基于动态再结晶软化理论的Ti-22Al-25Nb合金新型本构关系模型
来源期刊:中国有色金属学报(英文版)2019年第3期
论文作者:孙宇 张恒 万志鹏 任丽丽 胡连喜
文章页码:546 - 557
关键词:Ti-22Al-25Nb;热变形;本构关系;EBSD技术
Key words:Ti-22Al-25Nb; hot deformation; constitutive relation; EBSD technique
摘 要:依据热压烧结制备Ti-22Al-25Nb合金热模拟压缩所得实验数据,研究合金在热变形温度为975~1075 °C、应变速率为0.001~1 s-1条件下的热变形行为。通过对数据的分析,建立包含Z参数模型、动态再结晶临界模型与动态再结晶动力学模型的新型本构关系模型。实验结果表明:Ti-22Al-25Nb合金的热变形激活能为410.172 kJ/mol,且临界应变与峰值应变之间的比值为0.67。此外,所建立的本构关系模型的预测值在应变速率为0.1 s-1、应变量小于0.1条件下与实验值相差较大,但整体上流动应力水平预测值与实验值吻合较好。并采用EBSD技术对动态再结晶动力学模型的预测精度进行分析。
Abstract: The hot deformation behavior of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy fabricated by hot compressed sintering was investigated under various conditions of compression tests in the deformation temperature range of 975-1075 °C with 20 °C intervals and the strain rate range of 0.001-1.0 s-1. Based on the experimental data, a novel constitutive relation combining a series of models was developed, including Zener-Hollomon parameter (Z), DRX critical model and kinetics model. The results show that the hot-deformed activation energy Q is calculated to be 410.172 kJ/mol, the ratio of critical strain (εc) to peak strain (εp) is a constant value of about 0.67. The predicted stress obtained by the established constitutive equations matches well with the true stress from experimental data. Despite large errors occur at the stage where strain rate is 0.1 s-1 and the values of true strain are less than 0.1, the stage of large strain should be more concerned during plastic forming. Furthermore, the predicting accuracy with the DRX kinetics model was testified by an electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) technique.
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 29(2019) 546-557
Yu SUN1, Heng ZHANG1, Zhi-peng WAN1, Li-li REN2, Lian-xi HU1
1. National Key Laboratory for Precision Hot Processing of Metals, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China;
2. China Nuclear Industry 23 Construction Co., Ltd., Beijing 101300, China
Received 11 June 2017; accepted 12 October 2018
Abstract: The hot deformation behavior of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy fabricated by hot compressed sintering was investigated under various conditions of compression tests in the deformation temperature range of 975-1075 °C with 20 °C intervals and the strain rate range of 0.001-1.0 s-1. Based on the experimental data, a novel constitutive relation combining a series of models was developed, including Zener-Hollomon parameter (Z), DRX critical model and kinetics model. The results show that the hot-deformed activation energy Q is calculated to be 410.172 kJ/mol, the ratio of critical strain (εc) to peak strain (εp) is a constant value of about 0.67. The predicted stress obtained by the established constitutive equations matches well with the true stress from experimental data. Despite large errors occur at the stage where strain rate is 0.1 s-1 and the values of true strain are less than 0.1, the stage of large strain should be more concerned during plastic forming. Furthermore, the predicting accuracy with the DRX kinetics model was testified by an electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) technique.
Key words: Ti-22Al-25Nb; hot deformation; constitutive relation; EBSD technique
1 Introduction
The Ti2AlNb-based alloy is considered to be a ternary intermetallic based on the stoichiometry Ti2AlNb which was designated the O phase on the basis of its orthorhombic structure [1]. A Ti2AlNb-based alloy with the composition of Ti-22Al-25Nb (at.%), developed independently by Beijing Iron and Steel Research Institute (China), possesses higher combinations of specific strength, toughness and creep resistance than conventional titanium aluminides such as TiAl-based and Ti3Al-based alloys [2,3]. Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy possesses desired mechanical properties at elevated temperature, which has excellent potential to be applied in engineering practice [4]. In spite of the advantages mentioned above, the industry application of Ti2AlNb- based alloy, however, is still restricted due to its limited plastic deformation ability at ambient temperature and narrow hot working temperature range. Therefore, it is imperative to carry out the secondary manufacturing process at elevated temperature to convey excellent workability to material by studying the effects of thermo- mechanical parameters (deformation temperature, strain rate and strain) regarding hot deformation behavior. Complex deformation mechanisms, such as work hardening (WH), dynamic recovery (DRV) and dynamic recrystallization (DRX), often occur in the metals or alloys with low stacking fault energy during hot deformation [5,6]. Generally, the high-temperature deformation is a competitive process of the strain hardening and dynamic softening mechanisms. Hence, developing the appropriate constitutive relationship to present the complex strain hardening and dynamic softening behavior of metals or alloys is fairly paramount [7,8]. Recently, most of constitutive models have been developed or improved to present the hot deformation behavior in terms of various kinds of materials, including steels [9-12], magnesium alloys [13-16], aluminum alloys [17,18] and titanium alloys [19-22]. The Arrhenius constitutive model and the Johnson-Cook material model, as common phenomenological constitutive models, have been extensively applied to predicting the flow stress of machining process. Conversely, a physical-based constitutive model considering material microstructure feature and flow softening mechanism has advantages in conditions of high temperature and high strain rate. In addition, the constitutive model defining the meaningful physical material constants is more suitable for finite element simulations. The public reports regarding the constitutive relationship model for Ti2AlNb-based alloys are also quite few. WEI et al [23] studied the flow stress of coarse-grained Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy within the temperature range of 1213-1263 K and the