流变铸造不同铁含量过共晶Al-Si合金在干摩擦条件下的磨损行为
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2016年第3期
论文作者:林冲 吴树森 吕书林 曾劲彪 安萍
文章页码:665 - 675
关键词:干摩擦;过共晶Al-Si合金;流变铸造;富铁相;磨损机理
Key words:dry sliding wear; hypereutectic Al-Si alloy; rheocasting; Fe-bearing compound; wear mechanism
摘 要:研究铁含量对流变铸造过共晶Al-17Si-2Cu-1Ni合金在干摩擦条件下磨损行为的影响。磨损测试是在销-盘式摩擦磨损试验机上进行的。结果表明,在同等载荷下,流变铸造合金试样比传统重力金属型铸造试样的磨损率小。细小颗粒状δ-Al4(Fe,Mn)Si2相和多边形状α-Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2相有助于提高流变铸造合金的耐磨性。随着细小富铁相体积分数的增加,流变铸造合金试样的磨损率减小。此外,随着载荷从50增大至200 N,流变铸造合金试样的磨损率增大。对于含3% Fe的流变铸造合金,在低载荷(50 N)时,磨损机制以氧化磨损为主;在高载荷时,磨损机制以氧化磨损和剥层磨损的联合作用为主。
Abstract: The effect of iron content on wear behavior of hypereutectic Al-17Si-2Cu-1Ni alloy produced by rheocasting process was investigated. The dry sliding wear tests were carried out with a pin-on-disk wear tester. The results show that the wear rate of the rheocast alloy is lower than that of the alloy produced by conventional casting process under the same applied load. The fine particle-like δ-Al4(Fe,Mn)Si2 and polygonal α-Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2 phases help to improve the wear resistance of rheocast alloys. As the volume fraction of fine Fe-bearing compounds increases, the wear rate of the rheocast alloy decreases. Moreover, the wear rate of rheocast alloy increases with the increase of applied load from 50 to 200 N. For the rheocast alloy with 3% Fe, oxidationwear is the main mechanism at low applied load (50 N). At higher applied loads, a combination of delamination and oxidation wear is the dominant wear mechanism.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26(2016) 665-675
Chong LIN1,2, Shu-sen WU1, Shu-lin  1, Jin-biao ZENG1, Ping AN1
1, Jin-biao ZENG1, Ping AN1
1. State Key Laboratory of Materials Processing and Die & Mould Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China;
2. School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Wuhan Institute of Technology, Wuhan 430073, China
Received 25 March 2015; accepted 26 August 2015
Abstract: The effect of iron content on wear behavior of hypereutectic Al-17Si-2Cu-1Ni alloy produced by rheocasting process was investigated. The dry sliding wear tests were carried out with a pin-on-disk wear tester. The results show that the wear rate of the rheocast alloy is lower than that of the alloy produced by conventional casting process under the same applied load. The fine particle-like δ-Al4(Fe,Mn)Si2 and polygonal α-Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2 phases help to improve the wear resistance of rheocast alloys. As the volume fraction of fine Fe-bearing compounds increases, the wear rate of the rheocast alloy decreases. Moreover, the wear rate of rheocast alloy increases with the increase of applied load from 50 to 200 N. For the rheocast alloy with 3% Fe, oxidation wear is the main mechanism at low applied load (50 N). At higher applied loads, a combination of delamination and oxidation wear is the dominant wear mechanism.
Key words: dry sliding wear; hypereutectic Al-Si alloy; rheocasting; Fe-bearing compound; wear mechanism
1 Introduction
Hypereutectic Al-Si alloys are widely applied in automotive industries due to their excellent wear resistance, low thermal expansion coefficient and high heat resistance [1,2]. Iron is a desirable element that can enhance the elevated temperature properties of the hypereutectic Al-Si alloys [3]. But the equilibrium solid solubility of Fe in aluminum is very low (max. 0.05%) [4], almost all Fe in Al alloys segregates during solidification and tends to form intermetallic compounds. The coarse needle-like or plate-like Fe-bearing compounds are detrimental to the room temperature mechanical properties [5].
The deleterious effects of iron on the mechanical properties can be minimized by various techniques. These include manganese addition [6], rapid solidification [7], melt superheating [8] and rheocasting process assisted with ultrasonic vibration (USV) [9,10]. Among these processes, rheocasting process is an attractive technique due to its uncomplicated process and low cost [11,12]. It has been proved that the Fe-bearing compounds of the hypereutectic Al-Si alloys with high Fe content can be effectively modified by rheocasting process, and the ultimate tensile strengths of the rheocast alloys at room temperature and 350 °C are improved significantly [4,13]. These alloys are often used as piston materials which require excellent wear resistance. It is therefore interesting to find out whether rheocast alloy is more wear resistant than the alloy produced by conventional casting process.
