DOI:10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.11.04
过时效阶段Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金的晶间腐蚀再敏化
王芝秀1, 2,朱 凡1,郑 凯1,贾 俊1,韦玉龙1,李 海1, 2,郑子樵3
(1. 常州大学 材料科学与工程学院,常州 213164;
2. 常州大学 江苏省材料表面科学与技术重点实验室,常州 213164;
3. 中南大学 材料科学与工程学院,长沙 410083)
摘 要:采用维氏硬度计和加速腐蚀试验,分别测试Al-1.1Mg-1.2Si-0.9Cu合金(质量分数,%)在220 ℃时效过程中硬化行为和IGC敏感性。结果表明:合金在过时效阶段能够发生IGC→PC→IGC的腐蚀行为转变,出现所谓的PC→IGC再敏化现象。过时效阶段晶界Q相出现连续→断续→连续的分布特征变化,决定其与无析出区能否构成连续腐蚀微电池,是合金发生IGC→PC→IGC转变的主要原因。利用晶界析出相粗化与长大过程同步进行、先后主导的观点能够合理地解释晶界Q相分布特征和无析出区宽度在过时效阶段的变化规律。
关键词:Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金;过时效;析出;晶间腐蚀;坑蚀
文章编号:1004-0609(2018)-11-2199-07 中图分类号:TG146.4 文献标志码:A
6000系Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金属于时效硬化铝合金,具有密度低、强度中等以及良好的成形性、耐蚀性、焊接性等,广泛应用于汽车制造、轨道交通和航天航空等领域。尽管6000系铝合金耐蚀性良好,但在一定合金化程度或时效状态下,该系合金具有较强的晶间腐蚀(Intergranular corrosion,IGC)敏感性。如添加Cu能够细化β相(Mg2Si)、引入Q相(Al4Mg8Si7Cu2或Al5Mg8Si6Cu2[1]),从而提高合金强度[2],但IGC敏感性也随之出现,并随Cu含量增加而增大[3-6]。此外,时效对IGC亦有显著影响[7-11]。一般来说,欠时效、峰时效状态下,合金IGC敏感性较强,而过时效能减轻、甚至消除IGC,如T78处理便是为了消除6056合金IGC而开发的一种双级过时效工艺[12]。
IGC是一种发生于晶界的局部电化学腐蚀行为,源于晶界区不同特征组织在腐蚀介质中形成连续分布的微电池、进而微电池阳极发生连续溶解造成的。时效硬化铝合金晶界区组织包括晶界析出相和紧邻晶界的无析出区(Precipitation free zone,PFZ)。 LARSEN等[5]、SVENNINGSEN等[8]、KAIRY等[13-14]研究表明,峰时效状态下,连续分布的晶界Q相或富Cu膜与连续分布的贫Cu的PFZ,二者之间具有较大的电位差,能够分别作为阴极和阳极并构成连续腐蚀微电池,从而造成Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金发生IGC。过时效过程中,连续分布的晶界Q相或富Cu膜不断粗化,逐渐形成大间距、断续分布状态,最终不能再与PFZ形成连续腐蚀微电池,相应地,合金IGC敏感性逐渐消失,转而发生点蚀(Pitting corrosion,PC),即峰时效合金在随后过时效过程中腐蚀行为只能发生IGC→PC转变,这是目前人们对Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金腐蚀行为演变过程的普遍认识。
