DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2017.04.009
卷取温度对高Ti高强钢组织及性能的影响
庞启航1,唐荻1,赵征志1,徐梅1,董陈1,刘亚坤2
(1. 北京科技大学 工程技术研究院,北京,100083;
2. 总参信息化部 济南军代室,山东 济南,250001)
摘要:利用扫描电镜(SEM)和透射电镜(TEM)等仪器研究卷取温度对高Ti微合金热轧高强钢显微组织和力学性能的影响。研究结果表明:随着卷取温度的升高,抗拉强度不断减小,屈服强度先增加再减小,伸长率不断增大。当350 ℃卷取时,试验钢拥有良好的综合力学性能,即抗拉强度为1 253 MPa,屈服强度为1 099 MPa,伸长率为13%,-20 ℃冲击功为102 J。这是因为该卷取温度略低于Ms点,试验钢显微组织由大量板条贝氏体(细小且交织)、少量马氏体和针状铁素体组成,这种显微组织能有效阻碍位错运动,从而提高强度。同时大角度晶界能够阻碍裂纹扩展,再加上板间的薄膜M/A,保证了材料的塑性和韧性。
关键词:工程机械;卷取温度;微观组织;强化机理
中图分类号:TG142.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-7207(2017)04-0910-07
Effects of coiling temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of high Ti microalloyed
ultra-high strength steel
PANG Qihang1, TANG Di1, ZHAO Zhengzhi1, XU Mei1, DONG Chen1, LIU Yakun2
(1. Institute of Engineering Technology, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China;
2. Jinan Military Representative Office, The General Staff of the Ministry of Information, Jinan 250001, China)
Abstract: The microstructure and mechanical properties of the steels with different coiling temperature were studied by utilizing scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The results show that with the increase of coiling temperature, the tensile strength gradually decreases, while the yield strength increases first and then decreases, and the elongation increases continuously. At coiling temperature 350 ℃, the experimental steel shows the best mechanical properties with tensile strength at 1 253 MPa, yield strength at 1 099 MPa and the elongation of 13%, while the Charpy impact energy is 102 J at -20 ℃. The main reason is that when the coiling temperature is slightly lower than martensite transformation temperature (Ms), the main microstructure of the tested steel is the fine and interlocking lath bainite and martensite. This microstructure can effectively block the dislocation motion to improve the strength. The large angle grain boundary can hinder the crack growth, and the thin film M/A between the laths can increase the plasticity and toughness of the materials.