The wear behavior of the Al-Si alloys with Fe has caught the attention of researchers in recent years. TAGHIABADI et al [14] studied the effect of Fe-rich intermetallics on the wear behavior of hypoeutectic Al-Si alloy (SAE F332). The results showed that high cooling rate and Sr modification could be used to refine the needle-like β phase, and these treatments improved the wear resistance of the alloy with 1.2% Fe. ABOUEI et al [15] investigated the effect of Fe-rich intermetallics on the wear behavior of eutectic Al-Si alloy (LM13) with 1.2% Fe. They found that high cooling rate and Mn addition could refine the Fe-rich intermetallics and improve the wear resistance of the alloy. NAKATA and USHIO [16] studied the effect of Fe content on wear resistance of thermal-sprayed Al-17Si-XFe (X=5, 10, 15, 20, 30, mass fraction, %) alloys coating on A6063 Al alloy substrate. They concluded that the most beneficial coating with good wear resistance and low friction coefficient could be obtained with Al-17Si-(10-15)Fe alloy powders. Recently, ALSHMRI et al [17] have investigated the dry sliding wear of aluminium-high silicon hypereutectic alloys formed by melt spinning and ribbon compaction. They found that the higher amounts of intermetallic-forming elements (Fe, Cu, Ni) were thought to be contributing to the wear resistance. However, reports on the effect of iron content on wear behavior of rheocast hypereutectic alloy are not available.
Based on the above considerations, this study was conducted to investigate the dry sliding wear properties of rheocast hypereutectic Al-17Si-2Cu-1Ni alloys with different Fe contents. The sliding wear mechanisms were also discussed based on observations of the worn surface, worn subsurface and wear debris.
2 Experimental
The alloys investigated had the compositions shown in Table 1 and were prepared with raw materials of Al-25.8%Si (mass fraction, the same in the following) and Al-10%Mn master alloys, commercial pure Al (99.8%), pure Fe (99.9%), pure Cu (99.99%), pure Ni (99.99%) and pure Mg (99.9%). The materials were melted in a resistance furnace, and then the tensile samples of these alloys with diameter of 8 mm were produced using rheocasting process assisted with USV [4,18]. The applied ultrasonic power was 1.6 kW, and the frequency of USV was 20 kHz. The USV treatment time was 1.5 min. For comparison, conventional gravity casting samples were also made using the same permanent mold without USV treatment under a pouring temperature of 750 °C. The samples were then heat-treated with T6 process (solution treatment at 510 °C for 7 h, followed by water quenching, then artificial aged at 190 °C for 10 h).
Table 1 Chemical compositions of hypereutectic Al-Si alloys (mass fraction, %)

The dry sliding wear tests were carried out on a pin-on-disk wear tester to evaluate room temperature (i.e., 25 °C) wear behavior of Al-17Si-2Cu-1Ni alloys with different Fe contents. The pins, 6 mm in diameter and 12 mm in length, were machined from the rheocast or conventional casting samples. The disc, with a diameter of 70 mm and a thickness of 10 mm, was made of AISI 52100 steel. The hardness of the disk was approximately HRC 58. Before the wear test, the surfaces of the Al-Si alloys pins and the counterface of the disc were polished to a surface roughness (Ra) of 0.8 μm.
The pins in horizontal orientation were loaded against the rotating steel disk through a dead weight loading system. The radius of the work formed on the disk by the pins was 28 mm. The tests were conducted at four different loads of 50, 100, 150 and 200 N. Sliding speed and distance were kept constant at 0.75 m/s and 1000 m, respectively.
The mass loss during wear test was measured using an electronic balance with a resolution of 0.1 mg. The pins were thoroughly cleaned with acetone in ultrasonic cleaner before and after the wear test. The wear rates were determined from the measured mass loss and expressed in terms of volume loss per unit sliding distance (m3/m). Each wear rate was averaged from the data obtained on at least three wearing pins.
After each test, the wear debris was collected and stored for further analysis. The worn surfaces and wear debris after sliding at different loads were examined using a Quanta 200 environmental scanning electron microscope (SEM) fitted with an energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX). Subsurface microstructures were also investigated at the cross-sections perpendicular to the worn surface. In order to highlight the differences in phase hardness, nano-indentation measurements (TI750, Hysitron) of different phases were also carried out. Indentations with a Berkovich type indenter were performed normally on the polished cross-sections by using a maximum load of 8 mN. An average of 5 indentations on one particle of different phases was analyzed.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Microstructures of alloys with and without USV treatment
Figures 1 and 2 present the as-cast microstructures of the alloys produced by different processes. As can be seen from Fig. 1, the addition of Fe to the hypereutectic Al-Si alloy leads to the precipitation of long needle-like β-Al5(Fe,Mn)Si and coarse plate-like δ-Al4(Fe,Mn)Si2 phases in the matrix [4,18]. The average length of long needle-like β and coarse plate-like δ phases are about 100 μm and 150 μm, respectively. The average grain size of primary Si in Fig. 1(a) is about 47 μm. After USV treatment, the coarse plate-like δ and the coarse primary Si phases were transformed into fine particles, as shown in Fig. 2. The average grain size of fine δ phase is about 19 μm. Besides, the amount and length of needle-like β phase are decreased greatly.