strain rate range of 3.3×10-4-3.3×10-2 s-1 by establishing Arrhenius constitutive equations of hyperbolic sine. YANG et al [24] investigated the hot deformation behavior of Ti-22Al-25Nb-1.0B alloy at the temperature of 1000-1200 °C and the strain rates of 0.001-1 s-1 through developing constitutive model based on the hyperbolic- sine equations. The relationship of deformed microstructure evolution with the ln Z value was established subsequently. ZHANG et al [25] conducted isothermal compression tests of Ti-22Al- 25Nb alloy prepared by quadruple consumable vacuum arc remelting at the temperature of 930-1080 °C with strain rates of 0.001-1 s-1. The flow behavior of the alloy was researched via establishing a hyperbolic-sine constitutive equation. A hot processing map was built to expound the microstructure evolution in hot processing too. Based on the analysis above, it can be known that the previously established constitutive relationship models of Ti2AlNb- based alloy do not explain the flow stress softening mechanism or still are not advanced sufficient to account for the whole complex dynamic mechanisms, especially for the powder metallurgy (P/M) Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy. Therefore, in the present work, the research aim is to study the flow softening behavior of a special P/M Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy by isothermal constant strain-rate compression tests over wide ranges of deformation temperature and strain rate. Generally, flow stresses influenced by various mechanisms can be described via different constitutive relations. A novel constitutive model is developed to characterize the flow stress softening behavior of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy during hot compression, and the work hardening and dynamic recrystallization softening behavior are also included. Furthermore, the prediction accuracy of the developed models is discussed in terms of statistical theory and microstructure evolution.
2 Experimental
The experimental material employed in the present research was Ti-22Al-25Nb (at.%) pre-alloyed powders obtained by argon gas atomization. The pre-alloy powders were high-energy milled by a planetary ball-milling machine, and subjected to sintering at 1100 °C and 50 MPa for 1 h in high vacuum followed by furnace cooling. Rotation speed of 400 r/min, ball-to- powder mass ratio of 40:1 and milling time of 2 h were applied to the ball-milling process. The XRD patterns and initial microstructure of the sintered billets are exhibited in Fig. 1. It can be depicted that the billets are typical three-phase microstructure where a large number of lamellar O phases participate in B2 grains and a small amount of α2 phases distribute along B2 grain boundaries.
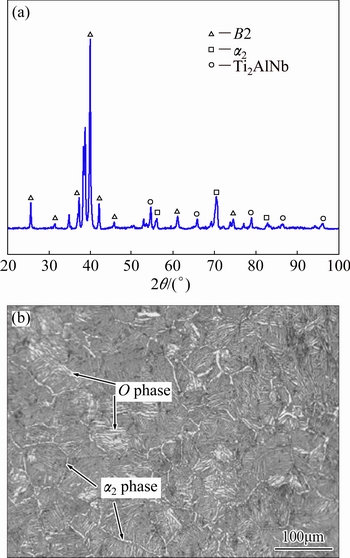
Fig. 1 XRD pattern (a) and initial microstructure (b) of sintered Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy billets
The cylindrical specimens with a diameter of 6 mm and a height of 9 mm for hot compression tests were cut from the hot-pressed billet uniformly to ensure the homogeneous performance. The axial of cylindrical specimens is parallel to the hot pressing direction. Subsequently, the isothermal compression tests were carried out on a Gleeble-1500 thermal simulator machine in a temperature range of 995-1075 °C with 20 °C intervals and a strain rate range of 0.001-1.0 s-1. The specimens were heated up to 900 °C with the rate of 15 °C/s firstly, continuously heated to the selected temperature at a rate of 10 °C/s, held for 3 min to eliminate thermal gradients, and finally deformed at a constant strain rate. After the true strain reached 0.65, the specimens were water quenched immediately to retain the deformed microstructure. It should be noted that graphite lubricant was used to minimize the friction. The stress-strain curves were recorded automatically during isothermal compression. In order to investigate the microstructure of isothermally compressed Ti-22Al- 25Nb alloy, the deformed specimens were cut parallel to the longitudinal compression direction for the microstructure observation by an electron back-scattered diffraction (EBSD) technique. Specimens for EBSD were mechanically polished and then electrobrightening tests were conducted with a solution of HClO4, N-butanol and methanol.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Flow behavior
The flow curves of the Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy at deformation temperature of 995-1075 °C and strain rate of 0.001-1.0 s-1 are presented in Fig. 2. It can be observed that the effects of the deformation temperature and strain rate on the flow behavior of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy are quite significant. Flow stress increases to the peak sharply at a very small strain. In the subsequent deformation period, the stress decreases gradually until a relatively stable stress appears, showing a dynamic flow softening effect. Generally, the true stress-true strain curve is available to indicate the intrinsic relationship of the flow stress with thermal-dynamic behavior. During the first stage of deformation, the work hardening, which is induced by dislocation reproduction and tangles, leads to the rapid increase of the flow stress when softening effect of dynamic recovery (DRV) is comparatively weak. With the augment of the deformation degree, dynamic recrystallization (DRX) occurs at a critical strain, resulting in softening effect strengthened and increase rate of flow stress slowing down. Then, the peak stress appears when the work hardening and dynamic softening reach the equilibrium. Thereafter, as strain increases further, the DRX degree increases and the dislocation density reduces. Thus, softening effect including both DRV and DRX exceeds work hardening, making flow stress decrease. Meanwhile, the nucleation and growth of new grains occur, i.e., sub-grains develop. Finally, steady-state flow stage appears at a large strain, resulted from dynamic equilibrium between the strain hardening and dynamic softening.
