


Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) 2248-2254
Effects of water hardness on selective flocculation of diasporic bauxite
LIU Wen-li, SUN Wei, HU Yue-hua
School of Minerals Processing and Bioengineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
Received 20 July 2011; accepted 7 March 2012
Abstract: The effect of electrolyte on settling behavior of kaolinite was studied. Effects of hard water on selective flocculation of diasporic bauxite was tested and the measures were taken to eliminate the effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in hard water. The results indicated that, not only the concentration of electrolyte ions but also the ionic valence of the electrolyte ions affects the settling behavior of kaolinite; hard water significantly affects its selective flocculation owing to Ca2+ and Mg2+; general dispersants could not eliminate the effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+. Self-made softening agent in our lab could weaken or eliminate the effects of hard water on flocculation processes. The results of molecular dynamics simulation show that softening agent molecules could restrict Ca2+ and prevent them from playing their roles, so as to eliminate the effects. The continuous pilot experiment results of bauxite flocculation were even better than those obtained in laboratory.
Key words: softening agent; hard water; bauxite; dispersant; flocculation
1 Introduction
Diasporic bauxite in China is characterized by high content of aluminum oxide and silica but low ratio of Al2O3 to SiO2 (average 5-6). Bauxite can be treated by Bayer process to produce aluminum oxide [1], unless the mass ratio of Al2O3 to SiO2 is larger than 10 [2,3], Bayer process could not economically produce aluminum oxide from diasporic bauxite because the high content of SiO2 caused high NaOH and energy consumption. Therefore, it is necessary to effectively remove aluminosiliate minerals such as kaolinite, pyrophllite and illite from bauxite to increase Al2O3/SiO2 ratio (A/S) of bauxite [4-6].
In diasporic bauxite ore, diaspore, the valuable mineral, accounts for only 70% of total mass, and the gangue minerals, such as kaolinite, pyrophyllite and illite, take up 30% mass yield. To separate these silicate minerals from diaspore, flotation provides a promising way. In previous studies, the direct flotation using oleic acid as collector [2,3] has been employed to de-silicate diasporic bauxite ore and proved to be an efficient method.
However, direct flotation can not solve such problems as dewatering and the effect on aluminum metallurgy [7,8]. Thereby, the reverse flotation with cationic collector was developed and some achievements were obtained.
Flocculation of fine particles using polymeric materials flocculant(s) and separation of such aggregates from particles of other component(s) in the dispersed phase is known as selective flocculation. Many researches on selective flocculating diaspore from diasporic bauxite have been carried out [9-12]. Some excellent results have been achieved in soft water system [13-16].
However, in Henan and Shanxi Provinces, China, where located the main diasporic bauxite deposits in China, the water is hard water containing a mass of Ca2+ and Mg2+ which will greatly affect the selective flocculation process of diasporic bauxite. The effects of electrolyte ions on dispersion and settling behaviors of diaspore and kaolinite directly affect the separation process efficiency of them.
This work aims to study the effects of the electrolyte in hard water on selective flocculation of diasporic bauxite, to explore the ways to eliminate or weaken the effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+ and discuss the elimination mechanism through molecule dynamics simulation method.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and reagents
Lumps of kaolinite were taken from Shanxi Province, China, and then crushed and ground in a laboratory porcelain mill. Particles with an average diameter of 3.85 μm were collected and used in settling tests. The chemical component of the material was analyzed, and the results are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Analytical results of chemical component for kaolinite (mass fraction, %)

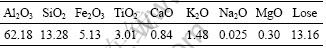
Bauxite ore used in these experiments were sampled from Henan deposits in China. Based on X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) analysis (Fig. 1), the compositions of the bauxite ore were diaspore (59.8%), illite (14%) and kaolinite (15%) (Table 2). The chemical composition of the bauxite ore is given in Table 3. The contents of Al2O3 and SiO2 in the bauxite ore are 62.18% and 13.28%, respectively, resulting in an A/S of 4.68.