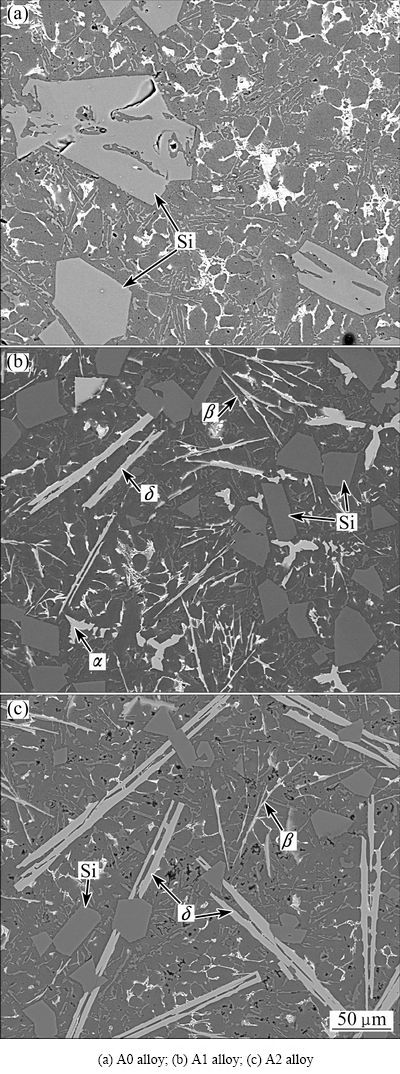
Fig. 1 Microstructures of as-cast Al-Si alloys with different Fe contents produced by conventional casting process
3.2 Wear behavior of alloys with and without USV treatment
Figure 3 represents the variation of wear rate as a function of applied load for the alloys with and without USV treatment. The wear rates of the conventional casting alloys are distinctly higher than those of the rheocast alloys at all loads. Thus, USV treatment offers the alloys better wear resistance than the conventional one. The wear behavior of Al-Si alloys is closely related to their microstructural features [14,19]. Hence, the superior wear resistance of the rheocast alloys could be attributed to the refinement of the Fe-bearing compounds and primary Si particles.
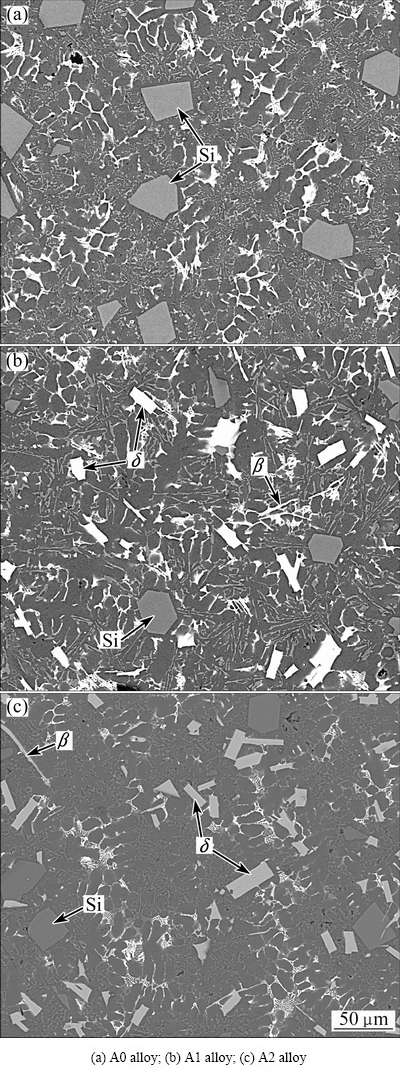
Fig. 2 Microstructures of as-cast Al-Si alloys with different Fe contents produced by rheocasting process assisted with USV
Figure 4 shows the SEM images of the subsurfaces of the alloys with and without USV treatment at the load of 200 N. As can be seen, the microstructure clearly reveals a mechanical mixing layer (MML), which is the outermost layer in all these micrographs. The MML commonly forms on the sliding surface of Al-Si alloy when it slides against a steel counterpart [20,21].
Furthermore, a deformation zone beneath the MML with material flow lines can also be seen, and the flow lines progressively bend towards the sliding direction. Finally, the undeformed material is beneath the deformation zone. Consequently, including the undeformed material, three distinct layers have been identified in the pins sliding against the steel disc. A schematic of these layers is illustrated in Fig. 5.
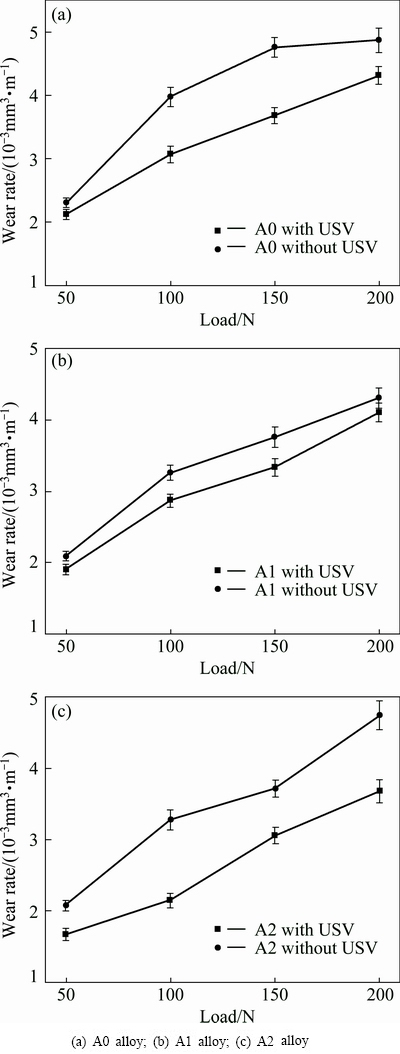
Fig. 3 Wear rates of alloys produced by different processes as a function of applied load
A high plastic shear strain is induced in the subsurface region during the sliding process [22,23]. This shear strain tends to cause plastic deformation in the subsurface region. As shown in Fig. 5, this region is classified as the deformation zone. Moreover, the closer the position to the worn surface is, the larger the shear strain is [24]. As a result, extensive fracture and fragmentation of the Fe-bearing compounds, primary Si and eutectic structure in the subsurface region occur. These ultrafine particles of the fragmented phases are redistributed and piled up near the surface region, which lead to the formation of MML.
