文章编号:1004-0609(2011)08-1801-07
应变速率对AZ61镁合金动态再结晶行为的影响
杨续跃1, 2,张之岭1,张 雷1,吴新星1,王 军1
(1. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083;
2. 中南大学 有色金属材料科学与工程教育部重点实验室,长沙 410083)
摘 要:采用光学显微镜、SEM/EBSD和组织定量分析技术研究AZ61镁合金在623 K、3×10-5~3×10-1 s-1下单向压缩时变形和动态再结晶行为。结果表明:AZ61镁合金的流变应力和动态再结晶行为强烈地受到应变速率的影响;随着应变速率的提高,稳态流变应力对应变速率的敏感性逐渐减弱,而峰值应力对应变速率的敏感性却呈先减弱后又显著增强的趋势。提高应变速率可加快动态再结晶进程,但高速变形初期产生更多的粗大 孪晶,不利于完全再结晶而导致稳态时的再结晶体积分数反而较低;在中低应变速率下动态再结晶以晶界弓出形核为主,而在高应变速率下则主要通过孪晶分割来进行;由应变速率引起变形机制的变化是导致不同动态再结晶行为的原因。
孪晶,不利于完全再结晶而导致稳态时的再结晶体积分数反而较低;在中低应变速率下动态再结晶以晶界弓出形核为主,而在高应变速率下则主要通过孪晶分割来进行;由应变速率引起变形机制的变化是导致不同动态再结晶行为的原因。
关键词:AZ61镁合金;高温变形;应变速率;动态再结晶;孪晶
中图分类号:TG 146.2 文献标志码:A
Influence of strain rate on dynamic recrystallization behavior of AZ61 magnesium alloy
YANG Xu-yue1, 2, ZHANG Zhi-ling1, ZHANG Lei1, WU Xin-xing1, WANG Jun1
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Nonferrous Metal Materials Science and Engineering, Ministry of Education, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: The deformation and dynamic recrystallization behavior of magnesium alloy AZ61 were studied at 623 K and 3×10-5-3×10-1 s-1 by optical and SEM/EBSD metallographic observation. The results show that the flow stresses and the dynamic recrystallization behavior are dependent on strain rates. With the increase of the strain rate, the strain rate sensitivity becomes weaker for steady state stresses while the strain rate sensitivity for the peak stress decreases firstly then increases obviously. Increasing strain rate can accelerate the process of dynamic recrystallization and the development of coarse  twins which are harmful to get a complete recrystallization structure leading to the decrease of fractional recrystallization. Bulging mechanism for dynamic recrystallization nucleation operates mainly at lower strain rate, whereas the dynamic recrystallization substructure developed at higher strain rate is characterized by twin intersections. The difference of deformation mode leads to the operation of different mechanisms of dynamic recrystallization nucleation.
twins which are harmful to get a complete recrystallization structure leading to the decrease of fractional recrystallization. Bulging mechanism for dynamic recrystallization nucleation operates mainly at lower strain rate, whereas the dynamic recrystallization substructure developed at higher strain rate is characterized by twin intersections. The difference of deformation mode leads to the operation of different mechanisms of dynamic recrystallization nucleation.
