文章编号:1004-0609(2010)04-0681-07
对流作用下枝为的相场晶生长行法
袁训锋,丁雨田,郭廷彪,胡 勇,唐向前
(兰州理工大学 甘肃省有色金属新材料省部共建国家重点实验室,兰州 730050)
摘 要:基于Wheeler等提出的纯扩散相场模型,建立耦合溶质场、温度场和流场的相场模型,采用有限差分法对控制方程进行数值求解,研究Ni-Cu合金凝固过程中单晶粒枝晶和多晶粒枝晶在强制对流作用下的生长行为。结果表明:熔体的流动显著改变凝固前沿的传热和传质,从而改变枝晶的生长行为。在流速为6.43 m/s的垂直强制对流作用下,上游枝晶受过冷熔体冲刷,枝晶尖端溶质浓度和温度低,实际过冷度大,枝晶生长迅速,稳态生长速度比纯扩散时增加28%;热量和溶质在下游富集,下游枝晶尖端溶质浓度和温度高,实际过冷度小,枝晶生长缓慢,稳态生长速度比纯扩散时减小26%。
关键词:Ni-Cu合金;相场法;强制对流;枝晶生长;凝固;溶质场;温度场;流场
中图分类号:TG244 文献标志码:A
Phase-field method of dendritic growth under convection
YUAN Xun-feng, DING Yu-tian, GUO Ting-biao, HU Yong, TANG Xiang-qian
(State Key Laboratory of Gansu Advanced Non-ferrous Metal Materials,
Lanzhou University of Technology, Lanzhou 730050, China)
Abstract: Based on the Wheeler model, the phase-field model was built by coupling with the concentration field, temperature field and flow field. An explicit finite difference numerical method was used to solve the phase-field model equations and simulate both of the single and multi-grain dendritic growth of Ni-Cu alloys in a forced flow. The results show that the fluid flow alters the local heat and solute transfer at the solidification front, thus the dendritic growth behavior is significantly influenced. Under forced flow with a flow velocity of 6.43 m/s, the temperature and the concentration of the upstream dendritic crystal are low because of the undercooled melt flushing, the greater actual supercooling of the upstream dendritic crystal makes the dendritic crystal become fast, the tip velocity at steady state increases by about 28% compared with the case without flow. The heat and solute are enriched in the downstream, the temperature and the concentration of the downstream dendritic crystal are high, the less actual supercooling of downstream dendritic crystal makes the dendritic crystal growth become slow, the tip velocity at steady state decreases by about 26% compared with the case without flow.