Obviously, the MML thicknesses of the alloys without USV are larger than those of the alloys with USV. This can be attributed to the difference of the size and morphology of Fe-bearing compounds and primary Si phase. The long needle-like β and coarse plate-like δ phases, which are hard and brittle, have relatively low bond strength with the matrix [18]. Hence, cracks can initiate easily in these brittle phases during sliding. In addition, the primary Si phase in the microstructure exists as discrete grains. As a result, the interfacial regions between the Si grains and the matrix are prone to microcracking. The larger the sizes of the Si grains are, the greater the microcracking tendency becomes [19]. As can be seen from Fig. 4(a), some coarse primary Si grains in the deformation zone are broken toward the direction of sliding. At the mean time, long needle-like β and coarse plate-like δ phases are fractured and align along the sliding direction, as shown in Figs. 4(c) and (e). Due to the poor bonding of the fragmented Fe-bearing compounds with the MML, the strength of the MML is weakened, thereby the initiation and propagation of microcracks are facilitated. However, the fine Fe-bearing compounds and primary Si phase can act as effective barriers for dislocation motion in the subsurface region during sliding, as illustrated in Figs. 4(b), (d) and (f). Investigations [4,18] have shown that the alloys treated by USV have a higher hardness than their counterparts without USV. The larger hardness values of the USV- treated alloys are most likely due to the strengthening of fine Fe-bearing compounds and primary Si phase to the matrix. For aluminum alloys in general, a harder material usually means higher strength. For this reason, the MML thicknesses of the USV-treated alloys are smaller than those of the alloys without USV treatment.
Based on the above analyses, it can be concluded that the small wear rate corresponds to the thin MML. An earlier study on the sliding wear behavior of Al-SiC composites has obtained similar result that the wear rate increases with increasing thickness of MML [25]. Thus, the wear rate of the conventional casting alloys is higher than that of the rheocast alloys.
3.3 Effect of Fe content on wear behavior of rheocast alloys
Figure 6 shows the effect of applied load on the wear rate of the rheocast alloys with different Fe contents. As can be seen, when the load increases from 50 to 200 N, the wear rate of each sample increases. The order of the wear rate of the alloys is: A0>A1>A2.
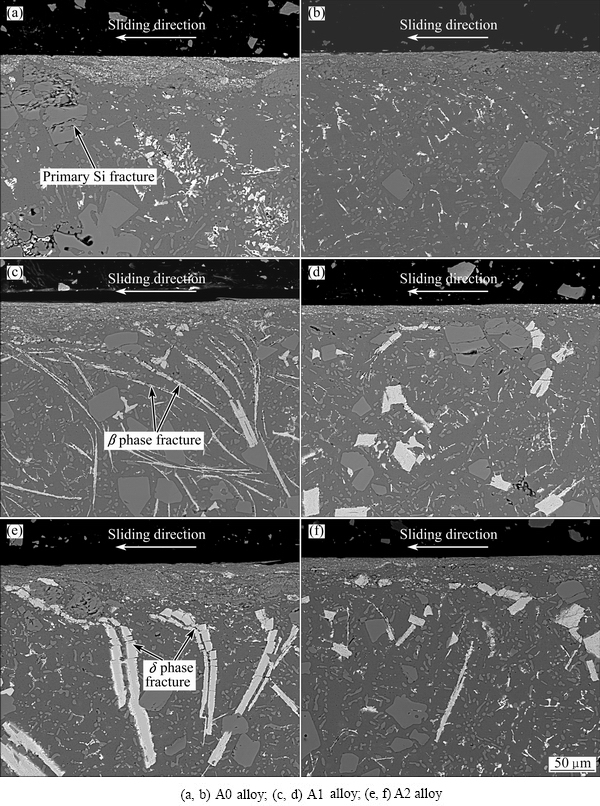
Fig. 4 SEM images of subsurfaces of alloys with (b, d, f) and without (a, c, e) USV treatment at 200 N
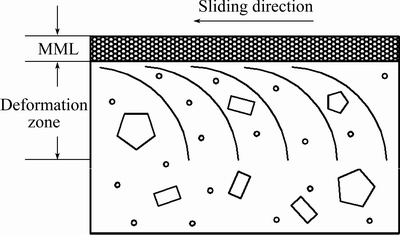
Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of MML and deformation zone beneath worn surface
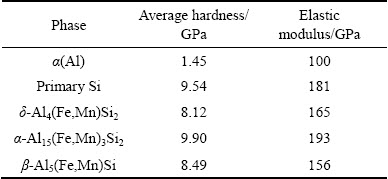
The reason why the wear rate of rheocast A1 alloy is lower than that of the rheocast A0 alloy is as follows. As shown in Fig. 2(b), the coarse plate-like δ phase is refined into fine particles in rheocast A1 alloy, and only few needle-like β phases remain. As a result, the deleterious effect of β phase on the wear resistance is almost eliminated. Furthermore, the addition of 0.8% Mn leads to the precipitation of the polygonal α-Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2 phase in A1 alloy [4]. The average grain size of α phase is about 25 μm, which is much smaller than that of the long needle-like β phase, as shown in Fig. 1(b). Besides, α phase has a better bonding with the matrix due to its polygonal morphology. Therefore, the possibility of crack formation in the interfacial regions between this phase and the matrix is declined during the sliding process. In particular, as can be seen from Table 2, the hardness of α-Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2 phase is 9.90 GPa, which is higher than that of primary Si (9.54 GPa) and δ (8.12 GPa) phases. Thus, apart from the fine particle-like δ phase, polygonal α-Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2 phase also helps to improve the wear resistance of rheocast A1 alloy.
