温压-原位反应法制备C/C-SiC材料过程中裂纹的形成机制
李 专,肖 鹏,熊 翔,杨 阳,旷文敏
(中南大学 粉末冶金国家重点实验室,湖南 长沙,410083)
摘 要:以短切炭纤维、石墨粉、硅粉、树脂和粘结剂为原料,采用温压-原位反应法制备C/C-SiC制动材料,研究C/C-SiC制动材料裂纹的形成机制。研究结果表明:树脂炭化裂解产生大量的气体产物,一部分气体产物碰到裂纹壁时受阻凝聚成含C,P,O和H等元素或自由基团的液滴,炭化后液滴转变成直径为2~4 μm的高含碳量碳球;另一部分气体产物沿着裂纹试图从试样中排出,当裂纹为封闭状态时便促使微裂纹向前扩展,直至材料开裂;在高温热处理过程中,硅粉熔化后与就近碳源反应生成连续的网络状SiC基体,它对裂纹的扩展有一定的抑制作用,并能愈合试样中的微裂纹。
关键词:C/C-SiC;温压-原位反应法;裂纹;制动材料
中图分类号:TB 331;TH 117.3 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2008)03-0506-06
Form mechanism of cracks in fabricated process of C/C-SiC frictional composites through warm compacted-in situ reacted process
LI Zhuan, XIAO Peng, XIONG Xiang, YANG Yang, KUANG Wen-min
(State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China)
Abstract: Based on reinforcements of carbon fibers and matrices of carbon and silicon carbide, C/C-SiC composites were fabricated through warm compacted-in situ reacted process. The forming mechanism of cracks during the process of warm compacted-in situ reaction was investigated. The results indicate that the resin emits a series of gas products during carbonization. A part of gas products agglomerate to fluid drops containing C, P, O, H, etc. while blocking at the wall of the crack, and then the drops convert to carbon ball with high carbon content after carbonization, with diameter of 2-4 μm. Other gas products try to release from composites. The gas pushes the tiny cracks to spread when there is no way to release until the crack spreads out of the composites. At the same time, the melted Si reacts with carbon to form continuous SiC matrix shape of network which restrains the spread of cracks or closes up tiny cracks of the composites.
Key words: C/C-SiC; warm compressed in-situ reaction; crack; braking composites
