DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-35905
镍基合金GH4169电子束焊接头高温稳定性
魏 祺,敖三三,王 泰,吴满鹏,罗 震
(天津大学 材料科学与工程学院,天津 300350)
摘 要:重点研究在给定的不同高温条件下,GH4169电子束焊焊接接头所表现出的高温稳定性。采用金相、SEM和拉伸等实验对经过不同高温氧化时间的试样进行显微组织观察和力学性能分析。结果表明:GH4169电子束焊缝中心区为树枝晶和胞状树枝晶,由于高温氧化时间和第二相颗粒钉扎作用的相互影响,晶粒随着高温氧化不断长大,直到25 h时,晶粒尺寸达到极大值;随后晶粒大小有减小的趋势,在50 h以后,晶粒继续变得粗大。焊接接头在650 ℃的高温氧化下,25 h时机械拉伸性能达到最佳,在75 h时接头的机械拉伸性能低于常温接头的性能;焊接接头经过长时间的高温氧化,表面会生成较致密的氧化膜。
关键词:高温合金GH4169;电子束焊;高温稳定性
文章编号:1004-0609(2020)-11-2578-08 中图分类号:TG456.7 文献标志码:A
GH4169由γ基体、δ相、碳化物和作为强化相的γ″(Ni3Nb)和γ′(Ni3(Al,Ti,Nb))等组成,是一种典型的铁-镍-铬类高温合金,因其优良的高温强度和高温抗氧化性能,在-253~650 ℃的温度范围内得到广泛应 用[1]。目前,GH4169合金已成为航空、航天和核能领域的关键材料[2]。同时,由于GH4169具有较强的抗应变时效开裂性能,因此,该合金也具备良好的可焊接性[3-4]。随着航空发动机以及燃气轮机的飞速发展,对GH4169合金及其焊接接头质量也提出了更高的要求,特别是要求镍基高温合金的接头能在680 ℃或者更高的服役温度条件下使用。然而当使用温度超过650 ℃时,合金的强度、塑性等一系列性能会迅速下降[5],因此,对GH4169焊接接头的高温稳定性的研究也日益迫切[5-6]。
相比于传统的熔焊方法[6-7],电子束焊作为一种先进的焊接技术,具有能量密度高、深宽比大、焊缝热影响区小、焊接残余变形小和在真空环境下焊缝纯净等优点,因而电子束焊接在航空航天这些高端制造领域正日益得到广泛应用[8]。同时,因其不会显著降低焊接接头的力学性能,电子束焊也逐渐被公认为是GH4169高温合金的最佳焊接方法。章晨阳[9]对6 mm厚的GH4169镍基高温合金为研究对象,采用电子束进行焊接。研究结果发现:当束流为 29 mA 时,能获得成形最优的焊缝,接头成形美观且无明显缺陷,接头横截面呈上宽下窄的钉形。王西昌等[10]通过研究添加活性剂的方法对GH4169合金薄板进行电子束焊接成形的影响,研究发现:添加适当的活性剂焊接,能够改善焊缝的表面成形,消除咬边等宏观缺陷。张明敏等[11]采用正交的试验方法,研究了电子束焊接参数对GH4169镍基高温合金焊缝形貌的影响。实验结果表明:影响熔深程度最大的参数依次为电子束流、影响熔宽程度最大的参数为加速电压,相比之下焊接速度对熔深熔宽影响最小。且实验所得的最佳参数组合解决了某航空发动机电子束焊对封严层的熔蚀问题。