文章编号:1004-0609(2011)12-3175-07
土壤腐蚀过程中高锡青铜的形貌变化和元素迁移
汤 琪1,王菊琳1,马菁毓1, 2
(1. 北京化工大学 材料科学与工程学院,北京 100029;
2. 中国文化遗产研究院 保护科学技术研究所,北京 100029)
摘 要:采用在含模拟土壤介质(0.010 4 mol/L Na2SO4+0.028 2 mol/L NaCl+0.016 4 mol/L NaHCO3)的土壤中埋藏铸造青铜试样的方法研究高锡青铜的土壤腐蚀规律;采用金相显微镜观察腐蚀前后青铜的结构变化,扫描电镜(SEM)并结合能谱(EDS)对微区成分进行分析;用X射线荧光光谱(XRF)检测埋藏试样周围土壤中元素含量,同时用残留因子fCu/Sn和fCu/Pb定量分析腐蚀产物中Cu、Sn和Pb的残留情况。结果表明:在该环境下高锡青铜腐蚀首先从α相与δ相界面开始,且α相先于δ相发生腐蚀,留下未腐蚀的岛屿状δ相;高锡青铜腐蚀过程中Cu优先向周围土壤中迁移,最终形成的含O、C腐蚀产物中富含Sn和Pb。
关键词:高锡青铜;土壤;腐蚀;迁移
中图分类号:TG 174 文献标志码:A
Morphology change and elements migration of bronze with high tin content after soil corrosion
TANG Qi1, WANG Ju-lin1, MA Jing-yu1, 2
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing 100029, China;
2. Protection Institute of Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Cultural Heritage, Beijing 100029, China)
Abstract: The soil corrosion rule of the bronze with high tin content was researched by burying the metal samples in the soil containing the simulated the edaphic elecrdyte (0.010 4 mol/L Na2SO4+0.028 2 mol/L NaCl+0.016 4 mol/L NaHCO3) aimed at simulating the underground water. The morphology change before and after the corrosion was observed by metalloscopy, and SEM combined with EDS was used to analyze the micro-area composition of the corroded sample. Further research with X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) was carried out to measure the content of the elements in the soil around the bronze sample. Then, factors fCu/Sn and fCu/Pb were used to make a quantitative analysis of the residual elements Cu, Sn and Pb in the corrosion products. The results show that the corrosion firstly occurs on the interface between the α phase and δ phase, α phase is prior to be corroded, with the island-shaped δ phase uncorroded and left. Cu is prior to diffuse into the surrounding soil, leaving the corrosion products containing O and C rich in Sn and Pb.
