MnO4-和银含量对铅银合金阳极电位衰减期电化学行为的影响
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2013年第7期
论文作者:张 伟 涂常青 陈艺锋 Houlachi GEORGEOS 肖 利
文章页码:2174 - 2180
关键词:电化学行为;铅银阳极;高锰酸根离子;电位衰减期;硫酸锌电解液
Key words:electrochemical behaviour; Pb-Ag anode; permanganate ion; potential decay periods; zinc sulphate electrolyte
摘 要:研究在电位衰变期间在酸性硫酸锌电解液中,MnO4- 和银的含量对5个通用铅银合金阳极电化学行为的影响。当阳极浸入不含 的酸性硫酸锌电解液中时,通过开路电位测定,发现Pb-0.72%Ag进入完全钝化状态所用的时间最短,紧接着的是阳极Pb-0.67%Ag、Pb-0.60%Ag、Pb-0.58%Ag和Pb-0.29%Ag-0.1%Ca。在5 h 的浸入期间,MnO4- 离子能加速钝化和增加阳极的腐蚀电流密度。通过交流阻抗法测定,发现在含有MnO4-的电解液中,阳极Pb-0.72%Ag具有最好的耐蚀性,紧接着的是阳极Pb-0.67%Ag、Pb-0.60%Ag,然后是阳极Pb-0.58%Ag和Pb-0.29%Ag-0.1%Ca。
Abstract: The effect of MnO4- and silver content on electrochemical behaviour of five commercial Pb-Ag alloy anodes was studied in acid zinc sulphate electrolyte with and without MnO4- ions at 38 °C during potential decay periods. When the anodes were immersed into acid zinc sulphate electrolyte without MnO4- ions, the Pb-0.72%Ag anode entered complete passivation state in the shortest time among the five anodes, followed by anodes Pb-0.67%Ag, Pb-0.60%Ag, Pb-0.58%Ag and Pb-0.29%Ag- 0.1%Ca by measurement of open circuit potential. During immersion of the anodes, MnO4- ions accelerated the passivation and increased the corrosion current density of the anodes. After immersion in zinc electrolyte with , the anode Pb-0.72%Ag had the best corrosion resistance, followed by anodes Pb-0.67%Ag, Pb-0.60%Ag, then the close anodes Pb-0.58%Ag and Pb-0.29%Ag- 0.1%Ca by the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) analysis.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23(2013) 2174-2180
Wei ZHANG1,2, Chang-qing TU3, Yi-feng CHEN1, Houlachi GEORGEOS 4, Li XIAO1
1. School of Metallurgical Engineering, Hunan University of Technology, Zhuzhou 412007, China;
2. Department of Mining, Metallurgy and Material Engineering, Laval University, Ste-Foy, Quebec, G1K 7P4, Canada;
3. China National South Aviation Industry Co. Ltd., Zhuzhou 412002, China;
4. LTE, Hydro-Quebec, 600 Avenue de la Mortagne, C.P. 900 Shawinigan, QC, G9N 7N5, Canada
Received 1 August 2012; accepted 24 December 2012
Abstract: The effect of MnO4- and silver content on electrochemical behaviour of five commercial Pb-Ag alloy anodes was studied in acid zinc sulphate electrolyte with and without MnO4- ions at 38 °C during potential decay periods. When the anodes were immersed into acid zinc sulphate electrolyte without MnO4- ions, the Pb-0.72%Ag anode entered complete passivation state in the shortest time among the five anodes, followed by anodes Pb-0.67%Ag, Pb-0.60%Ag, Pb-0.58%Ag and Pb-0.29%Ag- 0.1%Ca by measurement of open circuit potential. During immersion of the anodes, MnO4- ions accelerated the passivation and increased the corrosion current density of the anodes. After immersion in zinc electrolyte with  , the anode Pb-0.72%Ag had the best corrosion resistance, followed by anodes Pb-0.67%Ag, Pb-0.60%Ag, then the close anodes Pb-0.58%Ag and Pb-0.29%Ag- 0.1%Ca by the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) analysis.