In addition, it can be indicated that stress level decreases with the temperature and increases with the strain rate from Fig. 2. Such characteristic of flow stress curves can also be observed in other TiAl alloys [26-28]. Since lower strain rate can provide longer time for activation energy accumulation, while higher temperature is capable of supplying higher mobility for nucleation and growth of DRX grains and dislocation annihilation at grain boundary [29].
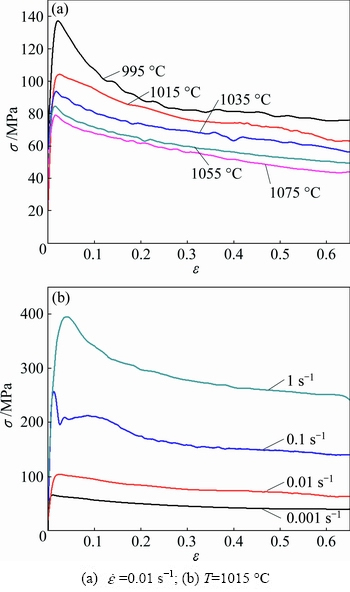
Fig. 2 True stress-strain curves of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy under various conditions
3.2 Establishment of novel constitutive model
3.2.1 Zener-Hollomon parameter
Generally, the Arrhenius-type constitutive equations (Eqs. (1)-(3)) can characterize the relationship between deformation parameters and flow stress state. As a temperature-compensated strain rate factor, Zener- Hollomon parameter (Z) is able to reveal the combined influences of temperature and strain rate on the stress, which is employed in this work [30-32]:
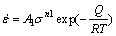 (ασ<1.2) (1)
(ασ<1.2) (1)
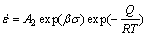 (ασ>1.2) (2)
(ασ>1.2) (2)
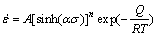 (ασ for all) (3)
(ασ for all) (3)
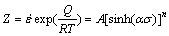 (4)
(4)
where σ is the flow stress (MPa), 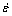 is strain rate (s-1), Q is the hot-deformed activation energy (kJ/mol), R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/(mol·K)), T is the thermodynamic deformation temperature (K), and A1, A2, A, n1 and n are material constants. Moreover, α can be obtained by Eq. (5):
is strain rate (s-1), Q is the hot-deformed activation energy (kJ/mol), R is the universal gas constant (8.314 J/(mol·K)), T is the thermodynamic deformation temperature (K), and A1, A2, A, n1 and n are material constants. Moreover, α can be obtained by Eq. (5):
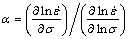 (5)
(5)
By taking the natural logarithm of both sides of Eq. (3), the deformation activation energy Q can be represented and calculated through Eqs. (6) and (7):
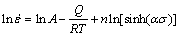 (6)
(6)
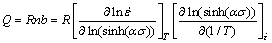 (7)
(7)
According to the peak flow stress data at different strain rates and temperatures, the value of α can be calculated to be 0.005864 from Figs. 3(a) and (b). In addition, the relationships of ln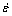 -ln(sinh(ασ)) and ln(sinh(ασ))-1/T were plotted, and then the values of n and b are confirmed: n=2.78 and b=17.755, as shown in Figs. 3(c) and (d), respectively. Thus, Q=Rnb= 410.172 kJ/mol and the precise formula for Z parameter can be ascertained.
-ln(sinh(ασ)) and ln(sinh(ασ))-1/T were plotted, and then the values of n and b are confirmed: n=2.78 and b=17.755, as shown in Figs. 3(c) and (d), respectively. Thus, Q=Rnb= 410.172 kJ/mol and the precise formula for Z parameter can be ascertained.
3.2.2 DRX critical model
In this study, the true stress-strain curves are supposed to be the result of synchronization function of DRV and DRX in the approach typified by the schematic curves of Fig. 4 [33]. The yield stress (σ0), at the beginning of curves, is obtained using the method of yield strength (σ0.2) corresponding to a total strain offset about 0.002. The highest curve (σrecov) represents the consequence from the operation of DRV alone, where there is no DRX in the process. The lower curve (σDRX) is regarded as a true stress-strain curve with existence of DRX. Evidently, the data from both curves are the same prior to critical strain (εc) and critical stress (σc), after which DRX occurs and thereby softening effect strengthens resulting in increasingly obvious difference between σrecov and σDRX curves. The difference of both curves is identified as △σs, resulting from the softening of DRX directly. At saturation, the asymptotic stress is obtained by σsat, which indicates the most dislocation density attributable to work hardening as well as the driving force for constant ongoing of DRX. The maximum of △σs is σsat-σss, where σss is the steady-state stress of σDRX curve. Finally, the fractional softening of arbitrary conditions is calculated by XDRX=△σs/(σsat-σss).