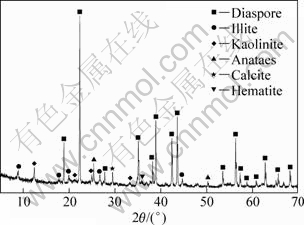
Fig. 1 XRD pattern of bauxite ore sample
Table 2 Minerals composition of bauxite ore (mass fraction, %)
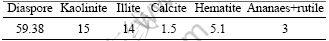
Table 3 Chemical composition of bauxite ore (mass fraction, %)
As the ion additive, ammonium chloride, calcium chloride and potassium chloride were analytical grade hydrochloric. Sodium carbonate, sodium hexameta- phosphate, sodium silicate, and sodium hydroxide were of analytical grade and used as dispersant. Softening agent was provided by our lab, whose molecular structure is shown in Fig. 2. Distilled water was used in settling tests of kaolinite.
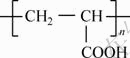
Fig. 2 Molecular formula of softening agent
2.2 Settling tests
In the settling tests, the kaolinite suspension was prepared by putting 3 g mineral sample into a glass beaker with 40 mL distilled water. The resultant suspension was stirred with an electromagnetic stirrer for 8 min at a speed of 1300 r/min for fully dispersion and 3 min at a speed of 300 r/min after adding flocculant or pH regulator. The suspension was poured gently into a 100 mL measuring cylinder, which was inverted 10 times. The cylinder was then kept immobilization on the level bed for 15 min, and the top 50 mL suspension was extracted by a latex tubing. The dried mass of solids was obtained after the bottom 50 mL suspension was leached. Results of the settling tests were reported in terms of aggregation efficiency (Ea), which was defined as:
Ea=m0/m×100% (1)
where M0 represents the dried mass of solids in the bottom 50 mL suspension; m represents the total mass of sample.
2.3 Flocculation experiments
The flocculation experiments of bauxite were carried out with soft water and hard water respectively to study the effects of hard water on selective flocculation process of bauxite.
The selective flocculation experiments of bauxite were carried out in a Lucite settling bucket of 20 cm in diameter with a capacity of 6000 mL according to the flow sheet shown in Fig. 3. Additional parameters on desilicating tests are also given in Fig. 3. For the desilicating balance calculations, desilicating products such as feed, tailings and concentrate were subjected to chemical analyses for determination of Al2O3 and SiO2.
2.4 Molecule dynamics simulation
The software package, Discover in Material Studio (Accelrys Software, Inc) with COMPASS force field, was used to study the process of softening agent restricting Ca2+ and Mg2+ to eliminate the negative effects on selective flocculation. Discover is a molecular simulation program in Material Studio, which provides a broad range of simulation methods to study molecular systems. The force fields in Discover provide the function of predicting the structure, energy, and properties of organic, inorganic, and biological systems as well as gas, liquid and solid. Molecular dynamics simulations generate information at microscopic level, including atomic positions and velocities.
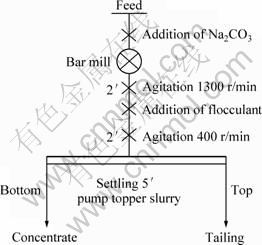
Fig. 3 Flow sheet of selective flocculation experiments
The isothermal-isometric molecular dynamics simulations (NVT-MD) [17,18] method was employed. In NVT ensemble, temperature change was controlled using Andersen method. Potential energy of each atom was derived from the COMPASS force field. The cutoff distance for van der Waals and electrostatic forces was 9.5 ?.