, the anode Pb-0.72%Ag had the best corrosion resistance, followed by anodes Pb-0.67%Ag, Pb-0.60%Ag, then the close anodes Pb-0.58%Ag and Pb-0.29%Ag- 0.1%Ca by the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) analysis.
Key words: electrochemical behaviour; Pb-Ag anode; permanganate ion; potential decay periods; zinc sulphate electrolyte
1 Introduction
In zinc electrowinning, the anode materials are lead alloys. However, pure lead has high overpotential and corrosion rate in the sulphuric acidic solution [1,2]. Small amount of Ag (0.7%-1.0%) alloyed with lead decreases the oxygen overvoltage, and increases the corrosion resistance of material. A well established custom in all electrolytic zinc plants is to use Pb-Ag alloys containing 0.7%-1.0% Ag as the anode material. The resulting benefits are a longer anode life and a lower Pb content in the cathodic zinc [3]. Also, Ag changes the structure of PbO [4] and increases the ratio of α/β-PbO2 in the corrosion layer for Pb-Ag alloy [5]. In addition, the introduction of silver in the alloy accelerates the oxygen evolution and the enhancement is proportional to the Ag content [6]. However, Pb-Ag has some shortages of higher overpotential of oxygen evolution and worse conductivity. Al/Pb-PANI-WC composite inert anode prepared by double pulse electrodeposition of WC and polyanilline particles with Pb2+ from an original plating bath, may be a suitable anode material in place of Pb-Ag alloy in zinc electrowinning [7-9].
During the polarization, the effects of Mn2+ on the corrosion rate of lead alloy have been studied by many people. Mn2+ ions in the electrolyte could be oxidized to MnO4- [10]. NEWHAM [11] established that the corrosion rate of Pb-Ag anodes in 1.8 mol/L H2SO4 solution decreases in the presence of Mn2+. It was found that the presence of Mn2+ in the electrolyte caused the formation of a thin layer of MnO2 on the anode. IVANOV and STEFANOV [12] found that the addition of 1.5-3 g/L to the zinc electrolyte can minimize the corrosion of lead anodes and reduce the contamination of cathodic zinc with lead [12,13]. ZHANG and HOULACHI [14] found that the addition of Mn2+ from 4 to 8 g/L to the zinc electrolyte gave almost the same overpotentials and then the overpotentials increased at concentration of Mn2+ of 10 and 12 g/L for Pb-Ag anode. Also, the corrosion rate of Pb-Ag alloy anode decreased with the MnSO4 addition.
In addition, adding MnSO4 to the zinc electrolyte could improve the structure of zinc deposit at low concentrations but decrease the current efficiency by few percent at concentration above 10 g/L [15,16]. However, higher concentration of manganese in the electrowinning can cause a significant decrease in current efficiency [14]. Also, with a longer operation time, the formation of MnO2 may increase the corrosion of lead anode [17,18].
Most electrolytes in zinc electrowinning contain Mn2+ ranging from 2 to 15 g/L. When manganese ions are oxidized at the anode, MnO2 and  are formed. Generally, industrial zinc electrolyte contains 100 mg/L MnO4- [1]. It is necessary to study the anodic corrosion behavior in zinc electrolyte containing manganese ion (Mn2+). In this work, 8 g/L Mn2+ in the form of MnSO4·H2O was added to the supporting electrolyte. After 5 h of electrolysis at 60 mA/cm2 using a Pb-Ag anode, the solution became violet red because of the formation of permanganate ions.
are formed. Generally, industrial zinc electrolyte contains 100 mg/L MnO4- [1]. It is necessary to study the anodic corrosion behavior in zinc electrolyte containing manganese ion (Mn2+). In this work, 8 g/L Mn2+ in the form of MnSO4·H2O was added to the supporting electrolyte. After 5 h of electrolysis at 60 mA/cm2 using a Pb-Ag anode, the solution became violet red because of the formation of permanganate ions.