Key words: AZ61 magnesium alloy; high temperature deformation; strain rate; dynamic recrystallization; twin
HCP结构的镁合金滑移系较少,低温塑性差,其变形多在高温下进行。与FCC结构的金属相比,镁合金的层错能较低,晶界扩散速度较高,更易发生动态再结晶[1]。利用动态再结晶细化晶粒可有效控制镁合金的组织和性能,在生产中具有非常重要的应用价 值[2-4]。
通常来讲,FCC结构的γ-Fe、Cu等低层错能金属的动态再结晶机制不随变形条件的改变而变化,而镁合金的动态再结晶机制却随着变形条件的不同而不 同[1, 5-11]。SITDIKOV和KAIBYSHEV[9]认为,纯镁在高压扭转和压缩变形时,在不同变形温度与变形量下分别发生了孪生动态再结晶、低温动态再结晶、连续动态再结晶、不连续动态再结晶;KAIBYSHEV和SITDIKOV[6, 10]也指出:纯镁在573 K变形时,在较低应变下同时发生孪生动态再结晶和连续动态再结晶,在较高应变下则只发生连续动态再结晶;GALIYEV等[11]认为ZK60镁合金在低温、中温、高温条件下动态再结晶的形核分别通过基面滑移与孪生、Friedel-Escaig 交滑移、位错攀移等方式进行,并指出由温度引起的不同变形机制导致再结晶机制的不同。对于应变速率,通常都是将其和变形温度一起作为Zener–Hollomon参数中的变量进行研究,利用此参数来确定变形条件与再结晶晶粒大小的关系[12-16],而有关应变速率对动态再结晶机制影响的研究目前还鲜见报道。对于实际生产来讲,提高应变速率意味着缩短生产周期,因此,在保证材料塑性的前提下,适当提高应变速率具有重要的经济意义;弄清楚应变速率和动态再结晶间的关系,在利用动态再结晶来改善镁合金的力学和加工性能时,具有重要的理论意义和实践价值。
本文作者采用光学显微镜、电子背散射衍射分析技术(EBSD),结合组织定量分析系统对微观组织进行了观测分析。从力学性能、显微组织演变和晶粒取向特征等方面对不同应变速率下AZ61镁合金的高温变形和动态再结晶行为进行了研究,探讨了应变速率对动态再结晶机制的影响规律。
1 实验
试验所选用的AZ61镁合金化学成分(质量分数,%)如下:Al 5.8,Zn 1.0,Mn 0.18,Cu 0.003,Mg余量。样品为直径8 mm×12 mm的挤压棒材,其轴向与挤压方向平行。样品在703 K退火6 h后,进行温度为623 K,应变速率为3×10-5~3×10-1 s-1的轴向压缩实验。当炉温调至加工温度时,将样品放入炉内静置10 min,然后进行压缩,达到一定变形后,5 s内将样品取出水淬。
将淬火样品沿压缩轴方向切成两部分,对剖面依次进行研磨、机械抛光和电解抛光,试样在6%(质量分数)苦味酸+94%甲醇溶液中侵蚀后,通过OLYMPUS光学显微镜观察显微组织。在组织定量分析中,将普通光学显微镜与图像分析仪结合起来组成组织定量分析系统,利用该系统配备的Analysis Imaging Processing 软件(以下简称为analySIS)处理光学显微镜下的显微组织图像,定量分析动态再结晶晶粒的体积分数。EBSD试样电解抛光后直接采用Sirion 200型场发射SEM和配置的美国TSL公司的OIM Data Collection 5.3及OIM Analysis 5.3软件对其取向进行观测和分析。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 高温单向压缩力学行为
图1所示为AZ61镁合金在623 K时不同应变速率下压缩时的真应力—真应变曲线。由图1可以看出:各曲线中应力值随着应变量的增大先增大后降低,均呈单峰型曲线;随着应变速率的增大,峰值应力及峰值应变都明显增大,同时材料进入稳态变形时的应变量也逐渐变大。这些都与FCC金属的动态再结晶特征十分相似[17]。但当应变速率为3×10-1 s-1时,曲线的变化与其他曲线又存在明显差别:材料屈服后经历了急剧加工硬化和急剧软化过程,而在其它中低应变速率下加工硬化和软化过程都较为平缓。
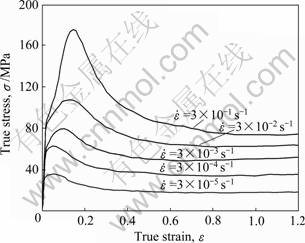
图1 AZ61镁合金在623 K、不同应变速率下变形时的真应力—真应变曲线
Fig.1 True stress—true strain curves of AZ61 Mg alloy deformed at 623 K and different strain rates
图2所示为峰值应力σp和稳态流变应力σss与应变速率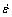 的关系。由图2可以看出,
的关系。由图2可以看出,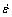 越高,σp和σss也越大,但二者增大的幅度却各不相同;随着