For simplification, molecular dynamics simulation was carried out in vacuum. The simulation box has dimensions of 100 ? × 100 ? × 100 ?, containing 5 softening agents, 5 carbonate ions, 5 calcium ions and 5 hydrogen ions. The number of these molecules is determined by the dosage of softening agent in practice. Total simulation time is 1000 ps, the time step is set to 1 fs, and the neighbor list updated every 5000 steps. The last 50000 steps were used for the analysis of softening mechanisms of softening agent.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Effects of electrolyte on dispersion and settling behavior of kaolinite
The effects of electrolyte on the settling behavior of kaolinite are presented in Fig. 4. Under the given conditions the effects of cations on colloidal stability are significant. Figure 4 indicates a strong increase of sediment yield of particles with increasing ionic concentration of the solution. When the concentration of cations reaches a certain value, the sediment yield begins to decrease. What is more, this significant increase depends not only on the ionic concentration but also on the valence of the cations. The trivalent Al3+ is most effective in aggregating the kaolinite particles, and the divalent Ca2+ ions are more effective than the monovalent Na+. These results are consistent with the Hardy-Schultz theory. HUANG [14] and CHEN [15] obtained the similar results.
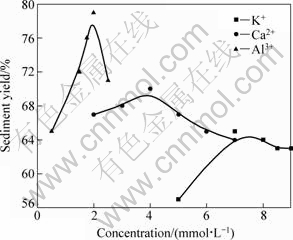
Fig. 4 Effects of electrolyte on settling behavior of kaolinite (Suspension concentration: 3%; Settling time: 15 min; Natural pH)
3.2 Effects of water hardness on selective flocculation
Different water sources were used in the experiments to study the effects of water hardness on selective flocculation processes of diasporic bauxite. The water samples were collected respectively from Changsha of Hunan Province and Zhengzhou of Henan Province, China. The analysis results from the Water Quality Monitoring Center of Changsha are shown in Table 4.
Table 4 Water quality monitoring results
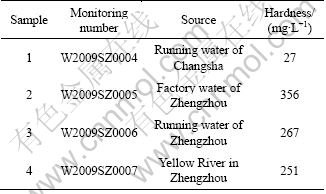
Table 5 presents the results of flocculation with different water sources, in which water hardness plays a negative role in selective flocculation process. In hard water samples the recovery and A/S of concentrate are especially lower than those in soft water samples.
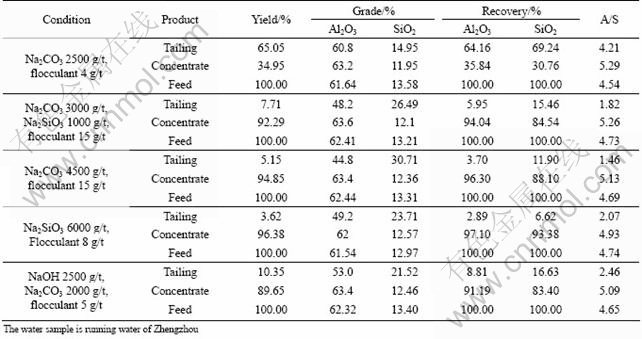
Incomplete dispersion of the bauxite particles is regarded as an important reason for the failure of the selective flocculation processes. As we all know, complete dispersion is the premise of selective flocculation process. Several dispersants were adopted in the flocculation experiments in hard water for complete dispersion of the particles. The results are listed in Table 6.
Plenty of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in water would occupy the active site on flocculant molecular and reduce their efficiency [19,20], leading to the competitive adsorption between ions and mineral particles.
From the results, we can see that the dispersants have positive effects on dispersion of particles in hard water since the recovery of concentrate is higher. The dispersion efficiency of the combination of sodium carbonate and sodium silicate is the best. However, it also should be noticed that the A/S of concentrate is still low due to the effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+. Dispersants could make the mineral particles completely disperse but could not eliminate the effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in hard water.
When the dispersants are added in hard water, Na2CO3, Na2SiO3 and NaOH would react with Ca2+ and Mg2+ and generate precipitates such as CaCO3, MgCO3, Ca(OH)2. The chemical reaction equations are shown as follows:
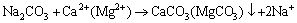 (2)
(2)
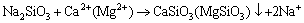 (3)
(3)
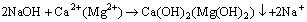 (4)
(4)
These precipitate particles in water tend to be adsorbed on flocculant molecule and prevent the mineral particles from being adsorbed. Since the precipitate particles have tiny size, they could be adsorbed on flocculant molecule prior to mineral particles.