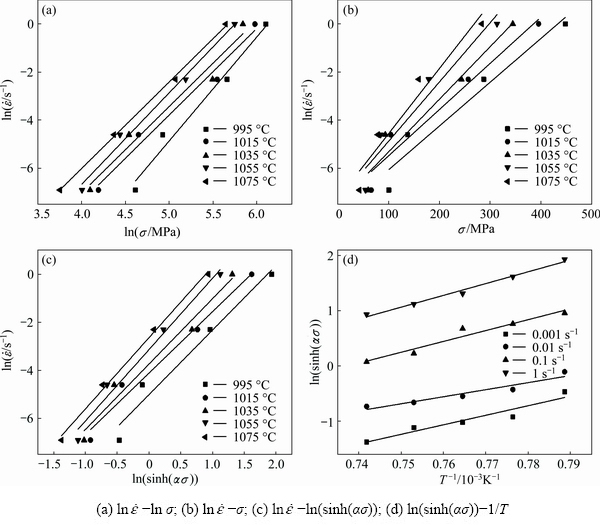
Fig. 3 Relationships of σ , T and 
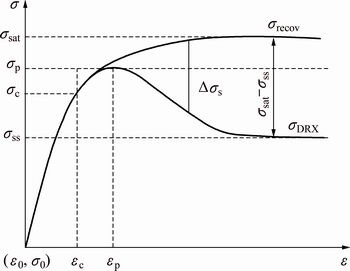
Fig. 4 Schematic illustration of typical flowing stress curves during hot process
In order to determine the characteristic parameters of critical values and at peak values applicable to all flow curves studied in this work, work-hardening rate θ=dσ/dε versus σ curves should be prepared. An example is shown in Fig. 5(a). The method proposed in Ref. [34] was used to confirm σc at the point where the second derivative of θ relative to σ, i.e.  2θ/
2θ/ σ2, is 0. Moreover, σp is defined as the point at which θ=0. Subsequently, the values of critical stress and peak stress were gained correspondingly according to σ-ε-θ curves in Fig. 5(b). Additionally, the θ-σ curves at various conditions were plotted, as shown in Fig. 6. It can be observed that the values of σc increase with the increasing strain rates and decreasing temperature.
σ2, is 0. Moreover, σp is defined as the point at which θ=0. Subsequently, the values of critical stress and peak stress were gained correspondingly according to σ-ε-θ curves in Fig. 5(b). Additionally, the θ-σ curves at various conditions were plotted, as shown in Fig. 6. It can be observed that the values of σc increase with the increasing strain rates and decreasing temperature.
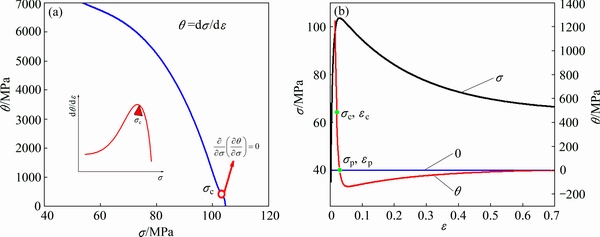
Fig. 5 θ-σ (a) and σ-ε-θ (b) curves of studied Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy deformed at 1015 °C and 0.01 s-1
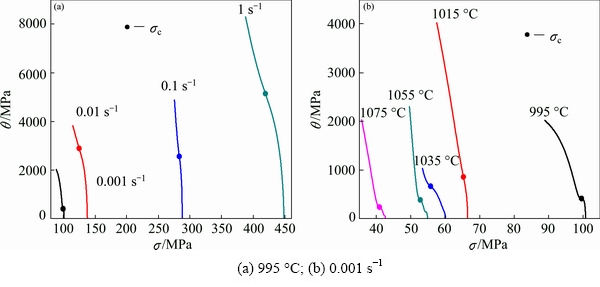
Fig. 6 θ-σ curves under various conditions
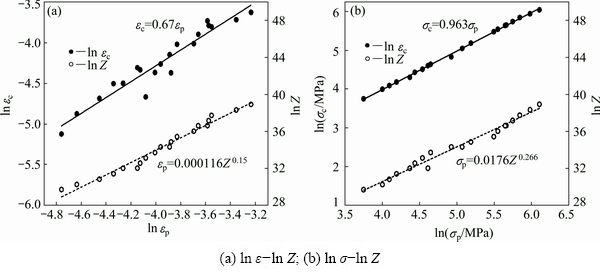
Fig. 7 Relationships among critical points, peak points and Z parameter
For more readily achieving the information at critical and peak points, the relationships among critical points, peak points and Z parameter were constructed in Fig. 7. The critical DRX model for the Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy was developed:
 ,
, 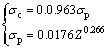 (8)
(8)
3.2.3 DRX kinetics model
Considering plastic strain (ε) in terms of dislocation density (ρ), the dependence of ρ on ε can be given by [35]
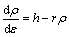 (9)
(9)
where h represents the athermal work-hardening rate and r is the coefficient of dynamic recovery at a constant
temperature and strain rate. As shown in the appendix of Ref. [33], the following description for the σrecov curve can be derived:
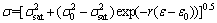 (10)
(10)
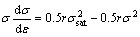 (11)
(11)
In order to ascertain the values of σsat and r, θσ-σ2 curves were plotted. The way to determine σsat and r is demonstrated in Fig. 8. It should be noted that the slope, the value of the derivative d(θσ)/d(σ2), is obtained through the experimental data before the onset of DRX. Besides, σsat is defined using the extrapolation of the θσ-σ2 curves to θσ=0.