王伦等[12]采用数值模拟的方法对商用航空发动机转子组件电子束焊进行焊接变形预测。通过理论计算和建立结构模型,分析得出焊接工艺参数对焊缝固有应变的影响规律,并通过加大扫描速度和改变约束方式可以明显减小焊接变形程度, 实现对转子组件电子束焊接变形进行的预测和调控。SHE等[13]对3 mm厚的GH4169镍基高温合金板进行电子束焊正交实验,研究了加速电压,束流和焊接速度对焊接接头性能的影响,从而获得了关于3 mm厚GH4169电子束焊的最优参数。从目前的研究现状来看,大多数研究工作都是针对GH4169高温合金的电子束焊工艺展开的,研究重点是不同工艺条件的下焊缝组织和接头力学和硬度等基本性能。从检索的文献资料来看,很少有对GH4169电子束焊焊接接头的高温稳定性方面的研究报告。
在航空发动机中的涡轮叶片和涡轮盘等转动件、核电站中的堆芯壳和岛球连接管等部件长期工作在高温、动载以及大载荷状态,在焊接接头部位容易形成局部应力集中,从而会导致疲劳裂纹等缺陷的产生,最终导致这类重工业器械核心部位发生开裂,这会对航空发动机、核电站和燃气轮机等的安全性能和使用性能造成很大的隐患,给人身、财产以及社会安全造成很大的损失。鉴于目前航空发动机、核电站等国防重工业的高速发展以及对GH4169高温合金焊接接头在高温服役条件下的安全使用性提出更高要求,本文重点研究在给定的不同高温条件下,GH4169电子束焊焊接接头所表现出的稳定性,并探究其在相应时间条件下的高温稳定性能。
1 实验
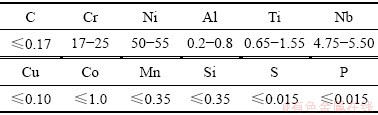
本试验选用的材料为4 mm厚的GH4169镍基高温合金,其化学成分如表1所列。
表1 GH4169高温合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of GH4169 superalloy (mass fraction, %)
为保证工件的对接精度以及避免工件表面的油污和杂质对焊缝质量造成影响,在电子束焊接前,使用砂纸对待焊板材进行机械清理,再用无水乙醇洗去工件表面的油污和杂质。
试样清洗前处理完成,进行装配完毕后,开始电子束焊接实验。本论文中,通过大量的工艺实验的前期摸索,确定了一组最优的工艺参数来进行GH4169的电子束对接焊。对焊接后的试样进行了系列的实验分析。
首先,沿着电子束焊接接头的横截面方向截取5组试样,取样位置如图1所示。将5组试样放入高温热处理炉中进行高温氧化处理,热处理炉从室温开始加热,保持炉内升温速率为5 ℃/min,当炉内温度到达650 ℃时,保持温度不变并开始计时。5组试样分别保温0、5、25、50、75 h,在每组试样达到保温时间后,取出并放入另一热处理炉(炉内温度650 ℃)进行随炉冷却到室温。在氧化试验前后使用精度为 0.1 mg的电子天平称取试样质量,称取得到的质量值为重复3次测量的平均值。其高温氧化工艺如图2所示。
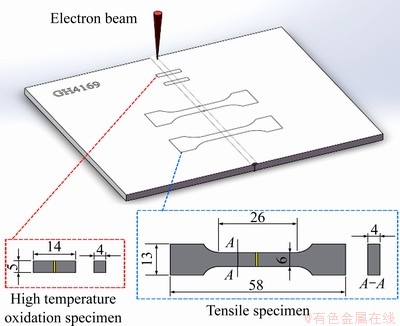
