200(9): 2978-2989.
[12] LU Y H, SHEN Y G, LI K Y. Nanostructured two-phase nc-TiN/a-(TiB2,BN) nanocomposite thin films[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2006, 253(3): 1631-1638.
[13] LU Y H, SHEN Y G, WANG J P, ZHOU Z F, LI K Y. Structure and hardness of unbalanced magnetron sputtered TiBxNythin films deposited at 500°C[J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 2007, 201(16-17): 7368-7374.
[14] CHOI K S, HONG Y S, KWON S H, CHOI J H, WANG Q M, KIM K H. Synthesis by a PECVD technique and mechanical properties of nc-Ti(B,N)/a-BN coatings [J]. Journal of Ceramic Processing Research, 2011, 12(2): 160-164.
[15] MITTERER C, MAYRHOFER P H, BESCHLIESSER M, LOSBICHLER P, WARBICHLER P, HOFER F, GIBSON P N, GISSLER W, HRUBY H, MUSIL J, VICEK J. Microstructureand properties of nanocompositeTi-B-N and Ti-B-C coatings [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 1999, 120-121: 405-411.
[16] PFOHL C, RIE K T. Wear-resistant PACVD coatings of the system Ti-B-N [J]. Surface and Coating Technology, 1999, 116-119: 911-915.
[17] WAGNER C D, NAUMKIN A V, KRAUT-VASS A, ALLISON J W, POWELL C J, RUMBLE J R. NIST Standard Reference Database 20, Version 3.5: NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database [M]. Gaithersburg, ND: U.S. Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology.
[18] MOULDER J F, STICKLE W F, SOBOL P E, BOMBEN K D. Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy [M]. Eden Prairie, MN: Physical Electronics Inc., 1995: 213.
[19] SHENG S H, ZHANG R F, VEPREK S. Phase stabilities and thermal decomposition in the Zr1-xAlxN system studied by ab initio calculation and thermodynamic modeling [J]. Acta Materialia, 208, 56(16): 4440-4449.
[20] VEPREK S. The search for novel, superhard materials [J]. Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology A, 1999, 17(5): 2401-2420.
[21] LASALMONIE A, STRUDEL J L. Influence of grain size on the mechanical behaviour of some high strength materials [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1986, 21(6): 1837-1852.
(Edited by LI Xiang-qun)
Corresponding authors: Kwang Ho KIM; Tel: +85-51-510-3391; E-mail: kwhokim@pusan.ac.kr;
Roman NOWAK; Tel: +358-9-470-2667; E-mail: nowak.roman5@gamail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(12)61794-4