Key words: High-tin bronze; soil; corrosion; diffusion
对青铜合金腐蚀规律的研究不仅是文物保护学也是金属腐蚀学研究领域的一项热门课题。典型的铸造青铜组织由α固溶体和(α+δ)共析体组成[1-4],有关青铜组织结构中α相和δ相的优先腐蚀问题争论已久,有的认为是α相(富铜相)优先腐蚀[5-6],有的认为α相及δ相(富锡相)中哪一相优先腐蚀取决于氧的含量[7]。许多研究表明[3, 8-9],青铜表面腐蚀产物中富锡,由此推断青铜中锡(或富锡相)优先于铜腐蚀形成腐蚀产物,或者铜优先于锡腐蚀并且铜流失造成锡富集。事实上,所观察到的腐蚀层是由于溶解的金属离子从基体向外迁移、沉积、流失;环境介质元素向内迁移,两者相结合所形成的[10]。所以,以往通过分析青铜表面腐蚀产物来推断腐蚀产生的原因,难以反映腐蚀产生的真实过程。
对金沙遗址出土青铜器表面成分和价态进行的分析表明,以超微晶颗粒存在于锈层表面的SnO2,使得青铜基体免遭进一步腐蚀[11]。对云南4件春秋战国时期青铜器中矛的检测中发现存在SnO2涂层,表明人们在青铜矛表面涂上一层锡的氧化物涂层以防腐蚀,并且证明锡的氧化物涂层的防腐效果最好[12]。
将金属埋藏在土壤中研究其腐蚀过程和规律是一种重要的土壤腐蚀研究方法,实验简单、可靠,能够在一定程度上模拟土壤腐蚀的真实环境,但复杂的土壤系统使得干扰因素很多,增加了对结果分析的难度。然而,在模拟土壤介质中进行实验又失去了土壤颗粒环境的真实性。为了尽可能降低土壤埋藏试验的复杂性和不可控制性,本实验将成分和浓度已知的模拟介质加入到清洗过的土壤中,通过在含模拟土壤介质的土壤中埋藏青铜以加速模拟出高锡青铜土壤腐蚀历程,将青铜腐蚀前后金相组织及成分变化与检测试样表面不同距离处土壤中所含元素种类及其含量变化相结合,从根本上揭示青铜腐蚀现象以及所含主要金属元素的迁移规律。
1 实验
实验用高锡青铜试样是采用传统铸造法自行冶炼、铸造的Cu-Sn-Pb三元合金,打磨光亮后经XRF测得其组成(质量分数,%)如下:Cu 72.8%、Sn 23.0%、Pb 4.2%。将试样切割成10 mm×10 mm×3 mm的方块,除油,用环氧树脂封固,依次用200#至800#水砂纸逐级打磨工作面,用去离子水清洗,酒精擦拭后,干燥备用。
实验用土壤取自北京安贞桥附近一施工处地下约10 m深,深挖土可以避免表层土中腐殖酸对土壤腐蚀性能的影响。土壤质地类型属于轻壤质、黄褐色。同时,为了尽可能降低土壤中原本存在的可溶性物质对实验的干扰,将土壤用自来水清洗3遍,去离子水清洗3遍,晾干粉碎后,用孔径约为1 mm的不锈钢网过滤,取下层细土作为实验中所用的土壤。向土壤中均匀喷洒pH值为8.05的含0.010 4 mol/L Na2SO4+ 0.028 2 mol/L NaCl+0.016 4 mol/L NaHCO3的模拟地下水溶液[13-14],参考湿度对X70钢腐蚀速率影响的规律[15],最后配制成含水量30%的腐蚀性土壤。
将试样粘贴在自制敞口长方形玻璃槽(25 cm×5 cm×5 cm)的一端,向每个槽中加入配置好的腐蚀性土壤900 g,随后用保鲜膜封住玻璃槽口。每隔7 d揭开保鲜膜一次,敞口放置约30 min,让空气进入。这样既可以保持土壤湿度又可以使氧气进入,模拟含氧环境下潮湿土壤中青铜的腐蚀规律。待埋藏120 d后将试样取出,同时分别在距离试样表面0、2、4、6和 8 cm处取尺寸约为1 cm×1 cm×0.5 cm的土样块,随后进行下述测试。
1) 金相显微组织观察
用毛刷除去腐蚀后青铜试样表面的土壤和腐蚀产物,为了不破坏腐蚀后的组织形态,试样略微抛光后在显微镜下观察。同时,对未进行土壤埋藏实验的青铜金相显微组织进行观察作为对比,步骤是把青铜试样依次用200~2000号水砂纸逐级打磨,再用2.5 μm金刚石研磨膏抛光,去离子水冲洗,用3%FeCl3酒精溶液刻蚀,再用去离子水冲洗并干燥后,在显微镜下观察。显微镜为德国Leica公司生产的Leica DM4000 M光学显微镜。
2) SEM-EDS微区成分测试
用能谱仪对扫描电镜下观察到的各不同区域成分进行测试。仪器型号及测试条件如下:日立公司S-3600N型扫描电镜,加速电压20 kV,样品用导电胶粘在样品台上观察。美国EDAX公司DX-100型X射线能量色散谱仪;测量环境为真空;工作电压为15 kV。