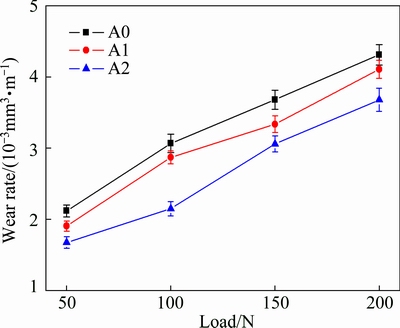
Fig. 6 Variation of wear rate versus applied load for rheocast alloys with different Fe contents
Table 2 Nano-indentation measurements of hardness and elastic properties of microstructure constituents present in rheocast A1 alloy in T6 condition
In addition, as shown in Fig. 6, the wear rate of rheocast A2 alloy is lower than that of rheocast A1 alloy. This is because the volume fraction of the fine Fe-bearing compounds increases with the increase of Fe content. The calculation shows that the volume fractions of fine Fe-bearing compounds in A1 and A2 alloys are 3.6% and 5.3%, respectively.
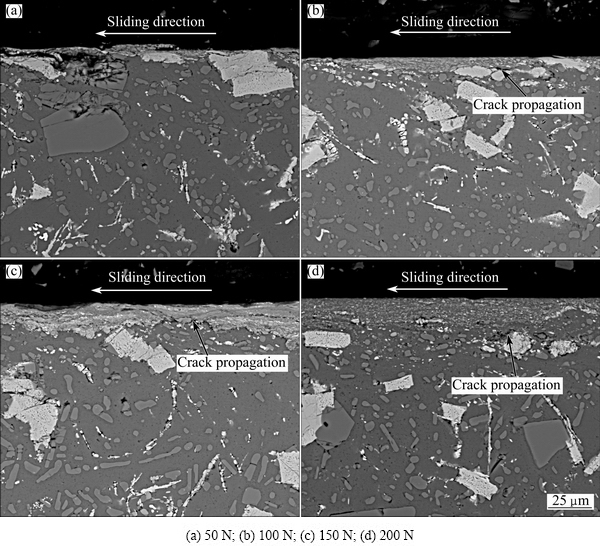
Fig. 7 SEM images of subsurface of rheocast A2 alloy at different loads
3.4 Wear mechanism of A2 alloy with USV treatment
As discussed in Sections 3.2 and 3.3, the variation of the wear rates of rheocast alloys with the applied loads shows similar trends. Moreover, at the load of 200 N, the characteristics of subsurfaces of rheocast alloys are almost the same. In particular, the wear rate of rheocast A2 alloy is the lowest among all the alloys studied. Therefore, the A2 alloy was choosen as the most representative of them to investigate the wear mechanism. The worn subsurface, worn surface and wear debris of this alloy under different applied loads were examined.
Figure 7 shows SEM images of the subsurface of pins of rheocast A2 alloy tested at different loads. The MML can be seen in the subsurface of rheocast A2 alloy at all loads, and the thickness of which increases with increasing the applied load. Some fine particle-like Fe-bearing compounds, which act as load supporting elements, can also be found in MML. Meanwhile, the wear rate of the rheocast A2 alloy increases with the increase of the applied load, as illustrated in Fig. 6.
EDX analyses of the MML of the rheocast A2 alloy at different loads are shown in Table 3. As can be seen, apart from Al, Si and Fe, O also presents in the MML. Moreover, Fig. 8 shows the subsurface SEM image and EDX mapping images for Al, Si, O and Fe elements of the rheocast A2 alloy at 200 N. The reason why the MML contains oxygen is that the frictional heating during sliding causes the formation of oxides. During the sliding process, these oxides, together with other particles mainly containing Al, Si and Fe, were compacted into the MML due to the repeated movement between the pin and the disc.
