无菌和有菌体系下砷黄铁矿氧化的电化学
李 骞,杨永斌,姜 涛,邱冠周
(中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘要:在无菌和有菌酸性体系下,对砷黄铁矿电化学氧化进行研究。研究结果表明:砷黄铁矿首先被氧化为As2S2,覆盖于电极表面,使电极表面发生钝化;随着电位升高,As2S2被氧化生成亚砷酸及亚砷酸被氧化为砷酸,亚铁离子被氧化成铁离子;细菌作用后增强了砷黄铁矿的反应性能,降低了其开始氧化的电位,砷黄铁矿被氧化的趋势增大,腐蚀反应速度有所提高,但细菌对砷黄铁矿电极的阳极反应过程机理并没有产生影响;在相同电位下,有细菌时的阻抗明显低于无细菌时的阻抗;在不同电位下,电极表面发生的电化学反应机理也不同,测定结果与线性扫描研究结果相吻合。
关键词:砷黄铁矿;氧化亚铁硫杆菌;电化学
中图分类号:TF111.31 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2007)01-0065-05
Electrochemical aspects of oxidation of arsenopyrite in the presence
and absence of thiobacillus ferrooxidans
LI Qian, YANG Yong-bin, JIANG Tao, QIU Guan-zhou
(School of Resources Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The electrochemical research of asenopyrite in the presence and absence of thiobacillus ferrooxidans in acidic growth media was investigated. The results show that asenopyrite is firstly oxidized to As2S2, which covers the electrode and the dissolution of arsenopyrite is retarded. As2S2 is oxidized to H3AsO3, H3AsO3 to H3AsO4, and Fe2+ is oxidized to Fe3+ with the increase of potential. The reactive nature of arsenopyrite is enhanced and the initial oxidation potential decreases when thiobacillus ferrooxidans are in the solution. The tendency of being oxidized and the corrosion rate increase compared to that in absence of thiobacillus ferrooxidans, but the reaction mechanism of arsenopyrite of anode process is not changed. The resistance in the presence of thiobacillus ferrooxidans is obviously lower than that in the absence of thiobacillus ferrooxidans. The proposed reaction mechanism confirms the results obtained in liner polarization satisfactorily.
Key words: arsenopyrite; thiobacillus ferrooxidans; electrochemistry