C/C-SiC制动材料具有密度低(约为2.0 g/cm
3)、抗氧化、耐腐蚀、制动平稳、摩擦因数高和环境适应性强(如湿态下摩擦性能不衰退)等优点
[1-3],是一种应用前景广阔的新型制动材料,已成功应用于航空、车辆工程、工程机械等领域
[4-5]。相对于高温热结构材料,普通制动材料不需求苛刻的力学性能。在制动材料摩擦磨损性能满足使用要求的前提下,要求尽可能缩短材料的制备周期,降低材料的生产成本。目前,国内外对C/C-SiC制动材料的研究主要集中在制备方法、材料的力学性能和摩擦磨损性能3个方面
[6-9],而对其他方面的研究较少。近年来,中南大学粉末冶金国家重点实验室研究开发了制备C/C-SiC制动材料的新工艺“温压-原位反应法”,此法具有工艺简单、过程易于控制、周期短、成本低等优点,是一种具有市场竞争力的工业化生产技术。目前,采用该法制备的C/C-SiC制动材料动摩擦因数在0.3%~0.39%之间可调,静摩擦因数≥0.4,弯曲强度≥65 MPa,压缩强度≥120 MPa,具有较好的摩擦磨损性能和力学性能。在前期研究中,发现采用温压-原位反应法制备C/C-SiC制动材料的过程中,材料易出现裂纹,导致材料各项性能下降。在此,本文作者采用温压-原位反应法制备C/C-SiC制动材料,研究C/C-SiC制动材料制备过程中裂纹的形成机制,以期为温压-原位反应法制备高性能C/C-SiC制动材料奠定应用基础。
1 实 验
1.1 试样制备
采用短切的东丽T700炭纤维为增强相,长度为2~12 mm;基体成分来源于石墨粉、树脂、硅粉、碳化硅粉和高含碳量粘结剂。首先,将短炭纤维、硅粉、石墨粉、碳化硅粉、树脂和粘结剂按一定配比均匀混合后温压(t≤200 ℃,p≤8 MPa)成C/C-Si素坯。然后,对素坯进行炭化处理(t≤900 ℃,氩气保护),在此过程中素坯中的树脂裂解转变为树脂碳。最后,在真空状态下和t≥1 400 ℃时进行高温热处理,通过Si/C原位反应在素坯中生成SiC相,得到最终的C/C-SiC制动材料,其工艺流程如图1所示。

图1 C/C-SiC制动材料的制备工艺
Fig.1 Fabrication processes of C/C-SiC frictional composites
1.2 分析测试与显微形貌观察
采用Ricoh Caplio GX8数码相机对试样进行宏观照相,用精度为0.2 mg的电子天平测定试样质量,进而得到其表观密度,利用JSM-6360LW型扫描电镜(SEM)分析试样裂纹表面及其组织微观形貌,用X射线能谱仪(EDX)分析微区成分。
2 实验结果与显微形貌分析
2.1 实验结果
根据每组成分配比各制备6个试样,经高温热处理后,试样1和试样3各有5片有开裂,试样2没有开裂,每组取1片试样作为分析对象。原材料主要物相组成和C/C-SiC材料的密度及其SiC理论含量见表1,其典型的开裂情况如图2所示。从图2(a)可以观察到裂缝存在于试样中间部分,裂缝呈台阶状伸出试样并造成试样分层。从图2(b)可以看出,裂缝导致试样表面形成1个凹坑,裂缝在凹坑边缘也呈台阶状伸出,其他试样的开裂情况均与这2种情况类似。
表1 C/C-SiC材料的原材料质量分数、密度和SiC含量
Table 1 Mass fraction of raw composites, density and SiC content of C/C-SiC composites
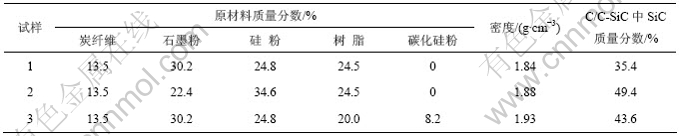

(a) 试样1;(b) 试样3
图2 试样裂口的宏观形貌
Fig.2 Optical macrographs of crack
2.2 试样的显微形貌分析
图3所示为C/C-SiC试样的SEM照片。从试样2的横截面形貌(图3(a))可以看出,试样纵向炭纤维与基体交替排布,有分层的趋势。基体内存在许多闭孔和微裂纹,这主要是因为炭化过程中气体产物释放会产生残留的气泡结构孔;进行高温热处理时,在加热或冷却过程中会形成热应力裂纹。图3(b)所示为试样3的裂纹表面形貌,可以看出裂纹在试样边缘往左呈台阶状上升,裂纹表面凹凸不平。