Table 5 Results of flocculation with different water source
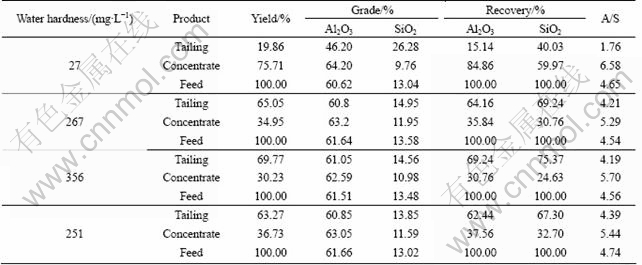
Table 6 Selective flocculation experiments using different dispersants in hard water
3.3 Effects of water softening agent on selective flocculation
In order to prevent Ca2+ and Mg2+ from reacting with dispersants and generating precipitate, before the addition of dispersants, some actions should be taken to eliminate the activity of Ca2+ and Mg2+.
Softening agent is a kind of water treatment agent for hard water. The mechanism of softening water is reaction with Ca2+ and Mg2+ through complexation or chelation. These reactions could restrict Ca2+ and Mg2+, but could not generate precipitate. Polyacrylate is a kind of softening agent made in our lab, which was used for hard water treatment. The results are shown in Table 7.
The addition of polyacrylate made a higher A/S and recovery of concentrate in hard water. It also indicates that inadequate or superfluous dosage of softening agent wouldn’t produce the desired results in these tests, and an appreciate A/S and recovery of concentrate could be obtained only at a certain dosage.
At an inadequate dosage, the effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+ in hard water could not be eliminated. When softening agent is excessively added, the redundant molecules are adsorbed on the diaspore particles. The process could obstruct the flocculant molecule to adsorb on diaspore particles, and affect the recovery and A/S of concentrate.
The mechanism of the softening agent is considered that the oxygen atoms of softening agent molecule react with Ca2+ and Mg2+ prior to the breaking bond on mineral particles surface. So appropriate quantity could completely restrict the freedom of Ca2+ and Mg2+ and no redundant molecule would affect the mineral particles. To verify the inference, the molecule dynamics simulation was carried out, and the results will be exhibited in the following section. The reaction formula is shown below:
 (5)
(5)
3.4 Continuous pilot experiment
Continuous pilot experiment was carried out according to the flow sheet shown in Fig. 5. Water used in this experiment was factory water from Zhengzhou shown in Table 3. Pretreatment of the water was carried out before it flew into the flocculation process. After 13 shifts, the average results obtained for each shift are shown in Table 8. The A/S of the concentrate increased from 4.71 to 6.69, and the recovery of Al2O3 was 81.25%. These results are even better than those obtained in laboratory.
3.5 Molecule dynamics simulation
Molecule dynamics simulation can reveal the effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+ on selective flocculation process of softening agent.
Figures 6 and 7 show the beginning state and final state of dynamics simulation of Ca2+ adsorbing on polyacrylate.