Key words: engineering machinery; coiling temperature; microstructure; strengthening mechanism
工程机械高强钢,主要用于挖掘机械、工程起重机械、铲土运输机械、矿山机械、混凝土机械,以及工业车辆等。随着工程机械向高参数化、大型化、轻量化发展,对工程机械构件材料的强韧性、成型性和焊接性提出更高的要求[1-4]。传统1 000 MPa级以上的工程机械用钢,大多数要经过复杂的调质处理,如GAO等[5]使用BQ&P或BQ&T热处理工艺使0.4C-Mn-Si-Cr系高强钢的抗拉强度达到1 700 MPa,同时具有25.2%伸长率和良好低温冲击韧性;康健等[6]通过合理的热处理工艺,使C0.17(Nb+V+Ti)0.08高强调质钢的屈服强度达到1 030 MPa,抗拉强度为1 080 MPa,伸长率为15.9%,-40 ℃冲击功为144 J的优良性能;方鸿生等[7]设计了一种经济型的0.2C-Mn-Si-Cr系贝氏体/马氏体复相钢,通过淬火+回火处理,使试验钢的抗拉强度大于1 500 MPa,屈服强度大于1 200 MPa,伸长率为11%~14%。复杂的热处理工艺不仅增加了生产周期、生产成本,更多的消耗了自然资源。同时为了在热处理过程中充分发挥固溶强化和析出强化的作用,高强钢的成分中碳和合金元素的含量比较高,这样不利于焊接和废钢回收再利用。因此,低碳微合金+热轧工艺直接生产1 000 MPa级以上的高强钢是一种新趋势。一般来说,钢中最常用的微合金化元素是Nb,V和Ti,其作用是析出强化和细化晶粒。与Nb和V微合金化相比,Ti微合金化的应用较少,这是因为Ti的化学性质活泼以及析出时对温度和冷却速度较敏感。目前对高Ti微合金化的研究只侧重于基体为铁素体的高强钢,且多为理论研究或实验室开发阶段,而通过Ti微合金化生产以马氏体、贝氏体或马贝复合组织为基体的高强钢的研究较少,通常Ti的添加量又比较低,一般质量分数小于0.1%。FUNAKAWA等[8]设计了0.04C-0.1Ti-0.2Mo系的高Ti热轧高强钢,其抗拉强度只有780 MPa;谢辉等[9]设计了Ti含量(质量分数)为0.10%~0.17%的热轧高强钢,其抗拉强度也只有820 MPa。据统计[10]我国TiO2的储量约为6.3亿t,几乎占世界总储量的45.6%,资源非常丰富,因此,生产钛微合金高强钢对提高我国钢铁行业的竞争力具有十分重要的意义。结合前人的相关研究,本文作者提出一种0.15Ti微合金高强度热轧带钢,重点研究卷取温度对试验钢组织与性能的影响,并探讨钛微合金化钢获得高强度的强化机制,从而确定最佳的生产工艺。
1 试验
试验钢的化学成分(质量分数,%)为0.09C,0.23Si,1.8Mn,0.04Nb,0.15Ti,0.04V,0.002B,0.036Al,0.003N,Fe余量。采用50 kg真空感应炉冶炼,将铸锭锻造成长度×宽度×高度为80 mm×80 mm×50 mm钢坯,在钢坯上切取直径×长度为4 mm×10 mm的试样,用德国DIL 805A热膨胀仪依据标准YB T 5127—1993测定试验钢相变点,得到试验钢的Ac1和Ac3分别为714和875 ℃,Ms为367 ℃,再结合试样的金相照片绘制静态连续冷却(CCT)曲线,如图1所示。将厚50 mm的钢坯在直径为350 mm试验轧机上,经6道次轧制成厚4 mm的钢板,其轧制工艺和冷却制度如图2所示,即将钢坯加热至1 200 ℃保温1 h,再经1 150~1 050 ℃粗轧,随后于1 000 ℃时开始精轧,终轧温度为870 ℃,轧后以大于35 ℃/s的冷却速度分别水冷至200(淬火),300,350,400和500 ℃,然后放入电阻炉中保温1.5 h后随炉冷至室温模拟卷取。
从轧后试验钢板中心部位切取金相试样,沿轧向研磨抛光将试样磨平、抛光,经体积分数为4%硝酸酒精侵蚀后置于Zeiss Axiovert 40MAT光学显微镜和LEO-1450型扫描电镜下观察;试验钢研磨后在室温下的电解液(15%高氯酸+85%乙醇,体积分数)中进行电解抛光,电压为15 V,电流为0.7~1.0 A,抛光时间为10~15 s,然后在具有EBSD功能的LEO-1450型扫描电镜上进行晶粒取向观察(加速电压为20 kV,步长为0.08 μm)。用线切割机从厚度4 mm热轧钢版上切取薄片,磨到50 μm厚度,冲成直径为3 mm的原片,然后电解双喷至穿孔,电解液为5%(体积分数)的高氯酸酒精溶液,双喷电压为35~45 V,最后在JEM-2100TEM透射电镜200 kV条件下分析试验钢中精细结构,同时用萃取复型样来观察析出相的分布、形貌和尺寸。据GB/T 228—2002沿钢板轧向切取标距为50mm的拉伸试样,在CMT4105型万能拉伸试验机上以2 mm/min的速度进行拉伸实验。冲击试样沿轧后钢板横向方向切取长度×宽度×高度为55 mm×10 mm×4 mm的夏比非标准试样,试验温度为-20 ℃。
