镁合金“固溶强化增塑”理论的发展和应用
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报2019年第9期
论文作者:刘婷婷 潘复生
文章页码:2050 - 2064
关键词:镁合金;强度;塑性;固溶强化增塑
Key words:magnesium alloys; strength; ductility; solid solution strengthening and ductilizing
摘 要:镁是密排六方结构金属,滑移系较少,其基面滑移阻力比柱面和锥面滑移阻力低很多,基面滑移启动后其他滑移系很难启动,导致镁合金室温和低温的塑性变形能力较差。重庆大学等单位研究发现某些特定原子固溶在镁中既能阻碍基面位错滑移提高强度,又能通过缩小基面与非基面滑移阻力差距促进非基面滑移开启而改善塑性,达到同时提高镁合金强度和塑性的目的。重庆大学镁合金科研团队把这一结果发展为“镁合金固溶强化增塑”合金设计理论(Solid solution strengthening and ductilizing, SSSD)。这一合金设计理论在过去十几年中已成为解决镁合金强度和塑性平衡优化的一条新途径。重庆大学应用该理论开发了多种新型高性能镁合金,其中10多个新合金已批准为国家标准牌号合金和国际标准牌号合金。
Abstract: Mg has a HCP structure with few slip systems, and the slip resistance for basal slip is much lower than that of prismatic and pyramidal slip. It is generally difficult to activate non-basal slip at room and low temperature, resulting in a poor ductility and formability of magnesium alloys. Chongqing University and other institutions have found that the solution of certain elements in Mg can not only improve the strength by hindering the basal slip, but also improve the ductility by reducing the gap of slip resistance between basal slip and non-basal slip. According to these results, Chongqing University has proposed a theory of alloy design —— solid solution strengthening and ductilizing (SSSD) for magnesium alloy, which has become a new way to optimize the strength-ductility balance of magnesium alloys in the past decade. Using SSSD theory, Chongqing University has developed many new high performance magnesium alloys, among which over 10 alloys have been included in GB/T national standard and ISO international standard.
DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2019.09.12
刘婷婷1, 2,潘复生2
(1. 西南大学 材料与能源学院,重庆 400715;
2. 重庆大学 国家镁合金材料工程与技术研究中心,重庆 40044)
摘 要:镁是密排六方结构金属,滑移系较少,其基面滑移阻力比柱面和锥面滑移阻力低很多,基面滑移启动后其他滑移系很难启动,导致镁合金室温和低温的塑性变形能力较差。重庆大学等单位研究发现某些特定原子固溶在镁中既能阻碍基面位错滑移提高强度,又能通过缩小基面与非基面滑移阻力差距促进非基面滑移开启而改善塑性,达到同时提高镁合金强度和塑性的目的。重庆大学镁合金科研团队把这一结果发展为“镁合金固溶强化增塑”合金设计理论(Solid solution strengthening and ductilizing, SSSD)。这一合金设计理论在过去十几年中已成为解决镁合金强度和塑性平衡优化的一条新途径。重庆大学应用该理论开发了多种新型高性能镁合金,其中10多个新合金已批准为国家标准牌号合金和国际标准牌号合金。
关键词:镁合金;强度;塑性;固溶强化增塑
文章编号:1004-0609(2019)-09-2050-14 中图分类号:TG146.2 文献标志码:A
随着全球资源能源危机的加剧和环境负担的增加,世界各国制定了越来越严格的能源消耗和环境保护要求,汽车等燃油交通运输工具的轻量化已成为发展的必然趋势。镁合金是目前工业上得到有效应用的最轻的金属结构材料之一,镁密度仅为1.74 g/cm3,约为铝密度的2/3,钛密度的1/3,钢密度的1/4,同时镁合金还具有较高的比强度和比刚度、优良的减振性、易于回收利用等一系列优点,广受材料和机械工作者的关注,被誉为“21世纪重要的绿色工程金属结构材料”。此外,镁在地球上的储量丰富,约占地壳质量的2.35%,其含量在金属元素中仅次于铝和铁含量。我国是世界上镁资源最为丰富的国家,约占全球镁资源总量的50%以上。因此,合理地利用我国镁资源的优势、加快高性能镁合金研发、促进镁合金工程化并推广应用对我国具有重要战略意义[1-2]。
相比铝合金及合金钢,镁合金绝对强度低、塑性与成形性差、易腐蚀等基础性问题严重制约了镁合金材料的广泛应用。为解决这些难题,近十多年来国内外研究者们在提高镁合金强度、塑性、成形性和耐蚀性等方面做了大量的工作。在提升镁合金强度方面,大量的研究集中在使用时效析出相强化镁合金等方 面[3-20]。例如,经时效析出强化后的Mg-11Gd-4.5Y- 1Nd-1.5Zn-0.5Zr(质量分数,%)镁合金抗拉强度可达517 MPa,屈服强度达482 MPa,但断裂伸长率仅2%[21]。经时效后的Mg-10Gd-5.7Y-1.6Zn-0.7Zr(质量分数,%)镁合金屈服强度可达473 MPa,而断裂伸长率却不足10%[22]。从这些研究可以看出,第二相析出(包括长程有序相)强化镁合金的效果比较显著,但合金的塑性也因第二相的产生而大幅度下降,使得析出强化的镁合金在工业上的应用受到限制。在提升镁合金塑性和耐蚀性方面,重庆大学潘复生团队开发的无熔剂纯净化技术制备的高纯度镁合金在提高塑性的同时,也显著提高了镁合金的耐蚀性[23-24]。在提升镁合金成形性方面,针对镁合金塑性变形特性和产业技术需求,重庆大学国家镁中心系统发展了镁合金新型非对称加工技术原理与体系,包括镁合金板材新型非对称挤压加工[25]、镁合金板材新型非对称改性[26]、镁合金棒材新型非对称制备加工[27]等,大大地提高了镁合金板材和棒材的室温成形性能。此外,重庆大学开发出了具有显著晶粒细化效果的镁基Al2Y、Al2Nd、Al2Ce等细化剂,使镁合金铸态晶粒细化效率超过80%,冶金质量显著改善,合金的成形性能显著提升[28-31]。这些研究工作在提升镁合金强度、或塑性、或成形性上取得了显著成效,但在解决镁合金高强度和高塑性(或成形性)的合理配合上仍不能令人满意。