Table 3 EDX analyses (mole fraction, %) of MML of rheocast A2 alloy at different loads
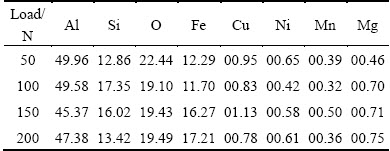
Figure 9 shows typical worn surfaces of rheocast A2 alloy at the applied loads of 50, 100, 150, and 200 N, respectively. At a low load of 50 N, the surface appears smooth with very fine scratches, as shown in Fig. 9(a).

Fig. 8 SEM image and EDX mapping of subsurface of rheocast A2 alloy at 200 N showing distribution of Al, Si, O and Fe within it
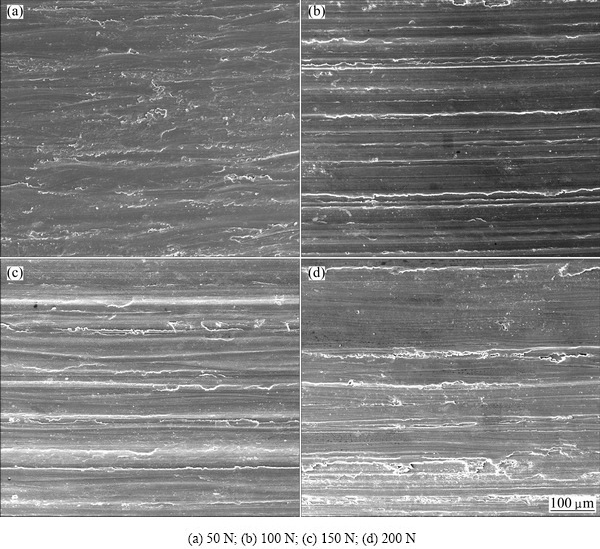
Fig. 9 SEM images of worn surfaces of rheocast A2 alloy at different loads
The long parallel grooves along the sliding direction, which are caused by the abrasion of entrapped particles, are clearly visible on the worn surface at 100 N (Fig. 9(b)). In addition, few small dimples can also be observed on the worn surface. With the increase of the applied load, the grooves become wider and deeper, and the size of the dimples is enlarged, as illustrated in Figs. 9(c) and (d).
The observation and analysis of the wear debris are a key factor to understand the wear mechanism. Figure 10 depicts the backscattered electron images of wear debris obtained from the sliding of rheocast A2 alloy at different loads. The EDX analyses of the debris generated at different loads are shown in Table 4. As can be seen, the chemical composition of the debris is similar to that of the MML shown in Table 3. Hence, it is suggested that the debris is mainly detached from the MML.
Table 4 EDX analyses (mole fraction, %) of debris of rheocast A2 alloy generated at different loads
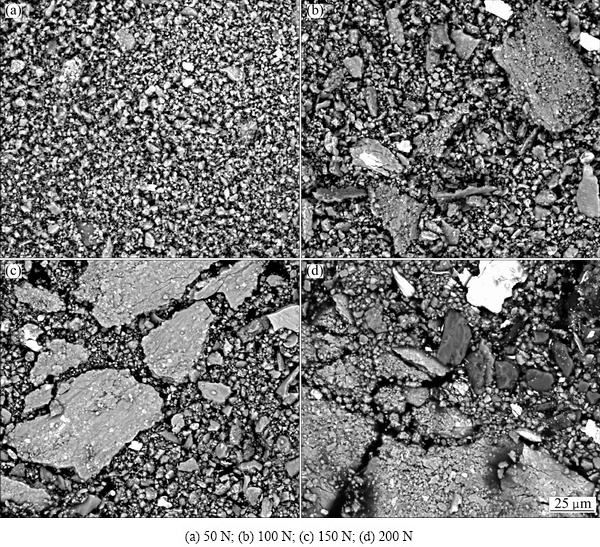
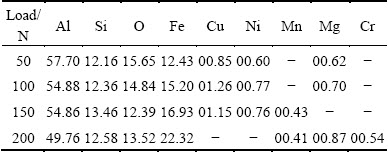

Fig. 10 SEM images of wear debris of rheocast A2 alloy at different loads
Comparing Fig. 9 with Fig. 7, it can be observed that the change in morphology of the wear debris is consistent with the change in worn surface appearance. When the load is 50 N, the wear debris is dark and is mainly in the form of fine particles, as shown in Fig. 10(a). The smooth worn surface and fine particle-like debris containing a large amount of oxygen suggest that oxidativon wear is the main wear mechanism at low applied load (50 N). At the load of 100 N, some irregular flakes appear in the wear debris, and the amount and size of the flakes increase with increasing load. When the applied load increases to 200 N, the wear debris consists of irregular flakes and fine particles. The appearance of irregular flake in the debris is indicative of delamination wear. As the load increases, the shear strain induced in the deformation zone increases. The large shear strain leads to pile-ups of dislocations in a finite distance from the surface, and this gives rise to the nucleation of voids [26]. These voids grow and coalesce, which leads to the subsurface crack propagation at last, as shown in Figs. 7(b)-(d). When the crack reaches a critical length, the material between the crack and the surface will shear, yielding a flake-like debris. Hence, at higher applied loads, the flake-like debris is generated by a process of subsurface delamination [27]. At the mean time, as shown in Figs. 10(b)-(d), apart from the irregular plate-like flakes and fine equiaxed particles, some white particles also present in the debris as the load increases. EDX analysis reveals that they are rich in Fe and emanate from the steel counterpart during the wear process, as shown in Fig. 11. The Fe particles in the debris are most likely produced by the abrasion between the steel counterface and the hard Fe-bearing compounds or primary Si particles dislodged from the alloy. Therefore, at higher applied loads, a combination of delamination and oxidation wear is the dominant wear mechanism, and abrasion wear is the assistant wear mechanism. As shown in Fig. 6, increasing the applied load causes an increase in the wear rate. This obviously can be attributed to the change of the wear mechanism at different loads.