Table 7 Selective flocculation experiments using softening agent
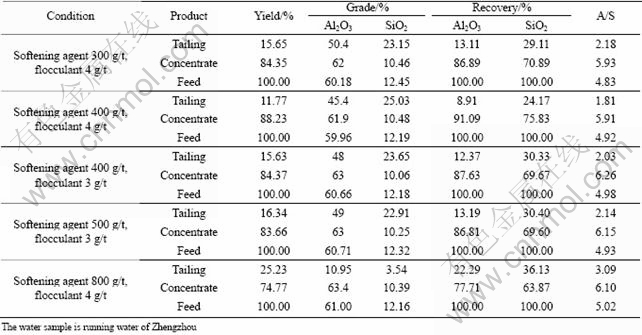
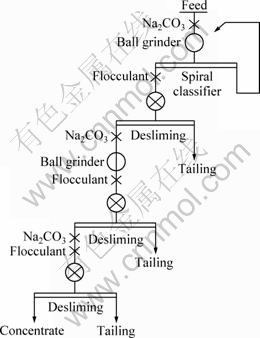
Fig. 5 Flow sheet of continuous pilot experiment
Table 8 Average results of shift work in continuous pilot experiment
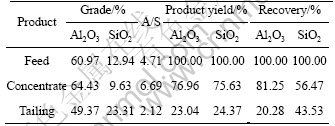
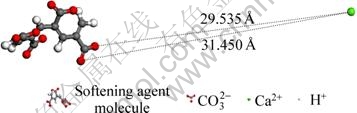
Fig. 6 Distance between softening agent molecule and Ca2+ at beginning state
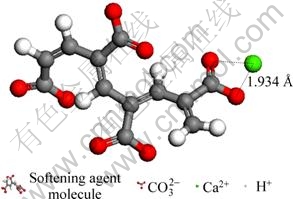
Fig. 7 Distance between softening agent molecule and Ca2+ at final state
At the beginning, Ca2+, CO32- and polyacrylate molecules are dispersant. After dynamics simulation, per Ca2+ is restricted by one polyacrylate molecule, which explains how polyacrylate eliminates the hard water effects.
From Fig. 6 and Fig. 7, we could see that at the beginning the distance between the two oxygen atoms (belong to the carboxyl of softening agent molecule) and Ca2+ are respectively 29.535 ? and 31.450 ? and at the final state (the stable state), these distance are 1.9 ? and 1.934 ?, which shows that Ca2+ and softening agent molecules can make a stable chemical bond, so Ca2+ is restricted by softening agent molecules.
Figure 8 shows energy change in the simulation process. The energy increasingly blows down till to a steady value. Therefore, at the final state the system potential is the lowest, and the system is the steadiest.
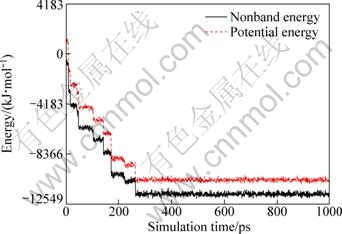
Fig. 8 Energy change in dynamics simulation
4 Conclusions
1) Electrolyte in solution severely impacts the settling behavior of kaolinite. The effects of electrolyte depend not only on the concentration but also on the ionic valence of the electrolyte ion. The order of ions effect on the settling behavior of kaolinite is Al3+>Ca2+>K+. Settling velocity of particles is faster with the increase of ionic concentration.
2) Hard water greatly affects the flocculating process due to Ca2+ and Mg2+. The same dosage of dispersant addition as that in soft water system could not fully make the particles disperse. Although particles fully dispersed with heavy addition of dispersants, the flocculating processes performed unselectively.
3) Certain softening agent could eliminate or weaken the effects of hard water on flocculating processes. Self-made softening agent performed well in these tests, since the A/S and recovery of concentrate were appreciating.
References
[1] JIANG Hao, HU Yue-hua, WANG Dian-zuo, QIN Wen-qing, GU Guo-hua. Structure of the adsorbed layer of cationic surfactant at dispore-water interface [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2005, 34(4): 500-501. (in Chinese)
[2] OUYANG Jian, LU Shou-ci. Character and processing research of Chinese bauxite resource [J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resource, 1995, (2): 24-27. (in Chinese)
[3] LIU Zhong-fan. Outlook of Chinese bauxite resource [J]. Light Metals, 2001(2): 4-9. (in Chinese)
[4] LU Yi-ping, QIU Guan-zhou, MILLER J D. Aggregation/dispersion of ultrafine silica in flotation agent solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2001, 11(5): 768-770.