3) XRF测试
用日本岛津公司生产的EDX-800HS X射线荧光光谱仪对所取土样成分进行测试。测量环境为真空;射线源为铑靶(Rh);工作电压:Ti-U 50 kV,Na-Sc 15 kV。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 组织结构及成分变化
SCOTT[16]根据锡含量不同将古代锡青铜分为高锡和低锡两类,锡含量小于17%的为低锡青铜,本实验中所用青铜锡含量为23.0%,属于高锡青铜。未埋藏和埋藏试样的金相组织如图1和2所示。从图1可看出,所铸造的青铜具有高锡青铜典型的α固溶体和(α+δ)共析体组织结构,依据Cu-Sn二元合金相图(见图3)[17],图1中含量较高的为(α+δ)共析体。同时,其间随机分布着游离态含铅夹杂物和一些铸造疏松、孔洞。
在含有模拟土壤介质的土壤中埋藏120 d的青铜,表面发生了严重腐蚀,组织形貌发生了变化(见图2)。在腐蚀不太严重的区域(见图2(a)和(b)),可以初步得出腐蚀基本都是沿着初生α组织和(α+δ)共析体边界进行,并且发生在初生α组织内。在腐蚀比较严重的区域(见图2(c)和(d)),可以初步得出呈岛屿状的黑色腐蚀区域是被(α+δ)共析体所包围且已基本发生完全腐蚀的初生α相,呈树枝状的黑色腐蚀区域是(α+δ)共析体中共析的α相腐蚀状况,(α+δ)共析体内的δ相基本没有发生腐蚀。
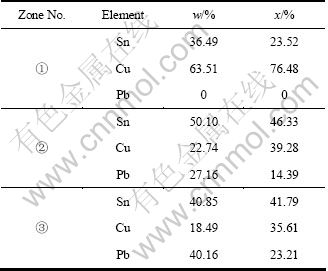
为了进一步确定优先腐蚀的是α相还是δ相,在SEM下找到了类似图2(d)所示的区域(见图4(a)),并对图中包含的所有区域,包括亮白色区域、灰色区域、黑色区域分别用能谱仪进行成分分析,结果如图4(b)、(c)和(d)所示。把3个区域中Cu、Sn和Pb 3种元素的质量分数和摩尔分数进行比较,结果如表1所列。
区域①。在SEM像中由于反光强而呈现亮白色,其含量和形貌类似于(α+δ)共析体中未发生腐蚀的δ相,EDS测试结果表明,区域①除含有微量C、N和O元素外,主要由Cu和Sn两种元素组成。表1中计算结果表明,该区域中Cu与Sn摩尔比为31:9.5。依据图3的合金相图,δ相是以金属间化合物Cu31Sn8为基体的固溶体,其Cu与Sn的理论摩尔比约为31:8,区域①与δ相的成分及含量非常接近,可以断定该区域为共析体中的δ相区,而且未发生腐蚀。

图1 FeCl3溶液刻蚀后的青铜基体的金相组织
Fig.1 Metallographs of bronze base after corrosion by FeCl3 solution
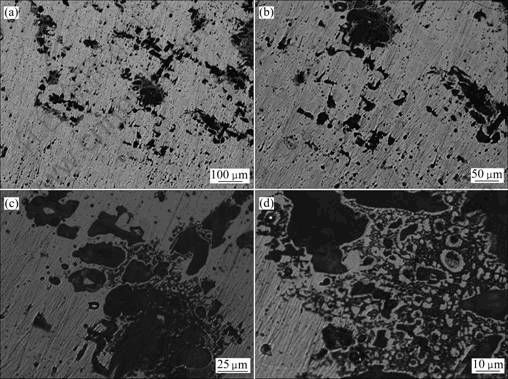
图2 土壤腐蚀后青铜试样的金相组织
Fig.2 Microstructures of bronze sample after buried in soil
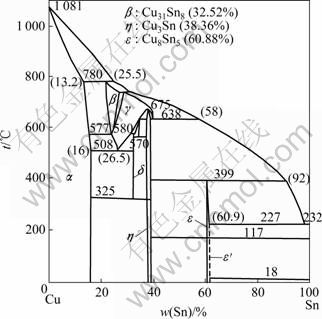
图3 Cu-Sn二元合金相图
Fig.3 Phase diagram of Cu-Sn alloy
区域②。在SEM像中为灰色无光泽连片区域,EDS测试结果显示,Cu与Sn摩尔比为0.85,根据图3,α相中Sn的含量为15.8%(质量分数)[17],即Cu与Sn摩尔比约为10;因此,不论与α相还是δ相的成分比较,均表明该部分由于腐蚀而使Cu迁移流失严重,残余Cu含量与原组成相比明显降低,而Sn和Pb的含量均比较高,尤其是Sn和O的含量也很高,可能形成了含氧的腐蚀产物。结合其腐蚀形貌,可以确定区域②是α相发生了腐蚀。
区域③。EDS测试结果与区域②的相似。Cu与Sn的摩尔比约为0.85,也是α相发生腐蚀的区域。但从其颜色和形貌看,又与区域②有区别,而且该部分中Pb、C含量要比区域②的高,所以,其中Pb、C腐蚀产物比区域②的高。
综上所述,在土壤中埋藏120 d的高锡青铜,腐蚀沿着α相和δ相的界面进行,且α相比δ相优先发生腐蚀。这与文献[18-20]中介绍的加入锡可提高铜合金的耐蚀性、或者高锡青铜比低锡青铜耐腐蚀是一致的。
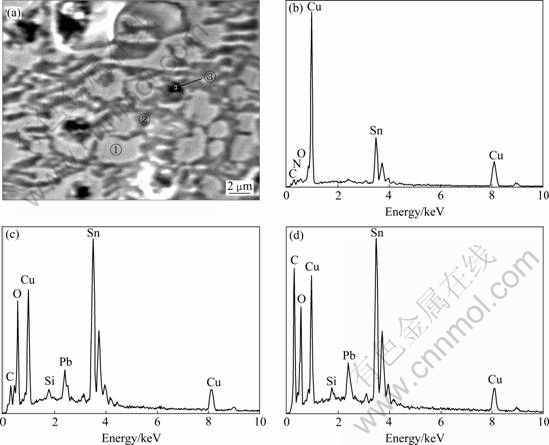
图4 高锡青铜腐蚀区域的SEM像及各区的EDS分析结果