然而,LI等[15]研究时效对一种Al-1.0Mg-1.1Si- 0.9Cu-0.05Fe-0.5Zn-0.01Ti(质量分数,%)6000系铝合金腐蚀行为的影响时发现,具有强烈IGC敏感性的峰时效合金在随后过时效过程中,IGC敏感性逐渐消失,转而发生PC,这与目前人们的普遍认识是一致的。然而,进一步过时效,合金再次发生IGC,即出现所谓的IGC再敏化现象。前一阶段IGC→PC转变与晶界Q相或富Cu膜发生粗化,由连续分布变成断续分布有关;对于后一阶段PC→IGC转变,目前鲜有研究报道。为了拓宽对铝合金IGC再敏化现象的认识,本文作者测试了一种6000系铝合金的时效硬化和腐蚀行为,观察和分析时效过程中晶界区组织特征及演变规律,并在此基础上,进一步明确提出过时效阶段6000系铝合金IGC再敏化的机理。
1 实验
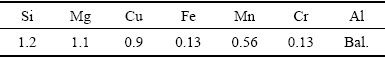
实验材料为实验室自制的2 mm厚的冷轧板材,化学成分见表1。板材经550 ℃,1 h固溶处理和室温水淬后,立即进行220 ℃时效。时效过程中,采用HXD-1000维氏硬度计测量硬度,加载力为9.8 N,保载时间15 s。每一样品测量10次,取平均值并作时效硬化曲线。
表1 实验合金的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of alloy (mass fraction, %)
根据《GB/T7998—2005铝合金晶间腐蚀测试方法》评估时效合金的IGC敏感性。时效样品经机械抛光、碱洗和酸洗,在(35±2) ℃的30 g/L NaCl+10 ml/L HCl溶液中浸泡24 h。然后,截取腐蚀样品横截面并抛光,在OLYMPUS CK40M金相显微镜上观察腐蚀行为,并测量最大腐蚀深度。
采用TECNAI F20高分辨透射电镜(High resolution transmission electron microscopy,HRTEM)观察时效合金的基体和晶界区组织特征,加速电压200 kV。样品经机械减薄至约100 μm,在约-20 ℃的30% HNO3+70% CH3OH(体积分数)混合溶液中双喷电解抛光,电流约50 mA,电压约12 V。
2 实验结果
2.1 时效硬化行为
图1所示为实验合金的220 ℃时效硬化曲线。由图1可以看出,时效过程中,合金依次经历欠时效、峰时效、过时效3个硬化阶段。550 ℃、1 h固溶处理及室温水淬后,合金硬度约86 HV1;随着220 ℃时效时间延长,硬度逐渐增加,并在时效0.6 h达到最大值约137 HV1,此时合金处于峰时效状态;继续时效,硬度不断下降,合金进入过时效阶段。
2.2 腐蚀行为
图2所示为220 ℃时效样品IGC测试后的抛光横截面金相照片。由图2可以看出,经0.03 h欠时效,样品横截面各处均发生IGC(即均匀IGC),最大腐蚀深度约215 mm(见图2(a));经0.6 h峰时效,合金IGC更为严重,最大腐蚀深度增加至约300 μm(见图2(b));过时效至1.4 h,试样横截面上仅某些位置发生IGC(即局部IGC),最大腐蚀深度也减小至约140 μm(见图2(c));继续过时效至5.6 h,合金IGC敏感性消失,仅发生PC,最大腐蚀深度约200 μm(见图2(d))。然而,当延长过时效至14 h,合金再次发生局部IGC,最大腐蚀深度约240 μm(见图2(e));继续过时效至139 h,合金再次发生均匀IGC,最大腐蚀深度进一步增加至约290 μm(见图2(f))。根据IGC测试结果可知,峰时效合金在随后过时效阶段,腐蚀行为依次发生IGC→PC→IGC转变。