图1 取样示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of specimens (Unit: mm)
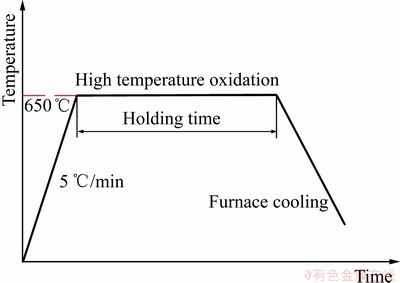
图2 高温氧化工艺曲线示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of high temperature oxidation process
对5组试样完成高温氧化处理后,在对应试样上取样,进行力学和微观组织的观察。对试样进行磨制和抛光处理后,再使用20 mL HCl+20 mL无水乙醇+ 1.5 g无水硫酸铜溶液进行腐蚀后,采用光学显微镜分析不同高温氧化条件下,焊接接头的微观组织。
按照标准ASTM E8进行拉伸试样的取样后,使用CSS 44110力学拉伸仪进行焊接接头的强度测试,其加载速率为5 mm/min。切取拉伸断裂后的断口,使用Hitachi S4800型扫描电子显微镜对断口形貌进行观察。
使用HUAYIN 1000A型显微硬度计对试样的硬度进行测量。选择加载载荷为1.96 N,保压时间为10 s,两个测量点之间间隔0.1 mm。
2 结果与分析
2.1 焊接接头微观组织分析
2.1.1 GH4169电子束焊接宏观接头形貌
图3所示为GH4169合金电子束焊接接头表面成形的宏观图片。由宏观形貌可知,焊接接头表面熔合良好,表面没有咬边和开裂等宏观缺陷,同时焊缝呈现均匀细密的鱼鳞纹。
图4所示为GH4169合金电子束焊接接头横截面的宏观形貌图。很明显:焊接接头呈现上宽下窄,横截面总体形貌呈现为钉形。这主要是由于电子束极高的能量密度条件下,扫描的电子束对于熔池上部有急剧的搅拌作用,在电子束表面聚焦的情况下,在熔池下部电子束能量发生了急剧的衰减从而导致焊缝底部的较窄[14]。
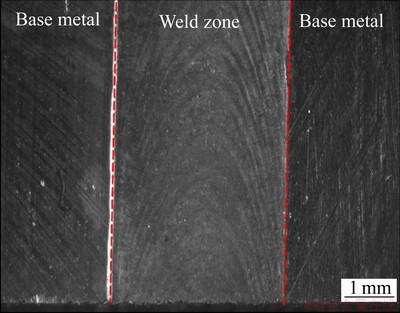
图3 焊接接头表面宏观图
Fig. 3 Macroscopic diagram of welded joint surface
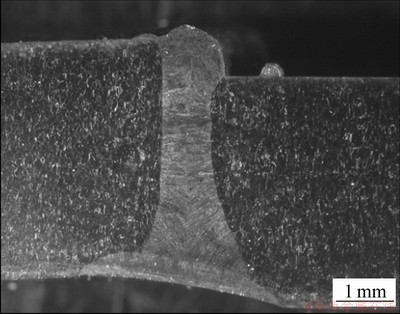
图4 接头横截面的宏观形貌图
Fig. 4 Macroscopic diagram of cross section of welded joint
2.1.2 不同高温氧化条件下GH4169电子束焊缝区微观组织特征
图5所示为不同高温氧化时间下焊缝中心区域的微观组织。从图5(a)可知,焊缝中心部分的γ基体的结晶形态主要是等轴晶,因为焊缝中心部位结晶时,液相中的温度梯度很小,使液相中的成分过冷区很宽,可以在液相内部形核,产生新的晶粒从而形成等轴晶。比较图5(b)、(c)、(d)和(e)可知,随着高温氧化时间的增加,除了晶粒有着明显的增大外,焊缝中心部位的等轴晶逐渐被胞状树枝晶替代。由图5(b)可知,在高温氧化5 h后,晶粒变化还不明显。由图5(c)可知,在高温氧化25 h处理后,焊缝中心已经出现部分较为明显的胞状树枝晶和树枝晶,其具有更小更密集的二次枝晶。由图5(d)和(e)可知,随着高温氧化时间的继续增加,焊缝中心处基本上全为胞状树枝晶和树枝晶,并且比25 h时的晶粒更加粗大,且枝晶的排列方向呈现得更加的杂乱无序,其主要原因是晶界能量较高,随着高温氧化的时间的增加,会发生晶界的迁移[15],使晶粒相互合并长大,从而使界面能降低。