从矿石中提取黄金的传统方法是氰化法。当金呈细粒浸染状被包裹在硫化物基质中时,常常要进行氧化焙烧,或采用化学氧化等方法进行预处理,使浸出剂能到达金的表面。与前2种预处理方法相比,生物预氧化法具有环境友好、费用低等优点[1-3]。砷黄铁矿的生物氧化可能是直接进行的,也可能是间接进行 的[4-5]。在直接氧化机理中,氧化亚铁硫杆菌固着在矿物表面上,促进矿物生物氧化。固着在矿石表面上的细菌使表面氧化电位改变,并通过S和Fe的氧化使其去极化[4,6-7]。在间接氧化机理中,砷黄铁矿的化学溶出是通过溶液中Fe3+的还原作用进行的,还原得到的Fe2+可被氧化亚铁硫杆菌再氧化[8]。由于细菌对铁离子的氧化、Fe3+对矿物的浸出作用、细菌对浸出过程中产生的元素硫的氧化作用、细菌呼吸氧得电子对阴极的加强作用,以及细菌对矿物的直接分解作用,各个过程都涉及电子转移,因此,必须应用现代电化学测试技术研究有细菌时砷黄铁矿浸出过程机理。闵小波[9]采用矿物粉末微电极研究了砷黄铁矿的电化学行为。砷黄铁矿细菌作用后的静电位低于未经细菌处理的电位;循环伏安扫描结果表明砷黄铁矿的氧化可产生元素硫和As3+,As3+进一步氧化成As5+,砷黄铁矿中砷最终以As5+酸根形式存在。细菌浸出后,砷黄铁矿表面将会生成低活性的砷酸铁、铁矾类物质的钝化层。张永柱等[10]利用电化学方法进行研究,认为细菌的作用是加速中间产物S0及As3+的氧化,促进FeAsS的分解。I.Lazaro等[11-14]认为砷黄铁矿在细菌作用下发生了如下反应:
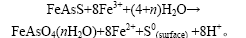
从能谱扫描结果中发现电极表面有S和FeAsO4;用扫描电镜观察电极表面发现生物氧化的程度要比化学氧化的程度强。目前,人们对酸性体系下砷黄铁矿氧化的电化学研究不多,对细菌存在时运用电化学测试技术研究矿物阳极氧化浸出机理的研究更少。在此,本文作者利用线性扫描、交流阻抗等电化学手段研究砷黄铁矿在无菌和有菌9K酸性体系下的氧化机理及电极过程动力学。
1 试 验
1.1 电解池及电极
电解池为三电极系统,以铂片电极做辅助电极,Ag/AgCl作参比电极。本文中所有电位数据都已校正为相对于标准氢电极(SHE)。工作电极在溶液中浸泡一定时间达到平衡后进行测量;每次测量时,均用不同型号的砂纸逐级打磨,最后用600号砂纸打磨成镜面,然后依次用甲醇、5 mol盐酸和二次蒸馏水清洗,以更新工作面。实验仪器为EG&G PAR公司的电化学测量系统(Potentiostat /Galvanostat Model 273A)。
按80?10?10的质量比分别称取砷黄铁矿粉(化学成分为As 46.0%,Fe 34.36%,S 19.64%,纯度为99.9%,粒度在0.074 mm以下达100%)、分析纯固体石蜡和光谱纯石墨粉,使石墨粉和矿粉充分混合均匀;把固体石蜡置于烧杯中加热熔化后,迅速加入已混合均匀的石墨粉和矿粉,快速搅拌均匀后立即压入制样模型中,马上用压片机压片,保持静压45 MPa 5 min。取出后,打磨成直径为15 mm、厚度为3 mm的圆柱体,放入特制的可旋转的“塑料王”圆柱型电极套中,粘接,制成碳糊电极(CPE)。电化学测试工作电极的有效面积约1 cm2。
1.2 溶液及菌种
电化学测量的基本介质为无铁9K培养基,电解质成分为:(NH4)SO4 3.0 g/L,KCl 0.1 g/L,K2HPO4 0.05 g/L,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g/L,Ca(NO3)2 0.01 g/L。菌种为氧化亚铁硫杆菌,实验前预先用9K培养基在30 ℃培养,达到指数生长期时停止培养,收集活性细胞培养液,倒入电解池作为电解液。溶液pH值为2.0。pH值采用pHS-3C型酸度计测定,用1 mol H2SO4进行调整。试验前用氮气排除溶液中的O2,使溶液中的氧浓度为0 g/mL(溶解氧浓度采用JPB-607型溶氧仪测定)。采用恒温水浴槽使溶液保持恒定的温度。
此外,采用日本Rigaku公司X射线自动衍射仪对电极表面氧化膜进行物相分析,辐射源为CuKα,工作电压为50 kV,电流为100 mA,2θ为10?~80?,扫描速度为2?/min。
2 试验结果及讨论
2.1 细菌氧化砷黄铁矿的线性极化曲线
图1所示为砷黄铁矿在温度为25 ℃、pH值为2.0、扫描速率为20 mV/min、静止条件下阳极线性极化曲线。可见,在整个电位范围内,无论有无细菌,只有1个阳极峰,在电压为0.2~0.3 V时产生。电压在0.8 V时电流急剧升高。对扫描到0.2~0.3 V处时的电极表面进行X衍射分析(见图2),确定发生了如式(1) 所示的反应,砷黄铁矿被氧化为As2S2,覆盖于电极表面,从而发生了钝化现象。随着电位升高,As2S2被氧化生成亚砷酸及亚砷酸被氧化为砷酸,亚铁离子被氧化成铁离子,反应式见式(2)~(4)[15]。细菌作用后,砷黄铁矿阳极极化曲线发生较大变化,砷黄铁矿的氧化电位提前,阳极极化电流明显增大,砷黄铁矿的溶解速度加快。