Fig.4 SEM image of bronze sample after buried and EDS analysis results: (a) SEM image; (b) Zone ①; (c) Zone ②; (d) Zone ③
表1 各微区能谱分析结果
Table 1 EDS analysis results of micro-zones
2.2 青铜合金各元素的溶解、迁移及残留
通过检测距试样表面不同位移处土壤所含元素及其含量变化,可以获得青铜合金元素的迁移规律。表2所列是在土壤中埋藏120 d的高锡青铜附近不同距离处元素含量及其变化,由于在6 cm和8 cm处没有检测到Cu、Sn、Pb中任何一种元素,所以只列出了0 cm、2 cm和4 cm的检测结果,发现Cu元素已经向周围土壤中迁移了至少4 cm,但在0~8 cm范围内并没有发现Sn和Pb元素。结合上述EDS检测结果,腐蚀区域中Sn和Pb含量很高,而Cu元素含量比α相和δ相中的低很多,说明Cu相对于Sn和Pb易于从腐蚀区域中向环境(此处为土壤)大量迁移。
表2 埋藏青铜周围土壤成分及含量检测结果
Table 2 Composition and content of soil around buried bronze

为了更清楚地揭示高锡青铜在土壤腐蚀结果中各元素由于溶解、迁移后残留腐蚀产物的状况,引入溶解因子的概念[9, 19, 21-22],溶解因子fCu/Sn、fCu/Pb表示腐蚀区域中Cu、Sn和Pb元素的溶解、迁移后残留腐蚀产物的情况。
以图4(a)中腐蚀区域②、③能谱分析结果作为原始数据进行计算。
 (1)
(1)
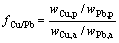 (2)
(2)
式中:wCu,p、wSn,p和wPb,p分别表示腐蚀区域中Cu、Sn和Pb元素的质量分数;wCu,a、wSn,a和wPb,a分别表示青铜合金(α+δ)共析体组织α相中Cu、Sn和Pb元素的质量分数。观察铸造高锡青铜的显微组织发现含铅颗粒基本上集中在(α+δ)共析体中,同时假设含铅颗粒全部分布在共析体的α相中,折算后α相中Cu、Sn和Pb元素的质量分数分别为72.63%、13.64%和13.73%。
当fCu/Sn或fCu/Pb=1时,该距离处残留的腐蚀产物中w(Cu):w(Sn)或w(Cu):w(Pb)与合金中的相同。当 0<fCu/Sn或fCu/Pb<1时,该距离处残留的腐蚀产物中w(Cu):w(Sn)或w(Cu):w(Pb)小于合金中的,说明该处Sn(或Pb)腐蚀产物残留的比例较大,Cu相对于Sn(或Pb)选择性腐蚀并优先迁移出去;当fCu/Sn或fCu/Pb>1时,该距离处残留腐蚀产物中w(Cu):w(Sn)或w(Cu):w(Pb)大于合金中的,说明该处腐蚀产物Cu残留的比例较大,Sn(或Pb)相对于Cu选择性腐蚀并优先迁移出去。数据计算结果如表3所示。
从表3可以看出,不同腐蚀区域的残留因子fCu/Sn、fCu/Pb均小于1,且部分计算结果接近于0,说明腐蚀产物中Sn、Pb残留的比例很大,腐蚀产物富Sn、Pb,大量的Cu相对于Sn、Pb优先迁移出去,这与在土壤中的测量结果是相符的。
表3 腐蚀产物的残留因子fCu/Sn和fCu/Pb
Table 3 Residual factor of fCu/Sn and fCu/Pb in corrosion products

3 结论
1) 高锡青铜在含有0.010 4 mol/L Na2SO4+0.028 2 mol/L NaCl+0.016 4 mol/L NaHCO3模拟地下水溶液的土壤中埋藏120 d后,腐蚀沿着α相和δ相的界面进行,并且α相比δ相优先发生腐蚀,腐蚀产物是Sn、Pb、Cu的含O、C化合物。δ相未发生腐蚀。
2) 在埋藏120 d后距离青铜表面0~4 cm的土壤中,只发现了Cu、Sn和Pb 3种元素,其中Cu元素已经向周围土壤中迁移了至少4 cm,说明Cu的腐蚀产物相对于Sn和Pb的腐蚀产物更易从腐蚀区域向环境迁移。
3) 腐蚀产物的残留因子fCu/Sn、fCu/Pb均小于1,且部分计算结果接近于0,说明腐蚀产物中Sn、Pb残留的比例很大,腐蚀产物富Sn、Pb,大量的Cu相对于Sn、Pb优先迁移出去。
REFERENCES
[1] 张晓梅, 原思训, 刘 煜, 周宝中. 周原遗址及渔国墓地出土青铜器锈蚀研究[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 1999, 11(2): 7-18.