Key words: Ni-Cu alloy; phase-field; forced flow; dendritic growth; solidification; concentration field; temperature field; flow field
枝晶组织是金属材料成形工艺过程中最常见的显微组织,它的形貌特征决定材料的性能。在凝固过程中,金属液的对流始终存在,它强烈地改变凝固过程中溶质场和温度场的分布,对枝晶的生长行为产生重要影响。因此,深刻理解和掌握金属液对流对枝晶生长的影响规律是有效预测和控制铸件性能的重要方面。在流场作用下,枝晶的生长行为逐渐成为国内外学者研究的热点。
近年来,国内外学者针对单质和合金,应用相场(Phase field,PF)[1-4]、前沿跟踪(Front tracking,FT)[5]、改进元胞自动机(Modified cellular automaton, MCA) [6-7]、格子Boltzmann[8-9]、元胞自动机-格子
Boltzmann[10-11](Cellular automaton-lattice Boltzmann, CA-LB)等方法研究对流作用下枝晶的生长规律。相场方法通过相场与温度场、溶质场和流场等其他外部场的耦合,可以直接模拟金属凝固过程中的溶质偏析、枝晶分支的形成、重熔等复杂现象,在微观组织模拟方面备受关注并得到较大的发展[12-17]。目前,耦合流场的相场法数值模拟主要集中在单质和合金等温凝固方面,对流场作用下合金非等温凝固过程中溶质场和温度场的分布以及枝晶生长机制缺乏了解。
本文作者基于Wheeler等[18]提出的纯扩散相场模型,进一步考虑成分过冷,枝晶择优生长方向和溶质再分配,建立耦合流场、溶质场和温度场的相场模型,对Ni-Cu合金凝固过程中单晶粒枝晶和多晶粒枝晶在强制对流作用下的生长行为进行模拟研究。
1 相场模型
相场法通过引入一个相场变量 来描述系统中各点的物理状态,在本研究中,在固/液界面上
来描述系统中各点的物理状态,在本研究中,在固/液界面上 在0→1范围内连续变化;
在0→1范围内连续变化; 为液相率,1-
为液相率,1- 为固相率。
为固相率。 =0时,表示为固相,
=0时,表示为固相, =1时,表示为液相。
=1时,表示为液相。
1.1 相场控制方程
相场控制方程可表达为
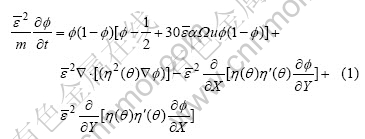
式中:u、t和X和Y均为无量纲变量且u=(T-Tm)/ (T-T0),t=t′/(ω2/κ),X=X′/ω,Y=Y′/ω;Ω=cp[ΔT+ mL(x′-x0)]/L,为无量纲过冷度;α=( ωL2)/ (12cpσTm),为系统的物理参量;m=μσTm/(κL),为界面动力学系数;
ωL2)/ (12cpσTm),为系统的物理参量;m=μσTm/(κL),为界面动力学系数; =δ/ω,为与界面层厚度有关的参量;η(θ)=1+ γcos(4θ),为各向异性因子;θ为界面法向与X正方向之间的夹角;γ为各向异性强度;T为温度;Tm为熔点;T0为系统初始温度;ΔT为热过冷度;X′和Y′为距离;δ为界面层厚度;ω为参考长度;t′为时间;κ为热扩散率;μ为界面迁移率;mL为液相线斜率;cp为定压比热容;L为单位体积的结晶潜热;σ为界面能;x0为过冷熔体初始浓度(摩尔分数);x′为熔体实际浓度(摩尔分数)。
=δ/ω,为与界面层厚度有关的参量;η(θ)=1+ γcos(4θ),为各向异性因子;θ为界面法向与X正方向之间的夹角;γ为各向异性强度;T为温度;Tm为熔点;T0为系统初始温度;ΔT为热过冷度;X′和Y′为距离;δ为界面层厚度;ω为参考长度;t′为时间;κ为热扩散率;μ为界面迁移率;mL为液相线斜率;cp为定压比热容;L为单位体积的结晶潜热;σ为界面能;x0为过冷熔体初始浓度(摩尔分数);x′为熔体实际浓度(摩尔分数)。
1.2 耦合流场的温度场控制方程
耦合流场的温度场控制方程为

1.3 质量及动量方程
流体速度满足质量守恒和Navier-Stokes方程,将其与相场方程耦合得到如下形式:

式中:ρ、p和υ分别为密度、压强和流体的运动粘度系数; 为单位体积的界面耗散力,定义为
为单位体积的界面耗散力,定义为 =-2υ(1-
=-2υ(1- )2
)2 hV/
hV/ 2,保证流速在固相(
2,保证流速在固相( →0)时为0,在液相(
→0)时为0,在液相( →1)时衰减,常数h为2.757。本研究计算忽略压力项。
→1)时衰减,常数h为2.757。本研究计算忽略压力项。
1.4 耦合流场的溶质场方程
耦合流场的溶质场控制方程为
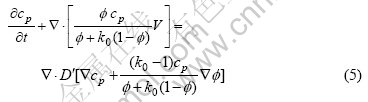
式中:D′为有效溶质扩散系数。如果Ds和Dl表示固液相的溶质扩散系数;k0为溶质平衡分配系数。D′可
表示为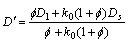 。
。
2 计算方法
2.1 相场参数及材料性能参数的取值
本研究模拟的Ni-Cu合金参数:Tm=1 594.5 K,L=2 100 J/cm3,cp=4.83 J/(K?cm3),x0=40.38%,σ= 3.38×10-5 J/cm2,υ=2.7×10-3 cm2/s,κ=0.27 cm2/s,Dl= 1.0×10-5 J/cm2,Ds=1.0×10-9 J/cm2,k0=0.86,mL= 0.821 1,μ=175.3 cm/(K?s),ω=2.1×10-4 cm,α=419,m=0.017, =0.005,γ=0.05。
=0.005,γ=0.05。
2.2 数值计算方法
对于传输方程(2)采用交替隐式格式求解,控制方程(1)、(3)、(4)和(5)同时采用显示差分格式求解。由于温度场方程所采用的交替隐式格式具有任意的稳定性,所以整个计算过程的稳定性受以下条件约束:

式中:m′=max(Dl,m,Pr);k′为考虑到方程中非线性项而设计的修正系数,一般取1~2;Pr=υ/κ为普朗特常数。在计算中取ΔX=ΔY=0.005,Δt=2.0×10-5。
2.3 初始条件和边界条件
假设初始晶核半径为R,过冷熔体以一定速度V从计算区域上边界流入,从下边界流出,计算区域模型的示意图如图1所示。
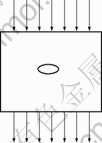
图1 计算区域模型的示意图
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of computational domain model
当X2+Y2≤R2时, =0,u=0,VX=0,VY=0,x′=x0;当X2+Y2>R2时,
=0,u=0,VX=0,VY=0,x′=x0;当X2+Y2>R2时, =1,u=-1,VX=0,VY=U,x′=x0。在计算区域的边界上,相场、温度场、速度场、溶质浓度场采用Neumann条件。
=1,u=-1,VX=0,VY=U,x′=x0。在计算区域的边界上,相场、温度场、速度场、溶质浓度场采用Neumann条件。
3 结果与分析
3.1 对流对单晶粒枝晶的生长形貌的影响
为了对有、无对流作用下的枝晶生长行为进行比较,分别模拟纯扩散和强制对流条件下Ni-Cu合金枝晶的生长过程。计算区域网格数为800×800,将半径为10个网格数且择优方向与水平夹角为0?的球形初始晶核放置于计算区域的中心。图2(a)所示为纯扩散条件下,合金初始浓度x0=40.38%(摩尔分数),过冷度ΔT=100 K和凝固时间t=40 000Δt时单晶粒枝晶相场形貌。图2(b)所示为Ni-Cu合金在流体入口速度为6.43 m/s的垂直强制对流条件下,其他模拟条件同图2(a)时的单晶粒枝晶相场形貌。从图2中可以看出,在纯扩散条件下,枝晶的4个最优生长方向均衡生长,枝晶的形貌具有很好的对称性;在垂直强制对流作用下,4个最优方向的生长情况不再相同,上游枝晶臂最长,水平方向枝晶臂次之,下游枝晶臂最短,枝晶生长的对称性被破坏。
3.2 对流对单晶粒枝晶生长溶质分布的影响