In some Zn plants, there are significant periods (potential decay period) of time when the current is off, 2 h once a week and 12-16 h every 3 months which affects the stability of the anodes. However, the information of the effect of Mn2+ and MnO4- on the performance of Pb-Ag anodes during the potential decay without polarization after electrowinning is limited. In this work, the experiments of 5 h open circuit potential after electrowinning in the zinc electrolyte with permanganate ions were carried out. The purpose is to investigate the electrochemical behaviour of Pb-Ag anodes during potential decay after 5 h polarization at 60 mA/cm2 by the open circuit potential measurements and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) at the open circuit potential.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and sample preparation
The composition of the electrolyte used in this work was as follows: Zn2+ 60 g/L; H2SO4 180 g/L; Mn2+ 8 g/L; Cl- 250 g/L; glue 3 g/L.
Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4·7H2O), manganese sulphate (MnSO4·H2O) from Sigma-Aldrich Fine Chemicals, sodium chloride and sulphuric acid from Merck KGaA were used to prepare the supporting electrolyte with double distilled water. Gelatin (glue) was product of BDH Inc. The chemicals met ACS specifications (except gelatin) and were used as received without further treatment. All concentrations of H2SO4 and Zn2+ stated in this paper are initial concentrations.
The anodes used in this work were made of laminated Pb-Ag and Pb-Ag-Ca alloys with surface treatment. The Anode 1 is a Pb-0.3%Ag-Ca alloy, the Anodes 2 and 3 are Pb-0.6%Ag alloy, while Anodes 4 and 5 are Pb-0.7%Ag alloys, but they have different impurities for example of Fe. Their chemical composition analyzed semi-quantitatively using X-ray fluorescence method is given in Table 1.
Table 1 Chemical composition of five Pb-Ag alloy anodes

According to the information from the suppliers of the anodes, all of the five commercial anodes were cold-rolled. Anode 1 is a Pb-Ag-Ca alloy; Anodes 2-5 are made of Pb-Ag alloy. Anodes 4 and 5 have the same composition, but Anode 5 was treated with shot-peening method. The cathodes were made of platinum for corrosion rate measurements. The Pb-Ag alloy plates were cut into small pieces of 10 mm×10 mm×10 mm and then connected with a plastic isolated copper wire and cast in acrylic resin. The electrical contacts were made with plastic isolated copper wires and the piece was cast in acrylic resin. The exposed area surface was 1 cm2. Before being introduced into the electrolytic cell, the working surfaces of the cathodes were ground with SiC abrasive paper (Leco Corporation) down to 600 grit, washed with double distilled water and wiped immediately with tissue paper. The working surface area was always 1 cm2. The surface preparations for the Pb-Ag anodes were divided into two kinds of situations: when the original surface (as-cast) was examined, no polishing was carried out, and the surfaces were just washed with organic solvent and distilled water; when the bulk of the anodes was examined, the original surface was removed by grinding using abrasive paper in the same manner as the surface preparation of the cathodes.
2.2 Experimental setup
The electrolytic cell was a 1 L double-walled cell containing 800 mL of electrolyte heated by a flow of thermostated water in the double wall ((38±0.5) °C). The electrolyte was magnetically stirred during the experiments. The anode and cathode were mounted in a Teflon made holder and the distance between them was fixed at 2 cm. The reference electrode was mercurous sulfate electrode (MSE): Hg, Hg2SO4|sat. K2SO4 (0.636 V vs SHE). A saturated K2SO4 salt bridge was used to keep the reference electrode close to the anode. The experimental setup was an EG&G Princeton Applied Research 273 potentiostat/galvanostat controlled by an IBM computer. The software SoftCorr M352 was used for acquisition of the polarization data. The electrochemical impedance measurements at the open circuit potential were carried out using PowerSINE in Electrochemical PowerSuite of Advanced Measurement Technology, Inc. over the frequency range from 100 kHz to 100 mHz. The amplitude of the sinusoidal was 10 mV. All the experiments were duplicate or triplicate. The reproducibility for corrosion potential was ±4 mV, and that for corrosion current was ±0.2 μA/cm2 (in passive state).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructure of anodes
Figure 1 shows the microstructure of rolled Pb-Ag and Pb-Ca-Ag alloys anodes. It is seen from Fig. 1 that Anodes 2 and 3 possess oriented structure through the rolling direction. They contain more silver than Anode 1 and the silver-containing phase is distributed rather uniformly in the alloy and alternatively with the lead-rich phase. Anodes 4 and 5 have a different structure from Anodes 2 and 3. The silver-containing phase is more concentrated at the grain boundaries.