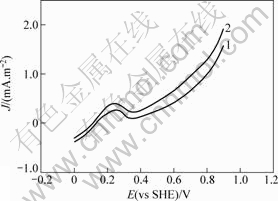
1—无菌体系;2—有菌体系
图 1 在无菌和有菌体系下砷黄铁矿粉末电极
阳极极化曲线
Fig.1 Anodic processes of arsenopyrite in the presence and absence of thiobacillus ferrooxidans
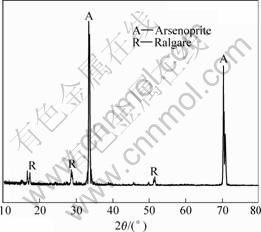
图 2 0.2~0.3 V时电极表面的X射线衍射谱
Fig.2 XRD pattern of arsenopyrite electrode surface
at 0.2-0.3 V
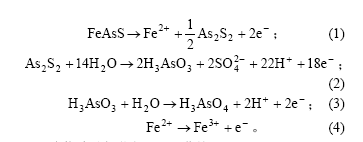
2.2 砷黄铁矿氧化的Tafel曲线
图3所示为砷黄铁矿电极在无菌和有菌酸性体系中的强极化曲线。可见,在有菌酸性体系中,砷黄铁矿电极的腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流与在无菌酸性体系中的相比均有所升高。腐蚀电位升高,表明在细菌的作用下砷黄铁矿发生化学反应的吉布斯自由能降低;腐蚀电流增大则表明,在细菌的作用下,砷黄铁矿的腐蚀反应速度有所提高。
由 Tafel斜率的测试结果(见表1)可知,砷黄铁矿电极的阳极Tafel斜率在无菌和有菌2种情况下几乎相等,但阴极Tafel斜率在有菌的情况下则有所增大。在25 ℃时,2.303RT/F≈59 mV。若取α≈β=0.5,则可近似计算出电子反应Tafel斜率为59 mV。这与砷黄矿电极在有菌和无菌2种情况下的阳极Tafel斜率相符。这样,可以得到砷黄铁矿电极的阳极反应速度控

1—有菌体系;2—无菌体系
图 3 无菌和有菌体系下砷黄铁矿电极强的Tafel曲线
Fig.3 Tafel curves of arsenopyrite electrode in the
presence and absence of thiobacillus ferrooxidans
制步骤的得失电子数n≈2。由此可见,在无菌酸性体铁系和有菌酸性体系中,砷黄铁矿电极的阳极Tafel斜率相等,即砷黄铁矿电极在有菌和无菌2种情况下的阳极反应传递电子数相等,表明细菌对砷黄铁矿电极的阳极反应过程机理并没有产生影响。所不同的是,在细菌的作用下砷黄铁矿电极阴极过程的传递电子数发生了变化。表明砷黄铁矿电极的阴极过程机理(或反应历程)在细菌的作用下发生改变。这也许与氧化亚铁硫杆菌所参与的砷黄铁矿的氧化反应中,氧是其最终的电子受体有关。
表 1 无菌和有菌体系下砷黄铁矿电极的Tafel参数
Table 1 Tafel parameters of arsenopyrite electrode in the
presence and absence of thiobacillus ferrooxidans

2.3 细菌氧化砷黄铁矿的极化阻力
图4所示为砷黄铁矿阳极在无菌和有菌2种情况下的线性极化曲线测量结果。为了保证极化曲线的线性度,电位扫描范围控制在静止电位(即自腐蚀电位) ±10 mV范围内。由图4可见,在无菌和有菌2种情况下,砷黄铁矿电极的阳极极化曲线均呈较好的线性关系。
对图4中2条直线进行回归分析,在无菌酸性体系中,极化曲线的直线回归方程为:

1—有菌体系;2—无菌体系
图 4 在无菌和有菌体系下砷黄铁矿线性极化曲线
直线段及回归曲线
Fig.4 Liner polarization and regression curves of
arsenopyrite electrode in the presence and absence
of thiobacillus ferrooxidans
E=0.213 8+0.049 69I。 (5)
回归系数r=0.999 17。
在有菌酸性体系中,极化曲线的直线回归方程为:
E=0.411 8+0.021 21I。 (6)
回归系数r=0.999 83。
由(5)和(6)2个回归方程可以得到砷黄铁矿电极在无菌酸性体系和有菌酸性体系中的极化阻力RP和腐蚀电位Ecorr。在无菌酸性体系中,砷黄铁矿电极[16-17]的Rp=ΔE/ΔI=49.69 Ω,Ecorr=213.8 mV;在有菌酸性体系中,砷黄铁矿电极的Rp=21.21 Ω,Ecorr=411.8 mV。