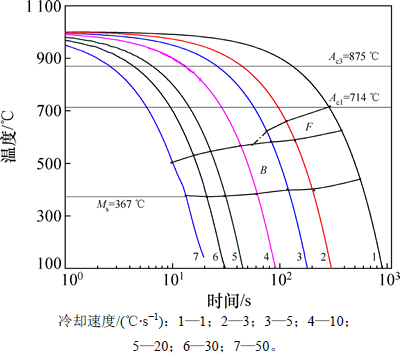
图1 试验钢的静态CCT曲线
Fig. 1 Static CCT curves of tested steels

图2 试验钢的控轧控冷工艺图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of thermo mechanical control process of tested steels
2 试验结果与分析
2.1 力学性能
图3所示为卷取温度对试验钢力学性能和-20 ℃冲击功的影响。由图3(a)可知:随着卷取温度的升高,抗拉强度先缓慢降低而后急剧降低,当500 ℃卷取时,抗拉强度最小值为977 MPa;屈服强度随卷取温度的升高,先升高至最大值1 133 MPa,再降低至最小值779 MPa,最后趋于平稳,总体变化趋势比较剧烈;而试验钢的伸长率随卷取温度的升高而增加,呈现“M”趋势,当500 ℃卷取时,伸长率最大为15%。由图3(b)可知:随着卷取温度的升高,-20 ℃的冲击功(AKV)先升高后降低趋于平稳,在350 ℃卷取时,试验钢的AKV有最大值,说明在此温度下其具有最优的塑/韧性。综上所述,当350 ℃卷取时,试验钢达到了1 200 MPa级热轧高强钢的力学性能指标,即抗拉强度为1 253 MPa,屈服强度为1 099 MPa,伸长率为13%,冲击功为102 J。
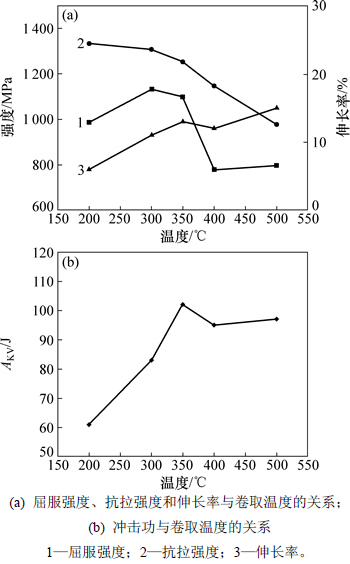
图3 卷取温度对试验钢力学性能的影响
Fig. 3 Effects of coiling temperature on mechanical properties of tested steels
2.2 显微组织
图4所示为不同卷取温度下试验钢的扫描电镜(SEM)像。试验钢轧后直接淬火组织为板条马氏体,各组板条束相互取向不同,交叉分割,同一板条束内各板条块取向一致,且板条块界非常清晰,板条宽度为0.5~1.2 μm,如图4(a)所示。由图4(b)可见:300 ℃卷取时,试验钢的组织由更细小板条马氏体、回火马氏体和少量铁素体组成,同时在原奥氏体晶界、板条束界和板条块界上弥散分布着细小的碳化物,这是因为当试验钢轧后快速冷却至Ms以下时,形成了淬火马氏体(板条结构),在随后300 ℃卷取过程中,部分淬火马氏体分解为低碳马氏体和ε碳化物组成的混合物[11],这相当于进行了低温回火,再加上过冷度减小(相对于直接淬火),板条组织无法充分转变,因此,板条结构变得细且浅,板条间距略有所增加为0.5~1.3 μm;在冷速不变,卷取温度升至350 ℃时,此温度基本等于Ms点温度(即在下贝氏体和马氏体转变的交叉区域),因此显微组织由板条贝氏体、弥散分布的碳化物和马氏体构成。板条间距为0.3~1.1 μm,且相互交织形成互锁结构,这种组织结构能够有效地提高材料的强度和韧性,如图4(c)所示。当400 ℃卷取时,试验钢中板条贝氏体,被粒状贝氏体所取代,同时出现了M/A岛,这是因为在贝氏体转变过程中,碳原子不断地从贝氏体基体向奥氏体中扩散,使得剩余奥氏体内逐渐富碳,但岛内的碳含量富集程度尚达不到能析出碳化物的水平,故成为富碳奥氏体岛,在冷却过程中一部分将转变成马氏体,即M/A岛状组织[12],试验钢的有效晶粒粒度为0.8~2.0 μm,如图4(d)所示。由图4(e)可见:500 ℃卷取时,试验钢的组织由针状铁素和粒状贝氏体构成,其有效晶粒粒度为1.5~3.0 μm。
图5所示为在不同卷取温度下试验钢的透射电镜(TEM)像。由图5(a)可以看出:经300 ℃卷取,板条内部有较高的位错密度,板条宽度为25~30 nm;当卷取温度升至350 ℃时,板条内部位错密度减少,因为板条贝氏体(低碳)转变发生在贝氏体转变区的较低温度区,是切变和扩散混合型转变[12],由此推断板条组织为板条贝氏体,其宽度为30~50 nm,且在板条之间存在薄层状的M/A,如图5(b)中箭头所示;当400 ℃卷取时,试验钢的显微组织中已经观察不到板条结构,但可以观察到粒状贝氏体和短条状的M/A,如图5(c)中箭头所示。

图4 不同卷取温度下的试验钢SEM像
Fig. 4 SEM images of tested steels at different coiling temperatures

图5 不同卷取温度下的试验钢TEM像
Fig. 5 TEM images of tested steels at different coiling temperatures
3 讨论
3.1 卷取温度对力学性能的影响
