
Effect of polyethylene glycol on electrochemically deposited trivalent chromium layers
Joo-Yul LEE, Man KIM, Sik-Chol KWON
Department of Surface Technology, Korea Institute of Materials Science, 531 Changwondaero, Changwon,
Gyeongnam, 641-831, Korea
Received 18 June 2008; accepted 10 March 2009
Abstract: The structural characteristics of the trivalent chromium deposits and their interfacial behavior in the plating solution with and without polyethylene glycol molecules were observed by using various electrochemical methods such as cyclic voltammetry, open circuit potential transition, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectrometry. It is shown that the polyethylene glycol molecules make the reductive current density lower in the trivalent chromium plating system and promote a hydrogen evolution reaction through their adsorption on the electrode surface. And the trivalent chromium layer formed from the polyethylene glycol-containing solution has somewhat higher density of cracks on its surface and results in a lower film resistance, lower polarization resistance, and higher capacitance in a corrosive atmosphere. It is also revealed that the formation of chromium carbide layer is facilitated in the presence of polyethylene glycol, which means easier electrochemical codeposition of chromium and carbon, not single chromium deposition.
Key words: electrochemical deposition; trivalent chromium; polyethylene glycol
1 Introduction
Hexavalent chromium has been widely used as a surface coating material due to its excellent physical, mechanical and electrochemical characteristics. But now it confronts worldwide environmental restrictions because of its hazardous effects on the environment. Trivalent chromium electroplating has drawn a great attention for several decades as the most challengeable process to alternate the hexavalent chromium electroplating owing to its low toxicity[1]. However, it is difficult to electro-chemically reduce the trivalent chromium ions due to the formation of kinetically inert outer orbital octahedral complexes in the aqueous medium and their bonding nature of d2sp3 hybridization [2]. This kinetic inertness results from the 3d3 electronic configuration of trivalent ion, whose orbital charge distribution makes ligand displacement very slow[3]. Actually, ligand displacement reaction of trivalent chromium complexes was reported to have half-time in the range of several hours. Various organic additives have been employed to enhance the surface characteristics such as leveling, brightness, anticorrosion, and structural compactness of electrodeposits in the area of metal and metal alloy electroplating[4-7]. Particularly, polyethylene glycol (PEG) was used in the plating solution as a surfactant to lower the surface energy of a cathode in the zinc, chromium and zinc-chromium alloy electroplating[7]. Hull cell tests show that the addition of PEG molecules in the trivalent chromium solution can enhance the homogeneity of trivalent chromium electrodeposits and the current efficiency at low current densities at optimum concentration. But, most researches were concentrated on revealing the relationship between complexants and trivalent chromium ions in the viewpoint of electrode kinetics, while just a few dealt with organic additives systematically to understand their roles in the electrochemical reduction and the development of thin film properties[8-19]. In this work, we aimed to structurally analyze the trivalent chromium layers to elucidate the role of the organic additives and PEG molecules during electrochemical deposition.
2 Experimental
The stock solution of trivalent chromium plating was composed of 0.05 mol/L Cr2(SO4)3 as a source of trivalent chromium ion, 0.1 mol/L HCOOH as a complexant, 0.07 mol/L H3BO3 as a buffering agent, (0.1 mol/L NH4Cl+0.1 mol/L KCl) as an mixed electrolyte system, and 1.3 mmol/L polyethylene glycol (PEG, M= 1 500) as an organic additive. The plating solution was adjusted at pH 2.3 and maintained at 30 ℃ during experiment. Trivalent chromium layers were deposited onto the stationary working electrode by potentiodynamic or potentiostatic polarization in the stock solution in the presence and in the absence of PEG molecules, followed by rinsing with purified water and drying with N2 gas. Cu plate (area 1 cm2), platinum plate (area 4 cm2), and Ag/AgCl (in saturated KCl) were used as working, counter, and reference electrodes, respectively, for the electrochemical experiments. The electrochemical preparation and characterization of trivalent chromium layer were made by using PGSTAT30 (Autolab, Netherland). For the impedance measurements, the instrument was controlled in the frequency range of 100 kHz-100 mHz with an AC wave of 5 mV peak-to-peak overlaid on a DC bias potential, and the impedance data were obtained at a rate of 10 points per decade change in frequency. The physical morphology of the trivalent chromium deposits was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JSM-5800, JEOL).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Cyclic voltammetry
Fig.1 shows the cyclic voltammograms of electro- chemical reduction of trivalent chromium ions in the PEG-free and PEG-containing solution. Actually, there was little difference in the onset potentials for the reduction of trivalent chromium ions between two systems except that PEG-containing solution represented lower current density than PEG-free solution. Low current density observed in the additive-containing solution is related with some phenomena such as adsorption of PEG molecules at the electrode/electrolyte interface, interaction between PEG molecules and trivalent chromium complexes in a solution, or interference of the reduction of trivalent chromium due to the competitive hydrogen evolution reaction[20-21]. We ascribe the low current density of this PEG- containing system mainly to the severe hydrogen evolution reaction, judging from the fact that there was no onset potential shift compared with PEG-free solution, which is a definite proof of ‘strong’ adsorption of organic additives at the electrode. This means that PEG- containing system is more susceptible to the hydrogen evolution reaction than PEG-free system in the course of trivalent chromium deposition process. As well, we also measured the relationship between scan rate and peak current and observed that the electrochemical reduction was limited by the mass transfer of trivalent chromium complexes both in the presence and in the absence of PEG molecules (not shown here). This also indicates that PEG molecules do not specifically interact with trivalent chromium complex on the electrode surface.