越高,σp和σss也越大,但二者增大的幅度却各不相同;随着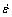 增大,σss对
增大,σss对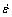 的敏感性逐渐减弱;σp对
的敏感性逐渐减弱;σp对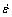 的敏感性先减弱后又显著增强,可明显分成3个阶段,各阶段对应的应力指数n分别为4.1、10.1和4.4。本实验条件下AZ61镁合金的流变应力表现出不同的速率敏感性,这很可能是由于不同应变速率下材料的变形机制不同引起 的[18]。以下选取3×10-3 s-1和3×10-1 s-1为代表进行微观组织研究。
的敏感性先减弱后又显著增强,可明显分成3个阶段,各阶段对应的应力指数n分别为4.1、10.1和4.4。本实验条件下AZ61镁合金的流变应力表现出不同的速率敏感性,这很可能是由于不同应变速率下材料的变形机制不同引起 的[18]。以下选取3×10-3 s-1和3×10-1 s-1为代表进行微观组织研究。
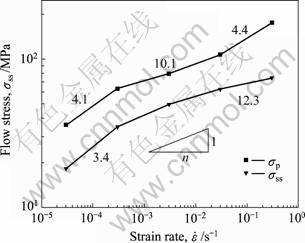
图2 应变速率对AZ61镁合金峰值应力σp和稳态流变应力σss的影响
Fig.2 Effect of strain rate on peak and steady state stresses of AZ61 Mg alloy deformed at 623 K
2.2 高温压缩变形过程中显微组织演化
图3所示为AZ61镁合金在623K时不同应变速率下变形后的显微组织。由图3可以看到,在应变速率为3×10-3 s-1下变形至真应变ε=0.15时(见图3(a)),多数原始晶界已发生凹凸,在锯齿状晶界以及晶界三叉节点处产生了一定量的动态再结晶晶粒;随着变形量的增大(见图3(c)),动态再结晶晶粒进一步增多,再结晶晶粒尺寸也稍有增大;继续变形至ε=0.5时,绝大多数粗大的原始晶粒已被细小的再结晶晶粒所取代(见图3(e))。在应变速率为3×10-1 s-1变形至ε=0.15时(见图3(b)),与图3(a)不同,绝大多数晶粒中产生了类似孪晶的带状组织,而原始晶界并没有出现凹凸现象,仅可看到非常少量的再结晶晶粒;但当ε达到0.3时(见图3(d)),就迅速发生了大范围动态再结晶;继续变形至ε=0.5时(见图3(f)),再结晶晶粒面积变化不大,组织中仍有少量未发生再结晶的粗大晶粒。比较图 3(e)和3(f)可知,在较低应变速率下变形时,动态再结晶进行得更加彻底,组织也更加均匀。
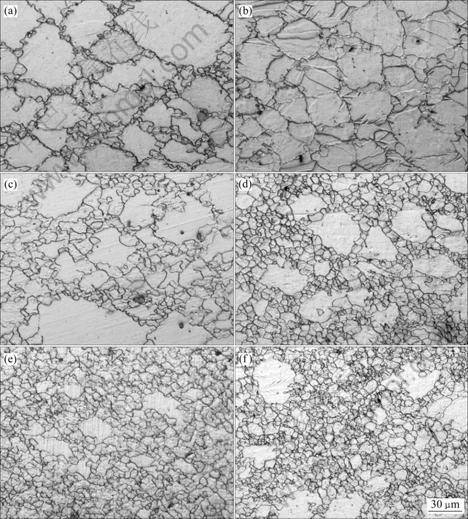
图3 AZ61镁合金在623 K、3×10-3~3×10-1下压缩变形至不同真应变时的显微组织
Fig.3 Microstructures of AZ61 Mg alloy deformed to different true stains at 623 K and 3×10-3-3×10-1 s-1: (a) ε=0.15, 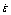 =3×10-3 s-1; (b) ε=0.15,
=3×10-3 s-1; (b) ε=0.15, 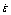 =3×10-1 s-1; (c) ε=0.3,
=3×10-1 s-1; (c) ε=0.3, 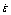 =3×10-3 s-1; (d) ε=0.3,
=3×10-3 s-1; (d) ε=0.3, 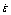 =3×10-1 s-1; (e) ε=0.5,
=3×10-1 s-1; (e) ε=0.5,  =3×10-3 s-1; (f) ε=0.5,
=3×10-3 s-1; (f) ε=0.5,  =3×10-1 s-1
=3×10-1 s-1
2.3 组织定量分析
为了更准确地分析不同应变速率下动态再结晶的特点,采用Analysis定量分析系统进行了定量分析。将图3(a)、(c)和(e)对应的再结晶晶粒与原始晶粒进行分类,其结果如图4所示,并准确获取再结晶晶粒尺寸和体积分数等信息,为进一步分析其晶粒尺寸变化与再结晶速率变化提供了可靠的判据。对图3进行处理后,绘制了如图5所示的不同应变速率下动态再结晶体积分数与真应变的关系曲线。由图5可以看到,AZ61镁合金在进入稳态变形之前,高应变速率下的动态再结晶速率比中低应变速率下的明显要快,但在稳态时的再结晶体积分数仅为70%;中低应变速率时,进入稳态变形前的动态再结晶速率虽然较为缓慢,但在稳态下的体积分数达90%以上。可见,提高应变速率可加快变形初期的动态再结晶进程,但不利于获得完全再结晶组织。