在合金设计方面,如何在提升镁合金强度的同时不损害塑性或在提高塑性的同时不牺牲强度,已成为国内外新型镁合金发展中的研究热点和重点。研究工作主要集中在两个方面:一方面,重点研究合金元素对镁层错能的影响和基面/非基面滑移变化的微观表现;另一方面,重点研究基面滑移阻力的提高对启动非基面滑移的影响。对第一方面的内容,NIE Jian-feng、单智伟等做了大量杰出工作[32],对后一方面的内容,重庆大学、西南大学等做了大量研究[33-34]。重庆大学潘复生团队等在研究合金元素对镁合金力学性能影响的过程中发现,某些特定原子固溶在镁中既能阻碍基面位错滑移,又能减小基面与非基面滑移阻力差异,使非基面滑移更容易开启,达到同时提高镁合金强度和塑性的目的,解决了镁合金塑性和强度的平衡优化问题。与国内外研究不同的是,这些发现重点突出了通过合金元素固溶缩小基面与非基面滑移阻力差距从而启动非基面滑移来提高镁合金塑性。针对这些发 现,潘复生团队提出了提高镁合金强度和塑性的合金设计新理论——“固溶强化增塑”(Solid solution strengthening and ductilizing, SSSD),并应用该理论成功开发了多种新型高性能镁合金。
1 镁合金塑性变形的特点
镁及镁合金的晶体结构为典型的密排六方结构(Hexagonal close-packed,简称HCP),理想的镁金属由密排面按照……ABABABAB……这样的顺序循环堆垛而成,镁晶体的晶格常数为a=3.21 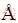 ,c=5.21
,c=5.21 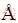 ,轴比c/a为1.623。镁合金与面心立方(奥氏体钢)和体心立方(铝合金、铁素体钢)金属的晶体结构不同,具有不同的滑移系与塑性变形机制[2]。
,轴比c/a为1.623。镁合金与面心立方(奥氏体钢)和体心立方(铝合金、铁素体钢)金属的晶体结构不同,具有不同的滑移系与塑性变形机制[2]。
在镁合金中,基面 滑移是最容易开动的滑移系,室温下的临界剪切应力(Critical resolved shear stress,CRSS)约为其他非基面滑移的1/100[35],因此,在室温和低温下镁合金塑性变形以基面滑移为主,如图1所示为镁单晶在不同温度下的临界剪切应力[36]。升高温度有利于启动非基面滑移,但会导致晶粒明显粗化。在室温条件下,基面
滑移是最容易开动的滑移系,室温下的临界剪切应力(Critical resolved shear stress,CRSS)约为其他非基面滑移的1/100[35],因此,在室温和低温下镁合金塑性变形以基面滑移为主,如图1所示为镁单晶在不同温度下的临界剪切应力[36]。升高温度有利于启动非基面滑移,但会导致晶粒明显粗化。在室温条件下,基面 滑移仅有两个独立滑移系,不满足Von-Mises屈服准则(即多晶体材料的均匀塑性变形至少需要5个独立的滑移系),更远低于面心立方和体心立方晶格的12个独立滑移系,这导致镁合金室温和低温塑性变形能力较差[37]。此外,两个独立滑移系均在同一个滑移面,无法协调沿着c轴方向的变形,且基面滑移临界剪切应力远低于柱面和锥面的,导致镁合金后续变形加工过程中极易产生基面织构,均匀成形能力较差,性能均匀性严重恶化。因此, 为了提高镁合金的均匀塑性变形能力,有必要通过对基面和非基面滑移阻力的调控,缩小基面与非基面滑移阻力之间的差距,促进非基面滑移开启,从而改善镁合金的塑性成形能力。
滑移仅有两个独立滑移系,不满足Von-Mises屈服准则(即多晶体材料的均匀塑性变形至少需要5个独立的滑移系),更远低于面心立方和体心立方晶格的12个独立滑移系,这导致镁合金室温和低温塑性变形能力较差[37]。此外,两个独立滑移系均在同一个滑移面,无法协调沿着c轴方向的变形,且基面滑移临界剪切应力远低于柱面和锥面的,导致镁合金后续变形加工过程中极易产生基面织构,均匀成形能力较差,性能均匀性严重恶化。因此, 为了提高镁合金的均匀塑性变形能力,有必要通过对基面和非基面滑移阻力的调控,缩小基面与非基面滑移阻力之间的差距,促进非基面滑移开启,从而改善镁合金的塑性成形能力。
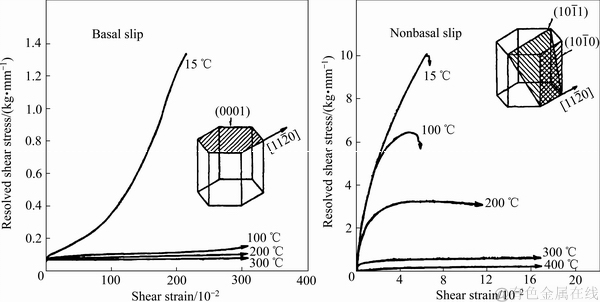
图1 不同温度下镁单晶的基面与非基面滑移的临界剪切应力[36]
Fig. 1 CRSS for basal and non-basal slip systems in magnesium at different temperatures[36]
2 “固溶强化增塑”合金设计理论的思路
在立方金属中,特别是在钢铁和铝合金材料中,固溶强化和析出强化一般都会降低材料塑性[38-39]。镁合金是六方晶体结构,析出强化降低塑性同样已得到大量的实验验证[4-7, 21, 40-41],但对固溶强化的研究却发现了一些新现象。自2002年以来,重庆大学潘复生团队等针对合金元素影响镁合金强度和塑性的机理做了大量研究,如Ag[42-43]、Nd[44-45]、Zn[46-47]、Mn[48-49]、Sn[32, 50]、Er[51-55]、Al[25, 56]、Y[57-58]、Ca[28, 59]、Ce[30, 60]、Li[31, 34]、Gd[61-62]、Sc[63]、Sr[64-65]等合金元素。在这些研究中,有关析出强化的研究都发现是合金的强度提高,塑性下降。重庆大学镁合金科研团队重点突出了元素固溶后基面与非基面滑移阻力变化如何影响塑性的研究。研究发现,某些特定元素原子固溶在镁中具有降低基面与非基面滑移阻力差异的独特作用,有利于非基面滑移的启动,进而提高镁合金的塑性。在2005年,潘复生及其合作者结合国内外研究工作提出了“固溶强化增塑”的合金设计思想,其主要思路见图2所示。
从图2可以看出,合金元素固溶在镁基体中,可增大或减小镁基面或非基面滑移阻力。当合金元素固溶后增大(或减小)基面和非基面的滑移阻力时,固溶体基面与非基面滑移阻力差值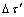 和镁基面与非基面滑移阻力差值
和镁基面与非基面滑移阻力差值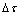 ,有
,有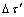 ≈
≈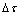 、
、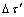 >
>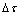 、
、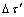 <
<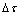 3种情况。当
3种情况。当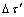 ≈
≈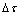 时(见图2(a)和(d)),元素固溶对基面与非基面滑移阻力差值的影响不大,并不能促进非基面滑移的开启,提高镁合金塑性;当
时(见图2(a)和(d)),元素固溶对基面与非基面滑移阻力差值的影响不大,并不能促进非基面滑移的开启,提高镁合金塑性;当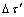 >
>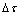 时(见图2(c),(f),(g)),元素固溶增大了基面与非基面滑移阻力差值,使非基面滑移的启动更为困难,不利于镁合金塑性的改善;当
时(见图2(c),(f),(g)),元素固溶增大了基面与非基面滑移阻力差值,使非基面滑移的启动更为困难,不利于镁合金塑性的改善;当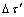 <