Thus, according to XDRX=△σs/(σsat-σss), the XDRX in each increment can be calculated. The modified Avrami equation [36,37] is usually expressed as
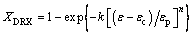 (12)
(12)
where XDRX is the recrystallized volume fraction, k and n are constants, εc represents the critical strain and εp is the strain at peak stress. Taking the natural logarithm of both sides of Eq. (12), the following formula is gained:
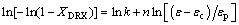 (13)
(13)
The relationships between ln[-ln(1-XDRX)] and ln[(ε-εc)/εp] were built under all test conditions, where n and ln k represent the slope and the intercept, respectively. Utilizing the method for all data, the average values of n and k were obtained, nd=0.91265 and kd=0.25345. The DRX kinetics model which is specified in the following form can be developed:
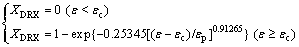 (14)
(14)
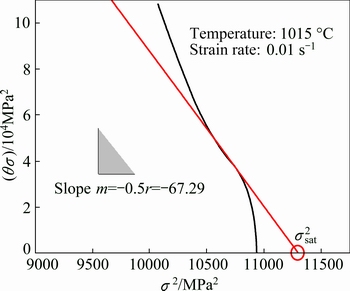
Fig. 8 θσ-σ2 curves of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy at 1015 °C and 0.01 s-1
For the sake of analyzing the XDRX evolution of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy as strain increases under various conditions, the XDRX-σ curves were plotted in Fig. 9. It can be apparently observed that DRX did not start until strain exceeded the critical strain (εc). Moreover, the volume fraction of DRX grains increases with the increasing strain and the evolution of XDRX-σ curves shows “firstly-quick and then slow” trend. Compared with the value of XDRX at a constant strain under different temperatures and strain rates, it is also found that the XDRX decreases at higher strain rates and increases with rising temperature. The phenomenon is contrary to the change of flow stress, as mentioned in Section 3.1. Besides, the prediction results of DRX kinetics model have a good agreement with the XDRX values from experiments.
3.3 Validation of constitutive equation
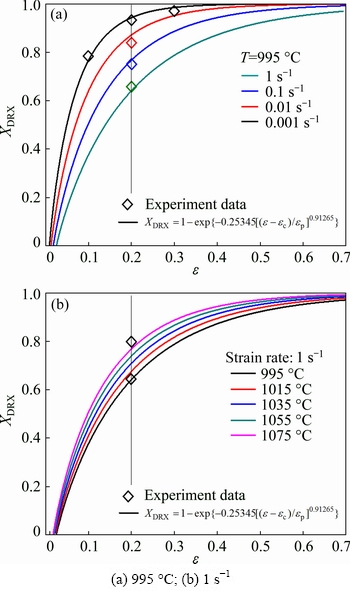
Fig. 9 XDRX evolution of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy with strain under various conditions: (a) 995 °C; (b) 1 s-1
For the purposes of modeling constitutive relation of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy during hot compression, it is necessary to formulate the obtained σsat, σss, σ0 and σc as functions of σp, where the latter is more conveniently and accurately measurable. The parameters for every flow curve derived from experiments are illustrated in Fig. 10. Obviously, the reasonably satisfactory matching results to the data are acquired:
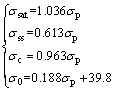 (15)
(15)
Another parameter r is displayed in a similar way in Fig. 11. It can be found that the value of r decreases with the increase of σp, which is in accordance with increasing Z parameter. This case occurs as the recovery rate is deemed to raise with rising deformation temperature and decreasing strain rate.
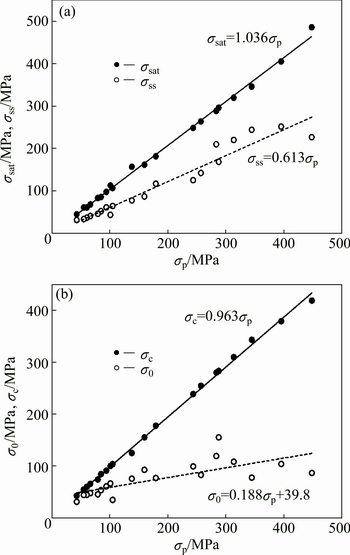
Fig. 10 σsat and σss data (a) as well as σ0 and σc data (b) determined on flow curves from compression tests
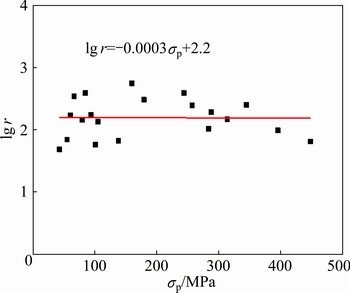
Fig. 11 Dependence of dynamic recovery coefficient r on σp
As a result, the constitutive equations including a series of models were developed completely to expound the flow behavior of the Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy during hot compression, as demonstrated as Eqs. (16)-(20). It can be used to plot true stress-true strain curves of the studied alloy at each temperature and strain rate which are not simply achievable under the practical experiment conditions:
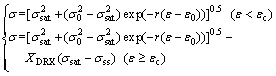 (16)
(16)
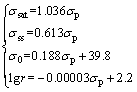 (17)
(17)
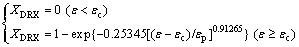 (18)
(18)
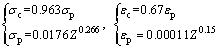 (19)
(19)
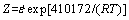 (20)
(20)
In order to verify the constitutive equations established in the present work, the comparison results of calculated and experimental σ-ε curves at different temperatures are shown in Fig. 12. Due to the complexity of stress evolution at small strains and gentle stress later, the collected data for calculation show the “first dense and then sparse” characteristic. Overall, it is supposed that the prediction results match well with the true stress values. It is also observed that the data with large error occur at the stage where strain rate is 0.1 s-1 and the values of true strain are less than 0.1. With regard to the plastic forming, it is beneficial that the large strain stage is better to be more concerned. Error statistical analysis is also illustrated according to Fig. 13. It can be found that the linear fitting coefficient (R) equals 0.992 in Fig. 13(a) and most of differences between calculated values and experimental values are pretty little in Fig. 13(b). Therefore, the constitutive equations developed in the present work are effective and can be performed to characterize deformation behavior of the studied Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy with reliability during hot compression, especially for the DRX behavior.