图6所示为不同高温氧化时间下(0~75 h)靠近熔合线附近焊接接头的微观组织。从图6中可以看出,GH4169电子束焊接头典型的接头形貌:即焊接接头的熔合区很窄,呈线状,并且热影响区也不太明显。这是因为电子束焊的能量密度集中,加热面积非常小,焊接速度快,使熔合区的高温停留时间极短,故近熔合线附近的母材受热影响小。由图6(a)可知,在未经高温处理下的焊接接头,靠近熔合区的焊缝区晶粒以胞状晶的形式进行生长,并且胞状晶的生长区域面积广。比较图6(b)、(c)、(d)和(e)可知,随着高温氧化时间的增加,胞状晶的生长区域逐渐减小,随着成分过冷程度逐渐增大,胞状晶逐渐转变为胞状树枝晶和树枝晶生长。并且在高温氧化环境下,γ基体晶粒有着不同程度的变大,并且树枝晶的主轴长度明显增长。在高温氧化25 h时,γ基体晶粒达到最大,并且树枝晶的主轴长度最长;在50 h时,晶粒大小有所减小;而在75 h时,晶粒尺寸又逐渐增大。这是由于GH4169高温合金的主要强化相γ″(Ni3Nb)是亚稳态的过渡相,在高温长期作用下,γ″相很容易聚集长大,并会发生γ″相向δ相的转变。在高温腐蚀的初期,γ″相还未发生相变,仅在高温的作用下,使奥氏体晶粒不断长大,在高温氧化25 h时长到最大。再随着高温氧化时间的增长,γ″相不断的粗化,δ相在晶界处不断析出,这些颗粒硬度较高,难以发生变形,会阻碍晶界的迁移,从而起到对晶界的钉扎作用,所以50 h时的晶粒大小会比25 h时的细小,而75 h时的晶粒再次粗大的原因则是高温氧化时间和第二相颗粒钉扎作用的相互影响的结果。
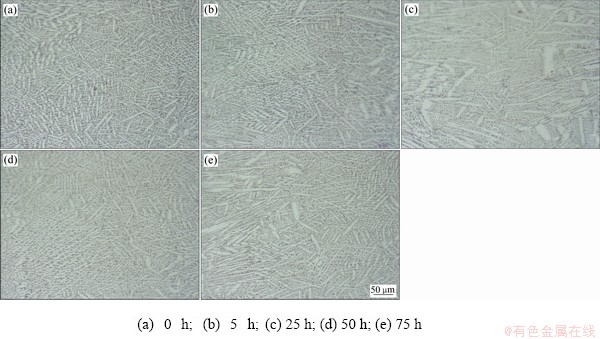
图5 不同高温氧化时间下焊缝中心的微观组织
Fig. 5 Microstructures of center of weld at different high temperature corrosion time

图6 不同高温氧化时间下靠近熔合线附近焊接接头的微观组织
Fig. 6 Microstructures of welded joint near fusion line at different high temperature corrosion time
图7所示为不同高温氧化时间下试件焊缝中心的SEM像。由于合金中的Nb含量很高,在焊缝凝固时,在枝晶间主要形成白色的Laves相和针状的δ相[16-17]。由图7(a)可知,在试件未经高温氧化时,Laves相和δ相在树枝晶晶界均匀析出,并且沿着枝晶晶界,具有明显的方向性。由图7(b)和(c)可知,在试件经过高温氧化5 h时,由于高温作用时间较短,枝晶间的析出相的分布与方向性不变,仅是析出相颗粒大小有减小的趋势。随着高温氧化的时间增加,到达25 h左右,使试件经历了类似均匀化处理的过程,枝晶间的Laves相和部分δ相溶入基体,并且析出物的分布不在具有方向性,基体晶粒大小明显变大。随着高温氧化的时间继续增加,由图7(d)知,δ相在枝晶的晶界和晶内重新析出,并且析出的颗粒大小相比于之25 h前的δ相明显增大,这是类似GH4169合金在650 ℃的一个长期时效过程,随高温时间的延长,主要强化相γ″逐渐粗化,且大量γ″相会转化为的δ相,在枝晶的晶界和晶内析出。