Figure 2 shows the microstructure of Anodes 4 and 5. It is seen that the shot-peening treatment of Anode 5 shows a certain change in the microstructure. It seems that the distribution of silver becomes more uniform.
3.2 Corrosion behavior of anodes at open circuit potential
3.2.1 Corrosion behavior in zinc electrolyte without permanganate ion
To examine the corrosion property of the five lead alloy anodes, the corrosion tests were conducted using polished specimens after removing the original surfaces. In these experiments, five cycles were carried out. In each cycle, the corrosion potentials of the five anodes at open circuit potential were recorded for every hour, and at the end of every hour, potentiodynamic polarizations (the potential scan range from -25 to 25 mV) were conducted to measure the corrosion rate. The potential vs time curves for the first four cycles of the five alloy anodes are presented in Fig. 3.

Fig. 1 Optical photos of rolled anodes
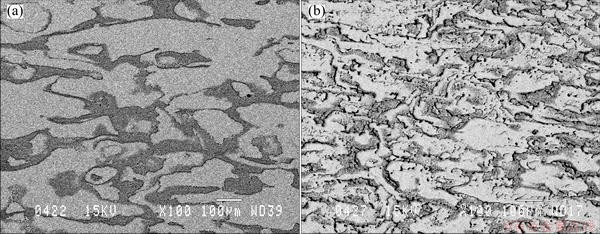
Fig. 2 Backscattered electron micrographs of Anode 4 (a) and Anode 5 (b)
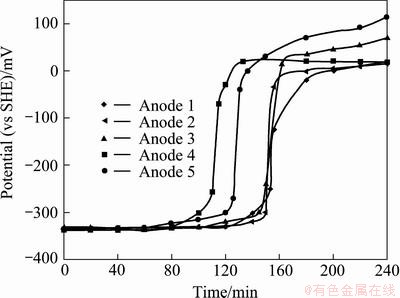
Fig. 3 Corrosion potential evolution of polished Anodes 1-5 in zinc electrolyte without MnO4- at 38 °C
It is seen from Fig. 3 that Anode 1 was in active corrosion state during the first 2 h of immersion. During the first half of the third hour of immersion, the potential rose gradually from -330 to -250 mV (increased by 80 mV) within 33 min; but from -250 to -125 mV (increased by 120 mV), it took only 2 min, and the electrode entered into passive state. After 2.5 h of immersion, the electrode kept in the passive state; the corrosion potential was 300 mV more positive than that before the passivation, and the corrosion current density dropped from 604 to 2.8 μA/cm2. The other anodes had similar transition behavior from active to passive state, but the transition times were different. Anodes 2 and 3 began to passivate after about 2.5 h of immersion like Anode 1, while Anode 4 began to passivate after 1.5 h of immersion, and entered into complete passivation after 2 h. The corrosion current density decreased from 2210 to 3.7 μA/cm2. Anode 5 began to passivate after 2 h of immersion and entered into the passive state after about 130 min of immersion. When the Pb-Ag anodes are immersed into the zinc electrolyte, the lead can react with H2SO4 (Pb+H2SO4→PbSO4), a non-conductive layer (PbSO4) forms on the surface of anodes. So all the five anodes entered into passivation after few hours of immersion in the zinc electrolyte.
Figure 4 shows the corrosion current density evolution of the five anodes as a function of immersion time. It is noticed that after 1 h of immersion, all the five anodes were in active corrosion state. Anode 4 had the highest corrosion current density (1499 μA/cm2), followed by Anodes 5 (1296 μA/cm2), 3 (1140 μA/cm2), 1 (1121 μA/cm2) and 2 (1115 μA/cm2). The Anode 4 entered into passive state most quickly, followed by Anodes 5, 2, 3 and 1. It is strange that Anode 5 began to passivate just at the end of the second hour, but it was not completely passivated. However, at the end of the second hour of immersion, the corrosion current density of Anode 5 was 52 μA/cm2, while those of Anodes 1, 2, 3 and 4 were 554, 1072, 181 and 61 μA/cm2, respectively. When all the five anodes were in passive state, the difference between their corrosion current density was not remarkable. For example, after 5 h of immersion, the corrosion current densities of the five anodes were all around 1 μA/cm2. It can be concluded that all the five anodes have low corrosion rates for a long term of immersion in the zinc electrolyte without permanganate ions. It can be found that all the five anodes entered into passivation after few hours of immersion in the zinc electrolyte without permanganate ions since passivation of Pb-Ag anodes can result in low corrosion rates of the anodes.