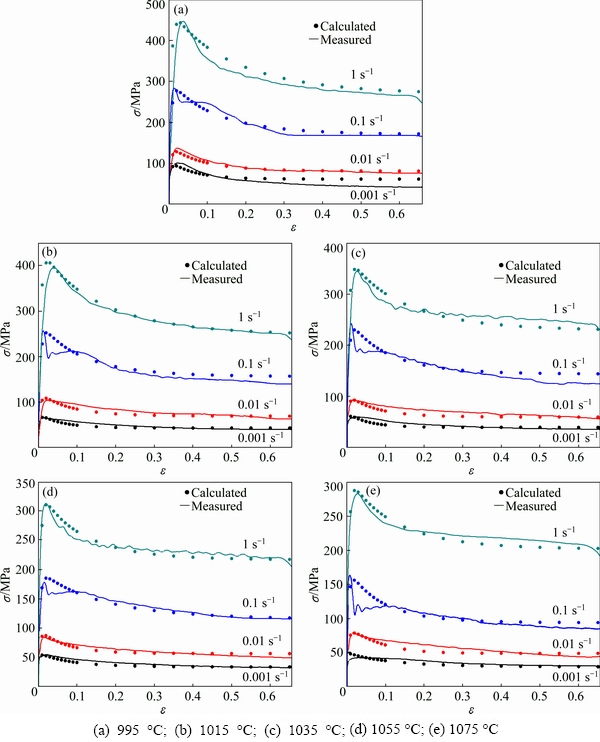
Fig. 12 Comparison of calculated and measured σ-ε curves at various temperatures
More importantly, EBSD analyses with different hot processing parameters were exhibited to confirm the DRX kinetics model. The variations of DRX grain fraction with strain, strain rate and deformation temperature were also studied. Figure 14 shows XDRX change with various strains at 995 °C and 0.001 s-1 while the variations with strain rate at 995 °C and strain of 0.2 and those with temperature at strain rate of 1 s-1 and strain of 0.2 are illustrated in Fig. 15. The grain misorientation distributions at strains of 0.1, 0.2 and 0.3 are shown in Figs. 14(b), (d) and (f), respectively. It is explicitly observed that low-angle (0°-10°) boundary (sub-boundary) fraction lessens with increasing the strain while 30°-40° and 90°-100° high-angle boundary proportion increases. According to Metallkunde dislocation theory, dislocation pile-up and tangle result in generating lots of sub-boundaries during the deformation. However, there hardly exist sub-boundaries inside DRX grains with smaller deformation. Therefore, as the strain increases, the volume fraction of deformed grains decreases but DRX grain proportion rises. The XDRX values with various thermomechanical parameters can be visually described on the basis of the undeformed material. It can also be found that DRX grain volume fraction reduces with increasing strain rate at low temperature and a constant strain, as shown in Fig. 15. These results are in consistence with the analysis of Fig. 9, where the XDRX values from experiments show a good agreement compared with the established DRX kinetics model.
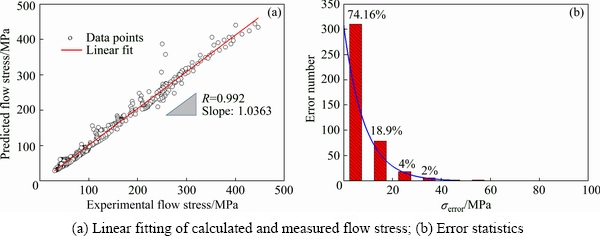
Fig. 13 Evaluation of constitutive model
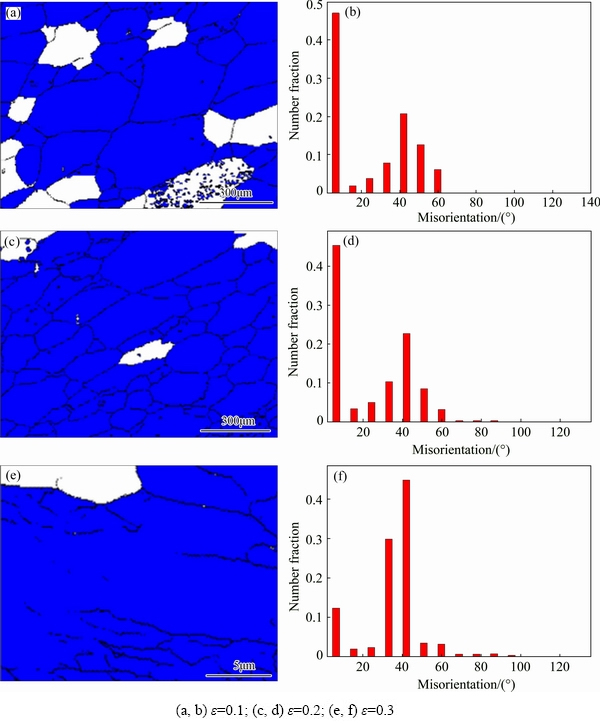
Fig. 14 Change of DRX grains (a, c, e) and grain misorientation distribution (b, d, f) at 995 °C and 0.001 s-1
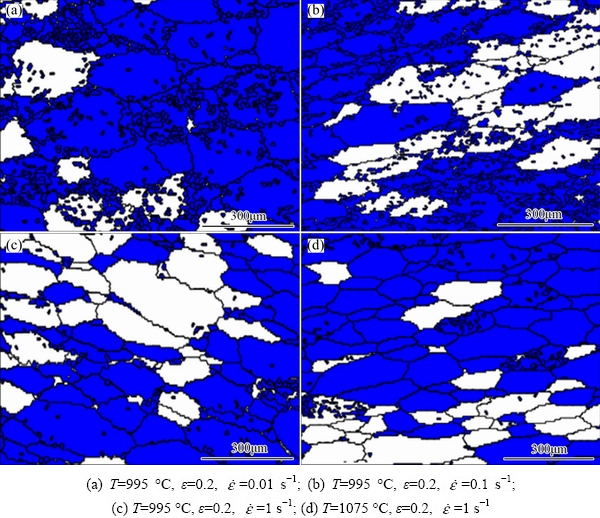
Fig. 15 DRX grain distributions under various conditions
4 Conclusions
(1) The hot-deformed activation energy Q for the studied alloy was obtained, where Z function can express the coupled effects of deformation temperature and strain rate on the flow stress. And, the DRX critical model revealing the relationships between critical points and peak points are established as
 ,
, 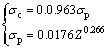
(2) The XDRX evolution was analyzed based on the modified Avrami equation. Moreover, the DRX kinetics model is validated well via the EBSD observation:
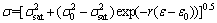
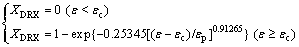
(3) The constitutive relationship equations to illuminate the deformation behavior of the P/M Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy are constructed. Through contrast of calculated values and experimental values, the applicability of complete model are verified well with the average error of 2.8 MPa and the average relative error of 0.9%.
References
[1] BANERJEE D. The intermetallic Ti2AlNb [J]. Progress of Materials Science, 1997, 42: 135-158.
[2] SUN Y, ZENG W D, MA X, XU B, LIANG X B, ZHANG J W. A hybrid approach for processing parameters optimization of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy during hot deformation using artificial neural network and genetic algorithm [J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19: 1014-1019.