图3所示为图2中单晶粒枝晶生长对应的溶质分布。从图3可以看出,在纯扩散条件下,各枝晶尖端附近的溶质扩散层分布相同,在枝晶中心Cu的浓度低,枝晶的溶质分布具有很好的对称性。在引入强制对流后,上游枝晶浓度低于下游枝晶浓度,各主枝浓度存在明显差异。图4(a)和(b)所示分别为图3(a)和(b)中模拟区域网格数i=400时Cu的浓度(摩尔分数)与位置的关系。从图4(a)中可以看出:无流动时,在远离枝晶的液相区Cu的浓度为合金初始浓度;在固液界面区域由于凝固析出的Cu不能充分扩散到液相中,从而富集在枝晶前沿使得Cu的浓度高于初始浓度;固相区由于凝固过程中的溶质再分配,Cu的浓度都低于合金的初始浓度。从图4(b)可以看出:当存在强制流动时,在远离枝晶的液相区Cu的浓度与合金初始浓度相差不大;下游固液界面和整个固相区Cu的浓度高于合金初始浓度,上游区域的固液界面和整个固相区的Cu浓度都低于合金初始浓度,这是由于金属液的流动将上游枝晶凝固析出的大量溶质带到下游,上游枝晶前沿溶质富集不严重,而下游区域富集大量的Cu使固相线严重右移,从而凝固析出的固相Cu浓度也高于合金初始浓度。

图2 单晶粒枝晶生长的模拟形貌
Fig.2 Simulated morphologies of single-grain dendritic growth (t=40 000Δt): (a) Without flow; (b) With forced flow
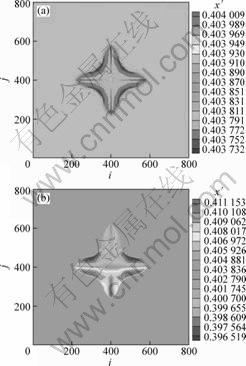
图3 单晶粒枝晶生长的溶质分布
Fig.3 Simulated single-grain dendrite solute profile (t= 40 000Δt): (a) Without flow; (b) With forced flow
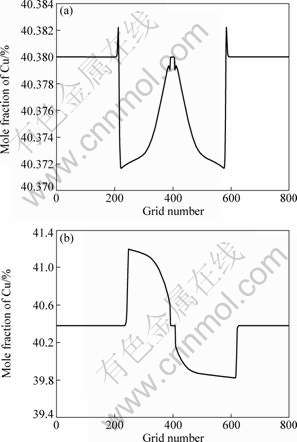
图4 纯扩散和强制对流作用下在模拟区域网格数为400时的溶质分布
Fig.4 Solution distribution of simulated fields in case of 400 computation grids: (a) Without flow; (b) With forced flow
强制对流对枝晶形貌的影响可解释为在合金凝固过程中发生溶质再分配,考虑成分过冷可得固液界面的过冷度为热过冷度(ΔT)和成分过冷度(mL(x′-x0))之和。一方面金属液的流动对上游枝晶冲刷,将凝固过程中释放的热量和溶质再分配析出的溶质带走,减少了上游枝晶尖端的热扩散层厚度和上游液相中的溶质浓度,两者都导致上游枝晶尖端的实际过冷度增大,枝晶生长迅速;另一方面,在下游,由于金属液流动从上游带来的溶质和热量以及自身凝固释放的热量和析出的溶质来不及扩散,造成尖端的热扩散层增厚和大量溶质富集,两者都使得下游枝晶尖端的实际过冷度减小,枝晶生长缓慢。因此,强制对流严重改变凝固前沿的温度场和浓度场的分布,从而对枝晶生长形貌产生很大的影响。
3.3 强制对流对枝晶尖端生长行为的影响
为了定量分析对流对枝晶生长行为的影响,本文作者计算强制对流作用下不同时刻的枝晶尖端生长速度,尖端温度和尖端溶质浓度(摩尔分数),并与和纯扩散条件下进行比较(见图5)。从图5可以看出,在凝固初始阶段,驱动枝晶生长的过冷度为初始过冷度,所有枝晶尖端都以较快的速度生长;随着枝晶的生长,枝晶凝固过程中释放大量的潜热和溶质再分配而析出大量的溶质,且在金属液的流动作用下部分潜热和溶质被带到下游,导致上、下游枝晶尖端的温度和下游尖端的溶质浓度迅速增加(虽然上游枝晶尖端的溶质浓度略微减小,但不足以影响总过冷度),使得枝晶尖端前沿的过冷度迅速减小,枝晶尖端生长速度迅速下降。经过一段时间后,溶质和潜热在界面前沿的释放与通过对流和扩散的迁移基本达到动态平衡,枝晶尖端温度和生长速度也逐渐趋于稳定。上游尖端的稳态生长速度比纯扩散时的大28%,下游尖端的稳态生长速度比纯扩散的小26%;上游尖端的稳态温度和稳态溶质浓度比纯扩散的分别低22%和1.2%,下游尖端的稳态溶质温度和稳态浓度比纯扩散的分别高20% 和1.9%。
3.4 强制对流作用下多晶粒枝晶的生长行为
为了研究强制对流作用下多晶粒枝晶的生长行为,先定计算区域的网格数为1 000×1 000。在计算区域放置5个晶核,A晶核位于计算区域的中心,择优方向取为á100?;其余4个晶核B、C、D和E随机分布,并随机的给予每个晶核一个择优生长方向。 合金流体入口速度为V=25.72 m/s,其他模拟计算条件与图2相同。
图5 单晶粒枝晶生长中尖端速度、尖端温度和尖端溶质浓度与凝固时间的关系