Fig.1 Cyclic voltammograms at copper electrode at 50 mV/s in solution containing 0.05 mol/L Cr2(SO4)3, 0.1 mol/L HCOOH, 0.07 mol/L H3BO3, 0.1 mol/L NH4Cl and 0.1 mol/L KCl with and without 1.3 mmol/L PEG
3.2 Open circuit potential transition
Fig.2 represents the transition of open circuit potentials of copper electrode in the trivalent chromium solution with and without PEG molecules. Open circuit potential reflects the amount of electroactive species at the electrode/electrolyte interface and informs the surface state, that is, the degree of adsorption of additives on the electrode which hinder the approach of metallic ions. PEG-containing solution showed higher open circuit potential than PEG-free solution by 10 mV or so, even though this potential deviation was not so consistent during measurement. Considering the cyclic voltammetric analysis, we assume that PEG molecules are weakly adsorbed on the electrode surface and cannot act as a practical barrier layer to induce specific surface reaction with incoming trivalent chromium complexes.
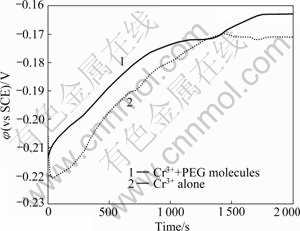
Fig.2 Open circuit potentials measured at copper electrode as function of time in solution containing 0.05 mol/L Cr2(SO4)3, 0.1 mol/L HCOOH, 0.07 mol/L H3BO3, 0.1 mol/L NH4Cl and 0.1 mol/L KCl with and without 1.3 mmol/L PEG
3.3 Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
Fig.3 depicts the electrochemical impedance spectra of trivalent chromium layers in the 0.5 mol/L NaCl solution at open circuit potential and anodic potential (0.10 V). Each chromium layer was prepared by potentiodynamic polarization from OCP to -1.6 V at 10 mV/s and the impedance spectra were fitted by using Randles equivalent circuits. Both impedance spectra were composed of two semicircles. A small semicircle appearing at high frequency region represents the charge transfer impedance (Rct-Cdl) for the active dissolution reaction of chromium layers by chloride ions, and a large semicircle at low frequency is related with the characteristics (or porosity) of chromium films themselves and the diffusion behavior of anions through the pores of deposits (Rf-Cf)[22].
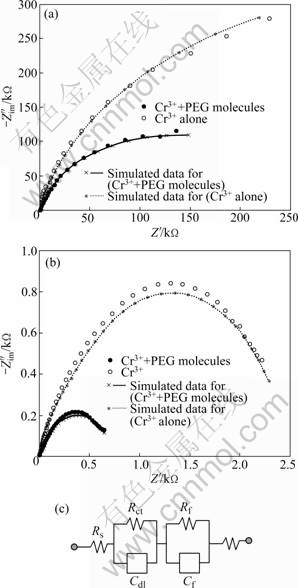
Fig.3 Impedance diagrams recorded at electrodeposited trivalent chromium layers at OCP (a) and at 0.10 V (b) (Experimental and simulated Nyquist plots for copper electrode covered with trivalent chromium layer are overlaid) and equivalent circuit used for impedance data analysis (c)
From the fitted results (not shown here), the trivalent chromium layer deposited from PEG-free solution was revealed to have larger charge transfer resistance and film resistance than the deposit from PEG-containing solution at both open circuit potential and 0.10 V. Especially, when the trivalent chromium layer was under the active dissolution condition, PEG-added chromium layer shows an abrupt increase in the film capacitance, which describes the increase of surface area, that is, rough surface. Therefore, this suggests that the PEG-free deposits should have more compact structure than the PEG-containing one, which is coarsely structured and of somewhat apparent crack (or pore) distributed along the thickness direction and makes the movement of chloride ions through the deposit easier, as confirmed from the surface images before and after the active dissolution in Fig.4.