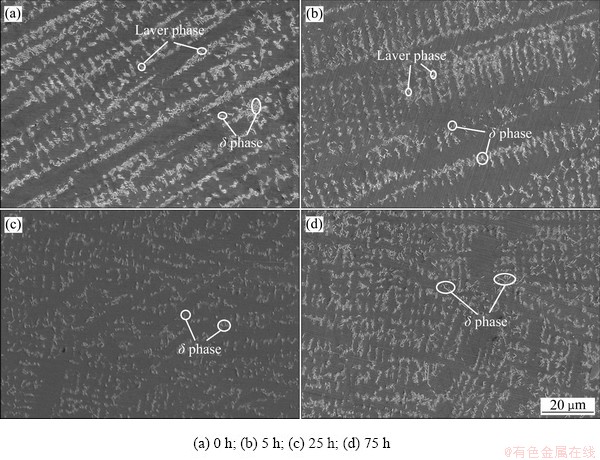

图7 不同高温氧化时间试件焊缝中心的SEM像
Fig. 7 SEM images of weld center with different high temperature corrosion time
2.2 焊接接头的显微硬度分析
显微硬度的分布情况可以反映出焊接接头各个区域的硬度变化规律,为了研究在不同高温氧化时间下焊接接头各区域组织的性能,利用显微硬度计对其硬度分布进行了测试,实验中硬度的测量路径是横穿焊缝并包含熔合区、热影响区及部分母材的一条直线。在不同的高温氧化时间下,电子束焊接接头表现出了不同的硬度。如图8所示,随着高温氧化时间的增加,各组试样的母材区平均硬度均是低于未高温处理试样的,这是由于高温作用,母材的晶粒长大,导致母材区的力学性能不断下降。未热处理的焊接接头焊缝区的平均硬度为403.6HV,低于母材的平均硬度408.4 HV。但是随着高温氧化的进行,焊缝区的平均硬度超过母材的,直到高温氧化75 h后,焊缝区的力学性能才再次低于母材的,这是由于前文所述焊缝区晶粒大小的变化规律是高温作用时间与第二相颗粒钉扎作用的相互影响的最终结果。
2.3 焊接接头的拉伸性能分析
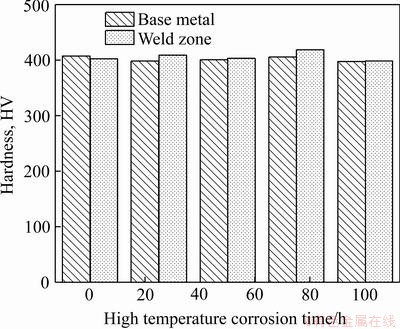
图8 不同高温氧化时间下的焊接接头硬度示意图
Fig. 8 Hardness distribution of welded joints under different high temperature corrosion time
图9所示为不同高温氧化时间(0、5、25、50、75 h)下GH4169高温合金电子束焊焊接接头的应力-应变曲线。GH4169合金母材最大拉伸为1121 MPa[12]。从图9中可以看出,未经高温氧化的试样拉伸强度为1109 MPa,焊缝的抗拉伸强度达到母材的98.9%,随着高温氧化时间的增加,焊接接头的强度和伸长率均不断增加,在高温氧化25 h时达到最大,其焊接接头的抗拉强度到达1357 MPa,应变为7.86%。25 h后随着高温热氧化时间增加,焊接接头的强度和伸长率均不断下降,在高温氧化75 h时,焊接接头的力学性能低于为未高温氧化的试样,其焊接接头的抗拉强度到达1045 MPa,应变为5.2%。这是由于在高温氧化较短的时间,近似于对焊接接头进行回火处理,降低了焊缝的残余应力,进而避免了裂纹的产生,如图10所示,未经高温处理的接头断口存在明显的二次裂纹,这会显著降低焊缝的力学性能,而经过25 h的高温氧化的接头焊接缺陷明显减少,韧窝区范围更大,接头塑韧性较好。但是随着高温氧化时间的延长,组织中主要的强化相γ″会不断的粗化并会在在晶界处析出脆硬相δ相,再加上晶粒不断粗化,会使焊接接头的塑韧性大大降低,最终在高温氧化75 h时,焊接接头的塑韧性低于未高温氧化处理焊接接头的。
