文章编号: 1004-0609(2006)06-0976-06
碳/碳化硅燃气舵的烧蚀及抗热震性
潘育松1, 2, 徐永东1, 陈照峰1, 成来飞1, 张立同1, 熊党生2
(1. 西北工业大学 超高温结构复合材料国防科技重点实验室, 西安 710072;
2. 南京理工大学 材料科学与工程系, 南京 210094)
摘 要: 利用等离子电弧风洞烧蚀实验装置模拟燃气舵的服役环境, 考核了碳/碳化硅(C/SiC)燃气舵的烧蚀性能, 探讨了燃气舵的烧蚀机理, 采用平面薄板模型对燃气舵的抗热震性能进行了初步分析。 结果表明: 燃气流的流动方向与燃气舵二者之间的夹角对燃气舵线烧蚀率的影响较大, 材料的线烧蚀率从前端沿气流方向(垂直燃气舵)的最大值1.007mm/s下降至厚度方向(平行于燃气舵)的最小值0.052mm/s, 二者相差近20倍; 燃气舵的烧蚀机制主要是粒子侵蚀和机械剥蚀共同作用; 同时, 材料所受到的热应力是引起材料失效的主要原因。
关键词: C/SiC复合材料; 燃气舵; 烧蚀; 抗热震 中图分类号: TB332
文献标识码: A
Ablation and thermal shock resistance properties of C/SiC jet vane
PAN Yu-song1, 2, XU Yong-dong1, CHEN Zhao-feng1,
CHENG Lai-fei1, ZHANG Li-tong1, XIONG Dang-sheng2
(1. National Key Laboratory of Thermostructure Composite Materials,
Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xian 710072, China;
2. Department of Material Science and Engineering,
Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China)
Abstract: The ablation properties of C/SiC composites jet vane were evaluated using the plasma wind tunnel ablation equipment. The ablation mechanism of C/SiC composites was explored and the thermal shock-resistance of the jet vane was analyzed by plane flake board model. The results show that the angle between the plasma gas flowing direction and jet vane present great influence on the ablation of C/SiC composites. The linear ablation ratio of the composites decreases from the maximal value of 1.007mm/s at the front direction of jet vane to the minimal value of 0.052mm/s at the brim direction of the component. The difference value between these two ablation ratios is at a factor of about 20. The ablation mechanisms of components are particles erosion and mechanical denudation. Material failure is mainly caused by the thermal stress.