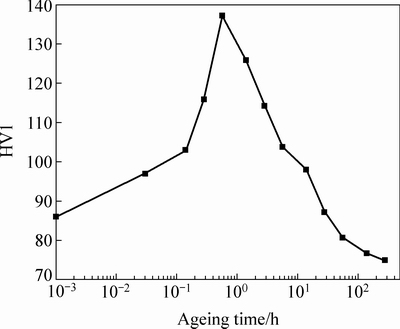
图1 经220 ℃时效合金的硬化曲线
Fig. 1 Hardness-time curve of alloy aged at 220 ℃
2.3 TEM像
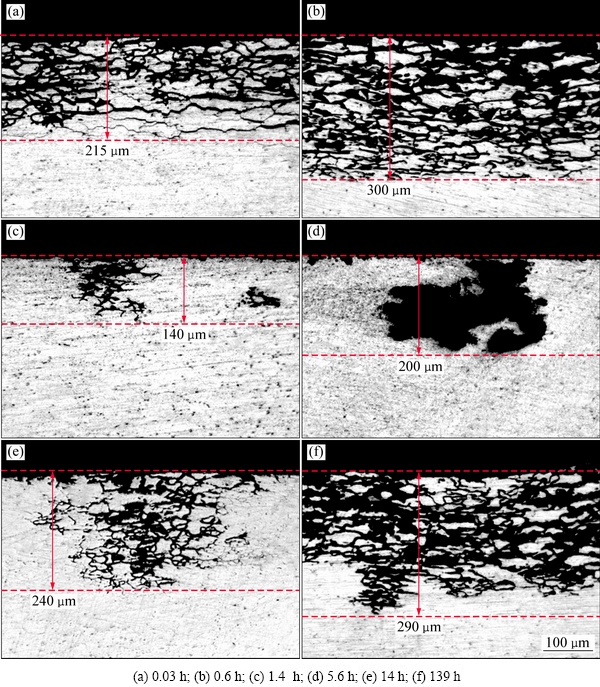
图2 时效不同时间的合金IGC测试后的抛光横截面形貌
Fig. 2 Optical images for polished cross-sections of IGC testing alloy aged at 220 ℃ for different time
经过220 ℃时效0.6 h、5.6 h和139 h后,实验合金分别处于峰时效、过时效和过时效状态(见图1),腐蚀类型分别为IGC、PC和IGC(见图2)。为了便于描述,根据时效硬化特点,文中将上述3种时效试样分别记为PA(220 ℃,0.6 h)、OA1(220 ℃,5.6 h)和OA2(220 ℃,139 h)。图3所示为PA、OA1和OA2试样的基体与晶界区TEM像。关于6000系Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金时效析出序列已有许多研究,综合起来可以看作过饱和固溶体(Supersaturated solid solution, SSSS)→原子团簇→GP区→β″→β′+Q′→β+Q+Si[2, 16-20]。其中,原子团簇是时效早期出现的Mg、Si、Cu等原子偏聚区域;GP区和针状β″相与基体完全共格,后者产生更强的晶格畸变,是峰时效合金中主要强化相;板条状Q′相和棒状β′与基体部分共格,强化效果较弱,常出现于过时效合金,偶尔出现在峰时效合金;β、Q、Si平衡相通常出现在严重过时效软化的合金中。根据Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金析出相形貌特征,220 ℃、0.6 h峰时效的PA试样基体析出相以β″相为主、含少量板条状Q′相(见图3(a)),而220 ℃、5.6 h过时效的OA1试样基体析出相则以Q′相为主、含少量棒状β′相(见图3(e))。与PA试样相比,OA1试样基体析出相数量减少、尺寸增大。过时效程度更严重的OA2试样(220 ℃、139 h)基体析出相类型与OA1试样相同,也是以Q′相为主,同时含少量β′相,但析出相数量进一步减少、尺寸进一步增大(见图3(i))。此外,从图3((a)、(e)和(i))还可以看出,影响合金强度的基体析出相数量也是按PA→OA1→OA2逐渐减少。因此,PA、OA1和OA2试样中基体析出相特征与时效硬化特点(见图1)是相吻合的。
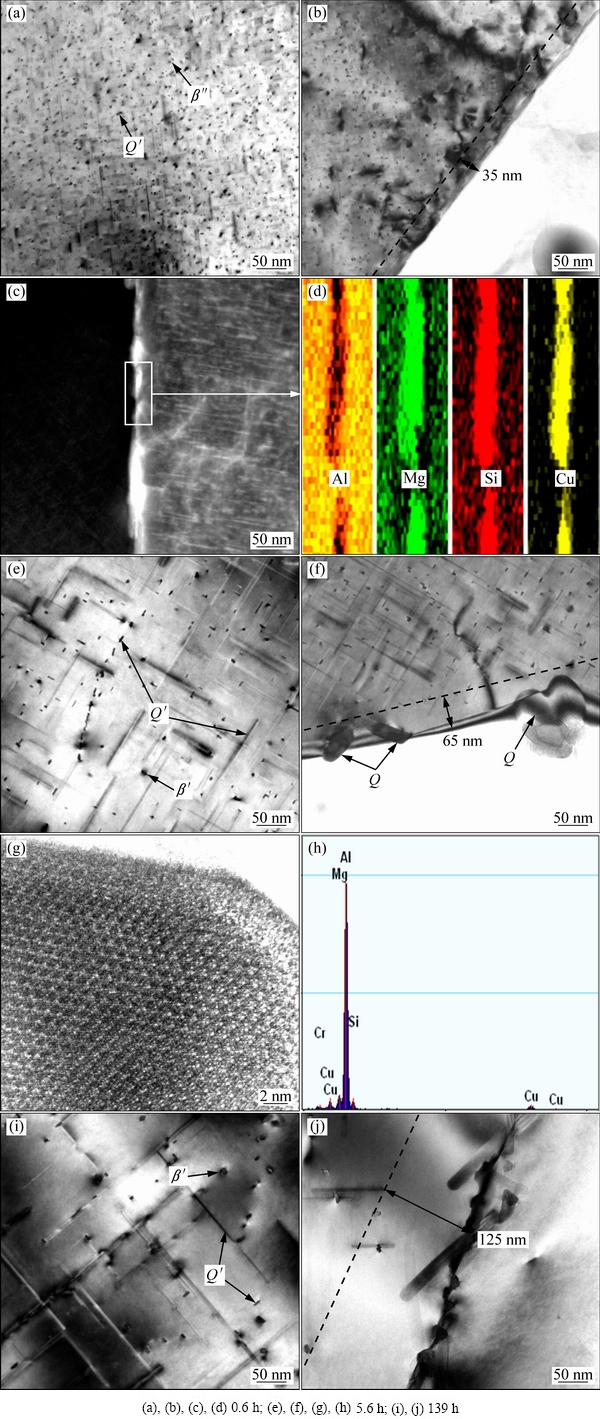
图3 经220 ℃时效不同时间经合金基体和晶界的TEM像
Fig. 3 TEM images of matrix and grain boundary of alloy aged at 220 ℃ for different time