Fig. 4 Comparison of corrosion current density for five polished anodes in zinc electrolyte without permanganate ion at 38 °C
Figure 5 shows the corrosion potential evolution of the five anodes during 5 h of immersion in the zinc electrolyte without  . It is seen that Anode 4 was still passivated most quickly, followed by Anodes 2, 5, 1 and 3. However, the passivation of the five anodes took place later than that in the case of immersion with inserted linear polarization experiments of every hour. This means that the linear polarization accelerated the passivation because of the anodic polarization of 25 mV vs open circuit potential. The corrosion current densities of all the five anodes at the end of 5 h immersion test were around 1 μA/cm2. It was almost the same as that in the case of immersion with linear polarization of every hour. It is observed that Anodes 4 and 5 had a similar corrosion current change manner. This is probably due to the same composition and similar microstructure in the bulk.
. It is seen that Anode 4 was still passivated most quickly, followed by Anodes 2, 5, 1 and 3. However, the passivation of the five anodes took place later than that in the case of immersion with inserted linear polarization experiments of every hour. This means that the linear polarization accelerated the passivation because of the anodic polarization of 25 mV vs open circuit potential. The corrosion current densities of all the five anodes at the end of 5 h immersion test were around 1 μA/cm2. It was almost the same as that in the case of immersion with linear polarization of every hour. It is observed that Anodes 4 and 5 had a similar corrosion current change manner. This is probably due to the same composition and similar microstructure in the bulk.

Fig. 5 Corrosion potential evolution of five anodes (polished) during 5 h of continuous immersion in zinc electrolyte without  at 38 °C
at 38 °C
3.2.2 Corrosion behavior in zinc electrolyte with permanganate ion
After 5 h of polarization at 60 mA/cm2 in the zinc electrolyte containing permanganate ions (MnO4-), the potential vs time curves (Fig. 6) of the five anodes are very different from those obtained in the solution without MnO4- (Fig. 5). It is seen that all the five anodes were passivated within a few minutes at the beginning of the immersion experiments. The corrosion potentials rose from about -300 mV (vs SHE) to 0 (vs SHE) immediately when the anodes were immersed into the solution. In this case, the corrosion current density of the five anodes at the end of 5 h immersion were 28, 36, 35, 31 and 25 μA/cm2, respectively. Comparing these corrosion current density with those obtained in the electrolyte without MnO4- ions (around 1 μA/cm2), it can be concluded that though the MnO4- ions accelerated the potential jump (passivation), the corrosion current density of the five anodes in the electrolyte with MnO4- ions were higher than those in the zinc electrolyte without MnO4- ions. It can be observed that the permanganate ions in the zinc electrolyte accelerated the corrosion rates of the Pb-Ag alloy anodes.

Fig. 6 Corrosion potential evolution of five anodes (polished) during 5 h of continuous immersion in zinc electrolyte with  at 38 °C
at 38 °C
The polarization resistances of five Pb-Ag alloy anodes were studied by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements at the open circuit potential in the zinc electrolyte with  ions at 38 °C as shown in Fig. 7.
ions at 38 °C as shown in Fig. 7.
It can be observed from Fig. 7 that Anode 4 had the highest polarization resistance in zinc electrolyte with  , followed by Anodes 5, 2, 3 and 1. It means that higher silver content causes higher corrosion resistance for the Pb-Ag anodes.
, followed by Anodes 5, 2, 3 and 1. It means that higher silver content causes higher corrosion resistance for the Pb-Ag anodes.