Fig.5 Relationship among tip velocity (a), tip temperature (b) and tip solute concentration (c) and time for single-grain dendritic growth

图6所示为Ni-Cu合金在强制对流作用下多晶粒枝晶的生长形貌演变过程的相场和溶质浓度场分布。图(a)-(c)为相场,图(d)-(f)为对应的溶质浓度场。从图6可以看出,在凝固初始阶段,多晶粒之间相互影响不明显,各枝晶在流场作用下独立生长,金属液流过枝晶,将溶质和潜热从上游迁移到下游,使得上游区域生长迅速,下游区域生长缓慢。随着凝固时间的延长,枝晶逐渐长大,枝晶间内部区域的枝晶臂生长主要受相邻枝晶的影响,相邻枝晶的温度场和溶质场发生重叠,重叠区域热扩散和溶质扩散受阻,温度升高,生长速度减慢甚至停止生长,枝晶的最优生长方向发生改变。在远离边界的外部区域,不受相邻枝晶影响的分支在流场作用下得到充分生长,上游区域的枝晶臂最长,水平方向的枝晶臂次之,下游区域的枝晶臂最短。此外,对C晶粒的演化过程进行观察发现,由于C晶粒最优生长方向与流体的流动方向既不平行也不垂直,在演化过程中各向异性程度减小。
4 结论
1) 基于Wheeler提出的纯扩散相场模型,进一步耦合溶质场、流场和温度场,建立了一个考虑成分过冷,枝晶择优生长方向和溶质再分配的相场模型。应用本模型对Ni-Cu合金凝固过程中的枝晶生长行为进行研究,在纯扩散条件下,枝晶在4个最优方向上均衡生长,枝晶的形貌和溶质的分布均呈现对称性。
2) 在有强制对流存在时,金属液的对流显著改变凝固前沿的溶质分布和温度分布,破坏枝晶生长的对称性。上游枝晶尖端的温度和溶质浓度低,生长速度快,其枝晶发达;下游枝晶尖端的温度和溶质浓度高,生长速度较慢,枝晶不发达。在流速为6.43 m/s的垂直强制对流作用下,上游尖端的稳态生长速度比纯扩散的大28%,下游尖端的稳态生长速度比纯扩散小的26%。
3) 多晶粒枝晶在强制对流作用下共同生长时,枝晶间的内部区域枝晶生长主要受相邻枝晶控制,远离边界的外部区域的枝晶生长主要受流场控制。此外,枝晶的最优生长方向与流场不平行也不垂直时,各向异性程度减小。
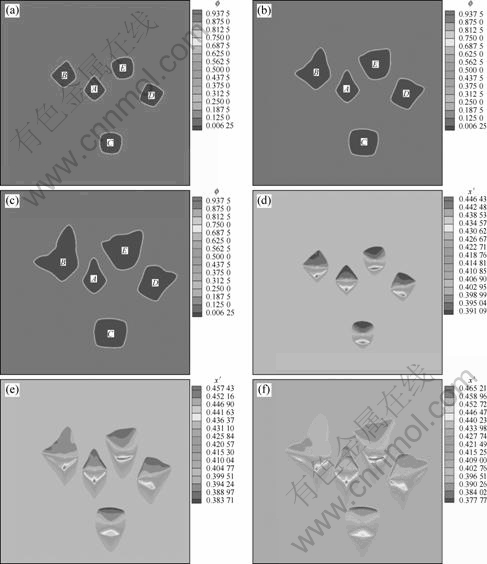
图6 强制对流作用下多晶粒枝晶生长的演变
Fig.6 Evolution of multi-grain dendritic growth in forced flow: (a), (b), (c) Phase field; (d), (e), (f) Concentration field
REFERENCES
[1] DIEPERS H J, BECKERMANN C. Simulation convection and ripening in a binary alloy mush using the phase-field method[J]. Acta Mater, 1999, 47(13): 3663-3678.
[2] TONHARDT R, AMBERG G. Dendritic growth of randomly oriented nuclei in a shear flow[J]. J Cryst Growth, 2000, 213(1/2): 161-187.
[3] TONHARDT R, AMBERG G. Phase-field simulation of dendritic growth in a shear flow[J]. J Cryst Growth, 1998, 194(3/4): 406-425.
[4] JEONG J H, GOLDENFELD N, DANTZIG J A. Phase field model for three-dimensional dendritic growth with fluid flow[J]. Phys Rev E, 2001, 64(4): 041602.
[5] AL-RAWAHI N, TRYGGASON G. Numerical simulation of dendritic solidification with convection: Two-dimensional geometry[J]. J Comp Phys, 2002, 180: 471-496.