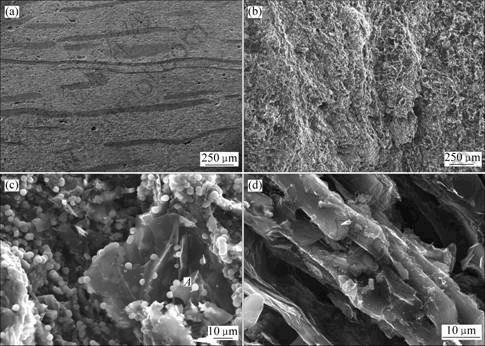
(a) 试样2的切口形貌;(b) 试样3的裂纹表面;(c) 试样1的裂纹表面;(d) 试样1切口的显微形貌
图3 C/C-SiC复合材料SEM照片
Fig.3 SEM photographs of C/C-SiC composites
图3(c)所示为试样1的裂纹表面形貌。可以看出裂纹表面存在许多颗粒状物质。与之相对应的是,试样1的切口形貌(图3(d))未见颗粒状物质。选取图3(c)中1个颗粒(A处)进行能谱分析(图4),以考察其成分分布。由试样的制备工艺可知,能谱图中的O和P峰是由于树脂中加入了6%~8%磷酸作为固化剂,在炭化过程中磷酸分解产生气体和磷的氧化物,炭化后磷的氧化物残留在树脂碳中[10],因此,试样能谱分析图中存在O和P峰。图中Si和C峰的存在说明颗粒表面有一层SiC。
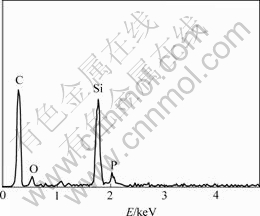
图4 图3(c )中A点处颗粒的EDAX图
Fig.4 EDAX pattern of particle at A point in Fig.3(c)
图5所示为试样1的X 射线衍射图。可见,试样1主要由C和SiC组成,同时含有少量残留Si。由图3(c)可知,A处为较规则的颗粒状物质,直径为2~4 μm,并且裂纹表面布满了许多这种颗粒。由于Si的理论熔点为1 404 ℃,而材料制备时原位反应的炉温为1 450 ℃,在此炉温下Si不能液化成球,只能与碳反应生成SiC[11]。另一方面,液相Si与C和SiC的润湿角分别为0?和37?,Si粉熔化后在炭纤维、基体碳的表面迅速润湿铺展,并与碳源接触反应生成SiC。因此,认为A处是含C,P,O和H等元素或基团的液滴炭化成的高含碳量的碳球,在高温热处理过程中,液态Si在碳球表面铺展并与表面的C反应生成SiC。

图5 C/C-SiC复合材料的XRD图
Fig.5 XRD pattern of C/C-SiC composites
3 裂纹的形成机制
试样在成形过程中,由于原料、混料及其他因素的影响,试样内部会形成微裂纹及闭孔等缺陷,这些缺陷在后续的工艺中都有可能发展成为裂纹源。
试样经温压成形后进行炭化处理(也称为高温裂解处理),其目的是使树脂裂解转化为树脂碳。随着炭化温度的升高,树脂逐步分解产生H2O,CO,CO2,CH4和H2等小分子气体产物[10]。分解产生的一部分气体碰到裂缝壁时受阻并在裂缝壁上凝聚成含C,P,O和H等元素或自由基团的液滴。另一部分气体沿着裂纹试图从试样中排出,当裂纹呈封闭状态时,气体便在裂纹尖端产生压应力,促使微裂纹向前扩展。在产生的新的裂纹空隙里,气体产物很快扩散填充并在其表面凝聚液滴,炭化产生更多的气体促使裂纹继续扩展,如此循环。随着炭化的进行,粘结剂中的氢、氧等原子不断减少,碳不断富集。最后,树脂炭化转变成基体碳,裂缝壁上的液滴转变成直径为2~4 μm、含碳量高的碳球,如图6所示。同时,树脂在转变成树脂碳的过程中体积收缩约20%,使得树脂碳内部存在微裂纹,成为后续工艺的裂纹源。

放大倍数:(a) 2 000;(b) 2万
图6 试样3微裂纹尖端的显微形貌
Fig.6 Micrographs of crack tip of sample 3
在随后的高温热处理过程中,Si粉熔化后迅速向就近的炭纤维和碳基体表面铺展润湿,并与所接触的碳源反应生成SiC。SiC层一旦形成,C-Si反应就由原来的接触反应转变为Si向SiC层中扩散传质到SiC/C界面的反应,反应速率取决于Si原子的扩散速度。钱军民等[12]通过计算得出:液态Si的润湿速度比扩散反应速度大5个数量级时,液态Si能够充分铺展,使得在炭纤维、基体碳和碳球上生成厚度较均匀的SiC层。同时,基体碳内部及基体与炭纤维之间由于膨胀系数不匹配产生热应力,导致裂纹进一步扩展,直至试样最后开裂。