研究结果表明,在氧化亚铁硫杆菌存在的腐蚀体系中,砷黄铁矿电极的极化阻力降低。根据腐蚀电化学理论,极化阻力RP反映了金属或半导体在所处腐蚀体系中的耐蚀性能。因此,砷黄铁矿电极在有菌酸性体系中的极化阻力小于在无菌酸性体系中的极化阻力,表明砷黄铁矿在有菌酸性体系中更容易被腐蚀;此外,在生物浸出过程中,由于细菌的作用使反应阻力降低,这是砷黄铁矿在菌液体系中更易被氧化的原因之一。
2.4 细菌氧化砷黄铁矿的交流阻抗
在温度为25 ℃、pH值为2.0、静止的条件下,频率为0.005~100 kHz的范围内研究在无菌和有菌2种情况下砷黄铁矿氧化的交流阻抗,交流阻抗谱如图5所示。其中:图5(a)所示为无细菌时的交流阻抗谱,图5(b)所示为有细菌时的交流阻抗谱;Zr为实部阻抗;Zi为虚部阻抗。
从图5可以看出,在相同电位下,有细菌时的阻抗明显低于无细菌时的阻抗。此外,在无菌和有菌2

(a) 无菌体系;(b) 有菌体系
V/mV: 1—300; 2—400; 3—500; 4—600; 5—800
图 5 在无菌和有菌体系下砷黄铁矿电极的交流阻抗谱
Fig.5 EIS of arsenopyrite electrode in the presence
and absence of thiobacillus ferrooxidans
种情况下,当电位升高时,容抗弧和电抗减小,界面电容增大;当电位为0.3 V时,容抗弧和电抗最大,界面电容最小。说明电极表面产生电化学反应,并形成钝化膜,阻碍阳极反应过程,使电化学电阻增大,电容减小;降低表面的腐蚀(氧化反应)速度使相角移向低频。该过程分别对应线性扫描曲线中的反应式(1)。当电位介于0.5~0.8 V时,随着电位的增大,电化学电阻降低很快,电容增大,电极过程为吸附钝化膜的迅速破裂阶段,容抗弧很快变小。这些结果与图1所示的线性伏安曲线相应电位区的形状有很好的对应关系。此外,当无细菌且电位介于0.5~0.8 V时,Nyquist图明显出现1个高频电容圈和1个低频电感圈,而当有细菌时,在低电位区和高电位区,Nyquist图都出现1个高频电容圈和1个低频电感圈(0.8 V除外),这表明电极表面出现2个电极过程。低频电感圈是解吸附作用过程所致,而高频电容圈则是吸附作用所致。当细菌存在时,这种解吸附作用和吸附作用更明显。
3 结 论
a.砷黄铁矿在酸性培养基中标准氢电极电压为0.2 V时开始氧化分解,砷黄铁矿首先被氧化为As2S2,覆盖于电极表面,使电极表面发生钝化。随着电位继续升高,As2S2被氧化生成亚砷酸及亚砷酸被氧化为砷酸,亚铁离子被氧化成铁离子。细菌作用后砷黄铁矿的反应性能增强,其开始氧化的电位降低。
b. 砷黄铁矿在有菌体系中电极的腐蚀电位和腐蚀电流与在无菌酸性体系中的相比均升高。腐蚀电位升高表明,在细菌作用下砷黄铁矿发生化学反应的吉布斯自由能降低;腐蚀电流增大则表明在细菌作用下,砷黄铁矿的腐蚀反应速度有所提高。
c. 砷黄铁矿电极的阳极Tafel斜率在无菌和有菌2种情况下几乎相等,分别为58.89 mV和59.56 mV,即砷黄铁矿电极在2种情况下的阳极反应传递电子数相等,表明细菌对砷黄铁矿电极的阳极反应过程机理并没有产生影响。在细菌作用下砷黄铁矿电极阴极过程的传递电子数发生变化,表明砷黄铁矿电极的阴极过程机理在细菌作用下会发生改变。
d. 在无菌或有菌2种情况下,砷黄铁矿电极的反应阻力分别为49.69 kΩ和21.21 kΩ。反应阻力降低,这说明砷黄铁矿在氧化亚铁硫杆菌存在的情况下更容易被腐蚀。
e. 在相同电位下,有细菌时的阻抗明显低于无细菌时的阻抗;在不同电位时,电极表面发生的电化学反应机理也不同。测定结果与线性扫描研究所得结果相吻合。
参考文献:
[1] Gonzalez R, Gentina J C, Acevedo F. Continuous biooxidation of a refractory gold concentrate[C]// Amils R, Ballester A. Biohydrometallurgy and the Environment toward the Mining of 21st Century: Part A. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1999: 309-317.