不同于基体析出过程,时效过程中,偏聚于晶界过饱和溶质原子与从附近基体扩散而来的溶质原子,通常在晶界上直接析出Q、β平衡相[21-22],同时,晶界附近形成贫溶质的PFZ。对于峰时效PA试样,晶界析出相呈条状连续分布,PFZ半宽约35 nm(见图3(b));高角环形暗场TEM像(见图3(c))和元素图(见图3(d))分析均表明,晶界析出相同时含有Al、Mg、Si和Cu 4种元素,应为Q相[16]。对于过时效OA1试样,尺寸粗大的板条状晶界析出相呈现大间距、断续分布,PFZ半宽也增加至约65 nm(见图3(f));晶格条纹像(见图3(g))和能谱点分析(见图3(h))进一步表明,晶界析出相仍为Q相。对于过时效程度更高的OA2试样,晶界Q相尺寸进一步增大,甚至重叠堆积,从整体来看,呈现连续分布,PFZ半宽进一步增加至约125 nm(见图3(j))。以上TEM分析表明,在220 ℃过时效过程中,Al-1.1Mg-1.2Si-0.9Cu合金晶界Q相发生连续→断续→连续的分布变化,同时,晶界PFZ宽度持续增大。
3 分析与讨论
如前所述,时效硬化型6000系铝合金IGC敏感性源于在一定介质中,晶界析出相与PFZ能够形成连续腐蚀微电池。由图3可知,PA、OA1和OA2时效合金晶界析出相均为富Cu的Q相,晶界附近为贫溶质的PFZ。在3.5%NaCl(质量分数)溶液中,PFZ腐蚀电位约-0.876VSCE[23],Q相腐蚀电位约-0.970 VSCE[24]。李朝兴[24]进一步研究表明,Q相中Mg元素优先溶解,导致残留物中Cu、Si元素富集,腐蚀电位逐渐正移,最终形成Q相为阴极、PFZ为阳极的腐蚀微电池。类似的第二相活性元素优先溶解现象也见于Al-Cu-Mg合金中S相(Al2CuMg)[25]、Al-Cu-Li合金中T1相(Al2CuLi)[26]、Al-Mg-Si合金中β相(Mg2Si)[27]等。另一方面,PFZ总是沿晶连续分布,同时,峰时效PA试样中晶界Q相也是连续分布(见图3(b)、(c)、(d)),二者能够构成沿晶连续分布的腐蚀微电池,因此,PA合金具有严重IGC敏感性(见图2(b))。然而,过时效OA1试样中粗大的晶界Q相呈现板条状、断续分布(见图3(f)),与PFZ无法构成连续腐蚀微电池,因此,OA1合金无IGC敏感性(见图2(d))。对于过时效程度更为严重的OA2试样,晶界Q相紧密相邻、甚至重叠堆积(见图3(j)),整体呈现连续分布特征,与PFZ也能构成连续腐蚀微电池,从而导致OA2合金发生IGC(图2(f))。上述晶界区组织分析表明,实验合金在过时效阶段发生的IGC→PC→IGC转变是晶界Q相发生连续→断续→连续的分布变化、进而影响到与PFZ能否构成连续腐蚀微电池的必然结果。
以往研究者们认为,Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金晶界Q相在过时效阶段只存在降低界面能的自身粗化过程[5-11],这一观点可以解释过时效早期阶段的IGC→PC转变,但无法解释随后的PC→IGC转变。为此,LI等[15]研究认为,过时效阶段晶界Q相发生先自身粗化、后吸收附近基体析出相长大的连续过程。该观点能够解释过时效阶段的IGC→PC→IGC转变,却无法解释PA→OA1时晶界PFZ宽度增加的现象(见图3(b)和(f))。为了合理解释过时效阶段合金晶界Q相的分布特征变化规律,本文作者进一步提出同步进行、先后主导的晶界析出相粗化与长大过程的观点。时效硬化铝合金时效至峰值状态,过饱和溶质原子能够维持晶界析出相仿形析出与长大,从而呈现连续分布特征。当合金进入过时效阶段,基于过饱和溶质原子的晶界析出过程停止。为了降低析出相界面能,一方面,连续分布的晶界析出相上小曲率位置开始溶断,产生的溶质原子沿晶界向大曲率位置扩散,开始粗化过程。这一过程受控于溶质原子的晶界短路扩散,速度较快;另一方面,由于尺寸差异,邻近晶界的小尺寸基体析出相溶解,产生的溶质原子经PFZ扩散进入晶界,并沉淀于尺寸较大的晶界析出相,促进其长大,同时,造成PFZ宽度增加。这一过程受控于溶质原子的晶内体扩散,速度较慢。