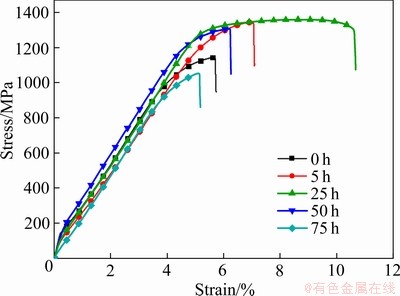
图9 不同高温氧化温度下的焊接接头应力-应变曲线
Fig.9 Tensile stress-strain curves of welded joints under different high-temperature corrosion temperatures
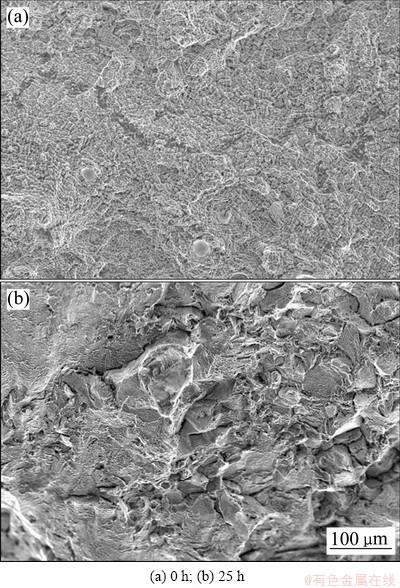
图10 焊接接头拉伸试样断口SEM像
Fig. 10 SEM images of fractured surfaces of flexural tested weldment
2.4 焊接接头的高温氧化性能分析
图11所示为高温热氧化不同时间下,各组试件高温氧化前后质量变化曲线。从图11中可以看出,随着高温氧化时间的增加,试件质量变化总体上不断增加,到50 h后趋于不变。这是由于高温氧化前期,试件表面氧化膜未完全形成或较薄,氧化反应持续进行。当高温氧化时间到达50 h后,氧化质量增加减慢,氧化层厚度不再显著增加,表明50 h后生成的氧化膜致密、保护性好,阻止了进一步的氧化过程,故GH4169合金抗高温氧化性能较强。
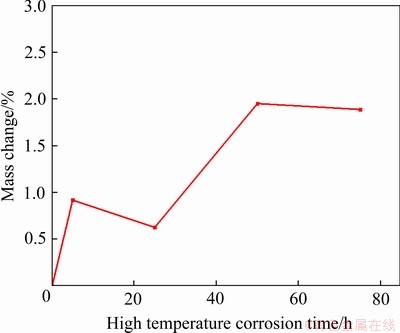
图11 GH4169合金650 ℃高温氧化质量变化曲线
Fig. 11 Corrosion quality change curve of GH4169 alloy at 650 ℃
3 结论
1) GH4169合金电子束焊的焊缝中心区为树枝晶和胞状树枝晶,接头在高温氧化的过程中晶粒大小受高温加热和晶界二次相析出的钉扎作用的相互影响,晶粒随着高温氧化不断长大,直到25 h时,晶粒尺寸达到极大值;随后,晶粒大小有减小的趋势,在50 h以后晶粒继续变得粗大。
2) GH4169合金电子束焊接接头经过高温氧化处理后,各组试样的母材区平均硬度均低于未高温处理试样的,且未热处理的试样焊缝区的平均硬度为403.6HV,低于母材的平均硬度408.4 HV,随着高温氧化的进行,焊缝区的平均硬度超过母材的,直到高温氧化75 h后,焊缝区的平均硬度再次低于母材的。
3) GH4169合金电子束焊接接头在650 ℃的高温氧化下,25 h时,机械拉伸性能达到最佳;在75 h时,接头的机械拉伸性能低于常温接头,故GH4169合金电子束焊接接头在650 ℃的高温氧化下不易工作超过 75 h。
4) GH4169合金电子束焊接接头经过长时间的高温氧化后,表面会生成较致密的氧化膜,对接头内部合金的保护性好,阻止了进一步的氧化过程。
REFERENCES
[1] 赵新宝, 谷月峰, 鲁金涛, 严靖博, 尹宏飞. GH4169合金的研究新进展[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2015, 44(3): 768-774.