<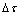 时(见图2(b),(e),(h)),元素固溶减小了基面与非基面滑移阻力差值,有利于非基面滑移的开启,镁合金均匀塑性变形能力提高。而基面滑移阻力的减小不利于合金强度的提升,图2(e)所示情况只能改善塑性,但会损失一定的强度,使得材料的工业应用受限。图2(b)和图2(h)所示为合金设计中应该追求的方向,其中图2(h)所示条件最有利于同时提高强度和塑性。因此,当设计合金成分时,选用能够使基面滑移阻力增加且基面与非基面滑移阻力差值减小的合金元素,既可以产生强化提高合金强度,又可以促进非基面滑移提高合金塑性,达到同时提高合金强度和塑性的效果,实现了“固溶强化增塑”的合金设计目的。
时(见图2(b),(e),(h)),元素固溶减小了基面与非基面滑移阻力差值,有利于非基面滑移的开启,镁合金均匀塑性变形能力提高。而基面滑移阻力的减小不利于合金强度的提升,图2(e)所示情况只能改善塑性,但会损失一定的强度,使得材料的工业应用受限。图2(b)和图2(h)所示为合金设计中应该追求的方向,其中图2(h)所示条件最有利于同时提高强度和塑性。因此,当设计合金成分时,选用能够使基面滑移阻力增加且基面与非基面滑移阻力差值减小的合金元素,既可以产生强化提高合金强度,又可以促进非基面滑移提高合金塑性,达到同时提高合金强度和塑性的效果,实现了“固溶强化增塑”的合金设计目的。
图2 “固溶强化增塑”合金设计理论思路
Fig. 2 Thoughts of designing alloys by solid solution strengthening and ductilizing
3 “固溶强化增塑”合金设计理论的理论计算
早期研究表明[66],对密排六方结构的镁来说,c/a轴比的变化将会改变原子间距,激发非基面滑移,从而提高镁合金的塑性。而后有越来越多的研究发现[67-70],轴比的增大或减小与开启非基面滑移的难易程度没有对应关系,由此可见,轴比的变化并不是激发非基面滑移的关键因素。
层错是晶体中普遍存在的材料本征特征,层错能则是对应于特定的相对滑动位移所形成的层错所需要的能量。近年来,大量研究认为层错能的变化与基面、非基面滑移系的启动及合金塑性变形能力有关[71-76]。重庆大学潘复生团队研究了多种固溶原子对镁层错能的影响,研究发现合金元素Al、Bi、Ca、Dy、Er、Ga、Gd、Ho、In、Lu、Nd、Pb、Sm、Sn、Y、Yb可明显降低I1层错能;合金元素Ca、Dy、Er、Gd、Ho、Lu、Nd、Sm、Y、Yb能大幅度降低柱面滑移系的非稳定层错能,有利于降低柱面位错滑移的临界分切应力;合金元素Ag、Al、Ca、Dy、Er、Ga、Gd、Ho、Li、Lu、Nd、Sm、Y、Yb、Zn有利于锥面滑移系的开启并提高镁合金的本征塑性[77-79]。
然而,这些有关层错能的研究都基于0 K下的第一性原理计算,为了更好地从理论上解释层错能与基面、非基面滑移系的启动及合金塑性变形能力之间的关系,有必要将0 K下对层错能的研究推广至有限温度。
潘复生团队[80]利用分子动力学模拟,采用次近邻修正嵌入原子势方法描述原子间的相互作用,研究了不同温度下多种合金元素对镁层错能的影响。对固溶含量为0~3%(摩尔分数)的Mg-Al、Mg-Zn和Mg-Y这3种合金,研究了基面 、基面
、基面 、柱面
、柱面
 和锥面
和锥面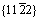
 4个滑移系在0~500 K的温度下的广义层错能,重点探讨了固溶原子含量变化和温度对于层错能的影响,以及层错能与微观塑性变形模式的联系。为了更好地解释层错能对各滑移系开动情况的影响,对MOITRA等[81]提出的塑性成形参数χ进行了修正,定义了基面和柱面滑移开动相关的参数
4个滑移系在0~500 K的温度下的广义层错能,重点探讨了固溶原子含量变化和温度对于层错能的影响,以及层错能与微观塑性变形模式的联系。为了更好地解释层错能对各滑移系开动情况的影响,对MOITRA等[81]提出的塑性成形参数χ进行了修正,定义了基面和柱面滑移开动相关的参数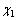 及基面和锥面滑移开动相关的参数
及基面和锥面滑移开动相关的参数 ,来说明同一温度下层错能与镁合金塑性成形能力之间的关系,分别如式(1)和(2)所示:
,来说明同一温度下层错能与镁合金塑性成形能力之间的关系,分别如式(1)和(2)所示:
 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
式中: 即基面{0001}
即基面{0001}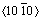 滑移系的稳定层错能;
滑移系的稳定层错能;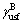 则是该滑移系中的不稳定层错能
则是该滑移系中的不稳定层错能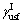 ;
; 为柱面滑移系稳定层错能和不稳定层错能的替代值;
为柱面滑移系稳定层错能和不稳定层错能的替代值;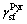 和
和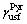 分别代表二级锥面上的稳定层错能
分别代表二级锥面上的稳定层错能 和不稳定层错能
和不稳定层错能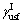 ;角标的Mg代表纯Mg的情况,X则代表含Mg-X合金的情况。由式(1)和(2)可知,纯镁的
;角标的Mg代表纯Mg的情况,X则代表含Mg-X合金的情况。由式(1)和(2)可知,纯镁的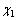 和
和 值为1,当
值为1,当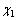 和
和 值大于1时,这时合金的塑性更好。图3所示为不同温度下Mg-Al、Mg-Zn和Mg-Y合金的
值大于1时,这时合金的塑性更好。图3所示为不同温度下Mg-Al、Mg-Zn和Mg-Y合金的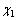 和
和 值随固溶原子增加的变化情况。可见Mg-Al合金的
值随固溶原子增加的变化情况。可见Mg-Al合金的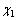 和χ2值在各成分和温度下基本小于1,且都随着Al的增加有轻微的下降。而Mg-Zn和Mg-Y合金的
和χ2值在各成分和温度下基本小于1,且都随着Al的增加有轻微的下降。而Mg-Zn和Mg-Y合金的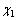 和χ2值基本均大于1,这两个合金的
和χ2值基本均大于1,这两个合金的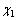 值都随着固溶原子的增加而上升,柱面滑移开动的倾向增加。
值都随着固溶原子的增加而上升,柱面滑移开动的倾向增加。 值则随着Zn原子含量增加有微弱地上升趋势。Mg-Y中
值则随着Zn原子含量增加有微弱地上升趋势。Mg-Y中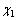 和
和 值都随着Y的增加有明显的增加趋势,且都高于Mg-Zn的计算结果。根据
值都随着Y的增加有明显的增加趋势,且都高于Mg-Zn的计算结果。根据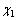 和
和 的计算结果可知,在同一温度下,固溶Al原子含量的增加并没有显著地改善镁合金非基面滑移开动的趋势,Zn含量的增加有利于镁合金非基面滑移系的开动,而Y含量的提高则明显地增加了镁合金非基面滑移开动的可能性。
的计算结果可知,在同一温度下,固溶Al原子含量的增加并没有显著地改善镁合金非基面滑移开动的趋势,Zn含量的增加有利于镁合金非基面滑移系的开动,而Y含量的提高则明显地增加了镁合金非基面滑移开动的可能性。
目前,大多数有关层错能变化对镁合金塑性影响的分析仅限于层错能增大或减小对位错滑移开启难易程度的影响。事实上,激活非基面滑移的根本是缩小基面与非基面滑移阻力的差距Δτ,而层错能与各滑移系滑移阻力有着直接关联。YASI等[82]通过修正Fleischer模型建立了0 K时部分二元固溶体合金基面层错能与基面滑移阻力CRSS之间的表达关系,如式(3)所示[82]:

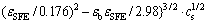 (3)
(3)
式中: 表示与纯镁相比固溶合金基面CRSS的变化,MPa;
表示与纯镁相比固溶合金基面CRSS的变化,MPa; 为固溶原子引起的尺寸错配;
为固溶原子引起的尺寸错配;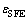 为固溶原子引起的化学错配(即层错能变化);cs为固溶原子浓度,%(摩尔分数)。此研究表明,层错能与固溶原子引起的尺寸错配能影响着基面滑移阻力CRSS,为定量分析层错能与滑移阻力之间的关系奠定了理论基础。在此基础上,作者应用式(3)计算了部分合金元素固溶后对镁基面滑移阻力CRSS变化的影响,包括合金元素在最大固溶度时基面滑移阻力CRSS变化
为固溶原子引起的化学错配(即层错能变化);cs为固溶原子浓度,%(摩尔分数)。此研究表明,层错能与固溶原子引起的尺寸错配能影响着基面滑移阻力CRSS,为定量分析层错能与滑移阻力之间的关系奠定了理论基础。在此基础上,作者应用式(3)计算了部分合金元素固溶后对镁基面滑移阻力CRSS变化的影响,包括合金元素在最大固溶度时基面滑移阻力CRSS变化 和固溶量为1%(摩尔分数)时基面滑移阻力CRSS变化
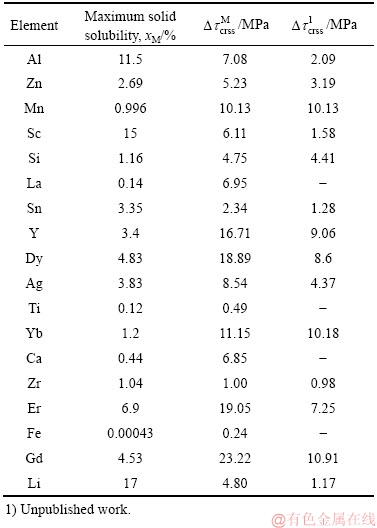
和固溶量为1%(摩尔分数)时基面滑移阻力CRSS变化 ,结果如表1所示。
,结果如表1所示。

图3 Mg-Al、Mg-Zn和Mg-Y合金的χ1和χ2值随固溶原子含量增加的变化[80]
Fig. 3 Changing values of χ1 and χ2 with elevated solute concentration[80]
从表1可知,Al、Zn、Y、Gd、Mn、Yb、Ag、Dy、Er等元素均可增加镁基面滑移阻力, 和
和 的值均为正值。比较
的值均为正值。比较 的值可知,相同含量下,Gd、Yb和Mn增加镁基面滑移阻力的效果最佳,其次为Y、Dy和Er。其中,Mn是这些元素中成本最低的元素,对发展高塑性低成本镁合金非常有利,但Mn的固溶度较低,最大固溶度也只接近1%(摩尔分数)。如何利用Mn的最大固溶度提高塑性和如何利用Mn的细小析出相细化晶粒进一步提高塑性是Mn在镁合金应用时必须同时考虑的问题。
的值可知,相同含量下,Gd、Yb和Mn增加镁基面滑移阻力的效果最佳,其次为Y、Dy和Er。其中,Mn是这些元素中成本最低的元素,对发展高塑性低成本镁合金非常有利,但Mn的固溶度较低,最大固溶度也只接近1%(摩尔分数)。如何利用Mn的最大固溶度提高塑性和如何利用Mn的细小析出相细化晶粒进一步提高塑性是Mn在镁合金应用时必须同时考虑的问题。
从表1同样可以看出,对Mg-Al、Mg-Zn和Mg-Y合金而言,Al、Zn、Y均可增加基面滑移阻力。对比 的值可知,在相同含量下,Y增加镁基面滑移阻力的效果最佳,其次为Zn、Al。由此可见,Al、Zn、Y固溶在镁基体中基面滑移阻力增加,使得基面位错运动困难,产生基面的固溶强化,从而使合金的屈服强度提高。结合分子动力学模拟结果,Zn、Y固溶有利于非基面滑移系的开启,提高合金的塑性。由此可见,Zn、Y固溶在镁基体中可同时提高合金的屈服强度和塑性,即Zn、Y固溶实现了“固溶强化增塑”。有关Zn、Y固溶对非基面滑移阻力影响的详细结果待后续报道。
的值可知,在相同含量下,Y增加镁基面滑移阻力的效果最佳,其次为Zn、Al。由此可见,Al、Zn、Y固溶在镁基体中基面滑移阻力增加,使得基面位错运动困难,产生基面的固溶强化,从而使合金的屈服强度提高。结合分子动力学模拟结果,Zn、Y固溶有利于非基面滑移系的开启,提高合金的塑性。由此可见,Zn、Y固溶在镁基体中可同时提高合金的屈服强度和塑性,即Zn、Y固溶实现了“固溶强化增塑”。有关Zn、Y固溶对非基面滑移阻力影响的详细结果待后续报道。
表1 不同固溶元素Mg的基面滑移阻力CRSS变化1)
Table 1 Basal CRSS changes of Mg with different solutes
4 “固溶强化增塑”合金设计理论的实验验证
“固溶强化增塑”合金设计理论可以采用应力应变曲线并结合粘塑性自洽(Visco-Plastic Self-Consistent)模型进行间接验证。图4(a)所示为Mg-X二元系合金拉伸工程应力应变曲线,包括Mg-2%Al、Mg-2%Y(质量分数)两个二元合金。由图4(a)可见,添加Al和Y可明显提高纯镁的屈服强度和断裂伸长率,Mg-2Al合金的强度最高,Mg-2Y合金的断裂伸长率最高。

图4 Mg、Mg-2Al、Mg-2Y合金拉伸工程应力应变曲线(a)及真应力-应变拟合曲线(b)
Fig. 4 Tensile stress-strain curves(a) and ture stress-strain curves(b) of Mg, Mg-2Al, Mg-2Y alloys
对纯Mg、Mg-2Al、Mg-2Y合金采用黏塑性自洽模型模拟了室温拉伸塑性变形过程(见图4(b)所示),并分析了Al和Y固溶对纯镁基面与非基面滑移阻力差值的影响,结果如表2所示。表2中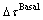 、
、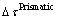 、
、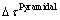 分别为Al和Y固溶后镁基面、柱面、锥面滑移阻力的变化,正值表示增加,负值表示减少;
分别为Al和Y固溶后镁基面、柱面、锥面滑移阻力的变化,正值表示增加,负值表示减少; 和
和 分别代表合金柱面与基面滑移阻力差值和锥面与基面滑移阻力差值。当Al固溶到Mg中,基面滑移阻力
分别代表合金柱面与基面滑移阻力差值和锥面与基面滑移阻力差值。当Al固溶到Mg中,基面滑移阻力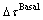 增加,产生固溶强化,锥面与基面滑移阻力差值变化不大,对锥面滑移系开启的影响不明显,而柱面与基面滑移阻力差值增大,柱面滑移启动较为困难。当Y固溶到Mg中,基面滑移阻力
增加,产生固溶强化,锥面与基面滑移阻力差值变化不大,对锥面滑移系开启的影响不明显,而柱面与基面滑移阻力差值增大,柱面滑移启动较为困难。当Y固溶到Mg中,基面滑移阻力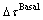 小幅度增加,产生固溶强化,柱面与基面滑移阻力差值
小幅度增加,产生固溶强化,柱面与基面滑移阻力差值 大幅下降,锥面与基面滑移阻力差值
大幅下降,锥面与基面滑移阻力差值 明显下降,均有利于柱面和锥面滑移的启动,从而提高合金均匀塑性变形能力。进一步,Mg-2Al合金基面滑移阻力增量较Mg-2Y合金大,因此Mg-2Al合金的屈服强度更高,而Mg-2Y合金的
明显下降,均有利于柱面和锥面滑移的启动,从而提高合金均匀塑性变形能力。进一步,Mg-2Al合金基面滑移阻力增量较Mg-2Y合金大,因此Mg-2Al合金的屈服强度更高,而Mg-2Y合金的 和
和 值比Mg-2Al合金的小很多,更有利于非基面滑移系的开启,故Mg-2Y合金比Mg-2Al合金的断裂伸长率高,塑性更好。由此可见,Al、Y添加对纯Mg塑性变形能力的影响规律与分子动力学模拟计算结果相同。
值比Mg-2Al合金的小很多,更有利于非基面滑移系的开启,故Mg-2Y合金比Mg-2Al合金的断裂伸长率高,塑性更好。由此可见,Al、Y添加对纯Mg塑性变形能力的影响规律与分子动力学模拟计算结果相同。
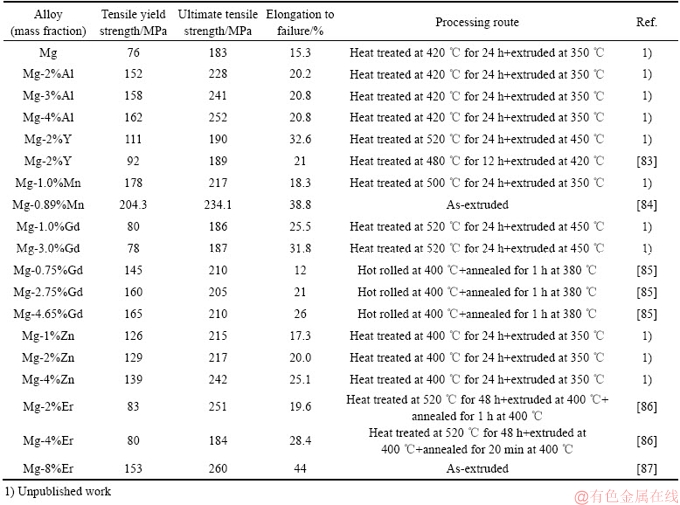