Key words: C/SiC composites; jet vane; ablation; thermal shock resistance
燃气舵是一种在火箭喷流中工作的特殊翼, 用于导弹的推力向量控制, 是一种最简单可靠的推力向量控制方式, 通常置于喷管出口的外部燃气流中, 通过控制它的偏转而达到改变喷流的方向。 早期的中程液体地-地导弹和运载火箭, 均采用石墨材料制作的燃气舵。 后来, 大型运载火箭和远程地-地导弹逐步发展起来, 燃气舵的升力已不能满足控制要求, 而被摆动喷管新技术取代。 随着地-地、 地-空、 舰-舰和反潜等战术固体垂直发射导弹的发展, 在控制上, 由于燃气舵方案具有许多优点而倍受设计师们青睐。 但是, 固体火箭发动机喷流不但有很高的温度和极强的腐蚀性, 同时, 为了消除燃烧振荡和提高发动机的比冲, 固体推进剂中一般添加大量的金属粉末。 在这些推进剂的燃烧产物中含有大量的Al2O3粒子, 它对燃气舵具有非常强的冲刷力。 石墨材料难以抵抗强大的冲刷力。 因此, 燃气舵必须采用高强度、 耐烧蚀和抗冲刷的难熔合金材料[1-7]。 虽然难熔金属材料具有抗烧蚀及抗热震等一系列优点, 但传统难熔金属材料的最大缺点是其密度太大, 从而影响火箭发动机的冲质比, 大大降低了火箭的工作效率。
C/SiC复合材料具有抗烧蚀、 抗腐蚀和耐冲刷等一系列优异的性能[8, 9]。 同时, 其最大的优点是密度低, 为传统难熔金属的1/9 ~ 1/10, 是一种优良的新型高温热结构材料。 当用于固体火箭发动机等高温热结构部件时, 可有效提高火箭发动机的工作效率。 德国宇航院已成功将C/SiC复合材料用于燃气舵[10], 而国内对此研究鲜有报道。 因此, 研究C/SiC复合材料燃气舵在固体火箭发动机喷流中的烧蚀性能十分必要。 基于以上目的, 本文作者对固体火箭发动机用C/SiC复合材料制备的燃气舵构件进行了地面模拟考核实验, 并对C/SiC复合材料燃气舵的烧蚀性能和烧蚀机理进行了分析; 同时对其抗热震性能进行了初步探讨, 为燃气舵的气动设计提供一定的实验数据。
1 实验
1.1 燃气舵的制备
C/SiC复合材料燃气舵由二维碳布迭层后通过化学气相浸渗法(CVI)工艺对其进行致密化制备而成。 CVI过程采用H2为载气, 通过鼓泡的方式将反应物CH3SiCl3引入到反应室内。 SiC的沉积条件: H2和CH3SiCl3混合摩尔比为10∶1, 沉积温度为1100℃[11, 12]。 图1所示为C/SiC复合材料燃气舵的实物形貌。
1.2 风洞烧蚀实验

图1 C/SiC复合材料燃气舵实物形貌图
Fig.1 Illustration of C/SiC composites jet vane
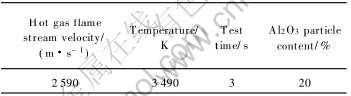
C/SiC复合材料燃气舵的烧蚀考核实验采用等离子电弧加热设备进行。 为模拟燃气舵的真实服役环境, 在电弧风洞产生的燃气流中加入Al2O3粒子, Al2O3粒子的平均粒径大于29μm, 小于100μm 。 C/SiC燃气舵的具体实验条件如表1所示。
表1 燃气舵风洞实验条件
Table 1 Test condition of jet vane
1.3 线烧蚀率测量
图1所示燃气舵的实物图中所标识的3个方向分别为测试燃气舵线烧蚀率的位置。 在每个方向上选定某一位置为参考位置, 利用千分尺分别测量燃气舵烧蚀前后边缘沿气流方向和前端沿气流方向相对于参考位置的变化, 将变化量除以烧蚀时间即得燃气舵在这两个方向上的线烧蚀率; 厚度方向的线烧蚀率为烧蚀前后燃气舵厚度的减少量随时间的变化率。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 燃气舵烧蚀性能
图2所示为C/SiC复合材料燃气舵烧蚀后在3个方向上的线烧蚀率Rd。 由图可知, 燃气舵沿各方向的线烧蚀率相差很大, 烧蚀极不均匀。 燃气舵在前端沿气流方向(Front direction)(图1)达到最大线烧蚀率1.007mm/s。 沿厚度方向(Parallel direction)的线烧蚀率为0.052mm/s, 二者相差近20倍。 边缘沿气流方向(Brim direction)的线烧蚀率为0.523mm/s, 其值介于前端沿气流方向和厚度方向之间。