根据上述初步分析,过时效阶段实验合金晶界Q相的分布特征变化可以如下讨论:峰时效合金连续分布的晶界Q相(见图3(c)和(d))具有较高的析出相界面能,当进入过时效阶段,短路扩散控制的晶界Q相的粗化过程能够快速进行,而同时发生的体扩散控制的基体Q相溶解促进晶界Q相长大过程相对较慢,尽管造成PFZ宽度增大(见图3(b)和(f)),但产生的溶质原子流尚不足以对晶界Q相分布特征产生显著影响。因此,在PA→OA1过时效早期阶段,晶界Q相分布特征主要体现为短路扩散控制的粗化过程:尺寸增加、数量减少、间距增大(见图3(f))。随着晶界Q相粗化程度的增加,析出相界面能逐渐降低,导致粗化速度不断放缓,但是,晶界Q相与基体Q相尺寸差异的增大(见图3(f)),导致小尺寸基体Q相溶解促进晶界Q相长大过程持续、甚至加速进行。因此,在随后OA1→OA2过时效阶段,晶界Q相吸收附近基体Q相的长大过程成为主要机制,导致PFZ宽度继续增加、晶界Q相尺寸继续增大,从而形成紧密相连、重叠堆积的整体连续分布特征(见图3(j))。显然,本文作者提出的同步进行、先后主导的晶界析出相粗化与长大的观点,不仅能够解释PA→OA1→OA2时效过程中实验合金晶界Q相连续→断续→连续的分布特征变化、进而导致IGC→PC→IGC的腐蚀行为转变,同时也可以解释晶界PFZ宽度持续增大的现象。
4 结论
1) 实验合金在过时效阶段能够发生IGC→PC→IGC腐蚀行为转变,即所谓的IGC再敏化现象。
2) 过时效阶段,实验合金IGC→PC→IGC腐蚀行为转变与晶界Q相发生连续→断续→连续的分布特征变化密切相关。
3) 提出了同步发生、先后主导的晶界析出相粗化与长大过程模型,能够较为合理地解释过时效阶段晶界Q相分布特征和PFZ宽度的变化规律。
REFERENCES
[1] BISWAS A, SIEGEL D J, SEUDMAN D N, Compositional evolution of Q-phase precipitates in an aluminum alloy[J]. Acta Materials, 2014, 75: 322-336.
[2] 陈江华, 刘春辉. AlMgSi(Cu)合金中纳米析出相的结构演变[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(10): 2352-2360.
CHEN Jiang-hua, LIU Chun-hui. Microstructure evolution of precipitates in AlMgSi(Cu) alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(10): 2352-2360.
[3] LIANG W J, ROMETSCH P A, CAO L F, BIRBILIS N. General aspects related to the corrosion of 6xxx series aluminium alloys: Exploring the influence of Mg/Si ratio and Cu[J]. Corrosion Science, 2013, 76: 119-128.