[3] BOEHLERT C J, MAJUMDAR B S, SEETHARAMAN V, MIRACLE D B. Part I. The microstructural evolution in Ti-Al-Nb O+Bcc orthorhombic alloys [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1999, 30: 2305-2323.
[4] JIA J B, ZHANG K F, LU Z. Dynamic recrystallization kinetics of a powder metallurgy Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy during hot compression [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 607: 630-639.
[5] LIN Y C, LI K K, LI H B, CHEN J, CHEN X M, WEN D X. New constitutive model for high-temperature deformation behavior of inconel 718 superalloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 74: 108-118.
[6] ZHAN H Y, WWANG G, KENT D, DARGUSCH M. The dynamic response of a metastable β-Ti-Nb alloy to high strain rates at room and elevated temperatures [J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 105: 104-113.
[7] LIN Y C, CHEN X M. A critical review of experimental results and constitutive descriptions for metals and alloys in hot working [J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32: 1733-1759.
[8] THOSSATHEPPITAK B, UTHAISANGSUK V, MUNGSUNTISUK P, SURANUNTCHAI S, MANONUKUL A. Flow behaviour of nickel aluminium bronze under hot deformation [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 604: 183-190.
[9] FERDOWSI M R G, NAKHAIE D, BENHANGI P H. Modeling the high temperature flow behavior and dynamic recrystallization kinetics of a medium carbon microalloyed steel [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2014, 23: 1077-1087.
[10] GAO X J, JIANG Z Y, WEWI D B, LI H J, JIAO J, ZHANG X M, HAN J T, CHEN D F. Constitutive analysis for hot deformation behaviour of novel bimetal consisting of pearlitic steel and low carbon steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 595: 1-9.
[11] VANINI S A S, ABOLGHASEMZADEH M, ASSADI A. Generalized constitutive-based theoretical and empirical models for hot working behavior of functionally graded steels [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013, 44: 3376-3384.
[12] HAN Y, WU H, ZHANG W, ZOU D N, LIU G W, QIAO G J. Constitutive equation and dynamic recrystallization behavior of as-cast 254SMO super-austenitic stainless steel [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 69: 230-240.
[13] QUAN G Z, SHI Y, YU C T, ZHOU J. The improved Arrhenius model with variable parameters of flow behavior characterizing for the as-cast AZ80 magnesium alloy [J]. Materials Research, 2013, 16: 785-791.
[14] ABBASI-BANI A, ZAREI-HANZAKI A, PISHBIN M H, HAGHDADI N. A comparative study on the capability of Johnson-Cook and Arrhenius-type constitutive equations to describe the flow behavior of Mg-6Al-1Zn alloy [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2014, 71: 52-61.
[15] MIRZADEH H. Constitutive behaviors of magnesium and Mg-Zn-Zr alloy during hot deformation [J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2015, 152: 123-126.
[16] WANG Z J, QI L H, WANG G, LI H J, MATTHEW S D. Constitutive equation for the hot deformation behavior of Csf/AZ91D composites and its validity for numerical simulation [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2016, 102: 90-96.
[17] LIN Y C, XIA Y C, CHEN X M, CHEN M S. Constitutive descriptions for hot compressed 2124-T851 aluminum alloy over a wide range of temperature and strain rate [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2010, 50: 227-233.