表3所示为一些二元镁合金实验和文献报道的力学性能数据。从表3可以看出,添加Al、Y、Mn、Gd、Zn、Er等合金元素均可提高纯镁的抗拉强度、屈服强度和断裂伸长率。还可以看出,相同工艺下,随着Gd、Zn等合金元素的含量增加,二元合金的强度和断裂伸长率随之增加。尽管有晶粒细化、析出强化、合金纯化等方面的影响,但实验和文献报道的二元合金变形和热处理工艺均在400 ℃左右,体现了固溶元素对合金性能的影响,且从实验和文献报道数据均可看出合金元素固溶可同时提高纯镁的强度和塑性的趋势,进一步验证了合金元素在镁中的“固溶强化增塑”作用。
表2 纯Mg、Mg-2Al、Mg-2Y合金力学性能及滑移阻力数据1)
Table 2 Tensile mechanical properties and slip resistance of Mg, Mg-2Al and Mg-2Y alloys1)
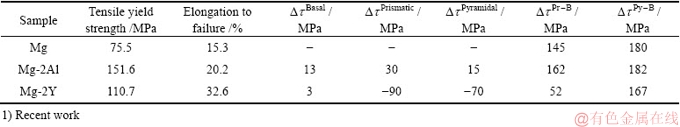
表3 一些二元合金力学拉伸学性能数据
Table 3 Tensile mechanical properties of Mg-X binary alloys
5 “固溶强化增塑”合金设计理论的应用
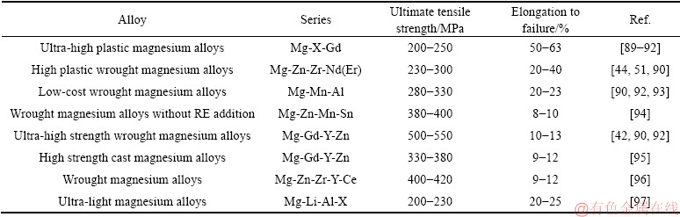
利用“固溶强化增塑”合金设计理论并结合长程有序相控制等途径,重庆大学镁合金科研团队开发了共二十多种新型高性能镁合金,包括超高强变形镁合金、超高强铸造镁合金、超高塑性镁合金、低成本高塑性镁合金、超轻合金、高电磁屏蔽性能镁合金、高导热性能镁合金等。图5所示分别为重庆大学镁合金科研团队开发的超高强变形镁合金[42](见图5(a))、高塑性含锰镁合金[84](见图5(b))、高强度高塑性铸造镁合金[88](见图5(c))、超高塑性镁合金[89](见图5(d))的拉伸力学性能曲线。此外,表4还列出了重庆大学镁合金科研团队开发的部分新型高性能镁合金及其性能。这些新开发的合金中,有16个已批准为国家标准牌号合金[90-91],9个已批准为国际标准牌号合金[92]。

图5 高性能镁合金的拉伸应力-应变曲线
Fig. 5 Stress-strain curves of high properties magnesium alloys
表4 重庆大学开发的部分新型高性能镁合金
Table 4 New high performance magnesium alloys developed by Chongqing University
6 结语
如何提高镁合金室温塑性和低温热成形能力是镁合金推广应用中亟待解决的问题。镁合金“固溶强化增塑”理论可以为高塑性镁合金的开发提供一条合金设计的新思路,在实现强度提高的同时改善镁合金的塑性。在“固溶强化增塑”的合金设计思路中,Mn的应用极有价值,一方面是因为Mn元素的成本极低,另一方面是因为Mn的低温固溶增塑效果非常显著并且有明显的析出效应,对发展低温成形的低成本超细晶变形镁合金有重要意义。由于镁合金的阻尼性能也和位错的可动性密切相关,“固溶强化增塑”理论也可以为解决强度提高同时阻尼性能变差的矛盾提供新的解决思路,即可以通过固溶合金的设计尝试实现“固溶强化增阻”。另外,钛合金、铍合金、锌合金等六方晶体结构金属的材料塑性都比较差,用“固溶强化增塑”来提高塑性和成形性也是值得探索的工作。
“固溶强化增塑”原理在新型镁合金设计和开发中的准确应用还需要在多个方面进一步完善和发展。一是不同温度下合金元素影响非基面阻力的准确计算难度很大,特别是多个元素交互作用下计算难度更大;二是实验验证的有效性和准确性有待进一步改善;三是缺乏大量准确的镁合金多元相图,合金元素固溶量变化目前并不完全清楚,大量热力学和动力学研究还亟待加强;四是在镁合金固溶、析出和位错等方面研究中,热力学、动力学研究和微观组织精准研究脱节现象依然严重,协同研究非常重要。
REFERENCES
[1] 潘复生, 韩恩厚. 高性能变形镁合金及加工技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007.
PAN Fu-sheng, HAN En-hou. High performance wrought magnesium alloy and its processing technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2007.
[2] 潘复生, 吴国华. 新型合金材料—镁合金[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2017.
PAN Fu-sheng, WU Guo-hua. New materials—Magnesium alloy[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 2017.
[3] LI Da-quan, WANG Qu-dong, DING Wen-jiang. Effects of heat treatments on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-4Y-4Sm-0.5Zr alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 448(1/2): 165-170.
[4] LI Jun-cai, HE Zong-ling, FU Peng-huai, WU Yu-juan, PENG Li-ming, DING Wen-jiang. Heat treatment and mechanical properties of a high-strength cast Mg-Gd-Zn alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 651: 745-752.
[5] DING Wen-jiang, LI Da-quan, WANG Qu-dong, LI Qiang. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-rolled Mg-Zn-Nd-Zr alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 483/484: 228-230.
[6] HE S M, ZENG X Q, PENG L M, GAO X, NIE J F, DING W J. Microstructure and strengthening mechanism of high strength Mg-10Gd-2Y-0.5Zr alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 427(1/2): 316-323.
[7] NIE Jian-feng. Precipitation and hardening in magnesium alloys[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2012, 43(11): 3891-3939.
[8] WANG Dan, FU Peng-huai, PENG Li-ming, WANG Ying-xin, DING Wen-jiang. Development of high strength sand cast Mg-Gd-Zn alloy by co-precipitation of the prismatic β′ and β1 phases[J]. Materials Characterization, 2019, 153: 157-168.
[9] XU C, ZHENG M Y, WU K, WANG E D, FAN G H, XU S W, KAMADO S, LIU X D, WANG G J, LV X Y. Effect of ageing treatment on the precipitation behaviour of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 550: 50-56.