[5] WANG Yu-hua, HU Yue-hua, LIU Xiao-wen. Flotation de-silicating from diasporic-bauxite with cetyl trimethylammonium bromide [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2003, 10(4): 324-328.
[6] ZHANG Guo-fan, FENG Qi-ming, LU Yi-ping, LIU Guang-yi, OU Le-ming. Effect of sodium hexametapho sphate on flotation of bauxite [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2001, 32(2): 127-130. (in Chinese)
[7] HU Yue-hua, JIANG Hao, QIU Guan-zhou. Solution chemistry of flotation separation of diaspore bauxite [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2000, 11(1): 125-130. (in Chinese).
[8] LI Hai-pu, HU Yue-hua, JI Yu-ren. Interaction mechanism between modified starchs and aluminum-silicate minerals [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2001, 11(4): 697-701. (in Chinese)
[9] READ A D. Selective flocculation separations involving hematite [J]. Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metallurgy: Section C, 1971, 80: 24-31.
[10] MOUDGIL B M, MATHUR S. Removal of dolomite and silica from apatite by selective flocculation [J]. Minerals and Metallurgical Processing, 1994, 11(4): 217-222.
[11] ATTIA Y A. Development of a selective flocculation process for a complex copper ore [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1977, 4(3): 209-225.
[12] WEISSENBORN P K, WARREN L J, DUNN J G. Optimization of selective flocculation of ultrafine iron ore [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1994, 42(3-4): 191-231.
[13] SUN Wei, LIU Wen-li, HU Yue-hua. Effect of anion macromolecular flocculant on selective flocculation of diaspore [C]//Proceeding of XXIV International Mineral Processing Congress. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 1352-1357.
[14] HUANG Chuan-bing. Study on selective flocculation separation of bauxite [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2006. (in Chinese)
[15] CHEN Xing-hua. Efficient dispersion and selective desliming of bauxite [J]. Changsha: Central South University, 2006. (in Chinese)
[16] WANG Dian-zuo. Flotation reagents—Fundamentals and application [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1982: 224-226. (in Chinese)
[17] SCHWENK C F, LOEFFLER H H, RODE B M. Dynamics of the salvation process of Ca2+ in water [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2001, 349: 99-103.
[18] CHEN Yi-jian, XU Gui-ying, YUAN Shi-ling, SUN Hai-ying. Molecular dynamics simulations of AOT at isooctane/water interface [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physico Chem Eng Aspects, 2006, 273: 174-178.
[19] YANG Ying, MA Fang, LI Fen, YAN Wan-ru. Flocculation morphology of bioflocculant and its influence factors [J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2009, 37(12): 91-94. (in Chinese)
[20] YANG Ying, MA Fang, WANG Qin. Research on effect of flocculation morphology of bionocculant by Ca2+ [J]. Journal of Harbin University of Commerce: Natural Sciences Edition, 2006, 22(6): 41-43. (in Chinese)
水的硬度对铝土矿选择性絮凝的影响
刘文莉,孙 伟,胡岳华
中南大学 资源加工与生物工程学院,长沙 410083
摘 要:通过絮凝实验和分子动力学模拟的方法,研究硬水中Ca2+、Mg2+ 离子对铝土矿选择性絮凝的影响。结果表明:除了电解质浓度,电解质离子的价态也对选择性絮凝产生影响;硬水中的Ca2+和Mg2+ 离子显著地选择絮凝,且普通的分散剂不能减弱这些影响。实验室自制的软水剂可以削弱甚至消除这些影响。分子动力学模拟结果显示,软水剂可以限制Ca2+,防止他们发生作用,因此可以消除影响。铝土矿连续絮凝实验结果好于实验室实验结果。
关键词:软水剂;硬水;铝土矿;分散剂;絮凝剂
(Edited by YUAN Sai-qian)
Foundation item: Project (2005CB623701) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: SUN Wei; Tel: +86-731-88830623; E-mail: sunmenghu@126.com
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61456-8