[18] KORDKHEILI S A H, ASHRAFIAN M M, TOOZANDEHJANI H. A rate-dependent constitutive equation for 5052 aluminum diaphragms [J]. Materials and Design, 2014, 60: 13-20.
[19] PILEHVA F, ZAREI-HANZAKI A, GHAMBARI M, ABEDI H R. Flow behavior modeling of a Ti-6Al-7Nb biomedical alloy during manufacturing at elevated temperatures [J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 51: 457-465.
[20] PORNTADAWIT J, UTHAISANGSUK V, CHOUNGTHONG P. Modeling of flow behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy at elevated temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 599: 212-222.
[21] PENG W W, ZENG W D, WANG Q J, YU H Q. Comparative study on constitutive relationship of as-cast Ti60 titanium alloy during hot deformation based on Arrhenius-type and artificial neural network models [J]. Materials and Design, 2013, 51: 95-104.
[22] FAN X G, YANG H, GAO P F, ZUO R, LEI P H. The role of dynamic and post dynamic recrystallization on microstructure refinement in primary working of a coarse grained two-phase titanium alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2016, 234: 290-299.
[23] WEI Z, YAO Z, QIN C. Effects of process parameters on the superplastic behavior of coarse grain Ti2AlNb alloy [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014, 43: 209-213.
[24] YANG J L, WANG G F, JIAO X Y, LI X, YANG C. Hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of Ti-22Al-25Nb-1.0B alloy prepared by elemental powder metallurgy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 695: 1038-1044.
[25] ZHANG H, LI H J, GUO Q Y, LIU Y, YY L M. Hot deformation behavior of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy by processing maps and kinetic analysis [J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2016, 31: 1764-1772.
[26] WAN Z P, SUN Y, HU L X, YU H. Experimental study and numerical simulation of dynamic recrystallization behavior of TiAl-based alloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2017, 122: 11-20.
[27] LIU B, LIU Y, ZHANG W, HUANG J S. Hot deformation behavior of TiAl alloys prepared by blended elemental powders [J]. Intermetallics, 2011, 19: 154-159.
[28] SUN Y, HU L X, REN J S. Investigation on the hot deformation behavior of powder metallurgy TiAl-based alloy using 3D processing map [J]. Materials Characterization, 2014, 100: 163-169.
[29] LIAO H C, WU Y N, ZHOU K X, YNAG J. Hot deformation behavior and processing map of Al-Si-Mg alloys containing different amount of silicon based on Gleebe-3500 hot compression simulation [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 65: 1091-1099.
[30] SHUKLA A K, MURTY S V S N, SHARMA S C, MONDAL K. Constitutive modeling of hot deformation behavior of vacuum hot pressed Cu-8Cr-4Nb alloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 75: 57-64.
[31] ZHANG P, HU C, ZHU Q, DING C G, QIN H Y. Hot compression deformation and constitutive modeling of GH4698 alloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 65: 1153-1160.
[32] SELLARS C M, MCTEGART W J. On the mechanism of hot deformation [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1966, 65: 1136-1138.
[33] JONAS J J, QUELENNEC X, JIANG L, MARTIN E. The Avrami kinetics of dynamic recrystallization [J]. Acta Materialia, 2009, 57: 2748-2756.
[34] POLIAK E I, JONAS J J. A one-parameter approach to determining the critical conditions for the initiation of dynamic recrystallization [J]. Acta Materialia, 1996, 44: 127-136.
[35] ESTRIN Y, MECKING H. A unified phenomenological description of work hardening and creep based on one-parameter models [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1984, 32: 57-70.
[36] LAASRAOUI A, JONAS J J. Recrystallization of austenite after deformation at high temperatures and strain rates—Analysis and modeling [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1991, 22: 151-160.
[37] SERAJZADEH S, TAHERI A K. Prediction of flow stress at hot working condition [J]. Mechanics Research Communication, 2003, 30: 87-93.
孙 宇1, 张 恒1, 万志鹏1, 任丽丽2, 胡连喜1
1. 哈尔滨工业大学 金属精密热加工国家级重点实验室,哈尔滨 150001;
2. 中国核工业二三建设有限公司,北京 101300
摘 要:依据热压烧结制备Ti-22Al-25Nb合金热模拟压缩所得实验数据,研究合金在热变形温度为975~1075 °C、应变速率为0.001~1 s-1条件下的热变形行为。通过对数据的分析,建立包含Z参数模型、动态再结晶临界模型与动态再结晶动力学模型的新型本构关系模型。实验结果表明:Ti-22Al-25Nb合金的热变形激活能为410.172 kJ/mol,且临界应变与峰值应变之间的比值为0.67。此外,所建立的本构关系模型的预测值在应变速率为0.1 s-1、应变量小于0.1条件下与实验值相差较大,但整体上流动应力水平预测值与实验值吻合较好。并采用EBSD技术对动态再结晶动力学模型的预测精度进行分析。
关键词:Ti-22Al-25Nb;热变形;本构关系;EBSD技术
(Edited by Bing YANG)
Foundation item: Project (51405110) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project (2014M551234) supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation; Project (20132302120002) supported by the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education, China; Project (HIT. NSRIF. 2014006) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China; Project (LBH-Z14096) supported by the Heilongjiang Province Postdoctoral Fund, China
Corresponding author: Lian-xi HU; Tel/Fax: +86-451-86418613; E-mail: hulx@hit.edu.cn
DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(19)64963-0