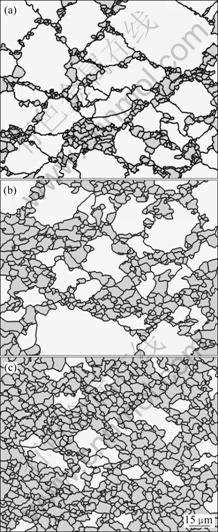
图4 AZ61镁合金在623 K、3×10-3 s-1下变形至不同真应变时的定量组织
Fig.4 Quantitative microstructures of AZ61 Mg alloy deformed to different stains at 623 K and strain rate of 3×10-3 s-1: (a) ε=0.15; (b) ε=0.3; (c) ε=0.5
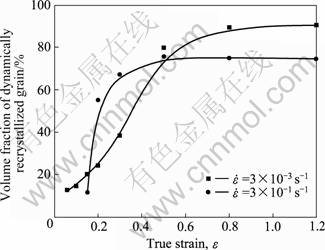
图5 AZ61镁合金在不同应变速率下变形时的动态再结晶体积分数与真应变的关系曲线
Fig.5 Relationship between volume fraction of dynamically recrystallized grains of AZ61 Mg alloy deformed at 623 K and 3×10-3-3×10-1 s-1 and true strain
图6所示为AZ61镁合金在3×10-3 s-1和3×10-1 s-1下变形至峰值应变时的EBSD分析结果。其中,图6(a)和(b)所示为以EBSD菊池带绘制的衬度图;图6(c)、(d)、(e)和(f)所示分别为沿图6(a)和(b)中直线L1、L2、L3和L4上的取向变化(扫描步长为0.4 μm),其中θ表示横线上的点与点之间的相对取向差,Σθ则表示扫描中各点相对于起始点的累积取向差。
由图6(a)可看出,在3×10-3 s-1时,细小的再结晶晶粒主要分布在锯齿状晶界以及晶界三叉节点处,同时,在部分原始晶粒内部有低角度变形带产生,其界面的相对取向差都在0~3°范围内,累积取向差小于7°(见图6(c)和(d)),该变形带也可称为扭折带[19],它是在主滑移系受阻时,滑移面发生弯折而形成的低角度位错界面,其形成与晶体取向、变形温度和变形程度密切相关[20]。这些低角度变形带只能垂直于晶粒基面产生[20],随着变形量的增加,其界面取向差急剧增大,最终形成大角度晶界,将原始晶粒分割细化了[19]。由此可见,在中低应变速率时,动态再结晶以晶界弓出形核为主,通过变形带来分割细化晶粒也是其动态再结晶的重要方式。

图6 AZ61镁合金不同应变速率下变形至峰值应变时组织的EBSD分析结果
Fig.6 EBSD analysis results of AZ61 Mg alloy deformed to peak strain at different stain rates and 623 K (CD is compression direction): (a) 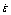 =3×10-3 s-1; (b)
=3×10-3 s-1; (b) 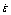 =3×10-1 s-1; (c)-(f) Point-to-point misorientation θ and cumulative misorientation Σθ measured along lines of L1(c), L2(d), L3(e) and L4(f)
=3×10-1 s-1; (c)-(f) Point-to-point misorientation θ and cumulative misorientation Σθ measured along lines of L1(c), L2(d), L3(e) and L4(f)
而在3×10-1 s-1下变形至峰值应变时,动态再结晶晶粒明显增多,大量细小的再结晶晶粒已经取代了部分原始晶粒(见图6(b))。图6(e)所示为沿再结晶区域中L3方向上的取向变化,可以看出,大部分细小晶粒界面取向差将近90°。图6(f)所示为沿原始晶粒内L4方向上的取向变化,其内部带状组织的界面取向差全部接近于90°,说明这些界面都是孪晶界,其对应的组织为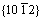 孪晶。变形前,大多晶粒的{0001}基面平行于压缩方向,但从图6(b)中可以看出,大部分晶粒的基面转至与压缩方向垂直,这可能是
孪晶。变形前,大多晶粒的{0001}基面平行于压缩方向,但从图6(b)中可以看出,大部分晶粒的基面转至与压缩方向垂直,这可能是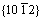 孪晶界迁移、扩展后占据整个晶粒所导致的[21]。通常认为单个