[10] LIN Dan, WANG Lei, LIU Yang, CUI Jian-zhong, LE Qi-chi. Effects of plastic deformation on precipitation behavior and tensile fracture behavior of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(10): 2160-2167.
[11] JANIK V, YIN D D, WANG Q D, HE S M, CHEN C J, CHEN Z, BOEHLERT C J. The elevated-temperature mechanical behavior of peak-aged Mg-10Gd-3Y-0.4Zr alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(7): 3105-3112.
[12] DAI Ji-chun, ZHU Su-ming, EASTON M A, ZHANG Ming-xing, QIU Dong, WU Guo-hua, LIU Wen-cai, DING Wen-jiang. Heat treatment, microstructure and mechanical properties of a Mg-Gd-Y alloy grain-refined by Al additions[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 576: 298-305.
[13] WANG Dong-shu, LI De-jiang, XIE Yan-cai, ZENG Xiao-qin. HRTEM studies of aging precipitate phases in the Mg-10Gd-3Y-0.4Zr alloy[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2016, 34(4): 441-446.
[14] PANG Song, WU Guo-hua, LIU Wen-cai, ZHANG Liang, ZHANG Yang, CONRAD Hans, DING Wen-jiang. Influence of cooling rate on solidification behavior of sand-cast Mg-10Gd-3Y-0.4Zr alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(11): 3413-3420.
[15] LI D J, ZENG X Q, DONG J, ZHAI C Q, DING W J. Microstructure evolution of Mg-10Gd-3Y-1.2Zn-0.4Zr alloy during heat-treatment at 773 K[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 468(1): 164-169.
[16] WANG Lu-yuan, HUANG Jian, PENG Yong, WU Yi-xiong. Precipitates evolution in the heat affected zone of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy in T6 condition during laser welding[J]. Materials Characterization, 2019, 154: 386-394.
[17] FAN Hai-dong, ZHU Ya-xin, EL-AWADY J A, RAABE D. Precipitation hardening effects on extension twinning in magnesium alloys[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2018, 106: 186-202.
[18] HE S M, ZENG X Q, PENG L M, GAO X, NIE J F, DING W J. Precipitation in a Mg-10Gd-3Y-0.4Zr (wt.%) alloy during isothermal ageing at 250 ℃[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2006, 421(1): 309-313.
[19] DAI Ji-chun, ZHU Su-ming, EASTON M A, XU Wen-fan, WU Guo-hua, DING Wen-jiang. Precipitation process in a Mg-Gd-Y alloy grain-refined by Al addition[J]. Materials Characterization, 2014, 88: 7-14.
[20] QIAN Sheng-nan, DONG Chuang, LIU Tian-yu, QIN Ying, WANG Qing, WU Yu-juan, GU Li-dong, ZOU Jian-xin, HENG Xiang-wen, PENG Li-ming, ZENG Xiao-qin. Solute-homogenization model and its experimental verification in Mg-Gd-based alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2018, 34(7): 1132-1141.
[21] YU Zi-jian, HUANG Yuan-ding, QIU Xin, WANG Guan-fu, MENG Fan-zhi, HORT Norbert, MENG Jian. Fabrication of a high strength Mg-11Gd-4.5Y-1Nd-1.5Zn-0.5Zr (wt%) alloy by thermomechanical treatments[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 622: 121-130.
[22] HOMMA T, KUNITO N, KAMADO S. Fabrication of extraordinary high-strength magnesium alloy by hot extrusion[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 61(6): 644-647.
[23] PAN Fu-sheng, CHEN Xian-hua, YAN Tao, LIU Ting-ting, MAO Jian-jun, LUO Wei, WANG Qin, PENG Jian, TANG Ai-tao, JIANG Bin. A novel approach to melt purification of magnesium alloys[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2016, 4(1): 8-14.
[24] PAN Fu-sheng, YANG Ming-bo, CHEN Xian-hua. A review on casting magnesium alloys: modification of commercial alloys and development of new alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2016, 32(12): 1211-1221.
[25] XUA Jun, JIANG Bin, SONG Jiang-feng, HE Jun-jie, GAO Peng, LIU Wen-jun, YANG Tian-hao, HUANG Guang-sheng, PAN Fu-sheng. Unusual texture formation in Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy sheets processed by slope extrusion[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 732: 1-5.
[26] HUANG G S, XU W, HUANG G J, LI H C, PAN F S. New method for improving formability of AZ31B Magnesium alloy sheets[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2009, 610/613: 737-741.
[27] HE Jun-jie, JIANG Bin, XIE Hong-mei, JIANG Zhong-tao, LIU Bo, PAN Fu-sheng. Improved tension-compression performance of Mg-Al-Zn alloy processed by co-extrusion[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2016, 675: 76-81.
[28] JIANG Bin, LIU Wen-jun, QIU Dong, ZHANG Ming-xing, PAN Fu-sheng. Grain refinement of Ca addition in a twin-roll-cast Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2012, 133(2/3): 611-616.
[29] ZENG Ying, JIANG Bin, HUANG De-hui, DAI Jia-hong, PAN Fu-sheng. Effect of Ca addition on grain refinement of Mg-9Li-1Al alloy[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2013, 1(4): 297-302.
[30] YIN Heng-mei, JIANG Bin, HUANG Xiao-yong, ZENG Ying, YANG Qing-shan, ZHANG Ming-xing, PAN Fu-sheng. Effect of Ce addition on microstructure of Mg-9Li alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(7): 1936-1941.
[31] JIANG Bin, YIN Heng-mei, YANG Qing-shan, LI Rui-hong, PAN Fu-sheng. Effect of stannum addition on microstructure of as-cast and as-extruded Mg-5Li alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(11): 2378-2383.
[32] LIU Bo-yu, LIU Fei, YANG Nan, ZHAI Xiao-bo, ZHANG Lei, YANG Yang, LI Bin, LI Ju, MA Evan, NIE Jian-feng, SHAN Zhi-wei. Large plasticity in magnesium mediated by pyramidal dislocations[J]. Science, 2019, 365: 73-75.
[33] LIU Guo-bao, ZHANG Jing, XI Guo-qiang, ZUO Ru-lin, LIU Shuang. Designing Mg alloys with high ductility: Reducing the strength discrepancies between soft deformation modes and hard deformation modes[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 141: 1-9.
[34] 柳杨露. Mg-Al和Mg-Y合金的第一性原理计算及实验研究[D]. 重庆:重庆大学, 2018: 27-42.
LIU Yang-lu. First-principles calculation and experimental study of Mg-Al and Mg-Y alloys[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2018: 27-42.
[35] CHANG Y, KOCHMANN D M. A variational constitutive model for slip-twinning interactions in hcp metals: Application to single-and polycrystalline magnesium[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2015, 73: 39-61.
[36] YOSHINAGA H, HORIUCHI R. On the nonbasal slip in magnesium crystals [J]. Transactions of the Japan Institute of Metals, 1964, 5(1): 14-21.
[37] MISES R V. Mechanik der plastischen Formanderung von Kristallen[J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 1928, 8(3): 161-185.
[38] 孙 刚, 王少华, 张显峰, 陆 政, 冯朝辉, 马志峰. 固溶处理及预拉伸变形对2197铝锂合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2011, 36(10): 75-78.
SUN Gang, WANG Shao-hua, ZHANG Xian-feng, LU Zheng, FENG Zhao-hui. Effect of solution treatment and prestretching deformation on microstructure and properties of 2197 Al-Li alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2011, 36(10): 75-78.
[39] 张继明, 喻春明. 时效对含Nb低合金高强钢显微组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2019, 40(6): 123-129.
ZHANG Ji-ming, YU Chun-ming. Effect of aging on microstructure and mechanical properties of low alloy high strength steel containing Nb[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2019, 40(6): 123-129.