ZHANG Xiao-mei, YUAN Si-xun, LIU Yu, ZHOU Bao-zhong. Research on the corrosion of bronzes from Zhouyuan site and Yu state cemeteries[J]. Sciences of Conservation and Archaeology, 1999, 11(2): 7-18.
[2] 洛阳铜加工厂中心试验室金相组. 铜及铜合金金相谱图[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1983.
Metallurgical Group of Luoyang Copper Processing Factory Central Laboratory. Diagrams of copper and its alloy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1983.
[3] 刘 煜, 原思训, 张晓梅. 天马-曲村周代晋国墓地出土青铜器锈蚀研究[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 2000, 12(2): 9-18.
LIU Yu, YUAN Si-xun, ZHANG Xiao-mei. Research on the corrosion of bronze wares excavated from Tianma-Qucun site of Jin state in Zhou Dynasty[J]. Sciences of Conservation and Archaeology, 2000, 12(2): 9-18.
[4] 凡小盼, 王昌燧, 金普军. 热处理对铅锡青铜耐腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2008, 28(2): 112-115.
FAN Xiao-pan, WANG Chang-sui, JIN Pu-jun. Effect of heat treatment on corrosion behavior of bronze[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2008, 28(2): 112-115.
[5] 罗武干, 秦 颍, 黄凤春, 胡雅丽, 王昌燧. 湖北省出土的若干青铜器锈蚀产物研究[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2007, 19(3): 157-161.
LUO Wu-gan, QIN Ying, HUANG Feng-chun, HU Ya-li, WANG Chang-sui. Study on corrosion products of some amcient bronzes excacated from Hubei province[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2007, 19(3): 157-161.
[6] 王 宁, 何积铨, 孙淑云, 肖 璘. 模拟青铜器样品在典型电解质溶液中的电化学行为研究[J]. 文物保护与考古科学, 2007, 19(4): 45-48.
WANG Ning, HE Ji-quan, SUN Shu-yun, XIAO Lin. Bronze samples in various typical electrolytes[J]. Sciences of Conservation and Archaeology, 2007, 19(4): 45-48.
[7] SCOTT D A. Bronze disease: A reviews of some chemical problems and the role of relative humidity[J]. Journal of the American Institute for Conservation, 1990, 29: 193-206.