[4] 王芝秀, 李 海, 顾建华, 宋仁国,郑子樵. Cu含量对Al–Mg–Si–Cu合金微观组织和性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(12): 3348-3355.
WANG Zhi-xiu, LI Hai, GU Jian-hua, SONG Ren-guo, ZHENG Zi-qiao. Effect of Cu content on microstructures and properties of Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloys[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(12): 3348-3355.
[5] LARSEN M H, WALMSLEY J C, LUNDER O, NISANCIOGLU K. Effect of excess silicon and small copper content on intergranular corrosion of 6000-series aluminum alloys[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(2): 61-68.
[6] SVENNINGSEN G, LEIN J E,  A, NORDLIEN J H, YU Y, NISANCIOGLU K. Effect of low Cu content and heat treatment on intergranular corrosion of AlMgSi(Cu) model alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(1): 226-242.
A, NORDLIEN J H, YU Y, NISANCIOGLU K. Effect of low Cu content and heat treatment on intergranular corrosion of AlMgSi(Cu) model alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(1): 226-242.
[7] SVENNINGSEN G, LARSEN M H, WALMSLEY J C, NORDLIEN J H, NISANCIOGLU K. Effect of artificial aging on intergranular corrosion of extruded AlMgSi alloy with small Cu content[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(6): 1528-1543.
[8] SVENNINGSEN G, LARSEN M H, NORDLIEN J H, NISANCIOGLU K. Effect of thermomechanical history on intergranular corrosion of extruded AlMgSi(Cu) model alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2006, 48(12): 3969-3987.
[9] 潘道召, 王芝秀, 李 海, 郑子樵. 双级时效对6061铝合金拉伸性能和晶间腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(3): 435-441.
PAN Dao-zhao, WANG Zhi-xiu, LI Hai, ZHENG Zi-qiao. Effects of two-step ageing treatment on tensile properties and intergranular corrosion of 6061 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(3): 435-441.
[10] 张海锋, 郑子樵, 钟 申, 罗先甫, 钟 警. 双级时效制度对6156铝合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(4): 1025-1032.
ZHANG Hai-feng, ZHENG Zi-qiao, ZHONG Shen,LUO Xian-fu, ZHONG Jing. Effects of two-step aging treatment on microstructure and properties of 6156 aluminum alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012,22(4): 1025-1032.
[11] 林 莉, 郑子樵, 李劲风. 时效制度对6156铝合金力学性能及腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(6): 1004-1009.
LIN Li, ZHENG Zi-qiao, LI Jin-fen. Effect of aging treatments on the mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of 6156 aluminum alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012,41(6): 1004-1009.
[12] DIF R, BES B, EHRSTRO M, SIGLI C, WARNER J T, LASSINCE P, RIBES H. Understanding and modeling the mechanical and corrosion properties of 6056 for aerospace applications[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2000, 331/337: 1613-1618.
[13] KAIRY S K, ROMETSCH P A, DAVIES C H J, BIRBILIS N. On the electrochemical and quasi in situ corrosion response of the Q-phase (AlxCuyMgzSiw) intermetallic particle in 6xxx series aluminium alloys[J]. Corrosion, 2017, 73: 87-99.
[14] KAIRY S K, ROMETSCH P A, DAVIES C H J, BIRBILIS N. On the intergranular corrosion and hardness evolution of 6xxx series Al alloys as a function of Si:Mg ratio, Cu content and ageing condition[J]. Corrosion, 2017, 73: 1280-1295.
[15] LI Hai, ZHAO Pei-pei, WANG Zhi-xiu, MAO Qing-zhong, FANG Bi-jun, SONG Ren-guo, ZHENG Zi-qiao. The intergranular corrosion susceptibility of a heavily overaged Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 107: 113-122.
[16] CHAKRABARTI D J,LAUGHLIN D E. Phase relations and precipitation in Al-Mg-Si alloys with Cu additions[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2004, 49(3/4): 389-410.
[17] MIAO W F, LAUGHLIN D E. Effect of Cu Content and pre-aging on precipitation characteristics in aluminum alloy 6022[J]. Metallurgical Materials Transactions A, 2000, 31(2): 361-371.
[18] WANG X, ESMAEILI S, LLOYD D J. The sequence of precipitation in the Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloy AA6111[J]. Metallurgical Materials Transactions A, 2006, 37(9): 2691-2699.