[40] HUANG Hua, MIAO Hong-wei, YUAN Guang-yin, WANG Zhong-chang, DING Wen-jiang. Fabrication of ultra-high strength magnesium alloys over 540 MPa with low alloying concentration by double continuously extrusion[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2018, 6(2): 107-113.
[41] HUANG Hua, YUAN Guang-yin, CHU Zhen-hua, DING Wen-jiang. Microstructure and mechanical properties of double continuously extruded Mg-Zn-Gd-based magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 560: 241-248.
[42] WANG Jing-feng, WANG Kui, HOU Fan, LIU Shi-jie, PENG Xing, WANG Jin-xing, PAN Fu-sheng. Enhanced strength and ductility of Mg-RE-Zn alloy simultaneously by trace Ag addition[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 728: 10-19.
[43] MIAO Jia-shi, SUN Wei-hua, KLARNER A D, LUO A A. Interphase boundary segregation of silver and enhanced precipitation of Mg17Al12 Phase in a Mg-Al-Sn-Ag alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 154: 192-196.
[44] ZHAO Ya-zhong, PAN Fu-sheng, PENG Jian, WANG Wei-qing, LUO Su-qing. Effect of neodymium on the as-extruded ZK20 magnesium alloy[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2010, 28: 631-635.
[45] ARRABAL R, MINGO B, PARDO A, MATYKINA E, MOHEDANO M, MERINO M C, RIVAS A, MAROTO A. Role of alloyed Nd in the microstructure and atmospheric corrosion of as-cast magnesium alloy AZ91[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 97: 38-48.
[46] PAN Fu-sheng, MAO Jian-jun, ZHANG Gen, TANG Ai-tao, SHE Jia. Development of high-strength, low-cost wrought Mg-2.0mass% Zn alloy with high Mn content[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2016, 26(6): 630-635.
[47] KOIZUMI T, EGAMI M, YAMASHITA K, ABE E. Platelet precipitate in an age-hardening Mg-Zn-Gd alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 752: 407-411.
[48] SHE Jia, PAN Fu-sheng, GUO Wei, TANG Ai-tao, GAO Zheng-yuan, LUO Su-qin, SONG Kai, YU Zheng-wen, RASHAD M. Effect of high Mn content on development of ultra-fine grain extruded magnesium alloy[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 90: 7-12.
[49] WANG Jing-feng, SONG Peng-fei, HUANG Song, PAN Fu-sheng. High-strength and good-ductility Mg-RE-Zn-Mn magnesium alloy with long-period stacking ordered phase[J]. Materials Letters, 2013, 93: 415-418.
[50] YU Zhao-peng, YAN Yu-hao, YAO Jia, WANG Cheng, ZHA Min, XU Xin-yu, LIU Yan, WANG Hui-yuan, JIANG Qi-chuan. Effect of tensile direction on mechanical properties and microstructural evolutions of rolled Mg-Al-Zn-Sn magnesium alloy sheets at room and elevated temperatures[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 744: 211-219.
[51] ZHANG Jing, MA Qi, PAN Fu-sheng. Effects of trace Er addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy[J]. Materials & Design, 2010, 31(9): 4043-4049.
[52] ZHANG Jing, LI Wei-guo, ZHANG Bao-xiang, DOU Yu-chen. Influence of Er addition and extrusion temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a Mg-Zn-Zr magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528(13/14): 4740-4746.
[53] ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Xu-feng, LI Wei-guo, PAN Fu-sheng, GUO Zheng-xiao. Partition of Er among the constituent phases and the yield phenomenon in a semi-continuously cast Mg-Zn-Zr alloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 63(4): 367-370.
[54] ZHANG Jing, LIU Min, DOU Yu-chen, LIU Guo-bao. Role of alloying elements in the mechanical behaviors of an Mg-Zn-Zr-Er alloy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2014, 45(12): 5499-5507.
[55] WANG Zhong-jun, JIA Wei-ping, CUI Jian-zhong. Study on the deformation behavior of Mg-3.6% Er magnesium alloy[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2007, 25(6): 744-748.
[56] ZHAO Zi-long, SUN Zi-wei, LIANG Wei, WANG Yi-de, BIAN Li-ping. Influence of Al and Si additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-4Li alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 702: 206-217.
[57] WANG Qing-hang, SHEN Ya-qun, JIANG Bin, TANG Ai-tao, CHAI Yan-fu, SONG Jiang-feng, YANG Tian-hao, HUANG Guang-sheng, PAN Fu-sheng. A good balance between ductility and stretch formability of dilute Mg-Sn-Y sheet at room temperature[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 736: 404-416.
[58] TAN J, SUN Y H, XIE H B, SUN B Z, QI Y. Atomic-resolution investigation of Y-rich solid solution with an invariable orientation in Mg-Y binary alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 766: 716-720.
[59] WANG Fang, HU Tong, ZHANG Yi-tan, XIAO Wen-long, MA Chao-li. Effects of Al and Zn contents on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Al-Zn-Ca magnesium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017, 704: 57-65.
[60] YANG Qing-shan, JIANG Bin, JIANG Wei, LUO Su-qing, PAN Fu-sheng. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Mn-Ce alloys under hot extrusion[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 628: 143-148.
[61] LIU Shi-jie, WANG Kui, WANG Jing-feng, HUANG Song, GAO Shi-qing, PENG Xing, HU Hao, PAN Fu-sheng. Ageing behavior and mechanisms of strengthening and toughening of ultrahigh-strength Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Mn alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 758: 96-98.
[62] TONG Xin, YOU Guo-qiang, WANG Yi-chang, WU Hong, LIU Wei-li, LI Pei-qi, GUO Wei. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on segregation and mechanical properties of as-cast Mg-Gd binary alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 731: 44-53.
[63] LIU Ting-ting, PAN Fu-sheng, ZHANG Xi-yan. Effect of Sc addition on the work-hardening behavior of ZK60 magnesium alloy[J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 43: 572-577.
[64] JIANG Bin, ZENG Ying, YIN Heng-mei, LI Rui-hong, PAN Fu-sheng. Effect of Sr on microstructure and aging behavior of Mg-14Li alloys[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2012, 22(2): 160-168.
[65] WU Lu, PAN Fu-sheng, YANG Ming-bo, WU Ju-ying, LIU Ting-ting. As-cast microstructure and Sr-containing phases of AZ31 magnesium alloys with high Sr contents[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(4): 784-789.
[66] HAUSER E F, LANDON R P, DORN E J. Deformation and fracture of alpha solid solutions of lithium in magnesium[J]. Transactions of the ASM, 1958, 50: 856-883.
[67] AKHTAR A, TEGHTSOONIAN E. Solid solution strengthening of magnesium single crystals-ii the effect of solute on the ease of prismatic slip[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1969, 17: 1351-1356.
[68] HU Guang-shan, ZHANG Ding-fei, ZHAO Ding-zang, SHEN Xia, JIANG Lu-yao, PAN Fu-sheng. Microstructures and mechanical properties of extruded and aged Mg-Zn-Mn-Sn-Y alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(10): 3070-3075.
[69] WANG Li-fei, HUANG Guang-sheng, QUAN Quan, BASSANI P, MOSTAED E, VEDANI M, PAN Fu-sheng. The effect of twinning and detwinning on the mechanical property of AZ31 extruded magnesium alloy during strain-path changes[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 63: 177-184.
[70] JIANG Bin, ZHOU Guan-yu, DAI Jia-hong, XIA Xiang-sheng, WAN Yuan-yuan, PAN Fu-sheng. Effect of second phases on microstructure and mechanical properties of As-cast Mg-Ca-Sn magnesium alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014, 43(10): 2445-2449.