孪晶界迁移、扩展后占据整个晶粒所导致的[21]。通常认为单个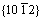 孪晶很难累积高的变形储存能,也就不可能成为有效的形核点,但在此应变速率下,孪生变形大范围发生,产生了较多的带状孪晶,部分孪晶间的相互交叉将原始晶粒分割为多个小晶粒[22],这极大地加快了动态再结晶的进程。由此可见,在高应变速率下,其动态再结晶主要是通过孪生及孪晶间的相互交叉分割细化晶粒来进行的。
孪晶很难累积高的变形储存能,也就不可能成为有效的形核点,但在此应变速率下,孪生变形大范围发生,产生了较多的带状孪晶,部分孪晶间的相互交叉将原始晶粒分割为多个小晶粒[22],这极大地加快了动态再结晶的进程。由此可见,在高应变速率下,其动态再结晶主要是通过孪生及孪晶间的相互交叉分割细化晶粒来进行的。
在高应变速率下,变形至峰值应变以后,由于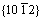 孪晶界的快速迁移,导致原始晶粒取向基本被
孪晶界的快速迁移,导致原始晶粒取向基本被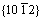 孪晶取向所取代,此时基面已转向垂直压缩方向,很不利于变形带的产生[20],因而,无法通过变形带来细化晶粒,使得其再结晶体积分数快速增至70%后基本不变。在中低应变速率下,由于变形初期很少发生孪生变形,孪晶分割晶粒作用不明显,使得再结晶过程相对缓慢;但是,大部分晶粒的基面平行于压缩方向,这有利于低角度变形带的形成,同时,随着变形量的增大,其密度和界面取向差不断增大[20],对晶粒的分割作用也逐渐增强,使得其再结晶体积分数较缓慢地增大直至90%以上。可见,由应变速率引起的变形机制的变化导致动态再结晶行为的不同是导致二者不同动态再结晶行为的原因。
孪晶取向所取代,此时基面已转向垂直压缩方向,很不利于变形带的产生[20],因而,无法通过变形带来细化晶粒,使得其再结晶体积分数快速增至70%后基本不变。在中低应变速率下,由于变形初期很少发生孪生变形,孪晶分割晶粒作用不明显,使得再结晶过程相对缓慢;但是,大部分晶粒的基面平行于压缩方向,这有利于低角度变形带的形成,同时,随着变形量的增大,其密度和界面取向差不断增大[20],对晶粒的分割作用也逐渐增强,使得其再结晶体积分数较缓慢地增大直至90%以上。可见,由应变速率引起的变形机制的变化导致动态再结晶行为的不同是导致二者不同动态再结晶行为的原因。
3 结论
1) AZ61镁合金在623 K压缩时,随应变速率的增大,稳态流变应力对速率敏感性逐渐减弱,而峰值应力对其敏感性却先减弱后又显著增强,可明显分为3个阶段。
2) 提高应变速率可加快变形初期的动态再结晶进程,但高速变形时产生了大量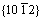 孪晶,其不利于形成低角度变形带,导致稳态时的再结晶体积分数反而较低。
孪晶,其不利于形成低角度变形带,导致稳态时的再结晶体积分数反而较低。
3) 在中低应变速率下,动态再结晶以晶界弓出形核为主;在高应变速率下动态再结晶则主要通过孪晶分割来进行。应变速率引起变形机制的变化是导致不同动态再结晶行为的原因。
References
[1] ION S E, HUMPHREYS F J, WHITE S H. Dynamic recrystallisation and the development of microstructure during the high temperature deformation of magnesium[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1982, 30(10): 1909-1919.
[2] RAVI KUMAR N V, BLANDIN J J, DESRAYAUD C, MONTHEILLET F, SU?RY M. Grain re?nement in AZ91 magnesium alloy during thermomechanical processing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 359(1/2): 150-157.
[3] TAN J C, TAN M J. Dynamic continuous recrystallization characteristics in two stage deformation of Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy sheet[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 339(1/2): 124-132.
[4] 杨续跃, 孙争艳, 张 雷. 室温多向多道次压缩变形制备亚微米和纳米级镁合金[J]. 金属学报, 2010, 46(5): 607-612.