卷取温度是热轧带钢最为关键的工艺参数,它决定材料的组织与性能,同时也决定强韧化机制。在淬火和较低的300 ℃卷取时,对强度有主要贡献的是位错强化和相变强化,由于淬火和卷取温度明显低于Ms点,因此,试验钢的组织基体为马氏体;同时,由于冷却速度比较快,将轧制过程中产生大量位错保留下来,加上较低的卷取温度抑制了碳及合金元素的扩散以及位错的释放,这样易于板条结构的形成,因此,大幅度地提高了试验钢的强度[13];但由于板条内位错密在变形中很难穿过板条晶界持续运动,同时,板条晶界处没有较软相来协调,这导致了其塑性和韧性低于350 ℃卷取时的试验钢。相对于直接淬火工艺,在300 ℃卷取过程中,显微组织中部分淬火马氏体分解,位错得以释放(相当于进行了低温回火处理),因此其强度略有减少,塑性和韧性提高。
当350 ℃卷取时,此温度正好处于下贝氏体和马氏体转变区间的交叉区域,即切变和扩散混合型控制转变的板条贝氏体极易生成,同时,随着卷取温度升高,碳及合金元素的扩散能力也有所增强,这样在生成板条贝氏体时,碳原子不断地从板条内向板条界面扩散,最后在板条间生成薄层状的M/A,而这种薄层状的M/A有利于改善材料的韧性[14],因此,试验钢伸长率和冲击性能明显提高。通过EBSD测得300 ℃和350 ℃卷取时试验钢90%晶粒的有效晶粒粒径分别为0.2~1.7 μm和0.2~1.4 μm。图6所示为300 ℃和350 ℃卷取时试验钢的电子背向散射衍射(EBSD)形貌,图中黑色线为高角度晶界取向(>15°),为板条晶界和相界面,红色线为低角度晶界取向(2°~5°),展现为位错和亚结构。由图6可以看出:相比300 ℃卷取,350 ℃卷取试验钢的位错和亚结构明显减少,同时大角度晶界(>50°)也明显减少,虽然大角度晶界能够有效阻止裂纹的扩展,提高材料的韧性[15],但350 ℃卷取时,试验钢的有效晶粒粒径更细小,此时细晶强化是主要强韧化手段。综上所述,该试验钢具有最佳的综合力学性能。
当400 ℃和500 ℃卷取时,试验钢显微组织分别以粒状贝氏体和针状铁素体为主,显微组织的变化导致了试验钢的强度明显降低,但仍然能够保持最低抗拉强度在950 MPa以上,是因为随着卷取温度的提高,析出强化作用逐渐增强。一般来说轧后快速冷却会抑制第二相析出,所以,本实验中第二相析出主要在轧制过程和卷取过程[9]。因此,在试验钢添加0.15Ti,同时复合添加少量Nb和V,利用Ti和Nb在高温轧制阶段碳氮化合物析出来钉扎位错,细化奥氏体晶粒[16],同时利用钒的碳氮化合物析出温度较低,来扩大析出的温度范围[17]。利用碳膜萃取法对试验钢在350 ℃和400 ℃卷取时试样中析出物的结构进行分析。400 ℃卷取时析出物粒径为5~10 nm,形状主要是圆形,比350 ℃卷取时析出物粒径(3~7 nm)要略大且析出量比较多,如图7(a)和7(b)所示;500 ℃卷取时,碳化物析出更多,在双喷试样的TEM图片中就能够发现大量析出物,其粒径为5~12 nm,如图7(c)所示。
3.2 最佳卷取温度时的强韧化机制分析
综上所述,350 ℃卷取时试验钢的综合力学性能最佳,其主要的强化方式可归纳为细晶强化、析出强化和位错强化。
1) 细晶强化。随着材料晶粒粒径的减小屈服强度不断提高。因为晶粒越细,单位体积内的晶粒界面越多,晶界的原子排列比晶粒内部的排列更加紊乱,导致位错密度较高[18]。晶界对正常滑移的位错产生缠结,使继续移动的阻力增大,宏观上表现为变形抗力增大,强度提高。根据Hall–Petch方程可以表示为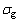
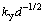 ,其中d为平均晶粒粒度,在本文中d取EBSD测量的有效晶粒粒径0.8 μm;对于低碳高强钢,ky为等于0.55 MPa·m1/2的常数。因此,细晶强化贡献量约为614 MPa。
,其中d为平均晶粒粒度,在本文中d取EBSD测量的有效晶粒粒径0.8 μm;对于低碳高强钢,ky为等于0.55 MPa·m1/2的常数。因此,细晶强化贡献量约为614 MPa。
2) 析出强化。根据Ashby-Orowan方程可以表示为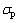
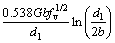 。其中:G为剪切模量,G=8.3×104 MPa;b为Burgers矢量,nm;d1为沉淀析出物的直径,nm;fv为沉淀析出物的体积分数,%。当温度较低时不利于碳和合金元素的扩散。因此,在350 ℃卷取时,碳化物二次析出比较少,大量析出物主要在轧制过程中产生,由图7(a)可知:析出物的平均直径约为5 nm,fv=0.025 1%,因此,析出强化贡献量约为101 MPa。