3.2.3 Effect of MnO4- ion and surface state on corrosion of anode
It was noticed that when the five anodes were immersed in the zinc electrolyte containing MnO4- ions, the anode had different potential vs time curve from that obtained in the zinc electrolyte without MnO4- ion as shown in Fig. 8. The potential curve was up immediately when the anode was immersed in the solution with MnO4- ions. The jump of the potential means the passivation of the anode. The lead anodes were passivated much more quickly in  ion contained solution than in MnO4- ion free solution. This is probably due to the high oxidation capacity of the MnO4- ion. In the solution containing MnO4- ion, the permanganate could accelerate the anode surface to be passivated quickly. However, even if the potential of the anode in the solution containing MnO4- ions was higher than that in the solution without MnO4- ion (Fig. 8), the corrosion rate in the former solution was higher than that in the latter solution. For example, after 5 h of immersion, the corrosion rate of the polished Anode 5 in the solution with
ion contained solution than in MnO4- ion free solution. This is probably due to the high oxidation capacity of the MnO4- ion. In the solution containing MnO4- ion, the permanganate could accelerate the anode surface to be passivated quickly. However, even if the potential of the anode in the solution containing MnO4- ions was higher than that in the solution without MnO4- ion (Fig. 8), the corrosion rate in the former solution was higher than that in the latter solution. For example, after 5 h of immersion, the corrosion rate of the polished Anode 5 in the solution with  ions was 55.4 μm/a; while that in the solution without
ions was 55.4 μm/a; while that in the solution without  ion was only 22.1 μm/a.
ion was only 22.1 μm/a.

Fig. 7 Polarization resistance of polished Anodes 1-5 measured by EIS in zinc electrolyte with MnO4- ions at 38 °C
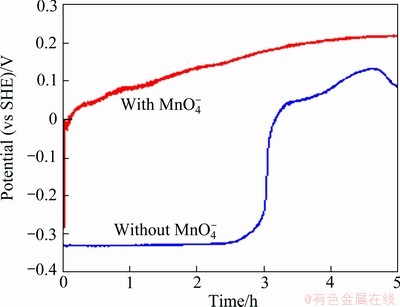
Fig. 8 Evolution of corrosion potential of polished Anode 5 in zinc electrolyte at 38 °C
It was also noticed that the anode with original surface was passivated more quickly than the anode with polished surface as shown in Fig. 9. This means that the original surface was helpful for the passivation of the anode because of the existing oxide film formed during the fabrication of the anodes. However, it could be also observed that after 3 h of immersion the passivation of the polished surface gave more noble potentials than that of the original surface, and this may show finally a better quality of passivation. Indeed, after 5 h of immersion, the polished Anodes 5 had a corrosion current of 0.9 μA/cm2, while the corrosion current for the Anode 5 with original surface was 3.3 μA/cm2.

Fig. 9 Evolution of corrosion potential of original and polished Anode 5 in zinc electrolyte without  at 38 °C
at 38 °C
4 Conclusions
Pb-0.6%Ag and Pb-0.58%Ag alloy anodes possess expressed oriented structure through the rolling direction. When the five anodes were immersed into acid zinc sulphate electrolyte without  ions, the Pb-0.72%Ag anode entered complete passivation state in the shortest time among the five anodes, followed by Pb-0.67%Ag, Pb-0.60%Ag, Pb-0.58%Ag and Pb- 0.29%Ag-0.1%Ca by measurement of open circuit potential. After 1 h of immersion in electrolyte without permanganate ion, the anode Pb-0.72%Ag had the highest corrosion current density (1499 μA/cm2), followed by Pb-0.67%Ag (1296 μA/cm2), Pb-0.58%Ag (1140 μA/cm2), Pb-0.29Ag-0.1%Ca (1121 μA/cm2) and Pb-0.60%Ag (1115 μA/cm2). At the end of 5 h immersion, the corrosion current densities of the five anodes were all around 1 μA/cm2. Also,