[71] CHINO Y, KADOB M, MABUCHI M. Enhancement of tensile ductility and stretch formability of magnesium by addition of 0.2 wt%(0.035 at%)Ce[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 494(1/2): 343-349.
[72] SANDLOBES S, ZAEFFERER S, SCHESTAKOW I, YI S, GONZALEZ-MARTINEZ R. On the role of non-basal deformation mechanisms for the ductility of Mg and Mg-Y alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59: 429-439.
[73] CHINO Y, KADOB M, MABUCHI M. Texture and stretch formability of a rolled Mg-Zn alloy containing dilute content of Y[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 513/514: 394-400.
[74] WU Z X, AHMAD R, YIN B L, SANDLOEBES S, CURTIN W A. Mechanistic origin and prediction of enhanced ductility in magnesium alloys[J]. Science, 2018, 359: 447-452.
[75] WU Z X, CURTIN W A. The origins of high hardening and low ductility in magnesium[J]. Nature, 2015, 526: 62-67.
[76] MOITRA A, KIM S G, HORSTEMEYER M F. Solute effect on the 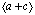 dislocation nucleation mechanism in magnesium[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 75: 106-112.
dislocation nucleation mechanism in magnesium[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 75: 106-112.
[77] LIU Guo-bao, ZHANG Jing, DOU Yu-chen. First-principles study of solute-solute binding in magnesium alloys[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2015, 103: 97-104.
[78] ZHANG Jing, DOU Yu-chen, LIU Guo-bao, GUO Zheng-xiao. First-principles study of stacking fault energies in Mg-based binary alloys[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2013, 79: 564-569.
[79] FANG Chao, ZHANG Jing, PAN Fu-sheng. First-principles study on solute-basal dislocation interaction in Mg alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 785: 911-917.
[80] 王煜烨. 基于分子动力学的镁合金层错能计算与研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019: 54-57.
WANG Yu-ye. Study and calculation on stacking fault energy of magnesium alloys based on molecular dynamics[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University. 2019: 54-57.
[81] MOITRA A, KIM G S, HORSTEMEYER F M. Solute effect on basal and prismatic slip systems of Mg[J]. Journal of Physics Condensed Matter An Institute of Physics Journal, 2014, 26(44): 2-11.
[82] YASI J A, LOUIS G H Jr, TRINKLE D R. First-principles data for solid-solution strengthening of magnesium: From geometry and chemistry to properties[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58: 5704-5713.
[83] WU B L, ZHAO Y H, DU X H, ZHANG Y D, WAGNER F, ESLING C. Ductility enhancement of extruded magnesium via yttrium addition[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(16/17): 4334-4340.
[84] YU Zheng-wen, TANG Ai-tao, WANG Qin, GAO Zheng-yuan, HE Jie-jun, SHE Jia, SONG Kai, PAN Fu-sheng. High strength and superior ductility of an ultra-fine grained magnesium-manganese alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015, 648: 202-207.
[85] NICOLE S D, DLE A, MATTHEW R B. The effect of Gd on the recrystallisation, texture and deformation behaviour of magnesium-based alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58(20): 6773-6783.
[86] WU B L, WAN G, DU X H, ZHANG Y D, WAGNER F, ESLING C. The quasi-static mechanical properties of extruded binary Mg-Er alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013, 573: 205-214.
[87] ZHANG J, XU C, JING Y, LV S, LIU S, FANG D, ZHUANG J, ZHANG M, WU R. New horizon for high performance Mg-based biomaterial with uniform degradation behavior: Formation of stacking faults[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 1-16.
[88] WU Xia, PAN Fu-sheng, CHENG Ren-ju, LUO Shu-qing. Effect of morphology of long period stacking ordered phase on mechanical properties of Mg-10Gd-1Zn-0.5Zr magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 726: 64-68.
[89] HU Y, ZHANG C, ZHENG T, PAN F, TANG A. Strengthening effects of Zn addition on an ultrahigh ductility Mg-Gd-Zr magnesium alloy[J]. Materials (Basel), 2018, 11(10): 1-13.
[90] GB/T 5153—2016. 变形镁及镁合金牌号和化学成分[S].
GB/T 5153—2016. Designation and composition of wrought magnesium and magnesium alloys[S].
[91] GB/T 19078—2016. 铸造镁合金锭[S].
GB/T 19078—2016. Magnesium alloys ingots for castings[S].
[92] ISO 3116:2019(E). Magnesium and magnesium alloys— Wrought magnesium and magnesium alloys[S].
[93] 喻正文. Mg_Mn系合金显微组织及力学性能的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2015: 95-96.
YU Zheng-wen. Investigation on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Mn series alloys[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2015: 95-96.
[94] QI Fu-gang, ZHANG Ding-fei, ZHANG Xiao-hua, XU Xing-xing. Effect of Sn addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-6Zn-1Mn (wt.%) alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 585: 656-666.
[95] 吴 夏. Mg-Gd-Zn系铸造镁合金组织和力学性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018: 84-93.
WU Xia. Investigation on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Gd-Zn series cast magnesium alloys[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2018: 84-93.
[96] LIU Li-zi, CHEN Xian-hua, PAN Fu-sheng, GAO Shang-yu, ZHAO Chao-yue. A new high-strength Mg-Zn-Ce-Y-Zr magnesium alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 688: 537-541.
[97] HE Jun-jie, JIANG Bin, YU Xiao-wen, XU Jun, JIANG Zhong-tao, LIU Bo, PAN Fu-sheng. Strain path dependence of texture and property evolutions on rolled Mg-Li-Al-Zn alloy possessed of an asymmetric texture[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 698: 771-785.
LIU Ting-ting1, 2, PAN Fu-sheng2
(1. School of Materials and Energy, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China;
2. National Engineering Research Center for Magnesium Alloys, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China)
Abstract: Mg has a HCP structure with few slip systems, and the slip resistance for basal slip is much lower than that of prismatic and pyramidal slip. It is generally difficult to activate non-basal slip at room and low temperature, resulting in a poor ductility and formability of magnesium alloys. Chongqing University and other institutions have found that the solution of certain elements in Mg can not only improve the strength by hindering the basal slip, but also improve the ductility by reducing the gap of slip resistance between basal slip and non-basal slip. According to these results, Chongqing University has proposed a theory of alloy design —— solid solution strengthening and ductilizing (SSSD) for magnesium alloy, which has become a new way to optimize the strength-ductility balance of magnesium alloys in the past decade. Using SSSD theory, Chongqing University has developed many new high performance magnesium alloys, among which over 10 alloys have been included in GB/T national standard and ISO international standard.
Key words: magnesium alloys; strength; ductility; solid solution strengthening and ductilizing
Foundation item: Project(2016YFB0301100) supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China; Project(51531002) supported by Natural the Science Foundation of China; Projects (cstc2017jcyjBX0040, cstc2018jcyjAX007) supported by the National Science Foundation of Chongqing, China; Project(cstc2018jcyj-yszxX0007) supported by the Chongqing Academician Special Fund, China
Received date: 2019-07-10; Accepted date: 2019-08-22
Corresponding author: PAN Fu-sheng; Tel: +86-23-65112635; E-mail: fspan@cqu.edu.cn
(编辑 龙怀中)
基金项目:国家重点研发计划资助项目(2016YFB0301100);国家自然科学基金重点项目(51531002);重庆市基础与前沿研究计划项目 (cstc2017jcyjBX0040,cstc2018jcyjAX0070);重庆市院士专项基金资助项目(cstc2018jcyj-yszxX0007)
收稿日期:2019-07-10;修订日期:2019-08-22
通信作者:潘复生,教授,博士;电话:023-65112635;E-mail:fspan@cqu.edu.cn