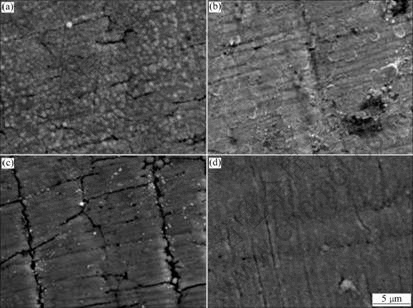
Fig.4 Surface SEM photographs of trivalent chromium layers before (a, b) and after (c, d) anodic polarization at -0.1 V for 400 s in 5% NaCl solution by potentiodynamic polarization from OCP to -1.6 V at 10 mV/s: (a), (c) Deposited in the presence of 1.3 mmol/L PEG; (b), (d) Deposited in the absence of 1.3 mmol/L PEG
3.4 Microstructure analysis
SEM microscopic images are obtained for the trivalent chromium deposits prepared by applying constant potential of -1.0, -1.2, and -1.6 V for 30 min in the presence and absence of PEG molecules. In Fig.5, no deposition happened in the PEG-containing solution (Fig.5(d)) at -1.0 V due to the more competitive hydrogen evolution reaction, as described in the cyclic voltammetric analysis in Fig.1. The occurrence of cracks on the chromium surface was dependent upon the applied potential in both solutions. As the applied potential became higher, the crack density and crack width got larger. Trivalent chromium layers formed from PEG-containing solution had a larger deposit grains and crack width compared with those from PEG-free solution. It is known that cracks develop when the hydrogen codeposited with chromium is released from matrix and the internal stress constraints are decreased and consequently the total volume of deposit is reduced[9]. Therefore, trivalent chromium deposition from PEG-containing solution is supposed to accompany much more hydrogen evolution and a hydrogen incorporation into the matrix in the form of a chromium hydride, which coincides with the result of cyclic voltammetry in Fig.1.

Fig.5 SEM photographs of trivalent chromium layers prepared by potentiostatic polarization for 30 min in solution containing 0.05 mol/L Cr2(SO4)3, 0.1 mol/L HCOOH, 0.07 mol/L H3BO3, 0.1 mol/L NH4Cl and 0.1 mol/L KCl with (a, b, c) and without (d, e, f) 1.3 mmol/L PEG: (a), (d) -1.0 V; (b), (e) -1.2 V; (c), (f) -1.6 V
4 Conclusions
It is observed that PEG molecules added in the solution make hydrogen evolution reaction more apparent during trivalent chromium deposition process without modifying the interaction with trivalent chromium complexes. Though PEG molecules are adsorbed on the electrode surface, they are not likely to act as a practical barrier layer to induce specific surface reaction with incoming trivalent chromium complexes due to their low adsorptivity. PEG molecules make the trivalent chromium layer more cracked, which may be ascribed to more active hydrogen evolution reaction and hydrogen incorporation into the matrix as a chromium hydride. This loose structure results in low polarization resistance and capacitance of thin chromium layer. Also, it is proved that the deposition of chromium carbide is made easier with the addition of PEG molecules in the solution.
References
[1] HONG G, SIOW K S, ZHIQUIAN G, HSHIEH A K. Hard chromium plating from trivalent chromium solution [J]. Plat and Surf Fin, 1997, 84: 69-75.
[2] MANDICH N V. Chemistry & theory of chromium deposition (Part 1)—Chemistry [J]. Plat and Surf Fin, 1997, 84: 108-115.
[3] BASOLO F, PEARSON R G. Mechanisms of inorganic reaction [M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1967: 141-145.
[4] BOZHKOV C, PETROVA M, RASHKOV S. The effect of nickel on the mechanism of the initial stages of zinc electrowinning from sulphate electrolytes (Part II): Investigations on aluminium cathodes alloyed with iron impurities [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1990, 20: 17-22.