ions, the Pb-0.72%Ag anode entered complete passivation state in the shortest time among the five anodes, followed by Pb-0.67%Ag, Pb-0.60%Ag, Pb-0.58%Ag and Pb- 0.29%Ag-0.1%Ca by measurement of open circuit potential. After 1 h of immersion in electrolyte without permanganate ion, the anode Pb-0.72%Ag had the highest corrosion current density (1499 μA/cm2), followed by Pb-0.67%Ag (1296 μA/cm2), Pb-0.58%Ag (1140 μA/cm2), Pb-0.29Ag-0.1%Ca (1121 μA/cm2) and Pb-0.60%Ag (1115 μA/cm2). At the end of 5 h immersion, the corrosion current densities of the five anodes were all around 1 μA/cm2. Also,  ions accelerated the passivation and increased the corrosion current density of the five anodes during the 5 h immersion of the five anodes. In addition, after 3 h of immersion the passivation of the polished surface gave more noble potentials than that of the original surface. Moreover, after 14 h of immersion of the five anodes in zinc electrolyte with
ions accelerated the passivation and increased the corrosion current density of the five anodes during the 5 h immersion of the five anodes. In addition, after 3 h of immersion the passivation of the polished surface gave more noble potentials than that of the original surface. Moreover, after 14 h of immersion of the five anodes in zinc electrolyte with  , the anode Pb-0.72%Ag had the best corrosion resistance, followed by anodes Pb-0.67%Ag, Pb-0.60%Ag, then the anodes Pb-0.58%Ag and Pb-0.29Ag-0.1%Ca by the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). It means that a higher silver content caused a higher corrosion resistance for the Pb-Ag anodes.
, the anode Pb-0.72%Ag had the best corrosion resistance, followed by anodes Pb-0.67%Ag, Pb-0.60%Ag, then the anodes Pb-0.58%Ag and Pb-0.29Ag-0.1%Ca by the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). It means that a higher silver content caused a higher corrosion resistance for the Pb-Ag anodes.
Acknowledgments
The first author is very grateful to Dr. GHALI and JIN for their advice and help, especially thank Dr. JIN for his great work.
References
[1] IVANOV I, STEFANOV Y, NONCHEVA Z, PETROVA M, DOBREV T S, MIRKOVA L, VERMEERSCH R, DEMAEREL J P. Insoluble anodes used in hydrometallurgy: Part I. Corrosion resistance of lead and lead alloy anodes [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 57: 109-124.
[2] IVANOV I, STEFANOV Y, NONCHEVA Z, PETROVA M, DOBREV TS, MIRKOVA L, VERMEERSCH R, DEMAEREL J P. Insoluble anodes used in hydrometallurgy: Part II. Anodic behaviour of lead and lead-alloy anodes [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 57: 125-139.
[3] LANDER J J. Silver-cobalt positive-grid corrosion in the lead-acid battery [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 1958, 105: 289-292.
[4] HEIN K, SCHIERLE T. Oxygen overvoltage at insoluble anodes in the system Pb-Ag-Ca (German) [J]. Erzmetall, 1992, 44: 447-451.
[5] PAVLOV D, MONAHOV B, PETROV D. Effect of Ag element on the formation of lead oxide layer [C]//6th European Lead Battery Conference. Prague, 1998: 3.2-1.
[6] YAMAMOTO Y, MATSUOKA M, KIMOTO M, UEMURA M, IWAKURA C. Potentiodynamic reactivation of a passivated lead negative electrode in sulphuric acid [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1996, 41(3): 439-444.
[7] XU R D, HUANG L P, ZHOU J F, GUAN Y Y, KONG Y. Effects of tungsten carbide on electrochemical properties and microstructural features of Al/Pb-PANI-WC composite inert anodes used in zinc electrowinning [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 125-126: 8-15.
[8] ZHAN P, XU R D, HUANG L P, CHEN B M, ZHOU J F. Effects of polyaniline on electrochemical properties of composite inert anodes used in zinc electrowinning [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22: 1693-1700.
[9] ZHOU J F, XU R D, CHEN B M. Study on electrochemical properties of Al/Pb-PANI-WC inert anodes [J]. Advanced Science Letters, 2011, 4: 1225-1229.
[10] VEREECKEN J, WINAND R. Influence of manganese (II) ions on the anodic oxidation of methanol [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1972, 17(2): 121-278.
[11] NEWHAM A H. Corrosion rates of lead based anodes for zinc electrowinning at high current densities [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1992, 22: 116-124.