YANG Xu-yue, SUN Zheng-yan, ZHANG Lei. Preparation of submicro and nanosized magnesium alloys by multiply compressed deformation[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(5): 607-612.
[5] LIU Z Y, BAI S, KANG S B. Low-temperature dynamic recrystallization occurring at a high deformation temperature during hot compression of twin-roll-cast Mg-5.51Zn-0.49Zr alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 60(6): 403-406.
[6] KAIBYSHEV R, SITDIKOV O. Dynamic recrystallization and mechanisms of plastic deformation[C]//TERRY R. Proceedings of ReX’96: The Third International Conference on Recrystallization and Related Phenomena. Monterey, CA (US): Monterey Institute of Advanced Studies, 1997: 203-209.
[7] XU S W, MATSUMOTO N, KAMADO S, HONMA T, KOJIMA Y. Dynamic microstructural changes in Mg-9Al-1Zn alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 61(3): 249-252.
[8] YIN D L, ZHANG K F, WANG G F, HAN W B. Warm deformation behavior of hot-rolled AZ31 Mg alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 392(1/2): 320-325.
[9] SITDIKOV O, KAIBYSHEV R. Dynamic recrystallization in pure magnesium[J]. Materials Transactions, 2001, 42(9): 1928-1937.
[10] KAIBYSHEV R, SITDIKOV O. On the role of twinning in dynamic recrystallization[J]. Fizika Metallovi Metallovedenie, 2000, 89(4): 70-77.
[11] GALIYEV A, KAIBYSHEV R, GOTTSTEIN G. Correlation of plastic deformation and dynamic recrystallization in magnesium alloy ZK60[J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49(7): 1199-1207.
[12] MAKSOUDA I A, AHMED H, R?DEL J. Investigation of the effect of strain rate and temperature on the deformability and microstructure evolution of AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 504(1/2): 40-48.
[13] BEER A G, BARNETT M R. Microstructure evolution in hot worked and annealed magnesium alloy AZ31[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 485(1/2): 318-324.
[14] WATANABE H, TSUTSUI H, MUKAI T, ISHIKAWA K . OKANDA Y, KOHZU M, HIGASHI K. Grain size control of commercial wrought Mg-Al-Zn alloys utilizing dynamic recrystallization[J]. Materials Transactions, 2001, 42(7): 1200-1205.
[15] FATEMI-VARZANEH S M, ZAREI-HANZAKI A, BELADI H. Dynamic recrystallization in AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 456(1/2): 52-57.
[16] GUAN Shao-kang, WU Li-hong, WANG Li-guo. Flow stress and microstructure evolution of semi-continuous casting AZ70 Mg-alloy during hot compression deformation[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2008, 18(2): 315-320.
[17] SAKAI T, JONAS J J. Dynamic recrystallization: Mechanical and microstructural considerations[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1984, 32(4): 189-209.
[18] KIM W J, CHUNG S W, CHUNG C S , KUM D. Superplasticity in thin magnesium alloy sheets and deformation mechanism maps for magnesium alloys at elevated temperatures[J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49(16): 3337-3345.
[19] YANG X Y, MURA H, SAKAI T. Dynamic evolution of new grains in magnesium alloy AZ31 during hot deformation[J]. Materials Transactions, 2003, 44(1): 197-203.
[20] 杨续跃, 姜育培. 镁合金热变形下变形带的形貌和晶体学特征[J]. 金属学报, 2010, 46(4): 451-457.
YANG Xu-yue, JIANG Yu-pei. Morphology and crystallographic characteristics of deformation bands in Mg alloy under hot deformation[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(4): 451-457.
[21] 李 萧, 杨 平, 孟 利, 崔凤娥. AZ31镁合金中拉伸孪晶静态再结晶的分析[J]. 金属学报, 2010, 46(2): 147-154.
LI xiao, YANG Ping, MENG Li, CUI Feng-e. Analysis of the static recrystallization at tension twins in AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2010, 46(2): 147-154.
[22] 杨续跃, 张 雷. 镁合金温变形过程中的孪生及孪晶交叉[J]. 金属学报, 2009, 45(11): 1303-1308.
YANG Xu-yue, ZHANG Lei. Twinning and twin intersection in AZ31 Mg alloy during warm deformation[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009, 45(11): 1303-1308.
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51071182)
收稿日期:2010-08-16;修订日期:2010-12-16
通信作者:杨续跃,教授,博士;电话:0731-88879195;E-mail: yangxuyue@mail.csu.edu.cn