4 裂纹形成的影响因素
4.1 温压工艺
温压工艺的影响因素主要包括温压温度、温压压力和保压时间。
适当的温压温度可保证物料中的树脂和粘结剂有良好的流动性,使粉料与纤维之间充分粘结,若温度低,则由于粉体流动性差而无法成形。但是,若温度过高,则会造成试样表面树脂反应剧烈,表面树脂的收缩速度大于内部树脂收缩速度而产生内应力。
若温压压力低,则初坯的密度低,但是,若温压压力过高,则会造成树脂和粘结剂溢出甚至试样破裂。同时,在温压过程中,树脂流动快,炭纤维流动 慢,树脂极易积聚或固化不完全,相应区域的炭纤维量偏低,这就造成试样组织不均匀,极易产生微裂纹。
若保压充分,则能为炭纤维提供足够的弛豫时间,减少坯体残余应力,从而减少材料内部微裂纹。
4.2 高温热处理
基体和炭纤维之间膨胀系数失配会导致界面产生微裂纹。在C/C-SiC制动材料中,T700碳纤维的纵向膨胀系数为2×10-6/℃,弹性模量Ef=280 GPa[13],而SiC的膨胀系数为4.8×10-6/℃,弹性模量Em=350 GPa。高温热处理的温度为1 450 ℃,冷却到室温时,因两者热膨胀系数不同而产生很大的热应力,此应力为松弛应力,导致两者界面产生微裂纹。
高温热处理后少量Si会残留在C/C-SiC材料中(图5)。当反应温度降到1 404 ℃(Si的熔点)时液Si开始凝固,在凝固过程中其体积膨胀约8.1%(液态Si密度为2.53 g/cm3,固态Si密度为2.34 g/cm3)[14]。体积膨胀导致应力产生,当应力大到一定程度并来不及释放时必然会产生微小裂纹。同时,由于SiC陶瓷基体与碳基体界面结合较弱,材料内部体积收缩产生的热应力主要通过基体与基体间的解离释放出来。
4.3 SiC含量
图7所示为2号试样切口的显微形貌。由图7(a)可以看到,基体与炭纤维结合紧密,基体内部看不到微裂纹。与之相应的是,试样1(图3(d))的显微组织可见大量微裂纹,同时,纤维上附有块状基体。由表1可知,开裂(试样1和3)和未开裂(试样2)除反应生成SiC的含量有较大差别外,其他成分大致相同。因此,SiC含量是影响试样开裂情况的主要原因之一。

放大倍数:(a) 2 000;(b) 1 000
图7 试样2的切口显微形貌
Fig.7 Micrographs of parallel section of sample 2
实际上,由于小孔毛细管力的作用,液态Si能浸渗到试样中极其微小的孔隙中与碳源反应。同时,由于Si粉均匀分布在基体中,使得液态Si与碳源能够在材料中局部区域生成连续网络状的SiC,如图7(b)中白色区域所示,它不但能抑制裂纹的扩展,同时会愈合试样中的微裂纹,因此,试样2较试样1和3更不容易开裂。同时,对比试样2和3可知,虽然最后试样中SiC含量相差不大,但是两者开裂情况完全不同,这进一步证明对裂纹扩展有阻碍作用的是反应生成的SiC,而非混料时加入的SiC。
5 结 论
a. 树脂炭化裂解产生H2O,CO,CO2,CH4和H2等小分子气体产物,分解产生的一部分气体碰到裂纹壁时受阻并在裂纹壁上凝聚成含C,P,O和H等元素或自由基团的液滴;另一部分气体沿着裂纹试图从试样中排出,当裂纹呈封闭状态时气体便促使微裂纹向前扩展,直至试样开裂。
b. 炭化过程中树脂中的氢、氧等原子不断以小分子气体产物的形式挥发,碳原子不断富集,磷酸不断分解。最后,树脂炭化转变成含一定磷的氧化物树脂碳,裂纹壁上的液滴炭化转变成直径为2~4 μm的高含碳量碳球。
c. 高温热处理过程中液态Si在炭纤维、基体碳和碳球表面铺展并与碳反应生成SiC,连续网络状的SiC对裂纹的扩展有一定的抑制作用,生成SiC的量越多,则试样越不容易开裂。
参考文献:
[1] Krenkel W, Heidenreich B, Renz R. C/C-SiC composites for advanced friction systems[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2002, 4(7): 427-436.