。其中:G为剪切模量,G=8.3×104 MPa;b为Burgers矢量,nm;d1为沉淀析出物的直径,nm;fv为沉淀析出物的体积分数,%。当温度较低时不利于碳和合金元素的扩散。因此,在350 ℃卷取时,碳化物二次析出比较少,大量析出物主要在轧制过程中产生,由图7(a)可知:析出物的平均直径约为5 nm,fv=0.025 1%,因此,析出强化贡献量约为101 MPa。
3) 位错强化。位错对钢材的塑性和韧性有双重作用。一方面,位错的合并以及在障碍处的塞积会使裂纹形成,从而使韧塑性降低;另一方面,由于位错在裂纹尖端塑性区内的移动可以缓解尖端的应力集中,使韧塑性又有所提高[19]。在350 ℃卷取试验钢中,由于大量细小的板条组织存在,从而产生了大量的大角度晶界,进而增加了位错运动阻力,阻碍了穿晶裂纹的扩展,最终提高钢板的塑韧性,因此,位错强化结合特定组织(相变强化)能够发挥更大强化作用。

图6 试验钢的EBSD形貌和晶界角度分布
Fig. 6 Microstructure and misorientation angle distributions of tested steels by EBSD

图7 不同卷取温度下试验钢中析出粒子分布
Fig. 7 TEM images of tested steels coiling at different temperatures
4 结论
1) 随着卷取温度的升高,抗拉强度不断减小,屈服强度先增加再减小,伸长率不断增大。当350 ℃卷取时,试验钢具有良好的综合力学性能,即抗拉强度为1 253 MPa,屈服强度为1 099 MPa,伸长率为13%,-20 ℃冲击功为102 J。这是因为该卷取温度略低于Ms点,试验钢显微组织由大量板条贝氏体(细小且交织)、少量马氏体和针状铁素体组成,这种显微组织能有效阻碍位错运动,从而提高强度。同时大角度晶界能够阻碍裂纹扩展,再加上板间的薄膜M/A,保证了材料的塑性和韧性。
2) 350 ℃卷取时,试验钢的强化方式可归纳为细晶强化、析出强化和位错强化。试验钢高Ti同时复合添加少量Nb和V的成分设计,使钢中第二相的析出温度范围扩大,但主要析出过程发生在轧制阶段,这样有效细化奥氏体晶粒,而轧后快速冷却抑制了晶粒长大,同时保留大量位错和缺陷,起到了位错强化作用;适当的卷取温度有效促进了组织相变,同时保证了碳化物二次析出,且抑制了碳化物长大,从而改善了试验钢的塑性和韧性,提高综合力学性能。
参考文献:
[1] 钱亚军, 余伟, 武会宾, 等. 热处理对1 000 MPa级工程机械结构用钢组织和性能的影响[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2010, 32(5): 599-604.
QIAN Yajun, YU Wei, WU Huibin, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 1 000 MPa grade structural steel for construction machinery[J]. Journal of University of Science & Technology Beijing, 2010, 32(5): 599-604.
[2] LI B, MONTEIRO S N, PENG Z, et al. Effects of heat treatment on transverse and longitudinal mechanical properties of engineering machinery steel WQ960[C]//Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials 2014. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2014: 191-198.
[3] HU S E, SUN W H, LIU X D, et al. Development and application practice of a 550 MPa grade steel plate in purpose to reduce weight for heavy machinery manufacture[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2014, 773: 518-524.
[4] ZHANG T, HOU H X, ZHAO T. Effect of heat treatment on the properties and precipitations of high strength steel plate for construction machinery[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 971/972/973: 240-243.