[5] WIART R, CACHET C, BOZHKOW C, RASHKOV S. On the nature of the ‘induction period’ during the electrowinning of zinc from nickel containing sulphate electrolytes [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1990, 20: 381-389.
[6] CACHET C, WIART R. Zinc deposition and passivated hydrogen evolution in highly acidic sulphate electrolytes: Depassivation by nickel impurities [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1990, 20: 1009-1014.
[7] AKIYAMA T, KOBAYASHI S, KI J, OHGAI T, FUKUSHIMA H. Role of polyethylene glycol in electrodeposition of zinc-chromium alloys [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 2000, 30: 817-822.
[8] VYKHODTSEVA L N, EDIGARYAN A A, LUBMIN E N, POLUKAROV YU M, SAFONOV V A. Composition, structure, and corrosion–electrochemical properties of chromium coatings deposited from chromium(III) electrolytes containing formic acid and its derivatives [J]. Russian J Electrochem, 2004, 40: 387-393.
[9] SAFONOV V A, VYKHODTSEVA L N, EDIGARYAN A A, ALIEV A D, MOLODKINA E B, DANILOV A I, LUBNIN E N, POLUKAROV YU M. Corrosion–electrochemical behavior of chromium deposits obtained from sulfuric acid solutions containing oxalates [J]. Russian J Electrochem, 2001, 37: 127-134.
[10] HWANG J Y. Trivalent chromium electroplating for baths containing hypophosphite ions [J]. Plat and Surf Fin, 1991, 76: 118-125.
[11] IBRAHIM S K, WATSON A, GAWNE D T. The role of formic acid and methanol on speciation rate and quality in the electrodeposition of chromium from trivalent electrolytes [J]. Trans IMF, 1997, 75(5): 181-188.
[12] TU Z, YANG Z, ZHANG J, AN M Z, LI W L. Cathode polarization in trivalent chromium plating [J]. Plat and Surf Fin, 1993, 78: 79-82.
[13] HONG G, SIOW S K, ZHIQIANG G, HSIEH A K. Hard chromium plating from trivalent chromium solution [J]. Plat and Surf Fin, 2001, 88: 69-75.
[14] MCDOUGALL J, EL-SHARIF M, MA S. Chromium electrodeposition using a chromium(Ⅲ) glycine complex [J]. J Appl Electrochem, 1998, 28: 929-934.
[15] KUZNETSOV V V, VINOKUROV E G, KUDRYAVTSEV V N. Effect of hydrodynamic electrolysis conditions on the kinetics of cathodic processes in chromium(III) sulfate electrolytes [J]. Russian J Electrochem, 2000, 36: 756-760.
[16] BERKH O, ESKIN S, ZAHAVI J. Effect of additives on electrodeposition of composite chromium coatings [J]. Plat and Surf Fin, 1994, 81: 62-64.
[17] EL-SHARIF M, MCDOUGALL J, CHISHOLM C U. Electrodeposition of thick chromium coatings from an environmentally acceptable chromium(Ⅲ)-glycine complex [J]. Trans IMF, 1999, 77(4): 139-144.
[18] EL REHIM S S, IBRAHIM M A M, DANKERIA M M. Thin films of chromium electrodeposition from a trivalent chromium electrolyte [J]. Trans IMF, 2002, 80(1): 29-33.
[19] DANILOV F I, PROTSENKO V S, BUTYRINA T E. Chromium electrodeposition kinetics in solutions of Cr(III) complex ions[J]. Russian J Electrochem, 2001, 37: 704-709.
[20] LEE J Y, KIM J W, LEE M K, SHIN J J, KIM H T, PARK S M. Effects of organic additives on initial stages of zinc electroplating on iron [J]. J Electrochem Soc, 2004, 151: C25-C31.
[21] KIM J W, LEE J Y, PARK S M. Effects of organic additives on zinc electrodeposition at iron electrodes studied by EQCM and in situ STM[J]. Langmuir, 2004, 20: 459-466.
[22] CHUNG S C, CHENG J R, CHIOU S D, SHIH H C. EIS behavior of anodized zinc in chloride environments [J]. Corr Sci, 2000, 42: 1249-1268.
Corresponding author: Joo-Yul LEE; Tel: +82-55-280-3518; E-mail: leeact@kims.re.kr
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(08)60357-X
(Edited by YANG Bing)