[2] 梁锦华, 黄启忠, 苏哲安, 等. 短纤维C/C-SiC复合材料的组织结构与断裂机制[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2005, 36(6): 924-929.
LIANG Jin-hua, HUANG Qi-zhong, SU Zhe-an, et al. Structure and fracture mechanism of short fibre reinforced C/C-SiC composites[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2005, 36(6): 924-929.
[3] Krenkel W, Berndt F. C/C-SiC composites for space applications and advanced friction systems[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 412: 177-181.
[4] Mhlratzer A. Production, properties and applications of ceramic matrix composites[J]. Ceramic Forum International, 1999, 76(4): 30-35.
[5] Developing ceramic materials for heave vehicle brake rotors [EB/OL]. [2005-09-06]. http://www.trucks.doe.gov/ research/ materials/CMC-brakes.htm.
[6] El-Hija H A, Krenkel W, Hugel S. Development of C/C-SiC brake pads for high-performance elevators [J]. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 2005, 2(2): 105-113.
[7] 肖 鹏, 熊 翔, 任芸芸. 不同成分对C/C-SiC材料摩擦磨损行为的影响与机理[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(7): 1040-1044.
XIAO Peng, XIONG Xiang, REN Yun-yun. Effect and mechanism of different components of C/C-SiC composites on friction and wear behaviors[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2005, 15(7): 1040-1044.
[8] Heidenreich B, Renz R, Krenkel W. Short fiber reinforced CMC materials for high performance brakes[C]//4th International Conference on High Temperature Ceramic Matrix Composites (HT-CMC4). Munich, Germany: Europe Ceramic Society, 2001: 68-74.
[9] Speicher M, Gadow R. Short fiber C/SiC composite with intermetallic matrix for disk brakes[C]//ACERS 101st Annual Meeting. Indianapolis, USA: The American Ceramic Society Bulletin, 1999: 25-28.
[10] Kyotani T, Moriyama H, Tomita A. High temperature treatment of polyfurfuryl alcohol/graphite oxide intercalation compound[J]. Carbon, 1997, 35(8): 1185-1203.
[11] 李俊生, 张长瑞, 曹英斌, 等. C/SiC材料表面Si/SiC涂层及其对基底结构的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2006, 23(6): 144-148.
LI Jun-sheng, ZHANG Chang-rui, CAO Ying-bin, et al. Si/SiC coatings on C/SiC composites and their effects on the structure of the substrate[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2006, 23(6): 144-148.
[12] 钱军民, 金字浩, 乔冠军. 木材陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(4): 716-724.
QIAN Jun-min, JIN Zi-hao, QIAO Guan-jun. Recent progress in research on wood ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2003, 18(4): 716-724.
[13] 熊 翔, 黄伯云, 肖 鹏. 准三维C/C复合材料的压缩性能及其破坏机理[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2004, 35(5): 702-707.
XIONG Xiang, HUANG Bai-yun, XIAO Pen. Compressive properties and fracture mechanism of quasi-3DC/C composites[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2004, 35(5): 702-707.
[14] 姜广鹏, 徐永东, 张军战. 反应熔体浸渗法制备C/SiC复合材料的显微结构与摩擦性能[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2005(1): 25-28.
JIANG Guang-peng, XU Yong-dong, ZHANG Jun-zhan. Microstructure and friction property of C/SiC composites made by reactive melt infiltration[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/ Composites, 2005(1): 25-28.
收稿日期:2007-08-18;修回日期:2007-10-22
基金项目:国家“863”计划资助项目(2006AA03Z560);湖南省杰出青年科学基金资助项目(06JJ1007)
通信作者:肖 鹏(1971-),男,湖南涟源人,教授,博士生导师,从事航空航天材料、C/C复合材料和陶瓷基复合材料的研究;电话:0731-8830131;E-mail: xiaopeng@mail.csu.edu.cn