[2] Gonzalez R, Gentina J C, Acevedo F. Biooxidation of a gold concentrate in a continuous stirred tank reactor: mathematical model and optimal configuration[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2004, 19: 33-42.
[3] Langhans D, Lord A, Lampshire D. Biooxidation of an arsenic-bearing refractory gold ore[J]. Minerals Engineering, 1995(8): 147-158.
[4] Sand W, Gehrke T, Jozsa P G, et al. (Bio)chemistry of bacterial leaching-direct vs. indirect bioleaching[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 59: 159-175.
[5] Ubaldini S, Veglio F, Toro L, et al. Biooxidation of arsenopyrite to improve gold cyanidation: study of some parameters and comparison with grinding[J]. Int J Miner Process, 1997, 52: 65-68.
[6] Tglesias N, Carranza F. Refractory gold-bearing ores: A review of treatment methods and recent advances in biotechnological techniques[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1994(34): 383-395.
[7] Miller D M, Hansford G S. Batch biooxidation of gold-bearing pyrite-arsenopyrite concentrate[J]. Miner Engineering, 1992, 5(6): 613-629.
[8] Konishi Y, Takasaka Y, Asai S. Kinetics of growth and elemental sulphur oxidation in batch culture of thiobacillus ferrooxidans biotechnol[J]. Bioengineering, 1994, 44: 667-673.
[9] 闵小波. 含砷难处理金矿细菌浸出基础理论及工艺研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学冶金科学与工程系, 2000: 33-39.
MIN Xiao-bo. Fundamental and technological studies on bioleaching of refractory arsenical gold concentrates by thiobacillus ferrooxidans[D]. Changsha: School of Metallurgy Science and Technology, Central South University, 2000: 33-39.
[10] 张永柱, 卢宜源, 张传福, 等. 含砷难处理金矿的细菌预氧化-氰化法提金研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 1994, 2(4): 17-22.
ZHANG Yong-zhu, LU Yi-yuan, ZHANG Chuan-fu, et al. Research on treatment of asenic-bearing gold ores by bacterial oxidation and gold leaching by cyanidation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1994, 2(4): 17-22.
[11] Lazaro I, Cruz R, Gonzalea I, et al. Electrochemical oxidation of arsenopyrite in acidic media[J]. Int J Miner Process, 1997, 50: 63-75.
[12] Cruz R, Lazaro I, Gonzalea I, et al. Surface characterization of arsenopyrite in acidic media by triangular scan voltammentry on carbon paste electrode[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1997, 46: 303-309.
[13] Sanchez V M, Hiskey J B. Electrochemical behavior of arsenopyrite in alkaline media[J]. Miner Metall Process, 1991, 2: 1-6.
[14] Sanchez V M, Hiskey J B. An electrochemical study of the surface oxidation of arsenopyrite In alkaline media[J]. Mctall Trans, B1988, 19: 943-949.
[15] 杨洪英, 杨 立, 魏绪钧. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌(SH-T)氧化毒砂的机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2001, 11(2): 323-327.
YANG Hong-ying, YANG Li, WEI Xu-jun. Mechanism on biooxidation of arsenopyrite with Thiobacillus ferrooxidans strain SH-T[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2001, 11(2): 323-327.
[16] 傅建华, 邱冠周, 胡岳华, 等. 浸矿细菌的超微结构及其特性[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 35(4): 562-568.
FU Jian-hua, QIU Guan-zhou, HU Yue-hua, et al. Ultrastructure and properties of leaching bacteria[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2004, 35(4): 562-568.
[17] 张传福, 闵小波, 柴立元, 等. 氧化亚铁硫杆菌生长迟缓期的影响因素[J]. 中南工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 1999, 30(5): 489-493.
ZHANG Chuan-fu, MIN Xiao-bo, CHAI Li-yuan, et al. nfluencing factor of lag phase in growth of thiobacllus ferrooxidans[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology: Science and Technology, 1999, 30(5): 489-493.
收稿日期:2006-05-10
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展项目(2004CB619204);国家自然科学基金创新研究群体项目(50321402)
作者简介:李 骞(1975-),男,甘肃静宁人,博士研究生,从事矿物加工研究
通讯作者:李 骞,男,博士研究生;电话:13207429207;E-mail: snt212@mail.csu.edu.cn