图2 燃气舵的线烧蚀率
Fig.2 Linear rate of jet vane
燃气舵在不同方向上烧蚀率的差异主要与Al2O3粒子的侵蚀有关。 粒子侵蚀作用主要包含两个部分: 粒子侵蚀产生的烧蚀和粒子撞击产生的热增量。 其中, 粒子的侵蚀与粒子流动速度vp、 质量流率、 半径Rp以及撞击角(粒子流线与壁面的夹角)αp等有关。 由粒子侵蚀产生的线烧蚀率为[13]:

粒子撞击到壁面时产生的热增量为[13]:

式中 Cν为撞击热增量系数, vp, x为粒子垂直于撞击面的速度分量。
由式(1)可知, 粒子侵蚀产生的线烧蚀率与粒子的撞击角有关, 撞击角越大, 粒子侵蚀产生的线烧蚀率越大。 在燃气舵的前端正对气流方向, 撞击角约为90°; 边缘沿气流方向的撞击角约为45°; 厚度方向的撞击角几乎为0°。 由此可知, 由粒子侵蚀产生的线烧蚀率在燃气舵前端沿气流方向最大, 而在厚度方向最小。 由式(2)可知, 粒子撞击到壁面时产生的热增量与粒子的撞击角和垂直于撞击面的粒子速度分量有关, 撞击角和粒子的垂直速度分量越大, 粒子产生的热增量越大。 热增量的增大必然导致材料的线烧蚀率的增加。 在燃气舵的3个烧蚀方向上, 前端沿气流方向垂直于撞击面的粒子速度分量和撞击角最大; 边缘沿气流方向次之; 而厚度方向最小。 这与实验结果相一致。
同时, 燃气舵线烧蚀率的不同还和气体流向与材料接触面的夹角有关。 在燃气舵前端沿气流方向, 燃气流的方向与烧蚀面垂直, 在厚度方向, 气流方向与材料的烧蚀面相切, 根据流体的边界层理论和传热学可知[14, 15], 气流方向与材料的烧蚀面相切时, 材料表面受到的气动冲刷力比材料前端沿气流方向受到的冲刷力要小, 同时向材料内部传递的热量也小于材料前端沿气流方向传递的热量。 由于以上各种因素的作用, 导致了燃气舵在不同的方向上其烧蚀率存在较大的差异。
2.2 燃气舵烧蚀机理
2.2.1 颗粒侵蚀效应
为了模拟燃气舵的真实应用环境, 实验过程中加入了Al2O3粒子。 图3所示为燃气舵烧蚀后颗粒侵蚀的显微形貌。 从图3中可看到, 材料表面有被Al2O3粒子撞击后留下的凹坑。 由于燃气流中大量高速高能固体粒子对材料表面的强烈撞击, 此时, 粒子带有的能量经过碰撞, 很快将能量传递给材料, 使得材料的局部表面在短时间内达到很高的温度; 反过来, 这些粒子本身也受到实验材料的反作用而破碎及熔化, 从而进一步使材料表面温度升高。 同时, 凹坑的存在将会增加材料表面的粗糙度, 从而引起热量的积聚, 加剧材料的烧蚀。 另一方面, 表面粗糙度的增大将导致流场分布不均匀, 这导致在材料的表面附近易形成涡流, 涡流的形成容易引起局部热量的聚集, 而局部热量的聚集又加重了材料的烧蚀, 材料烧蚀的加重易形成更大的涡流, 由此形成一个相互耦合和循环的过程, 导致材料烧蚀慢慢加重。
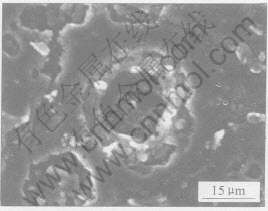
图3 Al2O3粒子侵蚀后的显微形貌
Fig.3 Microstructure of eroded jet vane by Al2O3 particle
2.2.2 机械剥蚀效应
燃气舵的烧蚀不仅有颗粒侵蚀, 同时还存在机械剥蚀现象, 纤维被气流冲刷而离开碳化硅基体, 如图4所示。 这主要是由于纤维和基体之间热膨胀系数存在差异而产生这种效应。 在高温燃气流作用下, 材料在极短时间内就会达到很高温度, 纤维和基体之间热膨胀系数的差异将产生热应力。 当它们所受热应力的强度超过纤维和基体之间的结合强度时, 纤维和基体将发生脱粘。 随后在高超音速燃气流的作用下, 纤维被冲刷走, 只留下基体。
2.3 燃气舵抗热震性能
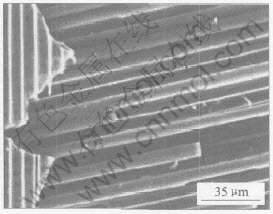
图4 纤维被剥蚀后的显微形貌
Fig.4 Microstructure of denudated fiber