[8] SCOTT D A. An examination of the patina and corrosion morphology of some Roman bronzes[J]. J Am Institute Conserv, 1994, 33(1): 1-23.
[9] SIDOT E, SOUISSI N, BOUSSELMI L, TRIKI E, ROBBIOLA L. Study of the corrosion behaviour of Cu-10Sn bronze in aerated Na2SO4 aqueous solution[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48: 2241-2257.
[10] ROBBIOLA L, TRAN T T M, DUBOT P, MAJERUS O, RAHMOUNI K. Characterisation of anodic layers on Cu-10Sn bronze (RDE) in aerated NaCl solution[J]. Corrosion Science, 2008, 50: 2205-2215.
[11] 陈善华, 刘思维, 孙 杰. 青铜文物的光电子能谱分析[J]. 材料保护, 2007, 40(2): 67-70.
CHEN Shan-hua, LIU Si-wei, SUN Jie. Photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of broze artifacts[J]. Materials Protection, 2007, 40(2): 67-70.
[12] 杨 群, 王怡林, 张鹏翔, 李朝真. 云南青铜防腐显微拉曼光谱EPMA研究[J]. 光散射学报, 2005, 17(2): 192-199.
YANG Qun, WANG Yi-lin, ZHANG Peng-xiang, LI Chao-zhen. The corrosion study of Raman spectra EPMA of bronze at Yunnan province[J]. Chinese Journal of Light Scattering, 2005, 17(2): 192-199.
[13] WANG Ju-lin, XU Chun-chun, L? Guo-cheng. Formation of CuCl and regenerated Cu crystals on bronze surfaces in neutral and acidic media[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2006, 252: 6294-6303.
[14] ASTMD 1384—01. Standard test method for corrosion test for engine coolants in glassware [S]. 2001.
[15] 费小丹, 李明齐, 许红梅, 李永强, 蔡铎昌. 湿度对X70钢在卵石黄泥土中腐蚀行为影响的电化学研究[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2007, 27(1): 35-37.
FEI Xiao-dan, LI Ming-qi, XU Hong-mei, LI Yong-qiang, CHAI Duo-chang. Influence of soil humidity on corrosion behavior of X70 steel in yellow pebble soil[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2007, 27(1): 35-37.
[16] SCOTT D A. Metallography and microstructure of ancient and historic metals[M]. London: The Getty Conservation Institute in Association with Archetype Books, 1991.
[17] 高 强. 最新有色金属金相图谱大全[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2005: 886-889.
GAO Qiang. A complete collection of diagram of non-ferrous metals[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2005: 886-889.
[18] 中国文化遗产研究院. 中国文物保护与修复技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 365.
Chinese Academy of Cultural Heritage. Preservation and restoration technic of Chinese cultural relics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 365.
[19] 《化工百科全书》编辑委员会. 冶金和金属材料[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2001: 876-877.
Editorial Office of Encyclopaedia on Chemical Industry. Metallurgy and metal material[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2001: 876-877.
[20] 李艳萍, 成小林, 程玉冰, 王志强. 考古现场青铜样品土壤埋藏腐蚀实验初探[J]. 考古与文物, 2006, 6: 95-98.
LI Yan-ping, CHENG Xiao-lin, CHENG Yu-bing, WANG Zhi-qiang. The corrosion testing of buried bronze at archaeological sites[J]. Archaeology and Cultural Relics, 2006, 6: 95-98.
[21] ROBBIOLA L, BLENGINO J, FIAUD C. Morphology and mechanism of formation of natural patinas of archaeological Cu-Sn alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 1998, 40(12): 2083-2110.
[22] 王菊琳, 许淳淳, 吕国诚. 三元青铜环境界面上物质转移的化学行为[J]. 材料研究学报, 2004, 18(3): 244-250.
WANG Ju-lin, XU Chun-chun, L? Guo-cheng. Chemical behavior of mass transfer at the bronze/environment interface[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2004, 18(3): 244-250.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家重大社会公益项目(2005DIB6J157);北京化工大学碳纤维及功能高分子教育部重点实验室资助
收稿日期:2010-11-18;修订日期:2011-03-26
通信作者:王菊琳,副研究员,博士;电话:010-89118653;E-mail: Julinwang@126.com