ZHAO Xin-bao, GU Yue-feng, LU Jin-tao, YAN Jing-bo, YIN Hong-fei. New research development of superalloy GH4169[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2015, 44(3): 768-774.
[2] ELEFTERIE C F, GURAGATA C, BRAN D, GHIBANB. Aeronautical requirements for Inconel 718 alloy[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 209(1): 012060.
[3] 申佳林, 朱学儒, 魏志坚, 梁 宇, 梁益龙, 江飞龙, 肖志祥. 焊后热处理对GH4169合金闪光焊接接头组织与性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2018, 47(12): 3839-3847.
SHEN Jia-lin, ZHU Xue-ru, WEI Zhi-jian, LIANG Yu, LIANG Yi-long, JIANG Fei-long, XIAO Zhi-xiang. Influence of post-weld heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of GH4169 alloy flash butt welded joint[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2018, 47(12): 3839-3847.
[4] DAMODARAM R, DAMAN S G S, RAO K P. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction welded alloy 718[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2013, 560: 781.
[5] 谢锡善, 董建新, 付书红, 张麦仓. γ″和γ′相强化的Ni-Fe基高温合金GH4169的研究与发展[J]. 金属学报, 2010, 46(11): 1289-1302.
XIE Xi-shan, DONG Jian-xin, FU Shu-hong, ZHANG Mai-cang. Research and development of γ″ and γ′ phase strengthened Ni-Fe based superalloy GH4169[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(11): 1289-1302.
[6] WANG Tian-fu, DI Xin-jie, LI Cheng-ning, WANG Jia-mei, WANG Dong-po. Effect of δ phase on microstructure and hardness of heat-affected zone in TIG-welded GH4169 superalloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2019, 32(8): 1041-1052.
[7] HERNANDEZ M, AMBRIZ R R, CORTESR. Assessment of gas tungsten arc welding thermal cycles on Inconel 718 alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2019, 29(3): 579-587.
[8] 陈国庆, 张秉刚, 冯吉才, 孙 毅. 电子束焊接在航空航天工业中的应用[J]. 航空制造技术, 2011(11): 42-45.
CHEN Guo-qing, ZHANG Bing-gang, FENG Ji-cai, SUN Yi. Application of electron beam welding technology in aerospace industry[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2011(11): 42-45.
[9] 章晨杨. GH4169合金电子束焊接头组织及疲劳裂纹扩展研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2017.
ZHANG Chen-yang. Study on microstructure and fatigue crack propagation of GH4169 superalloy electron beam welded joints[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2017.
[10] 王西昌, 左从进, 柴国明, 张连锋. 活性剂对 GH4169 薄板电子束焊接焊缝成形的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2009, 30(2): 83-86.
WANG Xi-chang, ZUO Cong-jin, CHAI Guo-ming, ZHANG Lian-feng. Effect of activating fluxes on appearance of weld in thin plate electron beam welding of nickel- basesuperalloy GH4169[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2009, 30(2): 83-86.
[11] 张明敏, 胡 玥, 吴家云, 李杲松. 电子束焊接参数对高温合金小熔深焊缝形貌的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2017, 46(1): 233-235.
ZHANG Ming-ming, HU Yue, WU Jia-yun, LI Gao-song. Effect of electron beam welding parameters on little penetration depth weld shape of high temperature alloys[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017, 46(1): 233-235.
[12] 王 伦, 潘 博, 黄怡晨, 李俐群. 航空发动机转子组件电子束焊变形预测[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(3): 111-117, 166.