[6] ZHU M F, LEE S Y, HONG C P. Modified cellular automaton model for the prediction of dendritic growth with melt convection[J]. Phys Rev E, 2004, 69(6): 1-12.
[7] 朱鸣芳, 戴 挺, 李成允, 洪俊杓. 对流作用下枝晶生长行为的数值模拟[J]. 中国科学E, 2005, 35(7): 673-688.
ZHU Ming-fang, DAI Ting, LI Cheng-yun, HONG Chun-pyo. Modeling of dendritic growth in the presence of convection[J]. Sci China E, 2005, 35(7): 673-688.
[8] MILLER W, SUCCI S, MANSUTTI D. Lattice Boltzmann model for anisotropic liquid-solid phase transition[J]. Phys Rev Letters, 2001, 86: 3578-3581.
[9] MILLER W, SUCCI S. A lattice Boltzmann model for anisotropic crystal growth from melt[J]. J Statistical Physics, 2002, 107: 173-186.
[10] 孙东科, 朱鸣芳. CA-LB模型模拟对流枝晶生长[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2007, 17(S1): 84-89.
SUN Dong-ke, ZHU Ming-fang. Cellular automaton-lattice Boltzmann model for modeling of dendritic growth in flowing melt[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metal, 2007,17(S1): 84-89.
[11] 杨朝蓉, 孙东科, 潘诗琰, 戴 挺, 朱鸣芳. CA-LBM模型模拟自然对流作用下的枝晶生长[J].金属学报, 2009, 45(1): 43-50.
YANG Chao-rong, SUN Dong-ke, PAN Shi-yan, DAI Ting, ZHU Ming-fang. CA-LBM model for the simulation of dendritic growth under natural convection[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2009, 45(1): 43-50.
[12] TONG X, BECKERMANN C. Velocity and shape selection of dendritic crystals in a forced flow[J]. Phys Rev E, 2000, 61(1): 49-52.
[13] 赵代平, 荆 涛, 柳百成. 相场方法模拟铝合金三维枝晶生长[J]. 物理学报, 2003, 52(7): 1737-1742.
ZHAO Dai-ping, JING Tao, LIU Bai-cheng. Simulating the three-dimensional dendritic growth of Al alloy using the phase-field method[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2003, 52(7): 1737-1742.
[14] 于艳梅, 杨根仓, 赵达文, 吕衣礼. 过冷熔体中枝晶生长的相场法数值模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2001, 50(12): 2423-2428.
YU Yan-mei, YANG Gen-cang, ZHAO Da-wen, L? Yi-li. Numerical simulation of dendritic growth in undercooled melt using phase-field approach[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2001, 50(12): 2423-2428.
[15] 龙文元, 蔡启舟, 陈立亮, 魏伯康. 二元合金等温凝固过程的相场模型[J]. 物理学报, 2005, 54(1): 256-262.
LONG Wen-yuan, CAI Qi-zhou, CHEN Li-liang, WEI Bo-kang. Phase-filed modeling of isothermal solidification in binary alloy[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2005, 54(1): 256-262.
[16] 陈玉娟, 陈长乐. 相场法模拟对流速度对上游枝晶生长的影响[J]. 物理学报, 2008, 57(7): 4585-4589.
CHEN Yu-juan, CHEN Chang-le. Simulation of the influence of convection velocity on upstream dendritic growth using phase-field method[J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2008, 57(7): 4585-4589.
[17] 邱文旭, 陈长乐, 马 强, 张利学. 对流下二元合金等温凝固过程的相场模拟[J]. 铸造, 2009, 58(3): 241-248.
QIU Wen-xu, CHEN Chang-le, MA Qiang, ZHANG Li-xue. Phase-field simulation of isothermal solidification in binary alloy with forced convection[J]. Foundry, 2009, 58(3): 241-248.
[18] WHEELER A A, MURRAY B T, SCHAEFER R J. Computation of dendrites using a phase field model[J]. Physica D, 1993, 66(1/2): 243-262.
(编辑 李艳红)
收稿日期:2009-06-04;修订日期:2009-10-20
通信作者:丁雨田,教授,博士;电话:0931-2757285;E-mail:dingyt@lut.cn