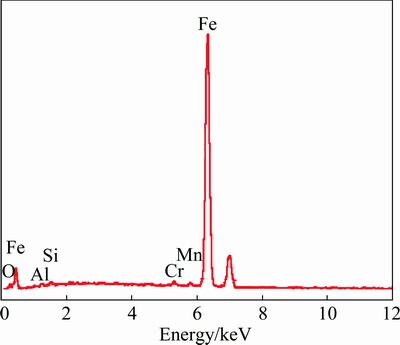
Fig. 11 EDX spectrum of white particles in Fig. 10
4 Conclusions
1) The coarse plate-like δ-Al4(Fe,Mn)Si2 and primary Si phases are refined in the rheocast Al-17Si- 2Cu-1Ni-(2,3)Fe alloys. The wear rate of the rheocast alloy is lower than that of the alloy produced by conventional casting process under the same applied load.
2) The fine particle-like δ-Al4(Fe,Mn)Si2 and polygonal α-Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2 phases help to improve the wear resistance of rheocast alloys. As the volume fraction of fine Fe-bearing compounds increases, the wear rate of the rheocast alloy decreases.
3) As the applied load increases from 50 to 200 N, the wear rate of rheocast alloy increases.
4) At the applied load of 50 N, oxidation wear is the main mechanism during the wear process of rheocast Al-17Si-2Cu-1Ni-3Fe alloy. At higher applied loads, a combination of delamination and oxidation wear is the dominant wear mechanism.
References
[1] ZHU Xue-wei, WANG Ri-chu, PENG Jian, PENG Chao-qun. Microstructure evolution of spray-formed hypereutectic Al-Si alloys in semisolid reheating process [J]. Transactionsof Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(6): 1766-1772.
[2] KIM J S, JANG G S, KIM M S, LEE J K. Microstructure and compressive deformation of hypereutectic Al-Si-Fe based P/M alloys fabricated by spark plasma sintering [J]. Transactionsof Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(7): 2346-2351.
[3] SHABESTARI S G, PARSHIZFARD E. Effect of semi-solid forming on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the iron containing Al-Si alloys [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509: 7973-7978.
[4] MONDOLFO L F. Aluminum alloys: Structure and properties [M]. London: Butterworths, 1976.
[5] LIN Chong, WU Shu-sen,  Shu-lin, AN Ping, WAN Li. Effects of ultrasonic vibration and manganese on microstructure and mechanical properties of hypereutectic Al-Si alloys with 2% Fe [J]. Intermetallics, 2013, 32: 176-183.
Shu-lin, AN Ping, WAN Li. Effects of ultrasonic vibration and manganese on microstructure and mechanical properties of hypereutectic Al-Si alloys with 2% Fe [J]. Intermetallics, 2013, 32: 176-183.
[6] HUANG H J, CAI Y H, CUI H, HUANG J F, HE J P, ZHANG J S. Influence of Mn addition on microstructure and phase formation of spray-deposited Al-25Si-xFe-yMn alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 52: 118-125.
[7] SRIVASTAVA A K, SRIVASTAVA V C, GLOTER A, OJHA S N. Microstructural features induced by spray processing and hot extrusion of an Al-18%Si-5%Fe-1.5%Cu alloy [J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54: 1741-1748.
[8] AHMAD R, MARSHALL R I. Effect of superheating on iron-rich plate-type compounds in aluminium-silicon alloys [J]. International Journal of Cast Metals Research, 2003, 15: 497-504.
[9] OSAWA Y, TAKAMORI S, KIMURA T, MINAGAWA K, KAKISAWA H. Morphology of intermetallic compounds in Al-Si-Fe alloy and its control by ultrasonic vibration [J]. Materials Transactions, 2007, 48: 2467-2475.
[10] LIN Chong, WU Shu-sen, ZHONG Gu, WAN Li, AN Ping. Effect of ultrasonic vibration on Fe-containing intermetallic compounds of hypereutectic Al-Si alloys with high Fe content [J]. Transactionsof Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(5): 1245-1252.
[11]  Shu-lin, WU Shu-sen, LIN Chong, HU Zu-qi, AN Ping. Preparation and rheocating of semisolid slurry of 5083 Al alloy with indirect ultrasonic vibration process [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 8635-8640.
Shu-lin, WU Shu-sen, LIN Chong, HU Zu-qi, AN Ping. Preparation and rheocating of semisolid slurry of 5083 Al alloy with indirect ultrasonic vibration process [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2011, 528: 8635-8640.