WANG Lun, PAN Bo, HUANG Yi-cheng, LI Li-qun. Prediction technology of electron beam welding deformation for aeroengine rotor components[J].Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(3): 111-117, 166.
[13] SHE Lü-bo, WEI Yan-hong, WANG Shao-gang, MA Ji-long, OU Wen-min. Welding parameter optimization of electron beam welded GH4169 superalloy based on orthogonal experiment and numerical simulation[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(2): 026567.
[14] 刘 政. W6/16Mn电子束焊接接头组织与性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.
LIU Zheng. Investigation on the microstructure and properties of W6/16Mn electron beam welded joints[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017.
[15] 顾亚桃, 杨明华, 陈 强. 20Cr2Ni4A钢奥氏体晶粒长大规律与高温渗碳工艺[J]. 金属热处理, 2019, 44(2): 198-203.
GU Ya-tao, YANG Ming-hua, CHEN Qiang. Austenitic grain growth law and high temperature carburizing process of 20Cr2Ni4A steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019, 44(2): 198-203.
[16] 刘艳梅, 孙文儒, 陈国胜, 王铁钢. GH4169合金凝固过程中Nb偏析的计算[J]. 有色冶金设计与研究, 2017, 38(6): 54-56.
LIU Yan-mei, SUN Wen-ru, CHEN Guo-sheng, WANG Tie-gang. Measurement of Nb segregation in GH4169 superalloy during solidification[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering & Research, 2017, 38(6): 54-56.
[17] 刘永长, 郭倩颖, 李 冲, 梅云鹏, 周晓胜, 黄 远, 李会军. Inconel718高温合金中析出相演变研究进展[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(10): 1259-1266.
LIU Yong-chang, GUO Qian-ying, LI Chong, MEI Yun-peng, ZHOU Xiao-sheng, HUANG Yuan, LI Hui-jun. Research progress on evolution of precipitates in Inconel 718 superalloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(10): 1259-1266.
Long-term aging stability of nickel-based superalloy GH4169 electron beam welded joints
WEI Qi, AO San-san, WANG Tai, WU Man-peng, LUO Zhen
(School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300350, China)
Abstract: The stability of GH4169 electron beam welding joints was studied under different high temperature conditions, and its high temperature stability performance under corresponding time conditions was explored. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the samples after different high temperature corrosion time were studied by optical microscope, SEM and tensile test. The results show that the center region of the weld of GH4169 alloy is dendritic and cellular dendritic. Due to the interaction between the high temperature corrosion time and the pinning effect of the second phase particles, the grains grow continuously with high temperature corrosion, reaching a maximum value at 25 h, and then the grain size has a tendency to decrease, and the grains continue to become coarse after 50 h. Under high temperature corrosion at 650 ℃, the mechanical tensile properties of the welded joints reach the best at 25 h, and the mechanical tensile properties of the joints at 75 h are lower than those of the joints without high temperature corrosion. A layer of dense oxide film will be formed on the surface of welded joint after a long time high temperature corrosion.
Key words: GH4169 superalloy; electron beam welding; high temperature stability
Foundation item: Project(2018YFB1107900) supported by the National Key R&D Program of China; Project(U1933129) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Civil Aviation Administration of China; Project(18JCQNJC04100) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City, China; Project(19JCZDJC39000) supported by the Key Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin, China
Received date: 2019-12-22; Accepted date: 2020-04-27
Corresponding author: AO San-san; Tel: +86-13672159533; E-mail: ao33@tju.edu.cn
(编辑 王 超)
基金项目:国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFB1107900);国家自然科学基金民航联合基金资助项目(U1933129);天津市自然科学基金资助项目(18JCQNJC04100);天津市自然科学基金重点项目(19JCZDJC39000)
收稿日期:2019-12-22;修订日期:2020-04-27
通信作者:敖三三,讲师,博士;电话:13672159533;E-mail:ao33@tju.edu.cn