[19] MURAYAMA M, HONO K, MIAO W F, LAUGHLIN D E. The effect of Cu additions on the precipitation kinetics in an Al-Mg-Si alloy with excess Si[J]. Metallurgical Materials Transactions A, 2000, 32(2): 239-246.
[20] 李祥亮, 陈江华, 刘春辉,冯佳妮, 王时豪. T6和T78时效工艺对Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金显微结构和性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2013, 49(2): 243-250.
LI Xiang-liang, CHEN Jiang-hua,LIU Chun-hui, FENG Jia-ni, WANG Shi-hao.Effects of T6 and T78 tempers on the microstructures and properties of Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloys[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2013, 49(2): 243-250.
[21] 廖元飞, 陈江华, 刘春辉, 李祥亮, 冯佳妮. Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金中晶界和晶内析出相粗化规律的研究[J]. 电子显微学报, 2012, 31(2): 116-123.
LIAO Yuan-fei, CHEN Jiang-hua, LIU Chun-hui, LI Xiang-liang, FENG Jia-ni. An electron microscopy study of precipitate coarsening in Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloys[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2012, 31(2): 116-123.
[22] YANG W, JI S, LI Z, WANG M. Grain boundary precipitation induced by grain crystallographic misorientations in an extruded Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 624: 27-30.
[23] BURLEIGH T D, LUDWICZAK E, PETRIL R A. Intergranular corrosion of an aluminium-magnesium-silicon-copper alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 1995, 51(1): 50-55.
[24] 李朝新. Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金晶间腐蚀机理的模拟研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2010.
LI Chao-xin. Simulation study on IGC mechanism of Al-Mg-Si-(Cu) alloy[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2010.
[25] BOAG A,HUGHES A E,GLENN A M,MUSTER T H,MCCULLOCH D. Corrosion of AA2024-T3 Part I: Localised corrosion of isolated IM particles[J]. Corrosion Science,2011, 53: 17-26.
[26] LI J F, ZHENG Z Q, LI S C, CHEN W J, REN W D, ZHAO X S. Simulation study on function mechanism of some precipitates in localized corrosion of Al alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49: 2436-2449.
[27] 李 海, 孟 林, 王芝秀, 黄 玲, 李 蔚, 宋仁国, 郑子樵. 残留结晶相对Al-Mg-Si-Cu合金晶间腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(12): 3300-3306.
LI Hai, MENG Lin, WANG Zhi-xiu, HUANG Ling,LI Wei, SONG Ren-guo, ZHENG Zi-qiao. Effect of residual constituents on intergranular corrosion behavior of Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloy[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(12): 3300-3306.
Re-sensitization to intergranular corrosion in Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloy during over-ageing
WANG Zhi-xiu1, 2, ZHU Fan, ZHENG Kai1, JIA Jun1, WEI Yu-long1, LI Hai1, 2, ZHENG Zi-qiao3
(1. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Changzhou University, Changzhou 213164, China;
2. Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Materials Surface Science and Technology, Changzhou University, Changzhou, 213164, China;
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 10083, China)
Abstract: Based on the Vickers hardness measurement and acceleration corrosion test, the hardening behavior and IGC susceptibility of an Al-1.1Mg-1.2Si-0.9Cu alloy (mass fraction, %) aged at 220 ℃ were investigated. The results show that the corrosion behaviors change in the sequence of IGC→PC→IGC during over-ageing of the peak-aged alloy, which verifies the re-sensitization to IGC. The transmission electron microscopy observation results indicate that the continuous→discontinuous→continuous distribution of grain boundary Q phase precipitates determines whether the continuous electrochemical microcouples can form along the grain boundaries, which is responsible for the transition of IGC→PC→IGC further. Furthermore, a mode of synchronous development and successive domination for coarsening and growth is proposed to explain reasonably the distribution of grain boundary Q phase precipitates and width of precipitate free zones during over-ageing.
Key words: Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloys; over-ageing; precipitation; intergranular corrosion; pitting corrosion
Foundation item: Projects(51671038, 51571038) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Projects(BK20151188, BK20171195) supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China
Received date: 2017-08-24; Accepted date: 2017-12-29
Corresponding author: LI Hai; Tel: +86-519-86330069; E-mail: Lehigh_73@163.com
(编辑 李艳红)
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(51571083,51671083);江苏省自然科学基金资助项目(BK20151188,BK20171195)
收稿日期:2017-08-24;修订日期:2017-12-29
通信作者:李 海,教授,博士,电话:0519-86330069;E-mail:Lehigh_73@163.com