[12] ZHAO Jun-wen, WU Shu-sen, WAN Li, CHEN Qi-hua, AN Ping. Evolution of microstructure of semisolid metal slurry in ultrasound field [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009, 45: 314-319.
[13] LIN Chong, WU Shu-sen,  Shu-lin, AN Ping, WAN Li. Microstructure and mechanical properties of rheo-diecast hypereutectic Al-Si alloy with 2% Fe assisted with ultrasonic vibration process [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 568: 42-48.
Shu-lin, AN Ping, WAN Li. Microstructure and mechanical properties of rheo-diecast hypereutectic Al-Si alloy with 2% Fe assisted with ultrasonic vibration process [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 568: 42-48.
[14] TAGHIABADI R, GHASEMI H M, SHABESTARI S G. Effect of iron-rich intermetallics on the sliding wear behavior of Al-Si alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 490: 162-170.
[15] ABOUEI V, SAGHAFIAN H, SHABESTARI S G, ZARGHAMI M. Effect of Fe-rich intermetallics on the wear behavior of eutectic Al-Si piston alloy (LM13) [J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31: 3518-3524.
[16] NAKATA K, USHIO M. Effect of Fe content on wear resistance of thermal-sprayed Al-17Si-XFe alloy coating on A6063 Al alloy substrate [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2003, 169-170: 443-446.
[17] ALSHMRI F, ATKINSON H V, HAINSWORTH S V, HAIDON C, LAWES S D A. Dry sliding wear of aluminium-high silicon hypereutectic alloys [J]. Wear, 2014, 313: 106-116.
[18] LIN Chong, WU Shu-sen, ZENG Jin-biao, AN Ping, WAN Li. Combined effects of ultrasonic vibration and manganese on Fe-containing inter-metallic compounds and mechanical properties of Al-17Si alloy with 3wt.%Fe [J]. China Foundry, 2013, 10: 148-154.
[19] PRASAD B K, VENKATESWARLU K, MODI O P, JHA A K, DAS S, DASGUPTA R, YEGNESWARAN A H. Sliding wear behavior of some Al-Si alloys: Role of shape and size of Si particles and test conditions [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1998, 29: 2747-2752.
[20] LI X Y, TANDON K N. Mechanical mixing induced by sliding wear of an Al-Si alloy against M2 steel [J]. Wear, 1999, 225-229: 640-648.
[21] LI X Y, TANDON K N. Microstructural characterization of mechanically mixed layer and wear debris in sliding wear of an Al alloy and an Al based composite [J]. Wear, 2000, 245: 148-161.
[22] TJPNG S C, WU S Q, ZHU H G. Wear behavior of in situ TiB2·Al2O3/Al and TiB2·Al2O3/Al-Cu composites [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 1999, 59: 1341-1347.
[23] DWIVEDI D K. Adhesive wear behaviour of cast aluminium-silicon alloys: Overview [J]. Materials and Design, 2010, 31: 2517-2531.
[24] PERRIN C, RAINFORTH W M. Work hardening behaviour at the worn surface of Al-Cu and Al-Si alloys [J]. Wear, 1997, 203-204: 171-179.
[25] VENKATARAMAN B, SUNDARARAJAN G. The sliding wear behaviour of Al-SiC particulate composites—II. The characterization of subsurface deformation and correlation with wear behavior [J]. Acta Materialia, 1996, 44: 461-473.
[26] SUH NAM P. The delamination theory of wear [J]. Wear, 1973, 25: 111-124.
[27] ZHANG J, ALPAS A T. Delamination wear in ductile materials containing second phase particles [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1993, 160: 25-35.
林 冲1,2,吴树森1,吕书林1,曾劲彪1,安 萍1
1. 华中科技大学 材料成形与模具技术国家重点实验室,武汉 430074;
2. 武汉工程大学 机电工程学院,武汉430073
摘 要:研究铁含量对流变铸造过共晶Al-17Si-2Cu-1Ni合金在干摩擦条件下磨损行为的影响。磨损测试是在销-盘式摩擦磨损试验机上进行的。结果表明,在同等载荷下,流变铸造合金试样比传统重力金属型铸造试样的磨损率小。细小颗粒状δ-Al4(Fe,Mn)Si2相和多边形状α-Al15(Fe,Mn)3Si2相有助于提高流变铸造合金的耐磨性。随着细小富铁相体积分数的增加,流变铸造合金试样的磨损率减小。此外,随着载荷从50增大至200 N,流变铸造合金试样的磨损率增大。对于含3% Fe的流变铸造合金,在低载荷(50 N)时,磨损机制以氧化磨损为主;在高载荷时,磨损机制以氧化磨损和剥层磨损的联合作用为主。
关键词:干摩擦;过共晶Al-Si合金;流变铸造;富铁相;磨损机理
(Edited by Yun-bin HE)
Foundation item: Project (2015M572135) supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation; Project (2012CB619600) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China
Corresponding author: Shu-lin  ; Tel: +86-27-87556262; E-mail: shulin317@hust.edu.cn
; Tel: +86-27-87556262; E-mail: shulin317@hust.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64156-0