烧蚀后C/SiC燃气舵的宏观形貌如图5所示。 由图可见, 燃气舵沿厚度方向出现层裂。 这主要与材料的抗热震性能和材料的层间剪切强度有关。 燃气舵热震行为可分为两个阶段: 燃气舵开始试车时的瞬间冲击加热阶段和试车后的冷却阶段。 在开始试车时的瞬间, 处于常温下状态的燃气舵突然遭受3200℃左右的燃气冲击, 温度以大于2000℃/s速度上升, 对燃气舵造成极大的热震。 这种瞬间导热, 由于热惯性的存在, 某处热扰动将不会瞬间为各点所感受, 即热量的传播速度较慢, 这样将会形成强烈的温度冲击波。 这种强烈的冲击波将会在材料内部形成很高的温度梯度, 使材料产生较高的动态热应力, 一旦超过材料的许用应力, 材料就会损伤[16, 17]。 同样, 在燃气舵试车后的冷却阶段材料内部也存在由温度梯度而产生的热应力。

图5 燃气舵烧蚀后的宏观形貌
Fig.5 Macrostructure of ablated jet vane
根据燃气舵的几何结构特点, 对燃气舵所受的热应力进行分析时, 可作为薄板来处理, 其受力情况示意图如图6所示。 在燃气舵突然加热和冷却的瞬间, 燃气舵y方向(对应厚度方向)的厚度较小, 垂直于y轴各平面上的温度相等; 但在x轴和z轴方向上, 燃气舵的表面和内部的温度有差异, 同时前后两个表面的胀缩受到限制(εx=εz=0), 因而产生热应力。 燃气舵y方向可以自由胀缩(σy=0)。
根据广义虎克定律:

联合式(3)、 (4)和(5) 解得

式中 ε为材料的应变; σ为材料所受的热应力; E为材料的弹性模量; α为材料的线膨胀系数; μ为泊松比; ΔT为材料所受的温差。
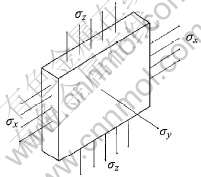
图6 薄板的热应力图
Fig.6 Thermal stress illustration of thin board
假设燃气舵在加热时, 舵板内任意一点的温度T是时间t和距离x的函数T=f(t, x)。 而在某一时刻任意点处的应力则决定于该点温度T和燃气舵在该时刻的平均温度Tav之间的差别, 根据式(6)很容易得出:
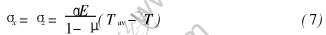
当表面温度突然改变时, 导致温度梯度和热应力的关系式(7)仍成立。 当燃气舵突然升至高温时, 温度分布呈抛物线状, 表面温度Ts比平均温度Tav高, 表面产生压应力, 中心温度Tc比平均温度低, 所以中心产生张应力。 根据以上分析, 燃气舵中最大热应力值σmax一般在表面及中心部位变化较大。 故要求其所受的热应力小于材料的极限强度σb, 式(7)经过变换可得材料中允许存在最大温差ΔTmax为

以上的分析只是从理论上求得了材料受热时所能承受的最大温差, 但是在真实的情况下极其复杂, 燃气舵部件是否出现热应力断裂, 与热应力σmax的大小有着密切的关系, 而材料所受的热应力又与材料的导热系数、 形状尺寸、 材料表面对环境进行热传递的能力等有关。 另外, 燃气舵是否出现热应力断裂还与热应力在燃气舵中的分布、 应力产生的速率和持续时间、 材料的均匀性、 以及原有的裂纹等情况有关。 因此, 不能简单认为ΔTmax就是材料允许承受的最大温度差。
从以上分析可知, 层间抗剪切强度较低是二维迭层C/SiC复合材料的典型缺陷, 难以抵抗复合材料在高温热震过程中所产生的强大热应力。 为了进一步提高复合材料燃气舵的层间抗剪切强度和抗热震性能, 必须改善纤维预制体的结构设计。
3 结论
1) C/SiC复合材料燃气舵沿气流不同方向的线烧蚀率存在很大的差异, 前端沿气流方向达到最大值1.007mm/s, 厚度方向达最小值0.052mm/s。 其线烧蚀率由高到低的顺序为: Rd(前端沿气流方向)>Rd(边缘沿气流方向)>Rd(厚度方向)。
2) C/SiC复合材料燃气舵的烧蚀机制是粒子侵蚀、 机械剥蚀和燃气冲刷共同作用。 粒子侵蚀对燃气舵的烧蚀性能具有很大的影响, 在不同的方向上, 粒子侵蚀对燃气舵线烧蚀率的贡献不同。
3) 从试车后燃气舵破坏的机理分析, 燃气舵在烧蚀过程中承受了很大热应力, 要成功应用C/SiC复合材料燃气舵必须改善纤维预制体的结构设计以进一步提高材料的层间剪切强度和抗热震性能。
REFERENCES
[1]高延玺, 金长江, 肖业伦. 推力矢量控制与推力矢量喷管[J]. 飞行力学, 1995, 13(2): 1-5.