[5] GAO G, ZHANG H, GUI X, et al. Enhanced ductility and toughness in an ultrahigh-strength Mn-Si-Cr-C steel: the great potential of ultrafine filmy retained austenite[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 76(5): 425-433.
[6] 康健, 卢峰, 王昭东, 等. 工程机械用 960 MPa级调质钢板的淬火工艺研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 32(1): 52-55.
KANG Jian, LU Feng, WANG Zhaodong, et al. Study on quenching process of 960 MPa quenched and tempered steel plates for construction machinery[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2011, 32(1): 52-55.
[7] 方鸿生, 刘东雨, 常开地, 等. 1 500 MPa级经济型贝氏体/马氏体复相钢的组织与性能[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2001, 13(3): 31-36.
FANG Hongsheng, LIU Dongyu, CHANG Kaidi, et al. Microstructure and properties of 1 500 MPa economical Bainite/Martensite duplex phase steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2001, 13(3): 31-36.
[8] FUNAKAWA Y, SHIOZAKI T, TOMITA K, et al. Development of high strength hot-rolled sheet steel consisting of ferrite and nanometer-sized carbides[J]. ISIJ International, 2004, 44(11): 1945-1951.
[9] 谢辉, 杜林秀, 胡军. 冷却工艺对低碳 Ti 微合金化热轧超高强钢组织性能的影响[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 35(4): 508-511.
XIE Hui, DU Linxiu, HU Jun. Effects of cooling parameters on microstructures and mechanical properties of hot rolled Ti-Microalloyed low-carbon ultrahigh-strength steels[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2014, 35(4): 508-511.
[10] 毛新平, 孙新军, 康永林, 等. 薄板坯连铸连轧 Ti 微合金化钢的物理冶金学特征[J]. 金属学报, 2006, 42(10): 1091-1095.
MAO Xinping, SUN Xinjun, KANG Yonglin, et al. Physical metallurgy for the titanium microalloyed strip produced by thin slab casting and rolling process[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 42(10): 1091-1095.
[11] 张可, 雍岐龙, 孙新军, 等. 回火温度对高Ti微合金直接淬火高强钢组织及性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2014, 50(8): 913-920.
ZHANG Ke, YONG Qilong, SUN Xinjun, et al. Effect of tempering temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of high Ti microalloyed directly quenched high strength steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014, 50(8): 913-920.
[12] 李鹤林. 高强度微合金管线钢显微组织分析与鉴别图谱[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001: 8-59.
LI Helin. Microstructure analysis and differential spectrum of micro-alloy high strength pipeline steel[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2001: 8-59.
[13] 杨德庄. 金属材料位错与金属强化机制[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 1991: 119-127.
YANG Dezhuang. Dislocation of metallic materials and metal reinforcement mechanism[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 1991: 119-127.
[14] WANG C, DING H, CAI M, et al. Characterization of microstructures and tensile properties of TRIP-aided steels with different matrix microstructure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 610: 65-75.
[15] WANG X, ZHAO A, ZHAO Z, et al. Mechanical properties and characteristics of nanometer-sized precipitates in hot-rolled low-carbon ferritic steel[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2014, 21(3): 266-272.
[16] JUNG J, LEE S J, KIM S, et al. Effect of Ti additions on micro-alloyed Nb TRIP steel[J]. Steel Research International, 2011, 82(7): 857-865.
[17] SAWADA M, ADACHI K, MAEDA T. Effect of V, Nb and Ti addition and annealing temperature on microstructure and tensile properties of AISI 301L stainless steel[J]. ISIJ International, 2011, 51(6): 991-998.
[18] 赵征志, 佟婷婷, 赵爱民, 等. 1 470 MPa 级双相钢的性能特征与强韧化机制[J]. 材料研究学报, 2014, 28(11): 828-834.
ZHAO Zhengzhi, TONG Tingting, ZHAO Aimin, et al. Mechanical properties and strengthen-toughening mechanism of 1 470 MPa grade dual-phase steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2014, 28(11): 828-834.
[19] MAO X, HUO X, SUN X, et al. Strengthening mechanisms of a new 700 MPa hot rolled Ti-microalloyed steel produced by compact strip production[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2010, 210(12): 1660-1666.
(编辑 杨幼平)
收稿日期:2016-04-17;修回日期:2016-06-22
基金项目(Foundation item):国家自然科学基金资助项目(51271035)(Project(51271035) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China)
通信作者:庞启航,博士研究生,从事先进超高强钢研究;E-mail:qihang25@163.com