[12] IVANOV I, STEFANOV Y. Electroextraction of zinc from sulphate electrolytes containing antimony ions and hydroxyethylated- butyne-2-diol-1,4: Part 3. The influence of manganese ions and a divided cell [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2002, 64: 181-186.
[13] ZHANG Q B, HUA Y X. Effect of Mn2+ ions on the electrodeposition of zinc from acidic sulphate solutions [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 99: 249-254.
[14] ZHANG W, HOULACHI G. Electrochemical studies of the performance of different Pb-Ag anodes during and after zinc electrowinning [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 104: 129-135.
[15] KIRYAKOV G Z, BAYNIETOVA F K, VAKHIDOV R S. Role of manganese in the electrolytic deposition of zinc [J]. Tr Inst Khim Akad Nauk S.S.R, 1958, 3: 72-81.
[16] ZHANG W S, CHENG C Y. Manganese metallurgy review: Part III. Manganese control in zinc and copper electrolytes [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2007, 89: 178-188.
[17] YU P, O’KEEFE T J. Evaluation of lead anode reactions in acid sulfate electrolytes: II. Manganese [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2002, 149: A558-A569.
[18] SCHMACHTEL S, TOIMINEN M, KONTTURI K,  O, BARKER M H. New oxygen evolution anodes for metal electrowinning: MnO2 composites electrodes [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 2009, 39: 1835-1848.
O, BARKER M H. New oxygen evolution anodes for metal electrowinning: MnO2 composites electrodes [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 2009, 39: 1835-1848.
张 伟1,2,涂常青3,陈艺锋1,Houlachi GEORGEOS4,肖 利1
1. 湖南工业大学 冶金工程学院,株洲 412007;
2. Department of Mining, Metallurgy and Material Engineering, Laval University, Ste-Foy, Quebec, G1K 7P4, Canada;
3. 中航工业南方动力机械公司,株洲 412002;
4. LTE, Hydro-Quebec, 600 Avenue de la Mortagne, C.P. 900 Shawinigan, QC, G9N 7N5, Canada
摘 要:研究在电位衰变期间在酸性硫酸锌电解液中,MnO4- 和银的含量对5个通用铅银合金阳极电化学行为的影响。当阳极浸入不含 的酸性硫酸锌电解液中时,通过开路电位测定,发现Pb-0.72%Ag进入完全钝化状态所用的时间最短,紧接着的是阳极Pb-0.67%Ag、Pb-0.60%Ag、Pb-0.58%Ag和Pb-0.29%Ag-0.1%Ca。在5 h 的浸入期间,MnO4-离子能加速钝化和增加阳极的腐蚀电流密度。通过交流阻抗法测定,发现在含有MnO4-的电解液中,阳极Pb-0.72%Ag具有最好的耐蚀性,紧接着的是阳极Pb-0.67%Ag、Pb-0.60%Ag,然后是阳极Pb-0.58%Ag和Pb-0.29%Ag-0.1%Ca。
的酸性硫酸锌电解液中时,通过开路电位测定,发现Pb-0.72%Ag进入完全钝化状态所用的时间最短,紧接着的是阳极Pb-0.67%Ag、Pb-0.60%Ag、Pb-0.58%Ag和Pb-0.29%Ag-0.1%Ca。在5 h 的浸入期间,MnO4-离子能加速钝化和增加阳极的腐蚀电流密度。通过交流阻抗法测定,发现在含有MnO4-的电解液中,阳极Pb-0.72%Ag具有最好的耐蚀性,紧接着的是阳极Pb-0.67%Ag、Pb-0.60%Ag,然后是阳极Pb-0.58%Ag和Pb-0.29%Ag-0.1%Ca。
关键词:电化学行为;铅银阳极;高锰酸根离子;电位衰减期;硫酸锌电解液
(Edited by Sai-qian YUAN)
Foundation item: Project (RDCPJ 346365-06) supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada; Project (51208193) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (11jj6034) supported by the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation.
Corresponding author: Wei ZHANG; Tel: +86-731-22183478; Fax: +86-731-22183465; E-mail: weizhang716@hotmail.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62714-4