GAO Yan-xi, JIN Chang-jiang, XIAO Ye-lun. Thrust vectoring control and thrust vectored nozzle[J]. Flight Dynamics, 1995, 13(2): 1-5.
[2]Bouscaurol A, Pietrzak M, de Fornel B. Comparison of Cartesian vector control and polar vector control for induction motor drives[J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 1998, 46: 325-337.
[3]刘志珩. 固体火箭燃气舵气动设计研究[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术, 1995, 216(4): 50-54.
LIU Zhi-heng. The aerodynamic design research of gas vane of solid rocket[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles, 1995, 216(4): 50-54.
[4]王鹏, 陈万春, 殷兴良. 空空导弹大角度姿态推力矢量控制研究[J]. 航天学报, 2004, 25(3): 142-146.
WANG Peng, CHEN Wan-chun, YIN Xing-liang. Large angle attitude thrust vector control an air-to-air missile[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2004, 25(3): 142-146.
[5]候清海. 浅述燃气舵气动测力实验方法[J]. 航空兵器, 2001, 6: 14-16.
HOU Qing-hai. Test method of measuring air dynamic force of jet vane[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2001, 6, 14-16.
[6]Costa Pereira N H, Borges J E. Study of the nozzle flow in a cross-flow turbine[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Siciences, 1996, 38(3): 283-302.
[7]张德雄, 李宏军. 近年固体火箭推进技术发展趋势[J]. 固体火箭技术, 1997, 27(4): 3-13.
ZHANG De-xiong, LI Hong-jun. A review of the recent advancements of solid rocket propulsion technology[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 1997, 27(4): 3-13.
[8]CHENG Lai-fei, XU Yong-dong, ZHANG Li-tong, et al. Corrosion of a 3D-C/SiC composite in salt vapor environment[J]. Carbon, 2002, 40: 877-882.
[9]YIN Xiao-wei, CHENG Lai-fei, ZHANG Li-tong, et al. Oxidation behaviors of C/SiC in the oxidizing environments containing water vapor[J]. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, A348: 47-53.
[10]EI-Hija A H, Krenkel W. Cost Analysis for the Manufacture of C/C-SiC Structural parts[C]. Krenkel W, Naslain R, Schneider H. Proceedings of High Temperature Ceramic Matrix Composites[C]. Viley VCH, 2001. 846-851.
[11]XU Yong-dong, ZHANG Li-tong. Three-dimensional carbon/silicon carbide composites prepared by chemical vapor infiltration[J]. J Am Ceram Soc, 1997, 80(7): 1897-1900.
[12]XU Yong-dong, ZHANG Li-tong`, CHENG Lai-fei, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of three-dimensional carbon/silicon carbide composites fabricated by chemical vapor infiltration[J]. Carbon, 1998, 36(7-8): 1051-1056.
[13]何洪庆. 固体火箭喷管烧蚀和传热的基本问题[J]. 推进技术, 1993(3): 22-28.
HE Hong-qing. Basic question of solid rocket motor nozzle ablation and thermal transmission[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 1993(3): 22-28.
[14]卞荫贵, 钟家康. 高温边界层传热[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986. 9.
BIAN Yin-gui, ZHONG Jia-kang. Thermal Transmission of High Temperature Boundary Layer[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1986. 9.
[15]杨世铭. 传热学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1997. 12.
YANG Shi-ming. Thermal Transmission[M]. Beijing: Senior Education Press, 1997. 12.
[16]宋桂明, 周玉, 王玉金, 等. 固体火箭发动机喉衬材料[J]. 固体火箭技术, 1998, 21(2): 51-55.
SONG Gui-ming, ZHOU Yu, WANG Yu-jin, et al. Throat materials for solid rocket motors[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 1998, 21(2): 51-55.
[17]牟科强, 徐克玷, 韦昂邦, 等. 几种高温材料抗燃气烧蚀性能研究[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 1995, 7(5): 89-91.
MOU Ke-qiang, XU Ke-dian, WEI Ang-bang, et al. Burn-off and erosion resistance of several high temperature materials to solid propellant[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 1995, 7(5): 89-91.
基金项目: 国防基础研究资助项目
收稿日期: 2005-10-25; 修订日期: 2006-03-06
通讯作者: 徐永东, 教授; 电话: 029-88494619; E-mail: ydxu@nwpu.edu.cn
(编辑何学锋)